Настройка переменных среды Windows может помочь сократить время, необходимое для набора команд в командной строке или, если вы часто пишете скрипты для собственных задач, сделать их более читаемыми. В большинстве случаев обычные пользователи добавляют записи в системную переменную среды PATH, хотя бывают и другие задачи.
В этой пошаговой инструкции базовая информация о том, как открыть переменные среды Windows 11 и Windows 10, создать или отредактировать их.
Что такое переменные среды
Переменные среды в Windows — записи о расположении системных папок, свойствах системы и другие, которые доступны для любой программы или скрипта.
Одна из наиболее часто используемых переменных среды — PATH, указывающая на папки, в которых выполняется поиск файлов, вызываемых в командной строке, терминале Windows, файле bat или из других источников. В качестве примера её назначения:
- Если вы откроете командную строку (или диалоговое окно «Выполнить»), введёте regedit и нажмете Enter — вы сможете запустить редактор реестра, не указывая полный путь к файлу regedit.exe, поскольку путь C:\Windows добавлен в переменную среды Path.
- Если же тем же образом в командной строке написать имя программы, путь к которой не добавлен в Path (chrome.exe, adb.exe, pip и другие), вы получите сообщение «Не является внутренней или внешней командой, исполняемой программой или пакетным файлом».
Если предположить, что вы часто используете команды adb.exe (например, для установки приложений Android в Windows 11), pip install (для установки пакетов Python) или любые другие то для того, чтобы не писать каждый раз полный путь к этим файлам, имеет смысл добавить эти пути в переменные среды.
Также вы можете добавлять и иные переменные среды (не обязательно содержащие пути), а в дальнейшем получать и использовать их значения в сценариях BAT (командной строки) или PowerShell. Пример получения и отображения значения системной переменной PATH для обоих случаев:
echo %PATH% echo $Env:PATH
Получить список всех переменных среды в командной строке и PowerShell соответственно можно следующими командами:
set ls env:
Редактирование переменных среды Windows 11/10
Прежде чем приступать, учтите: изменение системных переменных среды по умолчанию может привести к проблемам в работе системы, не удаляйте уже имеющиеся переменные среды. Возможно, имеет смысл создать точку восстановления системы, если вы не уверены в своих действиях.
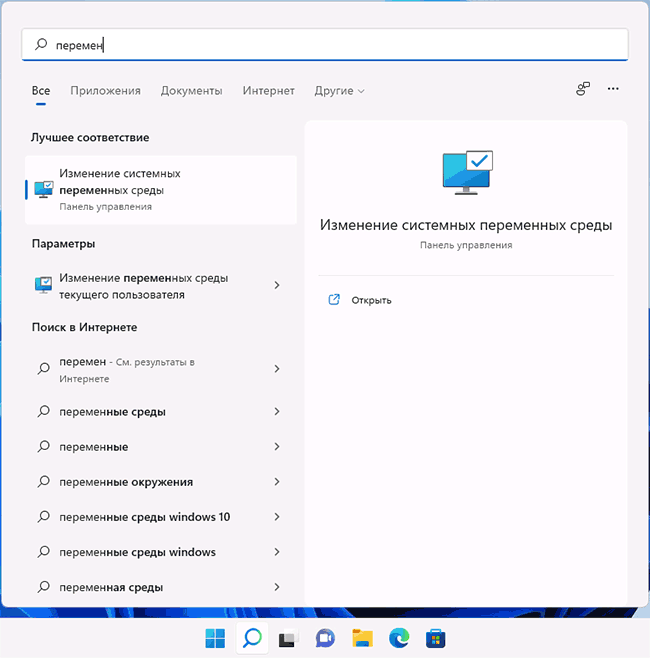
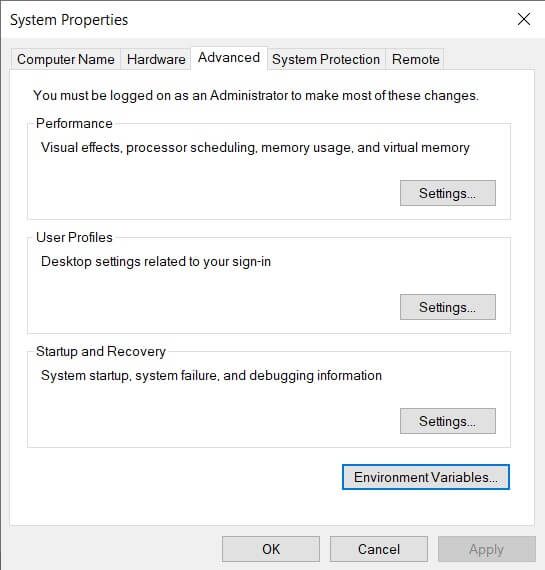
- Чтобы открыть переменные среды Windows вы можете использовать поиск в панели задач (начните вводить «Переменных» и откройте пункт «Изменение системных переменных среды») или нажать клавиши Win+R на клавиатуре, ввести sysdm.cpl и нажать Enter.
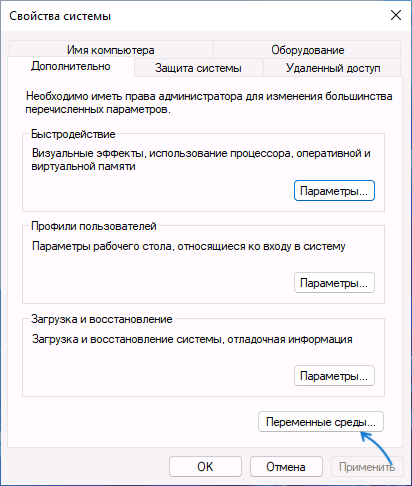
- На вкладке «Дополнительно» нажмите кнопку «Переменные среды…»
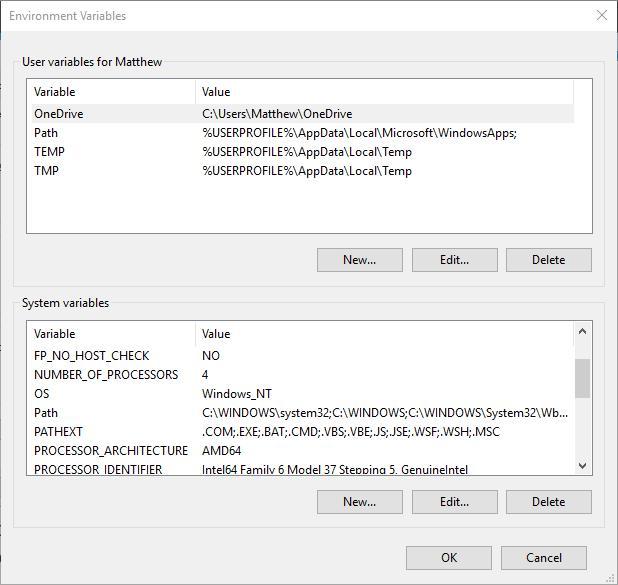
- В разделе «Переменные среды пользователя» (если требуется изменение только для текущего пользователя) или «Системные переменные» выберите переменную, которую нужно изменить и нажмите «Изменить» (обычно требуется именно это), либо, если необходимо создать новую переменную — нажмите кнопку «Создать». В моем примере — добавляем свои пути в системную переменную Path (выбираем эту переменную и нажимаем «Изменить»).
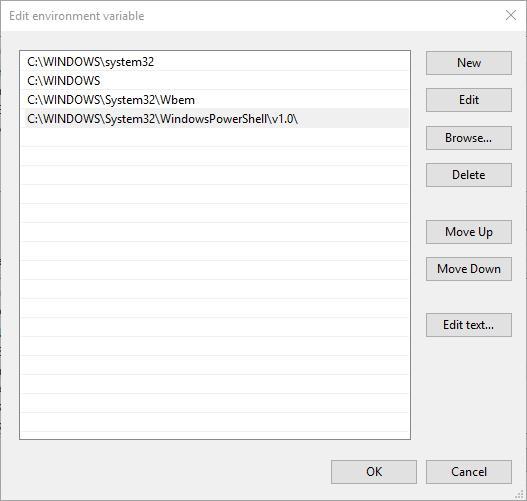
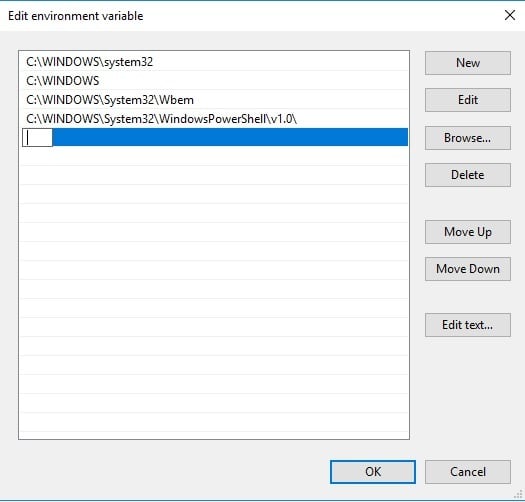
- Для добавления нового значения (пути) в системную переменную в следующем окне можно нажать кнопку «Создать», либо просто дважды кликнуть по первой пустой строке, затем — ввести нужный путь к папке, содержащей нужные нам исполняемые файлы.
- Также вы можете использовать кнопку «Изменить текст», в этом случае окно изменения системной переменной откроется в ином виде: имя переменной, а ниже — её значение. В случае указания путей значение будет представлять собой все пути, хранящиеся в переменной, разделенные знаком «точка с запятой».
- При создании новой переменной среды окно будет тем же, что и в 5-м шаге: необходимо будет указать имя системной переменной в верхнем поле, а её значение — в нижнем.
После создания или изменения переменной среды и сохранения сделанных настроек, переменная или обновленные значения сразу становятся доступны для текущего пользователя или в системе в целом в зависимости от того, какие именно переменные редактировались или создавались. Также есть методы добавления переменных среды в командной строке или PowerShell, подробнее в статье: Как добавить путь в переменную среды PATH
Windows 10 supports a number of legacy features from older versions of the operating system. One of those legacy features is the environment variable. Environment variables offer a useful way to control the way Windows operates with an extremely small footprint in terms of memory usage.
For example, one common environment variable is called PATH, which is simply an ordered text string containing a list of directories that Windows should look in when an executable file is called. The PATH environment variable allows users to quickly launch programs without having to know where those programs live on the hard drive.
Setting environment variables is very useful and, fortunately, very simple. In this article, we’ll go over how to find and set your environment variables in Windows 10.
- Once logged in to Windows, right-click the Windows button in the lower-left corner of your screen and click System from the Power User Task Menu that’s displayed on the screen.
- Under the System menu, you need to click the Advanced System Settings.
- If you can’t find Advanced System Settings there, type “advanced system settings” into the search box and hit return to bring it up.
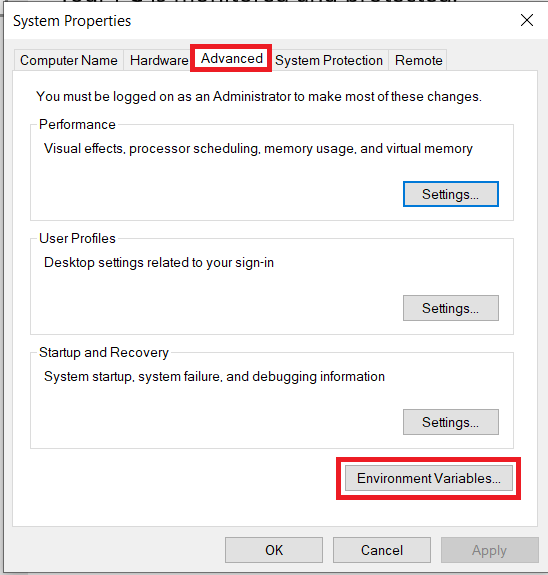
- Once Advanced System Settings is open, click on the Advanced tab, then look on the bottom-right side for the Environment Variables.
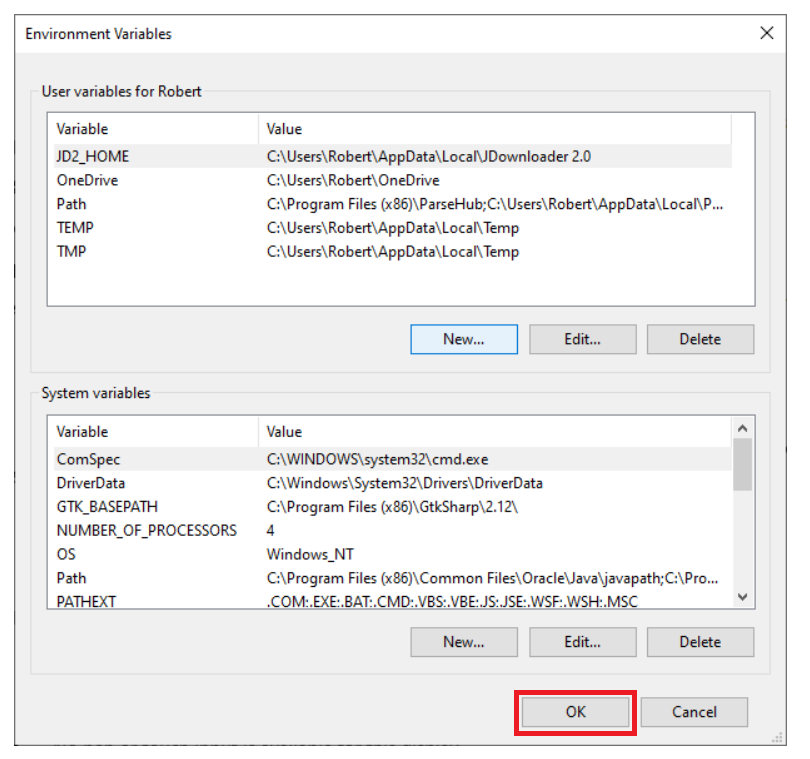
- Next, to create a new environment variable, click New. You might need to make a System variable depending upon what you’re doing.
- A dialog box will pop up, allowing you to enter a new variable name and to set its initial value:
- New adds a new environment variable.
- Edit lets you edit whatever environment variable you have selected.
- Delete lets you delete the selected environment variable.
- Save any changes that you make by clicking OK.
How to Find the PATH Variable in Windows 10
- Under the Environment Variables window, choose or highlight the PATH variable in the System Variables section shown in the window.
- After highlighting the PATH variable from System Variables, click the Edit button.
- You can add or modify the path lines with the directories you want your computer to look in for executable files.
- You will find that each different directory is separated with a semicolon, for example:
C:Program Files;C:Winnt;C:WinntSystem32
- You will find that each different directory is separated with a semicolon, for example:
- There are other environment variables in the System Variables section that you can examine by clicking Edit.
- Likewise, there are different environment variables, such as PATH, HOME, USER PROFILE, HOME and APP DATA, TERM, PS1, MAIL, TEMP, and so on. These Windows environment variables are very useful and can be used in scripts as well as on the command line.
- Once finished, you can test your changes by opening a new PowerShell window and entering the following:
$env:PATH
Frequently Asked Questions
Here is some more information about Environment Variables for you:
How Do I Find Environment Variables in Windows 10?
To find environment variables in Windows 10, you can follow the steps described above to find the environment variable information tucked away inside the system’s advanced settings.
Alternatively, if you just need to see what the variables are but don’t need to change them, you can simply open a command-line interface by hitting Ctrl +Esc and typing “cmd” in the command box, then type “set” in the command window. This prints out all the environment variables that are set on your system.
Why Can’t I Edit the Environment Variables?
There are several reasons that you may not be able to set these variables.
1. The first of your problems could be that you don’t have Admin rights. To set or edit this function, you must be the Administrator of the system.
2. If you are the Admin, yet the edit function is greyed out, try accessing the Environment Variables by accessing the Control Panel from the Start menu. Click on Advanced System Settings, then click Environment Variables.
Final Thoughts
Windows 10 environment variables make it incredibly easy to take control of your Windows device and make it run more efficiently. To find and set environment variables in Windows 10, follow the simple steps laid out in this article to get started.
Disclaimer: Some pages on this site may include an affiliate link. This does not effect our editorial in any way.
Send To Someone
Missing Device
Different programs and processes require different environments to run. On a single machine, Windows needs to make sure that all programs and processes can access the environments they need.
To do this, Windows needs to know the kind of environment every program requires to work. Windows must store this information somewhere for easier retrieval. Environment variables make that possible.
Environment variables are, in short, data storing mechanisms.
Let’s dig a little deeper to see how environment variables work and how you can create, edit, and delete them effectively.
What Are Environment Variables in Windows 10?
Environment variables are dynamic variables that store data related to creating different environments for different programs and processes.
To understand them better, let us take the example of a program that needs to use a built-in Windows tool to run.
For the program to use the tool, the program needs to know the tool’s location to access it. The program also needs to find out if it has permission to use the tool or not. Similarly, there are things that a program needs to know before it can use the tool.
So, a program can access all of this information by asking Windows. Windows then looks up environment variables (EVs) for this data and creates an environment in which that program can run.
In other words, EVs store data that is accessible to every program and process running on the system across all users. The data these variables store helps the programs run in the environment they were designed for.
Some of the most important EVs on Windows include PATH, HOMEPATH, and USERNAME. All of these variables contain values that any user and process of the system can access at any time. For instance, the USERNAME environment variable contains the name of the current user. Windows can look up this variable whenever it needs to find out the name of the current user.
How to Set Environment Variables in Windows 10?
First things first, if you want to set system-wide EVs, you need to have administrative privileges. So, if you are not the admin, inform your system administrator and ask for their help.
Now that you have admin privileges:
- Type Advanced system settings in the Start menu search box and select the Best match.
- In the System Properties box, click on Environment Variables to open the Environment Variables panel.
The EVs panel lists two types of variables depending upon your need. If you want to change EVs for the current user only and don’t want the changes to reflect system-wide, you will change User variables.
On the contrary, if you want system-wide changes, you will change System variables.
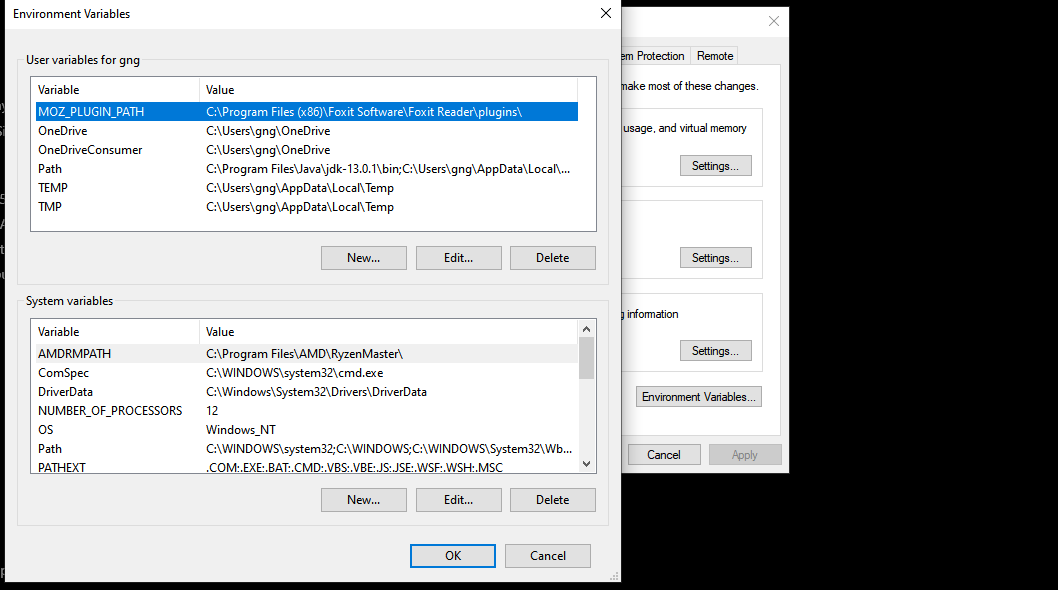
Let’s say you’ve just installed Java and want to add the java path to the EVs. To do this:
- Click on New under the User/System variables. This will open up the New User Variable box.
- Enter JAVA_HOME in the Variable name field and browse to the directory where you’ve installed Java to populate the path in Variable value.
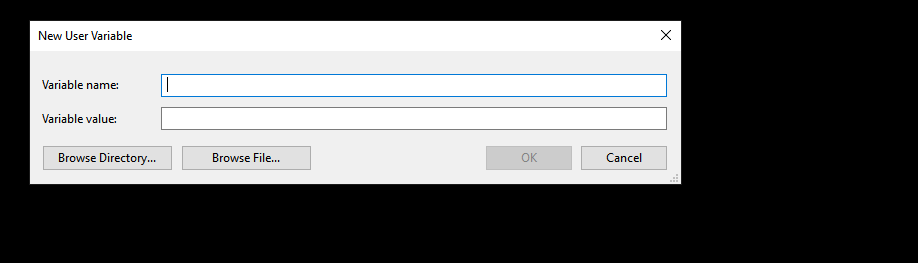
Pressing OK will add the JAVA_HOME variable to the PATH variable.
How to Edit Environment Variables
To edit different environment variables, select any variable from the list. Then, press Edit. This will open up the Edit environment variable panel. Here you can create, delete, and edit variables.
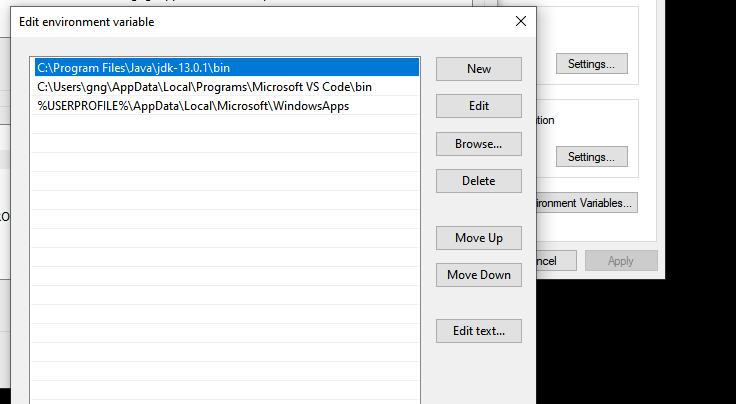
From the list of variables, select the one that you want to modify and click on Edit. Afterward, you can change the variable value to anything you like.
You can also delete the variables in a similar fashion.
What Is the Windows PATH Variable and How Can I Change it?
In simple terms, the PATH variable is an address book of programs and commands on your computer. Whenever you have a new program on your computer that you want to run from the command line interface, you must specify its address in the PATH variable.
A thing to remember here, not all programs are in the PATH environment variable. Only the programs that are meant to be used from the command line interface appear in the PATH variable. So, programs intended to be used from a Graphical User Interface don’t have their addresses in the PATH variable.
The way the process works involves Windows looking up the address for a certain command. Whenever you issue a command on a command line, Windows first searches the current directory for the command. If the OS can’t find it in the current directory, it looks up the PATH variable to find the address.
To enter an address in the PATH variable, the process is the same as before. Open up the Environment Variable box, select the PATH variable, and click on Edit.
In the Edit box, you can add, remove, and edit directories.
One final thing to remember, the PATH variable is not the same for every user on a system. So different users can list different directories without changing the variable for every user. So, if you want a tool to be available for every user, you have to edit the PATH variable under the System Variables.
Environment Variables in Windows 10 Store Data that Programs Need to Work
Programs need data to work. To make sure that data is available efficiently, Windows stores this data in global variables that all programs can access. These global variables are Environment Variables.
You can add, edit, and remove Environment Variables inside the Advanced System Settings panel.
Furthermore, if you have more than one user on a machine, user Environment Variables will be different for each user. For instance, one user may have listed a command under the PATH variable that won’t be available for other users.
On the other hand, system EVs are available for all users. These variables require admin privileges to edit or delete.
In short, EVs are Windows’ way to store important data. So, be sure you know what you are doing before modifying them.
Download Windows Speedup Tool to fix errors and make PC run faster
Environment Variables are responsible for storing information about the OS’s environment. Different apps and programs require different configurations and it is the job of Windows to ensure that each of them has the environment best suitable for them. Simply speaking, these Environment Variables are data-storing facilities. A PATH variable is one of the most useful of the kind and helps you to run any executable found within Paths without having to give the full path to the executable. In this article, we will be discussing how you can manually add or edit existing PATH environment variables on Windows 11 or Windows 10.
An Environment variable is useful in the sense that it influences how software processes take place. The data stored in them play an important role in the process. Our tutorial will help you set up PATH variables so that you can run executables from your custom directories. These PATH variables store shortcuts, so you can create them for the programs of your choice. A prerequisite to push PATH variables through is to grant administrative privileges, so make sure you have them enabled. If you want a more detailed explanation of what System & User Environment Variables are, you can read the linked post.
How to set PATH variables manually on Windows 11/10
Without further ado, let’s see how you can add or edit a PATH Environment Variable in Windows 11/10:
- Click on the Search menu on the Taskbar and open the Windows Settings
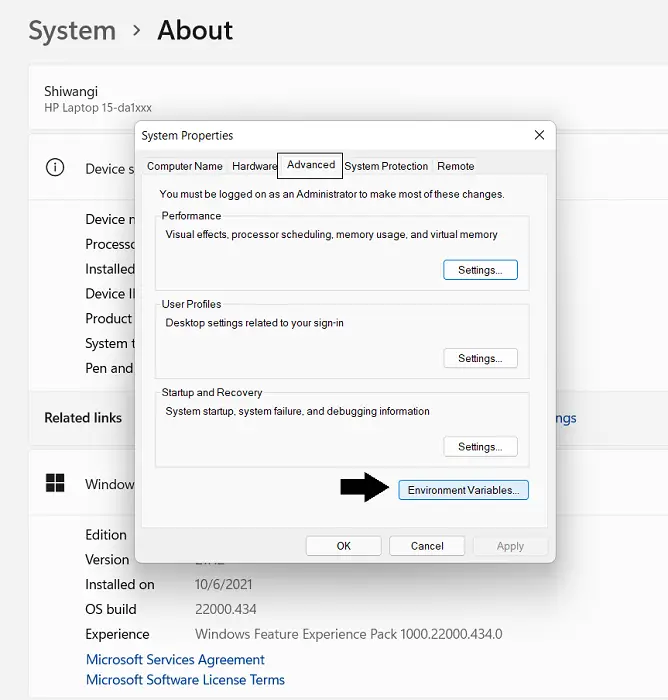
- From the Settings panel, click on the System option from the left menu pane
- Go to About and further click on Advanced System Settings. This will open a dialog box named System Properties
- Here, click on the Advanced tab and further click on the Environment Variables button on the bottom-right
- This will open the Environment Variables panel. Here, variables will be divided into two categories: System and User Variables. The former is applicable for system-wide changes while the latter is used to make modifications to the environment of a particular user. Make a decision based on the purpose of creating or editing a PATH variable and select PATH from a section
- Follow this by clicking on the Edit button
You can now modify the existing route lines with the ones you want your computer to access. This stuff may seem overwhelming to some of you and has very deep implications for some important PC processes, so you’re advised to express utmost caution.
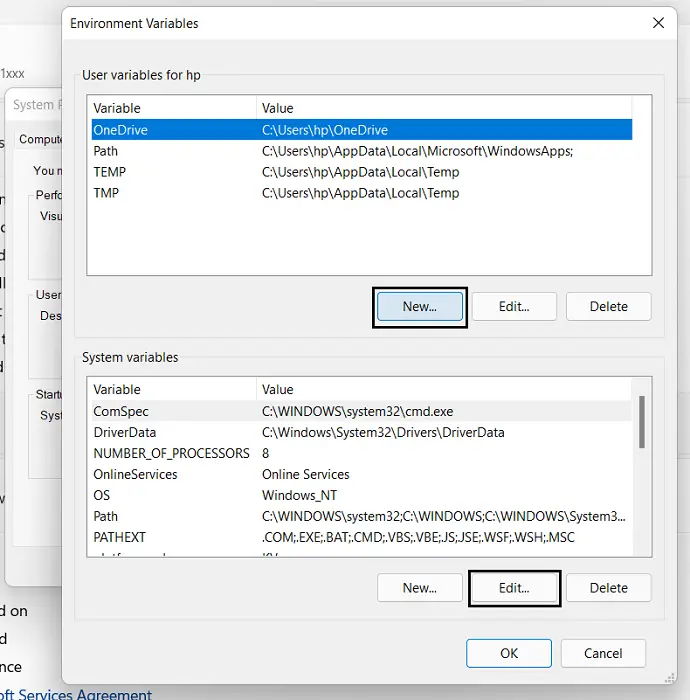
In order to add a new route, you can click on the ‘New’ button. You can delete a Path the same way. Here, you can just paste the Path of your choice, and if you’re unsure of it, then you can use the Surf option to go about searching for it. Once you’re done, click on Ok and a new PATH variable will now exist.
Our guide here explains how you can add Environment Variables to your Windows Context Menu.
Read: How to see Names and Values of Environment Variables in Windows
How do I change Environment Variables without admin rights?
Granting administrative rights may not be as easy when the PC isn’t yours, but you can still make changes to your environment variables. Via the Control Panel, you can modify the environment variables on a user account, but not System variables. Here’s how you can do that:
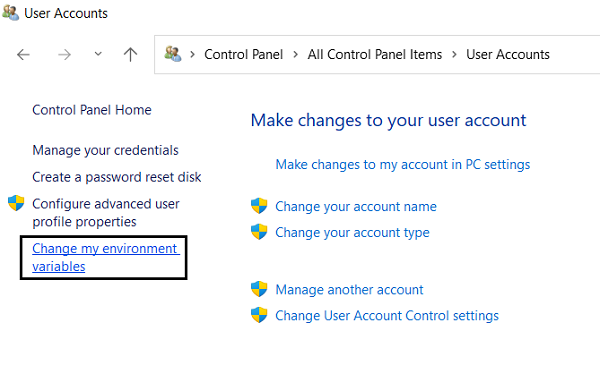
- Open the Control Panel
- Select to view them as ‘Small icons’ and click on User Accounts
- Here, you’ll see an option to your left named ‘Change my environment variables’
- This will open the same Environment Variables dialog box as before, except now the System Variables aren’t accessible and you can only make changes to User variables
TIPS:
- How to use Environment Variable Editor in PowerToys?
- Rapid Environment Editor is a powerful free Environment Variables Editor for Windows.
How do I change the Path in Windows Command Prompt?
A command line on your Windows Terminal (Command Prompt) can help you add a Path to your Path environment variable. The changes that we have discussed above can be implemented via the Command Prompt as well, but again, are limited to the User’s environment only. Here’s how:
- Search ‘CMD’ on the Taskbar search menu and select to run it as the administrator
- Enter the command ‘Pathman /au’ and follow it by the Path to the directory you want to append.
- Similarly, you can use a ‘Pathman/ru’ command to delete an existing Path to a directory
We hope that this post was helpful for you and that you can now take care of your Path environment variables with ease.
Shiwangi loves to dabble with and write about computers. Creating a System Restore Point first before installing new software, and being careful about any third-party offers while installing freeware is recommended.
Reader Interactions
Readers help support Windows Report. We may get a commission if you buy through our links.
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more
The Command Prompt tool is the last remnant of DOS (a former command-based operating system) preserved in Windows. You can open software and run handy tools, such as the System File Checker, with it.
For example, you can run SFC by entering sfc /scannow without specifying any path. To open third-party software in Windows 10, you usually need to input an entire directory in the Command Prompt.
What is the path environment variable in Windows?
The Edit environment variable window enables you to add new paths to third-party software to open the programs without entering their complete directories in the Command Prompt.
The path environment variable tells your system where to find the SFC, but not the software. Moreover, this variable could be a handy setting for those who often use the Command Prompt.
Microsoft even replaced the Edit System Variable dialog in earlier Windows platforms with a new Edit environment variable path window in Windows 10.
Users can edit this system path variable, and we will show you how to do this in the guide below.
-
1. Press the Windows key on your keyboard or the Start button on your taskbar to open the search box.
-
2. In the Windows search box, type advanced system settings and click on the result.
-
3. When the System properties window opens, select View advanced system settings.
-
4. Press the Environment Variables button to open the window shown below.
-
5. You need to select the Path in the System variables box. Selecting the Path and pressing the Edit button opens the window shown directly below.
-
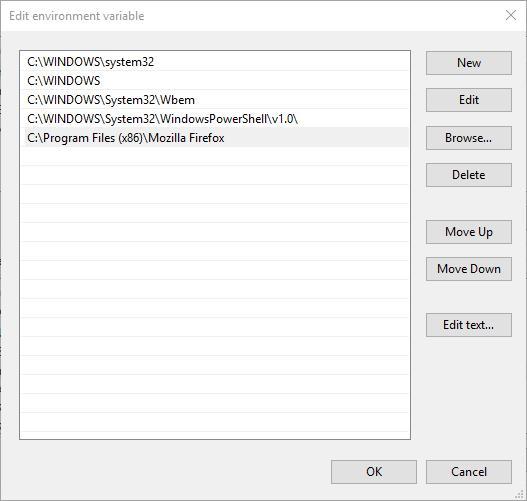
6. The Edit environment variable window above includes the following path:
C:\Windows\system32This is where the System File Checker tool is. To add your own path, press the New button.
-
7. Enter C: in the empty space and press the Browse button to select a folder (If you don’t enter something in the space for the new path, your selected folder directory replaces the path listed above it).
-
8. Select a folder that includes third-party software in the Browse for Folder window. For example, we selected a folder that includes Firefox.
-
9. Press the OK button on the Browse for Folder window to confirm the selection (The Edit environment variable window will include your selected path as in the snapshot below).
-
10. Click the OK button on the Edit environment variable window to close it.
-
11. Press the OK buttons on the Environment Variables and System Properties windows to close them.
-
12. Re-open the Windows search box and type cmd in it, then right-click on the result and select Run as Administrator, to open the app as below.
-
13. Now you can open the software path you added to the Edit environment variable window by entering its executable.
For example, if you added Firefox’s path to it you can open that browser by entering Firefox in the Command Prompt.
How can I edit the path on Windows 10?
The easiest way to edit the path variable in Windows 10 is through the View advanced system setting. There you can add, edit, or delete a path variable.
After that, you can set the path that’s of interest to you and modify it in any way you want.
- How to save text from the Command Prompt in Windows 10
- How to Fix Opera Browser if It Fails to Install or Download
- 10 Ways to Fix File Explorer Problems in Windows 10/11
- 16 Ways To Stop Firefox From Using Too Much Memory in 2022
- Windows Explorer stops when copying files? Fix it like a pro
A program’s executable doesn’t always match the exact software title. For example, we found that Opera’s executable was Launcher. As such, check the software’s executable title in File Explorer and then enter that in the Command Prompt.
You no longer need to enter C:\folder\sub-folder\sub-folder software title to open a program. This certainly comes in handy if you’re unsure of the software’s path.
This is a fairly simple process, and after following the steps above, setting, editing, or changing the path environment variable in Windows 10 should be more or less a formality.
If you have any other questions about the process, please leave them in the comments section below.
Matthew Adams
Windows Hardware Expert
Matthew is a freelancer who has produced a variety of articles on various topics related to technology. His main focus is the Windows OS and all the things surrounding it.
He is passionate about the tech world, always staying up-to-date with the latest and greatest. With an analytical view, he likes problem-solving, focusing on errors and their causes.
In his free time, he likes to read and write about history and tries to always develop new skills.