This guide provides a step-by-step process for installing and dual booting Arch Linux alongside Windows 10 or Windows 11.
Table of Contents
- Preparation
- Installation Process
- Fixing Windows Boot Menu Entry
- Additional Resources
- Author
Preparation:
I. Download Files:
- Download the latest Arch Linux ISO file from the official website.
- Download a tool like Rufus to create a bootable USB drive.
II. Create a Bootable USB Drive:
- Insert a USB drive with at least 8GB of space.
- Open Rufus and select the downloaded Arch Linux ISO file.
- Partition scheme:
- UEFI System: Select GPT partition scheme.
- Legacy System: Select MBR partition scheme.
- Leave the rest of the settings as default and click on «Start».
III. Prepare Windows Partition:
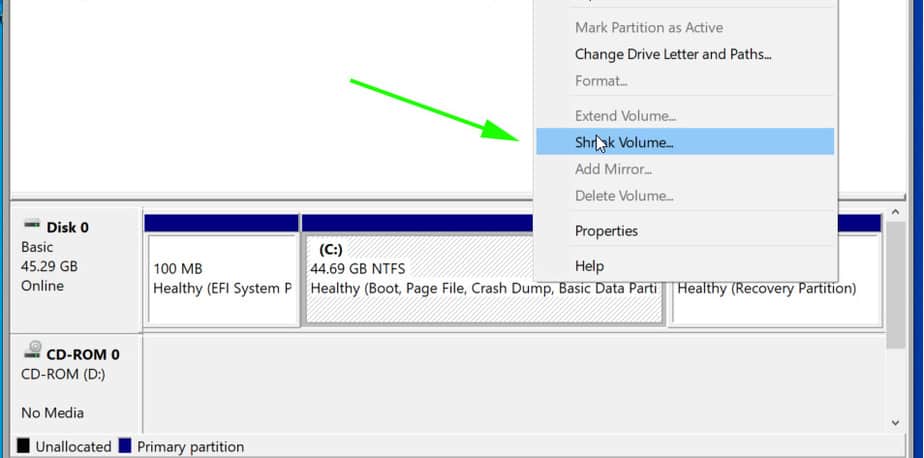
- Right-click on the Start menu and select «Disk Management».
- Locate your main Windows partition (usually the largest disk).
- Right-click on the partition and select «Shrink Volume».
- Allocate at least 40GB of free space for Arch Linux.
Installation Process:
I. Boot into Arch Linux:
- Restart your system and press the key to enter the boot menu (usually F12 or Escape).
- Select your USB drive to boot into Arch Linux.
- Disable Secure Boot (if applicable):
- If your system has Secure Boot enabled, you’ll need to disable it from the BIOS settings to boot Arch Linux successfully.
II. Connect to Wi-Fi (if applicable):
- Use the
iwctlcommand to list available Wi-Fi networks and connect to your desired network.
iwctl
# Scan for networks:
iwctl scan
# Connect to a network:
iwctl station <interface_name> connect <network_name>
# Enter password:
iwctl station <interface_name> set-key <password>
# Verify connection:
ping -c 2 google.com
III. Partitioning the Disk:
- List your disk partitions using:
lsblk- Identify your main disk (e.g.,
/dev/sda).
- Identify your main disk (e.g.,
- Use cfdisk to create partitions:
sudo cfdisk /dev/<your_main_disk_number> - Create the following partitions:
- EFI Partition (UEFI only): Size: 300MB, Type: EFI System
- Swap Partition: Size: Equal to your RAM size, Type: Linux swap
- Root Partition: Remaining free space, Type: Linux file system
- Write the changes made to the partitions.
IV. Formatting Partitions:
- Format the EFI partition (UEFI only):
mkfs.fat -F32 /dev/<efi_partition_name> - Format the root partition:
mkfs.ext4 /dev/<root_partition_name> - Format the swap partition:
mkswap /dev/<swap_partition_name>
V. Mounting Partitions:
- Mount the root partition:
mount /dev/<root_partition_name> /mnt - Mount the EFI partition (UEFI only):
mount /dev/<efi_partition_name> /boot/efi
VI. Installing Base System Packages:
- Install essential packages:
pacman -S base base-devel linux linux-headers linux-firmware nano networkmanager networkmanager-applet wireless-tools bluez bluez-utils git
VII. Generating fstab File:
- Generate the fstab file:
genfstab /mnt >> /mnt/etc/fstab
VIII. Entering the Installed System:
- Enter the installed system:
arch-chroot /mnt
IX. Configuring Time Zone and Locale:
- Set the time zone:
ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/<your_region>/<your_city> /etc/localtime
- Synchronize system time:
hwclock --systohc - Configure locale:
- Uncomment your desired language in
/etc/locale.gen. - Generate the locale file:
locale-gen - Set hostname:
echo "<your_hostname>" > /etc/hostname - Edit the
/etc/hostsfile usingnano.
- Uncomment your desired language in
X. Creating Username and Password:
- Set root password:
passwd - Add a new user:
useradd -m <username> - Set password for the new user:
passwd <username> - Add the user to the wheel group for administrative privileges:
usermod -aG wheel <username>
XI. Enabling sudo Privileges:
- Edit the
/etc/sudoersfile using nano and uncomment the line:wheel ALL=(ALL) ALL
XII. Installing Bootloader:
- Install bootloader and additional packages:
pacman -S grub os-prober ntfs-3g - Identify your main disk number using
lsblk. - Install grub on a UEFI system:
- If you encounter an error, install
efibootmgrusingpacman -S efibootmgrand rerun the previous command.
- If you encounter an error, install
grub-install --target=x86_64-efi --efi-directory=/boot --bootloader-id=grub
- Install grub on a legacy system:
grub-install --target=i386-pc /dev/<your_main_disk_number>
XIII. Generating Grub Configuration File:
- Generate the grub configuration file:
grub-mkconfig -o /boot/grub/grub.cfg
XIV. Installing Display and Audio Drivers:
- Install video and audio drivers:
pacman -S xfce4 xfce4-goodies - For Nvidia graphics cards, additionally install:
pacman -S nvidia nvidia-utils nvidia-settings
XV. Enabling Services at Startup:
- Enable network manager and bluetooth services:
systemctl enable networkmanager bluetooth
XVI. Installing Desktop Environment:
- Choose and install your preferred desktop environment:
- Gnome:
pacman -S gnome - KDE:
pacman -S plasma kde-applications - XFCE:
pacman -S xfce4 xfce4-goodies
- Gnome:
XVII. Enabling Display Manager:
- Enable the display manager corresponding to your desktop environment:
- Gnome:
systemctl enable gdm - KDE:
systemctl enable sddm - XFCE:
systemctl enable lightdm- If lightdm is not installed, install it using:
pacman -S lightdm lightdm-gtk-greeter - Enable it:
systemctl enable lightdm
- If lightdm is not installed, install it using:
- Gnome:
XVIII. Exiting and Rebooting:
- Exit the chroot environment:
exit - Reboot the system:
reboot
Fixing Windows Boot Menu Entry (if not appearing):
I. Boot into Arch Linux.
II. Identify Windows Partition: lsblk
III. Mount Windows Partition:
mount /dev/<windows_partition_name> /mnt/windows
IV. Edit /etc/default/grub:
- Edit the file using nano.
- Uncomment the line:
GRUB_DISABLE_OS_PROBER
V. Regenerate Grub Configuration:
grub-mkconfig -o /boot/grub/grub.cfg
VI. Reboot the system.
Additional Resources
Official Arch Linux Resources:
-
Arch Linux Wiki: The official Arch Linux Wiki is an incredibly comprehensive resource for all things Arch, including detailed installation guides, troubleshooting tips, and configuration options: wiki.archlinux.org.
-
Arch Linux Forums: The Arch Linux forums are a vibrant community where you can ask questions, get help from experienced users, and stay updated on the latest developments: bbs.archlinux.org.
Additional Tutorials and Guides:
- Video Tutorials: Many excellent video tutorials exist online that provide visual guidance through the installation process. Search for «Arch Linux dual boot Windows 10/11» on platforms like YouTube to find helpful resources.
- I recommend this awesome video by Sandip Sky.
Troubleshooting and Support:
-
Reddit Community: The r/archlinux subreddit is a great place to find answers to common problems, share experiences, and connect with other Arch Linux users: reddit.com/r/archlinux.
-
Comments in this Gist: Feel free to leave comments directly in this Gist if you have any questions or encounter specific difficulties.
-
Contact Me: Feel free to contact me directly through X.
Author
Yousef Saeed:
GitHub
LinkedIn
X
Инструкция для новичков, о том, как сделать красивый dualboot windows и archlinux (и других ОС) через efi без grub и лишних заморочек.
Фото для привлечения внимания:

Можете посмотерть в google как это ещё может выглядеть.
Сразу оговорюсь.
Предполагается, что вы уже поставили windows и archlinux, понимаете как размечать диски и что куда монтировать и осталось вам только разобраться с загрузчиком. Если нет, то рекомендую посмотреть для начала вот это видео.
Я пробовал различные варианты, как описано тут, тут и тут и прочие выкрутасы с efibootmgr. Пытался добавлять опции прямо в «BIOSе» — ничего хорошего у меня не получилось, то рут раздел не находит то ещё что-то. Да и сам подход к переключению систем (жать Esc при включении ПК для выбора системы) меня не очень радовал.
Провозившись весь выходной, нашёл для себя простое и элегантное решение — пакет refind-efi (ArchWiki).
Если коротко, — достаточно установить этот пакет (pacman -S refind-efi) и выполнить refind-install, — всё.
В /boot/efi/EFI/ будет создан каталог refind и в опции загрузки добавлен новый пунк «rEFInd boot manager ».
Предупреждение
CodeRush в комментарии добавил важное замечание:
Добавлю к этой статье предупреждение: запись в NVRAM из ОС — достаточно опасная операция, которая может приводить к «кирпичу» на некоторых моделях ноутбуков с BIOSами на платформе Phoenix SCT. У автора BIOS на платформе AMI Aptio, с ним таких проблем нет.
Именно поэтому я настоятельно не рекомендую использовать на ноутбуках как саму efibootmgr, так и все, что ее вызывает, и устанавливать любые загрузчики вручную, либо заменяя имеющийся загрузчик по умолчанию (fs0:/EFI/BOOT/bootx64.efi), либо прописывая новый загрузчик из UEFI Shell командой bсfg boot add 0 fs0:/path/to/bootloader.efi «My Fancy Bootloader» — это намного безопаснее.
Всё что вы делаете, вы делаете на свой страх и риск!
Теперь подробнее об установке и конфигурировании
Для начала сверим конфигурации.
В моём случае это:
- Windows 8.1
- Arch Linux x86_64 Kernel Release: 3.14.4-1-ARCH
Вывод lsblk:
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sda 8:0 0 119.2G 0 disk
├─sda1 8:1 0 300M 0 part
├─sda2 8:2 0 100M 0 part /boot/efi
├─sda3 8:3 0 128M 0 part
├─sda4 8:4 0 59.1G 0 part
├─sda5 8:5 0 9G 0 part /
└─sda6 8:6 0 50G 0 part /home
fdisk /dev/sda
Device Start End Size Type
/dev/sda1 2048 616447 300M Windows recovery environment
/dev/sda2 616448 821247 100M EFI System
/dev/sda3 821248 1083391 128M Microsoft reserved
/dev/sda4 1083392 125036543 59.1G Microsoft basic data
/dev/sda5 125036544 143910911 9G Linux filesystem
/dev/sda6 143910912 248768511 50G Linux filesystem
Раздел с типом «EFI System» созданный инсталятором windows, монтируем в /boot/efi/ ( /mnt/boot/efi/ ведь мы загрузились с liveiso верно?)
mkdir -p /mnt/boot/efi
mount /dev/sdaX /mnt/boot/efi
где X это номер вашего EFI раздела ( например mount /dev/sda2 /mnt/boot/efi ).
Далее перейдя в уже установленный arch ( arch-chroot /mnt/ ) устанавливаем сам refind:
pacman -S refind-efi
Если вдруг такой пакет не найден, поищите в yaourt:
yaourt refind
1 extra/refind-efi 0.7.9-1 [installed]
Rod Smith's fork of rEFIt UEFI Boot Manager - built with Tianocore UDK libs
refind-install
и если не было ошибок
reboot
После перезагрузки можно поставить в «биосе» в настройках приоритета загрузки «rEFInd boot manager » на первое место.

И не забудьте отключить «Secure Boot».
Profit!
В каталоге /boot/efi/EFI создана дирректория refind. В ней есть refind.conf в котором можно установить время отображения списка ОС и настроить внешний вид.
Refind сам находит установленные ОС и определяет параметры их загрузки. Так же мне очень понравилось что если вставлена загрузочная флешка или диск они тоже появляются в списке.
Мне понравилась тема Next-Theme (вы можете подобрать что-то на свой вкус), положил её в /boot/efi/EFI/refind/next-theme и прописал в конфиге:
icons_dir next-theme/icons
banner next-theme/background_1200.pngКонфиг хорошо документирован и вопросов вызывать не должен.
Буду благодарен за замечания и дополнения.
In this guide, you will learn how to Dual boot Arch Linux with Windows 10 on UEFI system. This guide assumes that you already have Windows 10 installed on your system.
Prerequisites
Before you begin configuring the dual-boot setup, ensure that the following requirements are met:
- A bootable installation medium of Arch Linux (Either USB or DVD). To download the latest Arch Linux ISO, proceed to the official Arch Linux download page. Once you have downloaded the ISO image, grab an 8GB USB drive and make it bootable using Rufus tool or any other application that can create a bootable USB drive.
- A fast and stable internet connection for downloading and installing software packages.
Step 1) Create a separate partition for installation of Arch Linux
For the dual boot setup to work, we need to create a separate partition on the hard drive on which Arch Linux will be installed. To do so, head over to the disk management utility by pressing Windows Key + R. In the dialogue box, type diskmgmt.msc and hit ENTER.
This launches the disk management utility displaying the various disk partitions on your hard drive. We are going to create an unallocated partition by shrinking the C drive. If you have a bigger partition than the C drive, feel free to use it for creating the separate partition,
So, we are going to right-click on drive C and select the ‘Shrink Volume’ option as shown
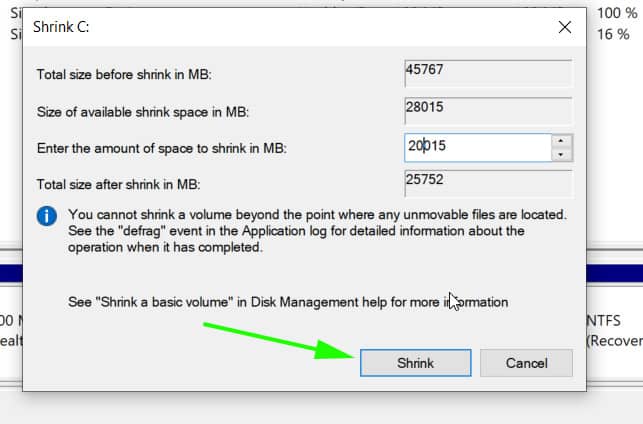
On the pop-up dialogue box that appears, we are going to specify the amount to shrink as shown. This is the amount that will be designated for the installation of Arch Linux. In our example, we have shrunk 20 GB of hard disk space will serve as the unallocated space.
Once you are satisfied, click on the ‘Shrink’ button.
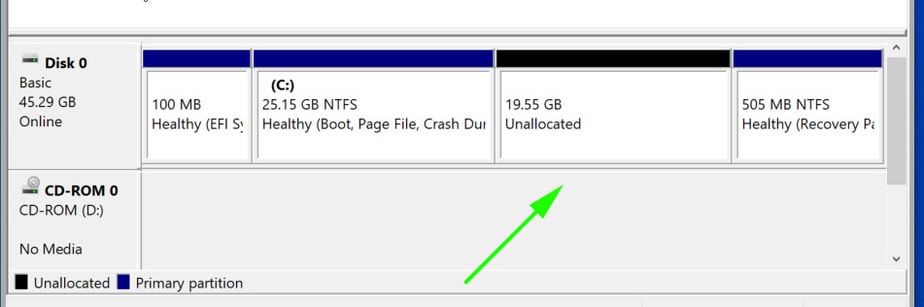
Your unallocated space will be indicated as shown below. In our case, we have set aside approximately 20G for the installation of Arch Linux.
With the unallocated partition in place, plug in your bootable USB and reboot your PC.
Step 2) Configure BIOS to boot from bootable medium
Before you begin with the installation process, it’s prudent to set the boot priority in the BIOS to select your bootable medium as the most preferred option. Depending on your vendor, you can press the Esc, or F10 key to enter the BIOS and navigate to the boot priority Menu.
Also note that we are using the UEFI mode for installation.
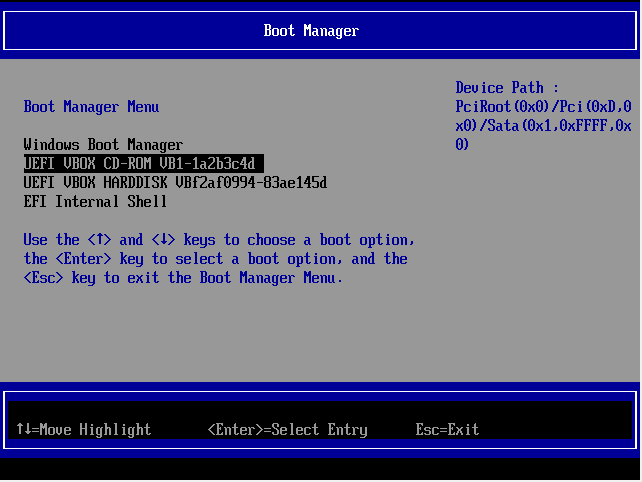
Once you have selected your boot medium, press the ESC button to continue with the booting process.
Step 3) Begin the installation of Arch Linux
On the bootup screen, you will be presented with options as shown below. Select the first option – Arch Linux install medium (x86_64, UEFI) and hit ENTER.
This initialize Arch Linux as evidenced by the boot messages on the screen.
After a few seconds, this ushers you to the prompt as shown below.
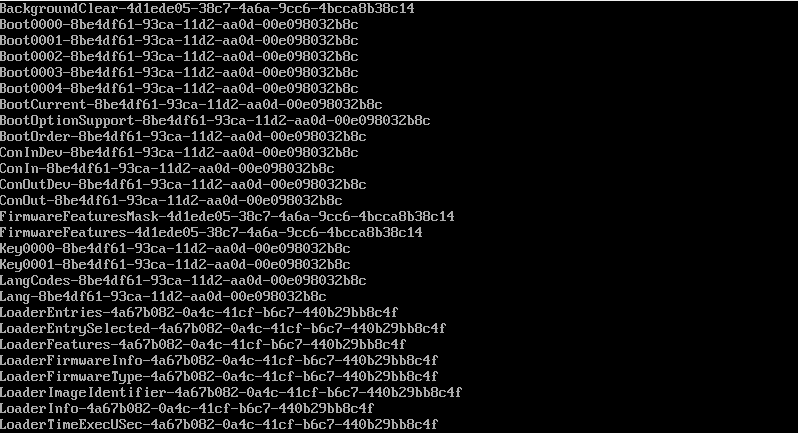
To confirm that you have EFI support, run the command:
# ls /sys/firmware/efi/efivars
You should get some entries on the screen as shown. If nothing is listed on your screen, then it means you are using MBR and this guide won’t work for you in configuring up a dual boot setup.
As you begin the installation, you might want to ensure that you have internet connectivity. Internet connectivity is crucial in setting time and date.
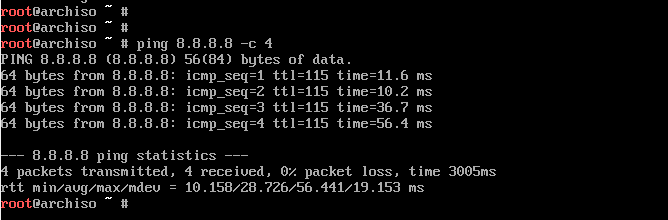
You can ping Google’s DNS as shown:
# ping 8.8.8.8 -c 4
You should get a positive reply as shown.
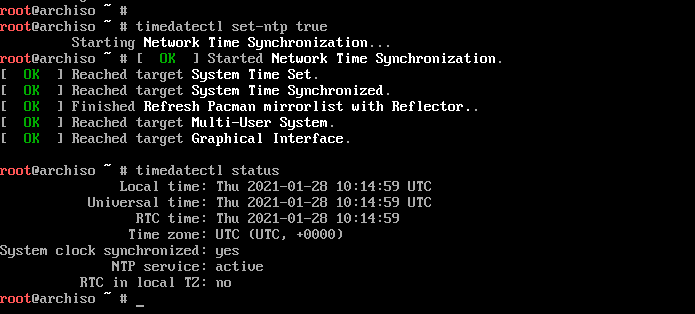
Step 4) Update time and date
Next, we are going to update the system time and date using the timedatectl command as shown.
# timedatectl set-ntp true
You can thereafter confirm the time and date using the command
# timedatectl status
Step 5) Create & format Linux partitions
Next, we are going to partition our hard drive and create some Linux partitions. An easy way of doing this is using the cfdisk utility. Run the command:
# cfdisk
This displays all the partitions available including Windows partitions.
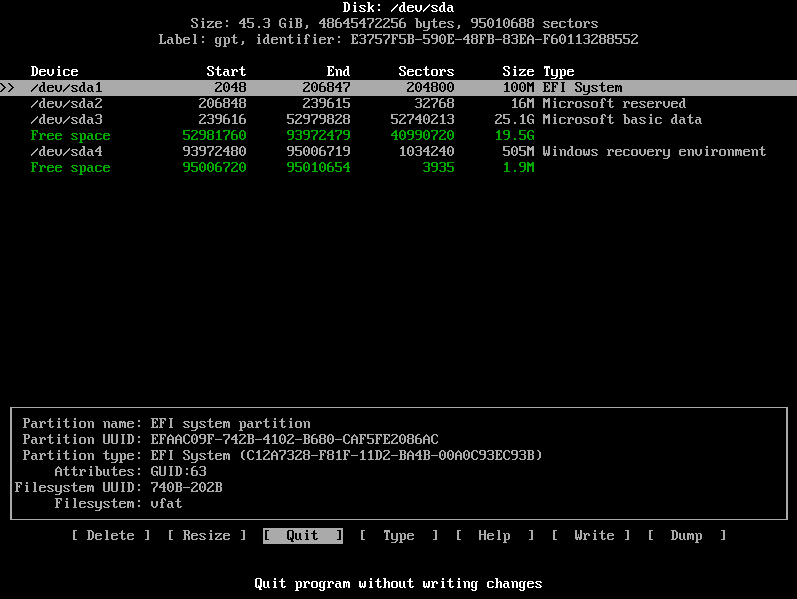
As you can see, we have some free space of 19.5G that we created earlier in step 1 from shrinking drive C on the Windows side. Using this partition, we shall create the following Linux partitions :
- Root partition / 12G
- swap partition 4G
To achieve this, we will navigate to the free space with 19.5G just after /dev/sda3 volume and hit ENTER. We will then specify the volume as 12G for the root partition as shown below. Then hit ENTER.
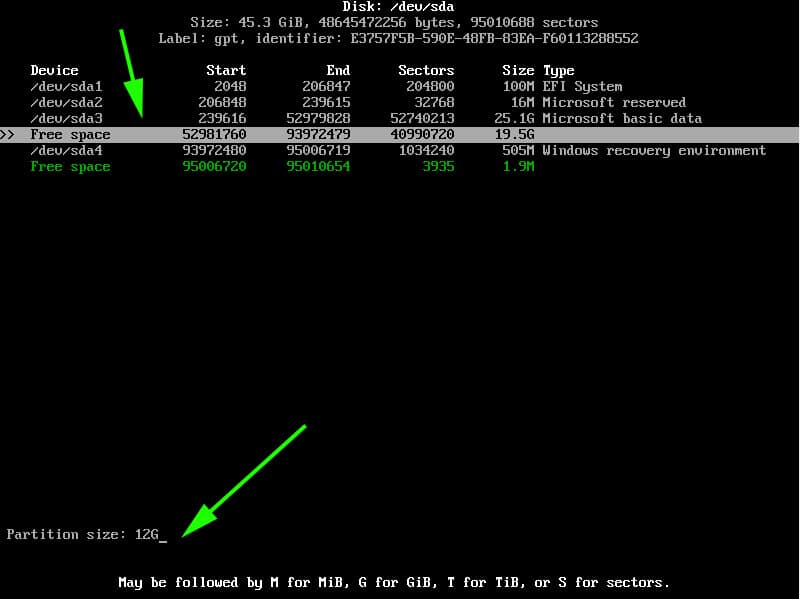
The root partition will be created with the Linux filesystem type as shown.
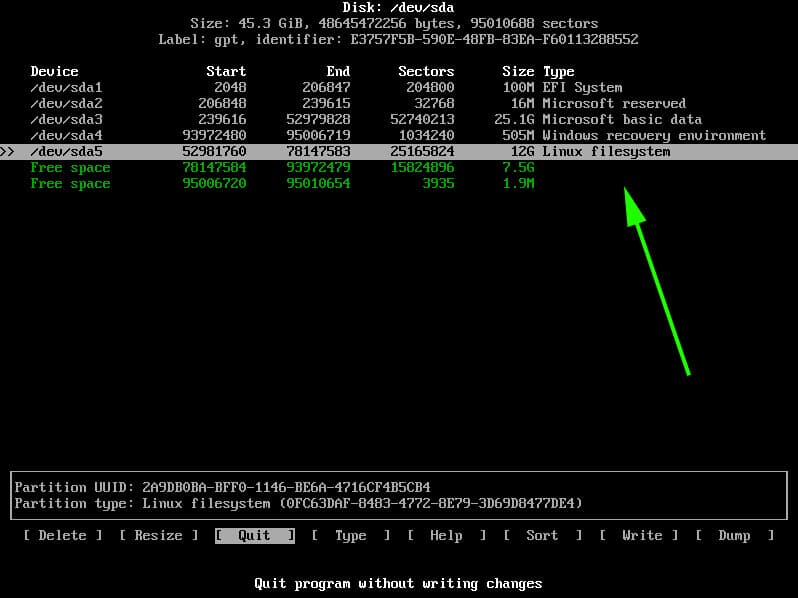
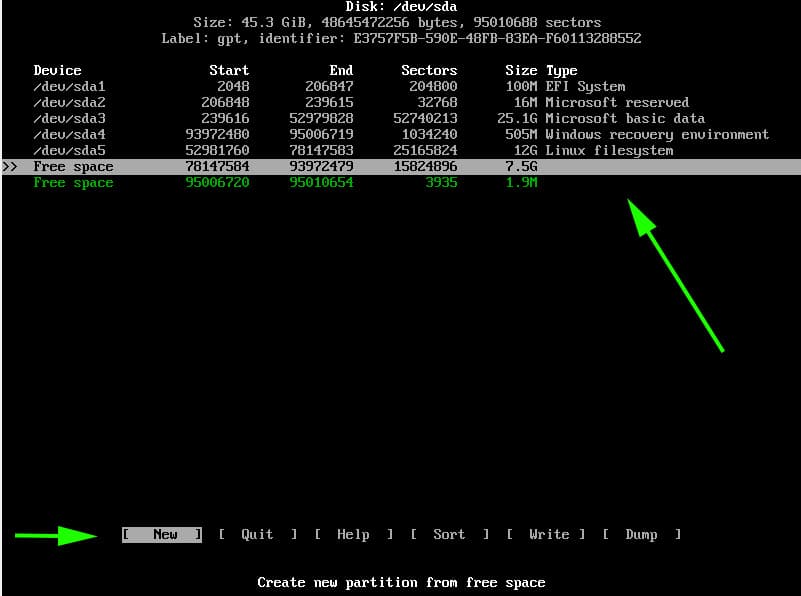
Next, we will create another partition for swap. Using the same method, we will proceed to the remaining free partition of 7G and select the ‘New’ option.
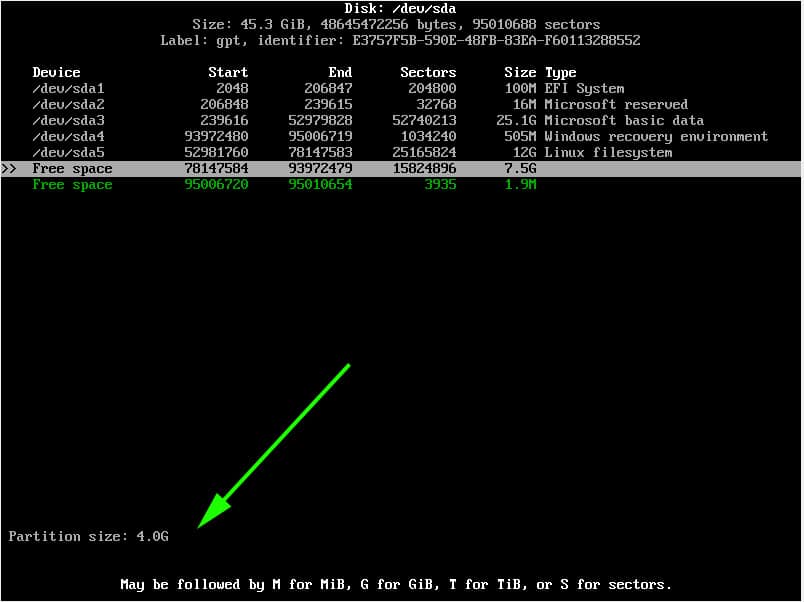
Specify the partition size as 4G
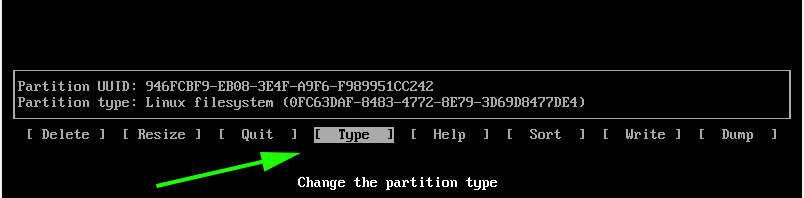
Since this will be our swap partition, we need to go the extra step and modify the partition type. Therefore, we will select the ‘type’ option and hit ENTER.
In the list that appears, select ‘Linux Swap’ and hit ENTER.
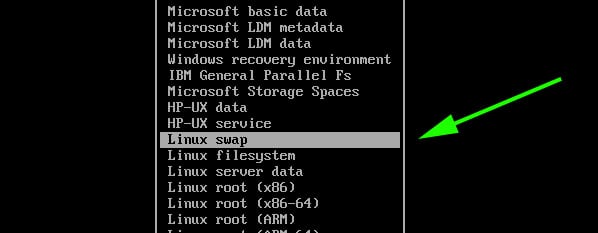
At this point, both the root and Linux swap partitions are created as seen from the partition table below.
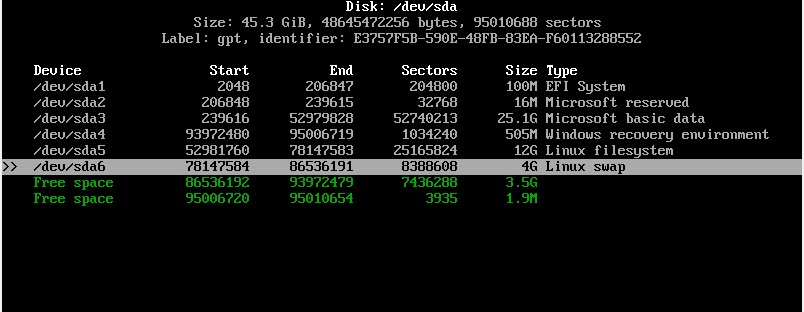
To save the partitions, select the ‘Write’ option and hit ENTER.
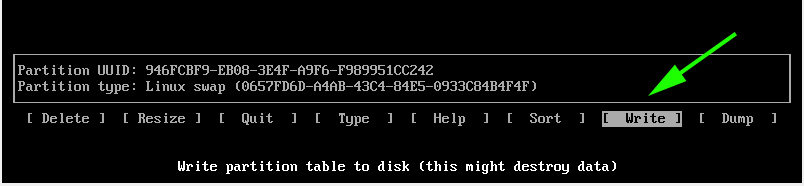
When prompted if you want to write the partition to disk, simply type ‘yes’ and hit ENTER.
To exit cfdisk utility, select the ‘Quit’ option and hit ENTER.
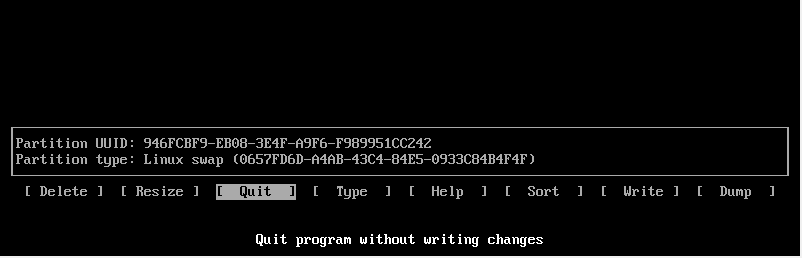
Step 6) Format and mount the partitions
For the partitions to become usable and available for use, we need to format them and later mount them.
To format the root partition, run the command:
# mkfs.ext4 /dev/sda5
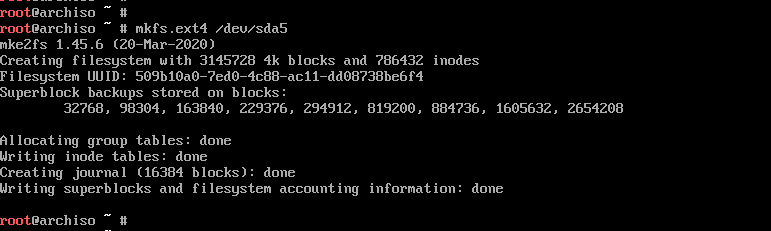
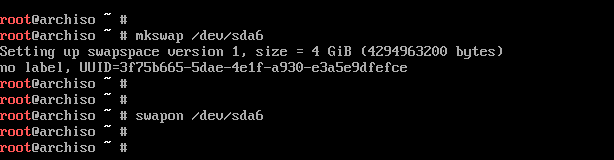
For swap partition, use the command:
# mkswap /dev/sda6
Then enable swap using the swapon command shown:
# swapon /dev/sda6
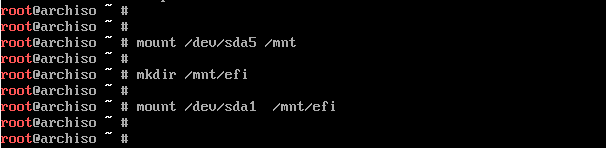
Next, mount the root partition to the /mnt directory
# mount /dev/sda5 /mnt
Additionally, we are going to create a directory for the EFI partition on which we will mount the Windows EFI system which , in our case is located on the /dev/sda1 partition.
# mkdir /mnt/efi
Then mount the EFI partition on the EFI mount point.
# mount /dev/sda1 /mnt/efi
Step 7) Install base system and other required Linux firmware packages
Next, we are going to install the central packages for our Linux system including the base and Linux-firmware packages.
# pacstrap /mnt base linux linux-firmware
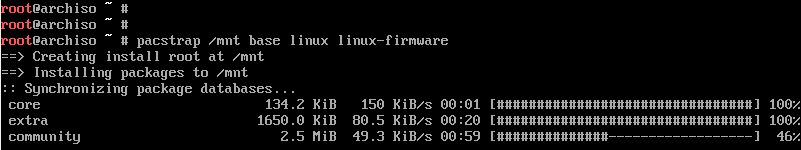
This is going to take quite some time. At this point, you can take a much-deserved break and head out for a stroll and grab some coffee. When the installation is successful, you should get the following output.
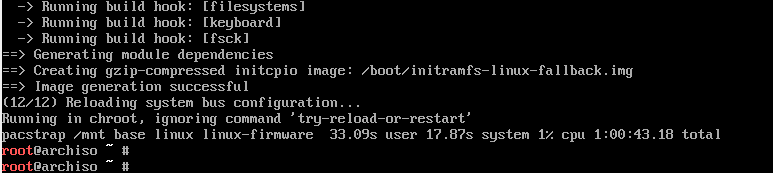
Step  Generate fstab file
Generate fstab file
The next step will be to generate the fstab file on the /mnt directory as follows.
# genfstab -U /mnt >> /mnt/etc/fstab
Step 9) Setup timezone
After generating the ftab file, navigate to the newly created root filesystem
# arch-chroot /mnt
You can verify that you are in the root filesystem using the command as shown.
# ls
Time zone information is found in the /usr/share/zoneinfo/ directory. To set your timezone, create a symbolic link to the /etc/localtime
Path.
# ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/US/Pacific /etc/localtime
Next, sync the hardware clock using the command:
# hwclock --systohc
Step 10) Set up locale
The locale determines the system language, currency format, numbering and date on your system. This information is contained in the /etc/locale.gen file. So, open the file using the vim editor.
# vim /etc/locale.gen
NOTE: To install the vim editor, use the pacman command as follows:
# pacman -Sy vim
Once you have accessed the file, scroll and uncomment your preferred locale. In this case, we have decided to go with en_US.UTF-8 UTF-8
Save and exit the file. Next generate the locale configuration using the command.
# locale-gen
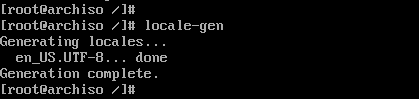
Next, create a new locale configuration file and save the locale as shown.
# echo "LANG=EN_US.UTF-8" > /etc/locale.conf
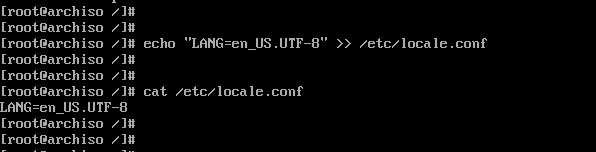
Step 11) Set up hostname
Next, we are going to configure the hostname of our Arch System. First, create a new file and specify the hostname as shown.
# echo linuxtechi > /etc/hostname
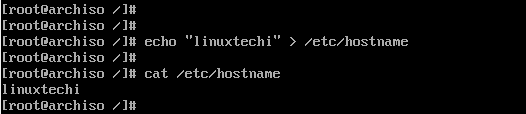
Afterwards, modify the /etc/hosts file as follows.
# echo "127.0.1.1 linuxtechi" >> /etc/hosts
Step 12) Install netctl Network Manager
To use the internet once the installation is complete and upon a reboot, we need to install a network manager. In this example we wil install the netctl network manager as follows
# pacman -Sy netctl
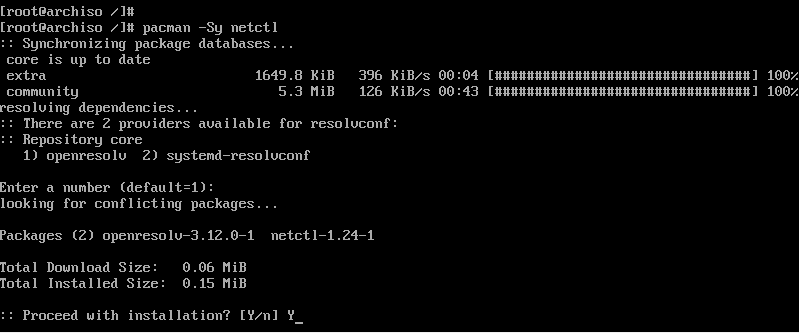
During the installation some optional dependencies for netctl are listed. We are going to install the following dependencies. These are:
- dhcpcd – For DHCP support
- wpa-supplicant – For wireless networking
- ifplugd – For wired connections networking
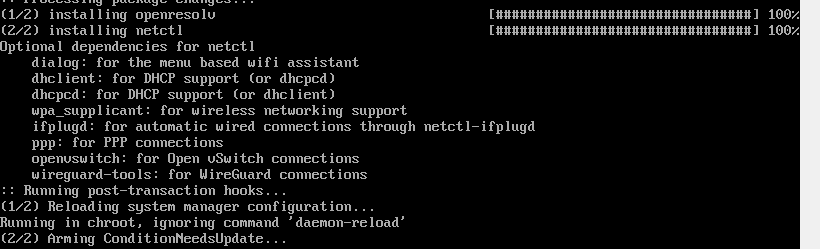
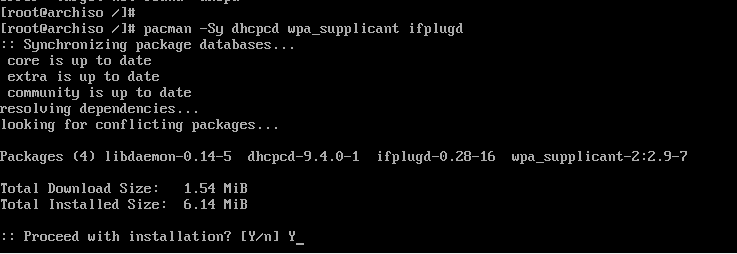
These dependencies will help you set up networking without a problem when you next boot in to Arch Linux.
To install the optional dependencies, run the command below:
# pacman -Sy dhcpcd wpa-supplicant ifplugd
Step 13) Create a regular user
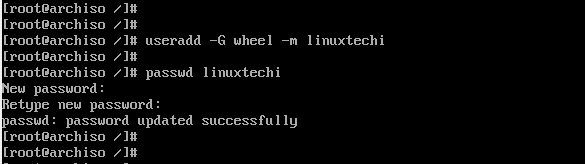
Next, we will create a regular user called linuxtechi and place him in the wheel group as follows.
# useradd -G wheel -m linuxtechi
The next step will be to assign a password to the user.
# passwd linuxtechi
Step 14) Install GRUB bootloader
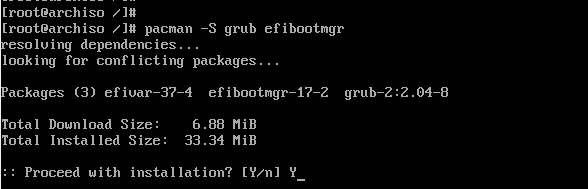
We are getting close to the finish line. In this step, we will install the grub bootloader to enable us boot into our Arch Linux system upon a reboot.
We will install the grub bootloader package alongside the efi boot manager package since we are using the UEFI mode.
# pacman -S grub efibootmgr
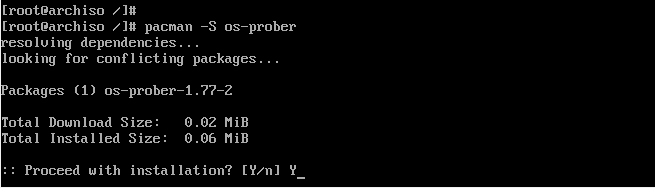
Next, install the os-prober package which will enable Arch Linux to detect the Windows operating system.
# pacman -S os-prober
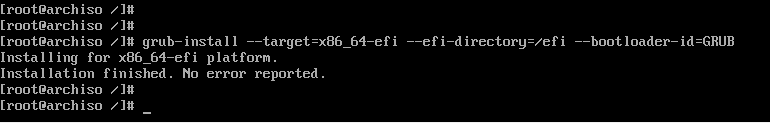
Then install grub on the EFI directory as shown.
# grub-install --target=x86_64-efi --efi-directory=/efi --bootloader-id=GRUB
And install a grub configuration file as shown.
# grub-mkconfig -o /boot/grub/grub.cfg
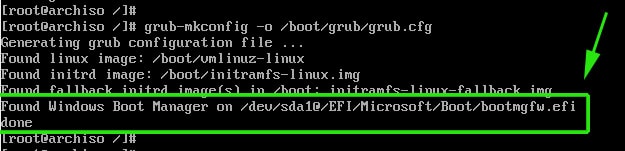
The last line is an indication that Arch has detected the presence of Windows Boot manager on /dev/sda1 partition. Perfect!
The finally, set a password for the root user as shown.
# passwd

Then exit and reboot your system.
# exit # reboot
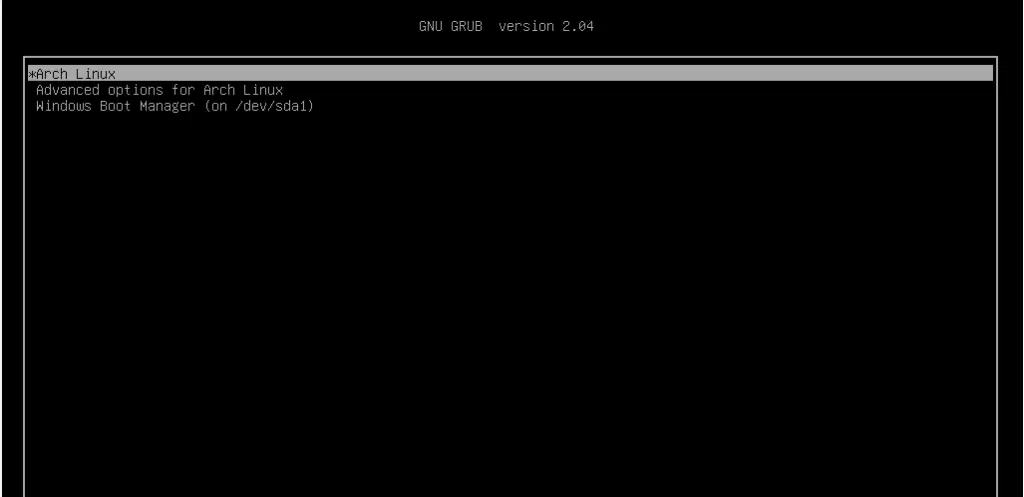
Step 15) Boot into Arch Linux
When booting, the GRUB bootloader will display various options including booting into Arch Linux, which is the first option, and also booting into Windows which is the last option in my case.
Log in as your regular user as shown
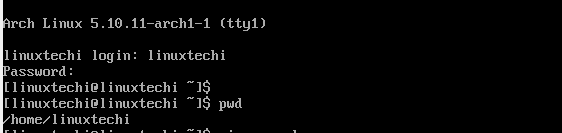
Step 16) Post Installation tasks
One of the things I noted when I logged in is that I do not have any internet connection. This is an issue caused by the default dhcp profile settings which need to be modified to accommodate the network interface attached to the Arch Linux system.
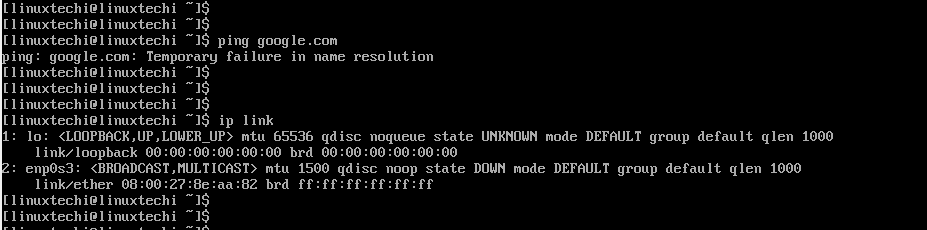
To find the interfaces attached run the command:
$ ip link
The output confirms that our network interface is enp0s3
We need to modify the ethernet-dhcp file in the /etc/netctl/examples/ path and edit out network interface.
But first, lets copy the file to the /etc/netctl directory.
Switch to the root user
# su
Copy the ethernet-dhcp file to the /etc/netctl directory.
# cp /etc/netctl/examples/ethernet-dhcp /etc/netctl/custom-dhcp-profile
Next, navigate to the /etc/netctl directory.
# cd /etc/netctl
Use the vim editor to edit the file.
# vim custom-dhcp-profile
The interface attribute is set to eth0.
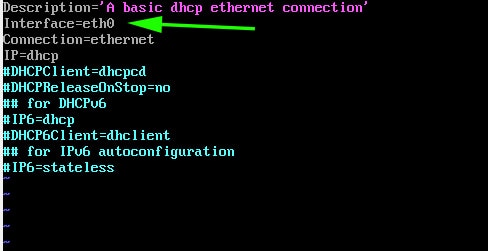
However, as we saw earlier, our network interface is enp0s3. Therefore, modify it to enp0s3. Additionally, uncomment the line starting with the DHCPClient parameter.
DHCPClient=dhcpcd
This enables the system to accept IP addresses using the dhcp service.
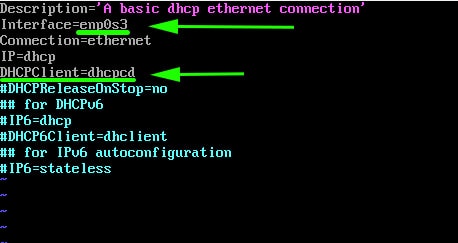
Save and exit the configuration file. Next, enable the custom dhcp profile.
# netctl enable custom-dhcp-profile
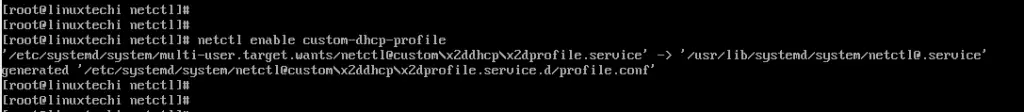
And finally enable the dhcp service.
# systemctl enable dhcpcd.service

Your interface should now pick an IP address from the router and you should have an internet connection.
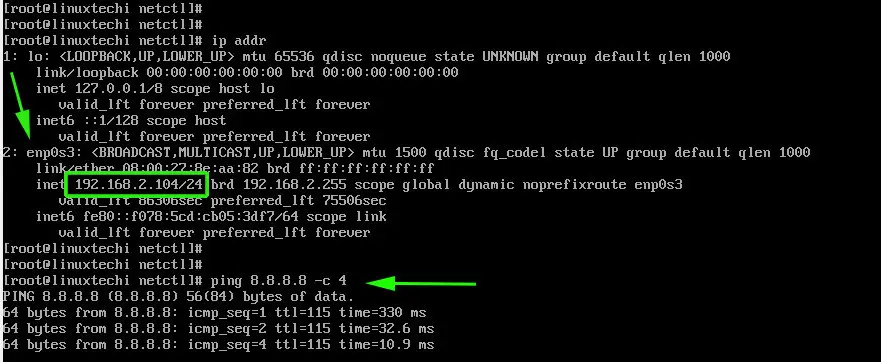
You can install an X windows system as shown,
$ sudo pacman -S xorg xorg-server
Then install a display manager. For example, to install GNOME, run:
$ sudo pacman -S gnome
Then start and enable gdm service
$ sudo systemctl start gdm $ sudo systemctl enable gdm
This brings us to the end of this lengthy topic. Hopefully, you are now in a position to Dual boot Arch Linux with Windows on UEFI system.
Read Also : How to Create and Configure Sudo User on Arch Linux
Dual Boot Arch Linux and windows 11/10 . Install Arch Linux With GUI alongside windows 11. This is a complete step by step tutorial of Arch linux installation 2024.
This Article walks you through the installation guide of Arch Linux With Plasma Desktop and dual Boot with windows 11. Using dual boot you can setup windows 11 and arch Linux on the same drive.
The Pre-requisites of this video
* You need Windows 11 or Windows 10 installed on your PC or laptop.
* An 8 GB or higher USB drive to create a bootable disk with ArchLinux
* At least 40GB of free space reserved from your existing drive.
Creating Free Space For ARCH LINUX
- Open command prompt and type DISKMGMT to access disk manager.
- View connected drives and their partitions.
- Identify the target drive (e.g., Drive 0) with its partitions.
- Choose the C Or D or Any Drive for ArchLinux and right-click on it.
- Select “shrink volume” to allocate free space for ArchLinux.Allocate a minimum of 40GB or more (type in MegaBytes, e.g., 200,000 MB).Click “shrink” to create unallocated free space

Download ArchLinux & Make Bootable USB
- Download the Arch ISO from HERE
- Connect a USB stick to your computer.Use Rufus to burn the downloaded ISO image to the USB drive.
Create System Restore Point
It is recommended to create a System Restore point before installing Archlinux. This option allows you to take a snapshot of the current state of the system. If something goes wrong with the Arch installation, you can use this backup to restore your system to normal.
BIOS Settings
- Reboot your computer.
- During the reboot, enter the BIOS settings using the keyboard shortcut (commonly F2, F9, or ESC).
- In UEFI BIOS, enable USB boot and set the USB drive as the primary boot order.
- Disable secure boot in the BIOS settings.
- If available, enable options like Microsoft’s third-party UEFI.
- Consider clearing any keys or certificates after disabling secure boot.
- Save the changes in the BIOS settings.
- Your system should now boot into ArchLinux from the USB drive.
- If the boot fails, use the boot menu to load Arch install media.
Increase Console FONT
Now, on your monitor, you will see a terminal expecting input. Note that the mouse functionality is disabled so you need to rely on the keyboard
Type setfont ter-132n and press enter to increase the size of the console.
Using iWCTL for WIFI Connection
If using built-in WiFi support, use the iwctl tool to connect to the internet.
- To find list of network interfaces type:
iwctl device list - To search for WIFI Networks type:
iwctl station wlan0 get-networks - To connect to WIFI network type:
iwctl station wlan0 connect WIFI_NAME - Once connected run :
ping google.comto check internet connection (Interrupt Ping with CTRL + C) - Then type the command to syncnorize the package database:
pacman -Sy - Then Type this command :
pacman -S archlinux-keyring
Create Partitions For Arch Linux
- Type
lsblkto list all connected drives on the PC. - Identify the main drives, focusing on SDA or NVME (ignore loops).
- NVME0n1 is MY drive with Windows 11, and SDA is the BootableUSB.

- Create partitions for Arch Linux using earlier free space.
- Type cfdisk /dev/nvme0n1 and press enter.
- Use arrow keys for selection and enter key for confirmation.

- Scroll to free space and create 3 partitions: EFI, ROOT, and swap.
- Create EFI partition (e.g., 800MB) with type EFI System.
- Create ROOT partition (e.g., 20GB or higher) with type Linux file system.
- Use remaining free space for swap partition with type Linux SWAP.
- Write changes to alter the disk and exit from CFDisk.

Formatting Partitions
- Type lsblk to view all newly created partitions
- NVME0N1P5 for EFI, NVME0N1P6 for Root, and NVME0N1P7 for Swap.
- Format the Arch EFI Partition (e.g., NVME0N1p5)
mkfs.fat -F32 /dev/nvme0n1p5 - Format the root partition (e.g., NVME0N1p6)
mkfs.ext4 /dev/NVME0N1p6 - Format the swap partition (e.g., nvme0n1p7)
mkswap /dev/nvme0n1p7
Mount Partitions
- Mount the root partition (e.g., NVME0n1p6) to the “mnt” directory.
mount /dev/nvme0n1p6 /mnt - Create a directory inside “
mnt” and name it “boot,” then mount the EFI partition to this directory.
mkdir /mnt/boot
mount /dev/nvme0n1p5 /mnt/boot
- Enable the swap partition by typing
swapon /dev/nvme0n1p7 - Verify proper mounting of all partitions by typing
lsblk

Installing ArchLinux
Now, it’s time to install the Arch Linux to the root partition which Is mounted to /mnt.
pacstrap -i /mnt base base-devel linux linux-headers linux-firmware amd-ucode sudo git nano vim neofetch htop cmake make bluez bluez-utils networkmanager cargo gcc mpvRun the above command to start installing the base system of Arch Linux. Accept the defaults. This will take some time, sit back, relax, and don’t interrupt the computer.
Generate File System Table (FSTAB)
It’s time to generate a file system table. If you notice, the NVME partitions are mounted to the live session of USB, but when we boot arch from the main drive we need to tell the system to mount all these partitions to the same location.
genfstab -U /mnt >> /mnt/etc/fstabCHROOT To Newley Installed system
So far we are running everything from the Live Session. It’s Time to enter, into the drive where we have installed Arch Linux. For that type:
arch-chroot /mnt
Now you can see the prompt has changed to something else, which means we have entered into the actual drive as a root user.
Change Root Password
Then type passwd and set the root password. This is a superuser account and is known as a top-tier user in Linux.
Adding a Standard User
Also, we are going to create a standard user by tying the below command and replace the username placeholder with your name
useradd -m -g users -G wheel,storage,video,audio -s /bin/bash USER_NAMEThen set the password by typing
passwd USER_NAMENow, we have added this new user to the wheel group and other groups. The Wheel group allows the user to access root privileges with a sudo command. For that, we need to edit the sudoers file. Type the below command
EDITOR=nano visudo
Uncomment the line in the image and save the changes with CTRL + O and CTRL + X to Exit.
SetupTimezone/Region
- Use
ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/and press tab to see the list of available options. - Choose the appropriate timezone, for example
ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Kolkata /etc/localtime - Synchronize the current time with the hardware clock using
hwclock --systohc

Setup System Language
It’s time to set a system language by generating a locale. Type the below command
nano /etc/locale.genScroll all the way and uncomment the below line in the image and save the changes. This is going to tell the system to use American English as the system locale.

Now type the below commands to generate a locale & Config file
locale-genecho "LANG=en_US.UTF-8" >> /etc/locale.confSetup Host Name
Now, type the below command to set up the hostname of this computer. In this case, I am going to say “archlinux” and save the changes
echo "archlinux" >> /etc/hostnameThen type nano /etc/hosts and add the below lines.

Make sure you replace the GREEN part with your hostname and save the changes
Grub-Installation
It’s time to install the grub boot loader which is going to help boot arch Linux. Type the below commands
pacman -S grub efibootmgr dosfstools mtoolsgrub-install --target=x86_64-efi --efi-directory=/boot --bootloader-id=GRUBgrub-mkconfig -o /boot/grub/grub.cfgEnable Services
systemctl enable bluetoothsystemctl enable NetworkManagerThen exit from Chroot by typing exit & Unmount the partitions by typing
umount -lR /mntShutdown the computer and eject the USB Stick
Connecting TO WIFI Using NMCLI
Once the system is restarted you can see the grub menu. From here you can boot into only Arch for now and Windows 11 boot entry will be missing.
We are going to fix that issue in a moment. For now, let’s just boot into Arch Linux. Now log in with your user account & increase the console font by typing below command
setfont -d- Check the status of all network interfaces:
nmcli dev status - Turn on the WIFI Radio:
nmcli radio wifi on. - View available wifi networks with the command specified
nmcli dev wifi list - Connect to wifi using the relevant command, replace placeholders with your network information and enclosing the password in double-quotes
sudo nmcli dev wifi connect WIFI_NAME password "WIFI_PASSWORD" - Update the PACMAN database with:
sudo pacman -Sy
Installing GUI
It’s time to install the desktop environment. For Plasma Desktop Run the below commands
sudo pacman -S xorg sddm plasma-meta plasma-wayland-session kde-applications noto-fonts noto-font-emoji ttf-dejavu ttf-font-awesomesudo systemctl enable sddmFor GNOME Desktop
sudo pacman -S xorg gdm gnome gnome-extra sudo systemctl enable gdmThen Reboot the system
sudo reboot nowand this time Arch Linux will boot With a GUI Environment
Fix Discover App Backend
The first thing to do after installing ArchLinux is to fix the Discover app backend. To do so open KONSOLE and type the below command to install flatpak and use it as a backend for discover.
sudo pacman -Sy flatpakInstall NVIDIA Drivers (Optional)
If you have a modern NVIDIA graphic card, it’s recommended to install NVIDIA proprietary drivers.
"This is completely optional, installing this package on older systems may or may not work, so please refer to this article"
Anyway, inside the konsole you can type the below command to set up NVIDIA drivers.
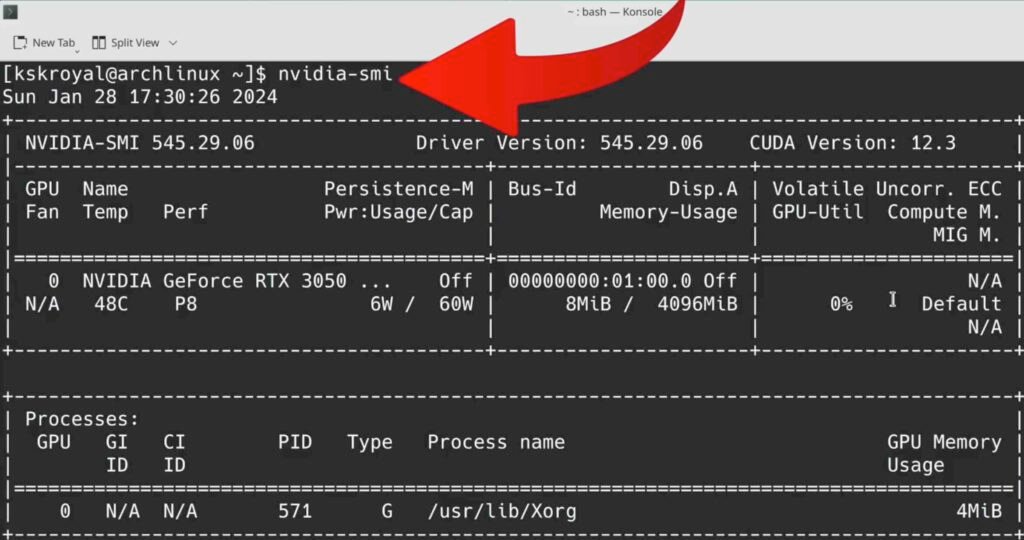
sudo pacman -Sy nvidia Once it’s done, reboot your computer. Now if I type nvidia-smi command inside the terminal you can see it shows the NVIDIA driver information.
Adding Windows Entry To GRUB
- Install OS-Prober with the command provided
sudo pacman -Sy os-prober - Edit the grub file,
sudo nano /etc/default/grub - Set the
GRUB_TIMEOUT=20 - Scroll to the bottom and uncomment the line related to os-prober.

Save changes with ctrl + o and exit with ctrl + x.
Run grub-mkconfig -o /boot/grub/grub.cfg to update the grub configuration.Verify that Windows boot manager is detected.

Reboot the system. Using the grub menu you can boot into either Arch or Windows 11
Removing ArchLinux From Dual Boot
- Reboot your computer and boot into Windows 11.
- Open Disk Management utility by typing diskmgmt in the search bar.
- Delete each new partition by right Clicking created during ArchLinux installation, starting with swap and root partitions.

- “Note that the LINUX EFI partition cannot be deleted using Disk Management“
- Open Command Prompt as an administrator and type
DISKPART - Type
list diskto view all connected drives, select the appropriate drive with
select disk 0 - Type
list partitionto view all partitions on the selected drive. - Identify the Arch EFI partition (e.g., partition 5).

- Select the Arch EFI partition with
select partition [number] - Type
DELETE PARTITION OVERRIDEto remove the partition. - Verify the deletion in Disk Management; the free space is now available.
- Utilize the gained free space to merge it back into Windows 11 partitions
Watch the YouTube Video:
1. Pre-Installation Preparation
Before touching partitions, back up any important files from your Windows system. Verify that Windows is installed in UEFI mode: in Windows press Win+R, run msinfo32, and ensure BIOS Mode is “UEFI” (Installing And Setting Up Arch Linux to Dual Boot Alongside Window 10 · GitHub). Also confirm Windows uses GPT, not MBR, in Disk Management. Next, disable “Fast Startup” in Windows (via Control Panel → Power Options) because it hibernates the disk and can block Linux from mounting it (Is it necessary to disable Fast Boot in Windows to dual boot with linux(EFISTUB)? — Unix & Linux Stack Exchange). In your PC’s UEFI/BIOS settings, disable Secure Boot if possible (this avoids bootloader signature issues) and Fast Boot (if present, to ensure the USB can boot).
Download the Arch Linux ISO from the official site and create a bootable USB. For example, use a tool like Rufus on Windows: select the ISO, set the partition scheme to GPT and file system to FAT32, and flash it (Installing And Setting Up Arch Linux to Dual Boot Alongside Window 10 · GitHub). This makes the USB UEFI-bootable. When done, reboot and enter your firmware’s boot menu (often by pressing a key like F12, F10, or Esc during startup) and choose the USB under UEFI devices (Installing And Setting Up Arch Linux to Dual Boot Alongside Window 10 · GitHub).
2. Booting Arch Linux in UEFI Mode
Boot the USB in UEFI mode. You should land at an Arch Linux prompt (typically as the root user, no password). If needed, set your keyboard layout (e.g. loadkeys us for US layout) and verify network connectivity next.
3. Internet Connection (Wi-Fi)
If you have a wired connection, it usually connects automatically via DHCP. Test it with ping -c 3 archlinux.org. For Wi-Fi, run:
rfkill unblock wifi
iw dev # identify your wireless interface name (e.g. wlan0)
wifi-menu wlan0 # (or your interface name) to select and connect to a network
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
After connecting, verify with ping -c 3 archlinux.org. A working connection is required for package installation (Installing And Setting Up Arch Linux to Dual Boot Alongside Window 10 · GitHub).
4. Disk Partitioning
WARNING: Be careful not to delete your Windows partitions. You may have already shrunk the Windows partition from Windows Disk Management to make free space. If not, reboot into Windows, open Disk Management (diskmgmt.msc), right-click the Windows (C:) partition, and choose Shrink Volume to free up at least ~20–50 GB (20000–50000 MB) for Arch (Installing And Setting Up Arch Linux to Dual Boot Alongside Window 10 · GitHub).
Back in Arch’s live environment, list disks with fdisk -l to identify your drive (e.g. /dev/sda). Use cfdisk (or fdisk/gdisk) to partition. Select your disk (e.g. /dev/sda) and a GPT label:
cfdisk /dev/sda
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
In the cfdisk menu, create new partitions in the free space:
-
EFI System Partition (ESP): If Windows is already in UEFI mode, an EFI partition (around 100–500 MB, FAT32) should exist (often
/dev/sda1). We will reuse that for the bootloader. If not present, create a new small (e.g. 500 MB) FAT32 partition and set its type to “EFI System” (How to Install Arch Linux: A Beginner’s Practical Guide). -
Swap Partition: Create a Linux swap partition. For example, if you have 8 GB RAM, make 8–12 GB here. After selecting “New”, accept the defaults to start at free space and enter the size (e.g.
12G), then set its type to “Linux swap” (How to Install Arch Linux: A Beginner’s Practical Guide). - Root Partition: Use the remaining space to create an ext4 root partition. Again select “New”, accept the remaining free space, and set the type to “Linux filesystem” (ID 8300) (How to Install Arch Linux: A Beginner’s Practical Guide).
Write the changes (“Write” in cfdisk) and confirm. Then quit cfdisk (How to Install Arch Linux: A Beginner’s Practical Guide).
5. Format and Mount Partitions
Format each partition to its filesystem:
mkfs.fat -F32 /dev/sda1 # Format EFI partition as FAT32 (if newly created; skip if reusing Windows EFI)
mkswap /dev/sda2 # Format swap partition
swapon /dev/sda2 # Enable swap
mkfs.ext4 /dev/sda3 # Format root partition as ext4
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
(Adjust /dev/sdXN numbers to match your EFI, swap, and root partitions.) Format and activate swap as shown (How to Install Arch Linux: A Beginner’s Practical Guide); format root as ext4 (How to Install Arch Linux: A Beginner’s Practical Guide).
Next, mount the new root partition and EFI partition (bootloader space). For example:
mount /dev/sda3 /mnt # Mount the root partition
mkdir -p /mnt/boot/efi # Create a mount point for EFI
mount /dev/sda1 /mnt/boot/efi # Mount the EFI (ESP) here
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
(This assumes /dev/sda1 is the EFI; use the correct device.) These commands are analogous to those shown in the guide (How to Install Arch Linux: A Beginner’s Practical Guide). Verify with lsblk that /mnt is your root and /mnt/boot/efi is your EFI.
6. Install the Base System
Install the core Arch system packages using pacstrap:
pacstrap /mnt base linux linux-firmware
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
This installs the base filesystem, the Linux kernel, and firmware for common devices (Comprehensive Arch Linux Installation Guide | Liquid Web). You can also add packages like base-devel or a text editor here (e.g. nano) as needed.
7. Configure the New System
Generate an fstab file so the system knows where to mount partitions on boot:
genfstab -U /mnt >> /mnt/etc/fstab
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
Review it with cat /mnt/etc/fstab to ensure it lists your root and EFI partitions correctly (Comprehensive Arch Linux Installation Guide | Liquid Web).
Now enter the new system environment with arch-chroot:
arch-chroot /mnt
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
You are now effectively “root” in your installed system. All following commands apply inside the new Arch system.
Timezone and Clock
Set your timezone, for example for New York:
ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/America/New_York /etc/localtime
hwclock --systohc
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
This links the appropriate zoneinfo file and generates /etc/adjtime (Comprehensive Arch Linux Installation Guide | Liquid Web) (Comprehensive Arch Linux Installation Guide | Liquid Web). Replace the path with your region/city.
Locale
Edit /etc/locale.gen, uncomment your locale (e.g. en_US.UTF-8 UTF-8), then run:
locale-gen
echo LANG=en_US.UTF-8 > /etc/locale.conf
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
These commands (and uncommenting the locale) are shown in the guide (Comprehensive Arch Linux Installation Guide | Liquid Web) (Comprehensive Arch Linux Installation Guide | Liquid Web). This sets the system language.
Hostname and Hosts
Set a hostname by creating /etc/hostname with your chosen name. For example:
echo "archpc" > /etc/hostname
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
Then edit /etc/hosts and add lines:
127.0.0.1 localhost
::1 localhost
127.0.1.1 archpc.localdomain archpc
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
Replace archpc with your hostname as shown (Comprehensive Arch Linux Installation Guide | Liquid Web).
Root Password and Initramfs
Set the root password:
passwd
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
Enter a secure password when prompted (Comprehensive Arch Linux Installation Guide | Liquid Web). Then rebuild the initial ramdisk:
mkinitcpio -P
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
This ensures the boot image is up-to-date (most tutorials include this step).
Create a Regular User (optional but recommended)
Create a normal user for daily use and add it to the “wheel” group (for sudo). For example:
useradd -m -G wheel -s /bin/bash username
passwd username
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
Give that user a password. Then install and enable sudo by editing /etc/sudoers with EDITOR=nano visudo and uncommenting the line %wheel ALL=(ALL) ALL.
8. Install the Bootloader (GRUB)
Install GRUB with UEFI support so you can boot Arch (and Windows). First, install the packages:
pacman -S grub efibootmgr os-prober
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
Here, os-prober helps detect Windows. Now install GRUB to the EFI directory and generate its config:
grub-install --target=x86_64-efi --efi-directory=/boot/efi --bootloader-id=GRUB
grub-mkconfig -o /boot/grub/grub.cfg
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
These commands create the GRUB UEFI entry (How to Install & Configure Arch Linux on UEFI Systems) (How to Install & Configure Arch Linux on UEFI Systems). If everything works, /boot/grub/grub.cfg will be generated and should include menu entries for both Arch and Windows. (If Windows is not listed, ensure os-prober was installed and re-run grub-mkconfig.)
9. Install KDE Plasma and SDDM
If you want a graphical desktop, install KDE Plasma and its apps. For a full set:
pacman -S plasma-meta kde-applications-meta
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
This pulls in the KDE desktop environment and standard KDE apps (How to Install Arch Linux: A Beginner’s Practical Guide). You may also install a graphical display server (xorg) if not already installed.
Enable the SDDM display/login manager (default for KDE) and networking (using NetworkManager, since you used NetworkManager earlier):
systemctl enable sddm
systemctl enable NetworkManager
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
This ensures KDE’s login screen and network service start at boot (How to Install Arch Linux: A Beginner’s Practical Guide). (You could also use dhcpcd or another network service if you prefer.)
10. Finalize and Reboot
Exit the chroot, unmount partitions, and reboot:
exit
umount -R /mnt
reboot
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
Remove the USB drive when the system shuts down. On reboot, you should see the GRUB menu offering Arch Linux and Windows. Select Arch to boot into your new system with KDE. Log in as your new user or root (depending on setup) and enjoy Arch Linux! (How to Install Arch Linux: A Beginner’s Practical Guide).
Common Pitfalls: Be careful not to overwrite the Windows partitions. Always confirm device names (/dev/sdX) before formatting. If GRUB doesn’t show Windows, ensure os-prober is installed and rerun grub-mkconfig. Disabling Fast Startup in Windows is essential; otherwise Linux will refuse to mount the Windows drive (Is it necessary to disable Fast Boot in Windows to dual boot with linux(EFISTUB)? — Unix & Linux Stack Exchange). Ensure your firmware is booting in UEFI mode (not legacy) for both OSes, or the dual-boot will fail.
Sources: Steps adapted from the official Arch Wiki and community guides (Comprehensive Arch Linux Installation Guide | Liquid Web) (How to Install Arch Linux: A Beginner’s Practical Guide) (How to Install Arch Linux: A Beginner’s Practical Guide) (How to Install & Configure Arch Linux on UEFI Systems) (How to Install Arch Linux: A Beginner’s Practical Guide), including Windows preparation notes (Is it necessary to disable Fast Boot in Windows to dual boot with linux(EFISTUB)? — Unix & Linux Stack Exchange) (Installing And Setting Up Arch Linux to Dual Boot Alongside Window 10 · GitHub).

 Generate fstab file
Generate fstab file