Last Updated :
07 Apr, 2025
We all know that one can easily create files using GUI options, but what if you can use a faster way to create files through the command-line interface? This is not a necessary but useful skill for anyone working with Windows. Whether you’re automating tasks, working on scripts, or preferring using the command prompt, knowing how to create a file in CMD can be incredibly useful.
This article will walk you through the steps to create a file using CMD, ensuring that you can efficiently manage your files directly from the command prompt.
Methods to Create A File on Windows using CMD
To start a new file on Windows using CMD, the following guidelines should be used. Let us start with the basic Echo Command.
Note: All of these methods should be executed in any certain directory. Otherwise, the operations will not completed. Use the CD Windows Command to enter into any certain Windows directory.
Method 1: Create Text File Using ECHO in Command Prompt
Step 1: Open CMD
- To create a file using CMD open CMD press Win + R key on your keyboard and type CMD to open CMD.
Step 2: Type ECHO Command
- Once the CMD opens execute the following command.
This method will directly save the file to the directory mentioned earlier. You have to put some text for it.
Command: echo. > Rapture.txt
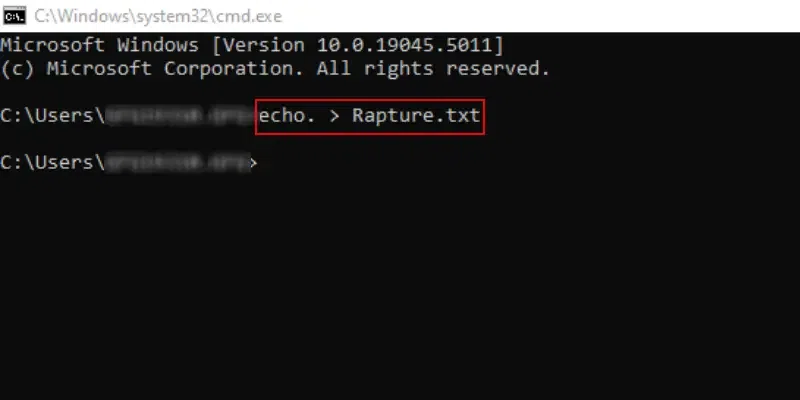
Congratulation! The New Text File on Windows is created using the Command Prompt with one simple command.
Method 2: COPY CON Command to Create a New File
Step 1: Use copy con in CMD
- You need to type «copy con» followed by the name of the file you wish to overwrite and once you’re done press the CTRL + Z to end the operation & the file will be directly saved to the directory.
Let’s understand this with the below-mentioned example where the file name = ‘Rapture’
Command: copy con Rapture.txt
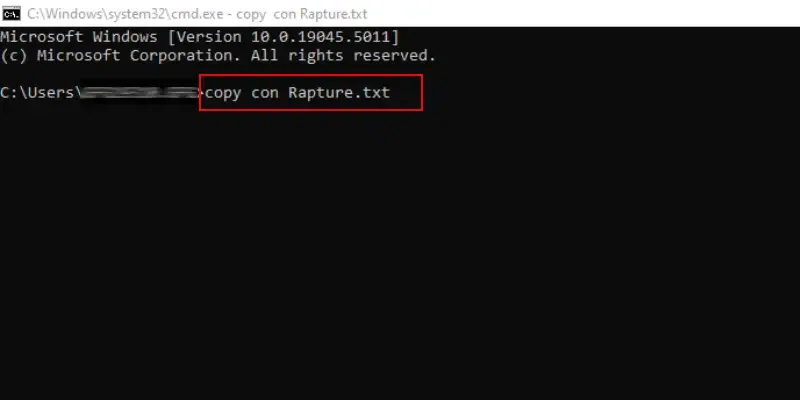
Hooray! We have successfully created a Text File on Command Prompt on Windows in a certain directory without opening it.
Method 3: Quick Guide to Create a File in CMD — NOTEPAD Command
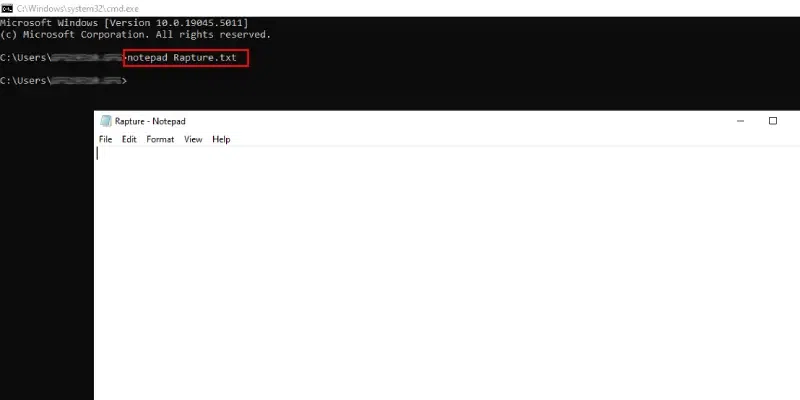
The following command can be used to open any Text File. Either, you can open the New File with any predefined name or any existing one in the certain directory. It will open the Notepad Windows Application, make changes there & press CTRL + S to save it.
Command: notepad Rapture.txt
Method 4: ‘fsutil’ Command to create a «specific» size file
The following command can be used to create a file in CMD for any specific size. Once you create the file, you do perform tasks accordingly.
For example: Let’s create a file of size 10 bytes with the filename as ‘Rapture’
Command: fsutil file createnew Rapture.txt 10
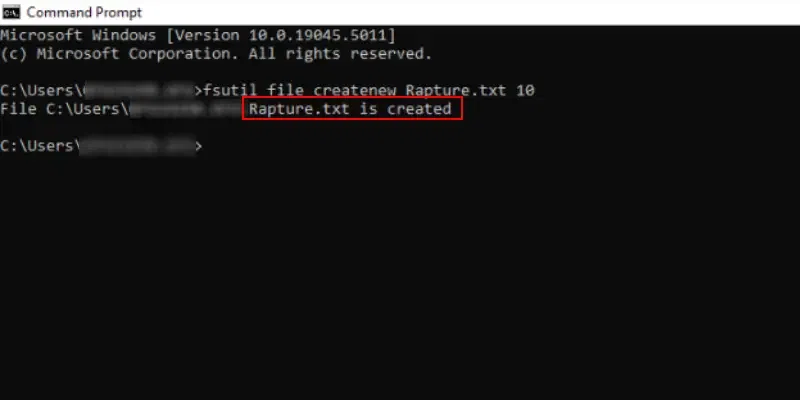
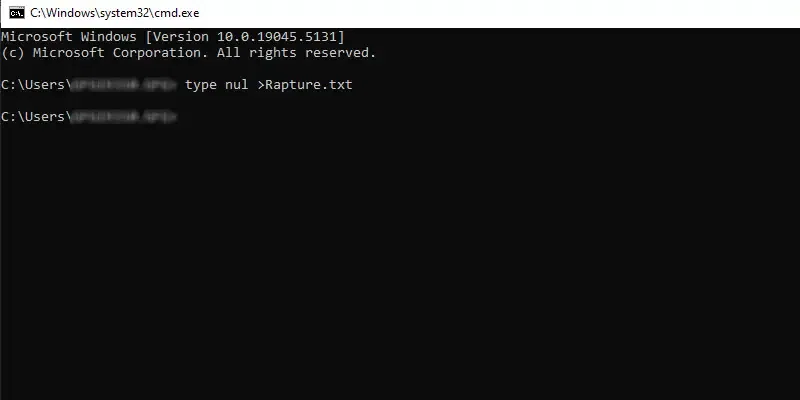
Method 5: «type nul» Command to create a new File
The type nul command in cmd can be used to create a new file wherein the «type nul» denotes to do nothing and starts with an empty file. Let’s understand this with an example below where the filename is ‘Rapture’.
Command: type nul >Rapture.txt
Conclusion
Mastering the ability to create a file in CMD is an essential part of becoming proficient with the command line in Windows. By using the right CMD command to create a file, you can streamline your workflow and perform tasks more efficiently. Whether you’re creating simple text files or working on more complex scripts, understanding how to make a file in CMD gives you greater control over your system.
Also Read
- Most Useful CMD Commands in Windows
- CMD Commands to Gather Information of a System
- How to Show all the previously connected WiFi Networks using CMD in Windows?
on January 3, 2009
We can create files from command line in two ways. The first way is to use fsutil command and the other way is to use echo command. If you want to write any specific data in the file then use echo command. If you are not bothered about the data in the file but just want to create a file of some specific size then you can use fsutil command.
To create file using echo
echo some-text > filename.txt
Example:
C:\>echo This is a sample text file > sample.txt C:\>type sample.txt This is a sample text file C:\>
To create file using fsutil
fsutil file createnew filename number_of_bytes
Example:
C:\data>fsutil file createnew sample2.txt 2000 File C:\data\sample2.txt is created C:\data>dir 01/23/2016 09:34 PM 2,000 sample2.txt C:\data>
Limitations
Fsutil can be used only by administrators. For non-admin users it throws up below error.
c:\>fsutil file /? The FSUTIL utility requires that you have administrative privileges. c:\>
To create a new file using the Command Prompt (cmd), you can use the `echo` command followed by redirection to specify the file name.
Here’s the command:
echo This is a new file > newfile.txt
This command will create a file named `newfile.txt` containing the text «This is a new file».
What is CMD?
The Command Prompt (CMD) is a command-line interpreter available in Windows operating systems. It provides a direct method to interact with the system, facilitating a variety of tasks including network configuration, system management, and file manipulation. Understanding CMD is essential for anyone looking to gain more control over their computing environment. Its power lies in its simplicity and efficiency, making it a favored tool among both beginners and advanced users.

Cmd Count Files: Master File Counting in Cmd
Creating a File in CMD
Understanding File Creation in CMD
Creating a file in CMD involves using a set of commands that interact with the computer’s file system. These commands allow users to generate new files, edit existing files, and manage file contents. This is particularly useful for scripting, automation, or simply manipulating data without needing to navigate through graphical interfaces.
The Basic Command: `echo`
One of the simplest ways to create a new file in CMD is by using the `echo` command. This command outputs a line of text or a variable value to the console or redirects it into a new file.
Syntax:
echo [text] > [filename]
Example:
echo Hello, World! > example.txt
In this example, the command creates a text file named `example.txt` in the current directory, containing the text «Hello, World!». If the file already exists, this command will overwrite its contents. To append text to an existing file instead, you can use `>>`:
echo This will be appended. >> example.txt
The `copy con` Command
Another method of file creation involves the `copy con` command, which allows users to create a file interactively by typing directly into the console.
Syntax:
copy con [filename]
Example:
copy con example2.txt
When you execute this command, CMD will enter an input mode, allowing you to type the content you want. After typing, press `CTRL + Z` followed by `ENTER` to save the file.
This method is particularly useful for quickly creating small files without needing to open an editor. However, be mindful that if you exit the input mode incorrectly, you may lose your work.
Utilizing `fsutil`
The `fsutil` command is another powerful tool for file manipulation, especially for advanced users. It enables more intricate file management, including sparse file creation.
Syntax:
fsutil sparse setflag [filename]
Example:
fsutil sparse setflag examplefile.txt
Using `fsutil` requires administrative permissions, making it suitable for advanced operations. This command allows the creation of large files while only allocating disk space as data is written.
Creating Different File Types
Creating various types of files in CMD is straightforward, and the aforementioned commands can be adapted to suit different formats.
Text Files
You can easily create text files (.txt) or other text-based files using the `echo` or `copy con` commands.
Batch Files
Batch files (.bat) can be created in CMD to automate tasks. An example command that creates a simple batch file could be:
echo @echo off > myscript.bat
This command creates a file named `myscript.bat`, which when executed, will hide its own command prompt output.
Other Formats
Creating files in other formats, such as .csv for spreadsheets or .log for logging purposes, only requires a change in the filename extension.
For instance:
echo Name, Age, Occupation > data.csv
This command creates a CSV file that could be used for data storage in spreadsheet applications.
Effortless File Transfers: Cmd Move Files Made Easy
Practical Tips and Tricks
Quick File Creation Shortcuts
Creating files can often be expedited through shortcuts or advanced techniques. For instance, using `tab completion` can save time when specifying file names or paths if you are creating files in directories that contain spaces.
Creating Files in Specific Directories
To avoid cluttering your working directory, it’s a good idea to specify the path when creating files. This can be accomplished easily by including the full path in your command.
Example:
echo Hello > C:\Users\YourName\Documents\example.txt
This command creates the file directly in the designated Documents folder, keeping your workspace organized.
Checking for File Existence
Before creating files, it’s wise to check whether a file already exists, thus preventing unintentional overwrites. You can achieve this using the `IF EXIST` command.
Example:
IF EXIST example.txt echo File exists.
This line of CMD will only output text if the specified file is found in the current directory.

How to Create Directory Using Cmd in Simple Steps
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Permission Denied Errors
If you encounter permission denied errors when attempting to create a file, it’s often due to restrictions set on the directory or the file being accessed. Running CMD as an administrator can help to overcome this limitation.
Path Not Found Errors
Path issues commonly arise when the specified directory does not exist or is incorrectly entered. Ensure that the paths used are correct and note that CMD is sensitive to spelling and case.
How to Create Folder Through Cmd Efficiently
Conclusion
The versatility of CMD in file creation allows users to efficiently manage their data with just a few commands. From the straightforward `echo` and `copy con` to the specialized `fsutil`, there are various methods to cater to your needs. Mastering these commands not only enhances your productivity but also grants greater control over your files and system environment.

Mastering Cmd Formatting: A Quick Guide
Additional Resources
Recommended Tools and Software
Enhancing your CMD experience may also involve using third-party tools that provide GUI interfaces for command line operations, or scripting environments tailored for automation.
Further Reading and Tutorials
For users looking to expand their knowledge, many online resources offer extensive CMD tutorials and community forums for discussion and troubleshooting.
Community and Support
Engaging with communities, whether through online forums or local user groups, can be invaluable in accelerating your CMD learning journey and exchanging knowledge with others.
Download Article
Download Article
Learning how to do simple file management at the Command Prompt (cmd) comes in handy when you’re learning to code. When you create files and folders at the command line, you can access, use, and manipulate those folders and files in Windows apps. We’ll show you how to create folders (directories) and text files at the Windows Command Prompt, and teach you commands for deleting unneeded files and folders.
-
Open the Command Prompt. The easiest way to do this is to press Win + S to activate the search bar, type cmd, and then click Command Prompt in the search results.
-
The prompt will open to C:\Users\YourName by default. If the directory is somewhere else, type cd path_to_directory and press Enter. Replace path_to_directory with the actual directory location.[1]
- For example, if you want to create a file on the Desktop, type cd desktop and press Enter.
- If the directory you’re looking for isn’t in your user directory (e.g., C:\Users\YourName), you’ll have to type in the whole path (e.g., C:\Users\SomeoneElse\Desktop\Files).
Advertisement
-
If you don’t want to create an empty file, skip to the next step.[2]
To create an empty file:- Type type nul > filename.txt.
- Replace filename.txt with whatever you want to call your new file. The «.txt» part indicates that this is a plain text file. Other common file extensions include «.docx» (Word document), «.png» (empty photo),and «.rtf» (rich text document). All of these file types can be read on any Windows computer without installing additional software.
- Press Enter.
-
If you don’t want to create a file with certain text inside, skip to the next step.[3]
Use these steps to create a plain text file that you can type into:- Type copy con testfile.txt, but replace testfile with the desired file name.[4]
- Press Enter.
- Type some text. This is a rudimentary text editor, but it’s good for quick notes or code. You can use the Enter key to go to the next line.
- Press Control + Z when you’re finished editing the file.
- Press the Enter key. You’ll see «1 file(s) copied,» which means your file is now saved with the name you created.
- Another way to do this is to run this command: echo enter your text here > filename.txt.
- Type copy con testfile.txt, but replace testfile with the desired file name.[4]
-
If you don’t want to create a file that’s a specific size, skip this step.[5]
To create a blank text file based on byte size, use this command:- fsutil file createnew filename.txt 1000.
- Replace filename with the desired file name, and 1000 with the actual number of bytes you’d like the file to be.
Advertisement
-
The easiest way to do this is to press Win + S to activate the search bar, type cmd, and then click Command Prompt in the search results.
-
Go to the directory containing the file you want to delete. The prompt will open to C:\Users\YourName by default. If the file is somewhere else, type cd path_to_directory and press Enter. Replace path_to_directory with the actual directory location.
- For example, if you want to delete a file from the Desktop, type cd desktop and press Enter.
- If the directory you want to view isn’t in your user directory (e.g., C:\Users\YourName), you’ll have to type in the whole path (e.g., C:\Users\SomeoneElse\Desktop\Files).
-
This displays a list of all files in the current directory. You should see the file you want to delete in this list.
- Using Command Prompt to delete files results in the files being deleted permanently rather than being moved to the Recycle Bin. Exercise caution when deleting files via Command Prompt.
-
Replace filename with the full name and extension of the file you want to delete.[6]
File names include file extensions (e.g., *.txt, *.jpg). This deletes the file from your computer.- For example, to delete a text file entitled «hello», you would type del hello.txt into Command Prompt.
- If the file’s name has a space in it (e.g., «hi there»), you will place the file’s name in quotations (e.g., del "hi there").
- If you get an error that says the file cannot be deleted, try using del /f filename instead, as this force-deletes read-only files.
Advertisement
-
The easiest way to do this is to press Win + S to activate the search bar, type cmd, and then click Command Prompt in the search results.[7]
-
The prompt will open to C:\Users\YourName by default. If you don’t want to create a new directory here, type cd path_to_directory and press Enter. Replace path_to_directory with the actual directory location.[8]
- For example, if you want to create a directory on your Desktop, you would type in cd desktop and press Enter.
- If the directory you’re looking for isn’t in your user directory (e.g., C:\Users\YourName), you’ll have to type in the whole path (e.g., C:\Users\SomeoneElse\Desktop\Files).
-
Replace NameOfDirectory with the name of the directory you wish to create.[9]
- For example, to make a directory named «Homework», you would type mkdir Homework.
-
This runs the command to create a folder with the desired name.
Advertisement
-
The easiest way to do this is to press Win + S to activate the search bar, type cmd, and then click Command Prompt in the search results.[10]
-
The prompt will open to C:\Users\YourName by default. If the directory you want to delete is somewhere else, type cd path_to_directory and press Enter.[11]
Replace path_to_directory with the actual directory location.- For example, if you want to delete a directory from your Desktop, type cd desktop.
- If the directory isn’t in your user directory (e.g., C:\Users\YourName), you’ll have to type in the whole path (e.g., C:\Users\SomeoneElse\Desktop\Files).
-
Replace DirectoryName with the name of the directory you want to delete.[12]
- For example, if you’re trying to delete your «Homework» folder, you’d type in rmdir /s Homework here.
- If the directory’s name has a space in it (e.g., «Homework assignments»), place the name in quotations (e.g., rmdir /s "Homework assignments").
-
[13]
- If you try to delete a directory that contains hidden files or directories, you’ll see an error that says «The directory is not empty.» In this case, you’ll have to remove the «hidden» and «system» attributes from the files inside the directory. To do this:[14]
- Use cd to change into the directory you want to delete.
- Run dir /a to view a list of all files in the directory and their attributes.
- If you’re still okay with deleting all of the files in the directory, run attrib -hs *. This removes special permissions from the undeletable files.
- Type cd .. and press Enter to go back one directory.
- Run the rmdir /s command again to delete the folder.
- If you try to delete a directory that contains hidden files or directories, you’ll see an error that says «The directory is not empty.» In this case, you’ll have to remove the «hidden» and «system» attributes from the files inside the directory. To do this:[14]
-
This will permanently remove the directory.[15]
Advertisement
Add New Question
-
Question
How can I create directories?
Subhodeep Roy
Community Answer
If you are creating a directory in C drive, the command will be»C:\MD {the name of the directory/folder}» then press Enter.
-
Question
How do I create a folder using CMD?
Navigate to where you want the subfolder created and type «mkdir «.
-
Question
How do I create a test file under the sub folder?
Change directory into the new sub folder and then on the next line, create your new test file. For example: cd mysubfolder $ type nul > newtextfile.txt
See more answers
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Video
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
-
Using Command Prompt to delete files results in the files being deleted permanently rather than being moved to the Recycle Bin. Exercise caution when deleting files via Command Prompt.
Advertisement
References
About This Article
Article SummaryX
1. Use the mkdir command to create a folder.
2. Use rmdir /s to delete a folder.
3. Use the copy con or echo command to create a file.
4. Use del to delete a file.
For tips on how to create a file inside a folder, read on!
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 1,585,483 times.
Is this article up to date?
Creating a file is a basic but important task that any computer user should know how to do. Especially as there are several different ways you can create new files in Windows, and most are quite easy and intuitive. Yes, some are visual and involve using only the operating system’s interface or your installed applications. Others rely on using commands that create files from the Terminal, in tools such as Command Prompt or PowerShell. Regardless of what you prefer, in this tutorial, you’ll learn a couple of different ways to create files in both Windows 10 and Windows 11. Without further ado, let’s begin:
1. Create a file on the desktop or using File Explorer
The easiest and most common way to create files in Windows is by using the right-click menu on the desktop or in File Explorer. Here are the steps you need to follow:
Go to the desktop and right-click or press and hold on an empty space. In the context menu displayed, click/tap or hover over New, then select the type of file you’d like to create.
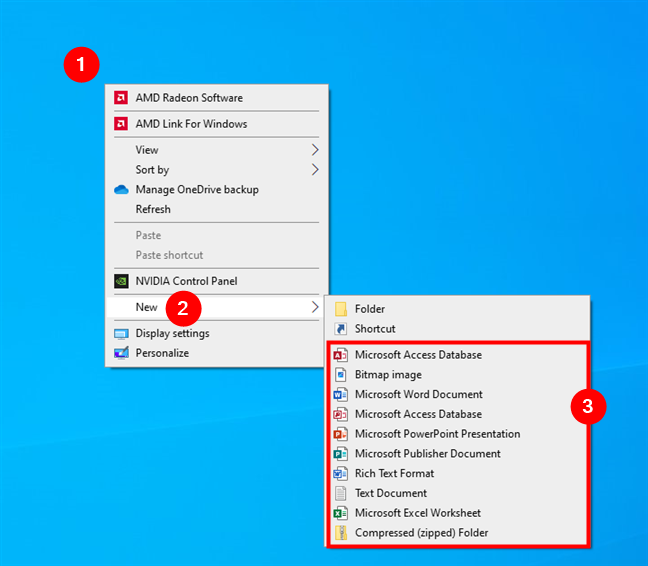
Right-click on the desktop, go to New, and choose the type of file to create
If you don’t want to create a file on the desktop, but rather in a folder on your computer, open File Explorer (Win + E) first. Then, navigate to the location where you want to create your file. For example, go to your user’s Documents folder. Right-click in the folder where you want to create a file, and either click/tap or hover over New. In the list of options displayed, select the type of file you want to create.
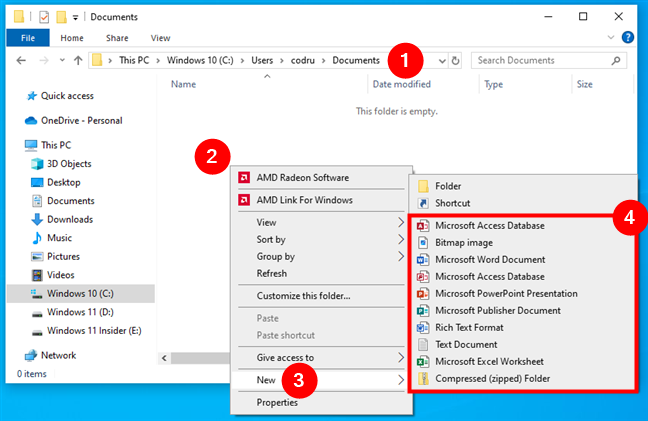
Follow the same steps to create a file in File Explorer
Depending on the software you have installed on your computer, the options you have can differ. However, they’ll usually include: Text Document (.txt), Bitmap image (.bmp), Microsoft Word Document (.docx), Microsoft Excel Spreadsheet (.xlsx), Microsoft PowerPoint Presentation (.pptx).
While in the previous screenshots you can see the options I have on my Windows 10 laptop, here’s what I get on my desktop PC running Windows 11:
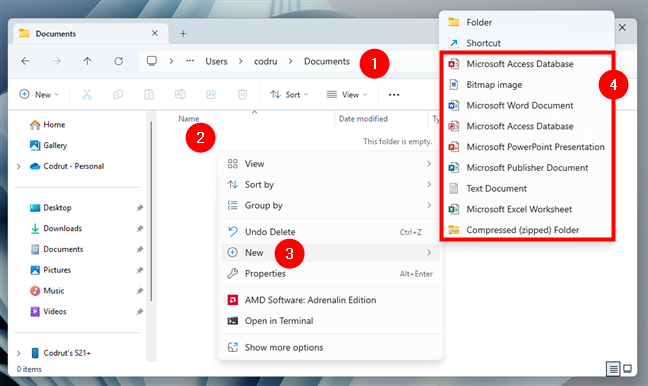
Right-click in an empty space, go to New, and choose the type of file to create
Once you select the file type, a new file or folder will appear with its name highlighted. Type a new name for the file and press Enter on your keyboard. This is what it looks like in the File Explorer of Windows 10:
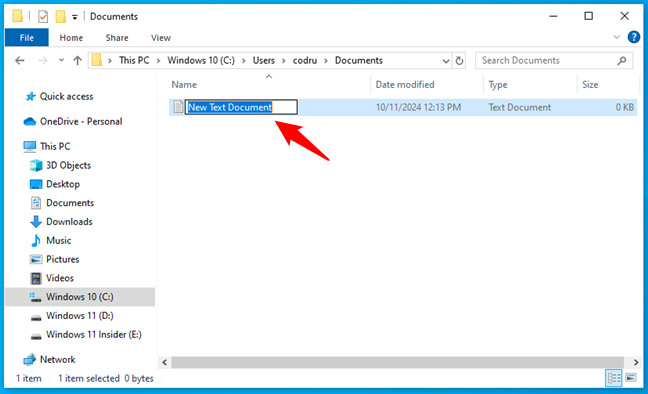
Creating a file in Windows 10
And here’s what to expect in Windows 11:
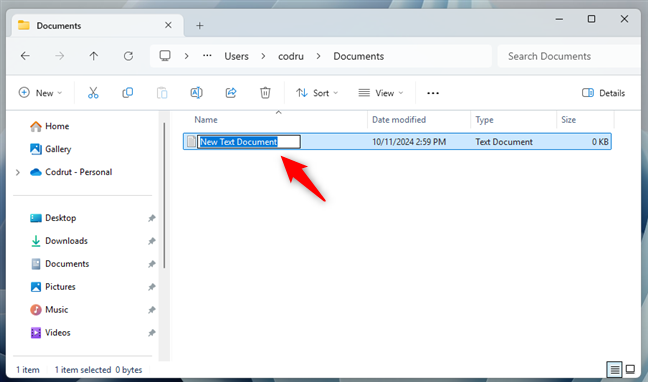
Creating a file in Windows 11
TIP: Besides some usual file types, the right-click menu also includes a few special options: Folder, Shortcut, and Compressed (zipped) Folder. The first one I mentioned — Folder — creates a folder when chosen, while Shortcut lets you make a shortcut, and Compressed (zipped) Folder helps you archive files and folders.
2. Create a file from an application
If you’re working in an application, you can create a file directly from there. Let’s take, for instance, Notepad, which works the same in both Windows 10 and Windows 11:
Open Notepad and start typing text.
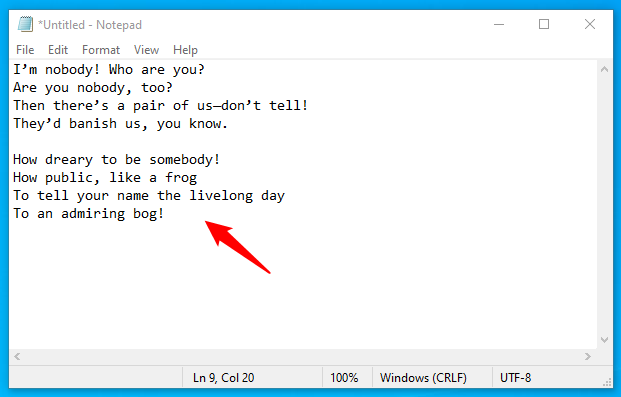
Open Notepad and type some text
When you’re done, open the File menu and choose Save As in the list of options displayed.
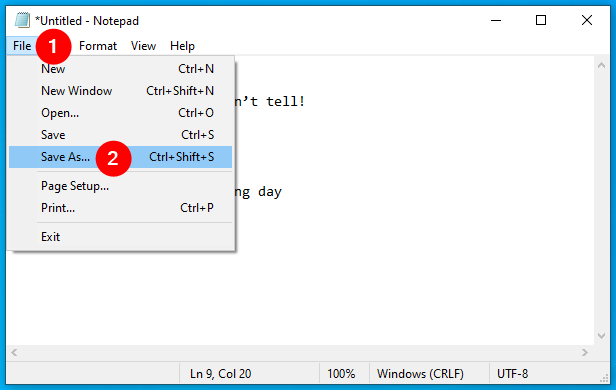
Go to the File menu and choose Save As…
Choose a location where to save the file, name it, and click Save.
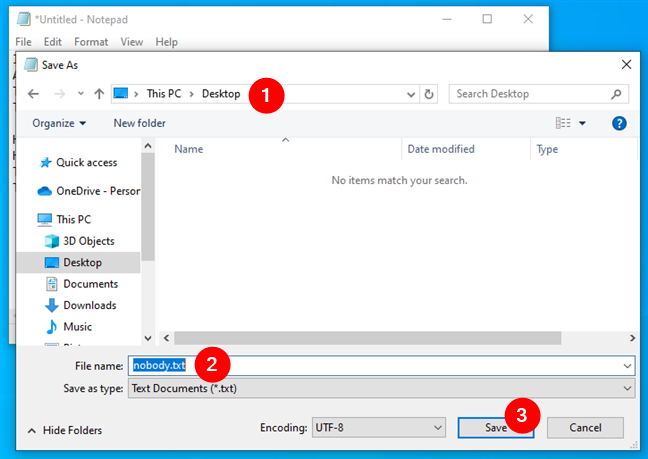
Select a location and choose a name for the file
That’s it! This works in most applications that allow you to create content. They all have options to create new files and save them on your computer. Just check the menus and toolbars in your app to find the way to create a new file.
TIP: Did you know that Windows also lets you create links for files and folders?
3. Create a file from the command line (CMD or PowerShell)
If you’re an advanced user, you may want to create files using Command Prompt or PowerShell. This is especially useful for creating text files or batch files with scripts.
How to create a file with Command Prompt (CMD)
Open Command Prompt either as a standalone app or as a tab in Windows Terminal and navigate to the directory where you want to create the file. You can do that by using the cd command followed by the folder path:
cd “path to folder”
For example, let’s say I want to create a file on my desktop. To get there, I need to execute the cd command like this:
cd C:\Users\codru\Desktop
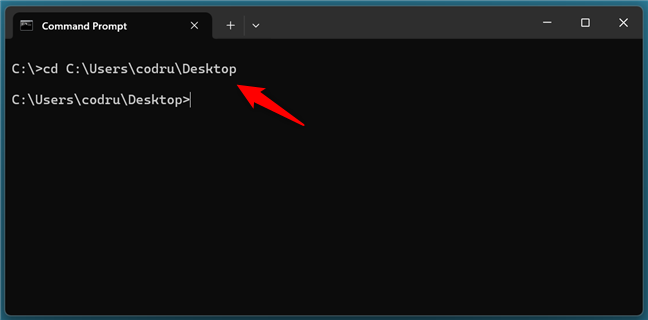
Go to the folder where you want to create a file
To create a text file, use the following command:
type nul > filename.ext
…replacing filename with the name and .ext with the extension you want your new file to have.
I chose to create a file called digitalcitizen.docx so I had to run this command:
type nul > digitalcitizen.docx
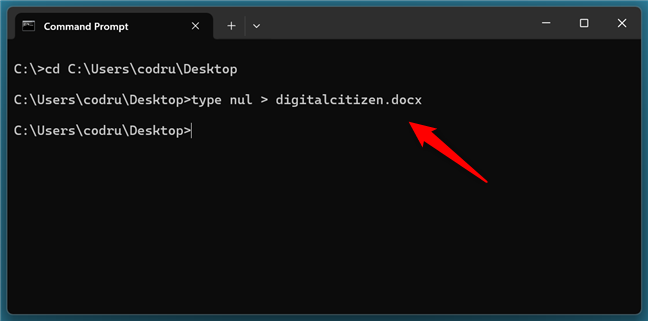
How to create a file from CMD
TIP: Did you know that there are also ways to create files with randomly generated dummy content, of any size you want?
This command immediately created the file on my desktop.
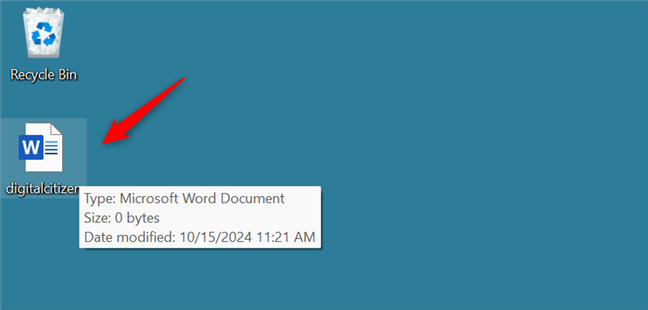
The file created with Command Prompt
IMPORTANT: Although you can use this method to create files with any extension, you can open and edit only the files with text content. In other words, files that use extensions like TXT, DOCX, LOG, or BAT. If you create files with other formats, like XLSX or PNG, for instance, attempting to open them will trigger errors about file format mismatching.
How to create a file with PowerShell
PowerShell also has its own ways of letting you create files. Open PowerShell and use the following command:
New-Item path\filename.ext -type file
…replacing path with the actual path to the folder where you want to create the file and filename.ext with the name and extension you want for it. For example, here’s how I can create a new text file called FreeCitizen on my desktop:
New-Item C:\Users\codru\Desktop\FreeCitizen.txt -type file
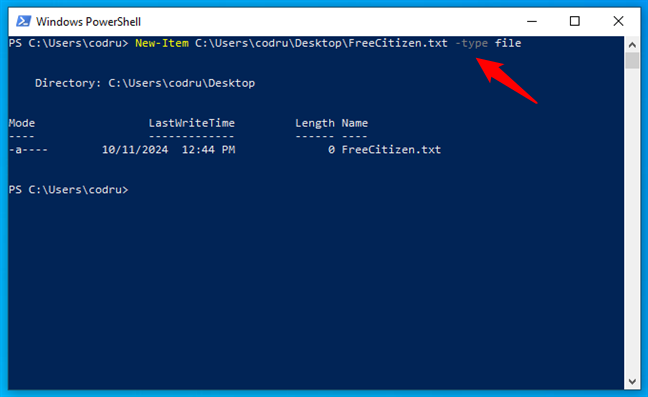
How to create a file in PowerShell
This created a blank file named FreeCitizen.txt on my desktop.
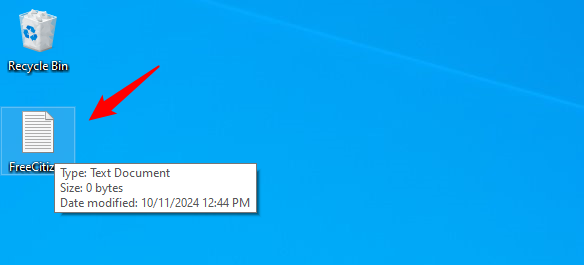
The file created with PowerShell
IMPORTANT: Although you can use this method to create files with any extension, only those with text content are properly formatted. If you create files with formats other than text, like XLSX or JPEG for example, they won’t be formatted correctly. For such files, you’ll need to document yourself on the specific modules and commands to use. Microsoft’s PowerShell Learning website is a great start for that.
Why did you want to learn to create files in Windows?
Now you know how to create files through File Explorer, apps, or using Command Prompt or PowerShell. As you’ve seen, there are plenty of options and methods to try out. Which one are you using most often and why did you look for this information on the internet? I’m curious so please let me know in the comments section below.


















