Что такое Docker Desktop
Docker Desktop — это инструмент для работы с Docker-контейнерами на локальной машине. Он упрощает процесс разработки, тестирования и развертывания приложений, позволяя взаимодействовать с контейнерами как через консоль, так и через удобный интерфейс.
Ключевые особенности:
- понятный графический интерфейс,
- удобное управление образами и контейнерами,
- встроенные инструменты для мониторинга,
- возможность разработки и тестирования без привязки к серверу,
- поддержка работы с Docker Compose.
Если вы только начинаете изучение Docker и хотите разобраться в основах, рекомендуем ознакомиться с отдельным вводным обзором. В нем разобрали принципы работы Docker, его основные компоненты и решаемые задач. Из текста вы узнаете, как создать и запустить контейнер, а также какую роль играет Kubernetes в связке c Docker.
О системных требованиях
Перед установкой Docker Desktop важно выбрать подходящий бэкенд для работы с контейнерами: WSL 2 или Hyper-V. Оба имеют свои особенности, так что от выбора будут зависеть и системные требования. Далее в тексте разберемся, когда и какой бэкенд подойдет лучше.
Когда нужен WSL
WSL 2 (Windows Subsystem for Linux 2) — это усовершенствованная версия подсистемы Windows для Linux, которая использует виртуальную машину с реальным Linux-ядром. В отличие от первой версии, WSL 2 обеспечивает лучшую совместимость с Linux-инструментами, технологиями и приложениями, а также более высокую производительность.
Преимущества использования WSL 2 с Docker Desktop
Работа с Linux-контейнерами. Docker изначально разрабатывали для работы в Linux-среде, поэтому большинство контейнеров в Docker Hub — это образы, ориентированные на Linux. Использование WSL 2 предоставляет Docker Desktop полноценную Linux-среду на Windows.
Повышенная производительность. WSL 2 значительно ускоряет выполнение контейнеров, что особенно заметно в сравнении с WSL 1 или Hyper-V, о котором мы расскажем дальше. Это преимущество обеспечивает полноценное Linux-ядро, которое позволяет Docker работать гораздо быстрее и с меньшими накладными расходами.
Работа с файловой системой Linux. В WSL 2 можно монтировать файловую систему Linux, что позволяет работать с кодом и данными в нативной Linux-среде. Это особенно важно при разработке приложений, которые будут запускаться в Linux-контейнерах и требуют специфической настройки среды — например, прав доступа или структуры каталогов.
Когда нужен Hyper-V
Рассмотрим ключевые сценарии, в которых предпочтительнее использовать Hyper-V.
Если система не поддерживает WSL 2
Некоторые сборки системы не позволяют включать необходимые компонентов для работы WSL 2 В частности, это касается старых версий Windows, а также устройств, которые не поддерживают Windows 10 Pro или 11 Pro, — WSL 2 для них недоступна, так как требует включенной виртуализации на уровне системы. В таких случаях можно использовать Hyper-V для виртуализации контейнеров и запуска Docker Desktop.
Для работы с Windows-контейнерами
Docker Desktop поддерживает как Linux-, так и Windows-контейнеры. Однако последние требуют прямого взаимодействия с ядром Windows, а WSL 2 предоставляет только Linux-среду. Hyper-V позволяет запускать Windows-контейнеры благодаря виртуализации Windows-системы.
Для изоляции и обеспечения безопасности
Hyper-V создает полноценные виртуальные машины, обеспечивая строгую изоляцию контейнеров друг от друга и от хост-системы. Это может быть важно в корпоративной среде или при работе с чувствительными данными.
Разница между WSL 2 и Hyper-V
Если вам нужны Linux-контейнеры и высокая производительность — выбирайте WSL 2. Если же требуется строгая изоляция или работа с Windows-контейнерами, Hyper-V будет предпочтительнее. Подробнее о разнице по ключевым критериям — в таблице:
| Критерий | WSL 2 | Hyper-V |
| Производительность | Высокая (нативное Linux-ядро) | Низкая (работа через полноценную ВМ) |
| Изоляция | Относительно низкая | Высокая (контейнеры изолированы) |
| Типы контейнеров | Только Linux-контейнеры | Linux- и Windows-контейнеры |
Системные требования Docker Desktop
При использовании WSL 2 в качестве бэкенда
- WSL версии 1.1.3.0 или новее.
- Windows 11 64-bit Home / Pro / Enterprise / Education, версия 22H2 или новее.
- Windows 10 64-bit Home / Pro / Enterprise / Education, версия 22H2 (сборка 19045) или новее.
- Включенная функция WSL 2 в Windows. Подробная инструкция есть в документации Microsoft;
- 4 ГБ ОЗУ.
- Включенная аппаратная виртуализация в BIOS на вашей локальной машине.
При использовании Hyper-V в качестве бэкенда
- Windows 11 64-разрядная Enterprise / Pro / Education, версия 22H2 или новее.
- Windows 10 64-разрядная Enterprise / Pro / Education, версия 22H2 (сборка 19045) или новее.
- Включенная функция Hyper-V. Подробнее об установке — в документации Microsoft;
- 4 ГБ ОЗУ.
- Включенная аппаратная виртуализация в BIOS на вашей локальной машине.
Установка WSL 2
1. Откройте PowerShell от имени администратора и введите команду wsl —install. Она выполняет следующие действия:
- включает дополнительные компоненты WSL и платформы виртуальных машин;
- скачивает и устанавливает последнюю версию ядра Linux;
- задает WSL 2 в качестве среды по умолчанию;
- скачивает и устанавливает дистрибутив Ubuntu Linux.
2. После успешной установки всех компонентов перезапустите компьютер.
Первичная настройка
1. Откройте установленный дистрибутив с помощью меню Пуск — найдите установленный дистрибутив (Ubuntu).
2. При первом запуске системы нужно создать имя пользователя и пароль для дистрибутива Linux.
3. Первичная настройка завершена, можно приступать к использованию WSL 2.
Альтернативный вариант — запустить WSL через PowerShell. Для этого введите команду wsl и система предложит произвести первичную настройку.
Установка Hyper-V
Для установки компонентов Hyper-V откройте PowerShell от имени администратора и выполните команду:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Hyper-V -All
Она установит все компоненты для работы Hyper-V, после чего нужно будет перезапустить компьютер.
Проверить корректность установки Hyper-V можно с помощью команды:
Get-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName *hyper*|ft
Установка Docker с бэкендом WSL 2
- Скачайте дистрибутив Docker Desktop с официального сайта и запустите установщик. Галочки оставьте на всех пунктах.
- После установки перезайдите в учетную запись и откройте ярлык Docker Desktop.
- Если все прошло успешно, вы увидите интерфейс инструмента:
Установка Docker с бэкендом Hyper-V
1. Скачайте дистрибутив Docker Desktop с официального сайта и запустите установщик. В инсталляционном окне уберите галочку Use WSL 2 instead of Hyper-V.
2. После установки перезайдите в учетную запись и откройте ярлык Docker Desktop.
3. Если установка выполнена корректно, программа запустится без ошибок и вы увидите интерфейс:
Запуск контейнера
Рассмотрим запуск первого контейнера на примере самого популярного образа — hello-world.
Поиск и скачивание образа
Поскольку вы только установили Docker Desktop, в системе нет образов контейнеров, которые можно запустить. Исправим это.
- Перейдите в раздел Images и нажмите кнопку Search images to run.
- Введите hello-world. В текущем окне на выбор есть две кнопки: Pull и Run. Если планируете для начала просто скачать образ, то выбирайте Pull. Если скачать и сразу запустить — Run.
- Оставляем стандартные настройки для запуска.
Проверка работы контейнера
Чтобы посмотреть запущенные контейнеры, перейдите во вкладку Containers и выберите созданный на прошлом этапе. В нашем примере для него было автоматически сгенерировано имя determined_jennings. Открыв контейнер, вы увидите сообщение, если настройка установка прошла успешно.
Как настроить запуск Docker при старте Windows
Для автозапуска Docker Desktop при авторизации на компьютере достаточно поставить галочку в настройках: Settings → General → Start Docker Desktop when you sign in to your computer.
После этого Docker Desktop будет запускаться автоматически при включении устройства.
Запуск Docker в облаке
Docker Desktop — удобный инструмент для локальной работы, но в ряде случаев может потребоваться облачная инфраструктура:
- если мощности вашего ПК не хватает для работы с контейнерами;
- если нужна среда для тестирования без нагрузки на локальную машину;
- если вы работаете с ML/AI и нужны видеокарты для обучения моделей.
1. В панели управления в верхнем меню перейдем в раздел Продукты → Облачные серверы.
2. Нажмем кнопку Создать сервер.
3. Выберем имя, регион и сегмент пула. Важно учесть, что от сегмента зависят доступные конфигурации и стоимость. После создания сервера менять сегмент пула нельзя.
4. В качестве источника выберите готовый образ, приложение, свой образ, сетевой диск или снапшот. В нашем случае — приложение Containers Ready с настроенной Ubuntu 22.04. Оно содержит:
- Docker версии 27.0.3;
- плагины для запуска Docker Compose версии 2.11.1;
- Portainer версии 2.20.3 — графический интерфейс для мониторинга и управления Docker-контейнерами, образами и сетью Docker.
5. Конфигурацию для примера возьмем базовую — 2 vCPU и 2 ГБ RAM, а в поле Диски выберем SSD Быстрый на 20 ГБ. Важно: это минимальные требования. Рекомендуем выбирать параметры серверы, исходя из ваших задач.
Помимо прочего, на этапе создания сервера или позже вы можете добавить GPU. При этом объем ОЗУ, который выделяется серверу, может быть меньше указанного в конфигурации — ядро ОС резервирует ее часть. Выделенный объем на сервере можно посмотреть с помощью команды sudo dmesg | grep Memory.
6. Для работы Containers Ready сервер должен быть доступен из интернета. Для этого создадим приватную подсеть и подключим публичный IP-адрес. В поле Сеть выберем Приватная подсеть и добавим новый публичный адрес. Подробнее о настройке подсети можно узнать в документации.
6. Добавьте SSH-ключ в поле Доступ. Подробнее о его генерации можно узнать в отдельной инструкции.
7. Ознакомьтесь с ценой и нажмите кнопку Создать сервер.
Сервер готов к использованию! Подробности о создании сервера с Сontainers Ready вы можете найти в документации. Если вам нужно запускать контейнеры с ML-моделями на мощных видеокартах, развернуть облачные серверы с GPU можно за несколько минут. Они помогут ускорить обучение нейросетей без закупки дорогого оборудования.
Читайте другие тексты о Docker
Docker is a powerful platform that allows you to develop, ship, and run applications inside lightweight containers. Install Docker on Windows to create consistent development environments, streamline deployment processes, and enhance system efficiency.
This guide will provide step-by-step instructions for installing Docker on Windows using the GUI or the command line.

Prerequisites
- A machine running Windows 10 22H2 or Windows 11.
- At least 4GB of RAM.
- A user account with administrator privileges.
- WSL 2 enabled.
Install Docker Desktop on Windows via GUI
Installing Docker via a GUI is simple, with a full desktop app, and it is great for beginners and GUI users. It involves downloading the Docker Desktop Installer from the official website and installing the program through a wizard.
Follow the steps in the sections below.
Step 1: Download Docker Desktop Installer
Download the Docker Desktop Installer for Windows x86/x64 from the official Docker website.
Note: A paid subscription is required if you plan to use Docker Desktop in large enterprises with over 250 employees or if your annual revenue exceeds $10 million USD. Docker is free for personal use, small businesses, and education. Refer to the official page for pricing details.
Step 2: Install Docker Desktop
The steps below will guide you through the installation process:
1. Find and double-click the downloaded installer to start the installation.
2. The installer initializes, and the configuration screen appears, allowing you to customize your setup.
Keeping the default options checked is recommended, as WSL 2 offers faster performance, better integration with the Windows filesystem, and uses fewer system resources compared to Hyper-V.
Uncheck the box to use Hyper-V instead if you need to run traditional Windows-based virtual machines or if you require stricter isolation and security controls than WSL’s.
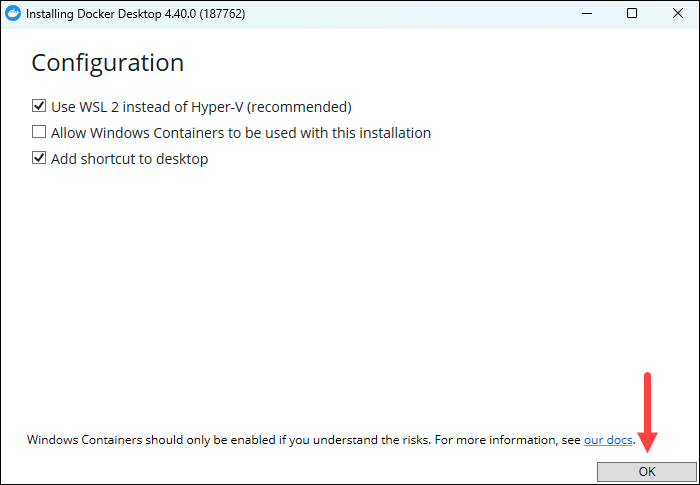
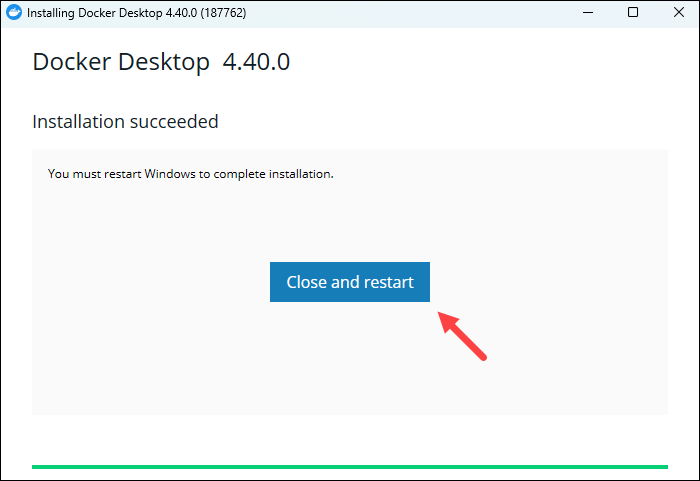
Click OK to start the installation.
3. When the process completes, click the Close and restart button to close the installer and reboot Windows for the changes to take effect:
Step 3: Start Docker Desktop
After installation, start the Docker tool manually:
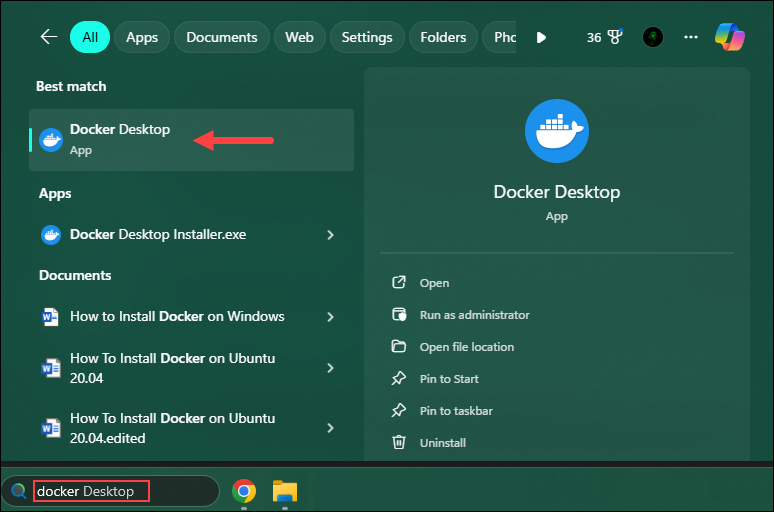
1. Press the Windows button and type Docker desktop to find the app.
2. Open the Docker Desktop app from the search results.
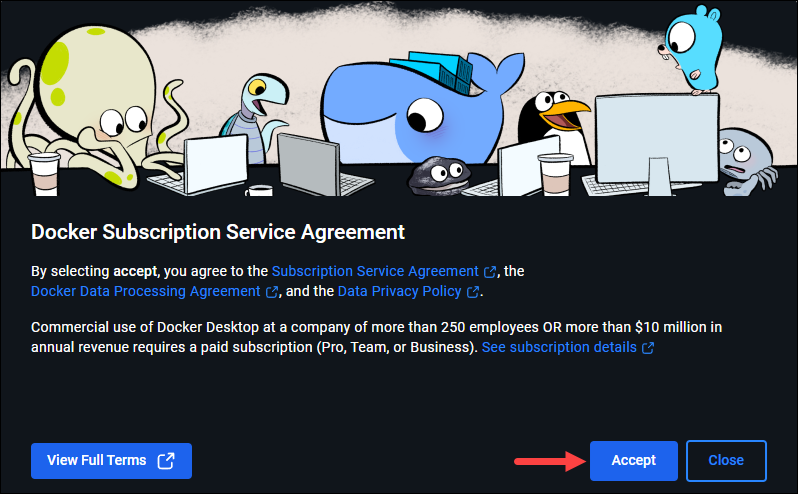
3. The app requires you to accept the Docker Subscription Service Agreement first. If you agree with the terms, click Accept to proceed.
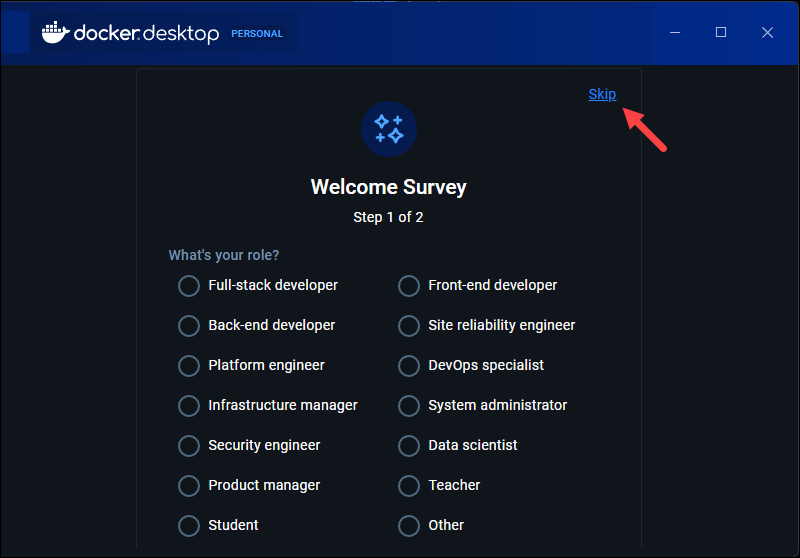
4. The app presents a Welcome survey. The survey is optional, and you can click Skip in the top right corner to move on to the sign-in step.
5. The Welcome to Docker screen appears, where you can sign in to Docker if you already have an account or create a new account. Complete the sign-in process to finish the installation.
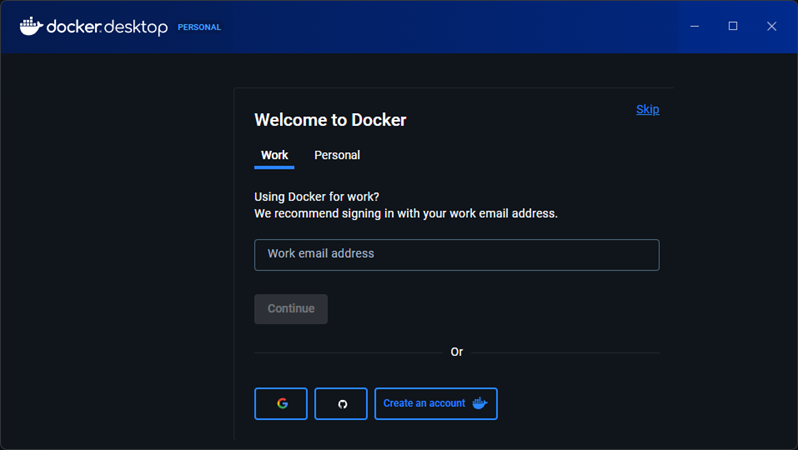
6. After signing in, the Docker Desktop dashboard opens, which means Docker Desktop is successfully running on Windows.
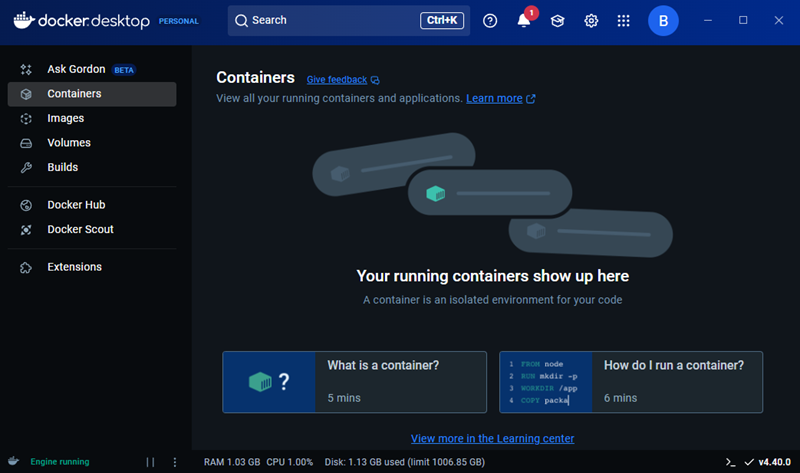
Install Docker Desktop via CLI
This method shows a terminal-based, manual setup that installs Docker in a Linux environment inside Windows, without using the GUI installer. The installation is silent, via PowerShell, and it is ideal for sysadmins or DevOps users who want automation or script-based installs.
Note that Docker still runs on Windows through the Docker Desktop app (with GUI components), even if it is installed and started via the terminal.
Step 1: Download the Installer
Download the Docker Desktop Installer and save it in an easily accessible location. Remember the path as you will need it in the following step.
Step 2: Install Docker
After you download the installer, there are two ways to install Docker Desktop, depending on which command line option you want to use:
Windows PowerShell
1. Open PowerShell as an administrator and use the cd command to navigate to the folder in which you downloaded the installer.
2. Run the command below to install Docker Desktop:
Start-Process 'Docker Desktop Installer.exe' -Wait --quiet install3. If prompted, click OK to complete the installation.
Command Prompt
1. Open Windows Command Prompt as an administrator and navigate to the installer location.
2. Run the command below to start the installation:
start /w "" "Docker Desktop Installer.exe" install3. When prompted, click OK to finish the installation.
The default installation location for Docker Desktop is C:\Program Files\Docker\Docker.
Step 3: Add User Account
If your admin account and user account are not the same, use the syntax below to add user accounts to Docker user groups:
net localgroup docker-users [user] /addReplace [user] with the respective username.
Step 4: Start Docker Desktop
Open the Docker Desktop app and sign in to your account to enable the Docker engine. Follow the steps outlined in Step 3: Start Docker Desktop section above, and when you finish, you can start using Docker.
Step 5: Verify Docker Installation
To verify that Docker installed correctly, pull a sample image. In PowerShell or the Command Prompt, run the command below:
docker pull nginx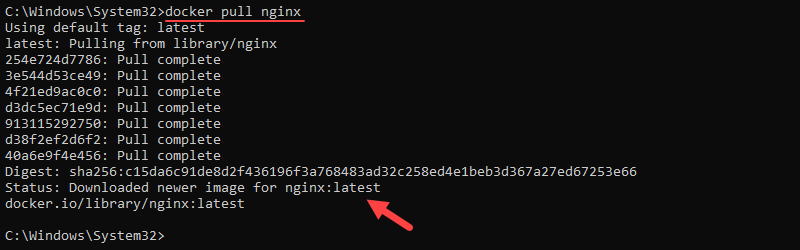
If the image pulls successfully, Docker Desktop has been installed correctly.
Install Docker on Windows via Command Line
This method shows how to bypass Docker Desktop completely and install the Docker Engine inside a Linux environment (Ubuntu on WSL). Installing Docker inside a Linux environment is closer to how Docker works natively on Linux systems. It is ideal for developers who want a lightweight, GUI-free, native-Linux experience or dislike Docker Desktop’s licensing or resource overhead.
Follow the steps in the sections below.
Step 1: Enable WSL
If you do not have WSL enabled, you must first install it. Open PowerShell or Windows Command Prompt as an administrator and run the following command:
wsl --installThe command enables the required features for running WSL and installs the default Linux distro (Ubuntu).
If you want a specific Linux distribution, you can specify it using the -d flag. In this tutorial, we will use Ubuntu 24.04:
wsl --install -d Ubuntu-24.04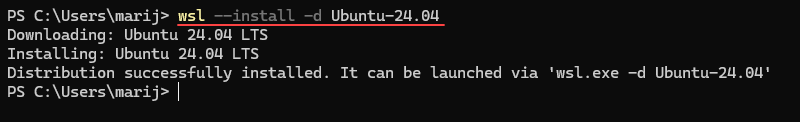
Step 2: Initialize Distro and Create User
After the installation, it is time to set up the Linux distribution.
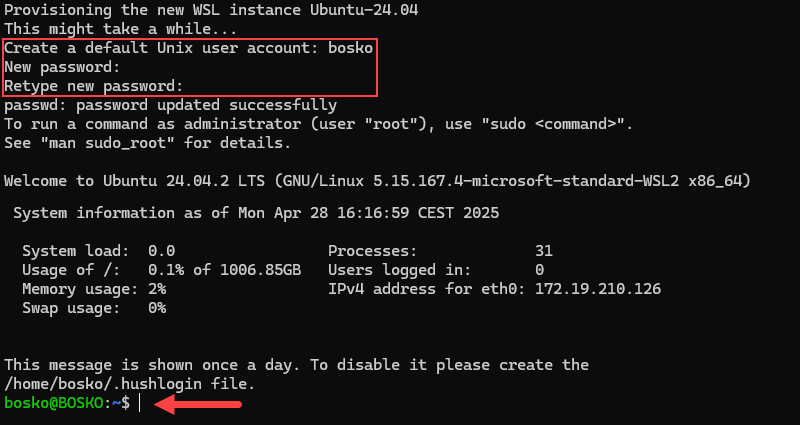
1. Press the Windows button and type Ubuntu to find the distribution. Press Enter to initialize it.
2. After the instance initializes, it prompts you to create a new default user account. Provide the username and password to start using Ubuntu within WSL.
Step 3: Install Docker
After initialization, the system is ready for Docker installation. Follow the steps below:
1. Update the system package index with:
sudo apt update2. Install the dependencies:
sudo apt install ca-certificates curl3. Set the permissions for the /etc/apt/keyrings directory that will hold the GPG key:
sudo install -m 0755 -d /etc/apt/keyrings4. Download the GPG key:
sudo curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc5. Change the key permissions:
sudo chmod a+r /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc6. Add the Docker repository to apt sources:
echo \
"deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
$(. /etc/os-release && echo "${UBUNTU_CODENAME:-$VERSION_CODENAME}") stable" | \
sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null7. Refresh the package index one more time to pull information from the Docker repository:
sudo apt update8. Install Docker and all required packages:
sudo apt install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-compose-plugin docker-buildx-pluginWait for the installation to complete. For more detailed instructions on enabling non-root access and a QuickStart guide on using Docker in Ubuntu, refer to our tutorial for installing Docker on Ubuntu.
If you have installed a different distribution on WSL, refer to our guides for installing Docker on Raspberry Pi, Rocky Linux and CentOS, or Debian.
9. After you set up and customize the installation to your needs, verify the installation with:
docker --versionThe output should print the Docker version if the installation completed successfully:

Conclusion
This tutorial showed how to install Docker on Windows using the GUI or the CLI. Installing Docker on Windows allows users to benefit from streamlined development processes, reliable application deployment, and greater operational efficiency.
Next, learn how to check and reduce Docker image size or set up and use a private Docker registry. If you already use Docker, download our handy Docker commands cheat sheet.
Was this article helpful?
YesNo
1,600 words, 8-minute read
Docker can be installed on Linux, mac OS, or Windows.
Requirements and installation instructions can be found on the Docker Docs help pages.
Install Docker on Linux #
Docker Desktop for Linux can be downloaded from Docker Hub. The installer includes the Docker server, CLI, Docker Compose, Docker Swarm, and Kubernetes.
Alternatively, the Docker command-line tool is available in official Linux repositories although these are often older editions. The latest edition is supported on recent 64-bit editions of popular Linux distros:
- Ubuntu (and derivatives such as Mint)
- CentOS
- Debian
- Fedora
Static binaries are available for other distros, although Googling “install Docker on [your OS]” may provide easier instructions, e.g. “install Docker on a Raspberry Pi”.
Follow the Docker documentation for your distro. For example, Docker for Ubuntu is installed with the following commands:
sudo apt-get remove docker docker-engine docker.io containerd runc
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install ca-certificates curl gnupg lsb-release
sudo mkdir -p /etc/apt/keyrings
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg
echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-compose-pluginTo run Docker commands as a non-root user (without sudo), create and add yourself to a docker group:
sudo groupadd docker
sudo usermod -aG docker $USERThen reboot to apply all changes.
Install Docker on macOS #
Docker Desktop for macOS Sierra 10.13 and above can be downloaded from Docker Hub. The package includes the Docker server, CLI, Docker Compose, Docker Swarm, and Kubernetes.
Two editions are available: stable and edge with experimental features. The stable version is best for most developers.
Double-click Docker.dmg to open the installer, then drag the Docker icon to the Applications folder. Double-click Docker.app in that folder to launch Docker.
After completion, the whale icon in the status bar indicates Docker is running and commands can be entered in the terminal.
Install Docker on Windows #
Docker Desktop for Windows requires either WSL2 or Hyper-V.
Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) 2 #
WSL allows you to run full Linux environments directly on Windows 10 or Windows 11.
IMPORTANT!
You can not install the Linux edition of Docker within a WSL-powered Linux distro. You must install Docker Desktop for Windows which allows Docker commands to be run in all Windows and Linux terminals.
WSL2 is the recommended default option for Docker on Windows. It is faster than Hyper-V and available in all editions of Windows 11 and Windows 10 from the May 2020 update (version 2004, OS build 19041).
To install WSL2:
-
Enable hardware virtualization support in your BIOS.
This will be active on most devices, but check by rebooting and accessing your PC’s BIOS panels – typically by hitting DEL, F2, or F10 as your system starts. Look for Virtualization Technology, VTx or similar options. Ensure they are enabled, save, and reboot.
WARNING! Be careful when changing BIOS settings – one wrong move could trash your PC.
-
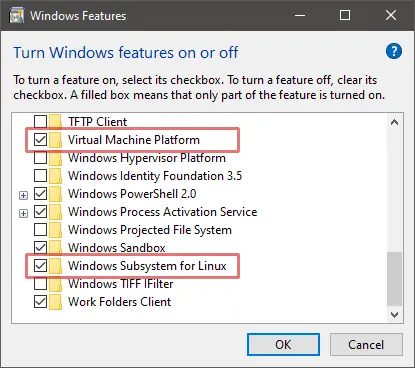
Enable the Virtual Machine Platform and Windows Subsystem for Linux options in the Turn Windows features on or off panel:
This can be accessed by hitting the Start button and typing the panel name or from Programs and Features in the classic Control Panel.
-
Reboot, then enter the following command in a Windows Powershell or
cmdprompt to set WSL2 as the default:wsl --set-default-version 2 -
Download and install your preferred distro by searching for “Linux” in the Microsoft Store app. Ubuntu is a good choice.
-
To complete the installation, launch your distro by clicking its Store’s Launch button or choosing its icon from the Start menu.
You may be prompted to install a kernel update – follow the instructions and launch the distro again.
-
Enter a Linux username and password. These are separate from your Windows credentials although choosing the same ones can be practical.
-
Ensure your distro is up-to-date. For example, on an Ubuntu bash prompt enter:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
You can now install Docker Desktop (see below). For the best performance and stability, store development files in your Linux file system and run Docker from your Linux terminal.
More information about installing and using WSL2:
- Windows Subsystem for Linux 2: The Complete Guide, and
- optionally, Windows Terminal: The Complete Guide.
Hyper-V #
The Microsoft Hyper-V hypervisor is provided free with Windows 10 and 11 Professional and Enterprise. (Windows Home users must use WSL2.)
To install Hyper-V:
-
Enable hardware virtualization support in your BIOS.
This will be active on most devices, but check by rebooting and accessing your PC’s BIOS panels – typically by hitting DEL, F2, or F10 as your system starts. Look for Virtualization Technology, VTx or similar options. Ensure they are enabled, save, and reboot.
WARNING! Be careful when changing BIOS settings – one wrong move could trash your PC.
-
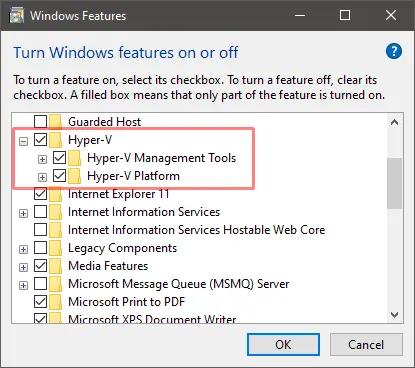
Enable the Hyper-V option in the Turn Windows features on or off panel then reboot.
This can be accessed by hitting the Start button and typing the panel name or from Programs and Features in the classic Control Panel.
You can now install Docker Desktop.
Install Docker Desktop for Windows #
Docker Desktop for Windows 10 and 11 can be downloaded from Docker Hub. The installer includes the Docker server, CLI, Docker Compose, Docker Swarm, and Kubernetes.
Two editions are available: stable and edge with experimental features. The stable version is best for most developers.
Double-click Docker Desktop Installer.exe to start the installation process. After completion and launch, the whale icon in the notification area of the task bar indicates Docker is running and ready to accept commands in the Windows Powershell/cmd terminal (and Linux if using WSL2).
Docker Engine Settings #
Docker uses WSL2 as the default engine when available. You will be prompted to confirm this choice during installation and after WSL2 is installed.
Alternatively, WSL2 can be enabled by checking Use the WSL 2 based engine in the General tab of Settings accessed from the Docker task bar icon. Unchecking the option reverts to Hyper-V.
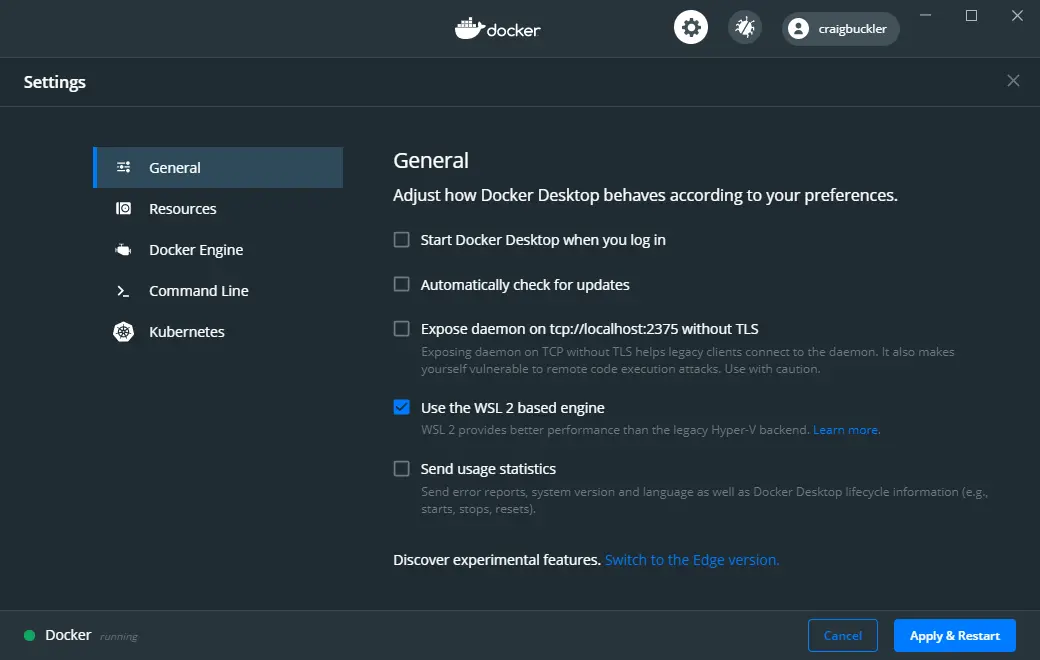
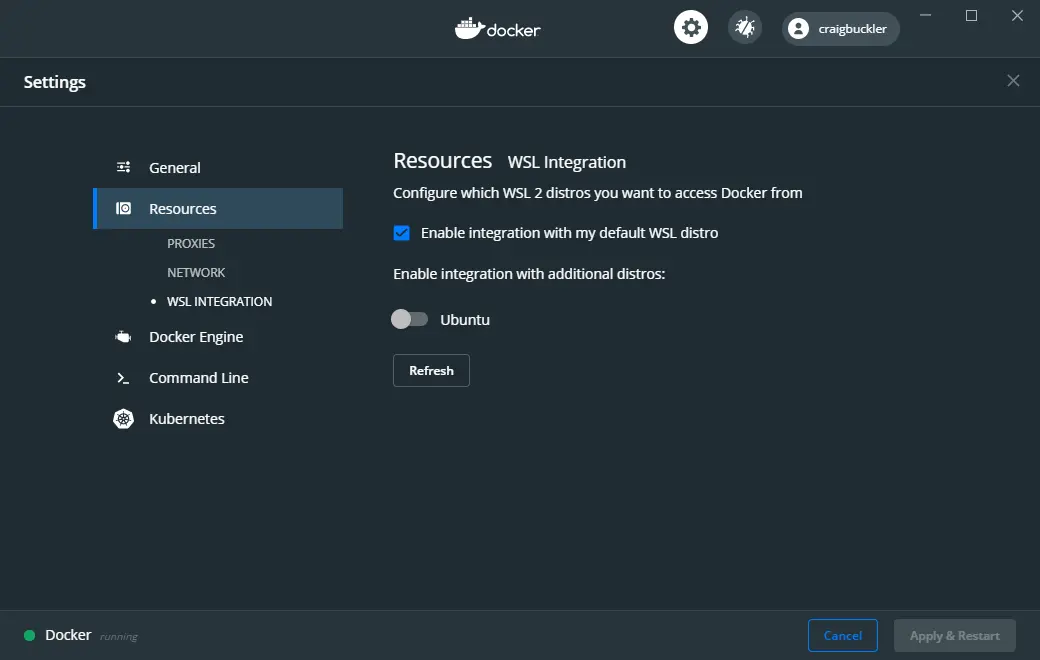
When using WSL2, at least one Linux distro must be enabled – the default is chosen. You can also permit Docker commands in other distros by accessing the WSL integration panel in the Resources section of the Docker Settings:
When using Hyper-V, Docker must be granted access to the Windows file system. Select the drives it is permitted to use by accessing the File Sharing panel in the Resources section of the Docker Settings:
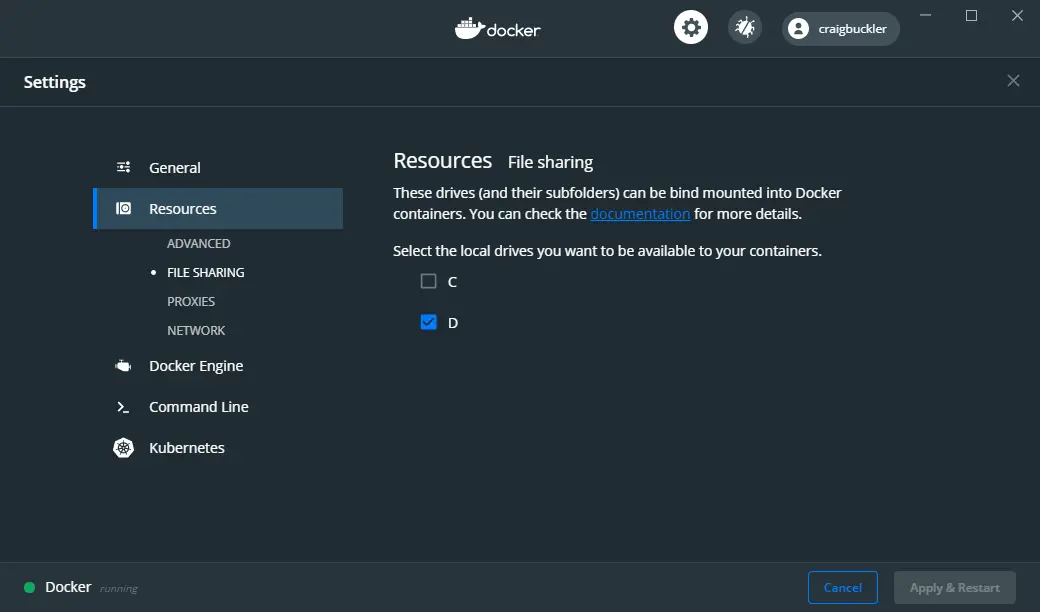
(This option was named Shared Drives in previous editions of Docker Desktop.)
Test your Docker installation #
Check Docker has successfully installed by entering the following command in your terminal:
docker versionA response similar to the following is displayed:
Client: Docker Engine - Community
Version: 19.03.12
API version: 1.40
Go version: go1.13.10
Git commit: abcdef0
Built: Mon Jun 22 15:45:36 2020
OS/Arch: linux/amd64
Experimental: false
Server: Docker Engine - Community
Engine:
Version: 19.03.12
API version: 1.40 (minimum version 1.12)
...etc...Ensure Docker Compose is working by entering:
docker-compose versionTo receive something like:
docker-compose version 1.27.2, build 8d51620a
docker-py version: 4.3.1
CPython version: 3.7.7
OpenSSL version: OpenSSL 1.1.1c 10 Sep 2019Optionally, try entering:
docker run hello-worldto verify Docker can pull an image from Docker Hub and start containers as expected…
Unable to find image 'hello-world:latest' locally
latest: Pulling from library/hello-world
1b930d010525: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:f9dfddf63636d84ef479d645ab5885156ae030f611a56f3a7ac
Status: Downloaded newer image for hello-world:latest
Hello from Docker!
This message shows your installation appears to be working correctly.Key points #
What you’ve learned in this chapter:
- How to install and configure Docker on your Linux, macOS, or Windows system.
- How to install Docker Compose.
- How to test the Docker installation.
The following chapters demonstrate how to use Docker during development…
…but to continue reading, you need to buy the book.
Do you want an easy-to-follow course which demonstrates how to use Docker and create practical web development environments on your Windows, macOS, or Linux PC?
Buy the «Docker for Web Developers» book & video course…
-
full course
$99 $50 £43 / €49
buy all
-
ebooks only
$30 $15 £13 / €15
buy books
-
videos only
$80 $40 £34 / €40
buy videos
plus your country’s sales tax where applicable

System Requirements:
1 . WSL 2 backend
- WSL version 1.1.3.0 or later.
- Windows 11 64-bit: Home or Pro version 21H2 or higher, or Enterprise or Education version 21H2 or higher.
- Windows 10 64-bit.
- We recommend Home or Pro 22H2 (build 19045) or higher, or Enterprise or Education 22H2 (build 19045) or higher.
- Minimum required is Home or Pro 21H2 (build 19044) or higher, or Enterprise or Education 21H2 (build 19044) or higher.
Turn on the WSL 2 feature on Windows. For detailed instructions, refer to the Microsoft documentation.
The following hardware prerequisites are required to successfully run WSL 2 on Windows 10 or Windows 11:
- 64-bit processor with Second Level Address Translation (SLAT)
- 4GB system RAM
- Enable hardware virtualization in BIOS. For more information, see Virtualization.
2.Hyper-V backend and Windows containers
- Windows 11 64-bit: Pro version 21H2 or higher, or Enterprise or Education version 21H2 or higher.
- Windows 10 64-bit:
- We recommend Home or Pro 22H2 (build 19045) or higher, or Enterprise or Education 22H2 (build 19045) or higher.
- Minimum required is Home or Pro 21H2 (build 19044) or higher, or Enterprise or Education 21H2 (build 19044) or higher.
For Windows 10 and Windows 11 Home, see the system requirements in the WSL 2 backend tab.
- Turn on Hyper-V and Containers Windows features.
- The following hardware prerequisites are required to successfully run Client Hyper-V on Windows 10.
- 64 bit processor with Second Level Address Translation (SLAT)
- 4GB system RAM
- Turn on BIOS-level hardware virtualization support in the BIOS settings. For more information, see Virtualization.
Install Docker Desktop on Windows:
- Download the installer using the download button at the top of the page, or from the docker.com/products/docker-desktop.
- Double-click Docker Desktop Installer.exe to run the installer. By default,
Docker Desktop is installed at {% embed %}C:\Program Files\Docker\Docker. - When prompted, ensure the Use WSL 2 instead of Hyper-V option on the Configuration page is selected or not depending on your choice of backend. If your system only supports one of the two options, you will not be able to select which backend to use.
- Follow the instructions on the installation wizard to authorize the installer and proceed with the install.
- When the installation is successful, select Close to complete the installation process.
If your admin account is different to your user account, you must add the user to the docker-users group:
- Run Computer Management as an administrator.
- Navigate to Local Users and Groups > Groups > docker-users.
- Right-click to add the user to the group.
- Sign out and sign back in for the changes to take effect.
Install from the command line:
After downloading Docker Desktop Installer.exe, run the following command in a terminal to install Docker Desktop:
$ "Docker Desktop Installer.exe" install
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
If you’re using PowerShell you should run it as:
Start-Process 'Docker Desktop Installer.exe' -Wait install
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
If using the Windows Command Prompt:
start /w "" "Docker Desktop Installer.exe" install
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
By default, Docker Desktop is installed at C:\Program Files\Docker\Docker.
The install command accepts the following flags:
-
--no-windows-containers:Disables the Windows containers integration -
--allowed-org=<org name>:Requires the user to sign in and be part of the specified Docker Hub organization when running the application -
--backend=<backend name>:Selects the default backend to use for Docker Desktop,hyper-v,windowsorwsl-2(default) -
--installation-dir=<path>: Changes the default installation location (C:\Program Files\Docker\Docker)
Start Docker Desktop:
Docker Desktop does not start automatically after installation. To start Docker Desktop:
- Search for Docker, and select Docker Desktop in the search results.

- Click on the Docker Desktop icon to launch the application.
- Docker Desktop may take a few moments to start up, especially if it’s the first time you’re running it after installation or after a system reboot.
- Once Docker Desktop is started, you should see its icon in the system tray (bottom-right corner of your screen, near the clock). The icon typically looks like a whale. You may need to click on the up arrow to reveal hidden icons.
- You can now start using Docker commands in your command prompt, PowerShell, or terminal to manage containers and images.
Рассмотрим установку Docker Desktop for Windows — это Community-версия Docker для систем Microsoft Windows.
Системные требования
- Windows 10 64-bit: Pro, Enterprise, Education (Build 16299 или выше).
Для успешного запуска Client Hyper-V в Windows 10 требуются следующие предварительные требования к оборудованию:
- 64 bit процессор c поддержкой Second Level Address Translation (SLAT).
- 4GB системной памяти.
- Поддержка аппаратной виртуализации на уровне BIOS должна быть включена в настройках BIOS.
Подготовка
Включаем функции Hyper-V Containers Window. Для этого переходим в панель управления – установка и удаление программ – включение или отключение компонентов Windows. Активируем пункт Hyper-V, который включает Hyper-V Managment Tools, Hyper-V Platform.
Также это можно выполнить через powershell или dism (все команды необходимо выполнять с правами администратора).
Powershell:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Hyper-V -All
DISM:
DISM /Online /Enable-Feature /All /FeatureName:Microsoft-Hyper-V
Установка
Скачиваем установщик Docker (Docker Desktop Installer) с Docker Hub.
Установка Docker Desktop включает Docker Engine, Docker CLI client, Docker Compose, Notary, Kubernetes и Credential Helper. Контейнеры и образы, созданные с помощью Docker Desktop, используются всеми учетными записями пользователей на компьютерах, на которых он установлен. Это связано с тем, что все учетные записи Windows используют одну и ту же виртуальную машину для создания и запуска контейнеров. При использовании Docker Desktop WSL 2 невозможно обмениваться контейнерами и образами между учетными записями пользователей.
Запускаем установщик Docker Desktop Installer.exe и ожидаем пока он скачает все необходимые компоненты.
После установки система потребует перезагрузки. Перезагружаемся и входим в систему.
После входа может возникнут запрос на установку дополнительного компонента WSL2. Переходим по ссылке и скачиваем необходимый пакет с официального сайта Microsoft.
После скачивания выполняем установку WSL2, после которой снова потребуется перезагрузка.
Настройка и запуск приложения
Входим в систему и ждем запуска всех служб Docker. Когда все службы будут запущены, мы увидим в трее классический значок Docker — это значит что служба установлена и запущена. Далее можно запустить приложение Docker desktop. Далее можно изменить настройки Docker при необходимости:

Рисунок 1 — Изменение параметров Docker desktop
Далее управление Docker выполняется через Powershell. Проверяем версию и выполняем тестовый запуск контейнера:

Рисунок 2 — Проверка версии Docker
После выполнения всех этих действий, Docker готов к использованию.
Нужна помощь? Настройки docker/docker swarm/docker compose мы осуществляем в рамках услуги DevOps-аутсорсинг.