You can use the Explorer to find (‘explore’) the files on your computer. It is the ideal program for organizing and retrieving your documents. How exactly does this program work and what can you do with it?
The editors are no longer updating this article. You can still consult this article, but the content may deviate from the current situation. Because Windows Vista is still little used, we are not making new articles and tips for this operating system. SeniorWeb members can contact PCHulp with questions, or exchange knowledge in the Windows Club.
Different operating system?
In this article, we’ll discuss File Explorer in Windows Vista.
- Do you have Windows 7? Then read the article ‘The Explorer (Windows 7)’.
- Do you have Windows 8.1? Then read the article ‘The Explorer (Windows 8.1)’.
What is the Explorer?
In Windows Explorer, you can see the files, folders, and locations on your computer. Windows Explorer lets you find, copy, and move files and folders, and rename files and folders. For example, you can move a document from one folder to another folder.
Where can I find the Explorer?
The File Explorer is ‘hidden’ in the Start menu. Click with the mouse on the button Start, then choose All programs and then desk accessories. You see the Windows Explorer standing in between. Click on it to open the program.
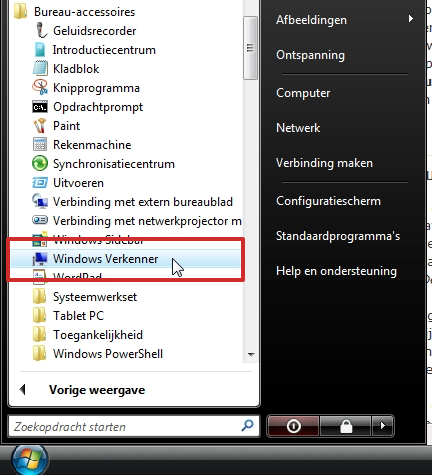
To place a shortcut to File Explorer on your Desktop, right-click on Windows Explorer. Then you choose Copy to…Desktop. The shortcut will be placed on the Desktop, and from now on you can open File Explorer from there (it’s that easy).
Using the keyboard shortcuts Windows Key+E, you can start the Explorer even more easily. Press the Windows key and the E key at the same time and the Explorer will start.
Appearance of the Explorer
The Explorer opens the folder by default Documents . You will see two split screens. On the left is an overview of the folders on your computer. On the right you can see the contents of the selected folder. You can double click on files in the right pane to open them. Want to look up something from another folder? Then browse to the relevant folder in the left window. You will then see the content appear on the right.
At the top of the Explorer you will see the menu bar, with the options File , To process , Image , Additional and Help . We will discuss these later in this article.
The menus
In addition to viewing and browsing files, File Explorer lets you add new files, rename them, and more. You can arrange this with the menus at the top of the menu bar. The procedure is always the same: in the main window, navigate to the desired folder or file. Then select the folder/file and use the menus at the top for further actions. We now go through them one by one.
File menu
If you have selected a particular folder in File Explorer, you can access it from the menu File add new files. For example, to add a new Word document to My Documents, navigate to this folder with File Explorer. Then click File > New.
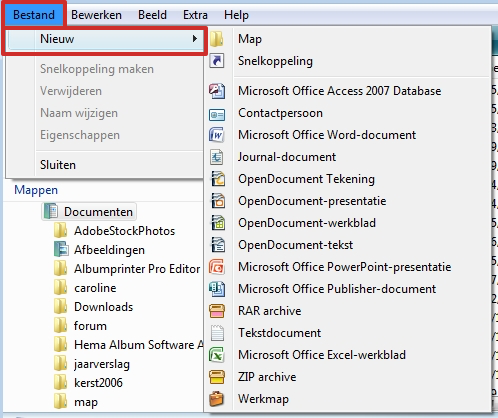
You then choose the desired file type, in this case Word document. You give it a name, and voila: the new file is added. In this way you can also create subfolders in My Documents, or in other folders.
You can also delete or rename selected files here.
Edit menu
Using this menu you can delete files, copy them, select the contents of an entire folder, or invert the selection. Be careful what you throw away: you should of course know how to throw away your personal documents, but it is better not to mess with system files or parts of Windows. To copy a file, select it with the mouse and choose Copy from this menu. Then navigate to the destination, and select To stick from this menu. The file you selected will now be copied to the destination location.
Menu Picture
This is a very useful menu. The option Toolbars expands the number of toolbars in the Explorer. This can be useful, but is not necessary. A check mark for the option status bar conjures up an extra bar at the bottom of your screen, containing information about the number of objects in the folder you selected.
The other options in the View menu are also useful. For example, you can specify whether you want to see details of the file names, or rather thumbnails (icons) of the files. If you are viewing photos that can be useful, what exactly can be seen in an image can often not be deduced from the file name. Icons allow you to see small representations of the images. Again, you can experiment with which view you like best.
You can also indicate here whether you want to sort the icons (or folder contents) by, for example Name or Type .
Menu Tools
The most interesting part of this menu are the Folder options.
This allows you to determine how you want the files to be displayed and which files you will and will not see. Scroll through the three tabs (General, Display and File types) and see what the options are.
Help menu
The Help menu opens the Windows Help and Support. By default, Help opens with information about “Folders.”
Standard buttons (1)
You will also find the standard buttons in the Explorer, which you can see on the right.
Use the arrow buttons to move to the previous or next folder. You can quickly search for files in the search box.
Standard buttons (2)
Under the buttons Organize and Image you will find options that can also be found in the main menu. Handy to the View button is that you can quickly change the layout of a folder. With the button To burn you can copy the contents of a folder to DVD or CD-ROM.
Now you are aware of the most important parts of the Explorer. View them at your leisure and discover their many possibilities!
This article is about the Microsoft Windows file listing browser. For exploring file system listings, see file browser. For exploring inside files, see file viewer.
«Windows Explorer» and «explorer.exe» redirect here. They are not to be confused with Internet Explorer (iexplore.exe).
Windows File Explorer
|
File Explorer on Windows 11 in Light App Mode showing special folders on Home, with the new command bar and tabs feature |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Initial release | August 15, 1995; 29 years ago |
| Stable release |
24H2 (10.0.26100.3915) (April 25, 2025; 9 days ago[1]) [±] |
| Preview release |
;Release Preview Channel 24H2 (10.0.26100.3915) (April 25, 2025; 9 days ago[2][3]) [±]
24H2 (10.0.26120.3941) (April 25, 2025; 9 days ago[4]) [±]
24H2 (10.0.26200.5570) (April 25, 2025; 9 days ago[5]) [±]
10.0.27842.1000 (April 23, 2025; 11 days ago[6]) [±] |
| Included with | Windows 95 and later |
| Predecessor | Program Manager, File Manager |
| Type | Shell, file manager |
File Explorer, previously known as Windows Explorer, is a file manager application and default desktop environment that is included with releases of the Microsoft Windows operating system from Windows 95 onwards. It provides a graphical user interface for accessing the file systems, as well as user interface elements such as the taskbar and desktop.
The application was renamed from «Windows Explorer» to «File Explorer» in Windows 8;[7] however, the old name of «Windows Explorer» can still be seen in the Windows Task Manager.
Windows Explorer was first included with Windows 95 as a replacement for File Manager, which came with all versions of Windows 3.x operating systems. Explorer could be accessed by double-clicking the new My Computer desktop icon or launched from the new Start Menu that replaced the earlier Program Manager. There is also a shortcut key combination: Windows key+E. Successive versions of Windows (and in some cases, Internet Explorer) introduced new features and capabilities, removed other features, and generally progressed from being a simple file system navigation tool into a task-based file management system.
While «Windows Explorer» or «File Explorer» is a term most commonly used to describe the file management aspect of the operating system, the Explorer process also houses the operating system’s search functionality and File Type associations (based on filename extensions), and is responsible for displaying the desktop icons, the Start Menu, the Taskbar, and the Control Panel. Collectively, these features are known as the Windows shell.
File Explorer is the default user interface for accessing and managing the file systems, but it is possible to perform such tasks on Windows without File Explorer. For example, the File ▸ Run menu option in Task Manager on Windows NT or later functions independently of File Explorer, as do commands run within a command prompt window.
After a user logs in, the explorer process is created by the userinit process. Userinit performs some initialization of the user environment (such as running the login script and applying group policies) and then looks in the registry at the Shell value and creates a process to run the system-defined shell – by default, Explorer.exe. Then Userinit exits. This is why Explorer.exe is shown by various process explorers with no parent – its parent has exited.
In 1995, Microsoft first released test versions of a shell refresh, named the Shell Technology Preview, and often referred to informally as «NewShell».[8] The update was designed to replace the Windows 3.x Program Manager/File Manager based shell with Windows Explorer. The release provided capabilities quite similar to that of the Windows «Chicago» (codename for Windows 95) shell during its late beta phases, however was intended to be nothing more than a test release.[9] There were two public releases of the Shell Technology Preview, made available to MSDN and CompuServe users: May 26, 1995, and August 8, 1995. Both held Windows Explorer builds of 3.51.1053.1. The Shell Technology Preview program never saw a final release under NT 3.51. The entire program was moved across to the Cairo development group who finally integrated the new shell design into the NT code with the release of NT 4.0 in July 1996.
Windows 98 and Windows Desktop Update
[edit]
With the release of the Windows Desktop Update (packaged with Internet Explorer 4 as an optional component, and included in Windows 98), Windows Explorer became «integrated» with Internet Explorer, most notably with the addition of navigation arrows (back and forward) for moving between recently visited directories, as well as Internet Explorer’s Favorites menu.
An address bar was also added to Windows Explorer, which a user could type in directory paths directly, and be taken to that folder.
Another feature that was based on Internet Explorer technology was customized folders. Such folders contained a hidden web page that controlled the way the Windows Explorer displayed the contents of the folder.
Windows ME and Windows 2000
[edit]
The «Web-style» folders view, with the left Explorer pane displaying details for the object currently selected, is turned on by default. For certain file types, such as pictures and media files, a preview is also displayed in the left pane.[10] The Windows 2000 Explorer featured an interactive media player as the previewer for sound and video files. However, such a previewer can be enabled in Windows ME through the use of folder customization templates.[11] Windows Explorer in Windows 2000 and Windows ME allows for custom thumbnail previewers and tooltip handlers. The default file tooltip displays file title, author, subject and comments;[12] this metadata may be read from a special NTFS stream, if the file is on an NTFS volume, or from a COM Structured Storage stream, if the file is a structured storage document. All Microsoft Office documents since Office 95[13] make use of structured storage, so their metadata is displayable in the Windows 2000 Explorer default tooltip. File shortcuts can also store comments which are displayed as a tooltip when the mouse hovers over the shortcut.
The right-hand pane, which usually just lists files and folders, can also be customized. For example, the contents of the system folders aren’t displayed by default, instead showing in the right pane a warning to the user that modifying the contents of the system folders could harm their computer. It’s possible to define additional Explorer panes by using DIV elements in folder template files.[14] This feature was abused by computer viruses that employed malicious scripts, Java applets, or ActiveX controls in folder template files as their infection vector. Two such viruses are VBS/Roor-C[15] and VBS.Redlof.a.[16]
Other Explorer UI elements that can be customized include columns in «Details» view, icon overlays, and search providers: the new DHTML-based search pane is integrated into Windows 2000 Explorer, unlike the separate search dialog found in all previous Explorer versions.[17]
Search capabilities were added, offering full-text searches of documents, with options to filter by date (including arbitrary ranges like «modified within the last week»), size, and file type. The Indexing Service has also been integrated into the operating system and the search pane built into Explorer allows searching files indexed by its database.[18] The ability to customize the standard buttons was also added.
Windows XP and Windows Server 2003
[edit]
There were significant changes made to Windows Explorer in Windows XP, both visually and functionally. Microsoft focused especially on making Explorer more discoverable and task-based, as well as adding several new features to reflect the growing use of a computer as a digital hub.
Windows Explorer in Windows Server 2003 contains all the same features as Windows XP, but the task panes and search companion are disabled by default.
The task pane is displayed on the left-hand side of the window instead of the traditional folder tree view. It presents the user with a list of common actions and destinations that are relevant to the current directory or file(s) selected. For instance, when in a directory containing mostly pictures, a set of «Picture tasks» is shown, offering the options to display these pictures as a slide show, to print them out, or to go online to order prints. Conversely, a folder containing music files would offer options to play those files in a media player or to go online to purchase music. Windows XP had a Media bar but it was removed with SP1. The Media Bar was only available with Windows XP RTM.
Every folder also has «File and Folder Tasks», offering options to create new folders, share a folder on the local network, publish files or folders to a website, and other common tasks like copying, renaming, moving, and deleting files or folders. File types that have identified themselves as being printable also have an option listed to print the file.
Underneath «Other Places» is a «Details» pane which gives additional information – typically file size and date, but depending on the file type, a thumbnail preview, author, image dimensions, or other details.
The «Folders» button on the Windows Explorer toolbar toggles between the traditional tree view of folders, and the task pane. Users can get rid of the task pane or restore it using the sequence: Tools – Folder Options – General – Show Common Tasks/Use Windows Classic Folders.
Microsoft introduced animated «Search Companions» in an attempt to make searching more engaging and friendly; the default character is a puppy named Rover (previously used in Microsoft Bob), with three other characters (Merlin the magician, Earl the surfer, and Courtney) also available. These search companions use the same technology as Microsoft Office’s Office Assistants, even incorporating «tricks» and sound effects, and they can be used as Office Assistants if their files are copied into the C:\Windows\msagent\chars folder.[19]
The search capability itself is fairly similar to Windows ME and Windows 2000, with one major addition: Search can also be instructed to search only files that are categorical «Documents» or «Pictures, music and video»; this feature is noteworthy largely because of how Windows determines what types of files can be classified under these categories. In order to maintain a relevant list of file types, Windows Explorer connects to Microsoft and downloads a set of XML files that define what these file types are. The Search Companion can be disabled in favor of the classic search pane used in Windows 2000 by using the Tweak UI applet from Microsoft’s PowerToys for Windows XP, or by manually editing the registry.
Windows XP improves image preview in Explorer by offering a Filmstrip view. «Back» and «Previous» buttons facilitate navigation through the pictures, and a pair of «Rotate» buttons offer 90-degree clockwise and counter-clockwise (lossy)[20] rotation of images. Aside from the Filmstrip view mode, there is a ‘Thumbnails’ mode, which displays thumbnail-sized images in the folder. A Folder containing images will also show thumbnails of four of the images from that folder overlaid on top of a large folder icon.
Web sites that offer image hosting services can be plugged into Windows Explorer, which the user can use to select images on their computer, and have them uploaded correctly without dealing with comparatively complex solutions involving FTP or web interfaces.[citation needed]
- Explorer gained the ability to understand the metadata of a number of types of files. For example, with images from a digital camera, the Exif information can be viewed, both in the Properties pages for the photo itself, as well as via optional additional Details View columns.
- A Tile view mode was added, which displays the file’s icon in a larger size (48 × 48), and places the file name, descriptive type, and additional information (typically the file size for data files, and the publisher name for applications) to the right.
- The Details view also presented an additional option called «Show in Groups» which allows the Explorer to separate its contents by headings based on the field which is used to sort the items.
- The taskbar can be locked to prevent it from accidentally being moved.
- Windows Explorer also gained the ability to burn CDs and DVD-RAM discs in Windows XP.
- Ability to create and open ZIP files, called «compressed folders», which is a file containing other files.[21][22]
- Ability to open Cabinet (.cab) files, another type of file that contains other files.[23]
- If a
.HTMor.HTMLfile is copied or moved, the accompanying_filessuffix folder is copied or moved among it automatically.[24]
ZIP and CAB files are integrated into the user interface so they can be browsed as if they were ordinary folders. Given that files contained inside ZIP files can not be opened directly, they are automatically extracted to a temporary location and launched with the associated program from the temporary location when opened, to make the appearance that the ZIP file is a real directory.[21]
Removed and changed features
[edit]
|
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (December 2012) |
- The sort order has changed compared to the one in Windows 2000. For file names containing numbers Windows Explorer now tries to sort based on numerical value rather than just comparing each number digit by digit.[25]
Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008
[edit]
Search, organizing and metadata
[edit]
Windows Explorer includes significant changes from previous versions of Windows such as improved filtering, sorting, grouping and stacking. Combined with integrated desktop search, Windows Explorer allows users to find and organize their files in new ways, such as stacks.[26][27] The new Stacks viewing mode groups files according to the criterion specified by the user.[27] Stacks can be clicked to filter the files shown in Windows Explorer. There is also the ability to save searches as virtual folders or search folders.[28] A search folder is simply an XML file, which stores the query in a form that can be used by the Windows search subsystem.[29] When accessed, the search is executed and the results are aggregated and presented as a virtual folder.[28] Windows Vista includes six search folders by default: recent documents, recent e-mail, recent music, recent pictures and videos, recent changed, and «Shared by Me».[30] Additionally, search operators for properties were introduced, such as kind:music.[31] Since at least Windows 7, comparison operators «greater than» and «less than» are supported to search for any supported attribute such as date ranges and file sizes, like size:>100MB to search for all files that are greater than 100 MB.[32] Attributes sortable and searchable in Windows Explorer include pictures’ dimensions, Exif data such as aperture and exposure, video duration and framerate and width.[33]
When sorting items, the sort order no longer remains consistently Ascending or Descending. Each property has a preferred sort direction. For example, sort by date defaults to descending order, as does size. But name and type default to ascending order.
Searching for files containing a given text string became problematic with Vista unless the files had been indexed. An alternative is to use the findstr command-line function.[34] After right-clicking on a folder one can open a command-line prompt in that folder.
Windows Explorer also contains modifications in the visualization of files on a computer. A new addition to Windows Explorer in Vista and Server 2008 is the details pane, which displays metadata and information relating to the currently selected file or folder. The details pane will also display a thumbnail of the file or an icon of the filetype if the file does not contain visual information. Furthermore, different imagery is overlaid on thumbnails to give more information about the file, such as a picture frame around the thumbnail of an image file, or a filmstrip on a video file.
The details pane also allows for the change of some textual metadata such as author and title in files that support them within Windows Explorer. A new type of metadata called tags allows users to add descriptive terms to documents for easier categorization and retrieval. Some files support open metadata, allowing users to define new types of metadata for their files. Out-of-the-box, Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 supports Microsoft Office documents and most audio and video files. Support for other file types can however be added by writing specialized software to retrieve the metadata at the shell’s request. Metadata stored in a file’s alternate data stream only on NTFS volumes cannot be viewed and edited through the summary tab of the file’s properties anymore. Instead, all metadata is stored inside the file, so that it will always travel with the file and not be dependent on the file system.[35]
Windows Explorer in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 also introduces a new layout. The task panes from Windows XP are replaced with a toolbar on top and a navigation pane on the left. The navigation pane contains commonly accessed folders and preconfigured search folders. Eight different views are available to view files and folders, including extra large, large, medium, small, list, details, tiles, and content. In addition, column headers now appear in all icon viewing modes,[27] unlike Windows XP where they only appear in the details icon viewing mode.[26] File and folder actions such as cut, copy, paste, undo, redo, delete, rename and properties are built into a dropdown menu which appears when the Organize button is clicked. It is also possible to change the layout of the Explorer window by using the Organize button. Users can select whether to display classic menus, a search pane, a preview pane, a reading pane, and the navigation pane. The preview pane enables users to preview files (e.g., documents or media files) without opening them. If an application, such as Office 2007, installs preview handlers for file types, then these files can also be edited within the preview pane itself.[36]
Windows Vista saw the introduction of the breadcrumb bar for easier navigation. As opposed to the prior address bar which displayed the current folder in a simple editable combobox, this new style structures the path into clickable levels of folder hierarchy (though falls back to the classic edit mode when a blank area is clicked), enabling the user to skip as many levels as desired in one click rather than repeatedly clicking «Up». It is also possible to navigate to any subfolder of the current folder using the arrow to the right of the last item. The menu bar is now hidden by default but reappears temporarily when the user presses Alt.
Check boxes in Windows Explorer allow the selection of multiple files.[37] Free and used space on all drives is shown in horizontal indicator bars. Icons of various sizes are supported: 16 x 16, 24 x 24, 32 x 32, 48 x 48, 64 x 64, 96 x 96, 128 x 128 and 256 x 256. Windows Explorer can zoom the icons in and out using a slider or by holding down the Ctrl key and using the mouse scrollwheel.[38] Live icons can display the content of folders and files themselves rather than generic icons.[39]
With the release of Windows Vista and Server 2008 and Windows Internet Explorer 7 for Windows XP, Internet Explorer is no longer integrated with Windows Explorer. In Windows Vista and Server 2008 (and in Windows XP as well if IE7 or 8 is installed), Windows Explorer no longer displays web pages, and IE7 does not support use as a file manager, although one will separately launch the other as necessary.
When moving or copying files from one folder to another, if two files have the same name, an option is now available to rename the file; in previous versions of Windows, the user was prompted to choose either a replacement or cancel moving the file. Also, when renaming a file, Explorer only highlights the filename without selecting the extension. Renaming multiple files is quicker as pressing Tab automatically renames the existing file or folder and opens the file name text field for the next file for renaming. Shift+Tab allows renaming in the same manner upwards.
Support for burning data on DVDs (DVD±R, DVD±R DL, DVD±R RW) in addition to CDs and DVD-RAM using version 2.0 of the Image Mastering API, as well as Live File System support was added.[40]
If a file is in use by another application, Windows Explorer tells users to close the application and retry the file operation. Also, a new interface IFileIsInUse is introduced into the API which developers can use to let other applications switch to the main window of the application that has the file open or simply close the file from the «File in Use» dialog. If the running application exposes these operations by means of the IFileIsInUse interface, Windows Explorer, upon encountering a locked file, allows the user to close the file or switch to the application from the dialog box itself.[41]
Windows Vista introduced pre-included support for the Media Transfer Protocol.[citation needed]
Removed and changed features
[edit]
The ability to customize the layout and buttons on the toolbars has been removed in Windows Vista’s Explorer, as has the ability to add a password to a zip file (compressed folder). The Toolbar button in Explorer to go up one folder from the current folder has been removed (the function still exists however, one can move up a folder by pressing Alt + ↑). Although still fully available from the menus and keyboard shortcuts, toolbar buttons for Cut, Copy, Paste, Undo, Delete, Properties and some others are no longer available. The Menu Bar is also hidden by default but is still available by pressing the Alt key or changing its visibility in the layout options. Several other features are removed such as showing the size on the status bar without selecting items, storing metadata in NTFS alternate data streams,[42] the IColumnProvider interface which allowed addition of custom columns to Explorer[43] and folder background customization using desktop.ini.
The ability to right-click a folder and hit «Search» was removed in Windows Vista Service Pack 1. Users must open the folder they wish to search in and enter their keywords in the search field located on the top right corner of the window. Alternatively, users can specify other search parameters through the «Advanced Search» UI, which can be accessed by clicking on the Organize Bar and selecting Search Pane under the Layout submenu. Pressing F3 also opens the «Advanced Search» interface.
Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2
[edit]
Windows Explorer in Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 supports libraries, virtual folders described in a .library-ms file that aggregates content from various locations – including shared folders on networked systems if the shared folder has been indexed by the host system – and present them in a unified view. Searching in a library automatically federates the query to the remote systems, in addition to searching on the local system, so that files on the remote systems are also searched. Unlike search folders, Libraries are backed by a physical location which allows files to be saved in the libraries. Such files are transparently saved in the backing physical folder. The default save location for a library may be configured by the user, as can the default view layout for each library. Libraries are generally stored in the libraries special folder, which allows them to be displayed on the navigation pane.
By default, a new user account in Windows 7 contains four libraries, for different file types: Documents, Music, Pictures, and Videos. They are configured to include the user’s profile folders for these respective file types, as well as the computer’s corresponding Public folders.
In addition to aggregating multiple storage locations, Libraries enable Arrangement Views and Search Filter Suggestions. Arrangement Views allow users to pivot their views of the library’s contents based on metadata. For example, selecting the «By Month» view in the Pictures library will display photos in stacks, where each stack represents a month of photos based on the date they were taken. In the Music library, the «By Artist» view will display stacks of albums from the artists in their collections, and browsing into an artist stack will then display the relevant albums.
Search Filter Suggestions are a new feature of the Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 Explorer’s search box. When the user clicks in the search box, a menu shows up below it showing recent searches as well as suggested Advanced Query Syntax filters that the user can type. When one is selected (or typed in manually), the menu will update to show the possible values to filter by for that property, and this list is based on the current location and other parts of the query already typed. For example, selecting the «tags» filter or typing «tags:» into the search box will display the list of possible tag values which will return search results.
The metadata written within the file, implemented in Vista, is also utilized in Windows 7. This can sometimes lead to long wait times displaying the contents of a folder. For example, if a folder contains many large video files totaling hundreds of gigabytes, and the Window Explorer pane is in Details view mode showing a property contained within the metadata (for example Date, Length, Frame Height), Windows Explorer might have to search the contents of the whole file for the meta data. Some damaged files can cause a prolonged delay as well. This is due to metadata information being able to be placed anywhere within the file, beginning, middle, or end, necessitating a search of the whole file. Lengthy delays also occur when displaying the contents of a folder with many different types of program icons. The icon is contained in the metadata. Some programs cause the activation of a virus scan when retrieving the icon information from the metadata, hence producing a lengthy delay.[35]
Arrangement Views and Search Filter Suggestions are database-backed features that require that all locations in the Library be indexed by the Windows Search service. Local disk locations must be indexed by the local indexer, and Windows Explorer will automatically add locations to the indexing scope when they are included in a library. Remote locations can be indexed by the indexer on another Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 machine, on a Windows machine running Windows Search 4 (such as Windows Vista or Windows Home Server), or on another device that implements the MS-WSP remote query protocol.[44]
Windows Explorer also supports federating search to external data sources, such as custom databases or web services, that are exposed over the web and described via an OpenSearch definition. The federated location description (called a Search Connector) is provided as a .osdx file. Once installed, the data source becomes queryable directly from Windows Explorer. Windows Explorer features, such as previews and thumbnails, work with the results of a federated search as well.
- Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 support showing icons in the context menu and creating cascaded context menus with static verbs in submenus using the Registry instead of a shell extension.[45]
- The search box in the Explorer window and the address bar can be resized.
- Certain folders in the navigation pane can be hidden to reduce clutter.
- Progress bars and overlay icons on an application’s button on the taskbar.
- Content view which shows thumbnails and metadata.
- Buttons to toggle the preview pane and create a new folder.
Removed or changed features
[edit]
In Windows 7, several features have been removed from Windows Explorer, including the collapsible folder pane, overlay icon for shared items, remembering individual folder window sizes and positions, free disk space on the status bar, icons on the command bar, ability to disable Auto Arrange and Align to Grid, sortable column headings in other views except details view, ability to disable full row selection in details view, automatic horizontal scrolling and scrollbar in the navigation pane and maintaining selection when sorting from the Edit menu.
Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012
[edit]
The file manager on Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 is renamed File Explorer and introduces new features such as a redesigned interface incorporating a ribbon toolbar, and a redesigned file operation dialog that displays more detailed progress and allows for file operations to be paused and resumed. The details pane from Windows Vista and 7 was removed and replaced with a narrower pane with no icons and fewer detail columns. But other details are displayed by hovering over the file’s name.[46][7]
Windows 10 and Windows Server 2016
[edit]
File Explorer’s icons were redesigned to fit with the more flat and simplified theming of Windows 10 as a whole. The window border padding is thinner than previous versions. Windows 10 Creators Update and later versions come with a new Universal File Explorer (also known as the UWP File Explorer). Although hidden, it can be opened by creating a shortcut pointing to «explorer shell:AppsFolder\c5e2524a-ea46-4f67-841f-6a9465d9d515_cw5n1h2txyewy!App» [47][48] A Dark mode was added to the software in 2018, to match similar themes available for other inbuilt Windows applications.[49]
Windows 10, version 1809 and Windows Server 2019
[edit]
A «dark mode» has been added to File Explorer in Windows 10, version 1809 and Windows Server 2019.[50] The Universal File Explorer also includes new features.[51][52]
Windows 10, version 1909
[edit]
Windows Search and OneDrive have been integrated into File Explorer’s search feature in Windows 10, version 1909.[53]
In Windows 11, File Explorer had undergone significant UI changes, with the Ribbon Interface dating back to Windows 7 having been reworked into a command bar. Translucency, shadows, and rounded geometry have also been added, following the Microsoft’s new Fluent Design System. In March 2022, Microsoft introduced adverts into File Explorer, but later stated that these were «not intended to be published externally» after significant negative media coverage.[54]
Windows 11 2022 Update
[edit]
On April 5, 2022, Microsoft announced that it would be adding tabs, favorites, and a new homepage to File Explorer.[55] These features were eventually introduced via an update to the Windows 11 2022 Update on October 18, 2022.[56]
Windows 11 2023 Update
[edit]
On 21 September, 2023, Microsoft announced that it would be adding a modern home page, address bar, search experience, and details pane, along with an update gallery pane.[57] This update was released to most Windows 11 users via an enablement package to Windows 11, 22H2. The full release is slated to come out with the full release of Windows 11 23H2. The new File Explorer is now based on XAML technology, instead of the former Win32 technology.
File Explorer can be extended to support non-default functionality by means of Windows shell extensions, which are COM objects that plug the extended functionality into Windows Explorer.[58] Shell extensions can be in the form of shell extension handlers, toolbars or even namespace extensions that allow certain folders (or even non-filesystem objects such as the images scanned by a scanner) to be presented as a special folder. File Explorer also allows metadata for files to be added as NTFS alternate data streams, separate from the data stream for the file.
Shell extension handlers are queried by the shell beforehand for modifying the action the shell takes. They can be associated on a per file type – where they will show up only when a particular action takes place on a particular file type – or on a global basis – which are always available. The shell supports the following extension handlers:
| Handler | Description | Can be implemented on | Required shell version |
|---|---|---|---|
| Context menu handler | Adds menu items to the context menu. It is called before the context menu is displayed. | Per file type | Windows 95 and later. Windows 7 introduced IExecuteCommand |
| Drag-and-drop handler | Controls the action upon right-click drag and drop and modifies the context menu that appears. | Global | Windows 95 and later |
| Drop target handler | Controls the action after a data object is dragged and dropped over a drop target such as a file. | Per file type | Windows 95 and later |
| Data object handler | Controls the action after a file is copied to the clipboard or dragged and dropped over a drop target. It can provide additional clipboard formats to the drop target. | Per file type | Windows 95 and later |
| Icon handler | Assigns a custom icon to an individual file amongst a class of file types. It is called before file icons are displayed. | Per file type | Windows 95 and later |
| Property sheet handler | Replaces or adds pages to the property sheet dialog box of an object. | Per file type | Windows 95 and later |
| Copy hook handler | Allows running, modifying or denying the action when a user or application tries to copy, move, delete, or rename an object. | Not associated with a file type | Windows 95 and later |
| Search handler | Allows shell integration of a custom search engine. | Not associated with a file type | Windows 95 through Windows XP |
| Infotip handler | Allows retrieving flags and infotip information for an item and displaying it inside a popup tooltip upon mouse hover. | Per file type | Windows Desktop Update and later |
| Thumbnail image handler | Provides for a thumbnail image to be generated and displayed along with its alpha type when a file is selected or the thumbnail view is activated. | Per file type | Windows Desktop Update and later. Windows Vista introduced a newer IThumbnailProvider interface that also shows thumbnails in the Details pane. The older IExtractImage is still supported but not in the Details pane.[59] |
| Disk Cleanup handler | Add a new entry to the Disk Cleanup application and allows specifying additional disk locations or files to clean up. | Per folder | Windows 98 and later |
| Column handler | Allows creating and displaying custom columns in Windows Explorer details view. It can be used to extend sorting and grouping. | Per folder | Windows 2000 and later |
| Icon overlay handler | Allows displaying an overlay icon over a shell object (a file or folder icon). | Per file type | Windows 2000 and later |
| Metadata handler | Allows viewing and modifying metadata stored in a file. It can be used to extend details view columns, infotips, property pages, sorting and grouping. | Per file type | Windows 2000 and later |
| Filter handler (IFilter) | Allows file properties and its contents to be indexed and searched by Indexing Service or Windows Search | Per file type | Windows 2000 and later |
| AutoPlay handler | Examines newly discovered removable media and devices and, based on content such as pictures, music or video files, launches an appropriate application to play or display the content. | Per file type category Windows XP only: per device and per file type category |
Windows XP and later |
| Property handler | Allows viewing and modifying system-defined and custom properties of a file. | Per file type | Windows Vista and later; on Windows XP if Windows Search is installed. |
| Preview handler | Renders enhanced previews of items without launching the default application when a file is selected. It can also provide file type-specific navigation such as browsing a document, or seeking inside a media file. | Per file type | Windows Vista and later |
Namespace extensions are used by Explorer and Common Dialogs to either display some data – which are not necessarily persisted as files – in a folder-like view or to present data in a way that is different from their organization on the file system. This feature can be exploited by a any hierarchical data source that can be represented as a file system like the Windows one, including Cloud-based implementation. Special folders, such as My Computer and Network Places in Windows Explorer are implemented this way, as are Explorer views that let items in a mobile phone or digital camera be explored. Source-control systems that use Explorer to browse source repositories also use Namespace extensions to allow Explorer to browse the revisions. To implement a namespace extension, the IPersistFolder, IShellView, IShellFolder, IShellBrowser and IOleWindow interfaces need to be implemented and registered. The implementation needs to provide the logic for navigating the data store as well as describing the presentation. Windows Explorer will instantiate the COM objects as required.[60]
While Windows Explorer natively exposes the extensibility points as COM interfaces, .NET Framework can also be used to write some types of extensions, using the COM Interop functionality of .NET Framework.[60] While Microsoft itself makes available extensions – such as the photo info tool[61] – which are authored using .NET Framework, they currently recommend against writing managed shell extensions, as only one instance of the CLR (prior to version 4.0) can be loaded per-process. This behavior will cause conflicts if multiple managed add-ins, targeting different versions of the CLR, are attempted to be run simultaneously.[62][63]
- Comparison of file managers
- List of alternative shells for Windows
Notes and references
[edit]
- ^ «April 25, 2025—KB5055627 (OS Build 26100.3915) Preview». Microsoft Support. Microsoft.
- ^ «Releasing Windows 11 Build 26100.3902 to the Release Preview Channel». Windows Insider Blog. April 10, 2025.
- ^ «April 25, 2025—KB5055627 (OS Build 26100.3915) Preview». Microsoft Support. Microsoft.
- ^ «Announcing Windows 11 Insider Preview Build 26120.3941 (Beta Channel)». Windows Insider Blog. April 25, 2025.
- ^ «Announcing Windows 11 Insider Preview Build 26200.5570 (Dev Channel)». Windows Insider Blog. April 25, 2025.
- ^ «Announcing Windows 11 Insider Preview Build 27842 (Canary Channel)». Windows Insider Blog. April 23, 2025.
- ^ a b «Microsoft switches to File Explorer name in Windows 8, bids farewell to Windows Explorer». The Verge. June 29, 2012. Archived from the original on August 17, 2012. Retrieved August 3, 2012.
- ^ Lineback, Nathan. «Misc Windows». toastytech.com. Archived from the original on July 3, 2018. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ John D. Ruley (September 1995). «NT Gets the Look But Not the Logo». How-To Columns. WinMag. Archived from the original on March 14, 2006. Retrieved September 4, 2009. Internet Archive
- ^ «Managing Files, Folders, and Search Methods: Microsoft TechNet». microsoft.com. Archived from the original on January 12, 2009. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ «Serenity Macros Home Page – Resources for MS Word». www.mvps.org. Archived from the original on June 27, 2018. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ Windows 2000 Registry: Latest Features and APIs Provide the Power to Customize and Extend Your Apps, MSDN Magazine, November 2000, archived from the original on April 15, 2003, retrieved August 26, 2007
- ^ «COM Objects and Structured Storage» Archived 2018-12-18 at the Wayback Machine, Windows Dev Center, May 31, 2018
- ^ Esposito, Dino (June 2000), More Windows 2000 UI Goodies: Extending Explorer Views by Customizing Hypertext Template Files, MSDN Magazine, archived from the original on August 24, 2007, retrieved August 26, 2007
- ^ Sophos, VBS/Roor-C threat analysis Archived 2007-11-30 at the Wayback Machine. Accessed August 26, 2007.
- ^ «Virus.VBS.Redlof.a», Virus Encyclopedia, Viruslist.com, January 15, 2004, archived from the original on October 28, 2007, retrieved August 26, 2007
- ^ Figure 1 Windows Shell Extensions, MSDN Magazine, June 2000, archived from the original on August 31, 2004, retrieved August 26, 2007
- ^ «What is Indexing Service?». msdn.microsoft.com. November 6, 2009. Archived from the original on January 1, 2011. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ «Is Microsoft Office 2003 still decent for general use on Windows 7, 8.1 and 10». answers.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on February 7, 2016. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ «What is Windows XP?». www.computerhope.com. Retrieved August 12, 2022.
- ^ a b «Windows XP – What’s new with files and folders». Windows. Microsoft. Archived from the original on May 23, 2007.
- ^ How to create and extract a Zip File in Windows ME/XP/2003
- ^ How To: Open a Cab file – Quote: «If you’re using Windows XP or Windows Vista, then your operating system has built-in support for opening Cab files.»
- ^ «Moving web pages saved by IE (HTM file & _FILES folder)». Directory Opus Resource Centre. May 4, 2009. Archived from the original on December 16, 2020. Retrieved December 16, 2020.
When Windows Explorer […] move a Web page both the HTML file and the directory are automatically moved together. […] Moreover, the user only has to drag EITHER part—the file or the directory and the other part will follow automatically. This way the page is kept intact irrespective of where Windows stores it.
- ^ The sort order for files and folders whose names contain numerals is different in Windows Vista, Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003 than it is in Windows 2000, support.microsoft.com, August 28, 2007, archived from the original on September 27, 2010, retrieved July 6, 2009
- ^ a b Shultz, Greg (August 10, 2006). «Examine the filtering, grouping, and stacking features in Windows Vista’s Windows Explorer». TechRepublic. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on December 22, 2015. Retrieved December 19, 2015.
- ^ a b c Reid, Rory (January 30, 2007). «Seven days of Vista — day 4: Stacking and filtering». CNET. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on December 22, 2015. Retrieved December 19, 2015.
- ^ a b Kaelin, Mark (July 17, 2007). «How do I… Save and refine desktop searches in Microsoft Windows Vista?». TechRepublic. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on November 17, 2015. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ Microsoft. «Saved Search File Format». MSDN. Archived from the original on December 10, 2015. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ Bentz, Ben (October 31, 2006). «Query Composition: Building a search upon another search». Shell: Revealed Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on December 15, 2006. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ Using search operators to find pictures, music and videos in Windows Vista
- ^ Windows 7: Find/Search Files By Date And Size
- ^ Windows Explorer Columns — Are you Fully Using Them?
- ^ «How to Search for Contents in Any File Type Without Indexing Service Enabled in Windows Vista and Windows 7». Wikihow.com. January 27, 2014. Archived from the original on March 19, 2017. Retrieved January 31, 2014.
- ^ a b Microsoft. «Add tags or other properties to a file». Windows How-to. Archived from the original on December 22, 2015. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ White, Nick (July 13, 2007). «10 Things – Windows Explorer Has a New Preview Pane». Windows Vista Team Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 15, 2007. Retrieved December 14, 2015.
- ^ Microsoft. «Pen and Touch Input in Windows Vista». MSDN. Archived from the original on December 22, 2015. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ Oiaga, Marius (September 27, 2006). «Quick Zoom on the Windows Vista Desktop and in Explorer». Softpedia. Archived from the original on December 22, 2015. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ McFedries, Paul (2008). Microsoft Windows Vista Unleashed. Sams Publishing. p. 87. ISBN 978-0-672-33013-1. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ Mangefeste, Tony; Walp, David (2006). «Optical Platform: Windows Vista and Beyond». Microsoft. Archived from the original (PPT) on June 4, 2011. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ Davis, Christopher (March 29, 2007). «Your File Is In Use… Demystified». Shell: Revealed Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on April 29, 2007. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ «Properties». msdn2.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on October 9, 2007. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ «IColumnProvider interface (Windows)». msdn2.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on April 17, 2008. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ «MS-WSP: Windows Search Protocol», MSDN Library, Microsoft, December 18, 2006, archived from the original on May 16, 2010, retrieved June 10, 2009
- ^ «Creating Shortcut Menu Handlers (Windows)». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on November 22, 2010. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ «Improvements in Windows Explorer». Archived from the original on November 7, 2011. Retrieved October 30, 2011.
- ^ «How to open UWP File Explorer on Windows 10 – Step by step». Windows Latest. May 7, 2017. Archived from the original on August 24, 2018. Retrieved August 24, 2018.
- ^ «Windows 10 Tip: Unlock the UWP File Explorer – Thurrott.com». Thurrott.com. May 6, 2017. Archived from the original on August 24, 2018. Retrieved August 24, 2018.
- ^ Blog, Windows Experience; Writer, Athima Chansanchai (April 1, 2019). «Windows 10 Tip: Dark theme in File Explorer». Windows Experience Blog. Retrieved May 7, 2024.
- ^ «Inspired by Insiders – Dark Theme in File Explorer». August 8, 2018. Archived from the original on August 12, 2018. Retrieved August 23, 2018.
- ^ «Microsoft updates universal File Explorer with new features in Windows 10 version 1809». Windows Central. Archived from the original on August 25, 2018. Retrieved August 24, 2018.
- ^ «UWP File Explorer has got new features in Windows 10 version 1809». Winaero. August 23, 2018. Archived from the original on August 25, 2018. Retrieved August 24, 2018.
- ^ «Windows 10 version 1909: new and changed features — gHacks Tech News». www.ghacks.net. October 2019. Archived from the original on October 25, 2019. Retrieved October 25, 2019.
- ^ Warren, Tom (March 15, 2022). «Microsoft says Windows 11’s File Explorer ads were ‘not intended to be published externally’«. The Verge. Retrieved July 28, 2022.
- ^ Warren, Tom (April 5, 2022). «Windows 11’s refreshed File Explorer gets tabs, favorites, and a new homepage». The Verge. Retrieved August 12, 2022.
- ^ Warren, Tom (October 18, 2022). «Windows 11’s new tabbed File Explorer and taskbar improvements are available today». The Verge. Retrieved October 18, 2022.
- ^ Mehdi, Yusuf (September 21, 2023). «Announcing Microsoft Copilot, your everyday AI companion». The Official Microsoft Blog. Retrieved October 31, 2023.
- ^ ShellExView v1.19 – Shell Extensions Manager for Windows, archived from the original on October 24, 2010, retrieved March 31, 2008
- ^ «Thumbnail Handlers (Windows)». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on June 19, 2018. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ a b Rensin, Dave (January 2004). «Create Namespace Extensions for Windows Explorer with the .NET Framework». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on May 8, 2008. Retrieved March 31, 2008.
- ^ «Microsoft Download Center: Windows, Office, Xbox & More». www.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on May 13, 2008. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ «MSDN Magazine Issues». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on May 21, 2008. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ Zhang, Junfeng (November 18, 2005). «Don’t do Shell Extension Handlers in .NET». msdn.com. Archived from the original on January 5, 2010. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- Sullivan, Kent. «The Windows 95 User Interface: A Case Study in Usability Engineering» (1996) for Association for Computing Machinery. (Sullivan was a developer on the Windows 95 UI team)
- How To Customize the Windows Explorer Views in Windows XP
- MSDN: Creating Shell Extension Handlers, Windows Dev Center, May 31, 2018
- The Complete Idiot’s Guide to Writing Shell Extensions, by Michal Dunn, March 15, 2006
- Namespace extensions – the undocumented Windows Shell, by Henk Devos, November 30, 1999
From Wikibooks, open books for an open world
Windows Explorer (referred to as Windows File Explorer in Windows 8 and later) is the application used to access the files and folders on your hard drive and removable storage devices.
Windows Explorer windows have been changed significantly in Windows Vista, as compared to Windows XP. The old menu bar is gone. The toolbar has been completely redesigned, as has the text box that holds the path to the current folder. The Back and Forward buttons are now next to the path bar and a search box has been added.
Explorer windows are also one of the first places that a new user will see the new Aero Glass feature. Explorer windows have no title or title-bar icon, and the glass effect extends down below the title bar to encompass the area around the navigation bar. The Back and Forward buttons are changed to highlight the glass effect. The whole thing is quite attractive.
As with prior (and future) versions of Windows Explorer, Back and Forward buttons are provided that work just like the same buttons do in a Web browser. Disabled buttons are clear and transparent; if clicking the button will do something, it turns a bright blue. The small down-pointing arrow next to the Forward button works like a Web browser’s History pane; if you click it, you will see a menu appear containing the past locations you’ve opened in this window. This is also one of the first places that a new user will see the new drop-down menu design in Windows Vista (which has also been changed to be more attractive than in Windows XP) — but there is a bug here! Ordinary menu items are not quite as tall as the entries in the list, and the ragged-looking, thin checkmark does not appear anywhere else. Other check boxes are much more sharp and are bigger than this one as well. This bug lasted all the way through the lifetime of Windows 7 and beyond.
This complex widget replaces the text field containing the file path (that old C:\something\something else text that dates back to the DOS days). The rightmost name in the text field is always the name of the folder you’re currently looking at. To the left is the name of the folder containing this folder, and so on all the way up to the top (which is not always the root directory of your hard drive). If you click on any of these folder names, you will travel to that folder. If you click on the small triangle separating two folder names, a pop-up menu will appear containing the names of all the subfolders in the folder to the triangle’s left. (The bold one is the one that you’re currently in, or a parent folder thereof.)
If for some reason you want to see that long DOS path (to paste a new path into it, for example), you can click on the blank space to the right of the current folder’s name and a text box containing the full path will appear.
This is the pane to the left of the files themselves. By default, this displays only a small number of “favorite” links. You will find a link to your Documents folder, your Pictures folder, your Music folder, a folder called Recently Changed that is actually a saved search (clicking it will make a list of the most recent documents you saved appear, going back in the order that you saved them, like the Documents submenu of the Windows 98 Start Menu). It also contains a folder called Searches and a link to your computer’s Public folder.
At the bottom of this pane you will find something that says “Folders” with a little up-arrow. This is similar to the Folders pane in Windows XP. If you click it, a hierarchical list of all the folders on your computer will appear, with the Desktop at the top. (If you’re looking for the C: drive, that can be found underneath the Computer entry.) The current folder will always appear highlighted in this list. Enabling this pane enables it for all Explorer windows at the same time.
Unlike the toolbar in the Windows XP version of Windows Explorer, the contents of this toolbar change to reflect the current folder you’re in as well as the file or folder you have selected. You will always find two menus on the left: Organize and Views. The Organize submenu contains a number of commands that apply to Windows Explorer in general, including commands to toggle the display of the various panes. It also contains a command right at the top called New Folder — which is extremely convenient, as under Windows XP, you always needed to use the New submenu, which contains a number of other items, all of which are never really used, and there is always a delay while Windows loads the submenu’s contents. (The New menu is still here, if for some reason you want it; you can find it if you right-click in the pane containing the currently displayed files.)
The Views menu is actually a split button. If you click on the icon or the word Views, the window will circle through the different ways it can display the icons in the current folder. If you click on the down-arrow itself, however, a pop-up menu will appear containing the names of all the views. You will find a slider here, which does not appear anywhere else in Windows Vista. This slider allows you to set an icon view size somewhere between the the presets. You can click the names of the views to the right of the slider to set them directly.
The other commands in the toolbar vary, but there is one item that needs to be pointed out. If you have a file selected, you will probably see a command called Open with a program’s icon next to it. Clicking this button will open the document currently selected in its default application (a Word document into Word, for example). However, if you click the down-arrow to the right of the word Open, a drop-down menu will appear listing all of the other programs on your computer that can also open this file. If you click one of them, the selected file will be opened in that application. Not all applications may support this feature.
There are several different ways you can view the contents of a folder; these are called the Explorer views. There are several sizes of icon view: Extra Large, which is 256 by 256 pixels; Large, which is 128 by 128 pixels; Medium, which is 64 by 64 pixels and new in Windows Vista; and Small, which is 16 by 16 pixels and, for some reason, was not present in Windows XP. The List view scrolls to the left and right and contains your files stacked up in columns; the Tiles view displays a 64 by 64 pixel icon, as well as one or two lines of extra information to the right of the icon, below its name. Details view, usually the default, uses a grid where there is one file or folder per row, and the columns are used to display different information about each icon, such as size or last-modified date.
In the Details view, the header is used to contain the column names and allow for resizing of the columns. However, in Windows Vista, this header appears in every view. If you click on one of the columns’ names, the icons or list will be sorted according to that attribute, in ascending order (A–Z, smallest first, and so on). If you click the name again, the icons will be sorted according to that attribute in descending order (Z–A, largest first, and so on). A tiny arrow will appear at the top-center of the column that is currently being sorted by.
When you move your mouse over one of these column names, a black arrow will appear to the right of the name. If you click on this, you will open a pop-up containing commands that permit grouping and filtering of the items in this folder according to that attribute. (A Sort button with much larger arrow is also provided here, if you can’t see the usual one.)
Проводник Windows – основное средство для работы с файлами и папками. Фактически каждый раз, вы открываете какую-либо папку, вы на самом деле наблюдаете окно программы Проводник. За один раз может быть открыто сразу несколько окон Проводник, в каждом из которых отображаются разные папки с различными параметрами отображения. Изучим основные элементы окна программы.
Некоторые из основных элементов окна перечислены далее.
- Адресная строка. В этой строке отображается текущее местоположение.
- Панель инструментов. Одна из основных панелей программы Проводник. На ней всегда расположены кнопки Упорядочить, Виды и Запись на оптический диск. В зависимости от того, с какими файлами вы работаете, содержимое панели инструментов будет меняться.
- Панель навигации. Панель позволяет перейти к интересующему вас файлу.
- Строка состояния. В этой строке отображаются различные параметры и характеристики выбранного файла или объекта. В частности, отображаются текущая открытая папка и размер файла.
- Панель подробностей. На этой панели также отображаются некоторые свойства выбранного файла, такие как Дата изменения, Размер и Дата создания.

Запустить программу Проводник можно несколькими способами. Самый простой – это щелкнуть правой кнопкой мыши на значке Пуск и выбрать команду Проводник. Также можно выбрать команду Пуск>Все программы>Проводник. Теперь рассмотрим более внимательно меню Упорядочить. Команды, расположенные в этом меню, позволяют производить с файлами и папками разнообразные действия. В частности, с помощью меню Упорядочить можно копировать, удалять и переименовывать файлы, отменять произведенные действия, просматривать параметры файлов и т.д.
Меню Виды используется для изменения внешнего вида и метода отображения файлов и папок в окне программы Проводник. Чтобы выбрать нужный тип, можно щелкнуть как на самой кнопке Виды, так и на стрелке рядом с ней, после чего вы сможете выбрать один из типов отображения, перечисленных далее. В последнем случае выбрать тип можно, перемещая мышью специальный ползунок.
- Огромные/крупные/обычные/мелкие значки. Крупные значки иногда выбирают люди с плохим зрением или обладатели мониторов со слишком большим разрешением.
- Список. В данном случае отображаются только названия файлов.
- Таблица. Файлы и данные о них представлены в виде таблицы.
- Плитка. Используются большие значки с описанием.

Для всех однотипных папок можно выбрать такой же тип, как и у текущей папки. Для этого выберите команду Упорядочить>Свойства папок и поиска. Затем перейдите на вкладку Вид и щелкните на кнопке Применить к папкам. Теперь для всех папок будет использоваться один тип отображения. Чтобы отменить общий вид для папок, снова перейдите на вкладку Вид и щелкните на кнопке Сброс вида папок. Также вы можете отменить произведенные изменения с папками после перезагрузки компьютера. Для этого на вкладке Вид перейдите к полю Дополнительные параметры и установите флажок Восстанавливать прежние окна папок при входе в систему.
Обратите внимание на панель Поиск, расположенную в верхней части окна. По мере того как вы будете вводить в эту панель название файла или папки, в основном окне программы Проводник будут отображаться те файлы или папки, название которых совпадает с вводимым вами значением. При этом поиск происходит не по всему жесткому диску, а только по текущей папке и расположенным в ней подпапкам.

Если для папки выбран достаточно крупный тип отображения, то вы сможете увидеть пример содержимого такой папки. То, что отображается в значке папки, зависит от ее содержимого. Это может быть текстовый файл или файл Word, файл презентации PowerPoint, таблицы Excel и т.д. Также в значке папки может быть представлен первый кадр видеофайла, обложка музыкального альбома или уменьшенная фотография. Другими словами, папки в Windows Vista являются в некоторой степени интерактивными объектами и позволяют вам сделать поиск нужных данных более простым и наглядным.
Теперь вернемся к меню программы Проводник и рассмотрим один из основных его элементов – адресную строку. Адресная строка в Windows Vista серьезно изменилась по сравнению с адресной строкой в Windows XP, причем до такой степени, что многим пользователям нововведение откровенно не понравилось. Адресная строка располагается в верхней части окна каждой папки и отображает путь к ней в виде отдельных ссылок, разделенных кнопками со стрелкой.
Многие, а быть может, и большинство негативных отзывов о новом интерфейсе Windows Vista вызваны привыканием пользователей к определенному интерфейсу. Действительно, не так просто научиться открывать папки в адресной строке программы Проводник в Windows Vista, когда на протяжении последних пяти лет в Windows XP пользователь привык к совершенно другому способу. Однако стоит вам потренироваться, как может оказаться, что новый способ более удобен и эффективен, чем старый, и что Microsoft не зря потратила столько времени на разработку Windows Vista.
Чтобы перейти к новой папке или новому окну, необходимо щелкнуть на соответствующей ссылке. Также можно щелкнуть на значке со стрелкой справа от ссылки и в открывшемся меню выбрать нужный объект. При этом в меню будут отображаться все вложенные папки или объекты, относящиеся к определенному окну. Например, если щелкнуть на значке рядом со ссылкой Компьютер, то в открывшемся меню можно будет выбрать один из дисков, оптических или портативных носителей.

Если вы решили ввести путь к папке или файлу вручную, сделать это можно так. Щелкните в свободной области адресной панели, справа от названия открытой в текущей момент папки. Название папки будет выделено, и вместо него вы сможете ввести нужный путь, такой, например, как C:\Папка. Кроме того, вместо щелчка мышью можно нажать комбинацию клавиш <Alt+D>. Вы также имеете возможность указать одну из типовых папок Windows. Например, если ввести в адресной строке слово Музыка, то будет открыта папка Музыка, по умолчанию предназначенная для хранения музыкальных файлов. Таким же образом можно открыть папки Компьютер, Документы, Игры, Корзина, Изображения и некоторые другие.
Многие принципы работы программы Проводник совпадают с работой обычного браузера. Например, вы можете вернуться к недавно открытой папке, щелкнув мышью на кнопке Назад. В свою очередь, щелкните на кнопке Вперед, чтобы вернуться обратно. Если щелкнуть на значке со стрелкой, расположенном справа от кнопок Вперед и Назад, откроется список недавно посещенных вами папок. При этом галочкой будет выделена папка, которая открыта в текущий момент.
Обратим внимание на панель навигации. Эта панель позволяет сразу перейти к необходимой вам папке, которую можно выбрать из списка. Чтобы отобразить или скрыть панель навигации, выберите команду Упорядочить>Раскладка>Панель навигации. В верхней части панели расположен раздел Избранные ссылки, с помощью которого можно перейти к основным пользовательским папкам Windows, таким как Документы, Изображения и Музыка.
Щелкните на ссылке Недавно измененные, чтобы просмотреть список объектов (файлов и папок), которые были созданы или изменены за последние 30 дней. Также вы можете щелкнуть на ссылке Поиски, чтобы открыть папку Поиски, где будут перечислены все объекты, которые вы искали последнее время. И, наконец, чтобы открыть папку, содержащую общие файлы, щелкните на ссылке Общие.
В папке Общие хранятся файлы, которые предназначены для использования не только вами, но и доступны всем пользователям локальной сети. Сетевой доступ с других компьютеров разрешен по умолчанию только к тем файлам и папкам, которые расположены в этой папке.
Изменять содержимое раздела Избранные ссылки можно таким образом.
- Чтобы изменить местоположение ссылок, перетащите их на новую позицию.
- Для того чтобы добавить новую ссылку, перетащите папку из основного окна программы Проводник или ссылку о сохраненном поиске из папки Поиски в список Избранные ссылки.
- Чтобы переименовать ссылку, щелкните на ней правой кнопкой мыши, выберите команду Переименовать, введите новое название и нажмите клавишу <Enter>. При этом будет переименована только сама ссылка; название папки, к которой относится ссылка, останется неизменным.
- Для того чтобы удалить ссылку, щелкните на ней правой кнопкой мыши и выберите команду Удалить ссылку.
- Наконец, чтобы восстановить первоначальный список ссылок, щелкните правой кнопкой на свободном пространстве раздела Избранные ссылки и выберите команду Восстановить прежнюю версию.
Под разделом Избранные ссылки расположен раздел Папки, один из основных разделов программы Проводник. В этом разделе все файлы, папки и диски представлены в виде так называемого иерархического дерева. В этом дереве по умолчанию доступны только основные элементы, и вы можете щелкать на значках с изображением стрелки, расположенных слева от значков папок и дисков, чтобы раскрывать или закрывать ветви этого дерева. Если щелкнуть на значке со стрелкой в заголовке Папки, раздел будет закрыт, и точно таким же образом его можно открыть.
Перемещаться по дереву можно не только с помощью мыши, но и клавиатуры. Зачастую это гораздо удобнее, особенно если знать соответствующие клавиатурные комбинации. Далее мы познакомимся с некоторыми из них.
- Клавиша<←> или <→>. Позволяет открыть или закрыть выбранную ветвь.
- Клавиша <Backspace>. Переход к родительской ветви.
- Комбинация клавиш <Alt+→>. Переход с родительской ветви к нижнему элементу открытого списка.
- Комбинация клавиш <Alt+←>. Переход с выбранного элемента дерева к самому верхнему элементу дерева.
- Клавиша <↑>. Переход к верхнему элементу списка.
- Клавиша <↓>. Переход к нижнему элементу списка.
- Клавиша <*> (символ звездочки на цифровой клавиатуре). Раскрытие всех элементов ветви, расположенных ниже выбранного элемента.
- Клавиша <Tab> или <F6>. Переход между различными элементами окна программы Проводник.
Если на навигационной панели слева от значка папки расположен значок в виде стрелки, следовательно, это папка содержит вложенные подпапки. В свою очередь, папка без такого значка или пустая, или содержит только файлы. Если вы заметили, что в окне не хватает определенной папки или что слева от папки, в которой нет вложенных папок, расположен значок в виде стрелки, нажмите клавишу <F5>, чтобы обновить содержимое навигационной панели.
ВикиЧтение
Компьютер на 100. Начинаем с Windows Vista
Зозуля Юрий
Общие сведения о Проводнике Windows Vista
Для просмотра содержимого папок используется программа Проводник. Ее не нужно запускать специально – достаточно открыть любую папку, и ее содержимое будет отображено в окне Проводника. Вы можете также встретить термин окно папки, который обычно служит для обозначения конкретной папки, которая открыта с помощью Проводника. При описании различных системных папок удобно пользоваться термином «окно папки», но не забывайте, что содержимое папок всегда отображается в Проводнике. Для знакомства с программой Проводник откройте, например, папку Документы, ярлык которой находится в меню Пуск (рис. 2.29).
Рис. 2.29. Содержимое папки Документы в окне Проводника
В окне Проводника Windows Vista можно выделить следующие основные элементы.
? Кнопки навигации. С помощью кнопок Назад и Вперед вы можете возвращаться к ранее просмотренным папкам.
? Адресная строка. В адресной строке отображается путь к текущей папке. Щелкнув на имени любой из родительских папок в адресной строке, вы можете перейти к ее просмотру, а с помощью щелчка на стрелке справа от названия папки можно перейти к одной из вложенных папок.
? Поле поиска. Вы можете находить нужный файл сразу же после ввода первых букв его имени, аналогично поиску программ в меню Пуск. Подробнее встроенный поиск будет рассмотрен в следующем уроке.
? Панель инструментов. На панели инструментов имеются кнопки для выполнения типичных действий с файлами и папками, причем перечень доступных кнопок автоматически изменяется в зависимости от того, какой файл или папка выбран в области просмотра.
? Панель навигации. Эта панель находится в левой части окна и служит для смены текущей папки. Панель навигации состоит из двух частей: списка Избранные ссылки, содержащего наиболее часто используемые папки, и панели Папки, где отображается полное дерево каталогов компьютера.
? Заголовки столбцов. В Windows Vista заголовки столбцов используются для сортировки, группировки и разложения по стопкам содержимого текущей папки.
? Содержимое папки. В области содержимого отображаются файлы и папки в виде значков. Для многих популярных типов файлов вместо обычных значков отображаются эскизы содержимого файла, а пользователи имеют возможность произвольно изменять размеры значков.
? Панель подробностей. Панель подробностей, или сведений, находится в нижней части окна и показывает подробную информацию о выделенном объекте.
Некоторые элементы интерфейса Проводника являются скрытыми, но при необходимости их можно вызвать. Например, для отображения меню достаточно нажать клавишу Alt или F10. Чтобы открыть панель предварительного просмотра, нажмите кнопку Упорядочить и выполните команду Раскладка ? Панель просмотра.
Данный текст является ознакомительным фрагментом.
Читайте также
Открытие папки в Проводнике Windows
Открытие папки в Проводнике Windows
С помощью объекта Shell.Application можно запустить Проводник Windows и открыть в нем определенную папку. Для этого используется метод Explore(), в качестве параметра которого указывается путь к открываемой папке; соответствующий пример приведен в
Глава 1 Windows Vista. Общие сведения
Глава 1
Windows Vista. Общие сведения
Начнем знакомство с новой операционной системой компании Microsoft – Windows Vista. С 2001 года, то есть появления Windows XP, Microsoft не обновляла линейку клиентских операционных систем. Появление новой, значительно переработанной версии Windows Vista ожидалось с
Общие сведения
Общие сведения
Для чего же оно вообще нужно, это дистанционное обучение? Кому оно может понадобиться? Оказывается, многим.– Наибольшее количество удаленно обучающихся составляют пользователи в возрасте от 25 до 30 лет. Для них обучение в классическом виде невозможно из-за
Общие сведения
Общие сведения
По своей сути группы новостей (телеконференции) представляют собой обмен письмами не с одним пользователем, а сразу с группой с помощью специальной программы. Впрочем, мы ничего специального искать не будем, так как работать с группами новостей нам поможет
Глава 1 Общие сведения о Windows 7
Глава 1
Общие сведения о Windows 7
В первой главе кратко вспомним, что представляет собой операционная система Windows 7, каковы ее основные свойства и как оценить ее
1. Общие сведения о драйверах устройств в системе Windows.
1. Общие сведения о драйверах устройств в системе Windows.
Естественно, каждая операционная система имеет собственную архитектуру и свои особенности функционирования драйверов. Но практически во всех современных ОС можно выделить следующие особенности, характерные для
Общие сведения
Общие сведения
Одним из достоинств модуля buZZ.Pro является возможность использования нескольких фильтров одновременно и гибкое управление их настройками. При выборе строки плагина из меню Filters (Фильтры) появляется так называемый стек – окно Custom (Настройка), в котором
1. Общие сведения о Windows
1. Общие сведения о Windows
Прежде чем приступать к установке Windows XP, вспомним, что подразумевается под словосочетанием «операционная система», что такое файл и папка. Не стоит пугаться умных слов, которые будут встречаться ниже. Если вы до конца не сможете понять разницу
Общие сведения
Общие сведения
Главная страница, посвященная .NET Compact Framework, находится по адресу http://msdn.microsoft.com/netframework/programming/netcf/default.aspx. Там можно найти все последние новости о рассматриваемой технологии, обновления программ, ссылки на другие полезные сайты, примеры.Технология .NET Compact
Общие сведения о слоях
Общие сведения о слоях
Слои – один из мощных механизмов визуального представления объектов, обеспечивающий при умелом использовании максимально удобную работу с проектной документацией.На чертеже плана этажа должны располагаться изображения конструктивных
Общие сведения о Windows ХР Professional
Общие сведения о Windows ХР Professional
Windows ХР является современной операционной системой, разработанной компанией Microsoft в 2001 г. При этом Windows ХР была выпущена в двух вариантах: Windows ХР Professional и Windows ХР Home Edition . Данные варианты являются основными, и именно их мы будем рассматривать
Общие сведения
Общие сведения
Во-первых, рассмотрим ключевые понятия. Архивация (запаковка) – это сжатие файлов. Для окончательного усваивания этого понятия представьте себе поролоновую губку – она с виду большая, но ее можно сжать и запихнуть в емкость гораздо меньшего объема. Архив
Общие сведения
Общие сведения
Система PascalABC.NET
PascalABC.NET – это система программирования и язык Pascal нового поколения для платформы Microsoft .NET. Язык PascalABC.NET содержит все основные элементы современных языков программирования: модули, классы, перегрузку операций, интерфейсы, исключения,
Общие сведения
Общие сведения
Электронная почта (E-mail) – один из первых сервисов Интернета, который до сих пор является самым популярным.Пользователи электронной почты могут обмениваться между собой письмами. Каждое письмо пользователь создает на своем компьютере, после чего
Общие сведения
Общие сведения
Макрос – это программа, написанная на некотором языке, которая используется обычно для автоматизации определенных процессов внутри приложений. В данном случае разговор пойдет о языках Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) и WordBasic (WB), которые Microsoft использует в своих
