Provide feedback
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly
Sign up
Choose a different version or distribution
Introduction
Before we begin talking about how to install Docker Toolbox on Windows 7 and above, let’s briefly understand – What is Docker?
Docker is a platform that uses OS-level virtualization to deliver software in packages called containers. More than that, it is a popular tool to make build and deployments easier.
You’ll install Docker Toolbox on Windows 7 and above in this tutorial. Also, we will answer some FAQs regarding Docker installation.
- Cross-platform portability: Docker Toolbox allows developers to build and deploy applications consistently across different operating systems.
- Easy setup: Docker Toolbox provides a simple and straightforward installation process for managing Docker containers on your local machine.
- Isolation and security: Docker Toolbox isolates applications in containers, ensuring they are secure and do not interfere with the host system.
- Resource efficiency: Docker Toolbox uses minimal resources, optimizing system performance and allowing for efficient utilization of hardware.
- Scalability: With Docker Toolbox, it’s easy to scale applications by quickly spinning up additional containers to handle increased workload demands.
Prerequisites
- 64-bit Windows 7 (or higher)
- Virtualization enabled
With Docker Toolbox you can use Docker on Windows systems which doesn’t meet the minimum system requirements (i.e. Windows 7) for Docker Desktop.
- Docker-Machine
- Kitematic, the Docker GUI
- Docker-Engine
- Oracle VM VirtualBox
- Docker-Compose
- Docker Quickstart Terminal App
Step 1 – Check your System Configuration
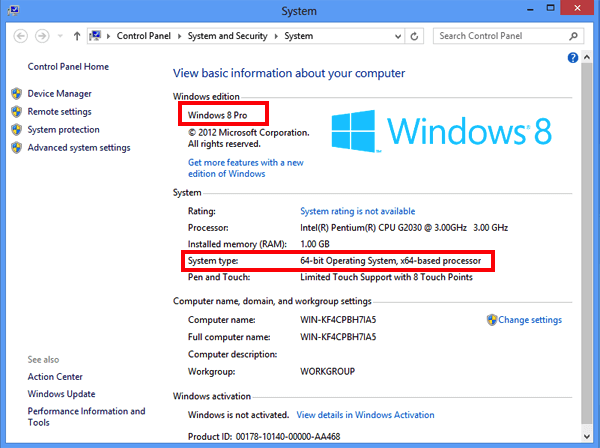
1) Check Windows OS version
- Go to “Control Panel -> System and Security -> System”.
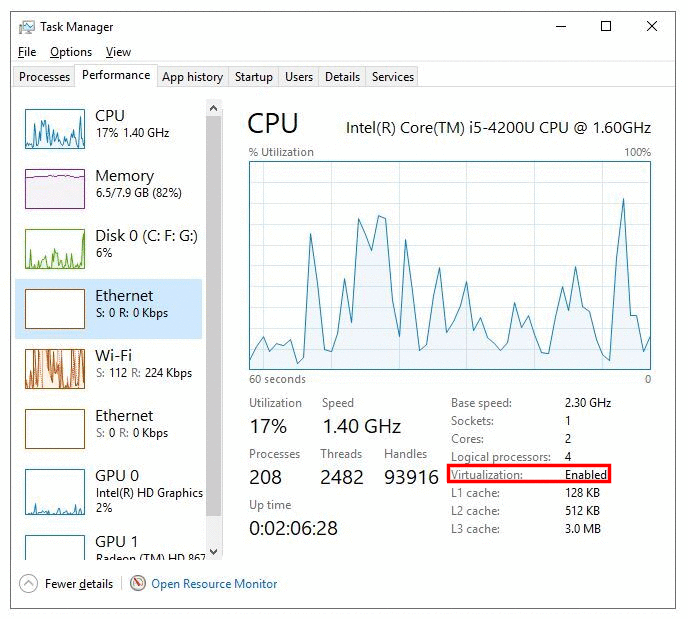
2) After that, verify if Virtualization is enabled or not?
- Now, Go to “Task Manager -> Performance”. Check if virtualization is enabled or not.
ℹ️
If virtualization is not enabled in your machine, please check how to enable it in your BIOS by following your manufacturer’s instructions.
1) Visit Toolbox Releases to download the latest version of Docker Toolbox.
Note: If VirtualBox is already installed in your machine then do not reinstall it with Docker Toolbox. When prompted, uncheck it.
ℹ️
Shut down the already running Virtual Box before starting the installation.
Note: You will get an unsigned warning (verified publisher dialog) during the installation process as Docker no longer maintains the download.docker.com url for Docker Toolbox.
2) Double click on the installer to install Docker Toolbox.
The installer launches the “Setup – Docker Toolbox” dialog.
Choose YES, if the Windows security dialog prompts you to allow the program to make a change.
3) After that, press Next to accept all the defaults and then Install.
4) Now, you will be notified by Windows Security that the installer will make changes. Ensure you are allowing the installer to make the necessary changes.
When it completes, another dialog box will open:
5) After that, uncheck “View Shortcuts in File Explorer” and press Finish.
Step 3 – Verify Installation
Follow these steps to verify your installation:
1) Your desktop should now have the following three icons:
- Docker Quickstart Terminal
- Kitematic
- Oracle VM VirtualBox
2) After that, launch the Docker Quickstart Terminal by clicking the corresponding icon. This will start the creation of the Docker machine and all its components.
- Click near the $ symbol to activate the terminal.
- Type the following command and press Enter:
docker run hello-world
Docker will download and run the “Hello world” container, and you will get a confirmation message in the terminal.
Docker is Installed Successfully on Windows
This indicates that your Docker installation is successful.
If you followed the process and everything went well, you should have Docker installed on your Windows machine, the service should be running and waiting to host containers with various apps.
What is Docker Toolbox?
Docker Toolbox is an installer for quick setup and launch of a Docker environment on previous versions of Mac and Windows systems that do not meet the requirements of the new Docker Desktop.
How can I verify if Docker Toolbox is installed correctly?
Open a command prompt or Docker Quickstart Terminal and enter the command docker version. It should display the Docker version information if installed correctly.
Which tools are included in Docker Toolbox?
Following tools are present in Docker Toolbox:
- Docker-Machine
- Docker-Engine
- Docker- Compose
- Kitematic, the Docker GUI
- Docker Quickstart Terminal App
- Oracle VM VirtualBox
What is Docker Engine?
It is a lightweight and powerful open source containerization technology combined with a workflow for building and containerizing your applications.
What is Docker Kitematic?
Kitematic automates the Docker installation and setup process and provides an intuitive graphical user interface (GUI) for running Docker containers.
Can I use Docker Toolbox to manage Docker Swarm clusters?
Yes, Docker Toolbox includes all the necessary tools to create and manage Docker Swarm clusters for container orchestration.
How can I update Docker Toolbox to the latest version?
To update Docker Toolbox, download the latest version from the Docker website and follow the same installation process as before. It will upgrade the existing installation.
Conclusion
We hope this simple tutorial helped you understand how to install Docker on your Windows machine. To learn more about Docker installation for Windows, check out the official Docker Toolbox install documentation.
If you have any queries, please leave a comment below, and we’ll be happy to respond to them for sure.
docker — DevOps Tutorials — VegaStack
VegaStack DevOps Tutorials publishes articles about Git, CI/CD, DevSecOps, Cloud, Developer Hacks, Docker, Kubernetes, DevOps News and more.
DevOps Tutorials — VegaStackSakshi .
Данная публикация является разбором особенностей контейнерной виртуализации Docker под системой Windows.
Она не претендует на роль исчерпывающей и по мере необходимости будет обновляться и дополняться.
За практическим руководством с нуля советую обратиться к этой публикации.
Содержание
- Предварительные настройки
- Выбор между Docker Toolbox on Windows или Docker for Windows
- Windows контейнеры и Linux контейнеры
- Особенности монтирования папок
- Монтирование с хост-машины или volume
- Особенности разметки диска GPT и MBR
- Docker Toobox to Windows
- Docker Swarm
- Проблемы с кодировкой
- Полезные ссылки
- Заключение
Предварительные настройки
Контейнерная виртуализация или виртуализация на уровне операционной системы Docker нативно работает только на дистрибутивах Linux и FreeBSD (экспериментально).
На Windows вам понадобится гостевая Linux система либо специальная минималистичная виртуальная машина с ядром Linux от разработчиков Docker, которая и ставится из коробки.
Само собой разумеется, что вы включили виртуализацию у себя в BIOS/UEFI
Пункт настройки может называться по-разному: VT-x, VT-d, Intel VT, AMD-V, Virtualization Technology.
Еще одним минимальным системным требованием будет разрядность системы x64 и версия не ниже Windows 7 Pro.
Выбор между Docker Toolbox on Windows или Docker for Windows
Появление Docker Toolbox on Windows и Docker Toolbox on Mac было большим событием.
Сборка включается в себя сам docker, утилиту docker-compose, утилиту для работы с виртуальной машиной docker-machine и клиент Kitematic.
Используется виртуальная машина (по умолчанию на VirtualBox) с минималистичным Linux окружением.
Позже для новых операционных систем выпустили Docker for Windows и Docker for Mac, которая на текущий момент является актуальной версией и продолжает развиваться.
Выбор между версиями не сложный:
— Если у вас Windows 10 x64 Pro, Enterprise или Education то включаем службу Hyper-V и ставим Docker for Windows.
Заметьте, что после включения службы Hyper-V пропадет возможность запускать и создавать x64 виртуальные машины на VirtualBox.
— Если же у вас другая версия Windows(7 Pro, 8, 8.1, 10 Home) то ставим VirtualBox и Docker Toolbox on Windows.
Несмотря на то, что Docker Toolbox разработчиками признан устаревшим работа с ним слабо отличается от Docker for Windows.
Вместе с установкой Docker Toolbox будет создана виртуальная машина.
В самом VirtualBox можно будет добавить оперативной памяти и ядер процессора на ваше усмотрение.
Windows контейнеры и Linux контейнеры
Docker for Windows предоставляет возможность переключать контейнеризацию между Linux и Windows версией.
В режиме Windows контейнеризации вы можете запускать только Windows приложения.
Замечу, что на май 2018 года в официальном Docker Hub существует всего 13 образов для Windows.
После включения Windows контейнеризации не забудьте добавить внешнюю сеть.
В конфигурационном файле docker-compose.yml это выглядит так:
networks:
default:
external:
name: nat
Особенности монтирования папок
На примонтированных volume-ах не кидаются события файловой системы, поэтому inotify-tools не работает.
Спасибо пользователю eee
Если вы разрабатываете свой проект и пользуетесь docker-compose вне домашней папки то вам нужно будет проделать некоторые манипуляции.
Используя Docker for Windows для монтирования нового диска у вашего локального пользователя обязательно должен стоять пароль, который будет использоваться для доступа к shared папки.
Особенность заключается в том, что монтируемые внутрь контейнера диск будет монтироваться как от удаленной машины //10.0.75.1/DISK_DRIVE по протоколу SMB.
Для Docker Toolbox диски монтируются в самом VirtualBox на вкладке «Общие папки»
Пример для диска «D»:

Права доступа к монтируемым файлам и папкам
Как бы вам не хотелось, но для всех примонтированных из хост-машины файлов и папок будут стоять права 755 (rwx r-x r-x) и поменять их вы не сможете.
Остро встает вопрос при монтировании внутрь файла закрытого SSH ключа, права на который должны быть только у владельца(например 600).
В данном случае либо генерируют ключ при создании образа, либо прокидывают сокет ssh-agent с хост-машины.
Монтирование с хост-машины или volume
Монтирование внутрь контейнера происходит с использованием сети и протокола SMB, следовательно, внутри контейнера диск «D:\» будет примонтирован из источника //10.0.75.1/D
Использование volume внутри контейнера отображается как монтирование локального диска /dev/sda1, что влияет на скорость работы.
Простым тестом копирование файла на обычном HDD скорость работы получилась следующая:
Такая разница в скорости скорее всего связана с тем, что в volume данные сбрасываются на диск постепенно, задействуя кеш в ОЗУ.
Особенности разметки диска GPT и MBR
Данный пункт не является истинной так как опровергающей или подтверждающей информации в интернете найти не смог.
Если на хост-машине таблица разделов MBR, то контейнер с MySQL/MariaDB может упасть с ошибкой:
InnoDB: File ./ib_logfile101: ‘aio write’ returned OS error 122. Cannot continue operation
По умолчанию в базе данных включеён параметр innodb_use_native_aio, отвечающий за асинхронный ввод/вывод и его надо будет выключить.
Данная проблема также встречается на некоторых версиях MacOS.
Docker Toobox to Windows
Главное правило: начинать работу с запуска ярлыка на рабочем столе «Docker Quickstart Terminal», это решает 80% проблем.
— Бывает возникают проблемы с отсутствия переменных окружения, решается командой:
eval $(docker-machine env default)
— Если все же возникают проблемы из разряда «docker: error during connect», необходимо выполнить:
docker-machine env --shell cmd default
@FOR /f "tokens=*" %i IN ('docker-machine env --shell cmd default') DO @%i
Название Docker Machine по умолчанию default.
Docker Swarm
Ни в Docker for Mac, ни в Docker for Windows — нет возможности использовать запущенные демоны в качестве клиентов кластера (swarm members).
Спасибо пользователю stychos
Проблемы с кодировкой
Используя Docker Toolbox(на Docker for Windows не удалось воспроизвести) нашлась проблема с тем, что русские комментарии в docker-compose.yml файле приводили к ошибке:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "docker-compose", line 6, in <module>
File "compose\cli\main.py", line 71, in main
File "compose\cli\main.py", line 124, in perform_command
File "compose\cli\command.py", line 41, in project_from_options
File "compose\cli\command.py", line 109, in get_project
File "compose\config\config.py", line 283, in find
File "compose\config\config.py", line 283, in <listcomp>
File "compose\config\config.py", line 183, in from_filename
File "compose\config\config.py", line 1434, in load_yaml
File "site-packages\yaml\__init__.py", line 94, in safe_load
File "site-packages\yaml\__init__.py", line 70, in load
File "site-packages\yaml\loader.py", line 24, in __init__
File "site-packages\yaml\reader.py", line 85, in __init__
File "site-packages\yaml\reader.py", line 124, in determine_encoding
File "site-packages\yaml\reader.py", line 178, in update_raw
File "c:\projects\compose\venv\lib\encodings\cp1251.py", line 23, in decode
UnicodeDecodeError: 'charmap' codec can't decode byte 0x98 in position 1702: character maps to <undefined>
[4176] Failed to execute script docker-compose
Полезные ссылки
Docker Toolbox on Windows
Docker for Windows
Практическое руководство по Docker
Заключение
Особенности работы с Docker контейнеризацией на системе Windows не отличается от работы на Linux за исключение разобранных выше.
В статье я умышленно не упомянул заметно низкую скорость работы контейнеров и overhead используя систему Windows как само собой разумеющееся.
Буду рад услышать ваши отзывы. Не стесняйтесь предлагать улучшения или указывать на мои ошибки.
Только зарегистрированные пользователи могут участвовать в опросе. Войдите, пожалуйста.
Какой версией Docker вы пользуетесь?
32% Docker Toolbox on Windows88
68% Docker for Windows187
Проголосовали 275 пользователей. Воздержались 196 пользователей.
Docker Toolbox: An Advanced Overview
Docker Toolbox is a legacy set of tools designed to facilitate the use of Docker on systems that do not meet the requirements for the standard Docker EngineDocker Engine is an open-source containerization technology that enables developers to build, deploy, and manage applications within lightweight, isolated environments called containers…. installation. It is particularly targeted at Windows and macOS environments that lack native support for Docker due to compatibility issues with hypervisor technologies. The Toolbox includes the essential components needed to create, run«RUN» refers to a command in various programming languages and operating systems to execute a specified program or script. It initiates processes, providing a controlled environment for task execution…., and manage Docker containers, encapsulated in a user-friendly interface. Though it has been largely superseded by Docker DesktopDocker Desktop is a comprehensive development environment for building, testing, and deploying containerized applications. It integrates Docker Engine, Docker CLI, and Kubernetes, enhancing workflow efficiency…., Docker Toolbox remains a vital tool for developers who work with older systems or need a lightweight alternative to Docker Desktop.
Understanding the Docker Ecosystem
Before diving into Docker Toolbox, it’s critical to understand the broader Docker ecosystem. Docker is an open-source platform that automates the deployment of applications inside lightweight containers. Containers are isolated environments that package an application and its dependencies, ensuring consistency across different computing environments. The core components of Docker include:
- Docker Engine: The runtime that allows you to build and run containers.
- Docker HubDocker Hub is a cloud-based repository for storing and sharing container images. It facilitates version control, collaborative development, and seamless integration with Docker CLI for efficient container management….: A cloud-based registryA registry is a centralized database that stores information about various entities, such as software installations, system configurations, or user data. It serves as a crucial component for system management and configuration…. where Docker images can be stored and shared.
- Docker ComposeDocker Compose is a tool for defining and running multi-container Docker applications using a YAML file. It simplifies deployment, configuration, and orchestration of services, enhancing development efficiency…. More: A tool for defining and running multi-container applications using a simple YAMLYAML (YAML Ain’t Markup Language) is a human-readable data serialization format commonly used for configuration files. It emphasizes simplicity and clarity, making it suitable for both developers and non-developers…. file.
With the rise of containerization, efficiency in development, testing, and production environments has dramatically improved. Docker Toolbox steps in for environments where users cannot leverage Docker Engine directly.
Components of Docker Toolbox
Docker Toolbox consists of several core components that work together to provide a complete containerization solution. Here’s a rundown of its key pieces:
1. Oracle VirtualBox
VirtualBox is a free and open-source virtualization software that Docker Toolbox uses to create a virtual machine (VM) to run the Docker Engine. Since Docker relies heavily on Linux kernel features, and many Windows and macOS systems do not run a native Linux kernel, VirtualBox provides the necessary abstraction layer. Inside this VM, Docker Engine can run as if it were on a native Linux system.
2. Docker Machine
Docker MachineDocker Machine is a tool that enables users to create, manage, and provision Docker hosts across various cloud providers and local environments, streamlining the deployment of containerized applications…. is a tool included in Docker Toolbox that enables users to create and manage Docker hosts (VMs) on different platforms. Using Docker Machine, users can set up a Docker environment inside the VirtualBox VM created earlier. It abstracts the complexity of managing the underlying VM while allowing users to interact with Docker seamlessly.
3. Docker CLI
The Docker Command Line Interface (CLI) is the primary way users interact with Docker and its containers. The CLI allows for a range of operations, from building images to managing containers and networks. The Docker CLI in Toolbox is essentially the same as that used in the full Docker installation, making it easier for users to transition between environments.
4. Kitematic
Kitematic is a graphical user interface (GUI) for managing Docker containers and images. While Docker is primarily command-line based, Kitematic provides a more visually appealing and user-friendly way to manage Docker resources. It offers features like one-click installations of popular images, easy containerContainers are lightweight, portable units that encapsulate software and its dependencies, enabling consistent execution across different environments. They leverage OS-level virtualization for efficiency…. management, and a visual representation of container stats.
5. Docker Quickstart Terminal
The Docker Quickstart Terminal is a terminal emulator configured specifically for Docker Toolbox. When launched, it automatically starts the VirtualBox VM and sets up the necessary environment variables, allowing users to start using Docker commands immediately without additional configuration.
Installation of Docker Toolbox
To use Docker Toolbox, you must first install it on your system. Here’s a step-by-step guide for both Windows and macOS users:
For Windows:
-
Download Docker Toolbox: Visit the Docker Toolbox GitHub Releases page to download the latest version of Docker Toolbox for Windows.
-
Run the Installer: Double-click the downloaded installer and follow the on-screen instructions. Ensure that you include VirtualBox in the installation options.
-
Launch Docker Quickstart Terminal: After installation, find the Docker Quickstart Terminal in your Start menu and open it. This will automatically create a Docker VM and set the environment.
For macOS:
-
Download Docker Toolbox: Head to the Docker Toolbox GitHub Releases page and download the .dmg installer.
-
Install Docker Toolbox: Open the .dmg file and drag the Docker Toolbox application into your Applications folder.
-
Launch Docker Quickstart Terminal: Open the Docker Quickstart Terminal from your Applications folder. It will set up a Docker VM and configure the environment for you.
Using Docker Toolbox
Once Docker Toolbox is installed and the Quickstart Terminal is running, you can start using Docker. Here’s how you can utilize its features effectively:
Creating a Docker Host
To create a new Docker host using Docker Machine, you can use the following command:
docker-machine create --driver virtualbox my-docker-hostThis command creates a new VM named my-docker-host. After the VM is created, you can start it using:
docker-machine start my-docker-hostTo set your environment variables to point to this new Docker host, run:
eval "$(docker-machine env my-docker-host)"Running a Container
To run a container, you can use the docker run command. For example, to run a simple web server using the Nginx imageAn image is a visual representation of an object or scene, typically composed of pixels in digital formats. It can convey information, evoke emotions, and facilitate communication across various media…., you can execute:
docker run -d -p 8080:80 nginxThis command pulls the Nginx image from Docker Hub (if it isn’t already present) and starts it in detached mode (-d), mapping portA PORT is a communication endpoint in a computer network, defined by a numerical identifier. It facilitates the routing of data to specific applications, enhancing system functionality and security…. 80 in the container to port 8080 on your host.
Managing Containers and Images
Docker Toolbox allows you to manage containers and images seamlessly. Use commands like docker ps to list running containers, docker images to see available images, and docker rm or docker rmi to remove containers and images respectively.
Using Kitematic
Kitematic provides a GUI for managing your Docker containers. To launch Kitematic, simply type kitematic in the Docker Quickstart Terminal. This will open a new window showcasing your available images and containers. You can pull images directly from Docker Hub, start and stop containers, and view logs, all from a user-friendly interface.
Networking with Docker Toolbox
Networking in Docker Toolbox can be slightly different from using Docker Desktop due to the VM layer provided by VirtualBox. By default, Docker Toolbox uses a special docker0 bridge networkBridge Network facilitates interoperability between various blockchain ecosystems, enabling seamless asset transfers and communication. Its architecture enhances scalability and user accessibility across networks….. Here are some essential points to remember:
Accessing Services
If you’ve mapped a port (like 8080 in the earlier example), you should access your services via the IP address of the VM created by Docker Machine. To find the IP address, use:
docker-machine ipYou can then access the serviceService refers to the act of providing assistance or support to fulfill specific needs or requirements. In various domains, it encompasses customer service, technical support, and professional services, emphasizing efficiency and user satisfaction…. in your web browser at http://:8080.
Custom Network Creation
You can create custom networks using Docker’s networking capabilities. For instance, to create a bridge networkA network, in computing, refers to a collection of interconnected devices that communicate and share resources. It enables data exchange, facilitates collaboration, and enhances operational efficiency…., you can run:
docker network createThe `docker network create` command enables users to establish custom networks for containerized applications. This facilitates efficient communication and isolation between containers, enhancing application performance and security.... my-custom-networkYou can then specify this network when running containers to facilitate communication between them.
Limitations of Docker Toolbox
While Docker Toolbox provides a great way to work with Docker on legacy systems, it does come with several limitations:
Performance Overhead
Using VirtualBox introduces some performance overhead compared to running Docker directly on a native Linux system. This can lead to slower container startup times and resource utilization.
Limited Features
Docker Toolbox lacks some of the advanced features available in Docker Desktop, such as KubernetesKubernetes is an open-source container orchestration platform that automates the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications, enhancing resource efficiency and resilience…. integration, advanced networking options, and integration with the latest Docker APIs.
Dependency on VirtualBox
Docker Toolbox relies heavily on VirtualBox, which may not be the preferred virtualization solution for all users. Users who prefer or require other virtualization technologies might find Docker Toolbox less appealing.
Alternatives to Docker Toolbox
With the introduction of Docker Desktop, which provides a more integrated experience for Windows and macOS users, Docker Toolbox has seen a decline in usage. For users who need a more modern containerization solution, here are some alternatives:
Docker Desktop
Docker Desktop is the official application for managing Docker containers on Windows and macOS. It integrates seamlessly with the host operating system and provides a more user-friendly interface, advanced features, and improved performance over Docker Toolbox.
WSL 2 (Windows Subsystem for Linux)
For Windows users, WSL 2 provides a lightweight Linux environment within Windows, allowing for a more native Docker experience. With WSL 2, users can run Docker directly without the need for a VM, thus improving performance and compatibility with Linux features.
Podman
Podman is an alternative container management tool that operates without a daemonA daemon is a background process in computing that runs autonomously, performing tasks without user intervention. It typically handles system or application-level functions, enhancing efficiency…. and offers a similar command-line interface to Docker. It is designed with a focus on security and can run in rootless mode, making it an excellent alternative for users concerned about container security.
Conclusion
Docker Toolbox remains a valuable tool for developers working with legacy systems or those seeking a lightweight alternative to Docker Desktop. By providing a complete set of tools for building, running, and managing Docker containers, it empowers users to harness the benefits of containerization even in environments that lack robust support for Docker.
Despite its advantages, users should be aware of its limitations and consider transitioning to Docker Desktop or other modern solutions as their systems permit. As containerization continues to evolve, understanding the various tools available, including Docker Toolbox, will help developers make informed decisions that align with their development and operational needs. Whether through command-line interfaces or graphical interfaces like Kitematic, Docker Toolbox offers a pathway to embracing container technology effectively.
In summary, Docker Toolbox may no longer be the cutting-edge solution for container management, but it plays a crucial role in the historical context of Docker’s development and usage, especially for those navigating legacy environments. As the landscape of containerization continues to advance, so too will the tools and best practices that enable developers to build and scale their applications efficiently.
No related posts.
Skip to content
How to install Docker Toolbox on Windows 10
In this tutorial, we will see how to install docker toolbox on Windows 10 Operating system.
How to install Docker Toolbox on Windows:
A step by step guide to install Docker toolbox.
System Information:
I am installing Docker toolbox on the below configurations. However, it is okay if your system meets the prerequisites also.
- Windows 10 Pro (64 Bit)
- RAM 8GB
- HDD 1TB
- Git 2.21
Prerequisites:
- Windows 8 Or High – 64 Bit Operating System
- RAM 2GB
- GIT 1.7 or Higher
Install Docker Toolbox on Windows:
Follow the below steps to download docker toolbox and install it. You can also see my previous article on how to install Docker Desktop on Windows 10 Operating system.
Get Docker Toolbox:
Download the latest Docker toolbox from the official website. Upon clicking the given link, you will be redirected to Docker Toolbox downloads page; there you could see the below options to download.

Click on the above highlighted Get Docker Toolbox for Windows button. An installer will be downloaded into your system.
Install Docker Toolbox:
Upon successful download, double click on the DockerToolbox.exe file, then you would see the below Setup Wizard.

Click on the Next button. Then you will be prompted to provide the installation directory. If you would like to give another location, you can click on the Browse button.

For now, I am leaving this as is and click on the Next button.
This window is used to select the components which you want to install.

On the above checklist, I deselect the Git for Windows as I have Git on my system already. You can select if you want and click on the Next button.

The above window provides some additional task to be performed along with installation – Like creating a desktop shortcut and setting the PATH to docker binaries so that you no need to set PATH manually.
Click on the Next button.

Review the selected components and click on the Install button.

You can see the installation process; if everything went well, you could see the below success window.

Click on the Finish button to close the window. Till now we installed the Docker Toolbox on Windows 10 operating system lets start to access this.
Access Docker Toolbox:
Upon successful installation, you could see the following three icons on your Windows desktop.
- Oracle VM VirtualBox
- Docker Quickstart
- Kitematic

Double click on Docker Quickstart icon, then you would see the below docker terminal (docker interactive shell).

Verification:
To verify the installation, check the docker version (docker –version), then you would see the installed docker version as a result.

Done!
References:
- Download Docker Toolbox
- Install Docker Desktop on Windows 10
Happy Learning:)
Share a word.
Related Posts
Page load link
