Docker-compose — это утилита, позволяющая запускать одновременно несколько контейнеров, используя при этом единый файл конфигурации всего стека сервисов, нужных вашему приложению. Например, такая ситуация: запускаем node.js webapp, которому нужна для работы mongodb, compose выполнит build вашего контейнера с webapp (традиционный Dockerfile) и перед его запуском запустит контейнер с mongodb внутри; так же может выполнить линк их между собой. Что крайне удобно как в разработке, так и в CI самого приложения. Так сложилось, что Windows пользователи были обделены возможностью использовать столько удобное средство, ввиду того, что официальной поддержки данной ОС все еще нет. А python версия для *nix не работает в окружении windows cmd, ввиду ограничений консоли Windows.
Для того, чтобы запустить docker-compose, мы можем использовать консольную оболочку Babun. Это, так сказать, «прокаченный» форк cygwin.
Итак, рецепт запуска docker-compose в Windows из консоли babun такой:
1. Скачиваем(~280MB!) и устанавливаем сам babun, узнать больше об этой оболочке можно на ее домашней странице babun.github.io;
2. Распаковываем архив (после установки полученную папку можно удалять);
3. Запускаем файл install.bat и ждем, пока пройдет установка;
4. После в открывшемся окне babun введем команду:
babun update
И убедимся, что у нас самая последняя версия оболочки (далее все команды выполняются только внутри оболочки babun);
5. Если вам не нравится дефолтный shell babun (используется zsh), его можно изменить на bash. Для этого вводим:
babun shell /bin/bash
6. Теперь нам нужно установить те самые зависимости Python, которых так не хватает docker-compose. Для этого выполним следующие команды по очереди:
pact install python-setuptools
pact install libxml2-devel libxslt-devel libyaml-devel
curl -skS https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py | python
pip install virtualenv
curl -skS https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mitsuhiko/pipsi/master/get-pipsi.py | python
7. Теперь мы готовы установить сам docker-compose:
pip install -U docker-compose
Если все прошло успешно, увидим:
{ ~ } » docker-compose --version
docker-compose 1.2.0
Если же вы получили ошибку, error python fcntl или сообщение о не найдом файле docker-compose, попробуйте найти файл docker-compose в папках /usr/local/bin, /usr/sbin и подобных, затем можно сделать симлинк на /bin/. либо добавить в системный PATH недостающий путь.
Для правильной работы docker-compose нужно иметь уже настроенное окружение консоли для работы с docker-machine или boot2docker, а так же сам клиент docker должен быть доступен в системном PATH. О том, что такое docker, docker-machine и как с ними работать отлично рассказывает официальная документация.
Для входа в окружение нашего хоста докера, запущенного в docker-machine, нужно выполнить:
eval "$(docker-machine env ИМЯ_МАШИНЫ)"
Либо тоже самое для boot2docker:
eval "$(boot2docker shellinit)"
Проверить правильность работы клиента docker можно так:
docker ps
Если получаем список контейнеров или просто заголовки таблицы, значит, все ок!
docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
Для запуска стека приложения переходим в каталог нашего приложения, где у нас уже должен быть заготовлен файл docker-compose.yml или fig.yml. Синтаксис yml файла описан тут.
Далее для запуска вводим команду:
docker-compose up
Если нужно запустить в фоне, добавляем -d. Compose построит нужный образ и запустит его согласно вашему файлу docker-compose.yml.
На этом все.
Спасибо за внимание, надеюсь было полезно.
p.s. Я умышлено не стал говорить о варианте запуска compose как контейнера, т.к. считаю его неудобным.
Last Updated :
24 May, 2024
Docker is a powerful Container platform that allows you to create containers where you can run, deploy, and develop applications without worrying about different dependencies, services, and limitations of the operating system. The best part is the isolation of the container so you can use this container on different platforms. Now let’s talk about the ecosystem of Docker.
- Docker Engine: It is the core part of Docker which handles the different functionalities of Docker.
- Docker Compose: It is a tool which is provided by Docker used to maintain multi-container-based applications.
- Docker Hub: it is a cloud platform where all the Docker images are stored similar to Git Hub.
What Is Docker Compose?
Docker Compose is a multi-container-based application tool that will allow you to contain all the configurations and requirements for docker image building in a single YAML file. It is the single place where you can see what kind of services are required for the particular image and then you can manage and execute the configurations with commands. These are the basic details mentioned in the Docker-Compose file.
- Services and Dependencies
- Docker Networking
- Docker Port-mapping
- Docker Volumes
- Docker Environment Variables etc…
How To Install Docker Desktop On Windows
Step 1: Download The Docker Desktop For Windows
- Go to official website of Docker and search Docker Desktop Download.
- Click on the «Docker Desktop For Windows» button.

Step 2: Install Docker Desktop
- Run the downloaded software through clicking on Install option.
- Follow the Installation Wizard instructions.
- During the Installation, make sure to enable ‘Hyper-V windows Features’ option is selected.

Step 3: Run Docker Desktop
- After the installation of Docker Desktop has done successfully. Close the Applications and open it again from the Start Menu.
Step 4: Enabling WSL 2 (Windows Subsystem For Linux)
- Docker Desktop uses WSL2 as its default backend. Ensure that you have WSL2 installed.
- Ensure to follow the instructions provided by Docker Desktop to enable WSL2 during the first run.

- When your system restart this windows occurs on your screen. Finally the setup of the Docker Desktop has done successfully.
Step 5: Verifying Installation
- Open your command prompt or power shell.
- Run the following command to check the Docker CLI installation.
docker --version
- Run the following command to verify the docker can pull and run the containers.
docker pull ubuntu:latest
How to Install Compose standalone on Windows
Step 1: Open Powershell
- Open Powershell on your windows system
- and run as an administrator

Step 2: Run the following command
[Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [Net.SecurityProtocolType]::Tls12

Step 3 : Now run this command to download specific docker-compose version
Start-BitsTransfer -Source "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/v2.24.5/docker-compose.exe" -Destination $Env:Program Files\Docker\docker-compose.exe
- in the -Source section you can specify the Docker-Compose version which you want to intsall.
- in the -Destination section you can specify the location where you download the file.
- after running this command wait until the downloading process is not completed.

Step 5: Verifying Installation
- After finishing the downloading process.
- Open your command prompt or power shell.
- Run the following command to check the Docker CLI installation.
docker --version
Docker Compose Tips And Tricks For Windows
Use Verified Images
Always use Verified Images it is a best practice which will give you confidence about the authenticity of an Docker Image. Verfied Images are well maintained and easy to understand because all process is well documented. The verified images is updated time to time and fixes bugs and issues related to Images. before using the image you can check on the Dockerhub and use only those images who have official tag and associated with well known organization.
- You can also use Docker inspect command to check the image is signed or not. this is the syntax
docker trust inspect IMAGE[:TAG] [IMAGE[:TAG]...]
Tip : you can check how does Docker Content Trust works and how it verify the images and if you want so you can also use it to verify your own Docker images.
Versioning
Mention the current Docker Compose version in the starting in your Docker File. so there might be less chance of getting the issues with the version. it is the best practice to use latest version and if you want so you can also specify the which O.S you use if you use light weight Os like alpine it will give you advantage and provide efficiency in fetching and pulling the request.
Efficient Catching In Layers
As we know that Time is everything. by following some simple techniques we can save the time, the steps in dockerfile is called as layers in docker compose. and when you run command for building the image so it go through each step. and docker temporarily store the layers which are rebuild. so the next time you rebuild the image so it will not taking too much time and redownload it. when you run the build command. it will speed up the process. The following are the simple techniques you follow for efficient catching:
- Take care of ordering of Layers.
- Use multi stage builds
- Take care of what files you are copying in Docker file
- If you want so can add large files to Dockerignore file i.e nodemodules.
Use Docker Volumes
Docker volumes are very useful feature. by using this feature you can share your data from one container to another container. you can mount your data to another container so if somehow your container are stopped are destroyed so your data is not destroyed with the container. and that’s how you saved your data. if you want so you can also create your custom volumes.
Enviroment Variables
Enviroment variables are the one of the most important factor of Docker File. Make sure to provide the Enviroment variable name according to it’s work which is readable and explain it’s related work and provide default values which will helps in different scenarios.
Special Tricks For Usage Of Docker Compose For Windows
- You can use some special Editors/Extentions which will highlight Docker syntax and it helps you to grab the right options.
- Docker required a large storage in your system so sometimes it will creating issues with low-end pc’s so you can use some alternatives of it or try to clear your storage time to time.
- make sure that the file you mentioned in docker compose file are in the same directory/project otherwise it will not getting access to it.
- You can explore the availability of creating your own network on your docker file which will give you the isolation which you required for better security.
- You can use caching techniques for saving the data. which will help you to reduce the image loading time.
Conclusion
Docker compose is a powerful tool for managing multi-container-based applications. by using Docker compose you can effectively manage what kind dependencies, servers , and networks etc required for your container. in this article we go through how we can install Docker Desktop to our system and what is Docker compose and some special tips and tricks how we can use Docker compose effectively.
Docker Compose lets you run complex applications using a single command. This means that containers can be deployed faster and more efficiently. Our tutorial guides you through the Docker Compose Windows installation step by step.
What are the requirements of Docker Compose on Windows?
Docker Compose is an integral part of Docker Desktop for Windows. To use the standalone version of Docker Compose, the following requirements must be met:
- Docker Engine: Compose is an extension of Docker Engine. So you need to have the Docker Server and Client binaries installed.
- Operating System: Windows, administrator rights
How to install Docker Compose on Windows step by step
To install and use Docker Compose, Docker Daemon and Docker Client should be running on your Windows server. Before getting started it’s best to ensure that the Docker service is running error-free.
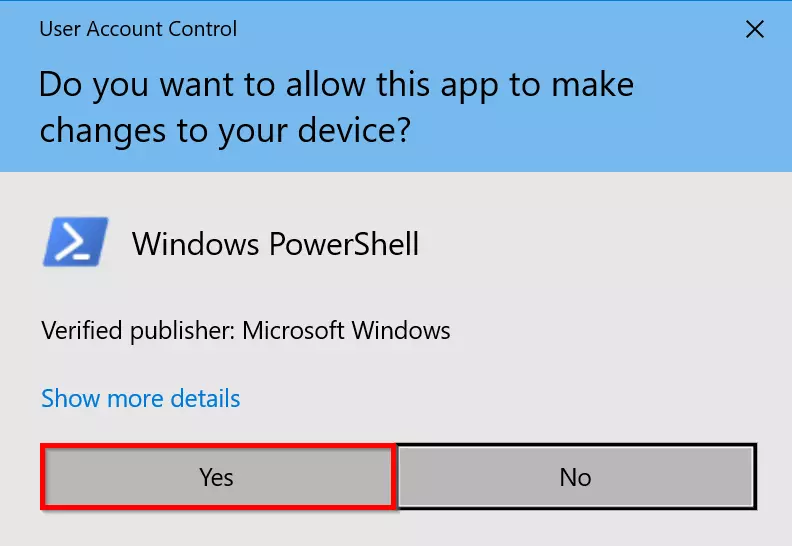
Step 1: Start PowerShell
First, launch PowerShell using your administrator rights. Confirm “Yes” to allow the app to make changes to your device.
Step 2: Set up TLS security protocol
GitHub requires TLS1.2 as the default security protocol. Run the following command in Windows PowerShell:
[Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [Net.SecurityProtocolType]::Tls12powershell
Step 3: Download and install Docker Compose
Download the latest version of Compose (v2.17.2) from GitHub:
Start-BitsTransfer -Source "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/v2.17.2/docker-compose-Windows-x86_64.exe" -Destination $Env:ProgramFiles\Docker\docker-compose.exepowershell
To install a different version, simply replace v2.17.2 in the target address with the desired version number.
Step 3: Test Docker Compose
Check if the installation was successful by displaying the current version of Compose:
docker compose versionpowershell
You should see the following output:
Ready to streamline your container management? Learning how to install Docker Compose is a key step in boosting your development workflow. Docker, with its robust set of tools like Docker Desktop and Docker Swarm, simplifies the process of running multi-container applications.
Whether you’re using Ubuntu, Windows, or macOS, getting Docker Compose up and running is crucial for enhancing your container orchestration skills.
You’ll dive into the installation process, covering the CLI commands and YAML configuration essential for setting up Compose services. This guide ensures you can manage Docker containers more efficiently, incorporating best practices for environment variables and network configuration.
By the end, you’ll be confident in installing Docker Compose, ready to manage complex applications with ease. I’ll walk you through each step, from downloading files to running your first Docker Compose command, providing you with a solid foundation in containerization.
How To Install Docker Compose: Quick Workflow
Installing Docker Compose can be achieved through several methods depending on your operating system and preferences. Here are the steps for installing Docker Compose on Linux, macOS, and Windows:
Method 1: Install Docker Compose Standalone
-
Download Docker Compose:
curl -SL https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/v2.33.1/docker-compose-linux-x86_64 -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
-
Apply Executable Permissions:
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
-
Create a Symbolic Link (Optional):
Ifdocker-composedoesn’t work, create a symbolic link:sudo ln -s /usr/local/bin/docker-compose /usr/bin/docker-compose
-
Test Docker Compose:
Use the commanddocker-compose --versionto verify installation.
Method 2: Install Docker Compose Plugin
-
Install Docker:
Ensure Docker is installed. If not, follow these steps:-
Update
apt: -
Install necessary packages:
sudo apt install ca-certificates curl gnupg lsb-release
-
Add Docker’s official GPG key:
sudo mkdir -p /etc/apt/keyrings
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg
-
Set up the Docker repository:
echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
-
Install Docker Engine:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
-
-
Install Docker Compose Plugin:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install docker-compose-plugin
-
Verify Installation:
Installing Docker Compose on macOS
The easiest way to install Docker Compose on macOS is by using Docker Desktop:
-
Download Docker Desktop from the official Docker website.
-
Install Docker Desktop using the downloaded installer.
-
Verify Docker Compose Installation:
-
Open Docker Desktop and check the version under About Docker Desktop.
-
Alternatively, use
docker compose versionin the terminal.
-
Installing Docker Compose on Windows
For Windows, Docker Compose is included in Docker Desktop:
-
Download Docker Desktop from the official Docker website.
-
Install Docker Desktop using the downloaded installer.
-
Verify Docker Compose Installation:
-
Open Docker Desktop and check the version under About Docker Desktop.
-
Alternatively, use
docker compose versionin the terminal.
-
Installing Docker Compose on Ubuntu

Installation Methods Overview
Experienced an urge to set things up like never before? Let’s dive straight into it.
Official Ubuntu APT repository provides a classic route. Plugged into its ecosystem, it simplifies getting everything aligned with Ubuntu’s mannerisms. It’s like slipping into a pair of well-worn shoes — dependable and straightforward.
Docker’s official GitHub repository is a treasure trove. GitHub not only provides the latest and greatest from Docker Inc. but lets you grab the binaries straight from the source. It’s the DIY of Docker installs.
Docker Desktop sits pretty for GUI enthusiasts. An alternative that transforms setup into a visual affair. Consider it forking over control for convenience, though mostly geared towards Windows and Mac OS.
Installing Docker Compose Using APT Repository
Updating system package lists. First things first, tap into those package lists. Keep them refreshed for any new treasures that Ubuntu might have tucked in there. A simple sudo apt update should do the trick.
Installing required dependencies comes next. Often forgotten, dependencies are more like shadow workers, essential yet unseen. Fetch them through a quick command if required.
Adding the Docker repository to Ubuntu’s sources list is crucial. This link opens the doors wide for everything Docker. A simple copy-paste genius turns your system into Docker’s best friend. Utilize curl or add-apt-repository for seamless addition.
Installing Docker Compose package completes the formalities. With sources set, watch as the magic unfolds with sudo apt install docker-compose. It’s almost like striking gold with this one.
Verifying installation and checking version is not just a formality. Validation is victory. Command docker-compose --version and view the confirmation right there in the terminal. You’re now on the path—no, the express runway—to containerization.
Installing Docker Compose from the Official GitHub Repository
Checking the latest available version is like earthing in on the freshest updates. Download something that doesn’t get stashed away under heaps of updates.
Downloading the correct binary for the system architecture is vital. Form and function wrapped in precise calculation. Fetch by pasting URLs often found right on the GitHub release page into your terminal.
Making the file executable hits next. The sly chmod +x command transforms it from inert to active. Like winding up a mechanical toy, this step readies Docker Compose for action.
Moving the binary to the appropriate directory shapes the last preparation. Use mv to place the executable in /usr/local/bin/. A strategic placement ensuring it’s ready at hand when summoned.
Verifying installation and checking version repeats its encore. A simple docker-compose --version heralds the arrival—proof positive of progress. From here, every step forward in Docker Compose’s journey on Ubuntu lies within reach.
Configuring Docker Compose
Understanding the docker-compose.yml File
Purpose of the YAML configuration file
This file is the backbone of Docker Compose—a blueprint, if you will, detailing how services talk, play, and function together. It simplifies container orchestration, allowing applications to be defined in straightforward code.
Basic structure and syntax
Dive into the YAML structure and you’ll find it remarkably approachable. Indentation speaks volumes here. A promise of simplicity in setting up even the most intricate container niceties without the overhead.
Key elements: services, networks, and volumes
Services are the stars—each a component of the larger app. Define them and watch them spring to life. Networks? They provide the communication channels. Volumes remember your data across container restarts.
Creating a Sample Docker Compose Configuration
Setting up a project directory
Start by making space—a folder. It’s your app’s new home on this digital cloud. Drop all related files here to maintain order, structure, clarity.
Defining services in docker-compose.yml
Connect services to images from places like Docker Hub or your private registry. Write it in the YAML configuration, and they appear as detailed living entities in your digital orchestra.
Exposing ports and defining environment variables
Ports open doors to the world. Environment variables inject flexibility, making sure your configuration adapts without hardcoding. Insert these lifelines and enable real utility.
Setting up persistent storage with volumes
Volumes? A safety net in a volatile world of containers. Define them carefully, making sure vital data persists beyond temporary shifts and ephemeral existences.
Running and Managing Containers with Docker Compose
Bringing up the environment (docker compose up)
A command, a single move. docker compose up breathes life into what’s written, turning YAML into running, communicating services. View this digital symphony unfold with ease.
Running containers in detached mode
Silence the chatter. Detached mode sends containers to the background, letting them work without clogging your command line. Your hands remain free, your console less burdened.
Listing running containers (docker compose ps)
Seek and ye shall find. A simple command lets you list all players in your ecosystem, showing status and relevant details at a glance—understanding without the fluff.
Stopping and restarting services
Need a fresh start or a casual halt? Just call for it. Stop, start, restart—commands that untangle or pause without a fuss. Stay in control, keep your domain poised and ready.
Working with Docker Compose Commands
Essential Commands for Managing Services
Starting and stopping services (up, down, start, stop)
Kick off with docker compose up. This gets services rolling, ready for action. Cooling down? Use docker compose down to pause everything. Space out your starts and stops with start and stop. Benefits of container orchestration come out clearer here—smooth transitions, everything controlled.
Restarting and killing services (restart, kill)
When good enough isn’t enough, restart services. Need total shutdown? Hit kill. A forceful stop, like pulling the plug but without harm. Control, adjust, repeat.
Viewing running services (ps)
List all the ongoing showdowns in a jiffy. Command docker compose ps brings running services, status, and more on your screen. Run, check, move on if all’s good.
Debugging and Logging
Viewing logs (logs)
Peek into logs with docker compose logs. Perfect for troubleshooting or just keeping tabs on those container whispers. Real-time feedback keeps you on top, no need for fancy practises.
Inspecting container details (docker inspect)
Curious eyes on containers? docker inspect. Lift the curtain on configurations, dig into depths with details. Know what’s in the play, get insights without fuss.
Troubleshooting common errors
Errors happen, they just do. Use logs, inspections, try the known fixes. Docker Compose, with its environment setup, minimizes many errors—still, no system without its quirks.
Managing Networks and Volumes
Creating and removing networks
Networks setup to make containers chat. Create them with ease, removing when not needed. Commands help carve and clean networks, ensuring proper trackways for containers.
Defining custom networks in docker-compose.yml
Look into docker-compose.yml and define beautiful, unique networks. Tailoring networks means better connectivity. Helps your services interact smoothly, avoiding choke points.
Managing persistent volumes
Volatility strikes? Not with volumes. Persist data beyond restarts, beyond fleeting runtime states. Define and maintain these containers’ memory banks, pivotal for Docker applications.
Copying Files and Running Commands in Containers
Copying files between host and container (cp)
Move files around like a pro. Use docker cp to shift files between your host and containers. Seamless, without hiccup. Makes Docker Compose even more fluid.
Executing commands inside running containers (exec, run)
Get into containers. Execute commands with docker exec, run, right from your terminal. Interaction at its finest, making updates or tweaks straight inside, like clockwork.
Testing the Docker Compose Installation
Deploying a Simple Test Application
Creating a directory for the project
First, let’s get organized. You’ll need a fresh directory to house your project. Something like mkdir my-docker-test, and you’re off to a good start.
Writing a minimal docker-compose.yml file
Time for the heart of your operation, the docker-compose.yml file. Keep it simple. Maybe:
version: '3'
services:
web:
image: nginx
ports:
- "80:80"
This sets the stage for a quick test.
Running a test service (hello-world or nginx)
With your YAML script ready, launch docker compose up. Choose nginx or the humble hello-world. Feel the thrill as the container births into existence, running with the efficiency Docker promises.
Accessing the service in a web browser
Next, view proof of life. Open a browser, type localhost, and take a peek. Nginx should greet you, affirming the universe’s order remains intact.
Verifying Proper Functioning
Checking container logs
Troubles lurk in logs, so check them. Use docker compose logs to assure all is running smooth. Watch out for red flags indicating issues.
Confirming service accessibility
Can you access your service? Great. If not, retrace steps. Check ports, maybe configuration tweaks. Verification here is a key step.
Reviewing network and volume setup
Networks and volumes, Docker’s touch of permanence. Peek into configurations once more. Are volumes saving data? Are networks intact? This is your fallback for when transient data needs permanent sanctuaries.
Advanced Docker Compose Features
Using Environment Variables in Docker Compose
Defining variables in a .env file
Drop your variables in a .env file. Think database credentials, API keys—sensitive stuff we keep behind the curtain. Basic syntax like DB_PASSWORD=secretpass does wonders.
Referencing environment variables in docker-compose.yml
Plug them into docker-compose.yml using ${VARIABLE}. Something like:
web:
image: "myapp:${TAG}"
Turns configurations into flexible setups that morph as needed.
Overriding default values
Defaults give foundation, but overrides rule the process. Set a standard, but tweak as scenarios demand. Agility at its best.
Scaling Services with Docker Compose
Running multiple instances of a service (docker compose up –scale)
Wanna handle more traffic? Use docker compose up --scale web=3. Watch as instances grow in sheer power, multiple containers leaping into action.
Load balancing between scaled services
Spread the love with load balancing. Docker manages requests, ensuring no container feels left out. Smooth distribution across your scalable orchestra.
Managing resource allocation for containers
Resource management is the name of the game. CPU shares, memory limits. Define carefully, allocate wisely. Keeps the Docker engine purring without overload.
Setting Up Multi-Container Applications
Running a database and web application together
Link a database with a web server in Docker Compose. YAML magic:
services:
db:
image: postgres
web:
image: myapp
These interconnected wonders converse flawlessly, speeding up the entire structure.
Configuring inter-container communication
Network bridges shorten the gaps. Set Docker networks, let containers find each other. Achieving chatty harmony without a glitch in communications.
Managing dependencies between services
Add depends_on to handle who starts first. Simple syntax ensures dependencies are honored. Docker takes the wheel to orchestrate these delicate dances.
Customizing Docker Compose Configurations
Using multiple configuration files (-f flag)
Going multi-environment? Break free from single files. Use -f to load specific configurations, whatever the need or whim demands—endless flexibility.
Overriding default settings for different environments
Defaults? Meet dynamic overrides. Production, testing, development—each calls for different settings. Tailor for purpose, achieve results. No DX clutter.
Uninstalling Docker Compose from Ubuntu
Removing the Docker Compose Plugin (APT Installation)
Running the apt remove command
Begin with your terminal. Run sudo apt remove docker-compose. Swift and straight. It strips away the plugin like it was never there. Say goodbye, but remember it’s not forever.
Cleaning up unused dependencies
After removal, those dangling dependencies linger. sudo apt autoremove addresses this, cleaning the slate. A clutter-free Ubuntu—pure efficiency, no excess baggage.
Removing the Docker Compose Binary (GitHub Installation)
Deleting the binary from the system
Navigate to where it lives, maybe /usr/local/bin/docker-compose. A simple sudo rm /usr/local/bin/docker-compose and poof—it’s gone. The binary vanishes, a delete perfected with permanence.
Removing associated configuration files
Not just about binaries; check for .docker remnants. These traces in your home directory house configuration artifacts. Removing them reverts your setup, clean as a whistle, ready to start anew—when you choose.
What is Docker Compose?
Docker Compose is a tool that helps you define and run multi-container Docker applications. With a simple YAML configuration file, you can manage multiple services, networks, and volumes.
It’s crucial for orchestrating applications that require different environments, like databases and application servers, working smoothly together.
How do I install Docker Compose on Ubuntu?
To install Docker Compose on Ubuntu, first, ensure Docker is installed. Then, download the current release from the GitHub repository using curl.
Follow with chmod to make it executable. Place the binary in a directory within your $PATH. Verify the installation by running docker-compose --version.
Can I install Docker Compose on Windows?
Yes, Docker Compose can be installed on Windows as part of Docker Desktop. Simply download Docker Desktop and follow the prompts.
Docker Compose comes bundled with it. Check its functionality by opening PowerShell or Command Prompt and typing docker-compose --version.
What are the prerequisites for installing Docker Compose?
Before installing Docker Compose, make sure Docker is installed on your system. You need a compatible operating system, like Linux, Windows, or macOS.
Also, ensure you have the necessary user permissions to install software or modify system files on your device.
How do I install Docker Compose on macOS?
For macOS, Docker Compose is included with Docker Desktop. Download Docker Desktop, then install it. After installation, verify everything is working by executing docker-compose --version in Terminal. This ensures docker-compose is ready for managing your containerized applications.
Do I need root access to install Docker Compose?
Yes, root access or administrative privileges are typically required to install Docker Compose. It’s necessary for placing the executable in system directories and making it executable. For security, consider creating a dedicated user with Docker access rather than using the root user.
How do I update Docker Compose?
To update Docker Compose, download the latest version using curl to overwrite the existing binary. You should check for updates regularly on the Docker GitHub repository.
Once downloaded, make it executable with chmod, and verify the new version by running docker-compose --version.
What is the Docker Compose version command?
The Docker Compose version command, docker-compose --version, allows you to check the currently installed version of Docker Compose on your system. Running this command will display the version number, helping you confirm successful installation or troubleshooting.
Can Docker Compose run without Docker?
No, Docker Compose cannot operate without Docker. It’s a tool built on top of Docker to handle multi-container configurations.
Docker must be installed and running on your machine for Docker Compose to function. Think of Docker as the engine and Docker Compose as the orchestrator.
How do I troubleshoot Docker Compose installation issues?
Troubleshoot Docker Compose by first checking your Docker installation. Ensure paths and permissions are correct.
Use verbose logging by adding --verbose to commands. Check for network issues if there are service startup problems. Search Docker forums and GitHub issues for solutions to known problems.
Conclusion
Mastering how to install Docker Compose is a critical step in leveling up your development game. With it, you can organize and manage multi-container applications with ease. Whether you’re working on Ubuntu or using Docker Desktop on Windows or macOS, you’ve got the tools now to set up and maintain powerful container environments. Navigating the process gets easier as everything is laid out neatly in YAML files.
Summarizing the Takeaways:
- Prepare your system: Ensure prerequisites like Docker are installed.
- Follow steps precisely: Commands and configuration must be exact for smooth operation.
- Verify and test: After setup, run a version check to confirm its success with
docker-compose --version.
You should feel confident managing containers and exploring new possibilities in app deployment. The world’s your oyster when you know how to integrate Docker Compose effectively into your workflow. Now, put that knowledge into action and enjoy streamlined application management!
If you liked this article about how to install Docker compose, you should check out this article about how to stop Docker container.
There are also similar articles discussing how to remove Docker images, how to create a Docker container, how to restart a Docker container, and how to ssh into Docker container.
And let’s not forget about articles on how to exit Docker container, how to check if Docker is running, how to install Docker, and how to start Docker daemon.
- Author
- Recent Posts
Bogdan is a seasoned web designer and tech strategist, with a keen eye on emerging industry trends.
With over a decade in the tech field, Bogdan blends technical expertise with insights on business innovation in technology.
A regular contributor to TMS Outsource’s blog, where you’ll find sharp analyses on software development, tech business strategies, and global tech dynamics.
