Duo integrates with Microsoft Windows client and server operating systems to add two-factor authentication to Remote Desktop and local logons and credentialed UAC elevation prompts.
Be sure to read through these instructions before you download and install Duo for Windows Logon.
Overview
Duo Authentication for Windows Logon adds Duo two-factor authentication to these Windows and Windows Server logon scenarios:
- Local or domain account logins
- Logins at the local console and/or incoming Remote Desktop (RDP) connections
- Credentialed User Access Control (UAC) elevation requests (e.g. Right-click + «Run as administrator») in v4.1.0 and later
Duo’s Windows Logon client does not add a secondary authentication prompt to the following logon types:
- Shift + right-click «Run as different user»
- PowerShell «Enter-PSSession» or «Invoke-Command» cmdlets
- Non-interactive logons (i.e. Log on as a Service, Log on as Batch, Scheduled Tasks, drive mappings, etc.)
- Pre-Logon Access Providers (PLAPs) such as Windows Always On VPN
- RDP Restricted Admin Mode
Important Notes
Please review all these compatibility and installation notes before proceeding.
- Installing Duo Authentication for Windows Logon adds two-factor authentication to all interactive user Windows login attempts, whether via a local console or over RDP, unless you select the «Only prompt for Duo authentication when logging in via RDP» option in the installer. If two-factor is enabled for both RDP and console logons, it may be bypassed by restarting Windows into Safe Mode (e.g. in case of a configuration error). If you wish to protect local console logons with Duo, please see the FAQ for some guidance on securing your Windows installation appropriately.
- Additional configuration may be required to log in using a Microsoft attached account. See Can I Use Duo with a Microsoft Account? for more information.
- Windows users must have passwords to log in to the computer. Users with blank passwords may not login after Duo Authentication installation.
- It’s a good idea to have your BitLocker recovery key available in the event you need to boot into safe mode to uninstall Duo.
- This application doesn’t support Surface Pro X or other devices with ARM processors. Installing Duo for Windows Logon on these devices may block logins, requiring uninstallation from Safe Mode.
- Review these Duo Knowledge Base articles for additional security recommendations:
- How can I prevent an attacker with compromised administrative credentials from disabling Duo for Windows Logon and bypassing MFA?
- Guide to Duo Authentication for Windows Logon and RDP Integration Security
- Can Duo protect local console logins in Windows?
- Duo application features like failmode, offline access, and UAC protection may be configured during installation or post-installation via Regedit or Group Policy. Please see our FAQ for more information.
Connectivity Requirements
This application communicates with Duo’s service on SSL TCP port 443.
Firewall configurations that restrict outbound access to Duo’s service with rules using destination IP addresses or IP address ranges aren’t recommended, since these may change over time to maintain our service’s high availability. If your organization requires IP-based rules, please review Duo Knowledge Base article 1337.
Effective June 30, 2023, Duo no longer supports TLS 1.0 or 1.1 connections or insecure TLS/SSL cipher suites. See Duo Knowledge Base article 7546 for additional guidance.
TLS Requirements
Effective June 30, 2023, Duo no longer supports TLS 1.0 or 1.1 connections or insecure TLS/SSL cipher suites.
The current version of Duo for Windows Authentication supports TLS 1.2 when installed on a version of Windows that also supports and uses TLS 1.2 or higher.
See the article Guide to TLS support for Duo applications and TLS 1.0 and 1.1 end of support for more information.
System Requirements
Windows Versions
Duo Authentication for Windows Logon supports both client and server operating systems.
Clients:
- Windows 10 (as of v1.1.8)
- Windows 11 (as of v4.2.0)
Servers (GUI installs only as of v4.0.0):
- Windows Server 2016 (as of v2.1.0)
- Windows Server 2019 (as of v4.0.0)
- Windows Server 2022 (as of v4.2.0)
- Windows Server 2025 (as of v5.0.0)
Ensure your system’s time is correct before installing Duo.
System Processor
Duo Authentication for Windows Logon does not support devices with ARM processors, like the Surface Pro X.
Visual C++ Redistributable
Duo Authentication for Windows Logon 4.3.16 and later depend on the Microsoft Visual C++ Redistributable. The Duo EXE installer (i.e. duo-win-login-5.0.0.exe) will also install the Visual C++ Redistributable package on your system if a compatible version is not already present.
Duo Factor Support
Duo for Windows Logon supports these factor types for online two-factor authentication:
- Duo Push (Duo Mobile)
- Duo Verified Push (as of v4.3.16)
- Duo Mobile Passcodes
- SMS Passcodes
- Hardware Token OTP passcodes (including Yubikey OTP)
- Phone Call
- Bypass Codes
U2F security key support is limited to Offline Access only.
Enroll Users Before Installation
Duo Authentication for Windows Logon doesn’t support inline self-service enrollment for new Duo users. Unenrolled users, that is, users that do not yet exist in Duo with an attached 2FA device, must be created manually by an administrator, imported by an administrator or self-enrolled through another application which supports Duo’s self-service enrollment (see Test Your Setup) before those users can log in with Duo for Windows Logon.
The Duo username (or username alias) should match the Windows username. When you create your new RDP application in Duo the username normalization setting defaults to «Simple», which means that the if the application sends the usernames «jsmith,» «DOMAIN\jsmith,» and «jsmith@domain.com» to Duo at login these would all resolve to a single «jsmith» Duo user.
Duo for Windows Logon supports Duo Push, phone callback or SMS passcodes, and passcodes generated by Duo Mobile or a hardware token as authentication methods. Duo users must have one of these methods available to complete 2FA authentication.
If the user logging in to Windows after Duo is installed does not exist in Duo, the user may not be able to log in to the system.
Read the enrollment documentation to learn more about enrolling your users in Duo.
See the Deployment Tip below to learn how you can use the New User Policy to deploy Duo for Windows Logon without enrolling your users first or requiring Duo authentication immediately after installation.
First Steps
Before moving on to the deployment steps, it’s a good idea to familiarize yourself with Duo administration concepts and features like options for applications, available methods for enrolling Duo users, and Duo policy settings and how to apply them. See all Duo Administrator documentation.
-
Sign up for a Duo account.
-
Log in to the Duo Admin Panel and navigate to Applications → Protect an Application.
-
Locate the entry for Microsoft RDP with a protection type of «2FA» in the applications list. Click Protect to the far-right to configure the application and get your integration key, secret key, and API hostname. You’ll need this information to complete your setup. See Protecting Applications for more information about protecting applications with Duo and additional application options.
-
No users can log in to new applications until you grant access. Update the User access setting to grant access to this application to users in selected Duo groups, or to all users. Learn more about user access to applications. If you do not change this setting now, be sure to update it so that your test user has access before you test your setup.
-
We recommend setting the New User Policy for your Microsoft RDP application to Deny Access, because no unenrolled user may complete Duo enrollment via this application.
-
If you’d like to enable Passwordless Operating System (OS) logon to Windows you can do that now in the «Passwordless Settings» section of the Duo application page, or return to the Admin Panel later to configure Passwordless OS Login after first verifying logon success with username, password, and two-factor authentication.
-
If you’d like to enable offline access with Duo MFA you can do that now in the «Offline Access Settings» section of the Duo application page, or return to the Admin Panel later to configure offline access after first verifying logon success with two-factor authentication.
-
Download the Duo Authentication for Windows Logon installer package. View checksums for Duo downloads here.
Treat your secret key like a password
The security of your Duo application is tied to the security of your secret key (skey). Secure it as you would any sensitive credential. Don’t share it with unauthorized individuals or email it to anyone under any circumstances!
Verified Duo Push for Windows Logon
Available in: Duo Essentials, Duo Advantage, and Duo Premier
Duo Authentication for Windows Logon version 4.3.16 and later supports Verified Duo Push with a numeric code. As 4.3.16 was a public preview Duo release, we recommend updating systems to version 5.0.0 or later. In addition, Verified Duo Push requires Duo Mobile 4.16.0 or later on Android 8+ or Duo Mobile 4.17.0 or later on iOS 16+, activated for Duo Push.
Applying an Authentication Methods policy enabling Verified Duo Push with a verification code to a Microsoft RDP Duo application will require users to enter the verification code during Windows logon into the Duo Mobile app when performing a Duo Push to authenticate.
To enable Verified Duo Push for Windows Logon:
-
Create a new custom policy or update an existing policy which enables both the Require Verified Duo Push and Require users to enter a verification code options in the Authentication Methods policy settings. Click Save Policy when done.
-
Apply the custom policy to your Microsoft RDP Duo application as a group or application policy. If you made the change in your global policy then the setting applies to all your Microsoft RDP Duo applications.
The policy setting takes immediate effect — there is no need to reinstall Duo Authentication for Windows Logon as long as clients have already installed v4.3.16 or later. Systems with older versions of Duo for Windows Logon will continue offering the standard Duo Push experience and must upgrade to a supported release. to use Verified Duo Push.
With this policy setting applied, users must enter the verification code shown on the Duo for Windows Logon prompt into the Duo Mobile authentication request.
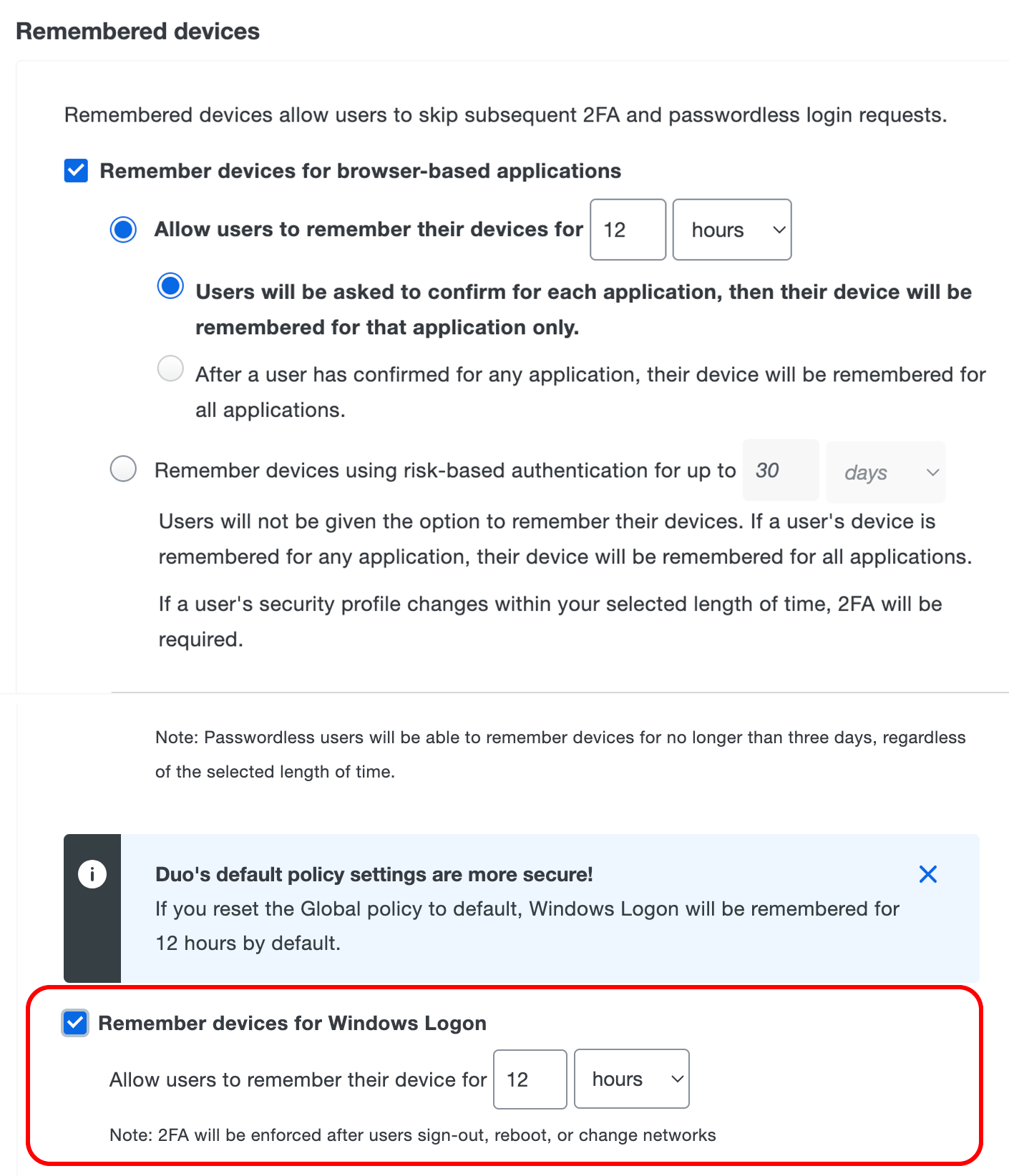
Remembered Devices for Windows Logon
Available in: Duo Essentials, Duo Advantage, and Duo Premier
Version 4.2.0 of Duo Authentication for Windows Logon adds support for local trusted sessions, reducing how often users must repeat Duo two-factor authentication. The Remembered Devices policy now includes a setting for Windows logon sessions, which when enabled offers users a «Remember me» checkbox during local console login for the duration specified in the policy.
When users check this box and complete Duo authentication, they aren’t prompted for Duo secondary authentication when they unlock the workstation after that initial authentication until the configured trusted session time expires. If the user changes networks, authenticates with offline access while the workstation is disconnected, logs out of Windows, reboots the workstation, or clicks the «Cancel» button during workstation unlock, Duo for Windows Logon invalidates the current trusted session and the next Windows logon or unlock attempt will require Duo authentication again.
To enable remembered devices for Windows Logon:
-
Create a new custom policy or update an existing policy for remembered devices which enables the Remember devices for Windows Logon option, and enter the number of hours or days you want a trusted Windows logon session to last. Click Save Policy when done.
-
Apply the custom policy to your Microsoft RDP Duo application as a group or application policy. If you made the change in your global policy then the setting applies to all your Microsoft RDP Duo applications, unless any of them have a policy assigned with conflicting remembered Windows Logon device settings.
The policy setting takes immediate effect — there is no need to reinstall the Duo Authentication for Windows Logon application after updating the remembered device policy as long as clients have already installed v4.2.0 or later. Systems with older versions of Duo for Windows Logon must upgrade to 4.2.0 or later to see the new option.
With this policy setting applied, users who log on to the local Windows console see an additional option on the Duo for Windows Logon prompt for remembering the device. This option will not display for RDP/remote logins to Windows systems with Duo Authentication for Windows Logon installed, regardless of the effective remembered devices policy setting for Windows Logon.
Administrators may revoke the Windows local trusted Duo session by unassigning a remembered devices policy for Windows Logon from a Microsoft RDP application, editing the policy attached to a Microsoft RDP application to disable the Windows Logon remembered devices setting, or by deleting the registry entry for the user session from the Windows client. Learn more about this in the Windows Logon FAQ.
Deployment Tip
To test Duo on your Windows system with a group of pilot users, we suggest setting your application’s New User Policy to «Allow Access» while testing. The pilot users that you’ve enrolled in Duo with an associated 2FA device get prompted to complete Duo authentication, while all other users will be transparently let through.
If you want to deploy Duo to your Windows systems but have no users complete 2FA until a specific date (after all user enrollment is complete), set the New User Policy to «Allow Access» and set the Authentication Policy to «Bypass 2FA». With these two policy settings in place users who have and who have not enrolled in Duo log in to the Windows system as usual without experiencing Duo.
If you chose to enable offline access on your application, then enrolled users who bypass 2FA due to the effective Authentication Policy would still be prompted to complete offline enrollment. To avoid confusion, we recommend leaving offline access off until you require users to complete Duo 2FA while online.
When you’re ready to require Duo authentication for all users of the target Windows system, change the «New User Policy» to «Deny access» and change the «Authentication Policy» to «Enforce 2FA». This will prompt all enrolled users to perform Duo 2FA after they type in their usernames and passwords, and prevent users who have not enrolled in Duo from logging in without 2FA.
Run the Installer
Installing Duo may require a reboot. Schedule your Duo installation during a maintenance window if unplanned system restarts is a concern.
-
Run the Duo Authentication for Windows Logon installer with administrative privileges.
If you receive an «Installation stopped» error from the Duo installer please refer to Duo KB article 6462 for remediation steps.
-
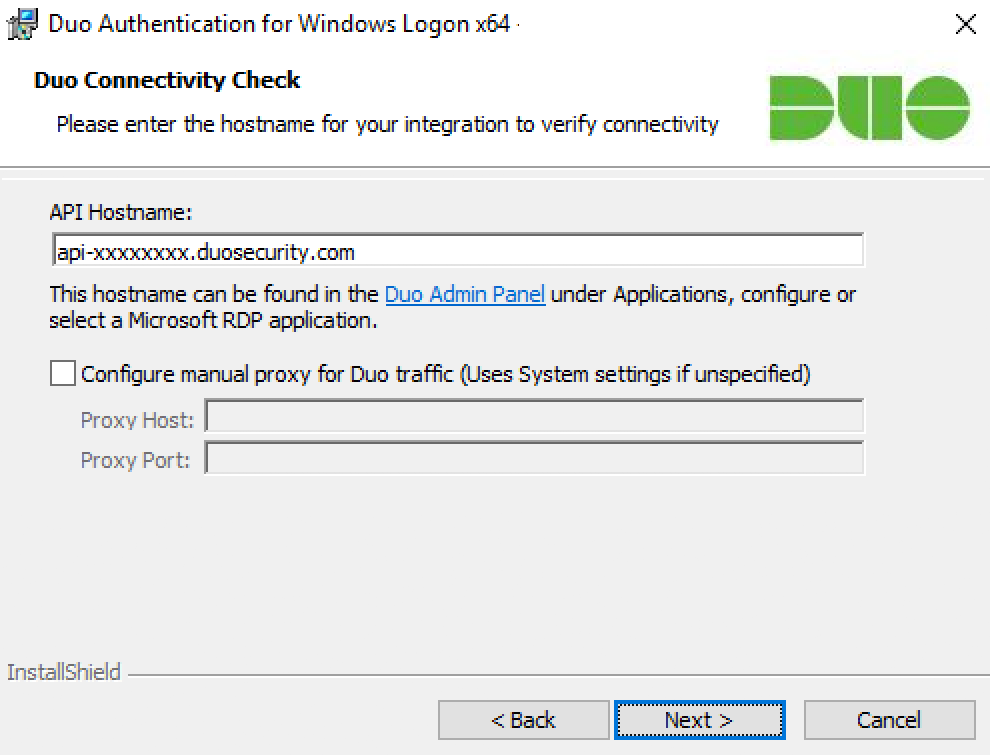
When prompted, enter your API Hostname from the Microsoft RDP application’s details page in the Duo Admin Panel and click Next. The installer verifies that your Windows system has connectivity to the Duo service before proceeding.
If the connectivity check fails, ensure that your Windows system is able to communicate with your Duo API hostname over HTTPS (port 443).
If you need to use an outbound HTTP proxy in order to contact Duo Security’s service, enable the Configure manual proxy for Duo traffic option and specify the proxy server’s hostname or IP address and port here.
-
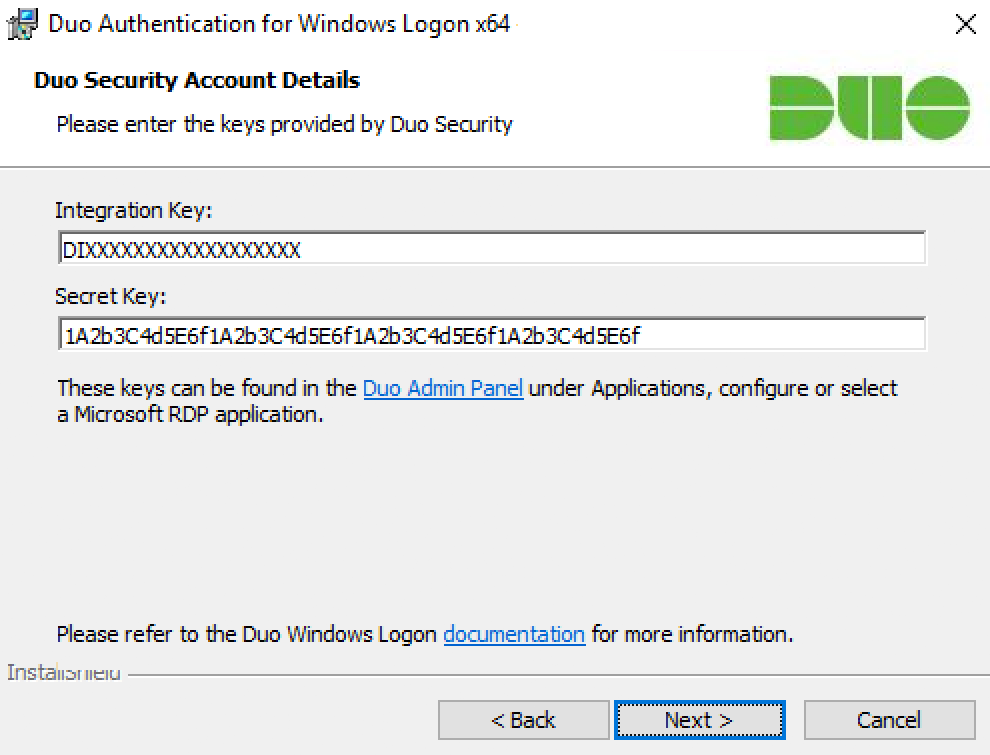
Enter your integration key and secret key from the Microsoft RDP application in the Duo Admin Panel and click Next again.
-
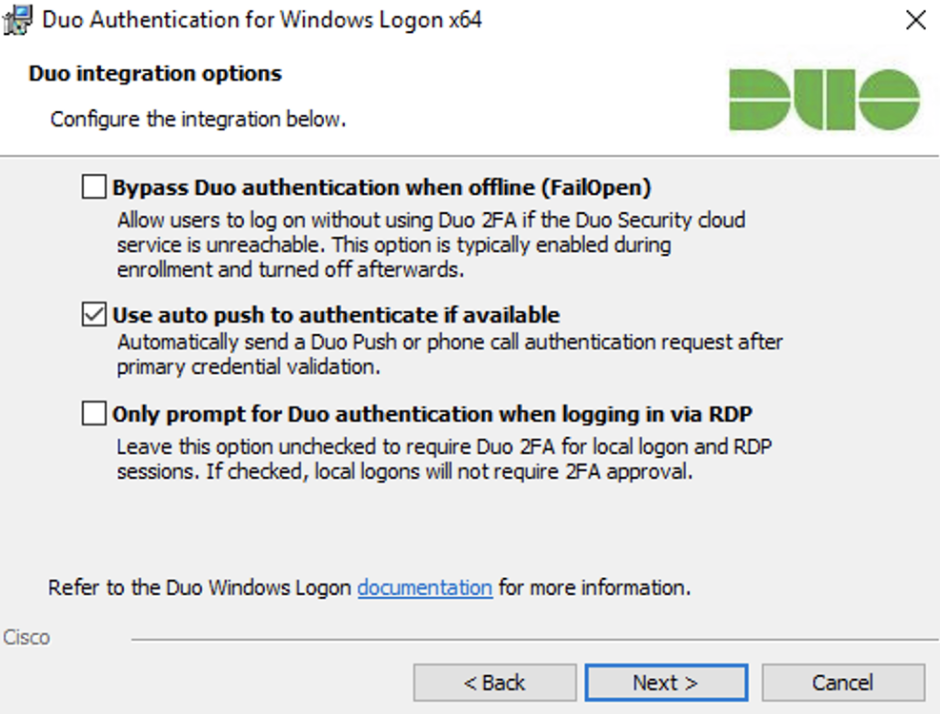
Select your integration options:
Setting Description Bypass Duo authentication when offline (FailOpen) Enable this option to allow user logon without completing two-factor authentication if the Duo Security cloud service is unreachable. If you plan to enable offline access with MFA consider disabling FailOpen.
Windows Logon 4.2.2 and earlier installers enable this setting by default. Windows Logon 4.3.0 installers default to fail closed. The
msiinstaller will preserve the selection made by a previously installed version on upgrade. Upgrades from previous versions using theexeinstaller will override the previous fail mode selection and default to fail closed.Use auto push to authenticate if available Automatically send a Duo Push or phone call authentication request after primary credential validation to the first capable device attached to the user. Checked by default and applies to all users of the target system. Only prompt for Duo authentication when logging in via RDP Leave this option unchecked to require Duo two-factor authentication for console and RDP sessions. If enabled, console logons do not require 2FA approval. If you want to enforce protected offline access to laptop logins, be sure you don’t check this box. If you do, laptop console logins won’t require any form of Duo MFA. -
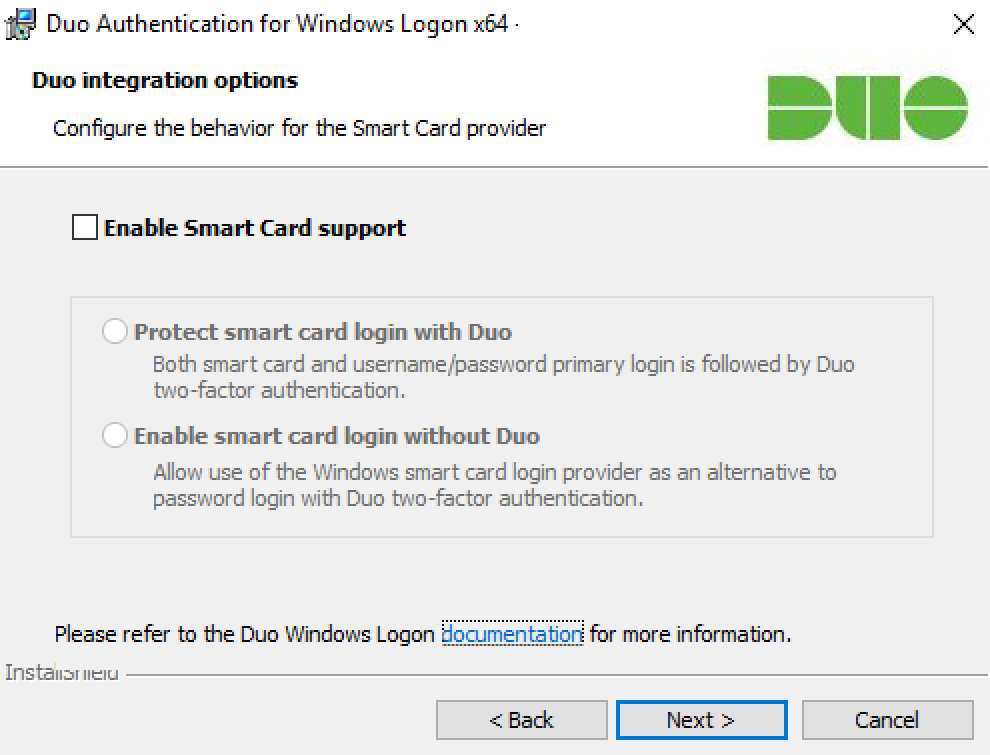
If you plan to use smart cards on the systems where you install Duo, click to Enable Smart Card Support and select your smart card options:
Setting Description Protect smart card login with Duo Select this option to require Duo authentication after primary login with username and password or primary authentication with a smart card. Supported for local console logins. Enable smart card login without Duo Select this option to permit use of the Windows smart card login provider as an alternative to Duo authentication. Smart card logins won’t require 2FA. These options only support the Windows native smart card provider. Available in version 3.1.1 and later.
-
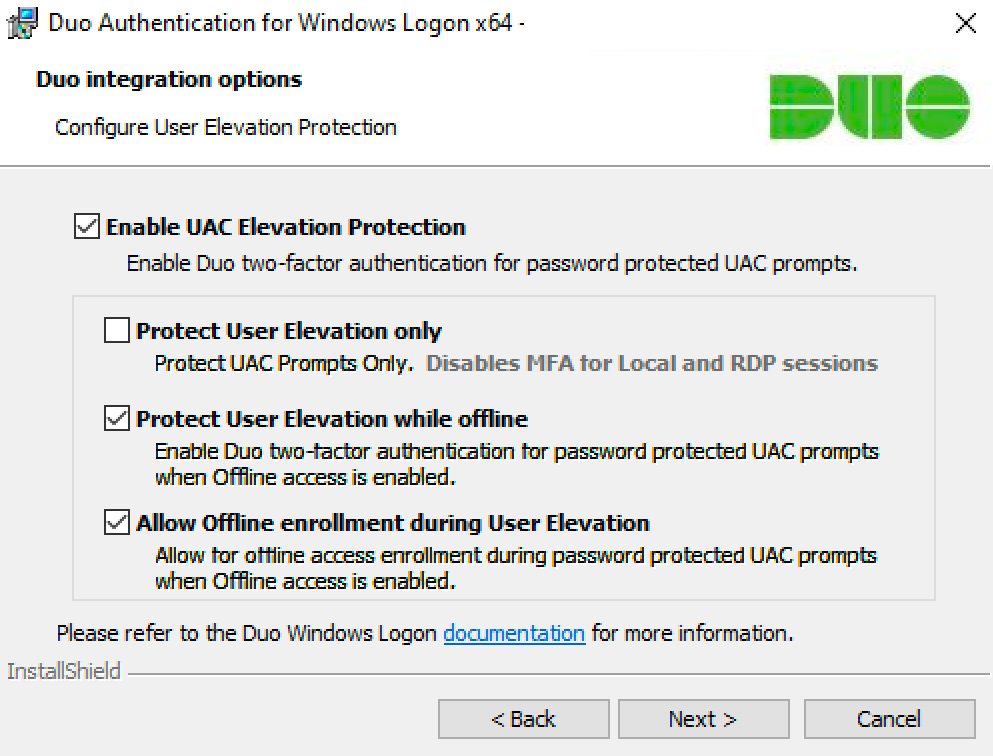
If you’d like to add Duo 2FA protection to account elevation via Windows User Account Control (UAC), click to Enable UAC Elevation Protection and select your elevation options:
Setting Description Protect User Elevation only Enable Duo two-factor authentication at password-protected UAC prompts only. If you check this box Duo will not prompt for 2FA at local or RDP login or workstation unlock. Protect User Elevation while offline Permit offline access authentication for password-protected UAC prompts if offline access is also enabled. Allow offline enrollment during User Elevation Allow and prompt for offline access enrollment during UAC password elevation if offline access is also enabled. Available in version 4.1.0 and later.
-
Click Next and then Install to complete Duo installation.
If you need to change any of your chosen options after installation, you can do so by updating the registry. See the Duo for Windows Logon FAQ for instructions on how to update the settings.
Test Your Setup
To test your setup, attempt to log in to your newly-configured system as a user enrolled in Duo.

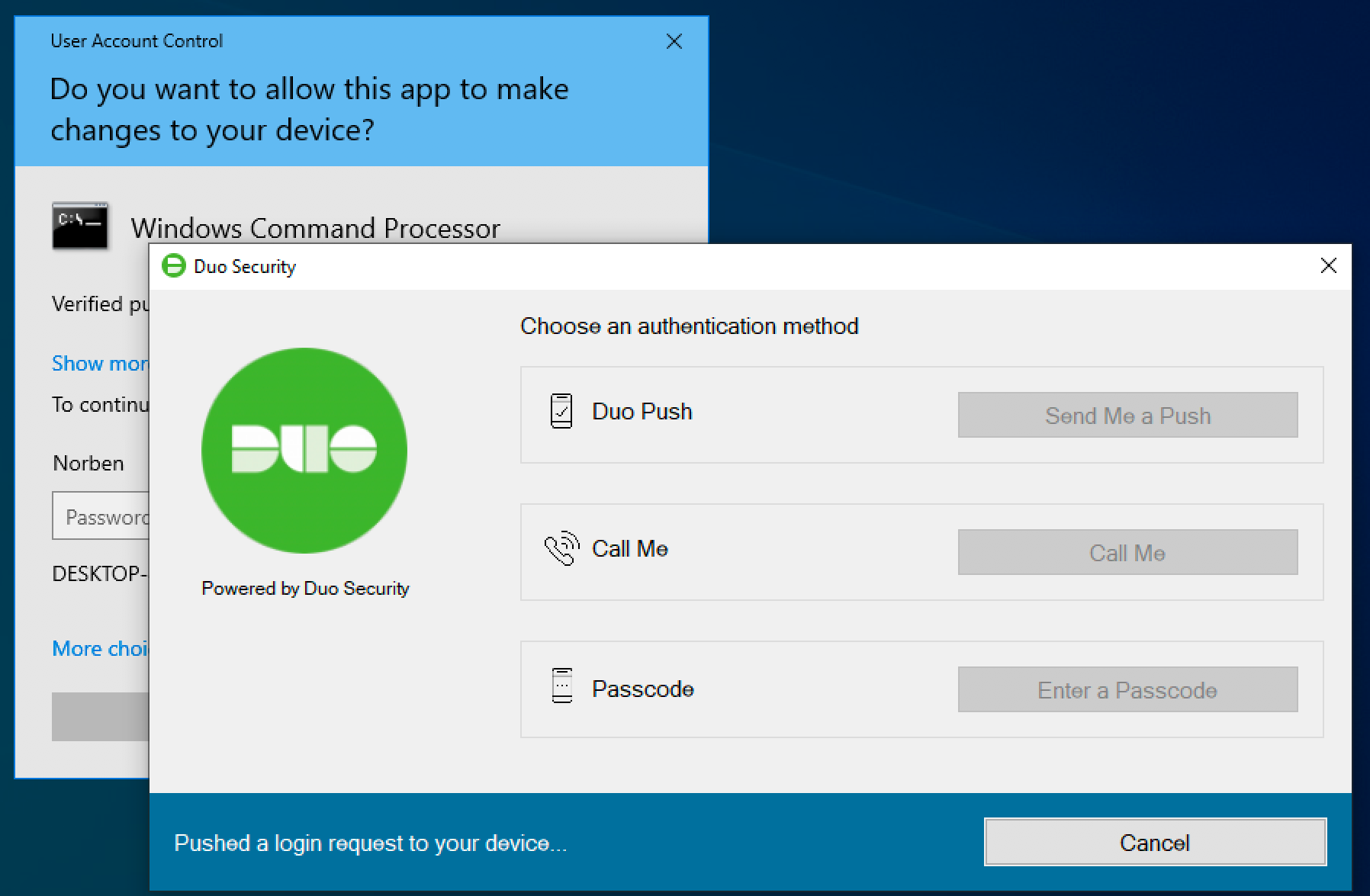
The Duo authentication prompt appears after you successfully submit your Windows credentials. With automatic push enabled (the default installation option), the prompt indicates that Duo pushed an approval request to your phone. Duo sends the push request to the first phone activated for Duo Push and associated with that Duo user.
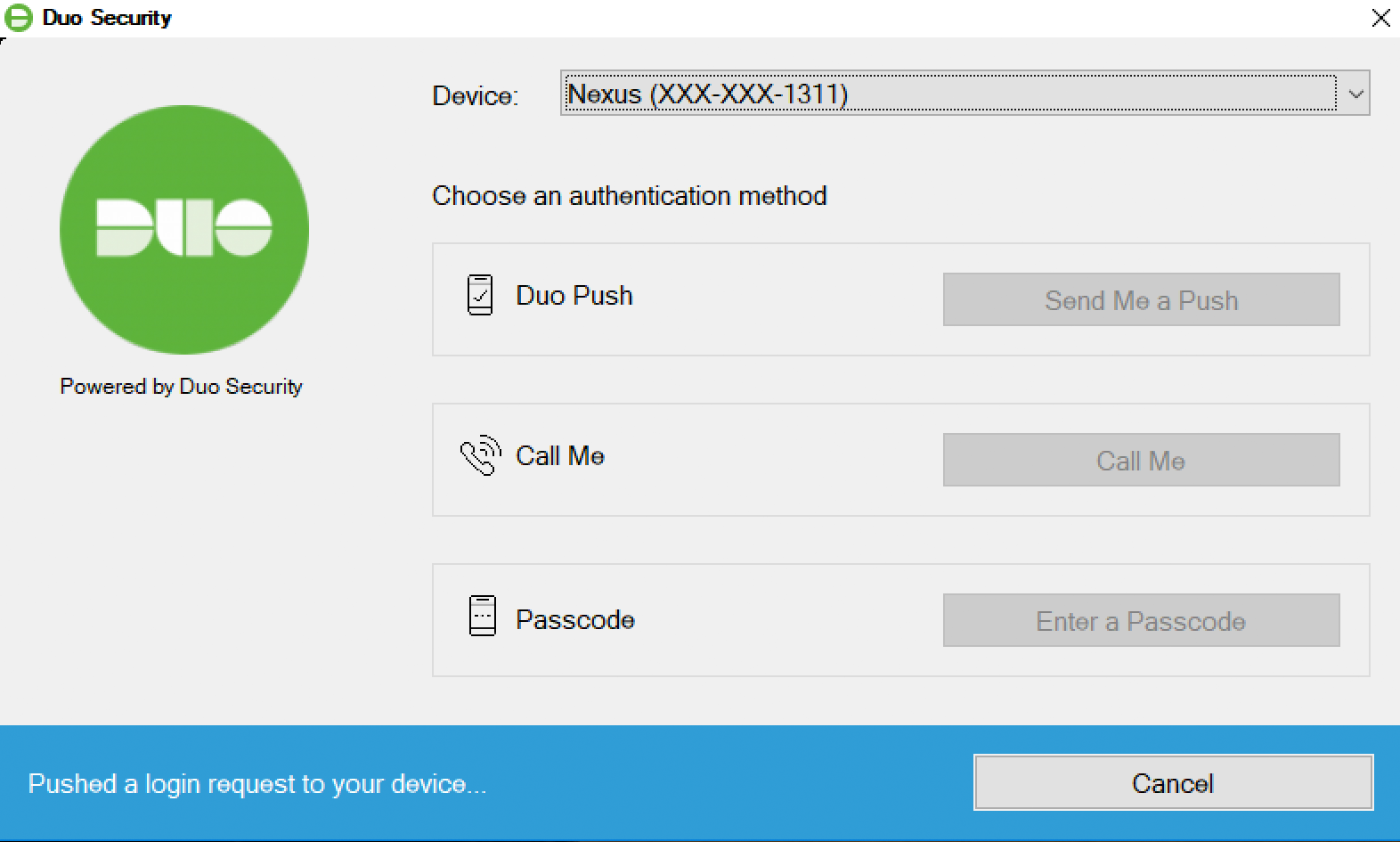
With automatic push disabled, or if you click the Cancel button on the Duo authentication prompt after a 2FA request was sent, you can select a different device from the drop-down at the top (if you’ve enrolled more than one) or select any available factor to verify your identity to Duo:
- Duo Push: Send a request to your smartphone. You can use Duo Push or Verified Duo Push if you’ve installed and activated Duo Mobile on your device.
- Call Me: Perform phone callback authentication.
- Passcode: Log in using a passcode generated with Duo Mobile, received via SMS, generated by your hardware token, or provided by an administrator. To have a new batch of SMS passcodes sent to you click the Send me new codes button. You can then authenticate with one of the newly-delivered passcodes.
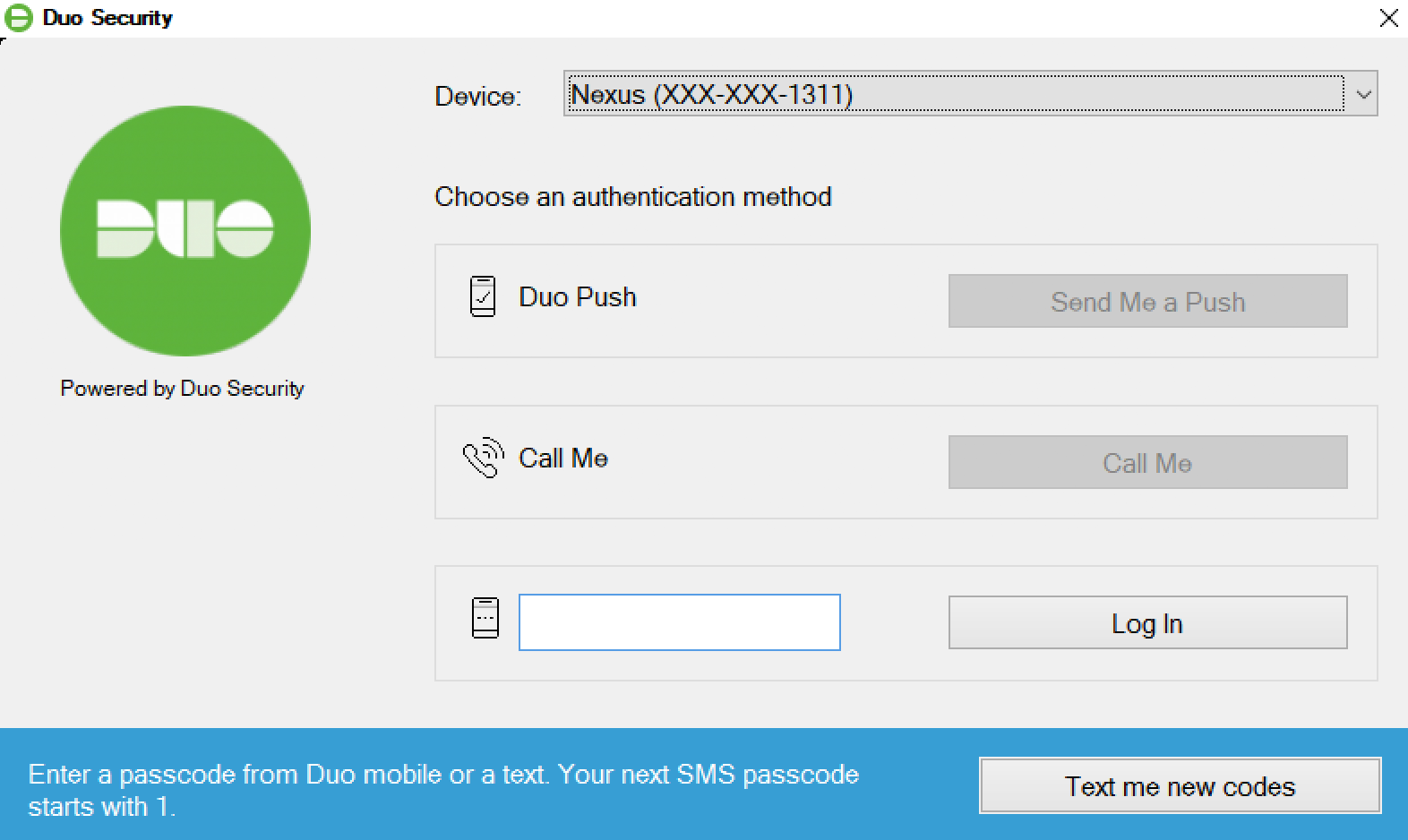
Verified Duo Push
If you applied a policy to your Microsoft RDP application that enables Verified Duo Push with a verification code for Windows Logon, Windows will display a three to six numeric code on-screen when you choose to use Duo Push to log in to that application. Users will need to enter this code into Duo Mobile to approve the login request.
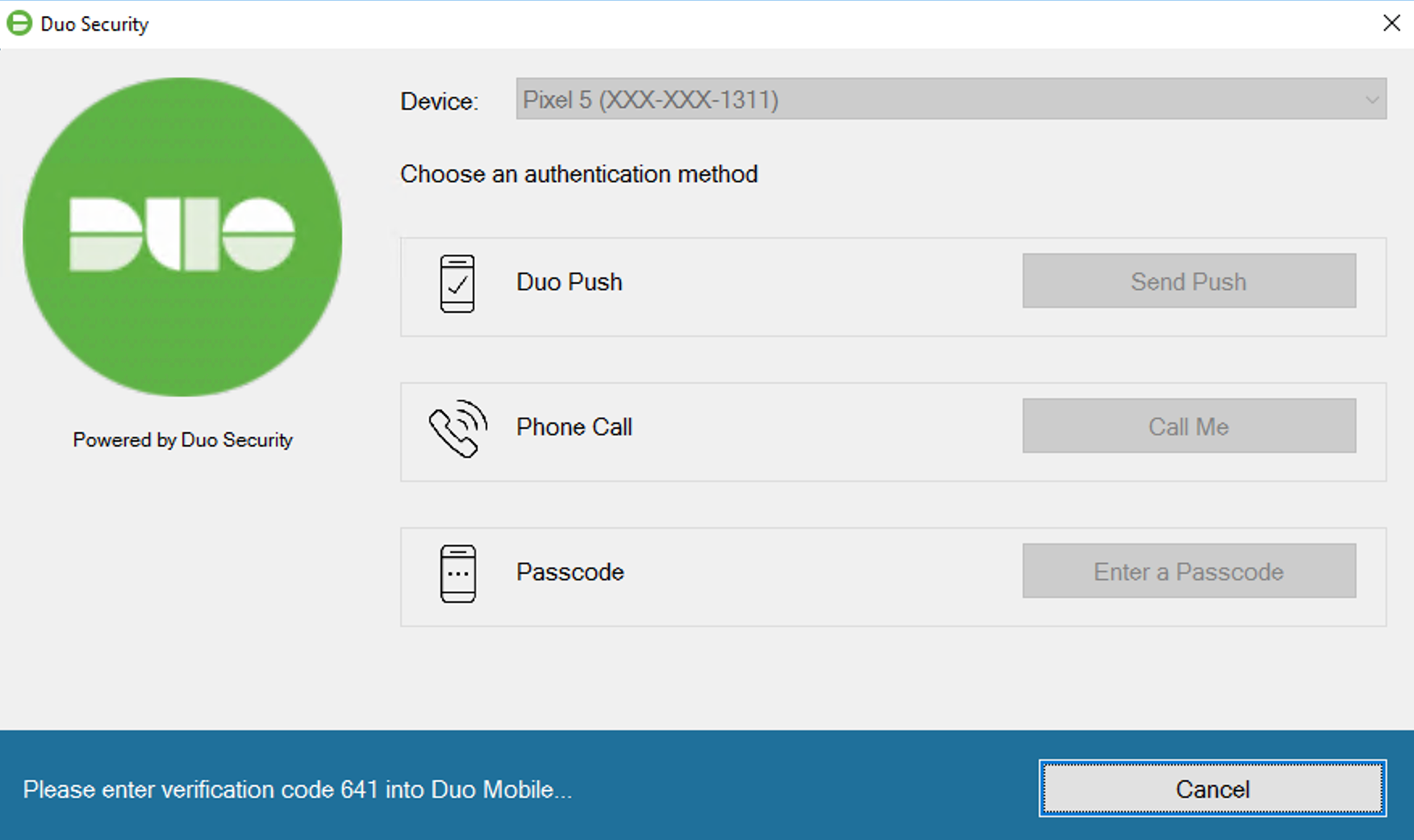
Remembered Device
If you applied a policy to your Microsoft RDP application that enables remembered devices for Windows Logon, then during Duo authentication at the local system’s console you’ll see the Remember me for… option, reflecting the number of hours or days you set in the policy.
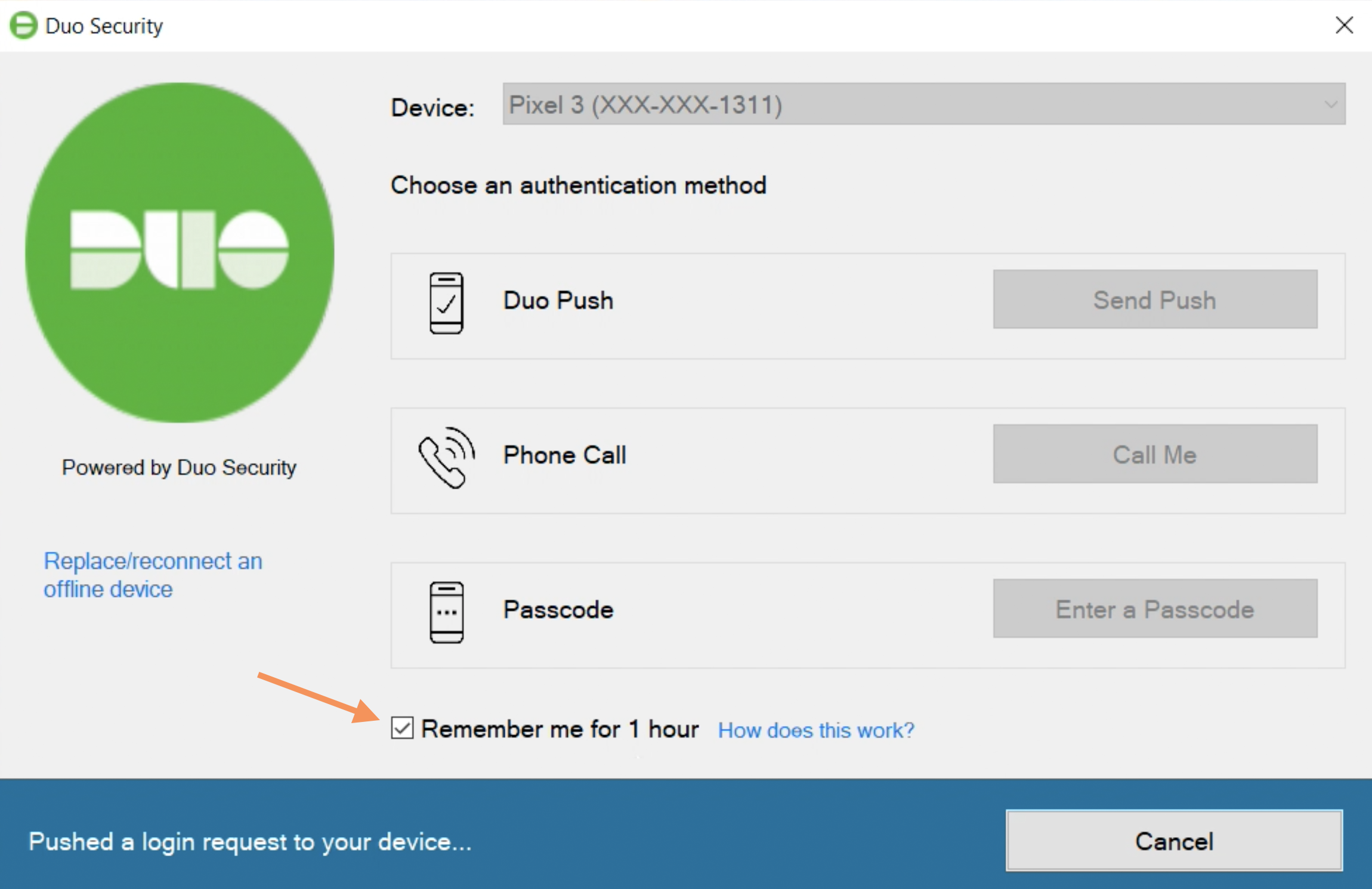
If you check this box when authenticating you won’t need to perform Duo second-factor authentication again for the duration specified on the prompt the next time you unlock the workstation to continue the logged-in Windows session.
Duo will prompt you to complete two-factor authentication at the next Windows logon or unlock after the remembered device session ends, and at that time you can choose to begin a new trusted logon session.
UAC Elevation
If you enabled User Elevation in Duo for Windows Logon v4.1.0 or later, you’ll see the Duo authentication prompt after you enter your password for a credentialed elevation request. The application you were trying to launch runs after you approve the Duo two-factor request. If you chose to remember the device at the Windows desktop login, then you won’t need to approve Duo authentication for UAC elevations made by the same logged-in account either until the trusted Duo session ends.
Remember: if you find that Duo Authentication for Windows Logon has locked you out of your Windows system (e.g. due to a configuration error), you can reboot into Safe Mode to bypass it.
See the Duo Knowledge Base article Why are users unexpectedly bypassing 2FA for Windows Logon (RDP)? for additional remediation steps.
Grant Access to Users
If you did not already grant user access to the Duo users you want to use this application be sure to do that before inviting or requiring them to log in with Duo.
Passwordless for Operating System (OS) Logon
Available in: Duo Essentials, Duo Advantage, and Duo Premier
Passwordless for Operating System Logon offers the option to logon without the manual requirement for users to provide a password at OS logon. With Passwordless OS Logon, the password is escrowed to Duo Mobile for secure storage (i.e., there is an arrangement in which the keys (private and public) are needed to decrypt encrypted data). This not only eases users’ entry to the OS, it also makes it more difficult for a bad actor to hijack an endpoint machine and then use a stolen password to escalate privileges. Subsequently, Passwordless OS Logon automatically invokes a Bluetooth push for users to authenticate with their biometrics or PIN via Duo Mobile to establish their session.
Passwordless for OS Logon Requirements
- Duo Essentials, Advantage, or Premier plan subscription
- Windows 10 21H2 or later or Windows 11.
- Trusted Platform Module (TPM) v2.0 enabled on the Windows device.
- Duo Authentication for Windows Logon 5.0.0 or later installed.
- Bluetooth v4.0 and later enabled on both the Windows and mobile devices.
- Duo Mobile installed and activated for Duo Push.
- Android 12+ and Duo Mobile version 4.64.0 or later.
- iOS 16+ and Duo Mobile version 4.62.0 or later.
- Duo Push enabled as an authentication method in the effective policy for users of the application.
Note: this solution does not support Remote Desktop connections or virtual machines.
- Supported Bluetooth adapters tested by Duo (only required for computers that don’t have Bluetooth built-in):
- Avantree DG45 Bluetooth USB adapter
- Ugreen CM656 Bluetooth adapter
- TP Link UP500
Other Bluetooth adapter models not tested by Duo may work. We strongly suggest you test Passwordless for OS Logon with one of the Bluetooth adapters you plan to use before purchasing them for all your users.
Test with Pilot Users
You have two options for testing Passwordless OS Logon with groups of pilot users before expanding it to all users of a given Duo Microsoft RDP application:
-
Create a new Microsoft RDP application in Duo with the Passwordless logon setting enabled for all users in the new application, and then use the integration key and secret key from the new application when you install the 5.0.0 Duo Authentication for Windows Logon release on the Windows systems belonging to your test users.
- After your successful pilot testing update the Duo installations on additional system to use the new Duo Microsoft RDP application, or update the configuration of existing Microsoft RDP applications to also allow Passwordless OS Logon.
-
Identify Duo groups containing your pilot users and then when you enable Passwordless for OS Logon in your existing Microsoft RDP application select those Duo pilot groups in the Limit access by groups option.
- After your successful pilot testing remove the pilot groups from the configuration to apply to all users, or add additional user groups to expand to selected users.
Passwordless for OS Logon Configuration
-
Return to your Microsoft RDP application page in the Duo Admin Panel. You may have given the RDP application a different name when you created it, but the «Type» will always be shown as «Microsoft RDP» in your applications list.
-
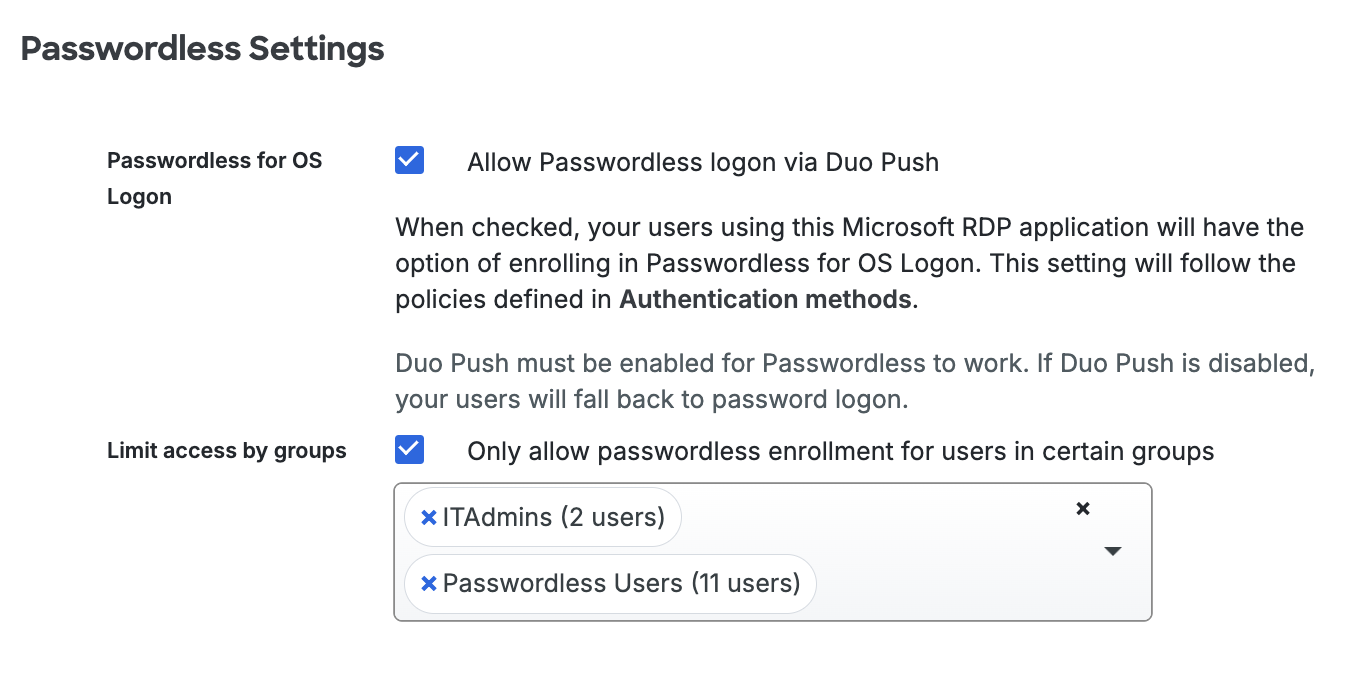
Scroll down to the bottom of the RDP application’s page to locate the Passwordless Settings. Check the box next to Allow Passwordless logon via Duo Push to enable passwordless for OS Logon.
When checked, users of this Microsoft RDP application will have the option of enrolling in Passwordless for OS Logon during local console logins. For this setting to work, Duo Push must also be enabled in your Duo policies as an allowed authentication method. Or if the user doesn’t have a device activated for Duo Push, users will fall back to password logon.
-
Check the Limit access by groups option to specify a group or groups of Duo users permitted to enroll in and use Passwordless OS Logon. Users who are not members of the groups you select here will continue using a password to log in to Windows.
-
Click the Save button.
Passwordless Logging
You will be able to see users that have access granted or denied, as well as Passwordless OS enrollment and Passwordless OS Logon as newly listed authentication methods in the Authentication logs.
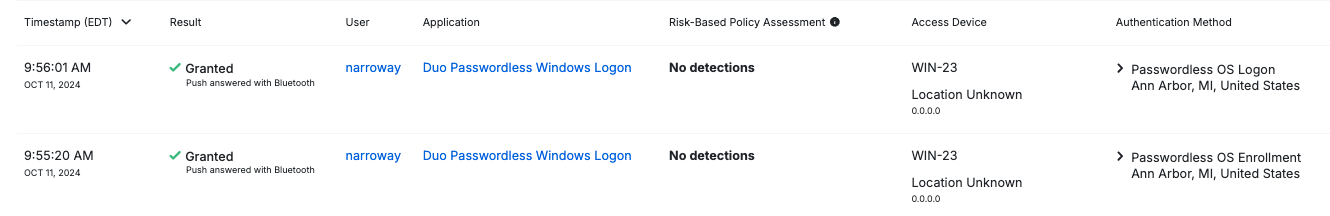
Passwordless OS Logon Enrollment and Login
The next time a user logs in to or unlocks the workstation while it’s online and able to contact Duo, the passwordless enrollment prompt displays after successful two-factor authentication.
Step through the guided enrollment process to setup passwordless authentication on that Windows system.
Once you’ve enrolled in Passwordless OS Logon, you will no longer need to enter a password to logon to that Windows system. If you log in to multiple Windows systems you’ll need to repeat the setup steps on each one to log in without a password.
Duo Mobile cannot restore Passwordless OS Logon accounts on a new mobile device. If you log on with a different mobile device, you’ll need to repeat the setup steps to log on to the same or different Windows system without a password.
See the full Passwordless OS Logon enrollment and authentication experience in the Duo User Guide for Windows Logon.
If users have issues with Passwordless OS Logon setup or use please see Duo Knowledge Base article 9088 for troubleshooting guidance.
Offline Access
Duo Authentication for Windows Logon v4.0.0 introduces offline access, allowing secure local logons to Windows systems even when unable to contact Duo’s cloud service.
Offline Access Requirements
- Duo Essentials, Advantage, or Premier plan subscription
- Duo Authentication for Windows Logon version 4.0.0 or later
- Disable the Bypass Duo authentication when offline (FailOpen) option. If you enabled FailOpen during installation, you can change it in the registry.
- Disable the Only prompt for Duo authentication when logging in via RDP option to use offline access with laptop or desktop local console logins. If you enabled Duo for RDP logins only during installation, you can change it in the registry.
Users must have either:
- Duo Mobile for Android or iOS version 3.22 or later (no Windows Phone support)
- One of the following supported U2F security key — ensure the key you plan to use does not require extended length encoding:
- Yubico brand keys supporting U2F/FIDO2 (Vendor ID 1050)
- Feitian ePass FIDO (Vendor ID 096E)
- Thetis FIDO (Vendor ID 1EA8)
We strongly suggest you test offline access with one of the security keys you plan to use before purchasing them for all your users.
HyperFIDO tokens are not supported for offline access activation, nor are simple OTP passcode tokens or Duo D-100 hardware tokens.
Note these functional limitations for offline access authentication devices:
- Users may only register one authenticator for offline access, so it is not possible to register backup devices for approving offline login. Registering a second offline device deactivates the first one.
- U2F security keys for offline authentication only work for local system console logins. It is not possible to use a security key attached to your local RDP client system to perform offline authentication at a remote Windows server. You can use a Duo Mobile offline passcode with a remote system.
- Remembered devices policy settings and local trusted sessions do not apply to offline access. If you choose to remember the device when you log in while online, and then unlock the Windows workstation while offline, the previously created trusted session ends and you will need to complete offline access authentication. When the workstation is back online, you will need to complete online Duo authentication to begin a new remembered device session.
Offline Access Configuration
-
Return to your «Microsoft RDP» application page in the Duo Admin Panel. You may have given the RDP application a different name when you created it, but the «Application Type» will always be shown as «Microsoft RDP» on the Applications page.
-
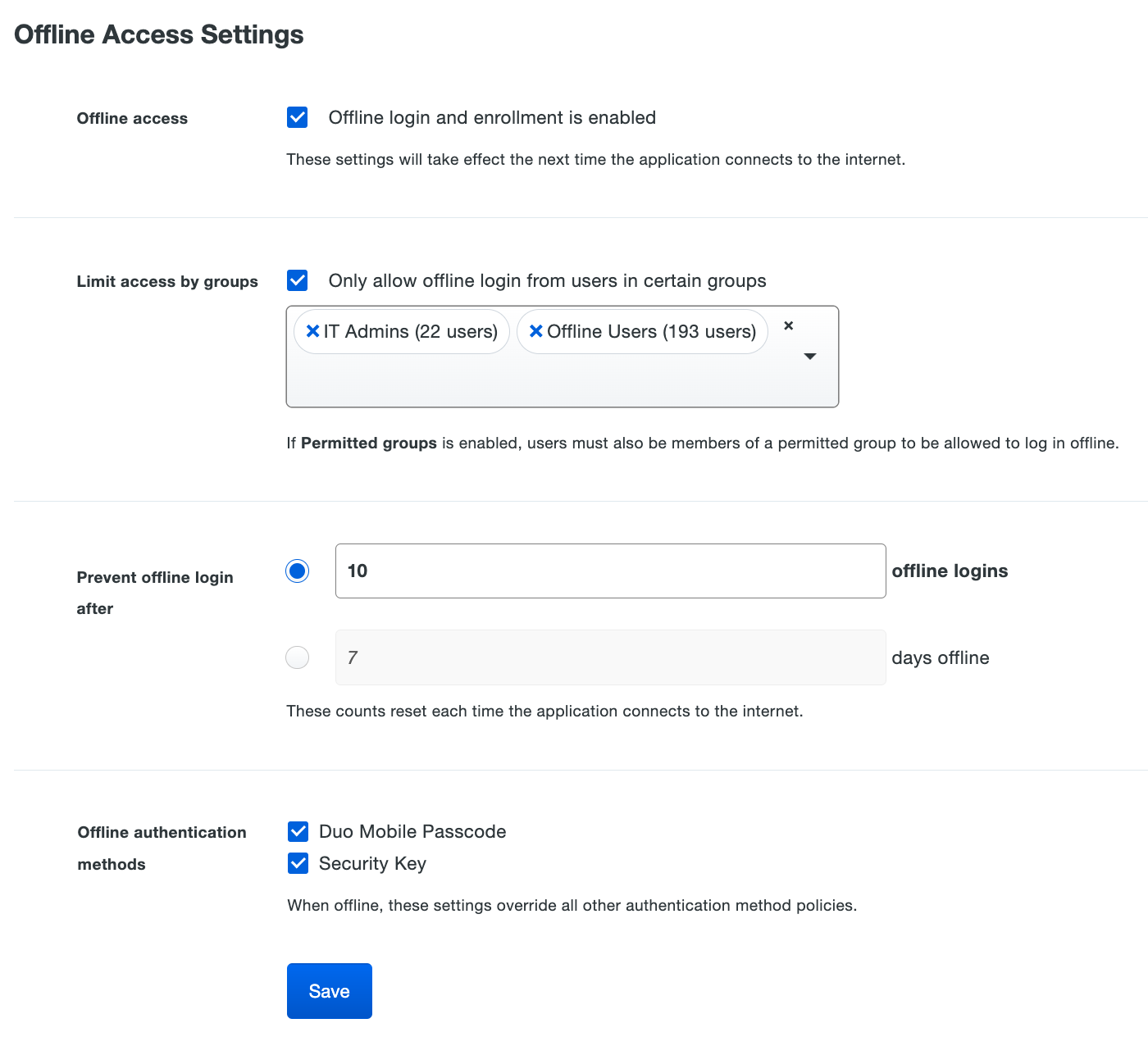
Scroll down to the bottom of the RDP application’s page to locate the Offline Access Settings. Check the box next to Enable offline login and enrollment to turn on offline access.
-
Check the Only allow offline login from users in certain groups to specify a group or groups of Duo users permitted to use offline access. Users who are not members of the groups you select here won’t be able to enroll in offline access or login in with MFA when the Windows system is unable to contact Duo, and instead are subject to your fail mode configuration (let in without MFA if you enabled fail open, or prevented from logging in if you disabled fail open).
After you configure this option, when a user logs into a Windows system while it’s online and can reach Duo and it has been greater than 24-30 hours since the last online authentication, Duo for Windows Logon will update the offline policies for all users on the system, including deprovisioning them for offline access if they are no longer members of the offline groups selected for offline login in the Duo Admin Panel.
If you also restricted user access to select permitted groups on your RDP application, users need to be members of both the permitted and the offline login groups to use offline access.
-
Choose from the two options for expiring offline access in the Prevent offline login after setting:
-
Enter the maximum number of offline logins allowed to users. With this option, there is no expiration date for offline access.
Users may log on to the Duo-protected Windows workstation while offline the number of times you specify here. They’ll need to reconnect their offline computer to the internet upon reaching this limit. The next time they perform an online Duo authentication, the computer’s offline counter resets.
-
Enter the maximum number of days offline, up to 365. With this option, there is no limit to the number of times a user logs in while offline during the allowed period.
Users need to reconnect their offline computer to the internet upon reaching the end of the period you define here. The next time they perform an online Duo authentication, the computer’s offline expiration date resets. If the user does not perform online Duo authentication before the maximum number of days specified here is reached, they can no longer log in offline, and so must connect to Duo’s service in order to log in at all.
-
-
Users may activate offline access using either the Duo Mobile application for iOS or Android, or a U2F security key. Both offline authentication methods are allowed unless you uncheck one in the Offline authentication methods setting. You may not uncheck both options.
Any authentication method enabled for offline access is always permitted, overriding any other policy setting restricting authentication methods for the RDP application.
-
Click the Save button.
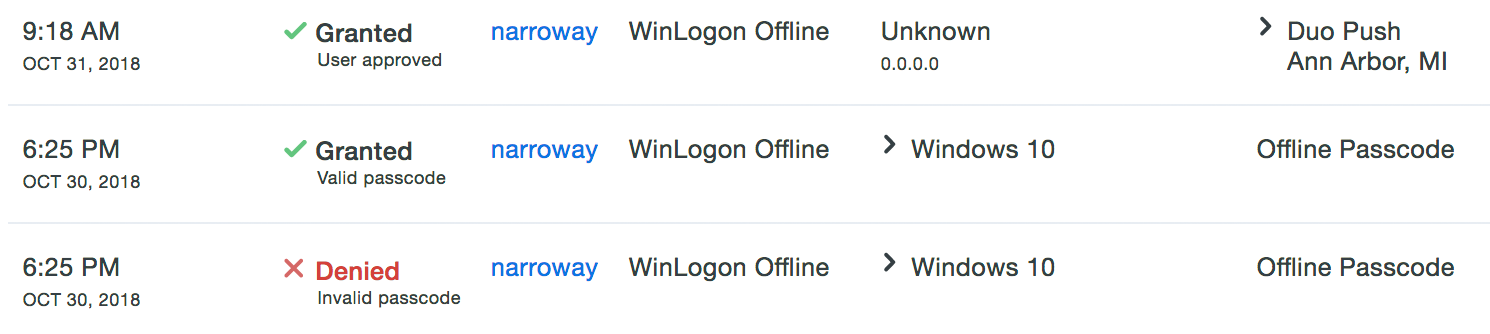
Offline Access Logging
No information about logins using offline access is reported in Duo Admin Panel authentication reports while the Windows system is offline. At the next online authentication, login events that occurred while the system was offline are sent to Duo’s service. These events show up in the Authentication Log with other user access results, and show the offline authentication method used.
Advanced Configuration
Change How Many Users May Use Offline Access
By default, five (5) users may enroll in offline access. To increase or reduce the number of users that may activate offline access on a given Windows client, use the Registry Editor (regedit.exe) with administrator privileges to create or update the following registry value:
Location: HKLM\SOFTWARE\Duo Security\DuoCredProv:
| Registry Value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
OfflineMaxUsers
|
DWORD | Create this value and set to the number of users you would like to have the ability to enroll in offline access on a given Windows system. Minimum value: 1; Maximum value: 50. If not set the default is 5. |
Once the maximum number of users have activated offline access, the next user receives an error when attempting to enroll in offline access.
Force Offline Reactivation for a User
To force offline reactivation for a previously activated user on a given Windows system, use the Registry Editor (regedit.exe) with administrator privileges to delete the entire registry key that includes the username from HKLM\SOFTWARE\Duo Security\DuoCredProv\Offline.
Prevent Offline Access Use on a Client
You may have Windows systems where no users should log in using offline access, regardless of the application setting in the Duo Admin Panel. To prevent offline authentication for any user on a given Windows client, use the Registry Editor (regedit.exe) with administrator privileges to create or update the following registry value:
Location: HKLM\SOFTWARE\Duo Security\DuoCredProv:
| Registry Value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
OfflineAvailable
|
DWORD | Create this value and set to 0 to disable offline access for all users. Your fail mode configuration applies to offline logins (either fail open or fail closed). |
Offline Access Activation and Login
The next time you (or your end user) logs in to or unlocks the workstation while it’s online and able to contact Duo, the offline activation prompt displays after successful two-factor authentication.
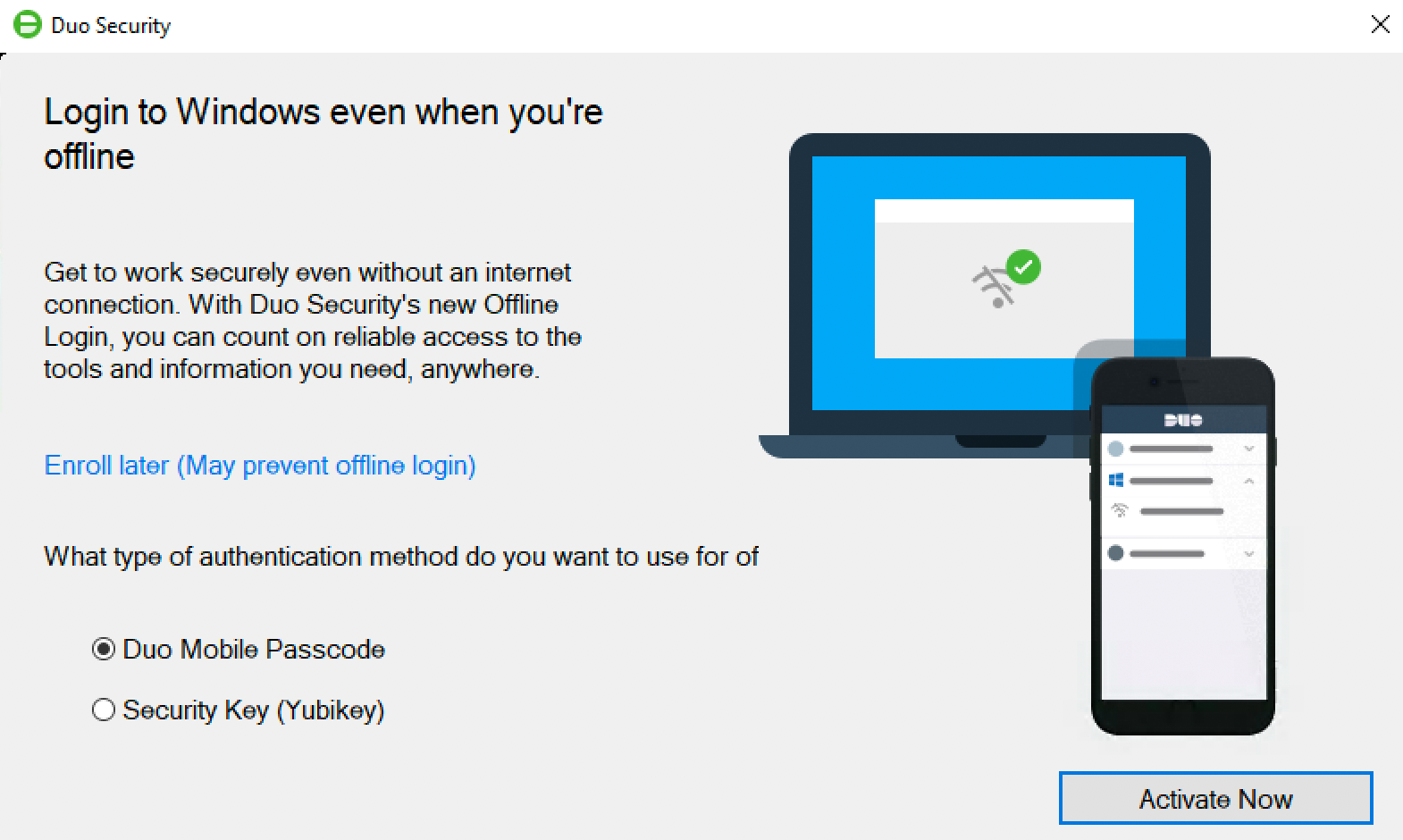
Step through the guided activation process to configure Duo Mobile or a U2F security key for offline MFA.
Once you’ve activated offline access for your account, when your computer isn’t able to contact Duo’s cloud service you’ll automatically be offered the option to login with an offline code or security key after successfully submitting your Windows username and password.
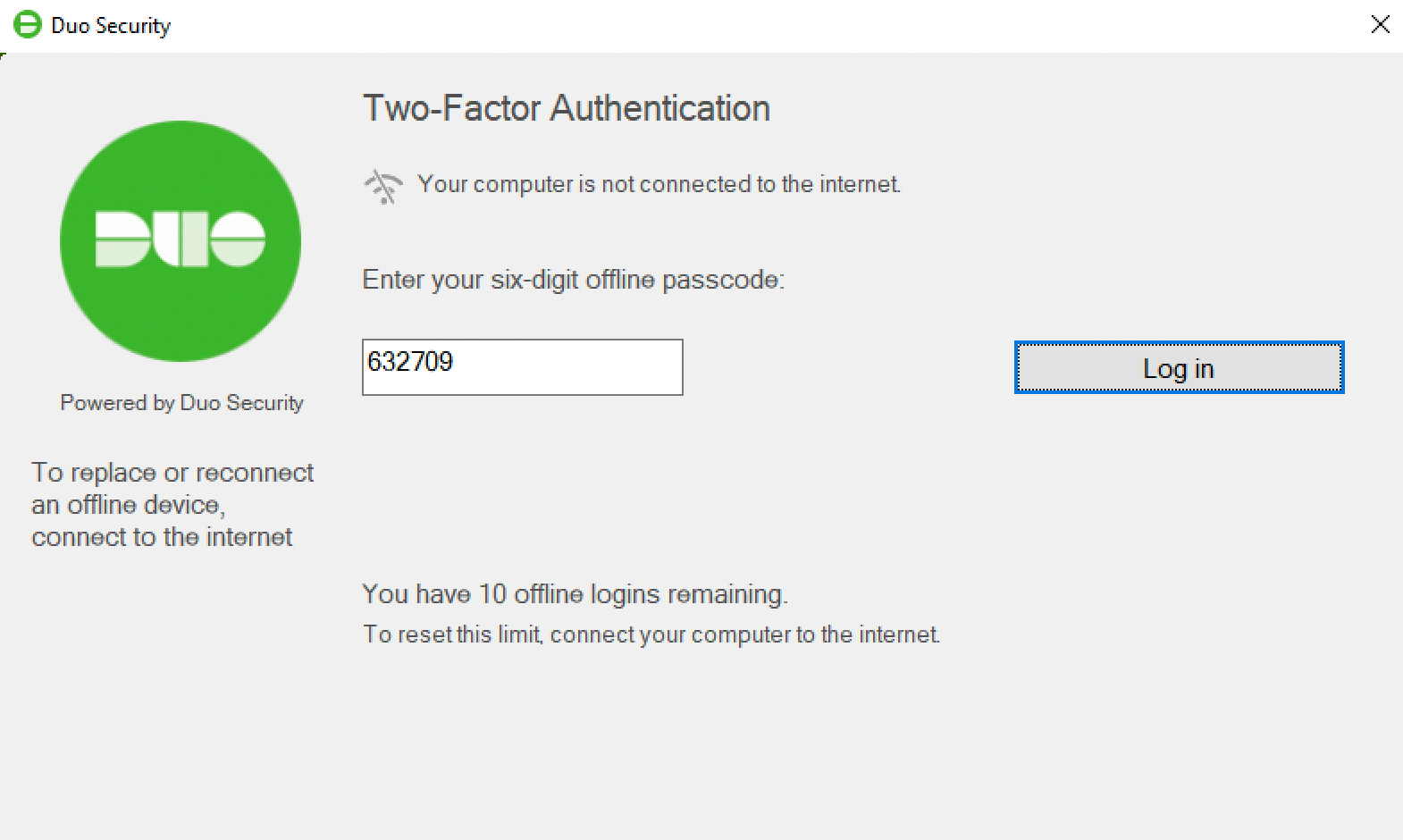
You can also reactivate offline access from the online Duo prompt. Note that only one authentication device — a single phone with Duo Mobile or a single security key — may be activated for offline login. Activating a second device via the reactivation process deactivates the first.
See the full offline activation and login experience in the Duo User Guide for Windows Logon.
Updating Duo Authentication for Windows Logon
Modifications made to the Duo Authentication for Windows Logon version 4.3.1 installer result in direct upgrades from version 4.3.0 to version 4.3.1 leaving the program information for 4.3.0 visible in Add/Remove Programs and the registry. This does not affect the installed 4.3.1 application’s operation. See the Duo for Windows Logon FAQ for more information.
You can upgrade your Duo installation over the existing version; there’s no need to uninstall first. The installer maintains your existing application information and configuration options.
-
Download the most recent Duo Authentication for Windows Logon installer package. View checksums for Duo downloads here.
-
Run the installer with administrator privileges and follow the on-screen prompts to complete the upgrade installation.
If you’re upgrading to a version that includes new installer options, the configuration screen for those options won’t be shown during an upgrade install. You’ll need to configure those new options via Regedit or GPO update. See the Configuration section of the FAQ to learn how to enable and configure Duo for Windows Logon options in the registry, or the Group Policy documentation to learn how to configure options with GPO.
Uninstalling Duo
If you’d like to remove Duo Authentication for Windows Logon from your system, open the Windows Control Panel «Programs and Features» applet, click on the «Duo Authentication for Windows Logon» program in the list, and then click Uninstall.
Do not delete the Microsoft RDP application from the Duo Admin Panel until you have uninstalled the Duo application from all Windows systems using that application. If you delete the Admin Panel application before uninstalling the Duo software you may block users from logging in to Windows.
Advanced Deployment and Configuration using Group Policy
Please see our Duo Authentication for Windows Logon Group Policy documentation.
Troubleshooting
Need some help? Take a look at the Windows Logon Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) page or try searching our Windows Logon Knowledge Base articles or Community discussions. For further assistance, contact Support.
If the Duo application denies access to your users, ensure that you have enrolled them in Duo with a username or username alias that matches the username they use to log into Windows, and with a 2FA device attached that is activated for Duo Push, can receive phone calls from Duo, or can generate a one-time passcode. If you applied a new user policy that allows access without 2FA expecting it to allow the blocked users through, this only has effect if the blocked users do not exist in Duo. Refer to these articles to learn more about user enrollment states and how they combine with policy settings to affect user logins.
- Why are Duo users being prompted to enroll or denied access when my New User Policy is set to allow access without 2FA?
- Guide to Duo User Enrollment States
Network Diagram
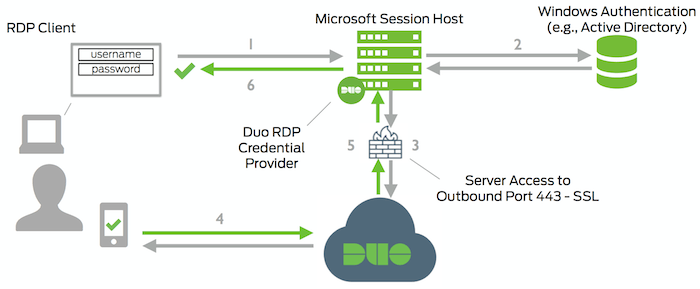
- RDP connection, console logon, or UAC elevation initiated
- Primary authentication of Windows credentials (domain or local user)
- Duo Windows Logon credential provider connection established to Duo Security over TCP port 443
- Secondary authentication via Duo Security’s service
- Duo Windows Logon credential provider receives authentication response
- RDP or console session logged in
Video Overview
Videos show the Duo Admin Panel experience prior to November 2024, Duo for Windows Logon installations prior to version 4.3.0, and Duo Mobile version 3.
Offline Access Video Overview
Duo integrates with Microsoft Windows client and server operating systems to add two-factor authentication to Remote Desktop and local logons.
General
Does Duo for Windows Logon use the traditional Duo Prompt?
No, the Duo for Windows Logon user interface is not shown in a browser iframe and while has a design similar to the traditional Duo Prompt it does not actually use the traditional Duo Prompt.
Is Duo for Windows Logon affected by the traditional Duo Prompt end of life?
No, Duo for Windows Logon is unaffected by the traditional Duo Prompt end of life and requires no action ahead of the traditional Duo Prompt end-of-support or end-of-life dates.
Can I update Duo for Windows Logon to use Duo Universal Prompt?
No, Duo Universal Prompt is exclusively available to Duo applications that use OIDC or the Duo Web SDK to show the Duo login prompt in a browser window. Duo for Windows Logon does not show a browser-based Duo login prompt.
Which versions of Duo for Windows Logon support Verified Duo Push?
Verified Duo Push support in Duo for Windows Logon was introduced in the preview release 4.3.16 and became generally available in version 5.0.0. We recommend updating any 4.3.16 preview installations to the most recent non-preview release.
Duo for Windows Logon releases 4.3.1 and earlier will not offer Verified Duo Push regardless of the effective authentication methods policy setting.
Can remembered devices be used over RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) connections?
No, RDP logins will not see the option to remember the device in the Duo for Windows 2FA prompt. Consider applying an authorized networks policy to the Duo Microsoft RDP application to minimize interactive Duo authentication for RDP users.
How are local trusted sessions created by the remembered device option invalidated or revoked?
An existing device trust session ends under any of the following conditions:
-
Changes to the operating system session state: When initialized the Duo credential provider determines if the Windows logon type is a workstation unlock or a new logon session. A new logon session will require Duo multi-factor authentication (MFA), and subsequent workstation unlocks bypass interactive MFA for the duration of the «Remember me» session.
- Confirm this by enabling debug logging, reproducing the issue, and checking for the this output in the
%PROGRAMDATA%\Duo Security\duo.logfile:CanTrustSession isUnlockSession=false “Session not trusted because it is login session, not unlock – secondary authentication required.”
- Confirm this by enabling debug logging, reproducing the issue, and checking for the this output in the
-
Change to network location: At each logon authentication attempt Duo snapshots and compares the network state of the user’s device to determine whether it differs from the most recent network used to create a local trusted session. If the network state has changed, Duo prompts for interactive MFA. Some changes to the network state that could invalidate a session are connecting to a different wireless or wired network, switching from a wired to wireless connection on the same network, or connecting to a VPN network.
- Confirm this by enabling debug logging, reproducing the issue, and checking for this output in the
%PROGRAMDATA%\Duo Security\duo.logfile:CanTrustSession hasNetworkChanged=true
- Confirm this by enabling debug logging, reproducing the issue, and checking for this output in the
-
Use of offline authentication: If a user logs in to or unlocks the workstation with Duo offline access, Duo prompts for interactive MFA at the next online login.
-
User action: If a user clicks the «Cancel» button during login of a local trusted session, Duo prompts for interactive MFA.
- Confirm this by enabling debug logging, reproducing the issue, and checking for this output in the
%PROGRAMDATA%\Duo Security\duo.logfile:User canceled trusted session login for user:
- Confirm this by enabling debug logging, reproducing the issue, and checking for this output in the
-
Policy change: If a Duo administrator removes the remembered devices policy from the Duo Microsoft RDP application or edits the policy to disable the «Remember devices for Windows Logon» setting, at the next logon or workstation unlock the local Duo application applies the policy change and prompts for interactive MFA.
-
Registry edit: The trusted session created by remembering the device adds a registry key at
HKLM\Software\Duo Security\DuoCredProv\Users\<UserSID>. If that registry key for a user is deleted, Duo prompts for interactive MFA. -
Trusted session length: If a trusted session length exceeds the limit set by an administrator in the Duo Admin Panel “Remember devices for Windows Logon” option, Duo prompts for an interactive MFA on the next Windows logon or unlock attempt.
- Confirm this by enabling debug logging, reproducing the issue, and checking for this output in the
%PROGRAMDATA%\Duo Security\duo.logfile:Session trust expired – secondary authentication required
- Confirm this by enabling debug logging, reproducing the issue, and checking for this output in the
-
Passwordless for Operating System (OS) Logon enabled: If Passwordless OS Logon is enabled for the Duo Microsoft RDP application in use, remembered devices policy settings have no effect. Passwordless for OS Logon removes the manual requirement for users to provide an OS password when logging into their workstation by automatically invoking a Bluetooth push for users to authenticate with their biometrics or PIN via Duo Mobile to resume their session.
Are there any issues installing Duo for Windows Logon on Active Directory domain controllers?
There was an issue seen with Duo Authentication for Windows Logon version 4.1.0, on Active Directory domain controllers that may trigger user lockouts. Version 4.1.1, released July 13, 2020, first corrected this issue and is suitable for installation on domain controllers, member servers, and workstations. We recommend first updating any domain controllers with 4.1.0 installed to 4.1.1 before then attempting to install the latest available version of Duo for Windows Logon.
Does Duo Authentication for Windows Logon support offline multifactor authentication?
Yes, MFA using a Duo Mobile passcode or supported U2F security key while a Windows system is unable to reach Duo’s service is supported in version 4.0 and later. Learn more about offline access.
Do offline sessions work with remembered devices?
No, a trusted device session created with the «Remember me» option during online Duo authentication does not maintain the trusted session for offline access, and an offline access login will not show the option to remember the device.
Which security keys are compatible with offline access with MFA?
Offline access for Windows Logon works with these security keys:
- Yubico brand keys supporting U2F/FIDO2 (Vendor ID 1050)
- Feitian ePass FIDO (Vendor ID 096E)
- Thetis FIDO (Vendor ID 1EA8)
Older Google Titan U2F keys with Vendor ID 096E will work, but newer Google Titan keys with Vendor ID 18d1 will not.
HyperFIDO tokens are not supported for offline access activation, nor are simple OTP passcode tokens or Duo D-100 hardware tokens. Do not use tokens that require extended length encoding.
Is it possible to use the same authentication device for both online and offline Windows Logon?
Yes, you may use these authentication devices for both online and offline access with a single device:
- An Android or iOS device with Duo Mobile activated for both online and offline 2FA.
- A hardware token that supports both OTP and U2F (like the YubiKey 5 series).
Learn more.
Does Duo support Windows Server Core installations?
Server Core installs were supported prior to Duo for Windows Logon version 4.0.0. Nano (headless) installs are not supported in any version.
Does Duo support Windows Server 2025?
Yes, Duo for Windows Logon version 5.0.0 and later supports Windows Server 2025 full desktop GUI installs.
Server Core and Nano (headless) installs are unsupported.
Does Duo support Windows 11 and Windows Server 2022?
Yes, Duo for Windows Logon version 4.2.0 and later supports Windows 11 64-bit clients and Windows Server 2022 full desktop GUI installs.
Server Core and Nano (headless) installs are unsupported.
Does Duo support Windows 10?
Duo Authentication for Windows Logon versions 1.2 and later support Windows 10.
We strongly recommend that you either uninstall Duo version 1.1.8 and older from your Windows PC or upgrade Duo to version 1.2 or later before upgrading your PC to Windows 10. If you do not update or remove Duo first you may not be able to log in to your computer after the OS upgrade completes.
If you find yourself unable to log in to Windows 10 with Duo installed, you can boot into Safe Mode and uninstall the Duo Credential Provider.
Does Duo support Windows Server 2016, 2019, or 2022?
Yes, Server 2016 full desktop GUI installs are supported starting with version 2.1.0. Duo for Windows Logon version 4.0.0 adds Server 2019 support and version 4.2.0 adds Server 2022 support.
Server Core installs are unsupported as of v4.0.0. Nano (headless) installs are unsupported by any release.
Does Duo support Windows Server 2012 or 2012 R2?
Microsoft ended extended support for Windows Server 2012 and 2012 R2 on October 10, 2023. Duo’s last day of support for installation and use of any Duo applications on Windows operating systems corresponds with the Microsoft end of support. Duo for Windows Logon v5.0.0 removed installer support for these versions. We strongly urge you to upgrade to a supported version of Windows Server.
Does Duo support Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, or Windows 8.1?
Microsoft end-of-support information for these Windows clients is as follows:
- Windows Vista extended support ended on April 11, 2017
- Windows 7 extended support ended on January 14, 2020
- Windows 8 extended support ended on January 12, 2016
- Windows 8.1 extended support ended on January 10. 2023
Duo’s last day of support for installation and use of any Duo applications on Windows operating systems corresponds with the Microsoft end of support. We strongly urge you to upgrade to a supported version of Windows.
Does Duo support Windows Server 2008, or Windows Server 2008 R2?
Microsoft ended extended support for Windows Server 2008 and 2008 R2 on January 14, 2020. Duo’s last day of support for installation and use of any Duo applications on Windows operating systems corresponds with the Microsoft end of support. We strongly urge you to upgrade to a supported version of Windows Server.
Can I use Duo with a Microsoft account?
Important Note for Windows 10 with the Fall Creators Update
There is a known issue with using Duo authentication and Microsoft/Live accounts after installing the Windows 10 Fall Creators Update (version 1709) released 10/17/17.
As a temporary workaround, you can allow the Windows Live credential provider, which restores the login prompt for Microsoft and Live.com accounts.
With this workaround in place, Microsoft and Live.com account users log in without Duo 2FA! Domain and local accounts still require Duo authentication.
To enable the Windows Live credential provider for Microsoft and Live.com accounts, use the Registry Editor (regedit.exe) with administrator privileges to create (or update) the following registry values:
Location: HKLM\SOFTWARE\Duo Security\DuoCredProv:
| Registry Value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
ProvidersWhitelist
|
REG_MULTI_SZ | {F8A0B131-5F68-486C-8040-7E8FC3C85BB6} |
For Windows systems not running the Windows 10 version 1709 update, you can authenticate with Duo Authentication for Windows Logon using a Microsoft attached account on a standalone system if you enable the local group policy setting «Interactive logon: Do not display last user name» and enroll the username of the Microsoft account in Duo.
To edit your local policy (must be a local administrator):
- Run the command gpedit.msc to open the Local Group Policy Editor.
- Navigate to Local Computer Policy → Computer Configuration → Windows Settings → Security Settings → Local Policies → Security Options.
- Double-click the Interactive logon: Do not display last user name setting.
- Select Enabled and click OK.
- Close the Local Group Policy Editor window.
You can also enable the setting via the registry. Create a new DWORD value dontdisplaylastusername set to 1 at HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System.
With this setting enabled you receive the «Other user» login dialog, where you can input your Microsoft account credentials.
On a domain-joined workstation this setting may be controlled by your administrator.
To determine the username of the Microsoft account on a Windows 10 computer, open the Windows User Manager (lusrmgr.msc), locate the Microsoft account in the list, and look at the Name field for that user. The Name value of the Microsoft account won’t be the full e-mail address that you use to sign in, but instead will be shown as a portion of the local part of the email address (the information before the @ symbol). When you have found the Name value for the Microsoft account, enroll that account in Duo. If you do not enroll the account in Duo with the correct username you may not be able to complete log in with the Microsoft account.
What logon interfaces can Duo protect?
Duo Authentication for Windows Logon provides two-factor authentication for RDP and local console logons, and credentialed UAC elevation prompts (e.g. Right-click + «Run as administrator»).
Duo’s Windows Logon client does not add a secondary authentication prompt to the following logon types:
- Shift + right-click «Run as different user»
- PowerShell «Enter-PSSession» or «Invoke-Command» cmdlets
- Non-interactive logons (i.e. Log on as a Service, Log on as Batch, Scheduled Tasks, drive mappings, etc.)
- Pre-Logon Access Providers (PLAPs) such as Windows Always On VPN
- RDP Restricted Admin Mode
How does Duo Authentication for Windows Logon work with NLA (Network Level Authentication)?
Network Level Authentication (NLA) for Remote Desktop Connection is an optional security feature available in Windows Vista and later. When NLA is enabled, remote connections pre-authenticate to the remote system when the RDP client connects before displaying a full remote session. When NLA is disabled, the Windows username and password is entered within the RDP client session after connecting.
When Duo Authentication for Windows Logon is installed on a system where NLA is enabled the RDP client prompts for the Windows username and password in a local system dialog. That information is used to connect to the remote system and passed through to the Remote Desktop manager. Once the RDP client has completed primary authentication the full Remote Desktop session is displayed, and the Duo Security prompt appears for two-factor authentication.
When Duo Authentication for Windows Logon is installed on a system where NLA is not required a full Remote Desktop session is displayed when the RDP client connects to the remote system. The Windows username and password are entered in the Remote Desktop window, and after the logon information is accepted the Duo Security prompt appears for two-factor authentication.
There are some security advantages to enabling NLA, but one of the drawbacks is that users with expired passwords are prevented from logging on to the remote system. More information about NLA and RDP can be found at the Microsoft site and on Wikipedia.
Does Duo Authentication for Windows Logon support web proxying?
Duo can use the HTTPS proxy server configured in your system-wide WinHTTP settings. Configure the proxy server(s) used by WinHTTP with the netsh command.
Duo Authentication version 2.0.0.71 and later also support proxying only Duo authentication traffic. Refer to the instructions for configuring a Duo only proxy.
Does Duo Authentication for Windows Logon work with third-party disk encryption software or other credential providers?
Duo’s credential provider cannot be chained with other credential providers present on your system. Disk encryption software that stores the Windows username and password provided before boot may no longer use those credentials to automatically log on to Windows.
Duo Authentication for Windows Logon version 2.1.0 permits use of the Windows smart card login provider as an alternative to Duo, meaning that users may choose to authenticate with either Duo 2FA or a PIV/CAC card. Duo for Windows Logon v3.1.0 adds support for smart cards logon with Duo 2FA at the local console.
Does Duo support Windows XP or Windows 2003?
Microsoft ended support for Windows XP on April 8, 2014 and for Windows Server 2003 on July 14, 2015. The last Duo release with XP and 2003 compatibility was version 1.1.8. Duo’s last day of support for installation and use of any Duo applications on these operating systems corresponds with the Microsoft end of support. We strongly urge you to upgrade to a supported version of Windows.
Are there any known issues with Windows 2003 and XP?
Duo’s legacy Windows Logon (RDP) integration for Windows 2003 and XP contained the following limitations:
- A reboot is required after installing or uninstalling the Duo Windows Logon integration.
- A password may be changed from the Windows password expiration warning dialog or the password expired prompt without first completing two-factor authentication.
Duo no longer supports any applications on Windows XP or Server 2003. We urge you to upgrade to a supported version of Windows.
Install and Uninstall
Does installing Duo Authentication for Windows Logon require a reboot?
Installing Duo may require a reboot depending on the state of your Windows system, and files in use during installation. Schedule your Duo installation during a maintenance window if unplanned system restarts is a concern.
You may be able to suppress the reboot during silent MSI install or upgrade with the flags /quiet /qn /norestart, so you can schedule the reboot at a better time.
Deployment via Microsoft Group Policy will always require a reboot before installation because software deployment GPOs targeting computers apply and install during the Windows pre-boot stage.
Does Duo Authentication for Windows Logon depend on any other software packages?
Duo Authentication for Windows Logon 4.3.16 and later depend on the Microsoft Visual C++ Redistributable. The Duo EXE installer (i.e. duo-win-login-5.0.0.exe) will also install the Visual C++ Redistributable package on your system if a compatible version is not already present.
Duo MSI installers (DuoWindowsLogon32.msi or DuoWindowsLogon64.msi) do not install the Visual C++ prerequisite package, nor do they prevent installation of Duo if the Visual C++ Redistributable is not present on the target system. The Visual C++ Redistributable must be installed separately from Duo Authentication for Windows Logon when using the Duo MSI installers.
Why do I see both version 4.3.0 and 4.3.1 installed on my computer after attempting an upgrade?
Modifications made to the Duo Authentication for Windows Logon version 4.3.1 installer result in direct upgrades from version 4.3.0 to version 4.3.1 leaving the program information for 4.3.0 visible in Add/Remove Programs and the registry. This does not affect the installed 4.3.1 application’s operation.
If you wish to remove the duplicate Duo Authentication for Windows Logon entry for 4.3.0 you may uninstall it without affecting the 4.3.1 installation. Uninstalling 4.3.1 will entirely remove the application from your system, and require reinstallation if you wish to continue using Duo.
Upgrades from version 4.2.2 and earlier to version 4.3.1 do not experience this, nor will upgrades from version 4.3.1 to later releases.
Can I silently install Duo Authentication for Windows Logon from a command line or PowerShell?
Yes, you can run the .exe or .msi installers from PowerShell or the Command Prompt. This has no required parameters, but if you do not supply the IKEY, SKEY, and HOST values from the command line make sure you have a Windows group policy object applying values for those settings, or make them present in the registry using another method, otherwise the Duo for Windows Logon application will not function.
Enter the following command into PowerShell or a Command Prompt to silently install Duo Security with automatic push on, fail open enabled, smart cards disabled, and protecting both RDP and console logons (this example uses v4.0.2, replace the file name with the version number you have downloaded):
duo-win-login-4.0.2.exe /S /V" /qn IKEY="DIXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX" SKEY="xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx" HOST="api-xxxxxxxx.duosecurity.com" AUTOPUSH="#1" FAILOPEN="#1" SMARTCARD="#0" RDPONLY="#0""Note that the parameter names passed to the installer (IKEY, SKEY, HOST, etc.) are case-sensitive!
The following table lists all the parameters and options that may be set via the command line installer (as of v4.0.2), noting default values if not specified in the command.
| Setting | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| IKEY | Your Duo RDP application’s integration key. | Blank; product will not function |
| SKEY | Your Duo RDP application’s secret key. | Blank; product will not function |
| HOST | Your Duo API hostname. | Blank; product will not function |
| AUTOPUSH | 1 to automatically send a push request, or 0 to disable automatic push. |
0 |
| FAILOPEN | 1 to allow access when Duo’s service is unreachable, or 0 to block access without Duo MFA. |
1 |
| RDPONLY | 1 to only require Duo for remote logons, or 0 to require Duo for console and RDP logons. |
0 |
| SMARTCARD | 1 to allow smart card login as an alternative to Duo, or 0 to disable the Windows smart card provider. |
0 |
| WRAPSMARTCARD | 1 to require Duo after smart card primary logon at the local console, or 0 to allow smart card logon without Duo approval afterward. |
0 |
| ENABLEOFFLINE | 1 to enable offline access (subject to the configuration in the Admin Panel), or 0 to completely disable offline access on the target system. |
1 |
| USERNAMEFORMAT | The username format sent to Duo. One of: 0 for sAMAccountName (narroway), 1 for the NTLM domain and username (ACME\narroway), or 2 for the userPrincipalName (narroway@acme.corp). |
1 |
| PROXYHOST | The hostname or IP address of an upstream HTTP proxy server for Duo communications | Not set |
| PROXYPORT | The port for HTTP proxy communications. | Not set |
| LOGFILE_MAXCOUNT | Number of rotated log files to be maintained. | Not set |
| LOGFILE_MAXSIZEMB | Size of rotated log file to be maintained in megabytes (MB). | Not set |
| UAC_PROTECTMODE | 0 to respect existing Duo authentication settings for logon, 1 to disable Duo at logon and only prompt during User Elevation, or 2 to enforce Duo 2FA at both logon and User elevation. |
0 |
| UAC_OFFLINE | 1 to enable offline access for User Elevation, or 0 to disable offline access for User Elevation. |
1 |
| UAC_OFFLINE_ENROLL | 1 to enable offline access enrollment during User Elevation, or 0 to prevent Offline Enrollment during User Elevation. |
1 |
When specifying a value for one of the DWORD options (a value of 0, 1, or 2), be sure to prefix it with a pound sign #, e.g. RDPONLY=#1.
This performs the install with the same settings in the previous example from the command line with Windows Installer (msiexec), using the 64-bit MSI installer included in the Duo Authentication for Windows Logon Group Policy MSI installers, template files, and documentation package. View checksums for Duo downloads here.
msiexec.exe /i DuoWindowsLogon64.msi IKEY="Integration Key" SKEY="Secret Key" HOST="API Hostname" AUTOPUSH="#1" FAILOPEN="#1" SMARTCARD="#0" RDPONLY="#0" /qnThe MSI installers and properties can also be used to create a transform file for use with with Active Directory Group Policy Software Publishing or other automated software deployment utilities. See the Duo Authentication for Windows Logon Group Policy documentation for more information.
Can I silently upgrade Duo Authentication for Windows Logon from a command line?
Enter the following command into a Command Prompt to silently upgrade an existing Duo installation using the MSI of a newer version, preserving the current integration information and installed options (as of v4.0.2):
msiexec.exe /qn /i "DuoWindowsLogon64.msi"For MSI upgrade installs of releases prior to v4.0.2, and to upgrade from v4.1.0 to 4.1.1 or later, include the options shown in this command:
msiexec.exe /quiet /i "DuoWindowsLogon64.msi" REINSTALL=ALL REINSTALLMODE=vomus IS_MINOR_UPGRADE=1To silently upgrade using a newer installer executable, enter this command (this example uses v4.1.3, replace the file name with the version number you have downloaded):
duo-win-login-4.1.3.exe /S /v/qnCan I silently uninstall Duo Authentication for Windows Logon from a command line or PowerShell?
Enter the following command into PowerShell or a Command Prompt to silently uninstall Duo for Windows Logon using the same version of the installer executable that you have installed on the system (so this example uses the v4.1.3 installer to remove v4.1.3 from the system):
duo-win-login-4.1.3.exe /S /v/qn /XIf you no longer have the same installer executable that matches the Duo installation you wish to remove, use msiexec to perform the uninstall. You will first need to determine the correct product code GUID for your installed version:
-
Launch the Registry Editor (regedit.exe).
-
Navigate down the tree to
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall. -
Examine the GUID keys until you locate the key with the
DisplayNamevalue of «Duo Authentication for Windows Logon». -
Copy the UninstallString value for the Duo Authentication for Windows Logon product from the registry (for example:
MsiExec.exe /X{BD789CFF-3C7A-4533-90F3-A3E5190A9D43}). -
Use the information from the registry to construct your silent msi uninstall command:
MsiExec.exe /qn /x {BD789CFF-3C7A-4533-90F3-A3E5190A9D43}
Can I deploy or configure Duo Authentication for Windows Logon using Group Policy?
Yes. Please refer to the Duo Authentication for Windows Logon Group Policy documentation.
How do I disable or uninstall Duo Authentication for Windows Logon in Safe Mode?
To disable Duo’s credential provider on Windows after booting in Safe Mode, run the following from an elevated command prompt:
Versions 1.2.0.14 and earlier
regsvr32 /u "C:\Program Files\Duo Security\DuoCredProv\DuoCredProv.dll"
regsvr32 /u "C:\Program Files\Duo Security\DuoCredProv\DuoCredFilter.dll"
Version 2.0.0 and later
regsvr32 /u "C:\Program Files\Duo Security\WindowsLogon\DuoCredProv.dll"
regsvr32 /u "C:\Program Files\Duo Security\WindowsLogon\DuoCredFilter.dll"
You can also uninstall the Duo Windows Logon integration while still in safe mode with a registry change and a service start.
- When booted into safe mode, launch the Registry Editor (regedit.exe).
- Drill down into the HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\SafeBoot\Minimal registry hive (if you are booted into regular safe mode) or down to HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\SafeBoot\Network (if you are booted into safe mode with networking).
- Right-click the Minimal or Network registry key (as appropriate for your currently booted mode) and click New → Key on the context menu. Name the new key MSIServer.
- From an elevated command prompt, run the command
net start msiserver. - You can now use Programs and Features on the Windows Control Panel to uninstall the Duo application.
For more information about Safe Mode refer to the instructions for your operating system: Windows 10, Windows 8/8.1 and 2012/2012 R2.
Windows 10 users may need the BitLocker recovery key in order to boot the system into safe mode. If you don’t have it available, use one of Microsoft’s recommendations to locate it.
Configuration
Where are the Duo for Windows Logon settings stored in the registry?
Duo Authentication for Windows Logon stores the installation settings in the registry at HKLM\Software\Duo Security\DuoCredProv.
If you’re managing the Duo client configuration with Windows Group Policy, then any setting configured by a GPO is stored as a registry value in HKLM\Software\Policies\Duo Security\DuoCredProv, and overrides the same setting configured at the default registry location.
Since GPO settings get reapplied periodically at the client system, any permanent changes to a setting configured via group policy should be made by editing the GPO to update the setting with the new value, not by updating the client registry.
How does offline access in Duo for Windows Logon interact with fail mode?
Enabling offline access on the RDP v4.0 or later application overrides the configured fail mode setting for users who activate offline access.
Users who have not activated offline access are subject to the fail mode setting e.g. if set to fail open, a user who did not activate offline access would be able to log in without completing Duo offline authentication. Disable «fail open» if you want to prevent users who did not activate offline access from logging in when the computer is offline.
How can I configure the fail mode?
When the fail mode is set to «fail open», it permits the Windows logon to continue if it is unable to contact the Duo service. You can set the fail mode during installation to «fail closed» by deselecting the «Bypass Duo authentication when offline» box during installation. This will deny all login attempts if there is a problem contacting the Duo service.
By default, Windows Logon 4.2.2 and earlier installers the fail mode is set to «fail open».
Windows Logon 4.3.0 installers will default to «fail closed». The msi installer will preserve the selection made by a previously installed version on upgrade. Upgrades from previous versions using the exe installer will override the previous fail mode selection and default to fail closed.
To change the fail mode after installation, use the Registry Editor (regedit.exe) with administrator privileges to create or update the following registry value:
Location: HKLM\SOFTWARE\Duo Security\DuoCredProv:
| Registry Value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
FailOpen
|
DWORD | Set to 1 to allow «fail open» for all users or 0 to restrict to «fail closed» (except for users who have activated offline access in v4.0 or later). Default: Fail open. |
If the Duo settings are managed by Windows Group Policy, those settings override any changes made via regedit. Update the «Duo Service: Fail Open if Unable to Contact Duo» setting in the GPO instead.
When modifying the FailOpen registry value on a Windows 2003 or XP system a reboot is required to make the change effective.
How can I configure automatic push?
When automatic push is enabled, Duo Authentication for Windows Logon automatically sends a push notification to the Duo Mobile app or a phone call to the user’s default device after submitting the Windows username and password. This is the installation default. You can choose to disable automatic push for all users of Duo for Windows Logon on a given system by deselecting the «Use automatic push to authenticate if available» box during installation.
To change the automatic push behavior for all users of the system after installation, use the Registry Editor (regedit.exe) with administrator privileges to create or update the following registry value:
Location: HKLM\SOFTWARE\Duo Security\DuoCredProv:
| Registry Value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
AutoPush
|
DWORD | Set to 0 to disable automatic push or 1 to enable it. |
If the Duo settings are managed by Windows Group Policy, those settings override any changes made via regedit. Update the «Client: Enable Auto Push» setting in the GPO instead.
When automatic push is disabled, Duo does not request logon verification until the user submits the name of an authentication factor at the Duo Authentication prompt.
How do I enable debug logging?
To enable debug logging, use the Registry Editor (regedit.exe) with administrator privileges to create the following registry value:
Location: HKLM\SOFTWARE\Duo Security\DuoCredProv:
| Registry Value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Debug
|
DWORD | Set to 1 to enable debug logging. Default: No debug logging. |
If the Duo settings are managed by Windows Group Policy, those settings override any changes made via regedit. Update the «Enable Debug Logging» setting in the GPO instead to enable debug logging globally, or if you just need to temporarily enable it to capture an issue update the HKLM\Software\Policies\Duo Security\DuoCredProv\debug registry value as well (this may be reverted at the client’s next GPO refresh).
The log file location is %PROGRAMDATA%\Duo Security\duo.log for version 1.1.8 and later, and %ProgramFiles%\Duo Security\DuoCredProv\duo.log for version 1.1.7 and earlier.
How can I configure log file rotation?
By default, Duo Authentication for Windows Logon will not rotate log files.
Version 4.0.6 and later supports log file rotation. To configure the log file rotation, use the Registry Editor (regedit.exe) with administrator privileges to create the following registry values:
Location: HKLM\SOFTWARE\Duo Security\DuoCredProv:
| Registry Value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
LogFileMaxSizeMB
|
DWORD | Set the size of log file to be maintained in megabytes (MB). Minimum Value: 1 Maximum Value: 4096 (decimal) |
LogFileMaxCount
|
DWORD | Set the number of log files to be maintained on disk. Minimum Vale: 1 Maximum Value: 100 (decimal) |
Both registry keys must be created and set to a value greater than 0 to enable rotation. Backup logs will increment starting at duo00.log through duo99.log. Log may be slightly larger than the defined size to ensure an authentication in-process is not split across log files.
Example setting: LogFileMaxSizeMB to 1 and LogFileMaxCount to 1 will result in Duo.log coexisting with duo00.log, both with a maximum size of 1MB.
Can Duo protect local console logins in Windows?
Yes, Duo Authentication for Windows Logon does provide protection for local console logins. However, it can be difficult to prevent an attacker with physical access to a system from compromising it. In particular, there are two significant threats you should take care to address:
-
Duo Authentication for Windows Logon can be bypassed by rebooting a Windows system into Safe Mode. To limit the effect of this, you should prevent all but a select group of users from logging in while Windows is running in Safe Mode (for example, via the registry DWORD value HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System\SafeModeBlockNonAdmins set to 1).
-
By default, the RDP integration will «fail open» if it is unable to contact the Duo service. A user with local console access might be able to disrupt a machine’s network connectivity (e.g. by unplugging an ethernet cord), thereby bypassing Duo authentication.
You can set the fail mode during installation to «fail close» by deselecting the «Bypass Duo authentication when offline» box in the Duo installer, or by configuring the Registry DWORD value HKLM\Software\Duo Security\DuoCredProv\FailOpen set to 0 to «fail closed». This will deny all login attempts if there is a problem contacting the Duo service.
To enable Duo authentication for both local console and RDP logins, clear the «Only prompt for Duo authentication when logging in via RDP» box during installation.
To change which logon connections are required to use Duo after installation, use the Registry Editor (regedit.exe) with administrator privileges to create or update the following registry value:
Location: HKLM\SOFTWARE\Duo Security\DuoCredProv:
| Registry Value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
RdpOnly
|
DWORD | Set to 0 to protect both RDP and local console logons or 1 to protect RDP logons only. |
If the Duo settings are managed by Windows Group Policy, those settings override any changes made via regedit. Update the «Client: Limit Two-Factor to RDP Logons Only» setting in the GPO instead.
Can I choose which username attribute gets sent to Duo?
Duo Authentication for Windows Logon defaults to sending the username in NTLM (or msDS-PrincipalName) e.g. DOMAIN\username to Duo’s cloud service as the Duo username. However, when you create your RDP application in Duo, the «Username normalization» option defaults to «Simple» normalization, so that Duo ignores anything preceding a backslash or after an at symbol in the username received in a logon request. This means Duo treats «narroway», «ACME\narroway», and «narroway@acme.local» as the same «narroway» user in Duo. Therefore, with the default username settings applied at both the Windows client and to the RDP application in Duo, we try to match the username only when looking for an existing user; essentially matching the sAMAccountName.
If the username sent to Duo by our Windows Logon application doesn’t match an existing Duo username, the user can’t complete Duo authentication. This causes issues when an organization has already enrolled Duo users with a different username format, like userPrincipalName (UPN).
Duo Authentication for Windows Logon version 3.1 and later allows specifying which Windows username attribute is sent to Duo’s service when authenticating.
To change which Windows username attribute gets sent to Duo, use the Registry Editor (regedit.exe) with administrator privileges to create or update the following registry value:
Location: HKLM\SOFTWARE\Duo Security\DuoCredProv:
| Registry Value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
UsernameFormatForService
|
DWORD |
Set to 0 to send the sAMAccountName as the Duo username (e.g. «narroway»). Set to 1 to send the NTLM domain and username as the Duo username (e.g. «ACME\narroway»). This is the default installation setting. Set to 2 to send the userPrincipalName as the Duo username (e.g. «narroway@acme.local»). |
If the Duo settings are managed by Windows Group Policy, those settings override any changes made via regedit. Update the «Duo Service: Specify format of username sent to Duo service» setting in the GPO instead.
If you want Duo for Windows Logon to send the NTLM or UPN username formats to Duo, and your Duo usernames or aliases are also NTLM or UPN format, then be sure to log in to the Duo Admin Panel and change the «Username normalization» option for your RDP integration from «Simple» to «None».
Whichever username format you choose, ensure that a matching username or username alias exists in Duo.
Why might an incorrect username get sent to Duo from a machine joined to Entra ID?
Duo for Windows Logon sends the username from the logon token by default. If the resulting username is incorrect for a machine joined to Entra ID, Duo for Windows Logon 4.3.0 and later can parse the username from the login string instead.
To change how the username gets parsed on an Entra ID-joined machine, use the Registry Editor (regedit.exe) with administrator privileges to create or update the following registry value:
Location: HKLM\SOFTWARE\Duo Security\DuoCredProv:
| Registry Value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
ParseUsernameAndDomain
|
DWORD |
Set to 0 to send the username from logon token. Default: Disabled Set to 1 to parse the username and domain from the username login string instead of the logon token. Enable this setting when devices joined to Entra ID send an incorrect username value to Duo. |
If the Duo settings are managed by Windows Group Policy, those settings override any changes made via regedit. Update the «Client: Parse Username and Domain» setting in the GPO instead.
Can Duo protect Remote Desktop Connection logons only?
It is possible to only enable Duo authentication for RDP sessions (and not local console logins). This can be set during the installation by checking the «Only prompt for Duo authentication when logging in via RDP» box.
To change which logon connections are required to use Duo after installation, use the Registry Editor (regedit.exe) with administrator privileges to create or update the following registry value:
Location: HKLM\SOFTWARE\Duo Security\DuoCredProv:
| Registry Value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
RdpOnly
|
DWORD | Set to 1 to protect RDP logons only or 0 to protect both RDP and local console logons. |
If the Duo settings are managed by Windows Group Policy, those settings override any changes made via regedit. Update the «Client: Limit Two-Factor to RDP Logons Only» setting in the GPO instead.
When modifying the RdpOnly registry value on a Windows 2003 or XP system a reboot may be required to make the change effective.
Is it possible to use a web proxy only for Duo Authentication for Windows Logon traffic?
Yes, Duo Authentication for Windows Logon version 2.0.0.71 and later supports proxying only Duo authentication traffic. This can be set during the installation by checking the «Configure manual proxy for Duo traffic» box and entering your proxy host and port information.
To change the HTTP proxy settings for the Duo application after installation, use the Registry Editor (regedit.exe) with administrator privileges to create or update the following registry value:
Location: HKLM\SOFTWARE\Duo Security\DuoCredProv:
| Registry Value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
HttpProxyHost
|
String | Hostname or IP address of an HTTP proxy. If set, will be used for communicating with Duo Security’s service. Must support the CONNECT protocol. Default: do not use a proxy. |
HttpProxyPort
|
DWORD |
Port to connect to on http_proxy_host. Enter port number as decimal. Default: ’80’.
|
If the Duo settings are managed by Windows Group Policy, those settings override any changes made via regedit. Update the «Duo Service: HTTP Proxy Hostname» and «Duo Service: HTTP Proxy Port» settings in the GPO instead.
If you do not already have an HTTP proxy deployed on your network you can use the Duo Authentication Proxy application to act as an HTTP proxy for Duo Windows Logon client connections. Install the Authentication Proxy on a server in your network that has direct internet access, add the HTTP proxy settings to the Authentication proxy configuration, and then update the Duo for Windows Logon proxy settings to point to that Authentication Proxy. See the HTTP Proxy instructions in the Authentication Proxy Reference for more information.
How do I allow smart card login instead of Duo Authentication?
Duo Authentication for Windows Logon v2.1.0 and later permits use of the Windows smart card login provider as an alternative to Duo. When this is enabled, user may choose to log on with either the built-in Windows smart card authentication and a DOD CAC or other PIV card, or with Windows primary username and password credentials followed by Duo two-factor authentication.
You can turn on smart card login during a clean install of Duo for Windows Logon by selecting the «Enable Smart card support» option followed by selecting «Enable smart card login without Duo» in the installer.
To enable smart card support after upgrading or installing v2.1.0 or later, use the Registry Editor (regedit.exe) with administrator privileges to create or update the following registry value:
Location: HKLM\SOFTWARE\Duo Security\DuoCredProv:
| Registry Value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
EnableSmartCards
|
DWORD | Set to 1 to allow smart card login as an alternative to Duo. Default: 0. |
If the Duo settings are managed by Windows Group Policy, those settings override any changes made via regedit. Update the «Duo Service: Enable Smart Cards» setting in the GPO instead.
How do I enable smart card login plus Duo Authentication?
With Duo Authentication for Windows Logon v3.1.0 and later, you can require Duo two-factor authentication for smart card users logging in at the local console. When this is enabled, user may choose to log on with either the built-in Windows smart card authentication and a DOD CAC or other PIV card, or with Windows primary username and password credentials. Both smart card and username/password primary login is followed by Duo two-factor authentication.
You can turn on smart card login during a clean install of Duo for Windows Logon by selecting the «Enable Smart card support» option followed by selecting «Enable smart card login with Duo» in the installer.
To enable smart card + Duo support after upgrading or installing v3.1.0 or later, use the Registry Editor (regedit.exe) with administrator privileges to create (or update) both of the following registry values:
Location: HKLM\SOFTWARE\Duo Security\DuoCredProv:
| Registry Value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
EnableSmartCards
|
DWORD | Set to 1 to enable the smart card credential provider. This may already be done if you selected the «Enable Smart card support» option during installation. |
WrapSmartCards
|
DWORD | Set to 1 to require Duo authentication after logging in with the smart card credential provider. Default: 0. |
If the Duo settings are managed by Windows Group Policy, those settings override any changes made via regedit. Update the «Duo Service: Wrap Smart Cards» setting in the GPO instead.
Can I permit use of other credential providers after installing Duo?
Installing Duo disables all other installed logon credential providers. You can enable the Windows smart card login provider in the Duo installer, but other credential providers (what your users may refer to as «logon tiles») are hidden.
Duo Authentication for Windows Logon version 3.1 and later allows re-enabling access to a hidden credential provider via the registry. A common use case for this would be to restore access to a password reset tool from the Windows logon screen.
Be aware that any credential provider you allow in this registry value is accessible without Duo two-factor authentication! Users who log in with a credential provider in the ProvidersWhitelist skip Duo authentication entirely.
Use the Registry Editor (regedit.exe) with administrator privileges to create (or update) the following registry values:
Location: HKLM\SOFTWARE\Duo Security\DuoCredProv:
| Registry Value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
ProvidersWhitelist
|
REG_MULTI_SZ | Populate the multi string value data with the GUIDs of the third-party credential providers to allow. You can find GUIDs for all registered credential providers on a system in HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Authentication\Credential Providers, or contact the application’s vendor for assistance determining the GUID for their credential provider. Supports multiple permitted GUIDs. |
Example registry value that permits the Microsoft FIM Password Reset client:
How many users can enroll in offline access with MFA per Windows client?
By default, five (5) users may enroll in offline access. To increase or reduce the number of users that may activate offline access on a given Windows client, use the Registry Editor (regedit.exe) with administrator privileges to create or update the following registry value:
Location: HKLM\SOFTWARE\Duo Security\DuoCredProv:
| Registry Value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
OfflineMaxUsers
|
DWORD | Create this value and set to the number of users you would like to be have the ability to enroll in offline access on a given Windows system. Minimum value: 1; Maximum value: 50. If not set the default is 5. |
Once the maximum number of users have activated offline access, the next user receives an error when attempting to enroll in offline access.
How can I remove a user’s existing offline activation?
To force offline reactivation for a previously activated user on a given Windows system, use the Registry Editor (regedit.exe) with administrator privileges to delete the entire registry key that includes the username from HKLM\SOFTWARE\Duo Security\DuoCredProv\Offline.
How can I completely prevent offline access with MFA at the Windows client?
You may have Windows systems where no users should log in using offline access, regardless of the application setting in the Duo Admin Panel. To prevent offline authentication for any user on a given Windows client, use the Registry Editor (regedit.exe) with administrator privileges to create or update the following registry value:
Location: HKLM\SOFTWARE\Duo Security\DuoCredProv:
| Registry Value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
OfflineAvailable
|
DWORD | Create this value and set to 0 to disable offline access for all users. Your fail mode configuration applies to offline logins (either fail open or fail closed). |
How do I enable and configure User Elevation to add Duo authentication to UAC prompts?
Available in version 4.1 and later, User Elevation adds Duo two-factor authentication to password-protected Windows UAC elevation attempts. By default. Duo UAC elevation protection is disabled. When enabled, Duo Authentication for Windows Logon will prompt for MFA on credentialed UAC elevation attempts.
You can enable and configure User Elevation during a clean install of Duo for Windows Logon by selecting the «Enable UAC Elevation Protection» option, followed by selecting your desired User Elevation configuration settings in the installer.
To enable and configure User Elevation after upgrading or installing v4.1.0 or later, use the Registry Editor (regedit.exe) with administrator privileges to create (or update) the following registry values:
Location: HKLM\SOFTWARE\Duo Security\DuoCredProv:
| Registry Value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
ElevationProtectionMode
|
DWORD | Create this value and set to 0 to disable UAC protection and only prompt for Duo 2FA at login, 1 to enable Duo only for UAC protection (no Duo 2FA at login) or 2 to enable Duo 2FA for both logon and UAC. Default: 0 |
ElevationOfflineEnable
|
DWORD |
Create this value and set to 0 to disable offline access for UAC elevation, or 1 to enable offline access for UAC elevation. Requires offline access enabled and ElevationProtectionMode set to 1 or 2. Default: 1
|
ElevationOfflineEnrollment
|
DWORD |
Create this value and set to 0 to disable enrollment in offline access during UAC elevation, or 1 to permit enrollment in offline access during UAC elevation. Requires offline access enabled and ElevationProtectionMode set to 1 or 2. Default: 1
|
How do I enable User Account Control credentialed elevation in Windows?
User Account Control (UAC) protects Windows systems and users from malicious software by prompting for additional approval before running an application with administrator privileges. Duo Authentication for Windows Logon v4.1.0 and later optionally adds two-factor authentication to password-protected UAC prompts. If you’ve enabled Duo User Elevation but you’re only getting asked to approve UAC elevation requests («Prompt for consent»), and aren’t required to enter your Windows password to approve the elevation request, you won’t be prompted for Duo when approving the UAC elevation request either.
You can configure User Account Control to require a password to approve elevation requests via registry edit or local/domain Group Policy.
To require password entry for UAC elevation with the Registry Editor, launch regedit.exe with administrator privileges to create (or update) the following registry values:
Location: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System:
| Registry Value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
ConsentPromptBehaviorAdmin
|
DWORD | Create this value and set to 1 to prompt administrators for credentials on the secure desktop (recommended), or 3 to prompt administrators for credentials on the interactive desktop. |
ConsentPromptBehaviorUser
|
DWORD | Create this value and set to 1 to prompt standard users for credentials on the secure desktop (recommended), or 3 to prompt standard users for credentials on the interactive desktop. |
To require password entry for UAC elevation with Group Policy, enable the following policy settings with Group Policy Management Console (gpmc.msc) or local Group Policy Editor (gpedit.msc):
Location: Computer Configuration\Policies\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\Security Options
| Policy Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| User Account Control: Behavior of the elevation prompt for administrators in Admin Approval Mode | Set to Prompt for credentials on the secure desktop or Prompt for credentials. |
| User Account Control: Behavior of the elevation prompt for standard users | Set to Prompt for credentials on the secure desktop or Prompt for credentials. |
Please refer to User Account Control Group Policy and registry key settings for additional information about UAC settings.
How do I enable remembered devices for Windows Logon?
Duo Essentials, Advantage, and Premier customers can apply a remembered devices policy to their Microsoft RDP Duo applications with the Remember devices for Windows Logon setting enabled and set to the number of hours or days desired.
Duo Authentication for Windows Logon version 4.2.0 and later will apply this policy setting to online authentications at the local console, offering the «Remember me» option in the prompt.
Earlier versions of Duo Authentication for Windows Logon must be upgraded to v4.2.0 or later to use this feature.
What logging is available for device authentication during a trusted session?
Duo records logins authenticated as a local trusted session in the Admin Panel Authentication Log with «Remembered Device» as the second factor. The local Windows Logon client log, found at %PROGRAMDATA%\Duo Security\duo.log, also shows the authentication type for the logon activity as a «Remembered Device».
How do I disable certificate pinning?
Certificate pinning was introduced in Duo Authentication for Windows Logon 4.3.16 as an additional security measure protecting communications between the client application and Duo’s cloud service.
It is enabled by default at install. To disable it, use the Registry Editor (regedit.exe) with administrator privileges and update the following registry value:
Location: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Duo Security\DuoCredProv\EnableCertPinning
| Registry Value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
EnableCertPinning
|
DWORD | Set to 0 to disable certificate pinning. Default: 1. |
If the Duo settings are managed by Windows Group Policy, those settings override any changes made via regedit. Update the «Duo Service: Certificate Pinning Available» setting in the GPO instead.
Troubleshooting
Using the Support Tool
If you open a case with Duo Support for an issue involving Duo Authentication for Windows Logon (RDP), your support engineer will need you to submit your registry configuration, recent debug log output demonstrating the issue, and other system configurations. Sensitive information, such as your Duo application’s SKEY, should not be sent to support.
We’ve made collecting troubleshooting information easy with a script that gathers all the necessary files, scrubs them of sensitive information, and creates a zip package ready for you to send to Duo Support. The script is included in version 4.0.6 and later at C:\Program Files\Duo Security\WindowsLogon\Winlogon-Diag.ps1.
The support tool performs the following actions:
- Runs
Invoke-Webrequestto determine if a connection to Duo is available. - Creates a zip file that contains all of the collected information.
- Captures the following information:
- Installed version and if it is deployed with GPO configuration.
- Debug status.
- Host information to DuoSupport.log:
- Hostname
- Username
- Domain
- System/Browser proxy settings
- Operating system version, build and bit
- Bitlocker status
- AV product
- TPM availability
- Timezone
- Exports list of all credential providers and filter from registry to
credprov.txtin zip file. - Copies
C:\ProgramData\Duo Security\duo.logto zip file. - Exports Duo Registry keys from
HKLM\Software\Duo Security\DuoCredProvtoDuoSupport.login zip file (excluding your SKEY). - Exports Duo Offline Registry keys from
HKLM\Software\Duo Security\DuoCredProv\OfflinetoDuoSupport.login zip file. - Optional: Export Application and/or Security Event logs to zip file.
- Saves the zip file to the current CMD location or chosen directory as
DuoSupport-year-month-date-time.zip.- For example: On Windows, the support file would be
C:\SupportScript\DuoSupport2019-06-06-04-28-17.zip.
- For example: On Windows, the support file would be
Additional PowerShell command options
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| -duodebug | Default is off; $true only enables debug in registry; $false only disables debug in registry. |
| -out | Sets the preferred log path; defaults to Desktop if not set. |
| -eventlogs | Exports application and/or security logs. Options: all, application, security |
| -days | Defines a selected number of days to export from both Duo native logs and event logs. |
| -tls | Exports Client TLS settings from registry. |
Running the Support Tool
Here’s an example of how you can use the Support Tool. In this example, debug is enabled, and security event logs from the last two days are exported.
-
Open an administrative PowerShell command-line session on the system where Duo is installed.
-
Enable debug.
PS C:\>.\Winlogon-Diag.ps1 -duodebug $true -
Reproduce the Duo issue you are experiencing.
-
Run a script to export the logs:
PS C:\>.\Winlogon-Diag.ps1 -out C:\testing\ -eventlogs security -days 2 -
Disable debug:
PS C:\>.\Winlogon-Diag.ps1 -duodebug $false
Why am I unable to log in to Windows after installing Duo?
In order for the Duo service to properly authenticate a Windows user account, the username in Windows must match the username or a username alias in the Duo account. If you receive a message like «The Duo native Windows client does not currently support unknown users», «The username you have entered is not enrolled with Duo Security», or «Access is not allowed because you are not enrolled in Duo.», then the account you are using to log into Windows does not match an enrolled Duo user.
- Log in to the Duo Admin Panel and make sure that you’ve added a user with a username that matches the Windows username.
- You will also need to manually enroll this user’s phone number so that the user can receive passcodes or phone calls, which are needed in order to authenticate.
- Once the user’s phone number has been added you may optionally install and enroll the Duo Mobile smartphone app, which will enable the «push» functionality for an RDP login.
- Now try to log in to Windows again.
If you receive the message «Unknown devices are not permitted by your administrator» then a Duo policy may be restricting your Windows system or 2FA approval device.
Please review your global policy, as well as any policies associated with your «RDP» application in the Duo Admin Panel. Commonly, issues occur with application or global policies that restrict allowed authentication methods or restrict operating systems by blocking access from Windows or specific Windows versions.
Users receive the error «Logon failure: the user has not been granted the requested logon type at this computer» when attempting to log in.
This error may be seen in Duo Windows Logon version 1.1.5 or later. Ensure that the users have been delegated the «Allow log on locally» rights for console logins, or have been delegated both the «Allow log on locally» and «Allow log on through Remote Desktop Connection» rights in the computer’s local or domain-level security policy. Please see the Group Policy Settings Reference for Windows and Windows Server for more information about these user rights assignments.
When logging in via Remote Desktop, my authentication is accepted but the Remote Desktop session is disconnected. How do I fix this?
You can increase the logon timeout if extra time is needed to complete authentication (for example, if users must type in a hardware token passcode). Create a new registry DWORD value HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp\LogonTimeout and set it to a decimal value greater than 60. You may need to cycle the TermService service or restart Windows recognize the change.
To increase the Remote Desktop logon timeout for multiple computers joined to an Active Directory domain with Group Policy, add the HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp\LogonTimeout value to a GPO (Group Policy object) as a registry preference item. Please see «Configure a Registry Item» at the Microsoft TechNet site for more information.
Why is Passwordless OS Logon not restricted to only the groups I selected in the Passwordless configuration?
Group restrictions for Passwordless OS Logon were not supported in the 4.3.16 public preview release. Update to Duo for Windows Logon version 5.0.0 or later.
Additional Troubleshooting
Need more help? Try searching our Windows Logon Knowledge Base articles or Community discussions. For further assistance, contact Support.
Часто у наших клиентов (обычно это небольшие организации без собственной IT службы) возникает необходимость предоставить доступ к своему серверу терминалов (о настройке и обеспечении отказоустойчивости будет отдельная статья) через глобальную сеть Интернет. Мы конечно же советуем так не делать, а использовать для подключения VPN (рекомендуем любимый нами SoftEther VPN Server), но если уж клиент настаивает, то стараемся максимально его обезопасить. И вот как раз про средства, которыми мы этого достигаем и пойдет речь в этой статье…
Первая программа, о которой мы расскажем называется Cyberarms Intrusion Detection and Defense Software (IDDS).
К сожалению, судя по всему, разработка была прекращена в 2017-м году, но тем не менее программа (с некоторыми нюансами — о них далее) работает даже на ОС Windows Server 2019.
Принцип действия довольно таки простой, но в тоже время эффективный: после нескольких неудачных попыток ввода пароля(количество для блокировки определено в параметрах) срабатывает Soft lock(подозрение в брутфорсе), в журнале создается инцидент и IP помечается как подозрительный. Если новых попыток не последовало, то спустя 20 минут адрес убирается из списка наблюдаемых. Если же перебор паролей продолжается, то IP адрес «злоумышленника» добавляется в запрещающее подключения правило брандмауэра Windows (должен быть в активированном состоянии) и тем самым подбор пароля с этого адреса временно прекращается, так как подключения полностью блокируются. Блокировка Hard lock продлится 24 часа — такой параметр выставлен по умолчанию. Вечную блокировку,»Hard lock forever», включать не рекомендуем, иначе количество IP в правиле брандмауэра быстро «распухнет» и программа будет тормозить.
Устанавливается программа просто — скачиваем архив с установщиком, распаковываем во временную папку. Cкачиваем и устанавливаем Microsoft Visual C++ 2010 x64 (vcredist_x64.exe) и только после этого запускаем пакет установщика Windows —Cyberarms.IntrusionDetection.Setup.x64.msi, потому как у setup.exe скачать и установить автоматически Visual C++ не получается.
Далее производим настройку — активируем агент для защиты RDP сессий «TLS/SSL Security Agent«, во вкладке «AGENTS«:
Вторая программа — Duo Authentication for Windows Logon and RDP
это инструмент для мультифакторной аутентификации от Duo Security (Cisco), коммерческий многофункциональный продукт, который безупречно работает и позволяет использовать смартфоны, токены и коды для 2FA.
Настраивается ПО немного сложнее предыдущей программы, но благодаря хорошей документации от разработчика довольно таки быстро.
-
Зарегистрируйте себе административный аккаунт, для доступа к панели управления (Личный кабинет). Рекомендуем сразу добавить еще одного администратора, потому как восстановить доступ с помощью разработчика довольно таки проблематично, а прецеденты с неожиданной утратой смартфона администратора возникают часто.
-
Войдите в панель администратора Duo и перейдите в Приложения (Applications).
-
Нажмите «Защитить приложение» и найдите в списке приложений запись для Microsoft RDP. Щелкните Защитить в крайнем правом углу, чтобы настроить приложение и получить ключ интеграции, секретный ключ и имя хоста API. Эта информация понадобится вам для завершения настройки (в процессе установки Duo Authentication for Windows Logon).
Мы рекомендуем установить политики по умолчанию для новых пользователей приложения Microsoft RDP значение «Запрет доступа«, поскольку ни один незарегистрированный в Duo пользователь не должен успешно проходить авторизацию. Но для этого вам будет необходимо добавить всех пользователей в Duo через панель управления вручную или, что намного удобнее, через импорт из Active Directory (об этом расскажем позже) и выслать им ссылку для активации приложения Duo Security, предварительно установленному на их смартфонах.
4. Загрузите и установите пакет установщика Duo Authentication for Windows Logon. Во время установки введите данные, полученные на предыдущем шаге.
Если вы хотите включить автономный доступ с помощью Duo MFA, вы можете сделать это сейчас в разделе «Настройки автономного доступа» на странице приложения Duo или вернуться в панель администратора позже, чтобы настроить автономный доступ после первой проверки успешного входа в систему с помощью двух-факторной аутентификации.
Также во время установки рекомендуем установить все 3 галки в чекбоксах — эти настройки позволят вам получать доступ в ОС без 2FA, например при использовании консоли гипервизора или при отсутствии подключения к серверам Duo (частый случай — большое расхождение по времени):
не лишним будет напоминание о безопасном хранении всех ключей:
Treat your secret key like a passwordThe security of your Duo application is tied to the security of your secret key (skey). Secure it as you would any sensitive credential. Don’t share it with unauthorized individuals or email it to anyone under any circumstances!
После установки Duo Authentication for Windows Logon можно добавить пользователя (своего, без привилегий администратора) и активировать приложение на смартфоне. Для этого переходим в раздел Users, жмем Add User — заполняем необходимые поля. Далее добавляем пользователю телефон (раздел Phones — Add Phone) и активируем Duo Moibile (ссылку для активации пользователю можно отправить SMS, если есть деньги на балансе или вручную через Email или другим удобным способом).
Теперь при подключении и успешной авторизации (по логину и паролю) пользователю будет отправлено Push уведомление на смартфон с активированным приложением Duo Mobile:
Если на смартфоне нет доступа в Интернет (и соответственно Push приходить не будут), то можно подтвердить авторизацию сгенерированным кодом (Passcode ) из приложения:
Настройка синхронизации пользователей с глобальным каталогом (Azure AD — Active Directory — LDAP) хорошо описана в документации разработчика, хочу лишь уточнить что это платный функционал. Основной компонент для синхронизации пользователей, это Duo Authentication Proxy — ПО, которое обеспечивает подключение к каталогу.
Если вы используете RDWEb (клиентский доступ или шлюз), то вам пригодится еще один компонент — Duo Authentication for Microsoft Remote Desktop Web. Настройка его аналогична Duo Authentication for Windows Logon и не должна вызвать затруднений.
Подводя итоги заметим, что рассмотренное ПО не является панацеей от всех бед для публичных сервисов (доступных из сети Интернет), потому как бывают уязвимости, эксплуатация которых позволяет злоумшленникам обходить даже такие меры по обеспечению безопасности ОС\инфраструктуры в целом. Поэтому требуется всегда комплесно подходить к этому вопросу — мониторинг, аудит и регламентные процедуры по обновлению позволят вам почувствовать себя защищенными в этом неспокойном мире. Берегите свои данные!
Только зарегистрированные пользователи могут участвовать в опросе. Войдите, пожалуйста.
Используете ли вы в своей инфраструктуре сервер терминалов?
58.43% Да, подключение к рдп исключительно через VPN52
35.96% Да, сервер терминалов доступен напрямую из Интернета32
Проголосовали 89 пользователей. Воздержались 17 пользователей.
Two-factor authentication is currently one of the best security practices for protecting users, data and systems. Duo is one of the leading platforms for using two-factor authentication in the enterprise as it protects many common on-premises and cloud applications by default.
For on-premises authentication, Active Directory is still king and Duo integrates seamlessly on Windows to protect unauthorized logins to console and RDP sessions. To do this, Duo has a Windows software client to install which provides secondary authentication to Duo after the initial authentication to Active Directory.
In this article, I’ll demonstrate some of the steps to setting up Duo for two-factor authentication on Windows.
Duo Admin Console
The first step is to create a new application in the Duo admin console to protect. The main purpose of this is to create an integration key, create a secret key, and obtain an API hostname. These are used in the Duo client software later on.
This page also gives you options to create user policies. For instance, you can set the username normalization policy so that DOMAIN\Username, username@domain, and username are all treated the same when logging into Windows with the Duo client software installed. Keep in mind that users must have the exact same username in Duo and in Active Directory for two-factor authentication to work correctly.
If the licensed being used allows, you can also configure only certain groups to authenticate to this application.
Run the Duo Windows Installer
When running the installer for Duo authentication for Windows, the first thing you will be prompted for is the API hostname, which is obtained on the application page from the previous section.
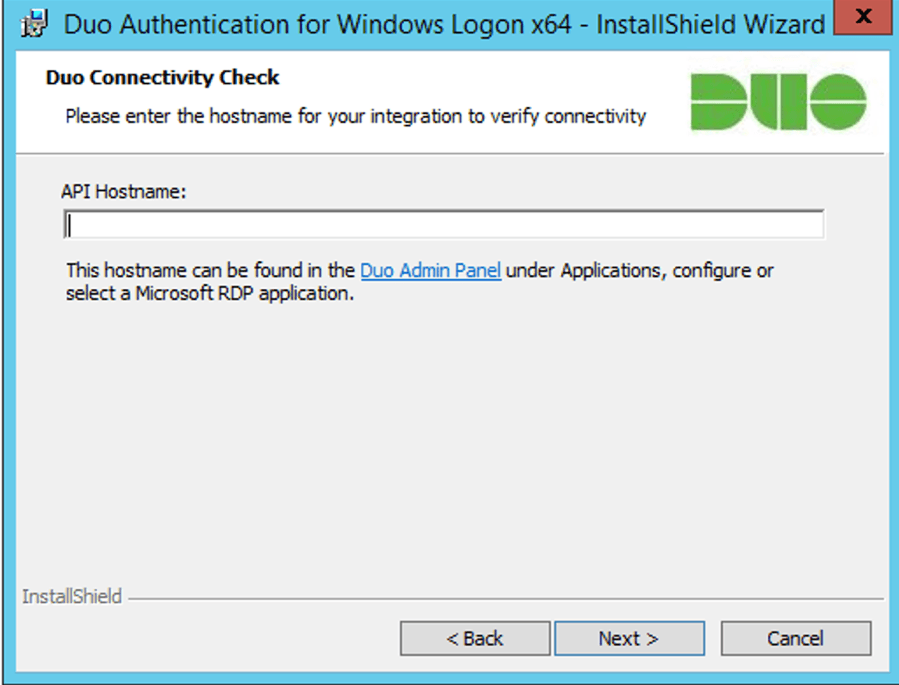
Next you will need to input the integration and secret keys from the previous section as well.
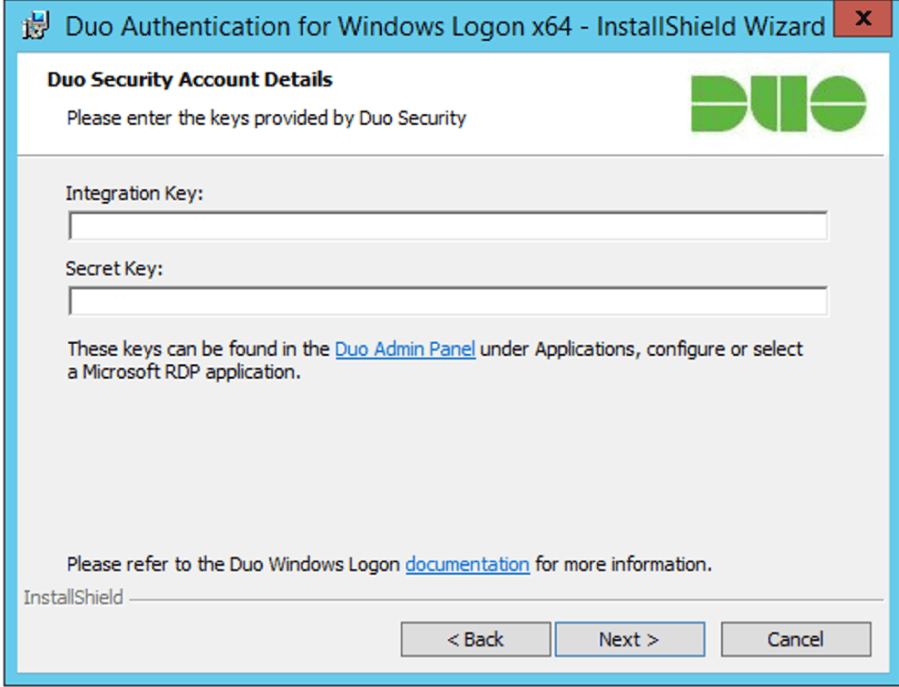
Finally, additional options can be used for the client software such as:
• Bypass Duo authentication when offline (FailOpen)
• Use auto push to authenticate if available
• Only prompt for Duo authentication when logging in via RDP
• Enable Smart card support
Testing the Windows Login
Now it’s time to test out Duo on a Windows machine. I log-in as usual to my workstation (I could also use RDP), but after I enter my username I am prompted with the following message:
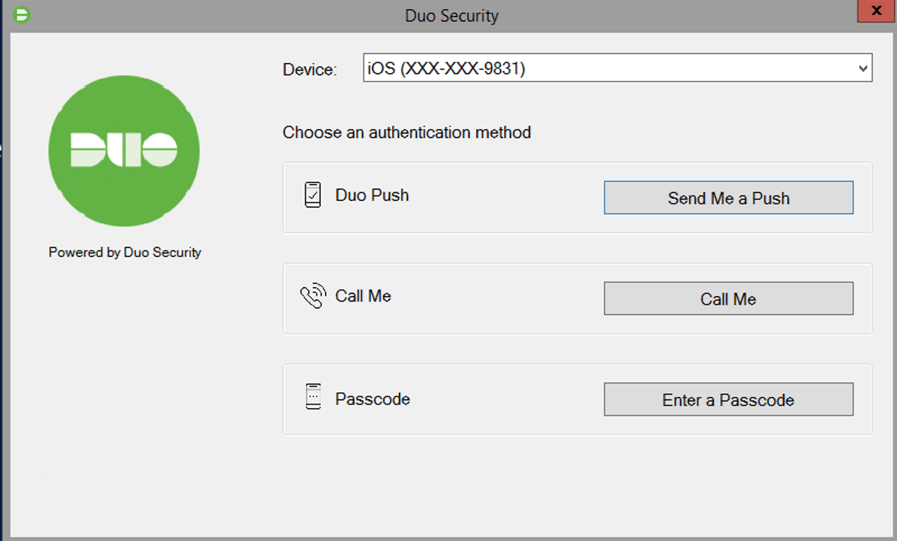
Depending on the Duo policies configured, a user can send a Duo push, call or enter a passcode in order to perform the secondary authentication for two-factor authentication.
A Duo push, means that a prompt will be send to accept on a mobile device configured for Duo, such as an iPhone. The “Call Me” option means that a number will be called by Duo, and the user will need to accept the call and press a key. The “Passcode” option is for when an authenticator app like Duo provides a temporary passcode for the user to enter.
Although there have been increases in hacking two-factor authentication, enabling this in an enterprise still provides a great layer of protection in the security scheme. Using Duo makes 2FA deployment in Windows a manageable task due to its integration with so many applications and platforms.
Why 2FA is needed for windows logon?
Today, there are a lot of cyber-attack attempts and threats from hackers. Most businesses use computers for their work and it is critical to keep your computers and data safe. You can add a duo security product for computer logon as a second-factor authentication. With this, even if your computer login credentials are compromised, you can still keep your data safe since hackers should go over one more security layer which is your duo 2FA.
Duo Authentication for Windows Logon adds Duo two-factor authentication to Windows desktop and server logins, both at the local console and incoming Remote Desktop (RDP) connections. Starting with version 4.1.0, you can optionally require two-factor authentication for credentialed User Access Control (UAC) elevation requests (e.g. Right-click + “Run as administrator”), depending on your organization’s Windows UAC configuration.
How to install and activate the Duo Authentication
1. Make sure your workstation matches the system requirements shown below
System Requirements
Duo Authentication for Windows Logon supports both client and server operating systems.
Clients:
- Windows 8.1
- Windows 10 (as of v1.1.8)
Servers (GUI and core installs):
- Windows Server 2012
- Windows Server 2012 R2
- Windows Server 2016 (as of v2.1.0)
- Windows Server 2019 (as of v4.0.0)
Ensure your system’s time is correct before installing Duo.
2. If you already have duo product, proceed to step 3. If not, follow the instruction here.
3. Click here to download the Duo Authentication for Windows Logon installer package.
If your workstation belongs to your company domain, it will request elevated permission for downloading. Please contact your IT department.
4. Sign in to the duo security admin portal, then go to Applications -> Protect an Application -> Search for RDP -> Click Protect for Microsoft RDP.
5. Go to Applications -> Microsoft RDP.
These details will be used when we configure the Duo Authentication for Windows Logon installer.

6. Run the Duo Authentication for Windows Logon installer package downloaded on step 3.
a. Click on Next.
b. Copy API Hostname shown on step 5 and paste it in, then click Next.

c. Copy Integration Key & Secret Key shown on step 5 and paste it in, then click Next.

d. Keep the settings as default and click Next.
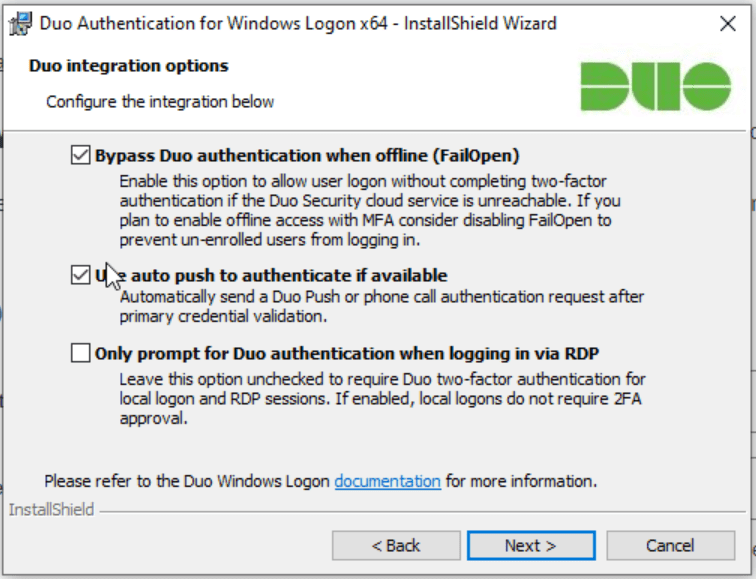
e. Keep the settings as default and click Next.

f. Keep the settings as default and click Next.

What is Password Protected UAC prompt?
When a user tries to do tasks that only system administrators are allowed to do, Windows will require an administrative account credential for security purposes. If you want to enable the duo two-factor authentication for password-protected UAC (User Access Control) prompts, click on Enable UAC Elevation Protection.
Verify the Duo 2FA for Windows Logon and RDP
1. Sign out from Windows and try signing in. You will get this prompt when signing in.

2. You will get a login request on your phone. Click on Approve.
You are now good to go!
Troubleshooting
Why do I not get notifications on the duo mobile app when signing in?
Make sure you have installed the duo mobile app on your phone first. You can simply go to App Store or Google Play Store, search for Duo Mobile, and install the software. If you already installed the software, but you still don’t get the notification, you should check the 2FA device on the duo security admin portal.
Go to 2FA devices -> Your device -> Device Info

This problem is mostly caused since you didn’t activate duo mobile from device info. Try it out after activating the duo mobile. If it still doesn’t work, please visit here for more information.
Why can’t I sign in and get this error message?
If you are not able to sign in and get the error message shown below, you probably didn’t add an alias for username on the duo security admin portal.

Go to Users -> Your name -> Username Aliases, then add your computer login username there.
For more information please contact us
Phone: (604) 757-9823
Email: [email protected]
You might be also interested in this article:
Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication