Most organizations are looking at running containers in their organization. However, much of what you read about containers revolves around Linux containers. However, what if you want to run containers on Windows Server? Windows Server Containers are a great way to run Windows applications with an extremely small footprint. However, since Windows containers require a Windows container host, we need to use a Windows Server container host to install Docker so we can run Docker containers using Windows Docker images. Windows Server 2022 is the latest Windows Server operating system from Microsoft that enables running Docker containers. Let’s look at how to install Docker on Windows Server 2022 and see the steps involved.
Table of contents
- What is Docker Engine and Docker Desktop?
- What are container images?
- Why run Docker containers on Windows Server?
- Windows Server 2022 containers new features
- Server 2022 Core image size reduction
- Longer support cycle for Windows Server 2022 container images
- Virtualized time zone
- Application compatibility
- IPv6 support
- Improved Kubernetes experience
- Solving docker container image kernel limitations
- Windows Server 2022 supports WSL installed
- Windows Server 2022 – Process isolation mode and Hyper-V isolation
- Install Docker on Windows Server 2022
- Install the Windows Server 2022 containers feature
- Install Hyper-V Role in Windows Server 2022
- Install DockerMsftProvider and install Docker
- Pull Windows Container image for Docker
- Run the Windows Docker Image
- Wrapping Up
Check out the video of the process if you would rather see it in video form:
What is Docker Engine and Docker Desktop?
Both the Docker engine and Docker desktop are widely used in the enterprise to run business-critical container image applications. Docker provides the container runtime that allows the container image applications to run on top of the physical host machine.
The process to install Docker Desktop is performed using the Docker Desktop installer and makes getting up and running with Docker containers very easy using the Docker Desktop application.
You can also interact with Docker using the command prompt or a PowerShell session to run Docker command parameters from the command prompt. Both the Docker Desktop and Docker command prompt environments require a Docker installation on your Windows Server host.
What are container images?
A container image is an image of all the requirements it takes to run an application. A container image are much lighter weight than full virtual machine. Virtual machines are full operating system installations
Why run Docker containers on Windows Server?
You may wonder why you would want to run Docker containers on Windows Server containers. One reason is that to run Windows Containers, you need to run Windows containers on Windows Server. This requirement is because containers share the kernel of the container host. So you can’t run Linux Containers on Windows Server and Windows containers on Linux.
Windows Server 2022 containers new features
Windows Server 2022 offers new container features that provide a great way to run Docker containers with the latest features and enhancements when compared to older Windows Server versions, such as Windows Server 2016. What are some of the new Windows Server 2022 container features?
Server 2022 Core image size reduction
The container image size is extremely important. The smaller the container image, the faster, more agile, and easier it is to run the containers. In Windows Server 2022, the Server Core container image RTM layer at GA is 2.76 GB uncompressed. This is a major improvement over Windows Server 2019 which was 3.47 GB uncompressed container size. It represents a 33% smaller footprint.
Longer support cycle for Windows Server 2022 container images
Five years of support and an additional five years of extended support is now offered for all Windows server 2022 containers.
Virtualized time zone
Windows Server 2022 containers support virtualized time zone configuration separate from the host. This virtualized time zone support is included in the instance for each container.
Application compatibility
You can use Group Managed Service Accounts with Windows containers to use Active Directory authentication.
IPv6 support
IPv6 is now supported with Kubernetes in Windows.
Improved Kubernetes experience
Microsoft is continuing to improve the Kubernetes implementation with Windows containers. Windows Server 2022 provides more restrictive subnets and multiple subnets for each Windows worker node.
Solving docker container image kernel limitations
You can solve some of these limitations by running a container host as a virtual machine. Regardless of whether the physical host is running Windows Server or Linux, you can run a hypervisor such as Hyper-V or Linux with Proxmox, XCP-NG, KVM, etc to run virtual machines of either variety.
You can also use nested virtualization if you want to have the capabilities of a Windows hypervisor or Linux hypervisor, regardless of what operating system your physical host is running. However, you must have enabled nested virtualization to benefit from this capability.
Windows Server 2022 supports WSL installed
Now, with Windows Server 2022, you can have WSL installed in a supported way without any hacks to get it to work. This provides another way to work with Linux containers using your Windows Server 2022 host.
Windows Server 2022 – Process isolation mode and Hyper-V isolation
Running containers with Process Isolation mode is the traditional way that containers run. Even though they share the host operating system kernel, each container is isolated through namespace, resource control, and other process isolation technologies.
One of the cool benefits of running Docker container images on Windows Server 2022 with Hyper-V isolation is the added security benefits from the Hyper-V role. The Hyper-V isolation mode offers enhanced security.
In isolation mode, each container runs inside of a highly optimized virtual machine that effectively gets its own kernel. This isolation enables hardware-level isolation between each container and container host.
The process to install Docker on Windows Server 2022 will include the following steps:
- Install the Windows Server 2022 containers feature
- Install Hyper-V in Windows Server 2022
- Install DockerMsftProvider and Docker
- Pull Windows container image for Docker
- Run the Windows Docker image
Install the Windows Server 2022 containers feature
Using the features wizards found in Server Manager, we can install the containers feature in Windows Server 2022 to run containers natively in Windows. The process is fairly straightforward. Run the Add roles and Features Wizard from Windows Server 2022.

On the Features screen, place a check next to the Containers feature.

Confirm the installation.

The containers installation is successful. You will be prompted to reboot your Windows Server 2022 host.

Install Hyper-V Role in Windows Server 2022
Next, for using Hyper-V isolation, we will need to have the Hyper-V role installed. Let’s quickly look at the Hyper-V role installation. On the Server Roles screen in Server Manager, place a check next to the Hyper-V role. Note you can also use the new Windows Admin Center to install roles in your Windows Server 2022 machine.

It will bring up the Add features that are required for Hyper-V.

Now we have the check placed next to Hyper-V, click Next.

Next, there will be a few screens of Hyper-V specific configuration.

You can go ahead and create the default Hyper-V virtual switch.

Decide if you want to allow live migration.

Configure the default storage location for Hyper-V virtual machines. Here, I am accepting the default settings.

Confirm the installation of the Hyper-V role and role features.

You will be prompted to reboot after the role is successfully installed.

Install DockerMsftProvider and install Docker
***Note*** DockerMsftProvider is now deprecated. However, leaving the below for posterity
Use the command found in the documentation here instead:
Invoke-WebRequest -UseBasicParsing "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/microsoft/Windows-Containers/Main/helpful_tools/Install-DockerCE/install-docker-ce.ps1" -o install-docker-ce.ps1
.\install-docker-ce.ps1Deprecated steps below:
Next, we will install the Docker provider and install Docker itself. We can use just a couple of commands from the Powershell session to install the module and package needed. We need to be in an administrator prompt. The order of operations is we need to first install the Provider and then we can install Docker from the provider.
Install-Module -Name DockerMsftProvider -Repository PSGallery -ForceThis command will prompt you to install the Nuget provider in order to install the module.

To install Docker, we can use the following command:
Install-Package -Name docker -ProviderName DockerMsftProviderYou will see the message that the package is not marked as trusted. You will need to allow the installation.

Next, we need to restart Windows Server 2022. You can do that from the PowerShell session using the Restart-computer cmdlet.
Pull Windows Container image for Docker
After the Server 2022 host reboots, we can pull the Windows container image in a PowerShell session or Windows Command Prompt:
docker pull mcr.microsoft.com/windows/servercore:ltsc2022
Run the Windows Docker Image
Finally, let’s run the Windows Docker image in Windows Server 2022. This is a simple Docker run command. You can first list out your images using the docker images ls command and then run the container interactively with the following:


Wrapping Up
The process of installing Docker in Windows Server 2022 is straightforward. We just need to install a role and feature and then pull the module and package from the command line. After that, we can successfully pull the latest Docker image for Server Core and then run our container. From this point forward, it is straightforward to run your Docker containers in Windows.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to install Docker on Windows Server. We’ll be showing you how to install it on Windows Server 2022, but the process is similar for earlier versions as well.
This installation guide is specifically for Windows Server. For instructions on Windows 10 and 11, click the link below.
How to Install Docker on Windows 10 & 11
Before We Begin…
Before installing Docker on Windows Server, there is something you need to be aware of:
- Docker on Windows Server is only for Windows containers; you can’t run Linux containers on Windows Server.
- If you want to run Linux-based containers, you’ll need to install Docker on a Linux machine.
- If you need to run Linux containers on your Windows Server, you’ll have to use Hyper-V to create a Linux virtual machine and then run Docker on that VM.
Demo: Install Docker on Windows Server
Microsoft provides a PowerShell script to install Docker Engine on Windows Server.
You can download the script by running the following command:
Invoke-WebRequest -UseBasicParsing "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/microsoft/Windows-Containers/Main/helpful_tools/Install-DockerCE/install-docker-ce.ps1" -o install-docker-ce.ps1Then run the script using the following command to install Docker:
.\install-docker-ce.ps1During the installation, if you encounter errors like "Failed to start service 'Docker Engine (docker)'" or "errors during connect", terminate the installation process by pressing CTRL+C and then run the installation script again.
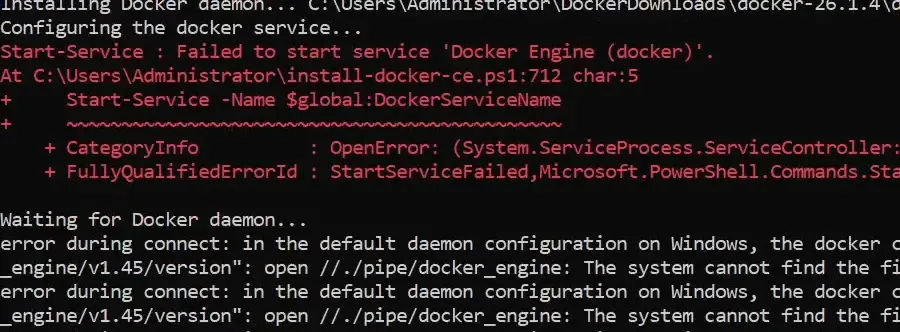
Docker installation requires a restart, so your Windows Server will automatically reboot in a few moments. Once the server is back up, it will finish the installation and show the message that Docker is installed.
To confirm that Docker Engine is installed, run the docker version command:
docker versionThe command will display the Docker Engine version installed on your Windows Server.
Server: Docker Engine - Community
Engine:
Version: 26.1.4
API version: 1.45 (minimum version 1.24)
Go version: go1.21.11
Git commit: de5c9cf
Built: Wed Jun 5 11:28:43 2024
OS/Arch: windows/amd64
Experimental: falseRunning Windows Containers
Remember, you can only run Windows containers on the Docker Engine for Windows Server.
You can find a list of official Windows-based OS images at this link.
Here is an example of starting a Windows Server 2022 container using the docker run command:
docker run -dt mcr.microsoft.com/windows/servercore:ltsc2022What Next?
Alright, now that you have Docker Engine up and running on your Windows Server, check out our tutorial on how to start containers using the docker run command.
Have you ever wondered if it’s possible to utilize the power of Linux’s development tools on your Windows Server 2022? Or perhaps you’ve maybe needed to deploy Docker applications while running your own Windows cloud instance? While this could seem impossible at a first glance, there is actually a way — by using WSL!
With WSL, short for Windows Subsystem for Linux, in addition to some extra help from the virtualization technology, you can easily install a Linux distribution onto your Windows Server! Not only that, but you can also get Docker and start deploying containers straight onto your server with ease!
In this tutorial, we are going to go over WSL and Docker in more detail, walking you through the installation process for both as well as giving you the minimum hardware requirements so that you can be sure that the software will run on your server.
What are WSL & Docker?
Before we can proceed to the installation and configuration process, it is important to have a look at both WSL and Docker as this will allow us to understand how they work, what their individual features are as well as what we can anticipate throughout the installation process.
WSL — run Linux on your Windows Server without emulation
As we previously mentioned, WSL is a powerful tool that enables you to run a full Linux kernel directly onto your Windows machine without having to use an emulator. This can save a lot of time, effort and help you configure your system much easier, ultimately combining the power and stability of Windows Server 2022 with the development flexibility that originates from Linux.
But what are the benefits to this emulator-less approach? Firstly, you can run any Linux distribution that you choose! This means that it doesn’t matter if you want to go for Ubuntu, CentOS or even newer distros like Rocky, everything is at your fingertips.
This means that if you are already accustomed to using a particular distribution, you can easily get it up and running on your Windows cloud server with zero effort. Additionally, with WSL, you also get access to tools like Bash, Vim and Python directly from the Windows environment!
Secondly, you get the privilege of not having to constantly switch between 2 different operating systems. With WSL you get the ability to share files, launch applications and use Linux software within your Windows server, saving you time, boosting your productivity and making your workflow optimized and efficient.
Docker — containerization & easy application deployment
Docker has been gaining popularity ever since its creation as an application because of its useful features.
With Docker you get the ability to essentially pack together everything a particular application needs in order to run on any machine in one single unit called a container. This container includes all software requirements, prerequisites and libraries meaning that the app will be able to run on any other machine immediately after being deployed without you having to worry about mismatching software versions or missing libraries.
In addition to this portability feature, Docker also supports isolation, meaning that each container can operate in its own isolated environment. This offers better security and prevents resource conflicts.
Not only that but Docker also offers exceptional scalability, allowing you to deploy or retrieve containers depending on your needs, which can be helpful for both big organizations and individual developers, which is why Docker is a go-to option for VPS and VDS servers and some are even looking for cloud servers with a pre-installed Docker application in order to save time and get directly to deploying.
What you need to consider before installing WSL
Before you can proceed to getting both WSL and Docker on your Windows server, it is crucial to check whether your system meets the minimum hardware requirements in terms of resources and configuration options.
Minimum system requirements
In order to get WSL and Docker up and running, it is recommended that your server has a 64-bit CPU that supports virtualization as well as a minimum of 4GB of RAM, while also being equipped with at least 2GB of storage space.
In terms of your Windows Server 2022 version, your system should be with a build of at least 19041 or above in order to meet the compatibility requirements. In this tutorial, we are going to be focusing on installing WSL on Windows Server 2022. For any older versions, you can check out the official Microsoft documentation.
How to install WSL on Windows Server 2022
In order to get WSL up and running, we are going to be using the Windows PowerShell. So, let’s begin!
Setting up WSL with Windows PowerShell
Start by opening up PowerShell and running it as an administrator.

Next, enter the following command and press Enter:
wsl —install
Your distribution will then be downloaded and installed automatically.

You will then need to restart your machine for the changes to take effect.

After the restart takes place, a terminal window will be opened and the WSL installation will automatically continue.

Finally, you’d be asked to create your default UNIX (Linux) user. Just enter the desired username and password and you will be able to take full advantage of the Linux environment!

How to configure WSL
When the setup process concludes, you are going to see your Linux distribution appear in the Start menu. You now have to launch it in order to begin the initial configuration.

IMPORTANT: Your Linux distribution could start downloading some additional components when launched for the first time, meaning that you will need to wait for the download to complete! Do not close any windows and don’t worry if it takes longer to load.
You might want to update all software packages of your Ubuntu operating system, which you can do with the following command:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeYou will be prompted to enter the password for your UNIX (Linux) user.

Afterwards, you will see a list of available upgrades, just enter Y when prompted to continue and install all of them.

Installing Docker Desktop on Windows
Once you have successfully installed WSL, you can then proceed to setting up Docker Desktop. Start by navigating to the official Docker website. Next, click on the Docker Desktop for Windows button, which is located on the top of the page and your download should begin momentarily.

Once downloaded, double-click on the Docker Desktop Installer.exe file to run the installer.
IMPORTANT: Make sure to check the Use WSL 2 instead of Hyper-V box before clicking OK.

This will initiate the installation.

When the installation finishes, you will be asked to log out in order for the necessary settings to be applied. Click on the Close and log out button.

After logging back in, you will be prompted to finalize the Docker Desktop installation. That’s it! Now you can access the Docker Desktop GUI with the shortcuts from your desktop and Start Menu.
Provide feedback
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly
Sign up
Adesoji Alu Follow
Adesoji brings a proven ability to apply machine learning(ML) and data science techniques to solve real-world problems. He has experience working with a variety of cloud platforms, including AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Platform. He has a strong skills in software engineering, data science, and machine learning. He is passionate about using technology to make a positive impact on the world.
4 min read
Containers have become a fundamental part of modern application development and deployment. Whether you’re looking to streamline development processes or run isolated applications efficiently, Docker containers offer the perfect solution. In this guide, we’ll explore how to run Docker containers on Windows Server 2022, an essential step for businesses and developers moving toward a containerized infrastructure.
What are Containers?
At their core, containers are isolated environments that bundle an application and all of its dependencies together. They share the host’s resources—such as the kernel, CPU, and memory—while remaining logically separated from the host system and other containers. This isolation ensures that applications can run independently without interference.
Unlike traditional virtual machines, which replicate an entire operating system, containers run on the host system’s OS, making them more lightweight and faster to spin up.
How Containers Work in Windows Server 2022
Running Docker containers on Windows Server 2022 leverages the Windows Hyper-V features. However, it’s important to note that Docker Desktop is not supported on Windows Server. Instead, containers are run directly using DockerMsftProvider—a specialized provider designed for Windows Server.
Before proceeding with containerization on Windows Server, make sure you have a basic understanding of virtualization technologies and the Hyper-V hypervisor.
Step-by-Step Guide to Running Docker Containers on Windows Server 2022
This guide walks through setting up and running Docker containers in Windows Server 2022, including creating a sample web server container.
1. Installing Docker on Windows Server
To install Docker on Windows Server 2022, you’ll need to run several PowerShell commands with administrator privileges:
Install-Module -Name DockerMsftProvider -Repository PSGallery -Force
Confirm NuGet installation with ‘Y’.
Next, install Docker using the provider:
Install-Package -Name docker -ProviderName DockerMsftProvider
Once Docker is installed, restart your server:
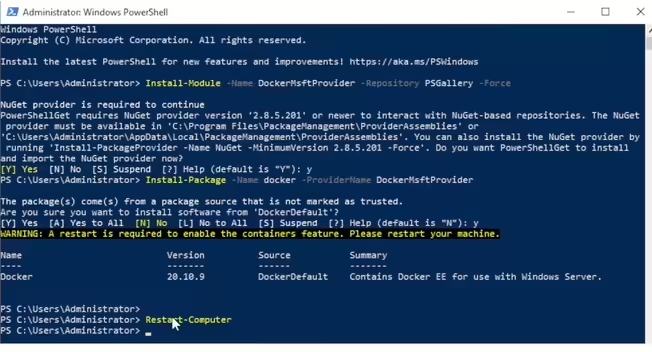
Docker is now ready to be used on your Windows Server 2022!
2. Creating a Dockerfile and a Simple Web Application
Docker containers are built using Dockerfiles—scripts that define how the container is structured. Follow these steps to create a basic web server container:
cd\
mkdir Containers
cd Containers
Create a new Dockerfile and open it for editing,Remember that it has no extension:
New-Item dockerfile
notepad dockerfile
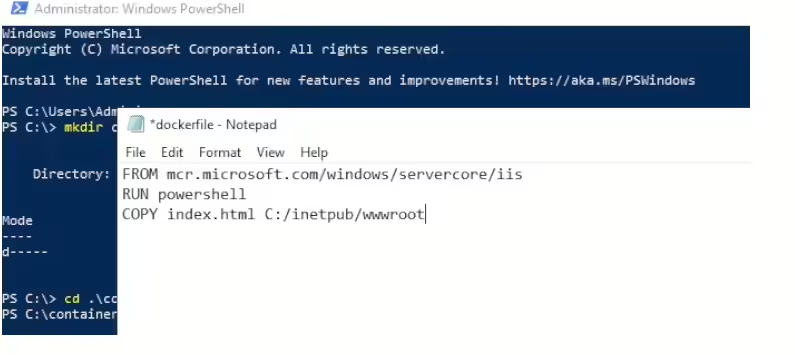
Add the following lines to the Dockerfile, which sets up a simple web server based on Windows Server Core with IIS:
FROM mcr.microsoft.com/windows/servercore/iis
RUN powershell
COPY index.html C:/inetpub/wwwroot
Next, create an HTML file that will be served by your web server:
New-Item index.html
notepad index.html
- New-Item index.html: This command creates a new file named
index.htmlin the current directory. If the file already exists, it will display an error unless you add the-Forceflag to overwrite it. - notepad index.html: This command opens the
index.htmlfile in Notepad, a basic text editor in Windows. You can use this to edit or add content to the file directly.
Add the following HTML code to the file:
<h1>Hello World!</h1>
<p>This is an example of a simple HTML page hosted on:</p>
<h2>container #1</h2>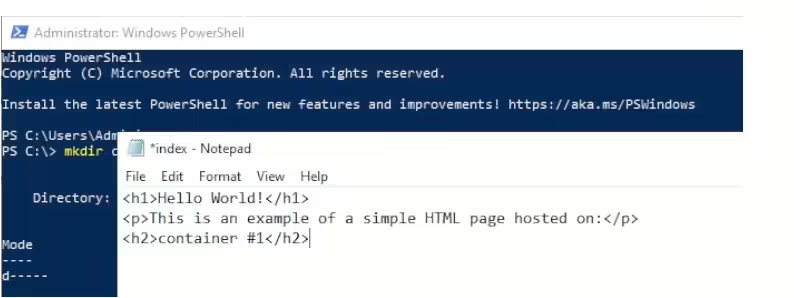
3. Building and Running the Container
Once the files are in place, it’s time to build and run the container:
Build the container from your Dockerfile:
docker build -t webserver .
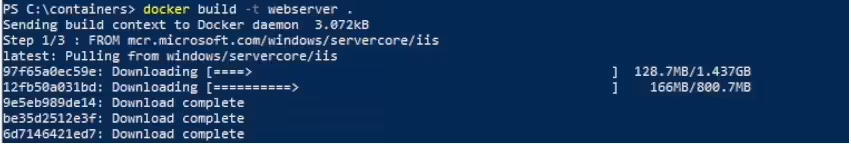
Check that the container image has been created:
Run the container:
docker run --name container1 -d -p 80:80 webserver
The -d flag runs the container in detached mode, and the -p 80:80 flag maps port 80 from the host to the container, making it accessible via HTTP.
4. Testing the Container
To verify the container is running, open a web browser on the host system and navigate to http://localhost. You should see the simple HTML page you created.
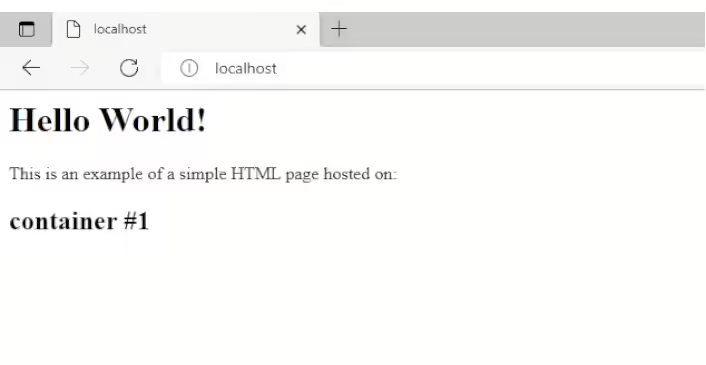
Alternatively, if you’re using another machine on the same network, you can access the containerized web server using the host’s IP address or computer name.
What Containers Can Be Used For
Containers are widely used for a variety of purposes, including:
- Microservices: Running individual microservices in containers ensures each service is isolated and can be updated independently.
- Development and Testing: Developers can spin up entire environments quickly, allowing them to work in consistent setups across teams.
- Deployment: Containers allow easy, repeatable deployments in production environments.
Conclusion
Running Docker containers on Windows Server 2022 provides a powerful way to manage applications in an isolated, lightweight environment. This guide offers a basic introduction to container creation and deployment using Docker, showing how even complex applications can be packaged and run with ease.
Remember, Docker Desktop is not supported on Windows Server, so these steps rely on the server’s Docker engine instead. As you grow more familiar with containers, you can scale your setup to support more advanced use cases.
Start experimenting with containers today and experience the agility and flexibility they bring to application development and deployment.
Reference
- DockerMsftProvider
