Do you want to delete a directory from Windows command prompt(CMD)? This post explains how to use the command rmdir to delete folders and their contents. You can also find examples for each use case of folder deletion – empty folders, non empty folders, folders with white spaced names etc.
Delete folder from CMD
Run the command rmdir on the folder.
rmdir directoryname
Example:
C:>rmdir emptydir C:>
How to delete a non empty folder
The simple rmdir does not work for folders having some content.
C:>rmdir nonemptydir The directory is not empty.
Use /s option to delete the folder contents along with the folder. This deletes all subfolders recursively.
C:>rmdir /S nonemptydir nonemptydir, Are you sure (Y/N)? y C:>
Force delete a folder without confirmation
To force delete directory, without being asked for confirmation, we can use /Q switch.
rmdir /Q /S nonemptydir
We can also use ‘rd’ in place of ‘rmdir‘. Both names refer to the same command. This command works on Windows 2000, Windows XP, Server 2003, Vista, Windows 7 and 10.
Deleting directory with white spaces in the name
Rmdir can delete files with whitespaces in the name, you just need to wrap up the folder name in double quotes as shown in the below example.
rmdir /Q /S "folder with spaces in the name"
Delete contents of a directory but keep the directory
The usecase here is to delete all the contents of the directory but keep the parent directory so that we do not need to create it again. rmdir /Q /S does not work here as it deletes the parent directory too. Rather the below commands should do the trick.
forfiles /P directory_path /M * /C "cmd /c if @isdir==FALSE del @file" forfiles /P directory_path /M * /C "cmd /c if @isdir==TRUE rmdir /S /Q @file"
This works in 2 steps – the first command deletes all files, whereas the second one deletes all subdirectories.
Errors
To delete a directory, you should have appropriate access permissions on the directory. Otherwise rmdir throws ‘Access denied’ error.

Sometimes it’s just faster to do things with the command line.
In this quick tutorial we’ll go over how to open Command Prompt, some basic commands and flags, and how to delete files and folders in Command Prompt.
If you’re already familiar with basic DOS commands, feel free to skip ahead.
How to open Command Prompt
To open Command Prompt, press the Windows key, and type in «cmd».
Then, click on «Run as Administrator»:
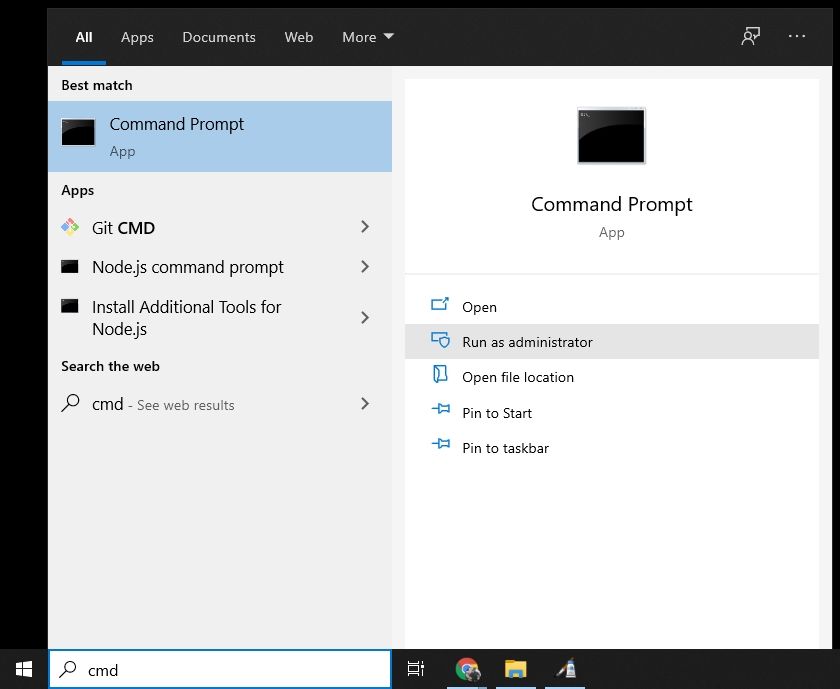
After that, you’ll see a Command Prompt window with administrative privileges:
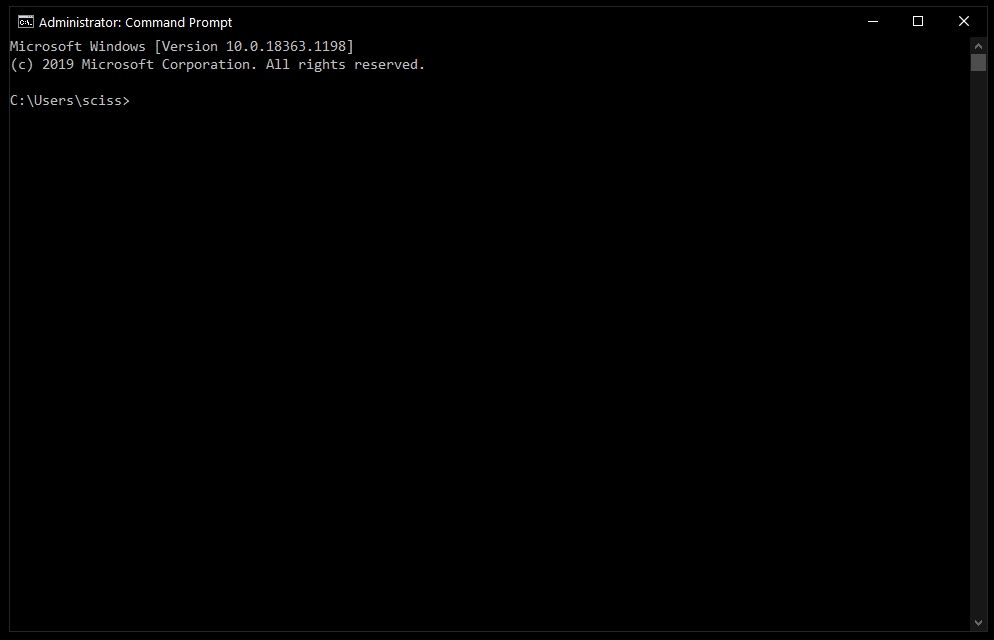
Screenshot of Command Prompt window
If you can’t open Command Prompt as an administrator, no worries. You can open a normal Command Prompt window by clicking «Open» instead of «Run as Administrator».
The only difference is that you may not be able to delete some protected files, which shouldn’t be a problem in most cases.
How to delete files with the del command
Now that Command Prompt is open, use cd to change directories to where your files are.
I’ve prepared a directory on the desktop called Test Folder. You can use the command tree /f to see a, well, tree, of all the nested files and folders:
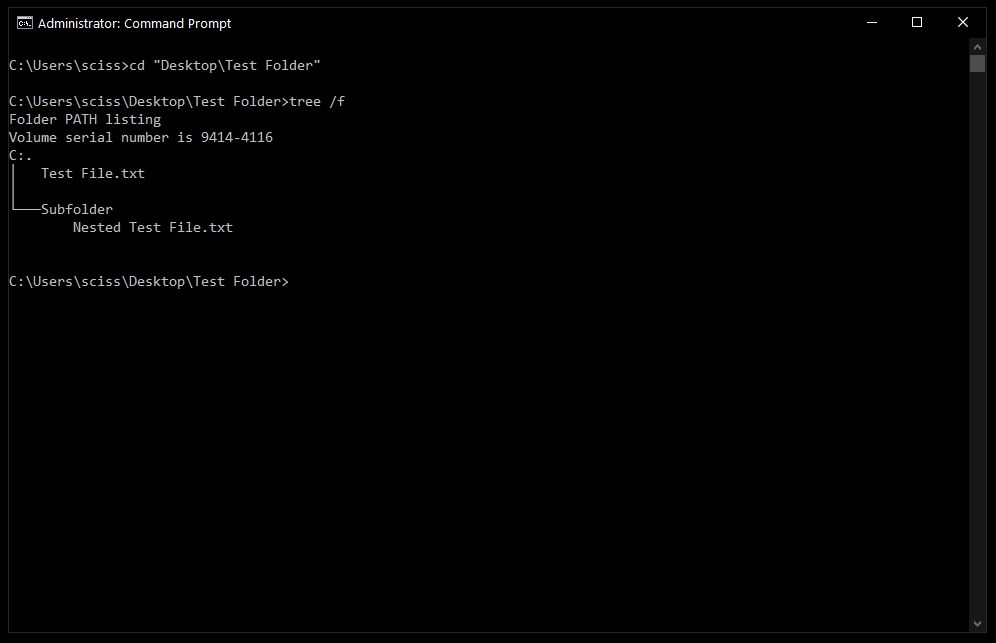
To delete a file, use the following command: del "<filename>".
For example, to delete Test file.txt, just run del "Test File.txt".
There may be a prompt asking if you want to delete the file. If so, type «y» and hit enter.
Note: Any files deleted with the del command cannot be recovered. Be very careful where and how you use this command.
After that, you can run tree /f to confirm that your file was deleted:

Also, bonus tip – Command Prompt has basic autocompletion. So you could just type in del test, press the tab key, and Command Prompt will change it to del "Test File.txt".
How to force delete files with the del command
Sometimes files are marked as read only, and you’ll see the following error when you try to use the del command:
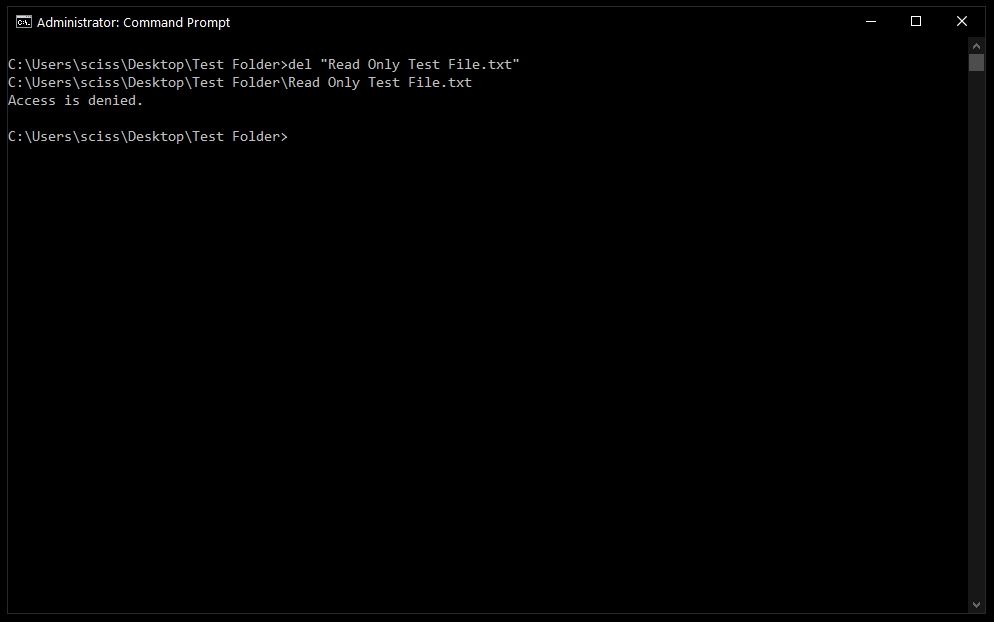
To get around this, use the /f flag to force delete the file. For example, del /f "Read Only Test File.txt":
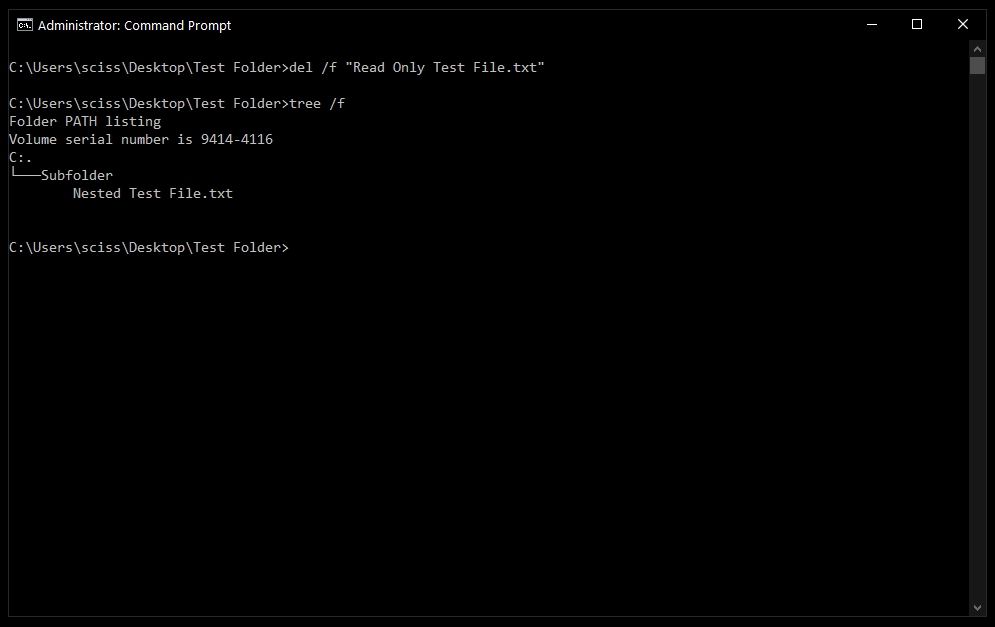
How to delete folders with the rmdir command
To delete directories/folders, you’ll need to use the rmdir or rd command. Both commands work the same way, but let’s stick with rmdir since it’s a bit more expressive.
Also, I’ll use the terms directory and folder interchangeably for the rest of the tutorial. «Folder» is a newer term that became popular with early desktop GUIs, but folder and directory basically mean the same thing.
To remove a directory, just use the command rmdir <directory name>.
Note: Any directories deleted with the rmdir command cannot be recovered. Be very careful where and how you use this command.
In this case I want to remove a directory named Subfolder, so I’ll use the command rmdir Subfolder:
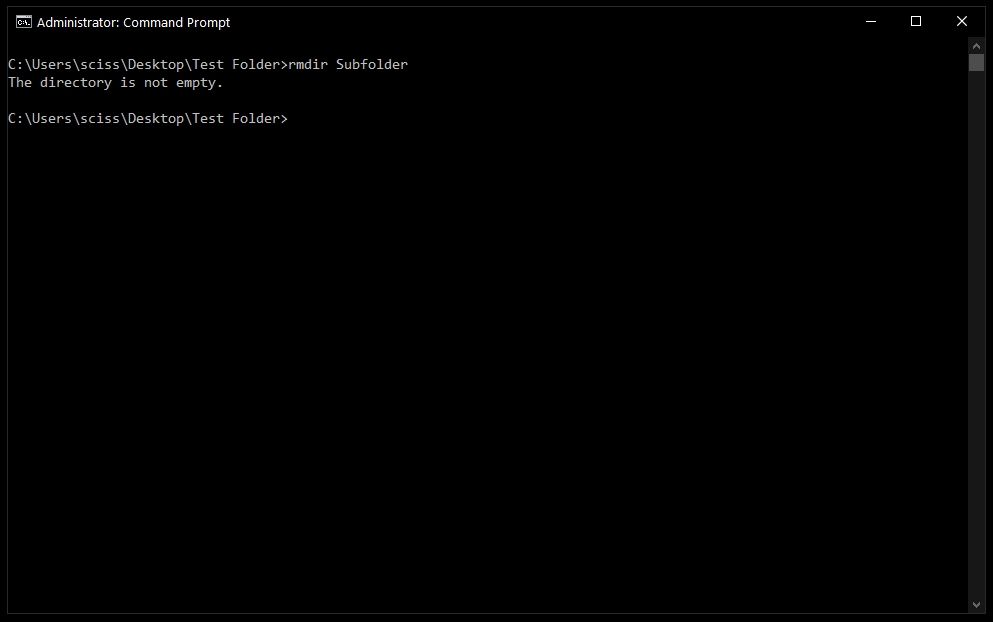
But, if you remember earlier, Subfolder has a file in it named Nested Test File.
You could cd into the Subfolder directory and remove the file, then come back with cd .. and run the rmdir Subfolder command again, but that would get tedious. And just imagine if there were a bunch of other nested files and directories!
Like with the del command, there’s a helpful flag we can use to make things much faster and easier.
How to use the /s flag with rmdir
To remove a directory, including all nested files and subdirectories, just use the /s flag:
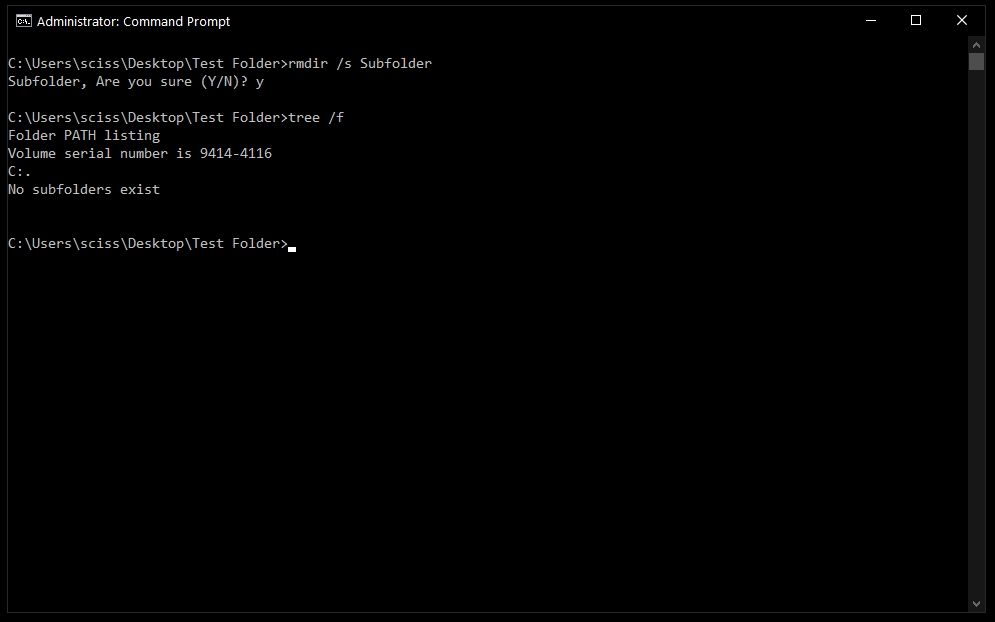
There will probably be a prompt asking if you want to remove that directory. If so, just type «y» and hit enter.
And that’s it! That should be everything you need to know to remove files and folders in the Windows Command Prompt.
All of these commands should work in PowerShell, which is basically Command Prompt version 2.0. Also, PowerShell has a bunch of cool aliases like ls and clear that should feel right at home if you’re familiar with the Mac/Linux command line.
Did these commands help you? Are there any other commands that you find useful? Either way, let me know over on Twitter.
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp’s open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
Last Updated :
16 May, 2024
While working on Windows devices, we used to work on Windows File Explorer for working with files. On File Explorer of Windows, the creation of new files as well as deleting old ones is one of the easiest processes. However, if your File Explorer is not responding, then the process to Delete Folder using CMD can be an alternative.
The Windows Command Prompt is the command line tool that executes different tasks with the help of Windows Commands. Using CMD in Windows, the File Creation for Windows can also be executed. If you are having trouble Deleting Files or Folders on Windows directly by right-clicking, then you can Delete files using CMD.
This article is going to discuss the commands required to Remove Files & Folders using the UsingCommand Prompt of Windows.
Table of Content
- Methods to Delete Files and Folders Using Command Prompt
- Method 1: Delete Files or Folders on CMD using DEL Command
- Method 2: Delete Files or Folders on CMD using RMDIR Command
- Delete a Folder and Subfolders in Command Prompt
Methods to Delete Files and Folders Using Command Prompt
To Erase Windows Files or Folders using CMD, the following guidelines should be used properly. Let us start with the DEL Command Execution.
Method 1: Delete Files or Folders on CMD using DEL Command
Note: DEL Command is used to delete a file. Here, we will take our sample file “hello.txt” located on the desktop, and try to delete it using the del command in CMD. Follow the steps given below to delete the file:
Step 1: Change the Path of the Directory in CMD and set it to the path of the file. Type the following command and press Enter.
cd desktop
Step 2: Delete the file hello.txt with the following Windows Command.
del hello.txt

Method 2: Delete Files or Folders on CMD using RMDIR Command
Note: RMDIR Command is used to delete the entire folder or directory. Here, we will take our sample folder named “Tasks” placed on the desktop and try to delete it using RMDIR Command in CMD.
Step 1: Change the Directory’s Path in Command Prompt and set it to the path of the folder.
cd desktop
Step 2: Delete the folder Tasks with the following command.
rmdir tasks

From the above discussion, this should become clear that the Deletion of Windows Files using CMD is a matter of a few seconds. You have to just move inside the Windows Directory using the Windows CD Command. And then, as per your choice execute any one of the Windows File Deletion Commands in CMD.
Delete a Folder and Subfolders in Command Prompt
Step 1: Open Command Prompt.
Step 2: Navigate to the directory where the folder you want to delete is located using the cd command.
Command: cd <FolderName>
Step 3: To delete a single folder, use the following command.
Command: rmdir <FolderName>
Step 4: To delete a folder and all its subfolders and files, just include “/s” in between the rmdir and <folderName>, use the following command.
Command: rmdir /s <FolderName>
Step 5: Press Enter to execute the command.
Also Read
- Useful CMD commands for daily use in Windows OS
- CMD Commands to Gather Information of a System
- How to Show all the previously connected WiFi Networks using CMD in Windows?
Conclusion
In this article, we explored how to use Command Prompt in Windows to delete files and folders efficiently when facing issues with File Explorer. We discussed two methods: using the DEL command to delete files and the RMDIR command to delete folders. Additionally, we provided a step-by-step guide on how to delete folders and subfolders using Command Prompt.
Все способы:
- Полезные советы перед удалением папок через консоль
- Способ 1: Использование команды RMDIR (RD) для директорий
- Способ 2: Использование PowerShell и команды Remove-Item
- Способ 3: Удаление через PowerShell с использованием конвейеров
- Популярные условия для фильтрации папок в PowerShell
- Способ 4: Использование команды DELTREE в режиме совместимости
- Вопросы и ответы: 0
Полезные советы перед удалением папок через консоль
Работа с папками через консоль Windows требует некоторой подготовки и понимания основных принципов. Перед тем как начать удаление директорий, нужно правильно определить путь к нужным папкам и научиться ориентироваться в консольном интерфейсе. Многие пользователи обходят стороной «Командную строку», считая ее слишком сложной. Однако несколько базовых приемов значительно упростят взаимодействие с ней. Точное указание пути является фундаментальным элементом для выполнения любых операций с папками в «Командной строке». Неверно указанный путь приведет к ошибкам или, что гораздо хуже, к удалению не тех директорий, которые планировалось удалить. Следующие практические рекомендации помогут избежать распространенных ошибок и сделают процесс удаления папок более эффективным.
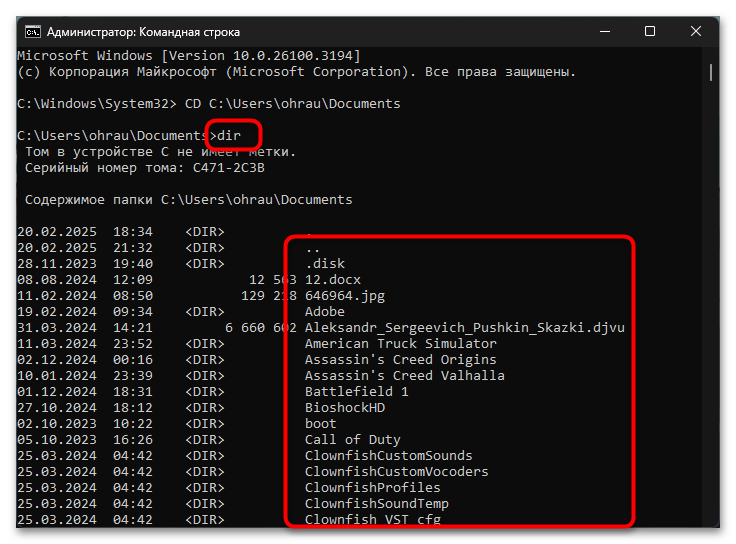
- Использование команды CD для навигации. Команда CD (Change Directory) дает возможность перемещаться между папками в файловой системе. Это устраняет необходимость постоянно вводить полный путь при каждой операции с папками. К примеру, введя команду
CD C:\Users\Username\Documents, вы перейдете в директорию Documents. После этого вы сможете выполнять операции с папками внутри нее, указывая только их имена без полного пути. Такой подход существенно сокращает объем ввода и минимизирует вероятность ошибок при написании пути. - Просмотр содержимого директории с помощью DIR. Перед тем как удалять папки, настоятельно рекомендуется проверить содержимое текущей директории с помощью команды DIR. Эта команда покажет полный список всех файлов и папок в текущем расположении. Такая предварительная проверка поможет убедиться, что вы находитесь в нужной директории, и точно определить названия папок, которые планируется удалить. Команда DIR также может использоваться с масками для фильтрации результатов, например
DIR /ADпокажет только папки в текущей директории. - Использование автодополнения с помощью клавиши Tab. Для ускорения ввода длинных путей к папкам и предотвращения опечаток, активно используйте клавишу Tab. Эта функция автоматически дополняет названия папок и файлов при вводе. Начните вводить путь или имя папки и нажмите Tab – система предложит возможные варианты завершения. Если нажать Tab повторно, можно переключаться между доступными вариантами. Эта функция особенно полезна при работе с папками, имеющими длинные или сложные названия с большим количеством символов.
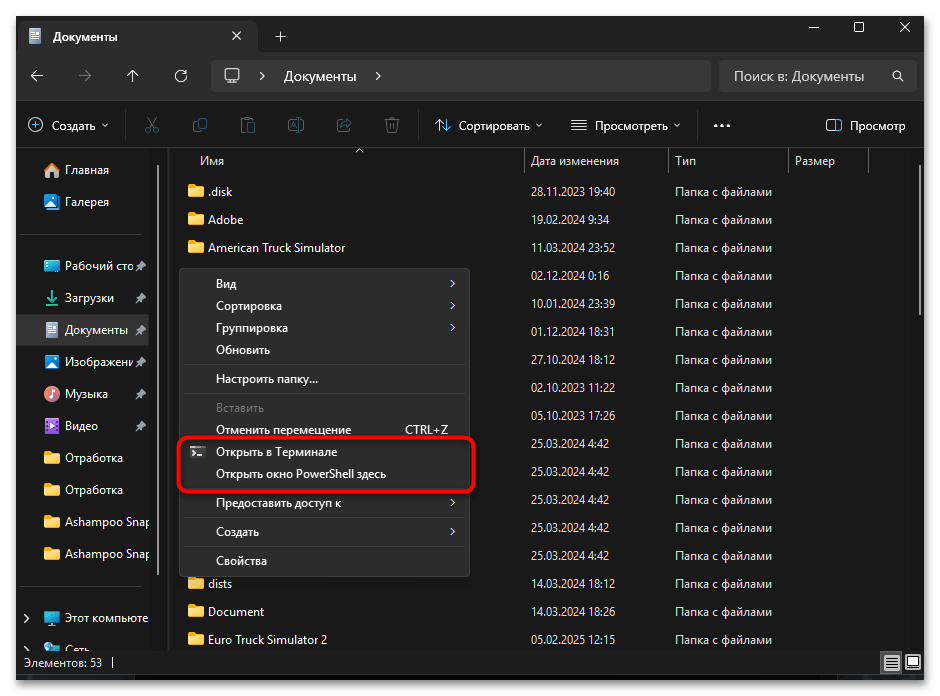
- Открытие «Командной строки» в определенной директории. Чтобы сразу открыть консоль в необходимой папке и избежать долгой навигации, воспользуйтесь проводником Windows. Перейдите к нужной директории в проводнике, после чего нажмите и удерживайте клавишу Shift, одновременно кликнув правой кнопкой мыши. В появившемся контекстном меню выберите пункт «Открыть окно командной строки здесь» или «Открыть окно PowerShell здесь». Этот прием позволяет мгновенно начать работу в требуемой директории без необходимости ручной навигации.
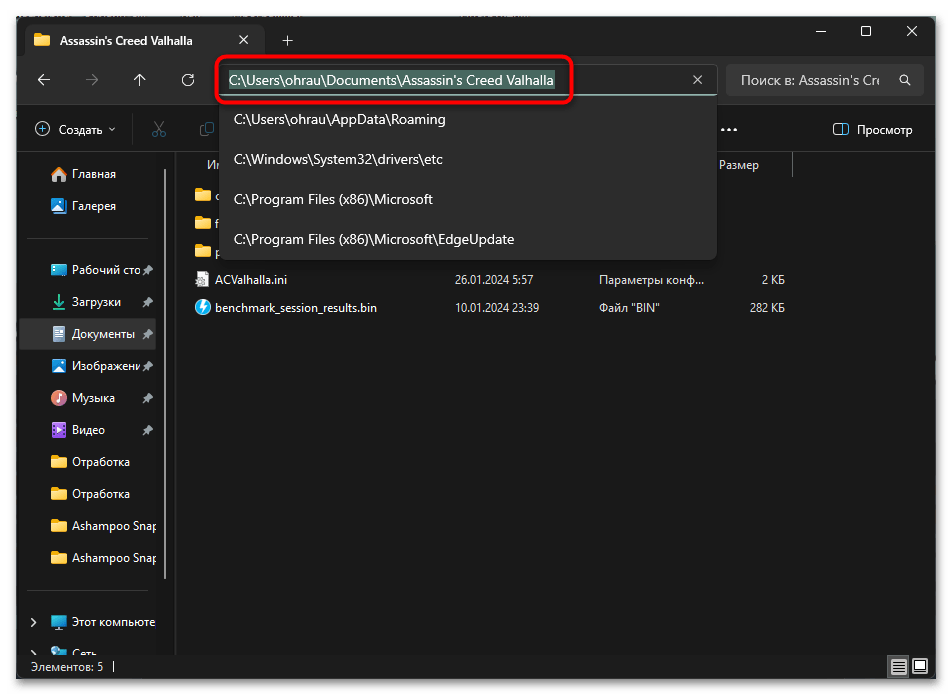
- Копирование пути из проводника Windows. Если вы сомневаетесь в точности пути к папке, скопируйте его напрямую из проводника Windows. Для этого перейдите к нужной директории в проводнике, щелкните в адресной строке для выделения пути и скопируйте его (Ctrl+C). Затем вставьте полученный путь в консоль (правый клик мыши или Ctrl+V в PowerShell). При вставке в классическую «Командную строку» может потребоваться заключить путь в кавычки, особенно если в нем содержатся пробелы или специальные символы.
Способ 1: Использование команды RMDIR (RD) для директорий
Удаление папок через консоль Windows является необходимым навыком для управления файловой системой без использования графического интерфейса. Существует специальная команда RMDIR (или сокращенно RD), разработанная именно для удаления директорий. Эта команда присутствует во всех версиях Windows и не требует установки дополнительного программного обеспечения. Изначально RMDIR создавалась для удаления только пустых директорий, однако при использовании определенных параметров она превращается в мощный инструмент для удаления целых структур папок со всем их содержимым. Это делает ее незаменимой при необходимости массовой очистки разделов жесткого диска или быстрой реорганизации файловой системы.
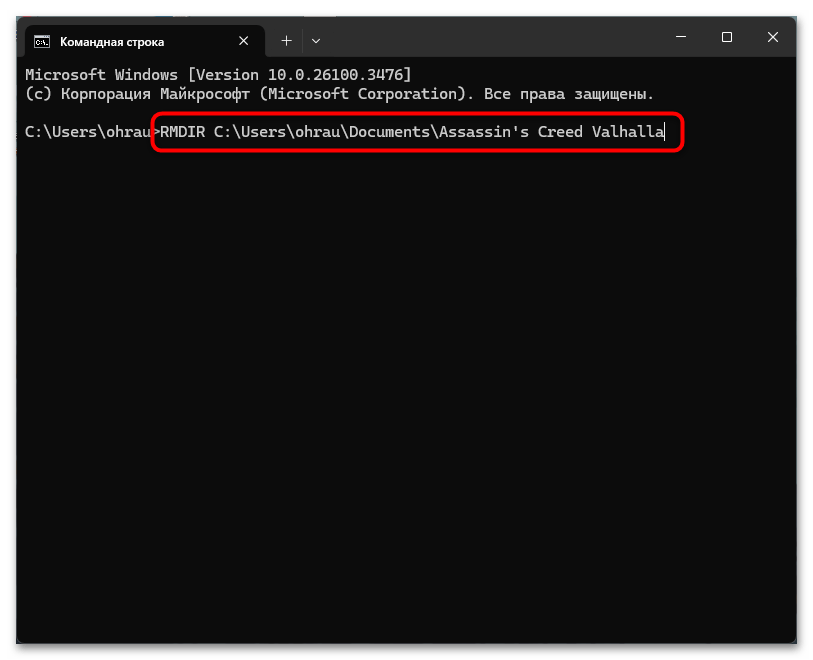
Для удаления папки с помощью RMDIR необходимо открыть «Командную строку» и ввести команду в следующем формате:
RMDIR путь_к_директории
или используя сокращенный вариант:
RD путь_к_директории
Команда RMDIR имеет два ключевых аргумента для работы с папками:
- /S. Этот параметр указывает на необходимость удаления не только самой директории, но и всех файлов и поддиректорий внутри нее. По сути, он превращает команду в инструмент для рекурсивного удаления целых ветвей файловой структуры. Если не использовать данный параметр, команда RMDIR сможет удалить только пустые директории и выдаст ошибку при попытке удалить папку, в которой есть файлы или другие папки. Поэтому при необходимости полного удаления непустой директории параметр /S является обязательным.
- /Q. Данный параметр отключает запрос подтверждения при удалении директории со всем ее содержимым. Обычно система запрашивает подтверждение в формате «Вы уверены (Y/N)?» перед удалением папки с файлами. Параметр /Q (от слова Quiet – тихий) позволяет пропустить этот запрос и выполнить удаление немедленно. Этот аргумент особенно полезен при автоматизации процессов или при необходимости удаления большого количества директорий. Однако его следует использовать с большой осторожностью, так как он устраняет последнюю защиту от случайного удаления важных данных.
Способ 2: Использование PowerShell и команды Remove-Item
Консоль PowerShell представляет собой более современный и функциональный терминал, доступный во всех актуальных версиях Windows. PowerShell предлагает расширенные возможности по сравнению с традиционной «Командной строкой» и включает в себя универсальную команду Remove-Item для управления как файлами, так и директориями. Данная команда отличается более гибким набором параметров и возможностью интеграции с другими командами PowerShell через систему конвейеров. Remove-Item обеспечивает более тонкий контроль над процессом удаления папок и предоставляет дополнительные опции для работы с защищенными или системными директориями.
Remove-Item путь_к_директории
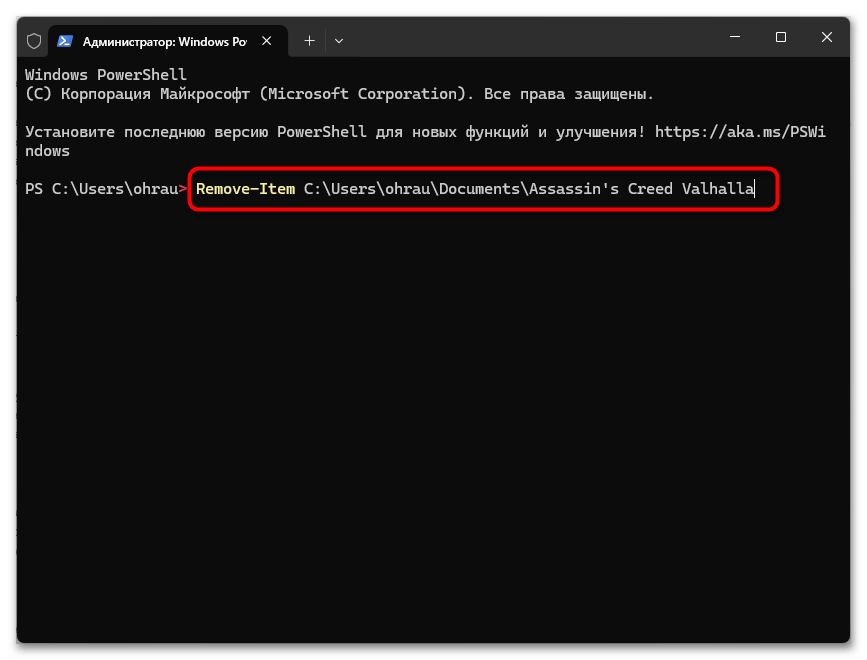
PowerShell также поддерживает сокращенный алиас для Remove-Item: rm путь_к_директории.
Команда Remove-Item имеет расширенный набор параметров для работы с директориями:
- -Recurse. Этот параметр позволяет рекурсивно удалять все содержимое директории, включая все вложенные файлы и поддиректории любой глубины вложенности. Функционально этот параметр аналогичен аргументу RMDIR /S, но интегрирован в экосистему PowerShell. Использование параметра -Recurse является обязательным, если необходимо удалить непустую директорию. Без него команда Remove-Item сможет удалить только пустые папки, аналогично базовой команде RMDIR.
- -Force. Обеспечивает принудительное удаление защищенных, скрытых и системных директорий, а также папок с особыми атрибутами. Данный параметр объединяет функциональность различных аргументов традиционной «Командной строки» и предоставляет более универсальный подход к преодолению ограничений доступа к директориям. Параметр -Force особенно полезен при необходимости удаления папок, созданных системой или другими программами с ограниченными правами доступа.
- -Confirm. Добавляет запрос подтверждения перед удалением каждого объекта, что обеспечивает дополнительный уровень контроля при массовом удалении. Использование данного параметра создает дополнительную защиту от случайного удаления важных папок и рекомендуется при выполнении операций с критически важными директориями или при работе в системных папках. Каждый раз перед удалением система будет запрашивать подтверждение, что позволяет более внимательно контролировать процесс.
- -WhatIf. Уникальный параметр PowerShell, который демонстрирует, какие действия будут выполнены при запуске команды, но не производит фактического удаления директорий. Данный режим позволяет безопасно моделировать результаты команды перед ее реальным выполнением, что особенно ценно при работе со сложными путями или при массовом рекурсивном удалении структур папок. Использование параметра -WhatIf помогает избежать непреднамеренного удаления важных директорий.
Способ 3: Удаление через PowerShell с использованием конвейеров
PowerShell предлагает продвинутый метод удаления директорий с использованием конвейеров (pipelines), который позволяет комбинировать несколько команд для более сложных операций с папками. Этот подход особенно полезен, когда необходимо выполнить выборочное удаление папок на основе определенных критериев, например, даты создания, размера или имени. Конвейеры в PowerShell предоставляют непревзойденную гибкость и возможность автоматизации процессов удаления директорий, которые невозможно достичь с помощью стандартной «Командной строки». Этот метод требует базового понимания принципов работы PowerShell, но предлагает значительные преимущества для опытных пользователей.
Get-ChildItem -Path путь -Directory | Where-Object {условие} | Remove-Item -Recurse -Force
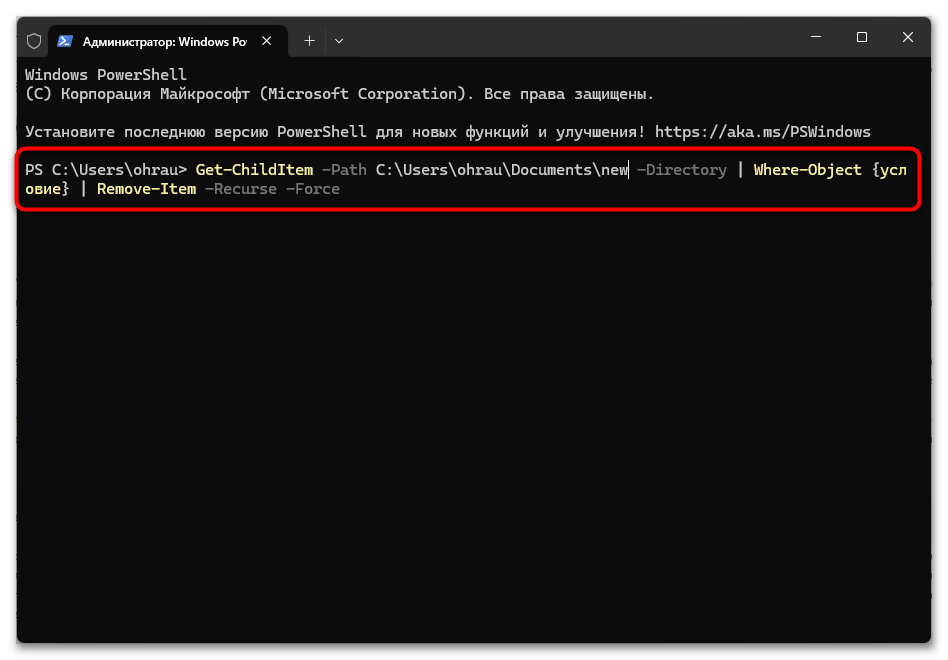
Этот метод включает несколько ключевых компонентов PowerShell:
- Get-ChildItem. Команда для получения списка объектов (файлов и папок) в указанной директории. Параметр -Directory ограничивает вывод только папками, исключая файлы из рассмотрения. Эта команда является начальным этапом конвейера и подготавливает список папок для последующей фильтрации. Get-ChildItem имеет множество параметров для глубокого поиска и фильтрации, включая -Recurse для поиска во вложенных директориях.
- Where-Object. Позволяет фильтровать результаты по различным критериям, таким как имя папки, дата создания или изменения, размер и другие атрибуты. Например, можно выбрать только папки, созданные раньше определенной даты или имеющие определенное слово в названии. Эта часть конвейера обеспечивает точный отбор директорий для удаления на основе заданных условий.
- Remove-Item. Финальная команда в конвейере, которая удаляет отфильтрованные директории. Использование параметров -Recurse и -Force обеспечивает полное удаление папок вместе со всем содержимым и преодоление ограничений доступа. Эта команда получает на вход только те папки, которые прошли через фильтры предыдущих команд в конвейере.
Популярные условия для фильтрации папок в PowerShell
При использовании конструкции Where-Object в PowerShell правильно сформулированные условия играют ключевую роль в точном отборе папок для удаления. Условия фильтрации позволяют указать конкретные характеристики директорий, которые необходимо обработать. Это значительно снижает риск случайного удаления важных папок и повышает точность операций массового удаления. Ниже приведены наиболее востребованные условия, которые можно использовать в команде Where-Object для эффективной фильтрации папок перед их удалением.
- Фильтрация по имени папки. Позволяет выбрать папки, содержащие определенный текст в названии:
Where-Object { $_.Name -like "*backup*" }выберет все папки, в названии которых есть слово «backup». Для точного совпадения используйте оператор -eq:Where-Object { $_.Name -eq "temp" }. Можно также использовать регулярные выражения с оператором -match:Where-Object { $_.Name -match "^log_\d+" }для поиска папок, начинающихся с «log_» и содержащих цифры. - Фильтрация по дате создания. Позволяет отбирать папки, созданные в определенный период:
Where-Object { $_.CreationTime -lt (Get-Date).AddDays(-30) }выберет папки, созданные более 30 дней назад. Для выбора папок, созданных в конкретный день:Where-Object { $_.CreationTime.Date -eq (Get-Date "2024-01-15").Date }. Также можно указать диапазон дат:Where-Object { $_.CreationTime -ge (Get-Date "2024-01-01") -and $_.CreationTime -le (Get-Date "2024-01-31") }. - Фильтрация по дате изменения. Позволяет выбирать папки по дате последнего изменения:
Where-Object { $_.LastWriteTime -gt (Get-Date).AddMonths(-1) }выберет папки, измененные за последний месяц. Для выбора давно неиспользуемых папок:Where-Object { $_.LastWriteTime -lt (Get-Date).AddYears(-1) }найдет директории, не изменявшиеся более года. - Фильтрация по атрибутам. Позволяет выбирать папки с определенными атрибутами:
Where-Object { $_.Attributes -match "Hidden" }выберет все скрытые папки. Для поиска только обычных папок без специальных атрибутов:Where-Object { -not ($_.Attributes -match "System|Hidden|ReadOnly") }. Можно комбинировать несколько атрибутов:Where-Object { $_.Attributes -match "Hidden" -and $_.Attributes -match "ReadOnly" }. - Фильтрация по размеру. Для подсчета размера папок и выбора по размеру можно использовать:
Get-ChildItem -Directory | ForEach-Object { $size = (Get-ChildItem $_.FullName -Recurse | Measure-Object -Property Length -Sum).Sum; [PSCustomObject]@{Name=$_.Name; Size=$size} } | Where-Object { $_.Size -gt 1GB } | Select-Object Name, @{Name="SizeGB";Expression={$_.Size/1GB}} | ForEach-Object { Remove-Item (Join-Path -Path $путь -ChildPath $_.Name) -Recurse -Force }. Это позволит удалить папки размером более 1 ГБ. - Комбинированные условия. Можно объединять несколько условий с помощью логических операторов -and и -or:
Where-Object { $_.Name -like "*temp*" -and $_.LastWriteTime -lt (Get-Date).AddDays(-7) }выберет временные папки, не изменявшиеся более недели. Другой пример:Where-Object { ($_.Name -like "*backup*" -or $_.Name -like "*archive*") -and -not ($_.Attributes -match "System") }выберет все папки резервных копий и архивов, не являющиеся системными.
Способ 4: Использование команды DELTREE в режиме совместимости
Для пользователей, знакомых с более старыми версиями DOS и Windows, может быть интересна возможность использования классической команды DELTREE. Хотя эта команда официально не поддерживается в современных версиях Windows, существует возможность эмулировать ее работу через создание специального макроса или алиаса в системе. DELTREE была популярна в эпоху DOS и ранних версий Windows благодаря своей простоте и эффективности при удалении целых директорий. Основное преимущество DELTREE заключалось в том, что она изначально была предназначена для рекурсивного удаления папок со всем содержимым, не требуя дополнительных параметров, как в случае с RMDIR /S.
DOSKEY DELTREE=RMDIR /S /Q $*
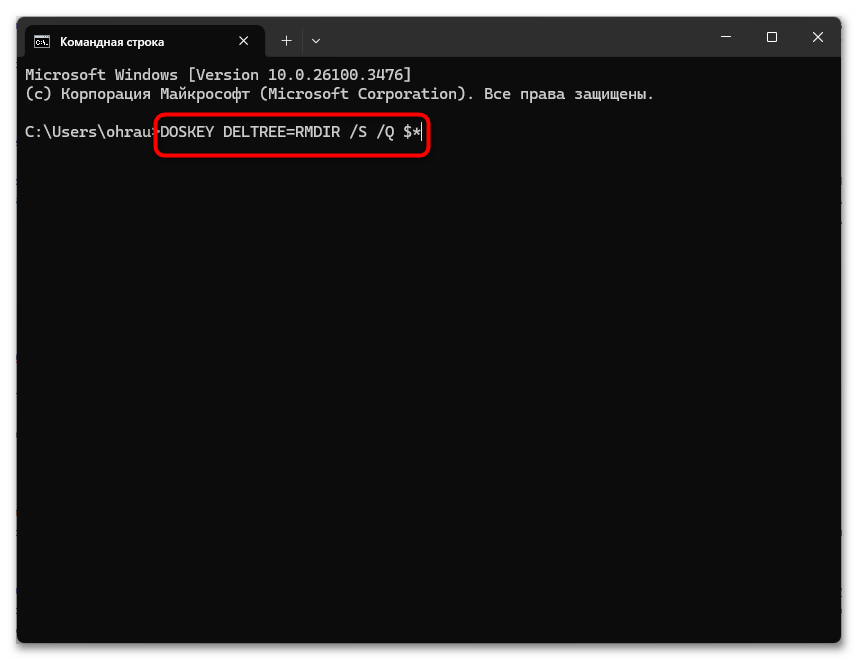
После создания этого алиаса можно использовать команду DELTREE следующим образом:
DELTREE путь_к_директории
Важные особенности использования DELTREE:
- Создание алиаса. Команда DOSKEY позволяет создать временный алиас DELTREE, который будет работать в текущей сессии «Командной строки». Чтобы сделать этот алиас постоянным, необходимо создать файл макросов и настроить автозагрузку этого файла при запуске консоли. Такой подход позволяет восстановить функциональность классической команды DOS в современных системах Windows.
- Автоматическое удаление. Созданный алиас DELTREE автоматически включает параметры /S и /Q для команды RMDIR, что обеспечивает рекурсивное удаление директорий без запроса подтверждения. Это делает команду более похожей на оригинальную DELTREE из DOS. Пользователю следует помнить, что такой алиас не запрашивает подтверждения, поэтому следует быть предельно внимательным при его использовании.
- Совместимость. Хотя этот метод эмулирует поведение классической команды DELTREE, важно понимать, что фактически выполняется команда RMDIR с параметрами. Поэтому все ограничения и особенности RMDIR также применимы к этому алиасу. Этот подход особенно полезен для пользователей, привыкших к синтаксису более старых операционных систем или при миграции скриптов с устаревших платформ.
Наша группа в TelegramПолезные советы и помощь
How to Delete Files and Folders Using Command Prompt in Windows 10
Command Prompt is a powerful tool in Windows 10 that provides users with the ability to execute commands to manage their system. One of its many uses is the ability to delete files and folders quickly and efficiently, often faster than using the graphical user interface (GUI). This article aims to explore the various methods of deleting files and folders using Command Prompt, alongside best practices, tips, and troubleshooting.
Introduction to Command Prompt
Command Prompt, or cmd.exe, is a command-line interpreter application available in most Windows operating systems. It allows users to run commands to perform various administrative tasks, ranging from managing files and directories to executing scripts and troubleshooting system issues. While many users rely on the graphical interface for everyday tasks, using Command Prompt can offer greater control and flexibility.
Accessing Command Prompt
Before you can use Command Prompt to delete files and folders, you’ll need to access it. There are several ways to open Command Prompt in Windows 10:
-
Using the Search Bar:
- Click on the search bar located on the taskbar.
- Type “cmd” or “Command Prompt.”
- Click on the application that appears in the search results.
-
Using the Run Dialog:
- Press
Windows + Ron your keyboard to open the Run dialog. - Type “cmd” and hit Enter.
- Press
-
Using Task Manager:
- Right-click on the taskbar and select “Task Manager.”
- Click on “File” in the top left corner, then select “Run new task.”
- Type “cmd” and check the box labeled “Create this task with administrative privileges” if elevated permissions are needed.
- Click “OK.”
-
From Windows Power User Menu:
- Press
Windows + Xor right-click on the Start button. - Select “Windows PowerShell” or “Command Prompt” from the list that appears.
- Press
Basic Command for Deleting Files and Folders
Deleting Files
Once you have Command Prompt open, you can delete files using the del command. The basic syntax is:
del [options] [file_path]For example, to delete a file named example.txt located in the C:Documents folder, you would use:
del C:Documentsexample.txtOptions for the del command:
/P: Prompts for confirmation before deleting each file./F: Forces deletion of read-only files./S: Deletes specified files from all subdirectories./Q: Enables quiet mode, which does not prompt for confirmation.
Deleting Folders
To delete folders, you’ll use the rmdir command. The basic syntax is:
rmdir [options] [folder_path]For example, to delete a folder named testFolder located in the C:Documents directory, the command would be:
rmdir C:DocumentstestFolderOptions for the rmdir command:
/S: Deletes all files and subdirectories within the specified directory./Q: Enables quiet mode, which does not prompt for confirmation.
Step-by-Step Guide to Deleting Files
Let’s look at the step-by-step process for deleting files using Command Prompt.
-
Open Command Prompt.
- Follow the methods described earlier to get access to Command Prompt.
-
Navigate to the Directory (Optional).
-
You can change your working directory to the location of the file you want to delete using the
cdcommand. For instance:cd C:Documents
-
-
Delete the File.
-
After navigating to the correct directory or if you command the full file path directly, type the
delcommand followed by the file name:del example.txt
-
-
Confirmation (If Required).
- If you’ve used the
/Poption, Command Prompt will prompt for confirmation before deletion. TypeYand press Enter to confirm.
- If you’ve used the
Step-by-Step Guide to Deleting Folders
To delete a folder, you can follow these steps:
-
Open Command Prompt.
- Use your preferred method to access Command Prompt.
-
Navigate to the Parent Directory (Optional).
-
Navigate to the directory where the folder you wish to delete is located:
cd C:Documents
-
-
Delete the Folder.
-
Use the
rmdircommand followed by the folder name:rmdir testFolder
-
-
Using the
/SOption for Non-Empty Folders.-
If the folder contains files or subfolders, you must use the
/Soption:rmdir /S testFolder
-
-
Confirmation (If Required).
- Similar to the file deletion process, you may need to confirm deletion if prompted.
Deleting Multiple Files and Folders
The Command Prompt allows you to delete multiple files and folders in one go. You can employ wildcards or specify multiple files.
Deleting Multiple Files Using Wildcards
For example, to delete all .txt files in a directory, you can use:
del C:Documents*.txtThis command deletes all text files in the C:Documents directory.
Deleting Multiple Directories
If you want to remove several folders, you can use the for command in conjunction with rmdir. Here’s an example that deletes multiple folders matching a specific name pattern:
for /D %i in (C:DocumentsTestFolder*) do rmdir /S /Q "%i"This command removes all folders beginning with “TestFolder” in the C:Documents directory.
Best Practices for Deleting Files and Folders
While deleting files and folders via Command Prompt can be powerful, it’s essential to follow best practices to avoid unintended data loss:
-
Double-Check File and Folder Names:
- Always ensure you have the correct file or folder name and path. Typos can lead to the unintended deletion of critical files.
-
Use the
/POption for Safety:- When working with commands that delete files, consider using the
/Poption to verify before deletion. This can safeguard against accidental deletions.
- When working with commands that delete files, consider using the
-
Backup Important Data:
- Before deleting files or folders, especially if they contain important data, make sure you have a backup.
-
Understand the Scope:
- Be aware of the scope of deletion. Using the
/Soption forrmdirwill delete all nested files and folders, which could lead to significant data loss if used improperly.
- Be aware of the scope of deletion. Using the
-
Testing in a Non-Critical Environment:
- If you are new to using Command Prompt, test the commands in a non-critical environment to ensure you understand how they operate.
-
Keep Command Prompt Open for History:
- If you’re executing multiple commands, you might want to keep the Command Prompt window open to use the command history. You can use the arrow keys to scroll through previously entered commands.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Working with the Command Prompt can sometimes lead to issues while deleting files and folders. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
-
Access Denied Errors:
- This usually indicates that you lack the necessary permissions to delete the file or folder. Ensure you have administrative rights by running Command Prompt as an administrator.
-
File in Use:
- If a file is currently open in another program, you won’t be able to delete it until you close that program. Make sure to close all applications that might be using the file.
-
Read-Only Files:
-
If you’re trying to delete a read-only file, use the
/Foption with thedelcommand to force deletion:del /F readOnlyFile.txt
-
-
File Path Too Long:
-
Windows has a maximum path length; if you encounter issues related to a path being too long, try using the
\?prefix to handle longer paths, like so:del \?C:verylongfilepathexample.txt
-
Recycle Bin and Permanent Deletion
When you delete files using the traditional GUI method (e.g., by right-clicking and selecting delete), they are often moved to the Recycle Bin. However, using Command Prompt’s del command deletes files permanently without sending them to the Recycle Bin, which can be advantageous for completely removing sensitive data. If you wish to recover files deleted via Command Prompt, third-party recovery software may be necessary.
Conclusion
Deleting files and folders using Command Prompt in Windows 10 is a straightforward process that, when done correctly, can greatly enhance your efficiency in managing system files. The command line provides an elegant and effective solution, particularly when dealing with multiple files or when the GUI is insufficient.
By following the steps outlined in this article, understanding the options available, adhering to best practices, and troubleshooting potential issues, you can significantly improve your file management skills. As with any powerful tool, practice and caution are key to ensuring a seamless experience with Command Prompt. Whether you’re a seasoned user or a beginner, mastering these techniques can provide you with a deeper understanding of Windows operating systems and enhance your overall computing experience.
