Last Updated :
02 Aug, 2024
When your Python code encounters a situation where it lacks the necessary permissions to access a file or directory, it raises PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied in Python. This article will explore how to address the Errno 13 Error in Python effectively.
What is PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission Denied in Python?
PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission Denied denotes a situation where a program attempts to execute an operation—such as file reading or writing—without the requisite permissions. This error typically arises when a user lacks the necessary privileges to access, modify, or execute a particular file or directory. The error message associated with Errno 13 explicitly indicates that permission is denied for the specified operation.
Error Syntax
PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied
below, are the reasons for the occurrence of PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied in Python:
- Improper File Path Handling
- Incorrect File Content in Python
Improper File Path Handling
This Python code opens a file named «GFG.txt» for writing and writes «Hello, world!» into it. However, the file path contains backslashes (\), which might cause issues if not handled correctly.
Python
with open(r"C:\Users\R.Daswanta kumar\OneDrive\Pictures\GFG\file\GFG.txt", "w") as file: file.write("Hello, world!")
Output:

Incorrect File Content with Python
Below, code to overwrite the content of a file named «GFG.txt» located at a specific path. If executed without sufficient permissions, Python will raise a PermissionError (Error 13) indicating a permission denied error.
Python
file_path = r"C:\Users\R.Daswanta kumar\OneDrive\Pictures\GFG\file\GFG.txt" with open(file_path, "w") as file: new_content = "New content to replace the existing content." file.write(new_content) print("File content modified successfully!")
Output:

Solution for PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission Denied in Python
Below, are the approaches to solve PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission Denied in Python:
- Proper File Path Handling
- Correct File Content in Python
Proper File Path Handling
Below, code defines a file path and opens a file named «GFG.txt» in write mode, enabling it to overwrite existing content. It then replaces the content with the specified new text and confirms successful modification.
Python
file_path = r"C:\Users\R.Daswanta kumar\OneDrive\Pictures\GFG\file\GFG.txt" with open(file_path, "w") as file: new_content = "New content to replace the existing content." file.write(new_content) print("File content modified successfully!")
Output
File content modified successfully
Correct File Content in Python
The following code first checks if the file exists, then attempts to modify its permissions to allow writing. If successful, it proceeds to overwrite the file’s content with new text. If the user lacks necessary permissions, it prints a message indicating permission denial. Finally, it confirms both the modification of file permissions and the content.
Python
import os file_path = r"C:\Users\R.Daswanta kumar\OneDrive\Pictures\GFG\file\GFG.txt" try: if os.path.exists(file_path): os.chmod(file_path, 0o666) print("File permissions modified successfully!") else: print("File not found:", file_path) except PermissionError: print("Permission denied: You don't have the necessary permissions to change the permissions of this file.") with open(file_path, "w") as file: new_content = "New content to replace the existing content." file.write(new_content) print("File content modified successfully!")
Output
File content modified successfully
Conclusion
In conclusion , To sum up, Error 13 is a frequent Python issue that arises from inadequate permissions when attempting to access certain files or folders. You may simply fix this problem and create reliable Python code by using the ‘os’ module, comprehending file permissions, and putting appropriate error handling in place.
Readers help support Windows Report. We may get a commission if you buy through our links.
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more
Python is designed to build websites, software, and more using a high-level programming language. However, users have recently reported receiving a permission denied error in Windows 11. Here’s how to fix PermissionError [Errno 13] Permission denied error in Python.
Because Python uses a general-purpose language, it can be used to build various programs rather than focusing on a specific variable.
For those wanting to learn more about developing and coding, Python is one of the easiest programming languages to learn, making it perfect for beginners.
Why do I get the permission denied error in Python?
Users encounter PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied error if providing Python with a file path that does not have permission to open or edit the file. By default, some files do not allow certain permissions. This error may also occur if providing a folder rather than a file.
If the file is already being operated by another process, then you may encounter the permission denied error in Python. If you’re receiving the Python runtime error, we offer solutions for that as well.
How do I fix the Python permission denied error in Windows 11?
1. Check file path
One of the leading causes of PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied is because Python is trying to open a folder as a file. Double-check the location of where you want to open the file and ensure there isn’t a folder that exists with the same name.
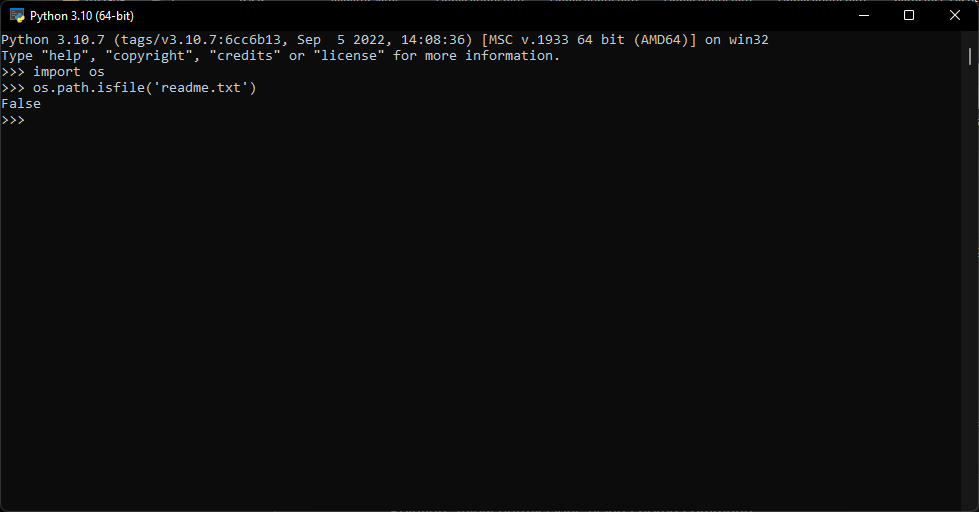
Run the os.path.isfile(filename) command replacing filename with your file to check if it exists. If the response is false, then the file does not exist, or Python cannot locate it.
2. Allow permissions using chomd
If the file does not have read and write permissions enabled for everyone, then you may encounter the permission denied error in Python. Try entering the chomd 755 filename command and replace filename with the name of your file.
This command gives everyone permission to read, write, and execute the file, including the owner. Users can also apply this command to entire directories. Running the ls -al command will provide a list of files and directories and their permissions.
3. Adjust file permissions
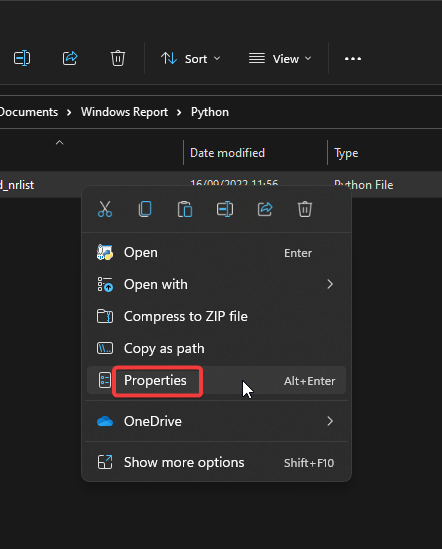
- Navigate to the location of your file in file explorer.
- Right-click on the file and select Properties.
- Click the Security tab then select your name under Group or user names.
- Select Edit and go through and check permissions.
- Click Apply then OK.
Adjusting the permissions of the file that you’re trying to open will allow Python to read, write, and execute the file.
- Recent Windows 11 update lets you disable profanity filter in voice typing
- Meta under fire after AI chatbot caught having sexual talks with minors
- OpenAI decides to reverse recent GPT-4o update after user find bot being overly appeasing
- Microsoft’s hotpatching for Windows Server 2025 to be subscription-based starting July
4. Turn off execution aliases
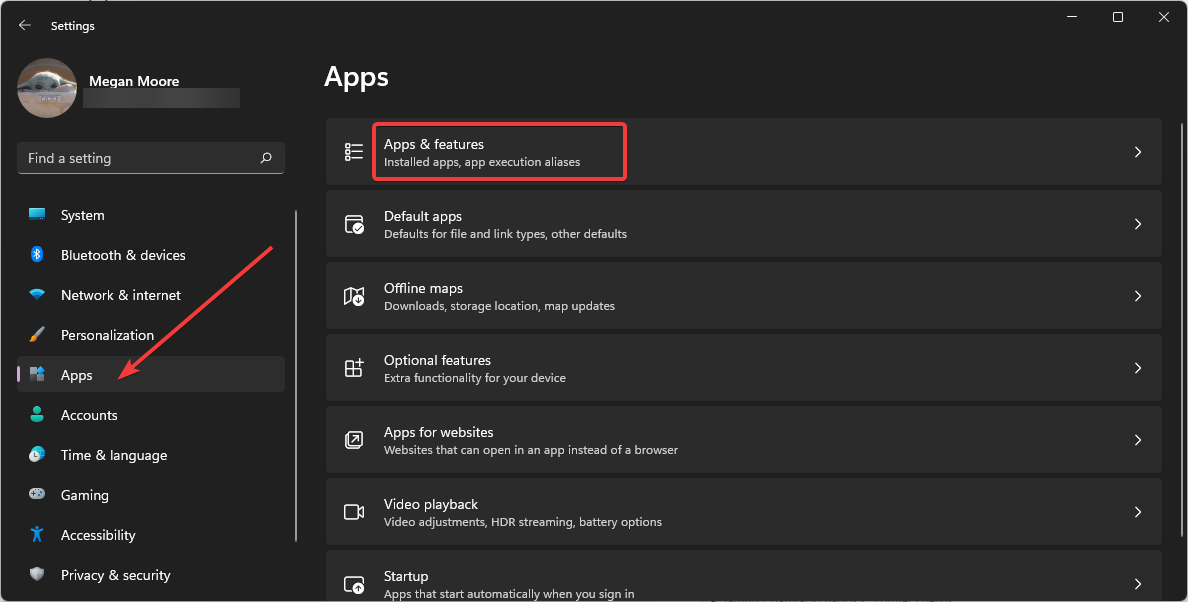
- Click on Start and open Settings (or press Windows + I).
- Open Apps then select Apps & features.
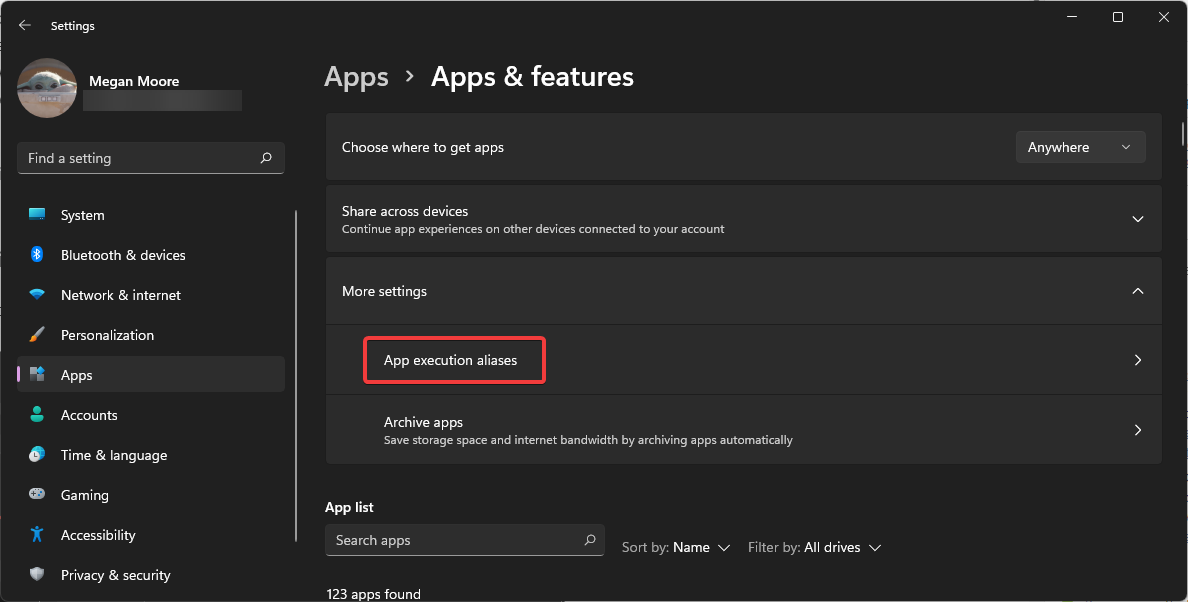
- Open the drop-down menu next to More settings.
- Click App execution aliases.
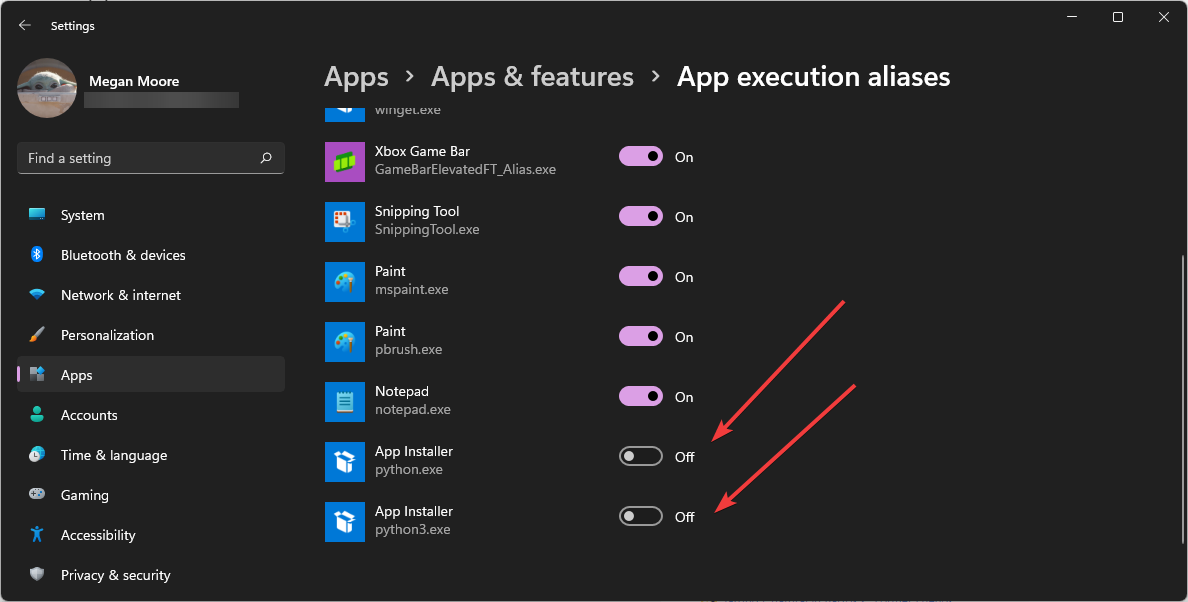
- Locate the two App Installers for python.exe and python3.exe and toggle both to Off.
Python was added to the Microsoft Store for version 3.7 which introduced permission denied errors because it created two installers: python.exe and python3.exe. Disabling the Microsoft Store versions of Python should fix the permissions denied error.
5. Update Windows and drivers
- Click on Start and open Settings (or press Windows + I).
- Scroll down and select Windows Update.
- Perform any available updates.
- Select Advanced options.
- Under Additional options, click on Optional updates.
- Run any driver updates.
If you’re suddenly encountering the Python permission denied error and none of the above solutions worked, then check for any Windows 11 updates and perform any available driver updates.
What is the latest version of Python?
As of the release of this article, the latest version of Python is 3.10.7, which is available for Windows 10 and newer and is not compatible with older versions, including Windows 7. Python supports Windows, macOS, Linux/UNIX, and more.
However, If users want to use older versions of Python, they can access releases 2.7 and newer, or they can download a specific version of a release.
If you want a quick way to open PY files on Windows 10 and 11, we offer a guide for that as well. To learn how to deal with errors, be sure to visit our Try-except-print in Python guide.
We also have a great guide on what to do if _xsrf argument missing from post, so don’t miss it. We also have a new guide on Cannot open shared object no such file or directory error, so don’t miss it.
Hopefully, one of the above solutions helped you fix the Python permission denied error in Windows 11. Let us know in the comments which step worked for you or if you have any suggestions for a different solution.
Megan Moore
Megan is a Windows enthusiast and an avid writer. With an interest and fascination in all things tech, she enjoys staying up to date on exciting new developments in the computer and gaming world.
When not falling down a rabbit hole of tech news and information, she enjoys painting, watching movies, and taking her dramatic husky for long walks.
- Author
- Recent Posts
I started writing code around 20 years ago, and throughout the years, I have gained a lot of expertise from hands-on experience as well as learning from others. This website has also grown with me and is now something that I am proud of.
Errno 13 permission denied is an error message when Python cannot read your file due to an error in your code or a conflict in the file system of your operating system. This article will show you other causes of this error message as well, and we’ll teach you how to fix them all.

Everything that you’ll learn will let you understand how Python handles files and how it responds if it encounters a problem in the process. Now, switch on your computer, and let’s solve the “permission denied” error in Python.
JUMP TO TOPIC
- Why Is Python Denied a Permission? All Possible Causes
- – You’re Reading a Folder Like a File
- – Python Is Not Permitted To Read the File
- – The File Is Opened in Another Program
- – There Is Forward Slash Before the Folder Name
- – You’re Using “Python 3.7” From Microsoft Store
- How To Solve the “Permission Denied Error” in Python? Simplified
- – Confirm That You’re Opening a File Using “OS.path.isfile()”
- – Grant Python Permissions To Read the File
- – Close the Application That’s Using the File
- – Remove the Forward Slash Before Your Folder
- – Toggle off Application Execution Aliases in Windows
- Conclusion
Why Is Python Denied a Permission? All Possible Causes
Python was denied permission because of the following:
- You’re reading a folder like a file
- Python is not permitted to read the file
- The file is opened in another program
- There is a forward slash before the folder name
- You’re using “Python 3.7” from Microsoft Store
– You’re Reading a Folder Like a File
The first cause of the “permission denied” error is when Python tries to open a folder name like a file using Python’s in-built “open()” function. By default, this function will open files in a directory, and it will return a file object. But it’s not designed to open a folder, and if you tell it to open a folder, that’s when the permission error occurs.
For example, the following code aims to open a file in a directory, but there is no reference to the file.
# results in a permission error.
file = open(“C:\\Users\\HP\\Desktop\\PIE\\PIE_CLE_01”)
# Read the file.
file_content = file.read()
# Print the file.
print(file_content)
# Close the file handle.
file.close()
– Python Is Not Permitted To Read the File
When Python is not permitted to read a file, it will also report a “permission denied” error. This happens because, on operating systems like Windows and Linux, you can configure file access for a user account.
So, if your user account does not have access to a file, any Python installation for your account cannot open the file. This means any attempt to open the file using the “open()” function in Python will result in a permission error.
– The File Is Opened in Another Program
In the Windows operating system, if a file is opened in an application, you can’t read it using Python. For example, if you’re working with “File_A.csv” in Microsoft Excel, Windows will not allow Python to open “File_A.csv” using its “open()” function.
This prevents conflicts where one application can make changes, and another can delete those changes at the same time. That’s because, when you open a file using the “open()”, you can change the file content.

– There Is Forward Slash Before the Folder Name
In Unix, if there is a forward slash before the folder name in your file-uploading code, you’ll run into the permission error. That’s because the forward slash before a folder’s name in Unix is a sign that the folder should be in the “root directory”.
This directory contains the core and sensitive files and directories of your Unix system, for example, “/bin/” and “/usr/”. However, ordinary processes like your file-uploading code don’t have permission to modify this “root directory”.
– You’re Using “Python 3.7” From Microsoft Store
If you’re using “Python 3.7” from Microsoft Store, you can encounter the “permission denied” error while working with Python. That’s because this Python has two executables, “python.exe” and “python3.exe” and this can create a conflict when working with files.
How To Solve the “Permission Denied Error” in Python? Simplified
You can solve the “permission denied error” in Python using the following:
- Confirm that you’re opening a file using “os.path.isfile()”
- Grant Python permissions to read the file
- Close the application that’s using the file
- Remove the forward slash before your folder
- Toggle off application execution aliases in Windows
– Confirm That You’re Opening a File Using “OS.path.isfile()”
Before your code opens a file, you should confirm that the “file” is a file using “os.path.isfile()”. The “isfile()” function accepts a “file path”, and it will return Boolean “true” if the path belongs to a file and “false” otherwise.
Now, the following is the updated code that was reading a folder name instead of a file. This time, we use “os.path.isfile()” to check the file path, and if it’s a file, you can read and print the file content.
# Assign a file path
file_path = “C:\\Users\\HP\\Desktop\\PIE\\PIE_CLE_01”
# Check the file
is_file = os.path.isfile(file_path)
# If it’s a file, open and print the file
# content.
if (is_file):
file = open(file_path)
# Read the file
file_content = file.read()
# Print the file
print(file_content)
# Close the file handle
file.close()
else:
print(“Not a file.”)
– Grant Python Permissions To Read the File
If you have “File_A.txt” that’s not accessible to your user account and your Python file (“File_B.py”), you can change the file permissions of “File_A.txt” or update the “file permissions” of the Python file, “File_B.py”.
On Windows, you can use the following steps to update the privilege of your Python file:
- Open Windows explorer and navigate to the location of the Python file.
- Right-click on it and select “Properties” to open a dialog window
- Select the “Security” tab and choose your account username under “Group or user names”.
- Click on “Edit” and set the permissions that are required. This will be “Full Control”, “Modify”, “Read & execute”, “Read” and “Write”.
- Save your changes using the “Apply” button and click on “OK” to confirm.
On Linux, you can change the file permission using the “chmod 755 your_file_name.extension” or “chown account_username:admin your_file_name.extension”.
The “chmod 755” command will give you read/write/execute privilege on “your_file_name.extension” and the latter is a valid file on your computer. While the “chown” command is short for “change ownership” and here, the command will assign you administrator rights on the file.
You can use command on your Linux terminal, and then you can read the file using Python and the “open()” function.
– Close the Application That’s Using the File
When another application has opened a file that you’ll like to read in Python, you should close the application. On Windows, you do the following:

- Locate the application’s icon on the Taskbar.
- Right-click on it and select “Close”.
However, if the application failed to close using the steps above, you can use the command prompt:
- Click on the “Start” menu and search for “cmd”.
- Right-click the command prompt and select “Run as administrator”.
- Type “tasklist” on the command line and hit “enter” on your keyboard.
- Locate the application from the command output and take note of its PID number.
- Type the following and replace 1234 with the application’s PID: taskkill /f /PID 1234
- Press enter on your keyboard to close the application.
- Return to your Python code, and it should have access to the file.
– Remove the Forward Slash Before Your Folder
While working on Unix, you should remove the forward slash from your folder name to prevent the permission error. So, in your code, if you have something like “path = ‘/folderX/folderY’” change it to “path = ‘folder1/folder2′”.
From the latter, we removed the forward-slash (“/”) before “folder1”, and this defaults it to the current working directory. This is safe, and Unix will not stop your code from uploading to “folder1”.
– Toggle off Application Execution Aliases in Windows
You can toggle off application execution aliases in Windows if you’re getting the permission “denied error” from the Python that’s installed from Microsoft Store. To do this, use the following steps:
- Click on the “Start” menu and select “Settings”.
- Locate “Apps” in the left sidebar and choose “Apps & features”.
- Open “More settings” and click on “App execution aliases”.
- Locate the application installers for “python3.exe” and “python.exe” and toggle them off.
- Switch back to your Python code, and it should read your file.
Conclusion
This article explains why Python shows the “errno 13 permission denied” error and how you can fix it. The following are what you should remember about this error:
- An attempt to read a folder name like a file will result in the permission denied error.
- You will get a permission error if your user account is not permitted to read a file.
- If an application like Microsoft Excel has the file opened, an attempt to read the file in Python will result in a permission error.
- You can solve the “permission denied” error by checking the validity of the file using “os.path.isfile()” or “chmod 755 your_file_name.extension”.
At this stage, you know how to solve and prevent the “Python permission” error. Teach your fellow Python developers your newly found knowledge by sharing our article.
hey guys… having an issue here… wondering if anyone has any ideas
Running auto-py-to-exe v2.27.0
Building directory: C:\Users\BDAWG~1.LAP\AppData\Local\Temp\tmpyqt33663
Provided command: pyinstaller --noconfirm --onedir --console "C:\Users\bdawg.LAPTOP-2CKTEBU7\Bot Business\Dentist Customer"
Recursion Limit is set to 5000
Executing: pyinstaller --noconfirm --onedir --console C:\Users\bdawg.LAPTOP-2CKTEBU7\Bot Business\Dentist Customer --distpath C:\Users\BDAWG~1.LAP\AppData\Local\Temp\tmpyqt33663\application --workpath C:\Users\BDAWG~1.LAP\AppData\Local\Temp\tmpyqt33663\build --specpath C:\Users\BDAWG~1.LAP\AppData\Local\Temp\tmpyqt33663
238375 INFO: PyInstaller: 5.4.1
238386 INFO: Python: 3.10.9
238401 INFO: Platform: Windows-10-10.0.22621-SP0
238418 INFO: wrote C:\Users\BDAWG~1.LAP\AppData\Local\Temp\tmpyqt33663\Dentist Customer.spec
238435 INFO: UPX is not available.
238450 INFO: Extending PYTHONPATH with paths
['C:\\Users\\bdawg.LAPTOP-2CKTEBU7\\Bot Business']
239589 INFO: checking Analysis
239593 INFO: Building Analysis because Analysis-04.toc is non existent
239609 INFO: Reusing cached module dependency graph...
239649 INFO: Caching module graph hooks...
239665 WARNING: Several hooks defined for module 'numpy'. Please take care they do not conflict.
239796 INFO: running Analysis Analysis-04.toc
239806 INFO: Adding Microsoft.Windows.Common-Controls to dependent assemblies of final executable
required by C:\Program Files\WindowsApps\PythonSoftwareFoundation.Python.3.10_3.10.2544.0_x64__qbz5n2kfra8p0\python.exe
239821 WARNING: lib not found: api-ms-win-appmodel-runtime-l1-1-0.dll dependency of C:\Program Files\WindowsApps\PythonSoftwareFoundation.Python.3.10_3.10.2544.0_x64__qbz5n2kfra8p0\python.exe
240051 INFO: Analyzing C:\Users\bdawg.LAPTOP-2CKTEBU7\Bot Business\Dentist Customer
An error occurred while packaging
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:\Users\bdawg.LAPTOP-2CKTEBU7\AppData\Local\Packages\PythonSoftwareFoundation.Python.3.10_qbz5n2kfra8p0\LocalCache\local-packages\Python310\site-packages\auto_py_to_exe\packaging.py", line 131, in package
run_pyinstaller()
File "C:\Users\bdawg.LAPTOP-2CKTEBU7\AppData\Local\Packages\PythonSoftwareFoundation.Python.3.10_qbz5n2kfra8p0\LocalCache\local-packages\Python310\site-packages\PyInstaller\__main__.py", line 179, in run
run_build(pyi_config, spec_file, **vars(args))
File "C:\Users\bdawg.LAPTOP-2CKTEBU7\AppData\Local\Packages\PythonSoftwareFoundation.Python.3.10_qbz5n2kfra8p0\LocalCache\local-packages\Python310\site-packages\PyInstaller\__main__.py", line 60, in run_build
PyInstaller.building.build_main.main(pyi_config, spec_file, **kwargs)
File "C:\Users\bdawg.LAPTOP-2CKTEBU7\AppData\Local\Packages\PythonSoftwareFoundation.Python.3.10_qbz5n2kfra8p0\LocalCache\local-packages\Python310\site-packages\PyInstaller\building\build_main.py", line 962, in main
build(specfile, distpath, workpath, clean_build)
File "C:\Users\bdawg.LAPTOP-2CKTEBU7\AppData\Local\Packages\PythonSoftwareFoundation.Python.3.10_qbz5n2kfra8p0\LocalCache\local-packages\Python310\site-packages\PyInstaller\building\build_main.py", line 884, in build
exec(code, spec_namespace)
File "C:\Users\BDAWG~1.LAP\AppData\Local\Temp\tmpyqt33663\Dentist Customer.spec", line 7, in <module>
a = Analysis(
File "C:\Users\bdawg.LAPTOP-2CKTEBU7\AppData\Local\Packages\PythonSoftwareFoundation.Python.3.10_qbz5n2kfra8p0\LocalCache\local-packages\Python310\site-packages\PyInstaller\building\build_main.py", line 409, in __init__
self.__postinit__()
File "C:\Users\bdawg.LAPTOP-2CKTEBU7\AppData\Local\Packages\PythonSoftwareFoundation.Python.3.10_qbz5n2kfra8p0\LocalCache\local-packages\Python310\site-packages\PyInstaller\building\datastruct.py", line 173, in __postinit__
self.assemble()
File "C:\Users\bdawg.LAPTOP-2CKTEBU7\AppData\Local\Packages\PythonSoftwareFoundation.Python.3.10_qbz5n2kfra8p0\LocalCache\local-packages\Python310\site-packages\PyInstaller\building\build_main.py", line 572, in assemble
priority_scripts.append(self.graph.add_script(script))
File "C:\Users\bdawg.LAPTOP-2CKTEBU7\AppData\Local\Packages\PythonSoftwareFoundation.Python.3.10_qbz5n2kfra8p0\LocalCache\local-packages\Python310\site-packages\PyInstaller\depend\analysis.py", line 268, in add_script
self._top_script_node = super().add_script(pathname)
File "C:\Users\bdawg.LAPTOP-2CKTEBU7\AppData\Local\Packages\PythonSoftwareFoundation.Python.3.10_qbz5n2kfra8p0\LocalCache\local-packages\Python310\site-packages\PyInstaller\lib\modulegraph\modulegraph.py", line 1415, in add_script
with open(pathname, 'rb') as fp:
PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied: 'C:\\Users\\bdawg.LAPTOP-2CKTEBU7\\Bot Business\\Dentist Customer'
Код:
import zipfile, os
import shutil
a = os.listdir(path="D:\домашка\G_ Arhangelskiy_-_Time_Draive\G_ Arhangelskiy_-_Time_Draive")
for i in a:
s='D:\домашка\G_ Arhangelskiy_-_Time_Draive\G_ Arhangelskiy_-_Time_Draive\\'+str(i)
b = os.listdir(path=s)
for j in b:
s1 = 'D:\домашка\G_ Arhangelskiy_-_Time_Draive\G_ Arhangelskiy_-_Time_Draive\\'+i+'\\'+j
shutil.copyfile(s1, "D:\домашка\G_ Arhangelskiy_-_Time_Draive\G_ Arhangelskiy_-_Time_Draive — копия")
os.remove('D:\домашка\G_ Arhangelskiy_-_Time_Draive\G_ Arhangelskiy_-_Time_Draive\\'+i)Ошибка:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:\Users\Alex\PycharmProjects\untitled\из папок.py", line 9, in <module>
shutil.copyfile(s1, "D:\домашка\G_ Arhangelskiy_-_Time_Draive\G_ Arhangelskiy_-_Time_Draive — копия")
File "C:\Users\Alex\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python36\lib\shutil.py", line 115, in copyfile
with open(dst, 'wb') as fdst:
PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied: 'D:\\домашка\\G_ Arhangelskiy_-_Time_Draive\\G_ Arhangelskiy_-_Time_Draive — копия'Что делать?
-
Вопрос задан
-
44445 просмотров
Не сработало скорее всего из за того, что «\» это спец. символ. Используется для обозначения таких вещей как конец строки (\n), табуляция (\t). В Вашем случае, скорее всего пыталась понять что значит \д, \G и т.д. Для написания символа \ в строках используют \\.
В зависимости от версии Python может быть проблема и в кодировке пути. Т.к. есть различие русских символов в UTF8 и cp1251 которая используется обычно в Windows.
Я бы написал так:
import os
from shutil import copyfile, rmtree
SOURCE = 'D:\\домашка\\G_ Arhangelskiy_-_Time_Draive\\G_ Arhangelskiy_-_Time_Draive'
DESTINATION = 'D:\\домашка\\G_ Arhangelskiy_-_Time_Draive\\G_ Arhangelskiy_-_Time_Draive — копия'
files = [f.path for f in os.scandir(SOURCE) if f.is_file()]
for file in files:
copyfile(file, DESTINATION)
rmtree(SOURCE)Как опытный разработчик на Python могу дать совет:
- Повторяющиеся значения выделить в отдельную переменную (лучше было бы в константу, но в Python нет констант). Это по поводу пути исходника, которую я выделил в SOURCE (есть такое соглашение, когда неизменяемые переменные пишут заглавными)
- Для удаления пути рекурсивно, есть rmtree в модуле shutils, а так же os.scandir более удобен чем os.listdir
- Установите линтер (flake8) и настройте свой редактор на использование его. По коду видно, что не используете линтер
Пригласить эксперта
Войдите, чтобы написать ответ
-
Показать ещё
Загружается…