Удаление больших файлов и папок – это то, с чем нам приходится жить при работе с компьютером под управлением Windows. При удалении больших файлов с помощью File Explorer сначала выполняется сканирование и анализ общего размера элементов или их общего количества, а затем начинается их удаление, при этом все время выдается отчет о проделанной работе.
Этот метод неоправданно расходует системные ресурсы на выдачу отчетов, которые можно было бы потратить на удаление содержимого.
К счастью, теперь можно мгновенно удалять большие файлы и папки, не расходуя системные ресурсы, с помощью командной строки. Если использование командной строки Windows вам не подходит, можно добавить эту опцию в контекстное меню всей ОС Windows и удалять любые файлы и папки, независимо от их размера, практически мгновенно из контекстного меню.
Интересно: Как уменьшить большой размер файла Windows.edb?
Удаление большого файла или папки из Командной строки
Мы уже обсуждали, как удалять файлы и папки с помощью Командной строки. Однако не все способы предусматривают немедленное удаление; некоторые из них занимают несколько секунд. В следующих шагах мы покажем, как быстро удалить большой файл или папку с помощью Командной строки.
*Примечание: *Приведенные в статье методы удаляют элементы навсегда, после чего файлы и папки невозможно восстановить и найти в корзине.
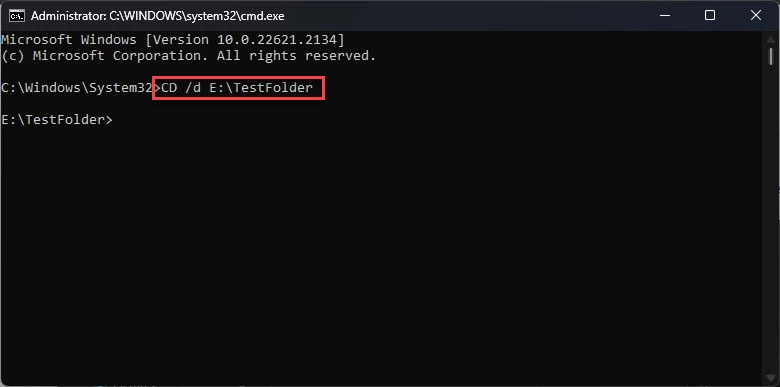
- Нажмите Win + R, чтобы открыть окно Run Command.
- Введите «cmd» и нажмите CTRL + Shift + Enter, чтобы открыть командную строку с повышенными привилегиями.
Для выполнения действий с некоторыми файлами и папками могут потребоваться права администратора. - Теперь с помощью команды
CDизмените каталог на папку, которую нужно удалить.CD /d [PathToFolder]
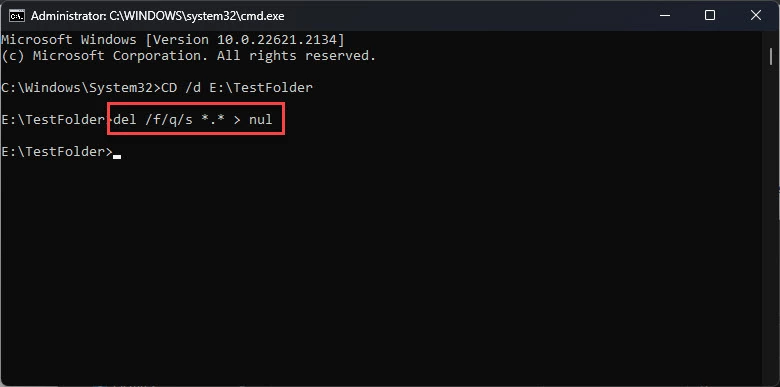
- Теперь выполните следующую команду для удаления всего содержимого этой папки без вывода на экран:
del /f/q/s *.* > nul
Команда
Delозначает удаление, ключ/f– принудительное выполнение команды, а ключ/q– тихий режим, то есть ввод данных пользователем не требуется. Переключатель/sиспользуется для рекурсивного режима, поэтому все вложенные папки и их элементы также будут удалены из текущего каталога. Переключатель*.*используется для выбора всего (любое имя файла и любое расширение файла), а переключатель> nul– для отключения консольного вывода.
В приведенном примере мы поместили файл размером 20 Гб в папку «TestFolder», и для удаления файла этой команде потребовалась почти 1 полная секунда.
Если вы хотите удалить всю папку, то используйте эту команду, заменив переменную на путь к папке:
rmdir /q/s [PathToFolder]
Удаление большой папки из контекстного меню
Если вы не любитель командной строки, то можно включить опцию быстрого удаления прямо в контекстном меню Windows. Таким образом, достаточно щелкнуть правой кнопкой мыши на любом большом файле или папке и быстро удалить его.
Но сначала необходимо выполнить следующие действия, чтобы включить опцию в контекстное меню.
*Примечание: *Этот процесс связан с внесением изменений в реестр Windows. Неправильная настройка критических значений в системном реестре может оказаться фатальной для вашей операционной системы. Поэтому мы настаиваем на создании точки восстановления системы или полной резервной копии образа системы, прежде чем приступать к выполнению этого процесса.
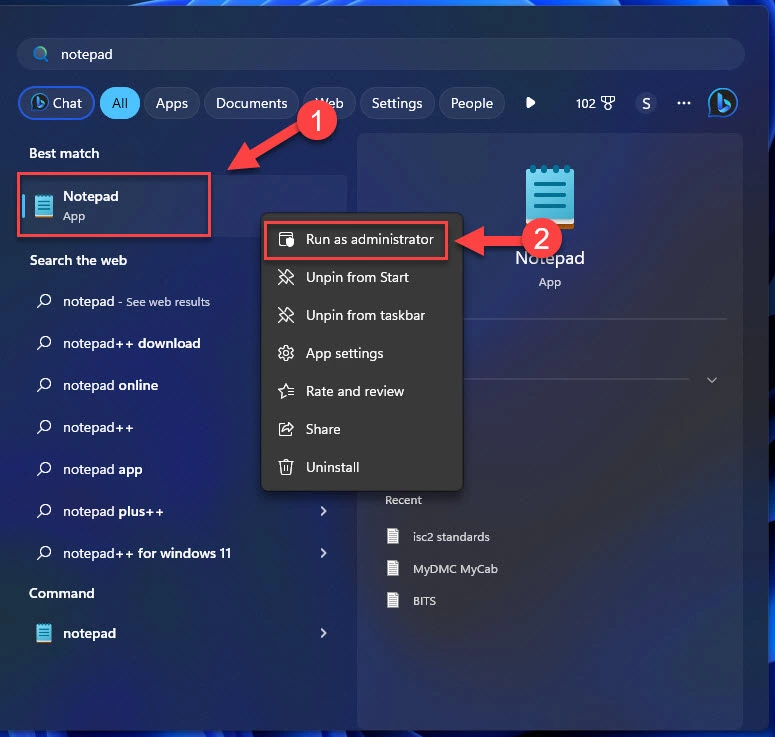
- Найдите «Блокнот» в меню Пуск, щелкните его правой кнопкой мыши и выберите «Запуск от имени администратора».«Блокнот» и нажмите кнопку «Сохранить как*».
- Вставьте следующий текст:
@ECHO OFF ECHO Delete Folder: %CD%? PAUSE SET FOLDER=%CD% CD / DEL /F/Q/S "%FOLDER%" > NUL RMDIR /Q/S "%FOLDER%" EXIT
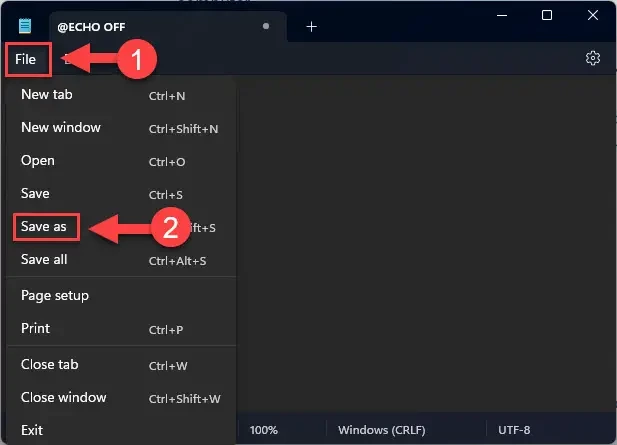
- Нажмите кнопку Файл, а затем «Сохранить как».
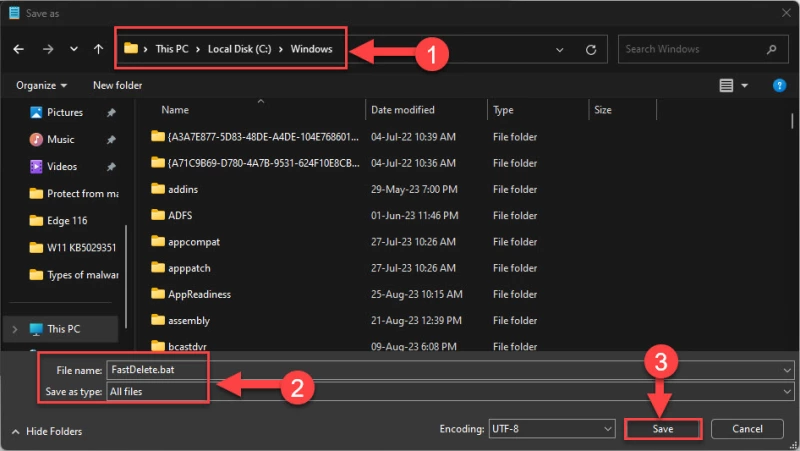
- Перейдите по следующему пути для сохранения файла:
C:\Windows
- Установите для параметра «Сохранить как тип» значение «Все файлы».»
- Введите имя файла, за которым следует «.bat».
*Примечание: *Запомните полное имя файла, так как оно понадобится позже. - Нажмите Сохранить.
- Нажмите Win + R, чтобы открыть окно Run Command.
- введите «regedit» и нажмите Enter.
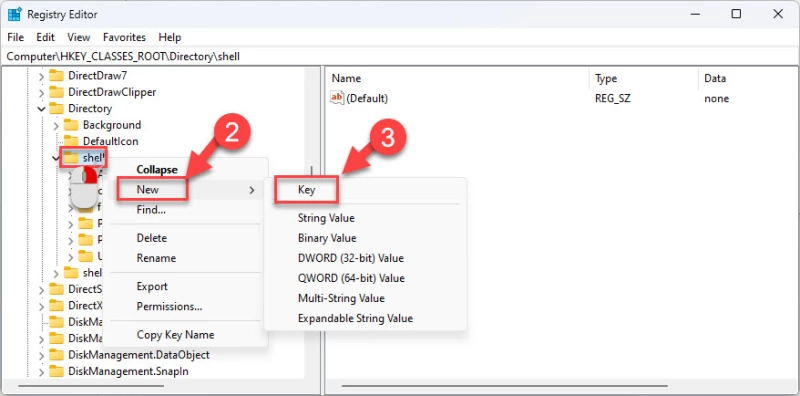
- Перейдите по следующему пути из левой панели:
Computer\HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\shell\
- Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши на клавише Shell, разверните New и нажмите Key.
- Назовите ключ «Fast Delete».
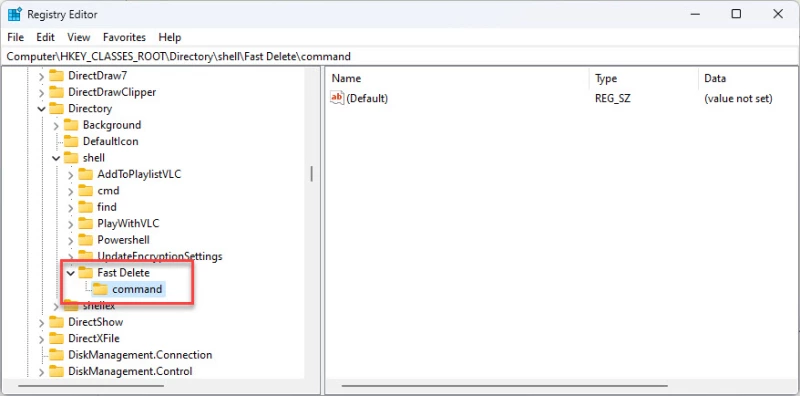
- Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши на ключе «Fast Delete», разверните New и снова щелкните Key. На этот раз назовите ключ «команда».
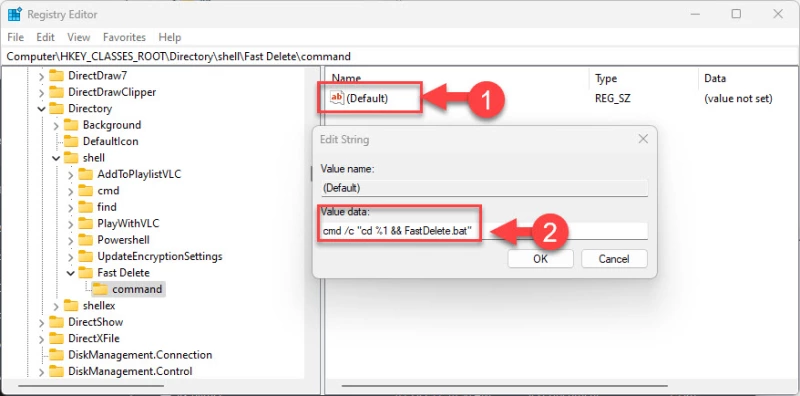
- Дважды щелкните на строковом значении «По умолчанию» в ключе команда, а затем вставьте в поле Значение_данных следующее значение, заменив имя пакетного файла на то, которое было задано в шаге 6.
cmd /c "cd %1 && [BatchFileName].bat"
- Нажмите Ok и перезагрузите компьютер.
Теперь при щелчке правой кнопкой мыши на большой папке вы увидите опцию «Быстрое удаление», которая позволит быстро удалить папку навсегда.

Заключение
Не тратьте свое время и ресурсы системы на удаление элементов значительного размера. Вместо этого воспользуйтесь одним из двух описанных в этой статье способов быстрого удаления больших файлов и папок.
The fastest way to delete large folders and files in Windows is to take the command-line approach. You could either do it manually via CMD or create and run a batch file for quick deletion. These two methods are a lot faster than the traditional way of deleting using the Windows Explorer delete option.
But before I go through the superfast way to delete large folders, here’s the reason why it takes so much time. If you are in a hurry, jump to the next section for the solution.
Why Does Windows Take Time to Delete Large Folders?
When you delete huge folders in Windows, you will notice that the process takes quite a bit of time to complete. It is the opposite of fast.
I keep backup folders of gHacks locally on a platter-based drive, and these folders come close to 30 Gigabytes in size with more than 140,000 files and 350 folders.
When I need to delete them again, it takes a long time if I run the delete operation in Windows Explorer. The problem is that Windows prepares to delete first. This includes running calculations first, which, in itself may take a very long time to complete. Then comes the deletion part, even if you choose to delete the folders permanently (force delete).
Then when the actual deleting takes place, Windows analyzes the process and posts updates to the file operation window.
It may take ten or twenty minutes, or even longer, to delete a large folder (of size greater than 10 GB, for instance) from your hard disk using Explorer on Windows devices.
Delete Large Folders in Windows Quickly Using CMD
If you run delete commands from the command line instead, you will notice that the operation completes a lot faster. You may notice that the operation needs just a fraction of the time that the same operation requires when you run it in Explorer.
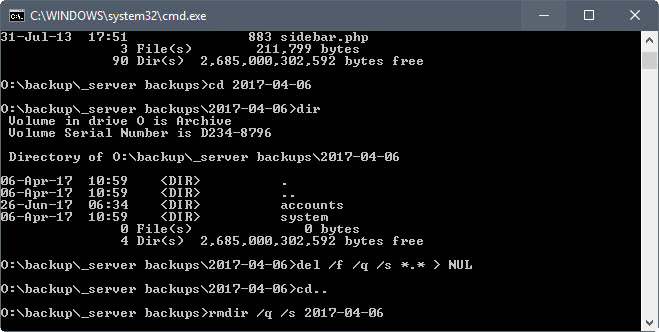
Matt Pilz, who wrote about this back in 2015 saw a reduction from 11 minutes to 29 seconds, which made the command line operation more than 20 times faster than the Explorer option.
The downside to this is that it requires the use of the command line. Matt suggested adding the commands to the Explorer context menu so that users could run them in Explorer directly. This makes it both faster and easier.
The two commands that users require are Del, for deleting files, and Rmdir, for removing directories.
Here’s the step-by-step process to delete large folders using CMD:
- Tap on the Windows-key, type cmd.exe and select the result to load the command prompt.
- Navigate to the folder that you want to delete (with all its files and subfolders). Use cd path, e.g. cd o:\backups\test\ to do so.
- The command DEL /F/Q/S *.* > NUL deletes all files in that folder structure, and omits the output which improves the process further.
- Use cd.. to navigate to the parent folder afterwards.
- Run the command RMDIR /Q/S foldername to delete the folder and all of its subfolders.
Here are descriptions of each of the commands used above.
DEL /F/Q/S *.* > NUL
- /F — forces the deletion of read-only files.
- /Q — enables quiet mode. You are not asked if it is ok to delete files (if you don’t use this, you are asked for any file in the folder, which can be time-consuming and therefore counter-productive).
- /S — runs the command on all files in any folder under the selected structure.
- *.* — delete all files.
- > NUL — disables console output. This improves the process further, shaving off about one quarter of the processing time off of the console command.
RMDIR /Q/S foldername
- /Q — Quiet mode, won’t prompt for confirmation to delete folders.
- /S — Run the operation on all folders of the selected path.
- foldername — The absolute path or relative folder name, e.g. o:/backup/test1 or test1
Method #2: Creating a Batch File for Quick Deletion
If you don’t need to run the command often, you may be perfectly fine running the commands directly from the command prompt.
However, if you do use it frequently, you may prefer to optimize the process. You may add the command to the Explorer context menu so that you can run it from there directly. This saves even more time without depending on a third-party software.
For this, the first thing you need to do is create a batch file. Create a new plain text document on Windows, and paste the following lines of code into it.
@ECHO OFF
ECHO Delete Folder: %CD%?
PAUSE
SET FOLDER=%CD%
CD /
DEL /F/Q/S «%FOLDER%» > NUL
RMDIR /Q/S «%FOLDER%»
EXIT
Save the file as delete.bat afterwards. Make sure it has the .bat extension, and not the .txt extension. You can do this by selecting Save as type as All Files.
The batch file comes with a security prompt. This provides you with an option to stop the process; important if you have selected the context menu item by accident. You can use CTRL-C or click on the x of the window to stop the process. If you press any other key, all folders and files will be deleted without any option to stop the process.
You need to add the batch file to a location that is a PATH-environment variable. While you may create your own variable, you may also move it to a folder that is already supported; e.g.: C:\Windows. In other words, you need to place this .bat file in C:\Windows so that the Windows registry can easily access it.
Do the following to add the new batch file to delete folders quickly to the Windows Explorer context menu. This can be executed in all major versions of Windows including Windows XP, Windows 7, and Windows 10.
- Tap on the Windows key, type regedit.exe, and tap in the Enter key to open the Windows Registry Editor.
- Confirm the UAC prompt.
- Go to HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\shell\
- Right-click on Shell and select New > Key.
- Name the key Fast Delete
- Right-click on Fast Delete, and select New > Key.
- Name the key command.
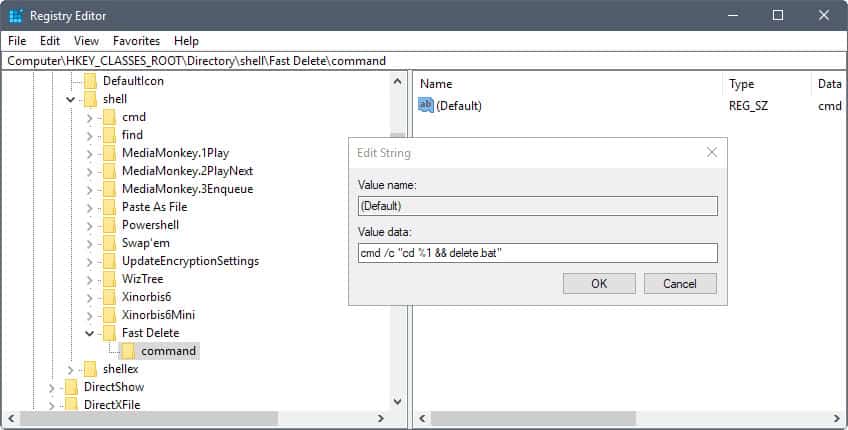
- Double-click on default of the command key.
- Add cmd /c «cd %1 && delete.bat» as the value.
If you want to speed up the deletion process even further, you can always check some third-party tool like byenow.
Summary
Article Name
Delete Large Folders in Windows Superfast Using CMD
Description
Delete large folders on Windows using command line operation. Or create a batch file to quickly delete heavy folders in Windows XP/7/10 via context menu.
Author
Martin Brinkmann
Publisher
Ghacks Technology News
Logo
Advertisement
On Windows 10, sometimes you need to delete folders containing many files, and using File Explorer can take a long time. The reason is that during the delete process, Windows 10 runs calculations, analyzes, and shows updates as files and folders get deleted on the screen, something that usually takes time when deleting a large folder with thousands of files and subfolders.
However, you can significantly speed up the process to only a few seconds using a few command lines. The only caveat is that you need to be comfortable using Command Prompt.
In this guide, you will learn the fastest way to delete large folders with thousands of files using command lines and the instructions to add an option on the right-click context menu to automate the process with just one click.
- Delete large folder fast using Command Prompt
- Delete large folder fast adding context menu option
Warning: Typing the wrong path may delete files in the wrong location, so use these instructions carefully. You have been warned.
Delete large folder fast using Command Prompt
To delete a large number of files on Windows 10 using the del and rmdir commands use these steps:
-
Open Start on Windows 10.
-
Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
-
Type the following command to navigate to the folder that you want to delete and press Enter:
%USERPROFILE%\path\to\folder
In the command, change the path to the folder you want to delete.
-
Type the following command to delete all the files in that folder without showing the output and press Enter:
del /f/q/s *.* > nul
In the command, we use the
/foption to force the deletion of read-only files. The/qoption enables quiet mode. The/soption executes the command for all files inside the folder you’re trying to remove. Using*.*tells the del command to delete every file and> nuldisables the console output improving performance and speed. -
Type the following command to go back one level in the folder path and press Enter:
cd..
-
Type the following command to delete the folder and all its subfolders, and press Enter:
rmdir /q/s FOLDER-NAME
In the command, we use the
/qswitch to enable quiet mode, the/soption to run the command on all the folders and FOLDER-NAME is the variable you need to specify to delete the folder you want.
Once you complete the steps, all the files and folders in the location will delete quickly from your device.
If you are not comfortable writing commands, you do not usually delete tons of files, or you are just looking for a faster way, it’s possible to add a right-click context menu option that will run a batch file for the data you want to delete.
To add a context menu option that will delete files and folders extremely fast on Windows 10, use these steps:
-
Open Notepad.
-
Copy and paste the following lines into the Notepad text file:
@ECHO OFF ECHO Delete Folder: %CD%? PAUSE SET FOLDER=%CD% CD / DEL /F/Q/S "%FOLDER%" > NUL RMDIR /Q/S "%FOLDER%" EXIT
-
Click on File.
-
Select the Save As option.
-
Save the file as quick_delete.bat, and ensure it uses the .bat extension.
-
Move the quick_delete.bat file to the
C:\Windowsfolder. (This step is necessary because the file must be on a location with a path environment variable, but you can always create your own if you’re up to the challenge.) -
Open Start.
-
Search for regedit and click the top result to open the app.
-
Browse the following path:
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\shell\
Quick tip: You can copy and paste the path in the address bar of the Registry to navigate to the path quickly.
-
Right-click the Shell (folder) key, select New, and click on Key.
-
Name the key Quick Delete and press Enter.
-
Right-click the newly created key, select New, and click on Key.
-
Name the key command and press Enter.
-
Double-click the command key default String on the right side.
-
Change the value of the key with the following line and click the OK button.
cmd /c "cd %1 && quick_delete.bat"
After you complete the steps, you can right-click a folder and select the Quick Delete option from the context menu to remove a large folder super fast.
While executing the command, you will get a security prompt preventing you from accidentally deleting files. You can always proceed by pressing any key, using the “Ctrl + C” keyboard shortcut, or clicking the “X” button to cancel the operation.
Why You Can Trust Pureinfotech
The author combines expert insights with user-centric guidance, rigorously researching and testing to ensure you receive trustworthy, easy-to-follow tech guides. Review the publishing process.
-
Home
-
News
- The Fastest Ways to Delete a Large Folder on Windows 10/11
The Fastest Ways to Delete a Large Folder on Windows 10/11
By Stella | Follow |
Last Updated
When you’re deleting a folder containing numerous files and a substantial size, it can take a considerable amount of time to completely remove the entire folder. Is it possible to delete large folders more quickly on a Windows computer? In this guide, MiniTool will introduce two methods.
If you delete some files and folders by mistake, you can use MiniTool Power Data Recovery to get them back. This best free data recovery software can help you recover lost and deleted files from all types of data storage devices. If you want to recover a large folder, you can also use this software.
MiniTool Power Data Recovery FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
To safeguard your data, you can use MiniTool ShadowMaker to back up your computer regularly. You can use this software to back up files to an internal hard drive, external hard drive, SD card, and more.
MiniTool ShadowMaker TrialClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Deleting a folder containing numerous large files and subfolders in File Explorer can be time-consuming. That’s because Windows needs to run calculations, analyze, and show updates as files and folders get deleted. The whole process will last for a while.
However, is it possible to delete large folders more quickly?
Of course, you can do it using special methods. In this post, we will introduce two methods:
- Way 1: Use Command Prompt to make Windows delete large folders fast.
- Way 2: Add the fast way to the context menu.
Which is the fastest way to delete a large folder? You can just try.
Way 1: Use Command Prompt to Delete Large Folders Faster
You can use the del and rmdir commands to delete a large folder faster. Here is a guide:
- Click the search icon on the taskbar and search for cmd.
- Right-click Command Prompt from the search result and select Run as administrator from the context menu. This will run Command Prompt as administrator on Windows.
- Copy the path of the folder you want to delete.
- Type cd path into Command Prompt and press Enter to navigate to the folder that you want to delete. In this step, you need to replace path with the folder path you have copied. For example: cd F:\large folder.
- Type del /f/q/s *.* > nul and press Enter.
- Type cd.. and press Enter to go back to one level in the folder path.
- Type rmdir /q/s foldername and press Enter to delete the folder and all its subfolders.
You can also create a script and modify the related registry key to add a new entry to the right-click context menu to delete large folders faster.
You can use these steps to do this job:
1. Create an empty txt file and open it.
2. Copy and paste the following content to Notepad:
@ECHO OFF
ECHO Delete Folder: %CD%?
PAUSE
SET FOLDER=%CD%
CD /
DEL /F/Q/S “%FOLDER%” > NUL
RMDIR /Q/S “%FOLDER%”
EXIT
3. Go to File > Save.
4. Change the file’s name to quick_delete and change the extension to .bat.
5. Go to C:\Windows, then cut and paste the quick_delete file to this location.
6. Press Windows + R to open Run, then type regedit into the Run box and press Enter to open Registry Editor.
7. Go to this path: HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\shell\.
8. Right-click the Shell (folder) key, then go to New > Key.
9. Name the key Fast Delete and press Enter.
10. Right-click the newly created key (the Fast Delete key), then go to New > Key.
11. Name the new key Command.
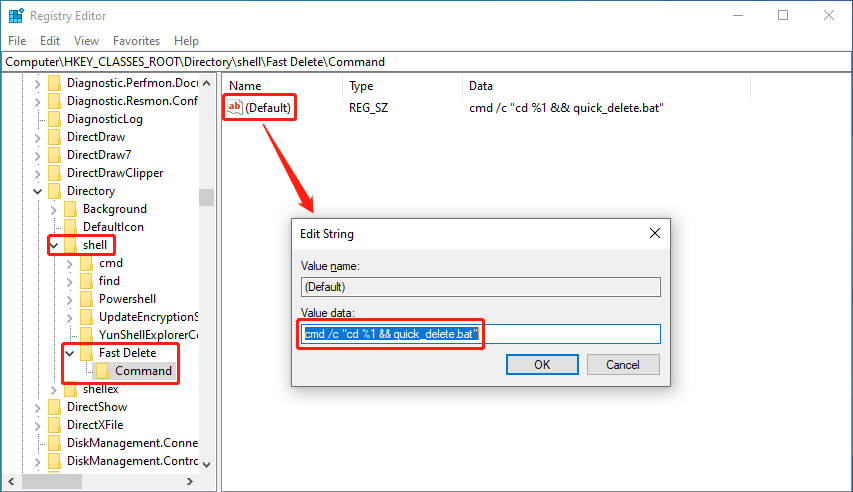
12. Double-click the default String in Command on the right panel, then enter cmd /c “cd %1 && quick_delete.bat” into the box of Value data.
13. Press OK to save the change.
14. Close Registry Editor.
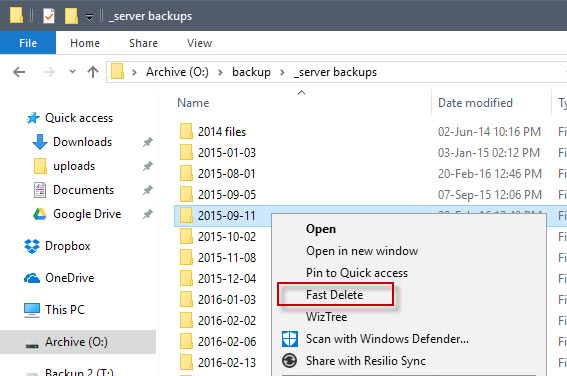
When you want to delete a large folder, you can right-click the target folder and then select Fast Delete from the context menu.
Command Prompt will pop up, asking you to press any key to continue. Just do it.
Bottom Line
These are the two methods to delete large folders faster on a Windows computer. You can select your preferred one to help you delete large folders more quickly. If you delete folders unexpectedly, you can use MiniTool Power Data Recovery to rescue them.
If you encounter issues when using MiniTool data recovery software, you can contact [email protected] for help.
About The Author
Position: Columnist
Stella has been working in MiniTool Software as an English Editor for more than 8 years. Her articles mainly cover the fields of data recovery including storage media data recovery, phone data recovery, and photo recovery, videos download, partition management, and video & audio format conversions.
How to Speed Up Folder Deletion Times by 20x or More!
The common way of deleting files and folders in Windows is via Windows Explorer (a.k.a. File Explorer). This method is perfectly acceptable under normal circumstances, but becomes a real drag when dealing with large and complex folder structures. There is, in fact, a significant amount of of overhead when you trigger the standard delete action in Windows including when either emptying the Recycle Bin or directly deleting files via Shift+Del.
Upon flagging a folder for deletion in the traditional fashion, Windows begins by calculating the total folder size, number of items contained within it, and the estimated completion time. This «Preparing to Delete» phase can consume a sizable amount of time itself depending on the contents being deleted. During the actual deletion process, Windows continues to query and report various statistics about the process including how many items are deleted per second, how many remain, the current item being deleted and so forth. You may also be prompted via the Windows dialog if any conflicts arise during the process.
As an example of folder complexity, I have recently been doing a lot of tests with various iterations of the Android NDK across several development machines. The latest Android NDK (r10e) is comprised of around 50,000 Files across 4,100 Folders and totals over 3.15GB in size. Deleting this directory in its extracted format can take up to fifteen minutes when using native Windows Explorer file operations, versus just seconds using the method described below.
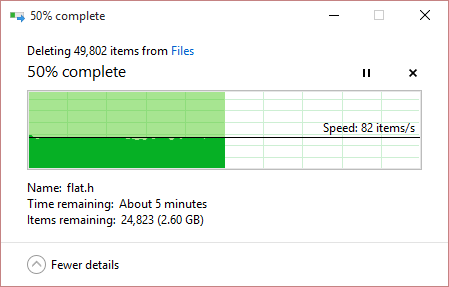
Deleting a large and complex folder via Windows Explorer can take a long time.
A much faster, bare metal approach to deleting large and complex folders in Windows is via the command line. Of course, repeatedly having to navigate directories while executing commands via a terminal quickly becomes a tedious experience. In this post, I will walk through the process of creating a simple batch file and wiring it up to a handy right-click context menu from Windows Explorer to delete sophisticated directories in a hurry and without interruption.
Deleting Files and Folders via Command Prompt
The commands required to perform folder and file delete operations via Command Prompt are quite straightforward.
Files can be deleted using the DEL (a.k.a. ERASE) command.
|
DEL [/P] [/F] [/S] [/Q] [/A[[:]attributes]] names ERASE [/P] [/F] [/S] [/Q] [/A[[:]attributes]] names |
There are a handful of optional parameters that can be appended to the DEL command to control its behavior. To see a description of each, enter DEL /? from the command prompt. The most important flags when wishing to delete all files across all nested directories include:
- /F — Force deleting of read-only files.
- /Q — Quiet mode, do not ask if ok to delete on global wildcard.
- /S — Deletes specified files from all subdirectories.
To delete all files in a particular directory and its subdirectories, you would first navigate to the directory in question using cd [PATH] and then execute the following line:
If you omit the /Q flag, you would have to manually verify the deletion of every single file—obviously not what you want when trying to delete a folder’s contents as quickly as possible. Likewise, without the /F flag, any files set to read-only would be ignored and would remain in-tact after the command has completed. The /S flag is significant as without it you would only be deleting all of the files in the root active directory.
While this method avoids the calculation expense required when deleting through Windows Explorer, the command as shown above will still output the location and deletion status of each file in the iteration. Although this can prove valuable at times, when iterating through thousands of files such output can congest the command’s performance. We can instead redirect output to a null location to avoid any on-screen rendering, as such:
Although it may seem like a moot point, the speed gained by merely omitting output is still quite measurable especially when deleting a massive number of items. Upon deleting the ~46,000 files from the NDK package, it took 38 seconds with console output enabled and 29 seconds with output disabled on a standard non-SSD hard drive, scraping off a quarter of the time. By comparison, the same deletion process via a standard Shift+Del in Windows Explorer took an agonizing 11 minutes.
Therefore, using the above command-line operation was over 20 times faster than going through Windows Explorer itself. [Note: When sending a folder to the Recycle Bin via Windows Explorer, it may seem to delete fairly fast on modern editions of Windows, but will still take substantial time when emptying from the Recycle Bin.]
Folders can be deleted using the RMDIR (a.k.a. RD) command.
|
RMDIR [/S] [/Q] [drive:]path RD [/S] [/Q] [drive:]path |
Like the DEL command, There are a couple optional parameters that can be appended to the RMDIR command to control its behavior. Both of these flags are essential when wishing to delete a folder and all of its sub-folders as fast as possible with no prompts:
- /Q — Quiet mode, do not ask if ok to remove a directory tree
- /S — Removes all directories and files in the specified directory in addition to the directory itself.
Technically, the RMDIR command with the above flags should be sufficient enough on its own to remove an entire directory tree in most cases. However, Microsoft’s documentation warns that this command «cannot delete a directory that contains files, including hidden or system files.» I believe that this statement is more applicable to older operating systems such as XP, likely to resolve malicious security flaws from the older DELTREE and PURGE commands. Regardless, I still prefer to run the DEL command described previously to ensure each file including read-only has been forcibly deleted before deleting the folders themselves via RMDIR. There is no measurable speed penalty for using both commands over just one.
To delete a particular directory and all of its subdirectories, you must enter the command:
|
RMDIR /Q/S [Absolute Path or Relative Folder Name] |
Note that this command will not work if you are currently in the directory trying to be deleted. Instead you should navigate to the parent directory via CD.. and then call the command by referencing the target folder.
Let’s Make a Batch File
To enable this functionality without having to continuously enter these commands, we will make a self-contained batch file. I recommend creating a dedicated folder on your hard drive to store small utility programs and batch files, such as ‘C:\Programs‘. Launch Notepad and paste the following snippet into it.
|
@ECHO OFF ECHO Delete Folder: %CD%? PAUSE SET FOLDER=%CD% CD / DEL /F/Q/S «%FOLDER%» > NUL RMDIR /Q/S «%FOLDER%» EXIT |
When done, select File > Save As and save it as «fastdel.bat» in quotes to your folder of choice (i.e., C:\Programs\). I have added a very basic prompt via the PAUSE command to allow a single opportunity to abort the deletion process. As soon as you press any key [except CTRL+C to abort or pressing ‘X‘ in corner to close window] the files and folders will be permanently and immediately deleted with the only possible chance of recovery via a third party software recovery application.
This batch file uses the currently active directory as the one to delete. It first stores this working directory in the FOLDER variable, then navigates to the root drive directory to avoid any operation conflicts. The DEL and RMDIR commands are then called on the original folder and the window will terminate upon completion. Be warned that if you double-click the batch file directly, the folder it resides in will be the target of deletion, so it would delete itself and any siblings or descendants! If you are exceptionally concerned about misfiring this batch file, you could create a more advanced ‘Yes/No’ confirmation prompt for verification using basic batch file commands.
To enable calling of this fast delete batch file from any computer directory, add the file’s directory location to your PATH environmental variable as follows:
- Press WINDOWS KEY + PAUSE/BREAK on your keyboard to open the System Information screen.
- Click on the Advanced System Settings link on the left.
- Under the Advanced tab in the System Variables section, double-click the PATH variable row.
- At the end of the Variable Value field, ensure there is a semicolon (;) and then add the full directory location to the batch file (i.e., C:\Programs\).
- Click OK to close the Edit System Variable prompt, OK again to close the Environmental Variables window, and OK again to close the System Properties.
With this in place, you should be able to open a new command prompt, navigate to any directory you wish to delete, then type FASTDEL to launch the folder deletion process.
Add Fast Delete Option to the Right-Click Context Menu
All that remains is to add an option to Explorer’s Context Menu so that we can right-click any folder and select Fast Delete from the pop-up menu. This adds the convenience of not having to manually launch a Command Prompt window or enter any console commands yourself. You’ll have to dig into the Registry to accomplish this, but it is very simple:
- Press WINDOWS KEY + R on your keyboard to open the Run dialog box.
- Enter regedit and press ENTER.
- Navigate to HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\shell\
- Right-click on the yellow shell key and select New > Key.
- Enter the name: Fast &Delete then press ENTER.
- Right-click on the yellow Fast &Delete folder just created, then select New > Key.
- Enter the name: command then press ENTER.
- Left-click on the yellow command key just created, then double-click the (Default) entry.
- In the Value Data field, enter: cmd /c «cd %1 && fastdel.bat» then press OK.
Now when you open Windows Explorer / My Computer and navigate to a directory you wish to delete, you can right-click on it and should see the «Fast Delete» option in the menu. The ampersand before the ‘D‘ when creating the key is optional, but will allow you to simply press ‘D‘ after right-clicking a folder to call the fast delete command. WARNING: If you use this keyboard shortcut instead of simply left-clicking the command option, the PAUSE line in the batch file I provided will override and the folder will delete immediately. Again, for safety reasons you may wish to implement a more elegant Yes/No prompt as suggested earlier; as a power user I prefer things to happen quickly with as little user input as necessary.
Note: If you have Cygwin installed and configured, you can also remove directories and files via rm -rf [path]. However, my own tests did not reveal any measurable speed improvements over the integrated method described in this article.
November 16, 2015 Update: I recently observed that the original batch file script I provided above did not compensate for paths with spaces in them. For example, if you had two folders ‘Test‘ and ‘Test Two‘ and right-clicked ‘Test Two’ to delete via the script, it would actually find the ‘Test’ folder and delete its contents instead. This has been amended by surrounding the paths in quotes.