On Windows 10, the Windows Defender Firewall is a security feature that checks incoming and outgoing network traffic and allows or blocks specific traffic depending on predefined rules.
Although every installation of Windows 10 comes with the same set of default rules, you can always create new custom rules to allow or block apps from accessing the network. If you have created multiple firewall rules, and you don’t want to lose you settings after a clean installation, or you want configure other devices with the same policy, you can export and import the Windows Defender Firewall rules using the advanced settings console and Command Prompt.
In this guide, you’ll learn the steps to export the current list of firewall rules as well as the steps to import the rules to a new installation of Windows 10.
- How to export and import firewall rules using Windows Security
- How to export and import firewall rules using Command Prompt
If you want to backup all the Windows 10 firewall rules, so you can then restore to another installation, you can use the Windows Security app.
Backing up firewall rules
To export firewall rules using Windows Security, use these steps:
-
Open Windows Security.
-
Click on Firewall & network protection.
-
Click the Advanced settings option.
Windows Security firewall advanced settings option -
Right-click the Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security on Local Computer item and select the Export Policy option.
Windows 10 firewall export rules option -
Select a location to store the list.
-
Type a descriptive name for the list – for example, firewall-rules.
Export firewall rules to wfw file -
Click the Save button.
-
Click the OK button.
Once you complete the steps, the firewall rules will export in the wfw file that you can easily import to the same or different computer.
Restoring firewall rules
To import firewall rules from an exported file, use these steps:
-
Open Windows Security.
-
Click on Firewall & network protection.
-
Click the Advanced settings option.
Windows Security firewall advanced settings option -
Right-click the Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security on Local Computer item and select the Import Policy option.
Windows 10 firewall import rules option -
Click the Yes button to confirm that importing a policy will overwrite all the current rules.
-
Select the .wfw file.
Import firewall rules to wfw file -
Click the Open button.
-
Click the OK button.
After you complete the steps, the policy will overwrite the current rules with the ones in the .wfw file.
How to export and import firewall rules using Command Prompt
Alternatively, you can also export and import firewall rules on Windows 10 using Command Prompt.
Exporting firewall rules
To export the current firewall policy using Command Prompt, use these steps:
-
Open Start.
-
Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
-
Type the following command to export the Windows Defender Firewall rules and press Enter:
netsh advfirewall export "C:\firewall-rules.wfw"
Export firewall rules using netsh command
Once you complete the steps, all the firewall rules will be exported to a .wfw, which you can then import on another installation of Windows 10.
Importing firewall rules
To import firewall rules on Windows 10 with Command Prompt, use these steps:
-
Open Start.
-
Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
-
Type the following command to export the Windows Defender Firewall rules and press Enter:
netsh advfirewall import "C:\firewall-rules.wfw"
Import firewall rules using netsh command
After you complete the steps, the firewall rules will import overwriting the device current policy settings.
We’re using Command Prompt, but you can also use the commands on PowerShell.
Why You Can Trust Pureinfotech
The author combines expert insights with user-centric guidance, rigorously researching and testing to ensure you receive trustworthy, easy-to-follow tech guides. Review the publishing process.
In this post I will show you how you can export/import Windows Firewall rules using PowerShell.
Sometime you might have a task, where you have to move software from one server to another, but it is not just always about moving file. You might also need to move firewall rules. If there are many rules, you might want to script your solution, to make sure that you don’t miss important details. In this post I will show you have you can export/import firewall rules, using some simple PowerShell cmd-lets.

Installing module Firewall Manager
Before we can start exporting firewall rules, we need to install the PowerShell module for Windows Firewall, that we will need for this task. The name of the module is Firewall-Manager. In order to install the module, you should run the following command from a PowerShell prompt:
PS C:\> Install-Module -Inbound -Name Firewall-Manager
Export Firewall Rule with PowerShell
Now we are ready to export a rule from a source server. For that we will use a cmd-let from the module we just imported named Export-FirewallRules. In the example below I will restore the firewall rule named DropBox:
PS C:\> Export-FirewallRules -Inbound -Name Dropbox -CSVFile c:\firewallExport.csv
Import Firewall Rule with PowerShell
Now where we have a csv file with Firewall rules we just exported, we are ready to go ahead and import the csv file on the target server.
PS C:\> Import-FirewallRules -CSVFile C:\firewallExport.csv
This command will import the rules from the CSV file into the target server with all the same settings and exceptions as on the source server.
Export Multiple Firewall rules
If you need to export multiple rules that is also possible using wildcard (*). E.g. if you want to export all rules starting with Microsoft you can use the following command:
PS C:\> Export-FirewallRules -Inbound -Name “Microsoft*” -CSVFile c:\firewallExport.csv
All the above examples are all with the -Inbound parameter. If you need to import and export outbound firewall rules you just use the -Outbound parameter instead.
More information about Export-FirewallRules
I hope you found this post useful. Feel free to drop me a comment or question below. For more information you can check out the Firewall-Manager project on GitHub here
How to Export and Import a Specific Firewall Rule in Windows 10
In Windows 10, you can configure Windows Firewall to have custom rules for a specific address, port or protocol. You can allow or block an app from accessing the Internet. Once you do this, it is a good idea to backup your Firewall configuration.However, Windows 10 allows only exporting and importing the entire rule set. Here’s a trick that we can use to export and import a specific rule only.
Having a backup of firewall rules is very useful. If you reinstall Windows 10, you will be able to restore your custom rules quickly. Or, if you need to reset the Windows Firewall configuration, then having the ability to restore the custom configuration is very time saving.
Before you continue, see how to block any app from accessing Internet with one click in Windows 10, Windows 8 and Windows 7.
Backup and Restore Firewall Rules
In Windows 10, there are several ways to create a backup of Firewall rules. You can use Windows Firewall with Advanced Security snap-in to create or restore rules, or you can do it with the built-in console command netsh. Both methods reviewed in the post
How to Backup and Restore Firewall Rules in Windows 10
Unfortunately, Windows 10 doesn’t offer an option to backup and restore individual Firewall rules. However, it is still possible with either PowerShell, or Registry Editor.
- Open PowerShell as Administrator.
- Change PowerShell Execution policy to Unrestricted.
- Type the following command:
Install-Module -Name Firewall-Manager, and hit the Enter key. - Answer [Y] to proceed.
- Answer [Y] to install the module from PSGallery.
- Type the following command and hit the Enter key:
Import-Module Firewall-Manager. - To export a specific firewall rule, type
Export-FirewallRules -Name "<Rule name>" -CSVFile "<Path to the CSV>" file. Specify the rule name you want to export, and provide the path to the CSV file the rule will be saved to. For example,Export-FirewallRules -Name "IRC Port" -CSVFile c:\data\winaero\irc_port.csv". - To import a firewall rule, type
Import-FirewallRules <path to csv file>. Provide the full path the CSV file that stores a previously exported rule. For example,Import-FirewallRules "C:\data\winaero\irc_port.csv".
You are done.
Note the Export-FirewallRules and Import-FirewallRules cmdlets support exporting/importing of multiple rules at once, and also can work with JSON files.
To learn more about them, execute Get-Help Export-FirewallRules:

Tip: In PowerShell, you can list existing Firewall rules as follows: Get-NetFirewallRule |Format-Table|more.

If you are not a fan of PowerShell, you can export and import a firewall rule using the Registry Editor.
Export and Import a Specific Firewall Rule with Registry Editor
First of all, you need to export all available firewall rules to a single file. You can find names for Firewall rules in PowerShell, as mentioned above, or with Windows Firewall with Advanced Security. Press Win + R and type wf.msc in the Run box to open it.

Click on Inbound Rules/Outbound rules on the left to see the list of rules.

To export all firewall rules using Registry Editor,
- Open the Registry Editor app.
- Go to the following Registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\SharedAccess\Parameters\FirewallPolicy. See how to go to a Registry key with one click. - Right-click on the FirewallRules folder on the left and select Export… from the context menu.
- Type in the file name for the *.reg file.
- Click on the Save button.
Now, the Registry file contains the entire set of your Firewall rules. You need to leave there only the rules you want to export, and delete all other lines.
Export Only Specific Rules to Registry File
- Right-click your *.reg file in File Explorer and select Edit from the context menu to open it in Notepad.
- Below the line
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\SharedAccess\Parameters\FirewallPolicy\FirewallRules], you will see all the rules listed. - Remove all of them except those you want to export. The following screenshot demonstrates how to keep only one rule in the file.
- Save the changes you made (Press Ctrl + S).
This way, you can make the reg file store only the specific rules you want to export. You can search for the rule name with Ctrl + F in Notepad to save your time.
Import Windows Firewall Rules from Registry File
- Locate the *.reg file that contains your Firewall rules in File Explorer.
- Double-click on it to merge it. Confirm the UAC prompt.
- Restart Windows 10 to ensure that the rules are properly applied.
You are done.
Support us
Winaero greatly relies on your support. You can help the site keep bringing you interesting and useful content and software by using these options:
If you like this article, please share it using the buttons below. It won’t take a lot from you, but it will help us grow. Thanks for your support!
Posted by
on May 22, 2017
Instead of manually configuring the same Windows Firewall rules on many different servers, we can import and export Windows firewall settings to transfer them between different servers.
We can also import the firewall rule policy file into a Group Policy Object (GPO) to apply it automatically throughout a whole domain.
This post is part of our Microsoft 70-744 Securing Windows Server 2016 exam study guide series. For more related posts and information check out our full 70-744 study guide.
Export Windows Firewall Settings
We can export windows firewall rules with both the graphical user interface (GUI) and command line interface (CLI). First we’ll start with the GUI then cover the CLI.
Graphical User Interface
Open Windows Firewall with Advanced Security, right click the top node and select “Export Policy…”
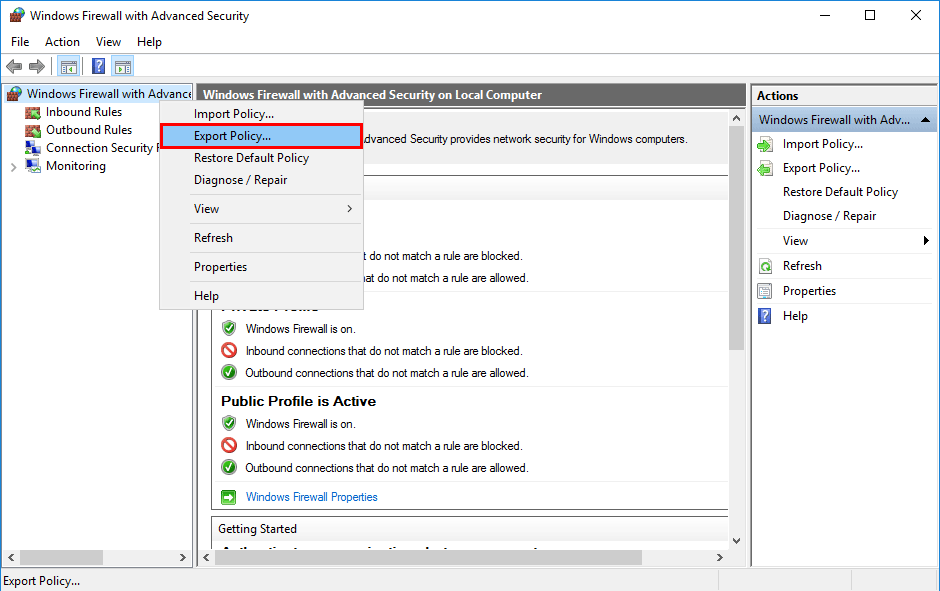
Save the file as a .wfw policy file.
You’ll be advised that the policy successfully exported with a pop up message.
Command Line Interface
This can also be done through the PowerShell or Command Prompt CLI instead with the netsh command, as shown below.
netsh advfirewall export "C:\fw-rules.wfw"
Import Windows Firewall Settings
We can import this file that we have exported to another server where we wish to also have the same set of firewall rules. Again we’ll first start with the GUI solution followed by how to do it in CLI.
Note that importing firewall rules will overwrite all existing firewall configuration and replace it with the exported contents of the .wfw file, you will be advised of this before proceeding in the GUI but not through CLI.
Graphical User Interface
open up Windows Firewall with Advanced Security, right click the top node as before, but this time select “Import Policy…”
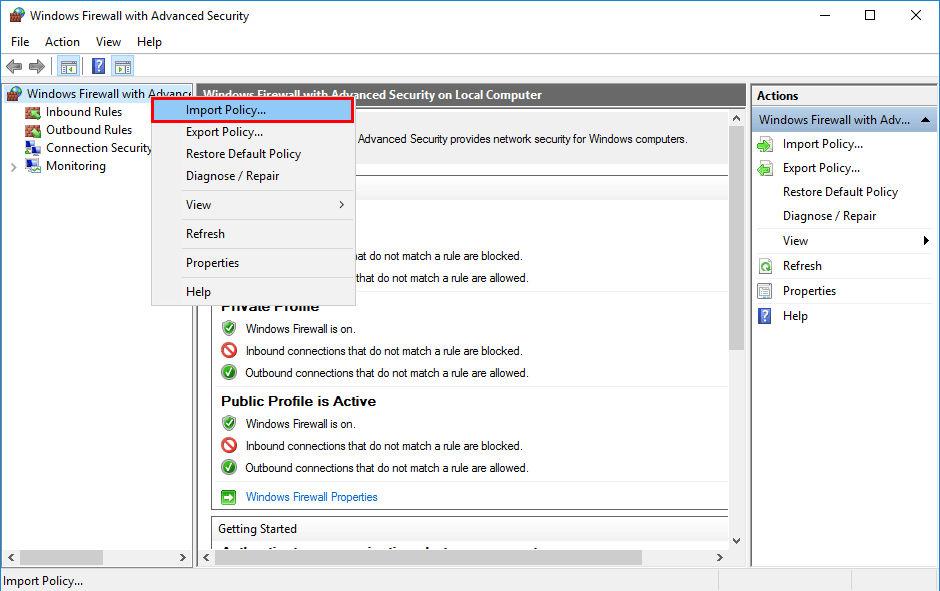
You’ll be warned that importing the policy will overwrite all current rules, select yes to proceed.
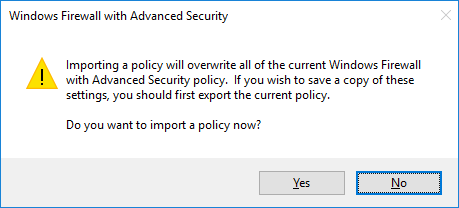
Next select the .wfw file that was exported previously.
Once the import has completed you’ll be advised by a pop up message.
Command Line Interface
This can also be done through the CLI instead with the netsh command, as shown below.
netsh advfirewall import "C:\fw-rules.wfw"
Note that if you import with the netsh command you will not be warned about overwriting all existing rules like you would be with the GUI.
Summary
As shown we can use either the GUI or CLI to import and export Windows Firewall settings in Windows Server 2016. This allows us to create a set of rules on a single server that we want to deploy elsewhere which is more efficient than implementing the same rules again and again on each server. We can also take this a step further and use group policy to deploy the exported firewall policy files in a domain.
This post is part of our Microsoft 70-744 Securing Windows Server 2016 exam study guide series. For more related posts and information check out our full 70-744 study guide.
In this blog, we will guide you on how to import and export Windows Firewall rules, providing practical insights and step-by-step guidance to streamline your firewall management.
To begin with, here is a quick step-by-step guide to importing or exporting Windows firewall rules in Windows 10 or Windows 11:
Export:
- Open Windows Firewall with Advanced Security.
- Right-click on “Windows Firewall with Advanced Security” and select “Export Policy”.
- Choose a location and save the file.
Import:
- Open Windows Firewall with Advanced Security.
- Right-click on “Windows Firewall with Advanced Security” and select “Import Policy”.
- Select the saved policy file and click “Open”.
- Confirm the import.
However, it’s important to note that this is just an overview of the steps. Therefore, we encourage you to continue reading the blog further to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the detailed steps required to import or export Windows firewall rules in Windows.
How to Export specific firewall rules on Windows 10 or Windows 11 ?
Exporting specific Windows Firewall rules on Windows 10 or Windows 11 can be accomplished using several methods, including the Command Prompt, PowerShell, Registry Editing, and the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security interface. Below are detailed steps for each method.
Method 1: Using Command Prompt
Open Command Prompt as Administrator:
- Firstly, press Windows + X and select Windows Terminal (Admin) or Command Prompt (Admin).
List Existing Firewall Rules:
- Next, to see all existing firewall rules, type the following command:
- netsh advfirewall firewall show rule name=all
- Subsequently, this will display a list of all firewall rules. Identify the specific rule you want to export.
Export Specific Firewall Rule:
- After that, use the following command to export a specific rule (replace RuleName with the actual name of the rule):
- netsh advfirewall firewall export “C:\path\to\your\firewall_rules.wfw” name=”RuleName”
Note: However, the export command does not support exporting individual rules directly. Instead, you can export all rules and then manually edit the exported file to keep only the desired rule.
Method 2: Using PowerShell
Open PowerShell as Administrator:
- To begin with, press Windows + X and select Windows Terminal (Admin) or Windows PowerShell (Admin).
List Existing Firewall Rules:
- Then, to see all existing firewall rules, type the following command:
- Get-NetFirewallRule | Format-Table -Property Name, DisplayName, Enabled
- As a result, this will display a list of all firewall rules. Identify the specific rule you want to export.
Export Specific Firewall Rule:
- Finally, use the following command to export a specific rule (replace RuleName with the actual name of the rule):
- Export-NetFirewallRule -Name “RuleName” -File “C:\path\to\your\firewall_rule.xml”
Also Check: How to fix Windows 10 hardware random MAC address not working ?
Method 3: Using Windows Firewall with Advanced Security
Open Windows Firewall with Advanced Security:
- First, press Windows + R, type wf.msc, and press Enter.
Locate the Specific Rule:
- Next, in the left pane, click on Inbound Rules or Outbound Rules depending on the type of rule you want to export.
- Then, find the specific rule you want to export in the list.
Export the Rule:
Unfortunately, the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security interface does not provide a direct export option for individual rules. Nevertheless, you can only export all rules using the following method:
- First, right-click on Windows Firewall with Advanced Security on Local Computer in the left pane and select Export Policy.
- Lastly, choose a location to save the exported file (e.g., firewall_policy.wfw).
Method 4: Registry Editing (Advanced users)
Caution: Incorrectly modifying the registry can lead to system instability. Proceed with caution and create a system restore point before making changes.
- To start, open Registry Editor (press Win + R, type regedit, and press Enter).
- Next, navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\SharedAccess\Parameters\FirewallPolicy\FirewallRules.
- Then, locate the specific rule you want to export.
- After that, right-click on the rule and choose “Export”.
- Finally, save the exported file as a .reg file.
Note: However, this method exports the entire rule, including its settings. Consequently, you might need to manually extract the specific information you require from the exported .reg file.
Method 5: Manually Editing Exported Rules
If you need to export specific rules, you can export all rules and then manually edit the exported file:
Export All Rules:
- First, use the Command Prompt or PowerShell to export all rules as described in the previous methods.
Edit the Exported File:
- Next, open the exported file (e.g., firewall_policy.wfw or firewall_rule.xml) in a text editor.
- Then, locate the specific rule you want to keep and remove the others.
Save the Edited File:
- Lastly, save the changes to create a file that contains only the specific rule you need.
How to Import specific firewall rules on Windows 10 or Windows 11 ?
In this section, we will explore the various methods to import specific firewall rules on Windows 10 and Windows 11, ensuring that your network security settings are tailored to your needs.
We’ll provide step-by-step instructions to help you seamlessly integrate your desired rules into your system. Below are detailed steps for each method.
Method 1: Using Command Prompt
Open Command Prompt as Administrator:
- Firstly, press Windows + X and select Windows Terminal (Admin) or Command Prompt (Admin).
Prepare the Import File:
- Next, ensure you have a .wfw file that contains the specific firewall rules you want to import. If you don’t have one, you can create it by exporting existing rules or manually editing an existing export.
Import the Firewall Rule:
- Then, use the following command to import the specific firewall rules from the file:
- netsh advfirewall import “C:\path\to\your\firewall_rules.wfw”
- Additionally, replace C:\path\to\your\ with the actual path to your .wfw file.
Verify the Import:
- Finally, to check if the rules have been imported successfully, run:
- netsh advfirewall firewall show rule name=all
Also Check: How to uninstall WordPad from Windows ?
Method 2: Using PowerShell
Open PowerShell as Administrator:
- To begin with, press Windows + X and select Windows Terminal (Admin) or Windows PowerShell (Admin).
Prepare the Import File:
- Subsequently, ensure you have an XML file that contains the specific firewall rules you want to import. You can create this file by exporting existing rules.
Import the Firewall Rule:
- After that, use the following command to import the specific firewall rules from the XML file:
- Import-NetFirewallRule -File “C:\path\to\your\firewall_rule.xml”
- Similarly, replace C:\path\to\your\ with the actual path to your XML file.
Verify the Import:
- Lastly, to check if the rules have been imported successfully, run:
- Get-NetFirewallRule | Format-Table -Property Name, DisplayName, Enabled
Method 3: Using Windows Firewall with Advanced Security
Open Windows Firewall with Advanced Security:
- First, press Windows + R, type wf.msc, and press Enter.
Import the Firewall Policy:
- Next, in the left pane, right-click on Windows Firewall with Advanced Security on Local Computer.
- Then, select Import Policy.
- After that, browse to the location of your .wfw file and select it.
- Finally, click Open to import the policy.
Verify the Imported Rules:
- Subsequently, check the Inbound Rules and Outbound Rules sections to ensure the specific rules have been imported successfully.
Method 4: PowerShell with Firewall-Manager Module
Install the Firewall-Manager module:
- To start, open PowerShell as an administrator.
- Then, run the following command:
- Install-Module -Name Firewall-Manager
Import the module:
- Next, import-Module Firewall-Manager
Import specific rules:
- However, while there’s no direct import command for specific rules, you can create new rules based on the exported data.
- Therefore, use the New-FirewallRule cmdlet to create new rules with the desired parameters.
Example:
- For instance, New-FirewallRule -Name “AllowPort80” -DisplayName “Allow HTTP” -Direction Inbound -Action Allow -Protocol TCP -LocalPort 80
Method 5: Manually Editing Imported Rules
If you want to import specific rules from a larger set, you can manually edit the exported files:
Export All Rules:
- First, use the Command Prompt or PowerShell to export all rules as described in previous guides.
Edit the Exported File:
- Then, open the exported file (e.g., firewall_policy.wfw or firewall_rule.xml) in a text editor.
- Next, locate the specific rule you want to keep and remove the others.
Save the Edited File:
- After that, save the changes to create a file that contains only the specific rule you need.
Import the Edited File:
- Finally, use the methods above to import the edited file containing only the specific rules.
How do I Export or Import Windows firewall rules to CSV ?
Exporting and importing Windows Firewall rules to and from a CSV file can be accomplished using PowerShell.
Below are the detailed steps for both exporting existing rules to a CSV file and importing rules from a CSV file.
Exporting Windows Firewall Rules to CSV
Open PowerShell as Administrator:
- First, press Windows + X and select Windows Terminal (Admin) or Windows PowerShell (Admin).
Export the Firewall Rules:
- Next, use the following command to export the firewall rules to a CSV file:
- Get-NetFirewallRule | Select-Object Name, DisplayName, Direction, Action, Protocol, LocalPort, RemotePort | Export-Csv -Path “C:\path\to\your\firewall_rules.csv” -NoTypeInformation
- Additionally, replace C:\path\to\your\firewall_rules.csv with the desired path where you want to save the CSV file.
Verify the Export:
- Finally, navigate to the specified location to ensure the CSV file has been created successfully.
Also Check: How to uninstall Windows Subsystem for Android (WSA) on Windows 10 ?
Importing Windows Firewall Rules from CSV
Prepare Your CSV File:
- To begin, create a CSV file (e.g., firewall_rules.csv) with the necessary columns. A simple structure might include columns like Name, DisplayName, Direction, Action, Protocol, LocalPort, and RemotePort. Here’s an example:
Open PowerShell as Administrator:
- Then, press Windows + X and select Windows Terminal (Admin) or Windows PowerShell (Admin).
Run the PowerShell Script to Import Rules:
- After that, use the following PowerShell script to read the CSV file and create the firewall rules:
- Make sure to replace C:\path\to\your\firewall_rules.csv with the actual path to your CSV file.
Verify the Imported Rules:
- Finally, after running the script, you can verify that the rules have been created by running:
- Get-NetFirewallRule | Format-Table -Property Name, DisplayName, Enabled
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering the import and export of Windows Firewall rules is a valuable skill for both IT professionals and home users.
Throughout this guide, we’ve explored various methods, including using Command Prompt and PowerShell to utilizing the Windows Firewall interface as well as advanced registry editing.
Furthermore, remember to choose the method that best suits your comfort level and needs.
Additionally, always exercise caution when modifying firewall settings to maintain your system’s security. Moreover, regularly backing up your rules is a smart practice to prevent data loss.
By following these step-by-step guides, you can efficiently manage your firewall rules across multiple systems, thereby ensuring consistent network security.
Source: [ superuser, howto.hyonix, winaero, pureinfotech ]
Frequently Asked Question’s (FAQ’s)
Can you export or import Windows Firewall rules ?
Yes, you can export and import Windows Firewall rules via Command Prompt, PowerShell, or the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security interface. This helps back up, replicate, and restore rules, streamlining firewall management and ensuring consistent security.
How do I allow file transfer through Windows Firewall ?
Access Windows Firewall settings, find the “Allow an app or feature through Windows Firewall” option, and ensure “File and Print Sharing” is checked for both private and public networks. Additionally, verify that file sharing is enabled on the specific folders you want to share.
How to import firewall rules to GPO ?
To import firewall rules into a GPO, export the configuration as a .wfw file, then use the Group Policy Management Editor to import it. This will overwrite existing rules in the GPO. Link the GPO to the relevant OUs for policy application.

















