Изоляция ядра — одна из функций защиты устройства Windows на основе виртуализации (Hypervisor-protected Code Integrity или HVCI), изолирующая сторонние процессы от процессов Windows, призванная повысить защиту от угроз, направленных на ядро Windows. Несмотря на пользу, в некоторых случаях её отключение может повысить производительность системы в играх и сторонних приложениях.
В этой пошаговой инструкции подробно о способах отключить изоляцию ядра в Windows 11 и Windows 10, а также дополнительная информация на тему, которая может оказаться полезной.
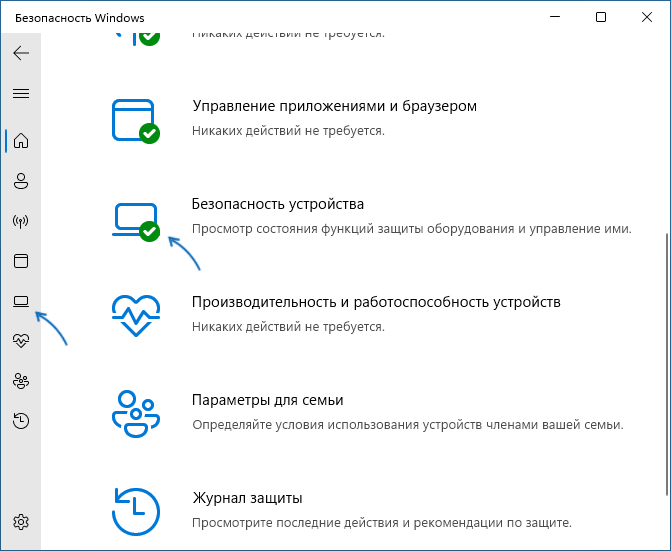
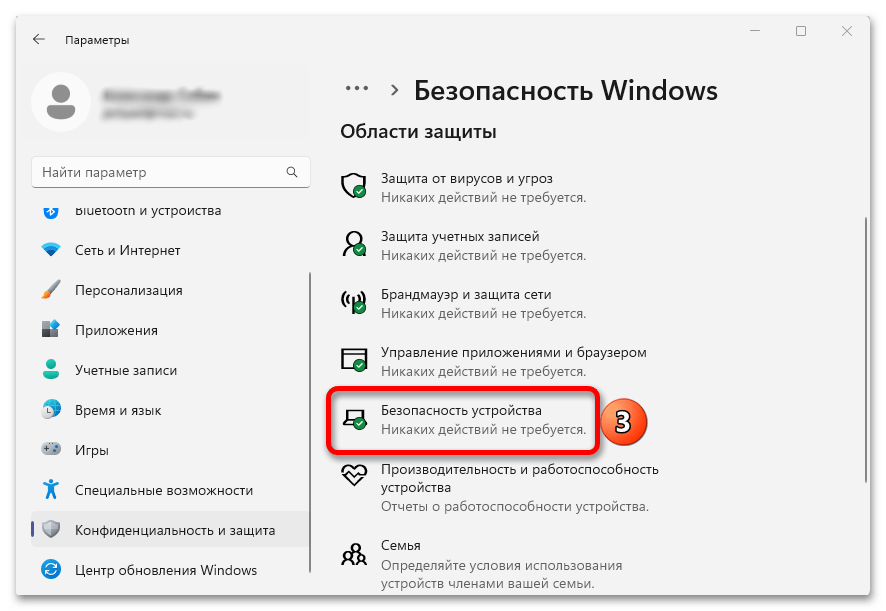
Отключение изоляции ядра в «Безопасность Windows»
Базовый способ — использование соответствующей настройки в окне «Безопасность Windows». Шаги для отключения изоляции ядра будут следующими:
- Откройте окно «Безопасность Windows», используя значок в области уведомлений или поиск в панели задач.
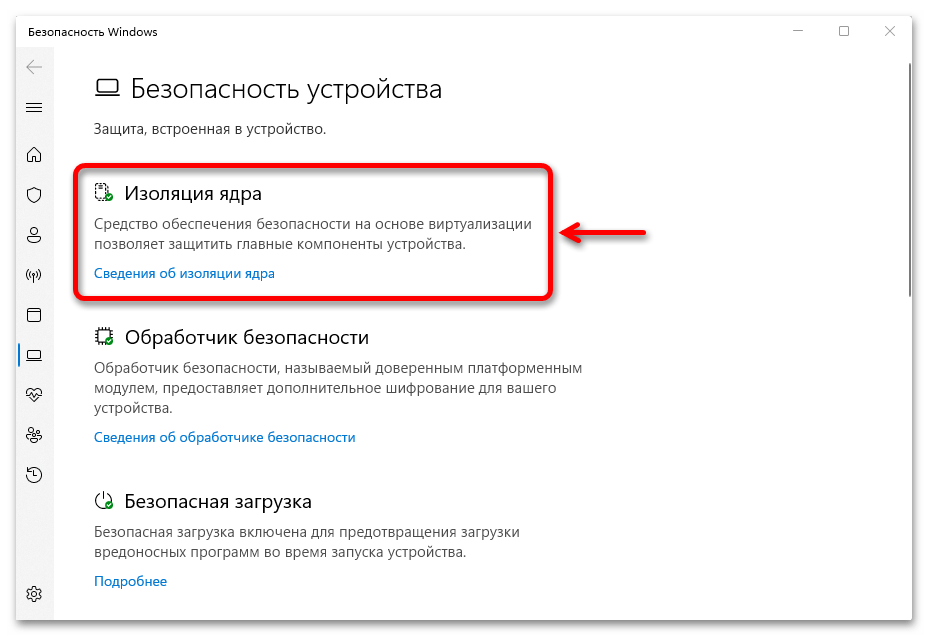
- В открывшемся окне «Безопасность Windows» перейдите в раздел «Безопасность устройства».
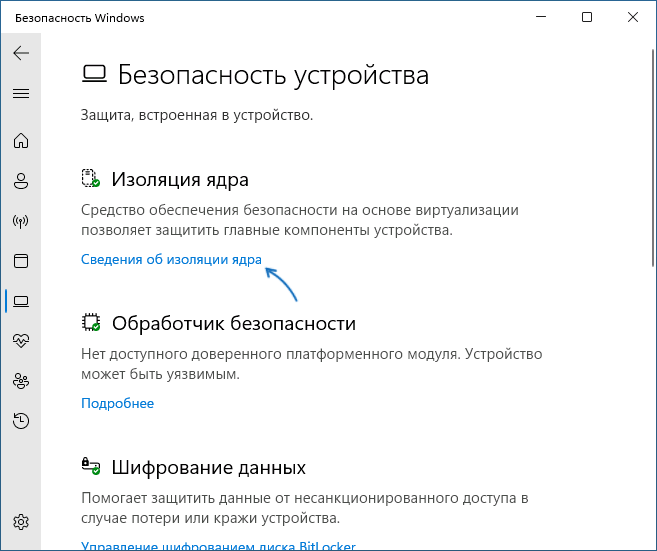
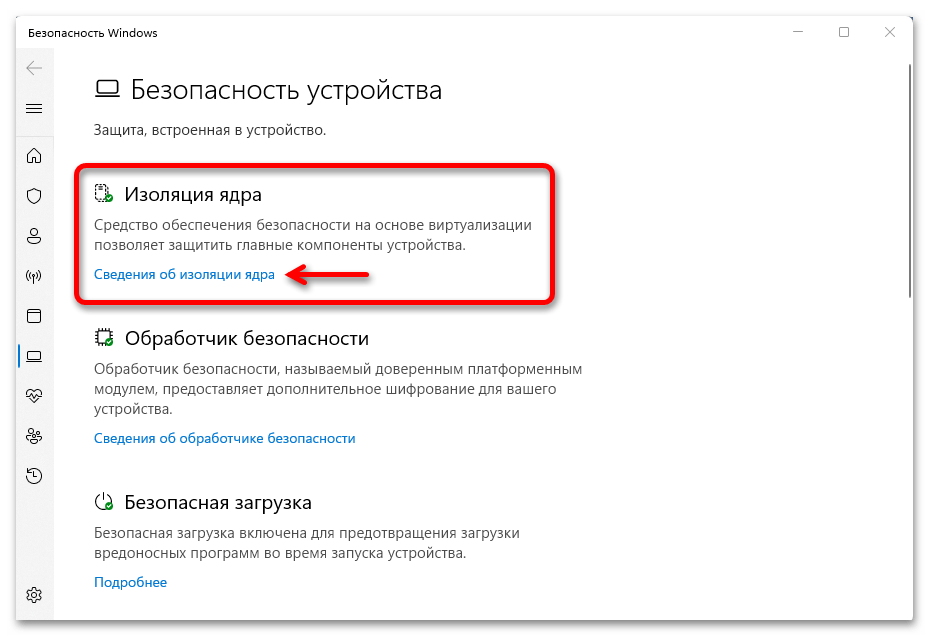
- В пункте «Изоляция ядра» нажмите «Сведения об изоляции ядра».
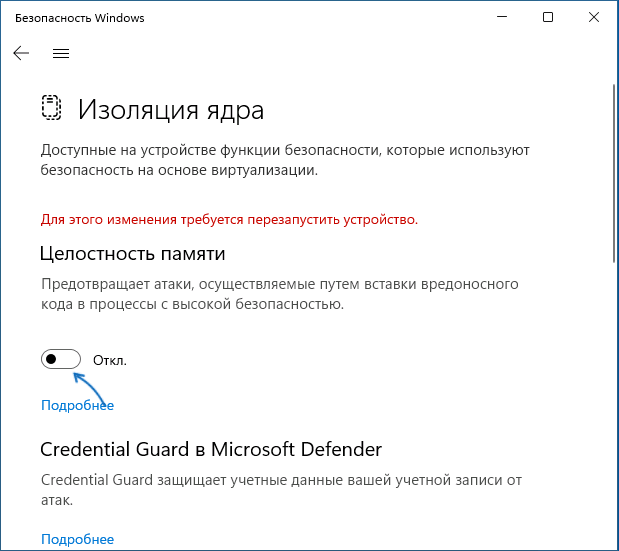
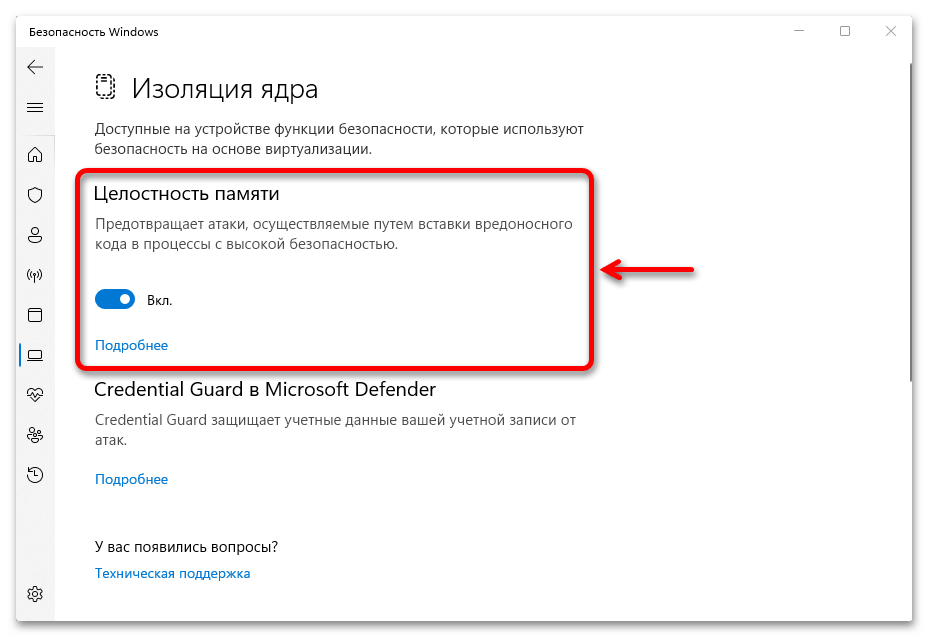
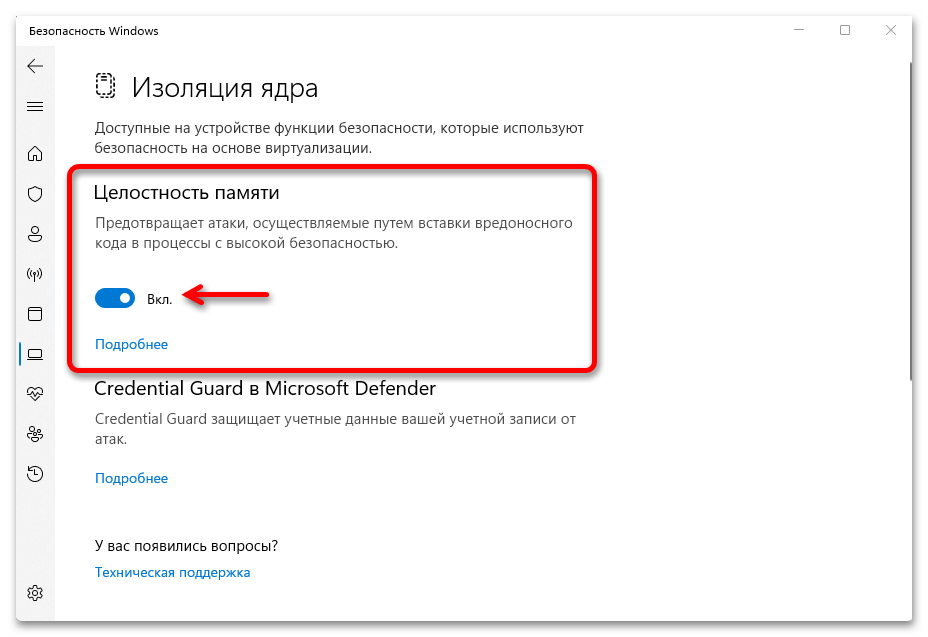
- Отключите пункты «Целостность памяти». При появлении запроса контроля учетных записей подтвердите действие.
- В случае, если отключение производится из-за невозможности работы какого-либо драйвера, также отключите пункт «Список заблокированных уязвимых драйверов».
- Появится уведомление о необходимости перезагрузки. Перезагрузите компьютер для применения сделанных настроек.
В результате изоляция ядра и основная её составляющая — «Целостность памяти» будут отключены.
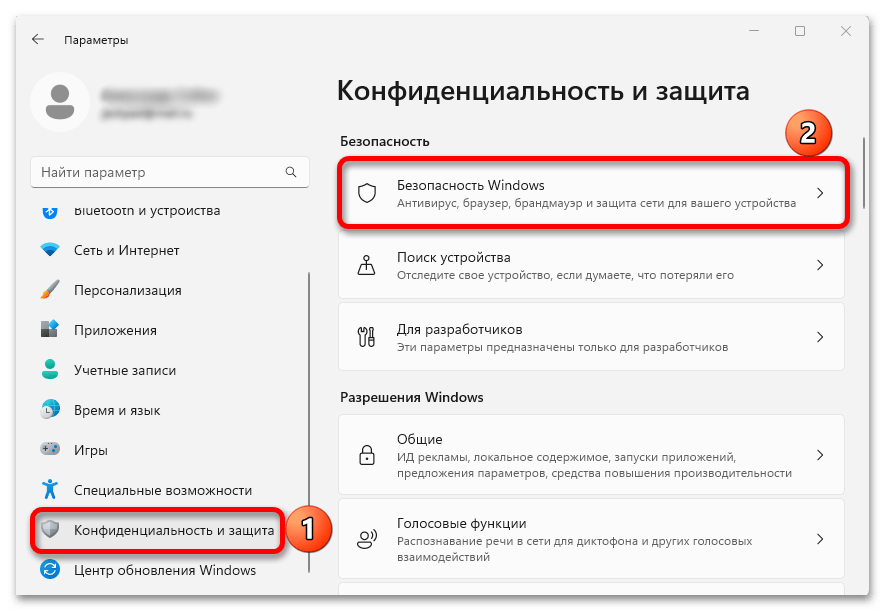
Примечание: открыть «Безопасность Windows» вы можете через «Параметры»:
- В Windows 11 — Параметры — Конфиденциальность и защита — Безопасность Windows
- В Windows 10 — Параметры — Обновление и безопасность — Безопасность Windows
Отключение в редакторе реестра
Вы можете полностью отключить функции изоляции ядра HVCI, используя редактор реестра. Для этого:
- Нажмите правой кнопкой мыши по кнопке «Пуск», выберите пункт «Выполнить», введите regedit и нажмите Enter.
- Перейдите к разделу реестра
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\DeviceGuard\Scenarios\HypervisorEnforcedCodeIntegrity
При отсутствии такого раздела, создайте его.
- В правой панели редактора реестра дважды нажмите по параметру DWORD с именем «Enabled» и измените его значение на 0.
- Примените настройки и перезагрузите компьютер.
В результате изоляция ядра и сопутствующие функции HVCI будут отключены на компьютере.
Вместо ручного редактирования реестра вы можете создать reg-файл со следующим содержимым:
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\DeviceGuard\Scenarios\HypervisorEnforcedCodeIntegrity] "Enabled"=dword:00000000
Либо использовать команду в командной строке, запущенной от имени Администратора:
reg add "HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\DeviceGuard\Scenarios\HypervisorEnforcedCodeIntegrity" /v "Enabled" /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f
Настройка HVCI в редакторе локальной групповой политики
Если на вашем компьютере установлена Windows 11/10 Pro или Enterprise, вы можете использовать редактор локальной групповой политики для отключения изоляции ядра и других функций HVCI:
- Нажмите клавиши Win+R на клавиатуре, введите gpedit.msc и нажмите Enter.
- Перейдите в раздел Конфигурация компьютера — Административные шаблоны — Система — Device Guard.
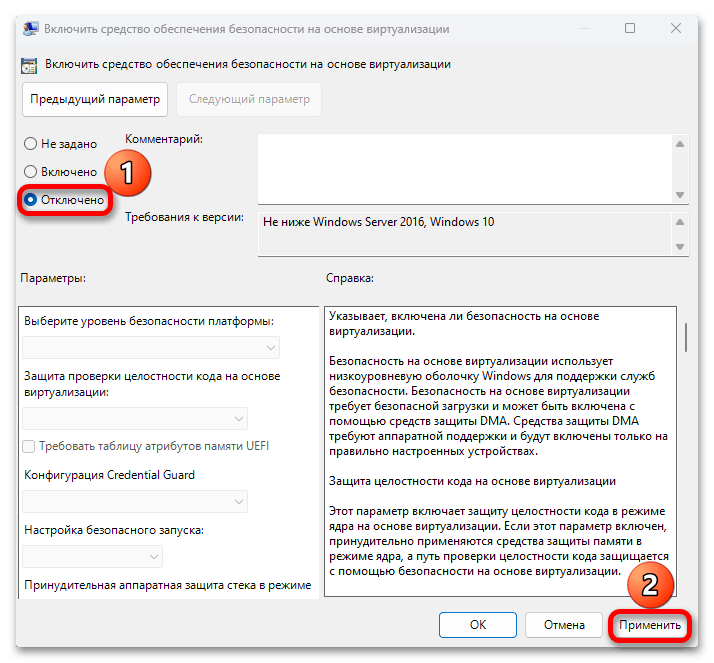
- Дважды нажмите по политике «Включить средство обеспечения безопасности на основе виртуализации».
- Установите значение «Отключено».
- Примените настройки и перезагрузите компьютер.
В результате функции изоляции ядра Windows будут полностью отключены.
Проверка статуса изоляции ядра
Проверить текущий статус функций безопасности на основе виртуализации можно с помощью команды PowerShell (Терминала Windows):
Get-CimInstance -ClassName Win32_DeviceGuard –Namespace root\Microsoft\Windows\DeviceGuard

На скриншоте видно, что все функции HVCI отключены (SecurityServicesRunning и VirtualisationBasedSecurityStatus равны 0).
Еще один способ проверить, включена ли изоляция ядра — в редакторе реестра открыть раздел
HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\CI\State
Если раздел отсутствует или параметр HVCIEnabled в нём равен 0, изоляция ядра отключена. При значении HVCIEnabled равном 1 — включена.

После отключения изоляции ядра безопасность Windows будет сигнализировать о проблемах в части «Безопасность устройства», а на значке в области уведомлений будет отображаться восклицательный знак. Чтобы этого не происходило, зайдите в раздел «Безопасность устройства» и нажмите «Закрыть» или «Закрыть все».

Насколько безопасно отключать изоляцию ядра Windows? Точного ответа о степени риска дать не получится. В общем случае, при отсутствии каких-либо проблем с производительностью и работой необходимых драйверов лучше оставлять встроенные функции безопасности Windows 11/10 включенными. Но, как отмечалось, иногда отключение изоляции ядра и целостности памяти позволяет повысить производительность в играх, что отмечала и Майкрософт.
Учитывайте, что не на всех устройствах изоляция ядра включена по умолчанию. Если она отключена, чаще всего причина — в неподдерживаемых драйверах устройств, список которых будет отображаться в «Безопасность Windows». Вторая возможная причина — отсутствие необходимых для работы HVCI функций виртуализации.
Описание технологии
Система безопасности Windows 11 давно не ограничивается штатной программой Microsoft Defender Antivirus. «Изоляция ядра» – еще одна защитная технология, которая обеспечивает безопасность устройства и операционной системы путем запуска важных процессов в специальной виртуализированной области.
Ее главная функция — «Целостность памяти», которая затрудняет получение злоумышленниками доступа к компьютеру через вредоносное программное обеспечение. Перед запуском приложения часть его кода отправляется в изолированную среду, созданную с помощью аппаратной виртуализации, а после проверки, если ничего подозрительного найдено не было, передается обратно операционной системе для выполнения.
В зависимости от устройства и версии ОС «Изоляция ядра» может поддерживать дополнительные функции. К таким относится «Защита ядра DMA», которая блокирует атаки с прямым доступом к памяти через периферийные устройства, подключенные к внешним и внутренним PCI-портам, например Thunderbolt или M.2.
Кроме того, может поддерживаться «System Guard» Защитника Windows – набор инструментов, способных отслеживать и блокировать попытки взлома устройства через прошивку еще до загрузки системы. А также функция защиты учетных данных, которая особенно полезна для офисных и школьных компьютеров, так как позволяет скрывать от мошенников маркеры доступа к различным ресурсам в одной организации.
Управление функцией
«Изоляции ядра» работает в пассивном режиме и каких-то специальных настроек не имеет. Главное, чтобы была включена «Целостность памяти». В Windows 11, по крайней мере в последних ее сборках, технология безопасности обычно активна по умолчанию, но мы на всякий случай покажем, где она находится, а заодно и как ее запустить.
- Сочетанием клавиш «Windows+I» открываем системные «Параметры», во вкладке «Конфиденциальность и защита» кликаем плитку «Безопасность Windows»,
затем «Безопасность устройства»,
находим блок «Изоляция ядра», жмем на ссылку «Сведения»,
и включаем «Целостность памяти».
- Альтернативный путь начинается с системного трея. Нажимаем стрелочку вверх на панели задач, кликаем иконку в виде щита,
переходим к инструментам защиты оборудования, а далее таким же образом активируем функцию.

Если все так замечательно, как описывают Microsoft, то, конечно, лучше, чтобы технология работала, но бывают случаи, в которых отключение «Целостности памяти» может пригодиться. И на это есть сразу несколько способов, которые подробно описаны в отдельной статье на нашем сайте.
Подробнее: Отключение изоляции ядра в Windows 11
Возможные проблемы
Учитывая принцип работы «Изоляции ядра», компьютер должен обязательно поддерживать технологию виртуализации и важно, чтобы она была включена везде, где это возможно, начиная с BIOS/UEFI.
Подробнее: Как включить виртуализацию в Windows 11
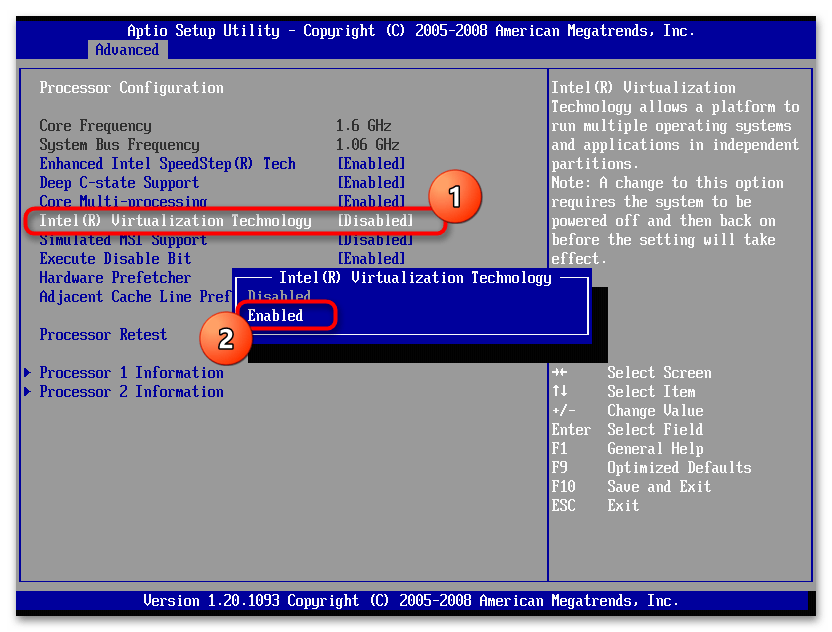
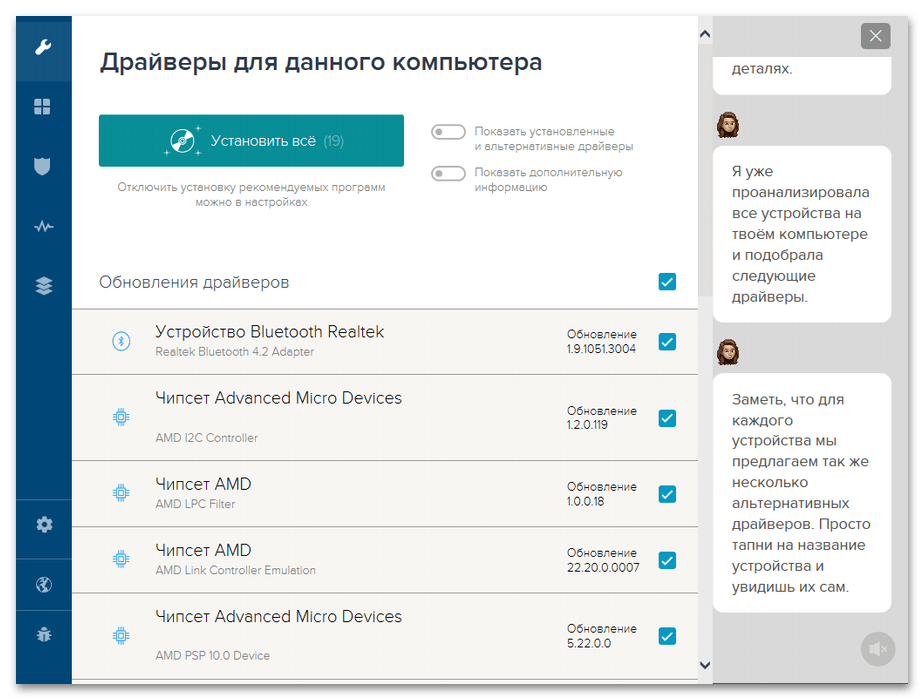
Кроме того, на компьютере могут быть установлены драйверы, которые несовместимы с этой технологией. И так как их запуск считается более приоритетным, блокируется защитная функция. Обычно это какие-нибудь устаревшие драйверы и тогда оптимальный вариант – обновить их.
Проблема в том, что определить, какие именно драйверы конфликтуют, иногда бывает сложно. Если у вас это получится, попробуйте получить обновления с помощью «Диспетчера устройств». Кроме того, наличие апдейтов можно посмотреть в «Центре обновления Виндовс» или воспользоваться специальными программами, которые подскажут, каких драйверов не хватает на компьютере.
Подробнее:
Как обновить драйвера на компьютере
Программы для установки драйверов
В нашем случае обновить драйверы не получилось, поэтому будем их удалять, но помним, что Microsoft такого делать не рекомендует, ведь есть вероятность, что какое-нибудь оборудование после этого перестанет отвечать. С другой стороны, может быть так, что раньше вы подключали какое-то устройство, а теперь перестали им пользоваться, а значит, и драйверы для него не нужны.
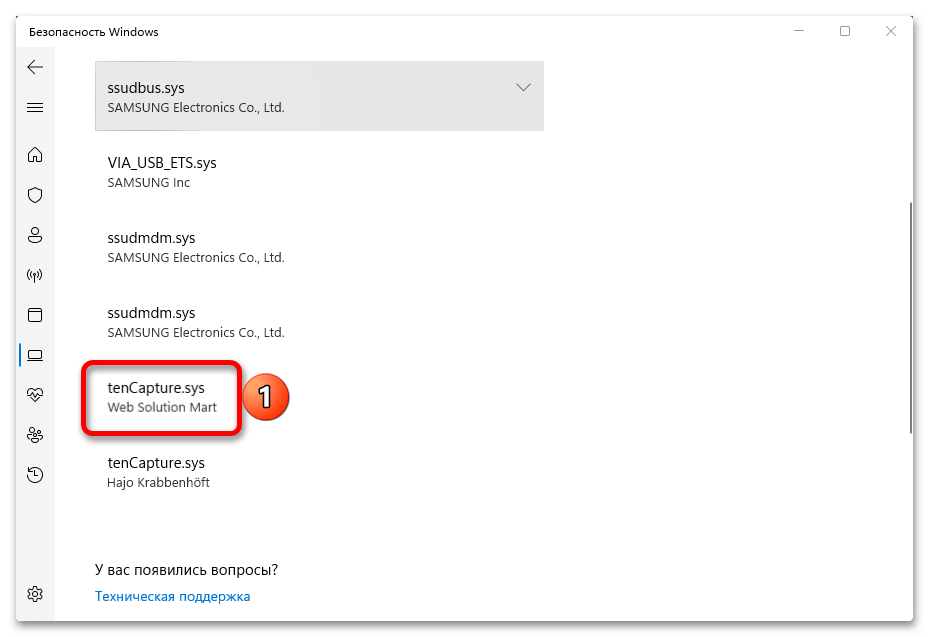
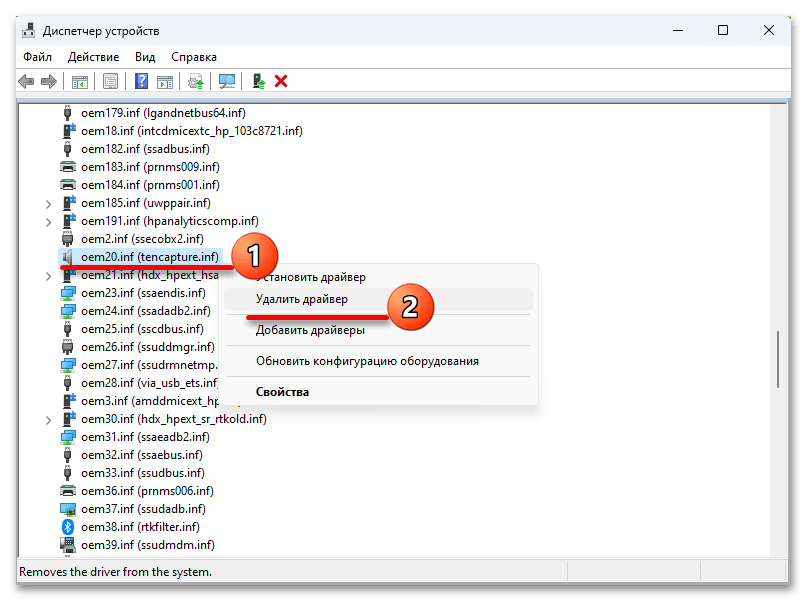
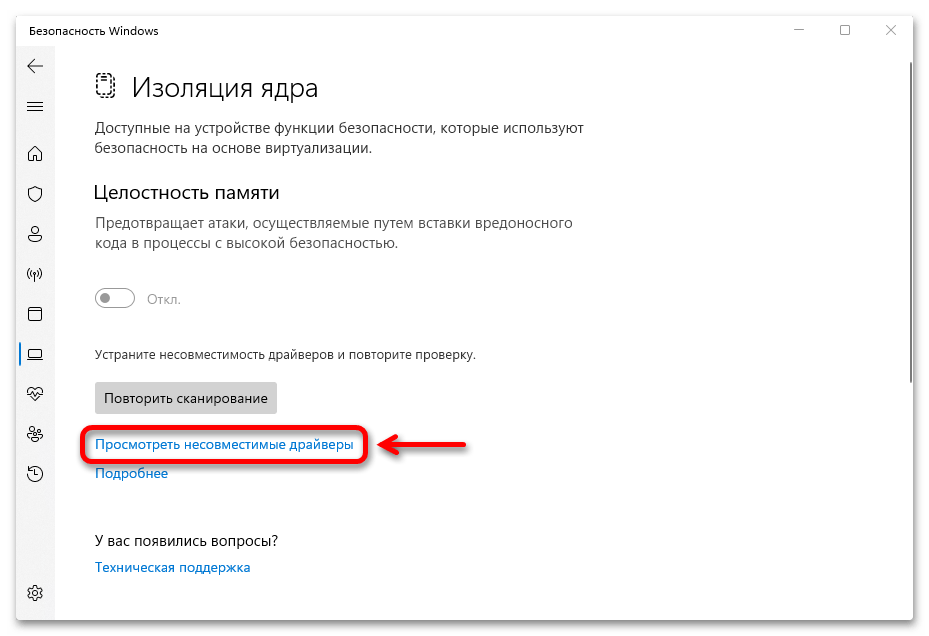
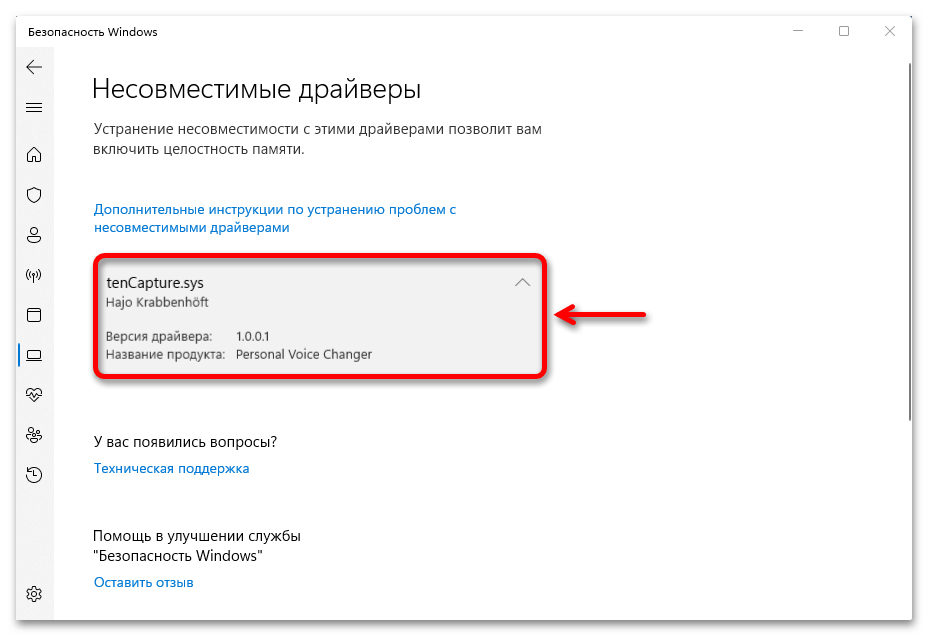
- Итак, если функция заблокирована из-за несовместимости драйверов, как это показано на скриншоте ниже, открываем их список.
- Теперь жмем на любой из них
и выясняем имя.
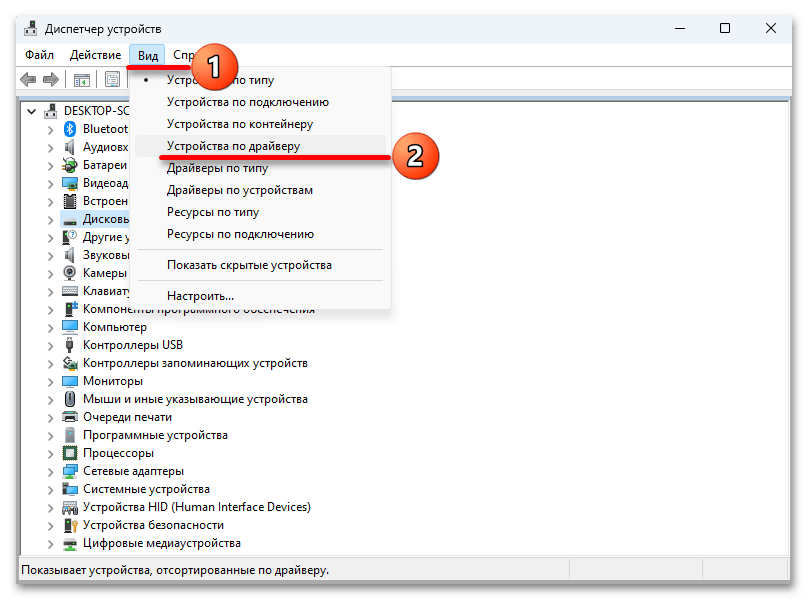
- Кликаем правой кнопкой мышки «Пуск» и вызываем «Диспетчер устройств».
- Открываем вкладку «Вид» и выбираем тип сортировки – «Устройства по драйверу».
- Находим нужную запись, правой кнопкой мышки открываем контекстное меню, жмем «Удалить»,
подключаем опцию принудительного удаления и подтверждаем операцию.
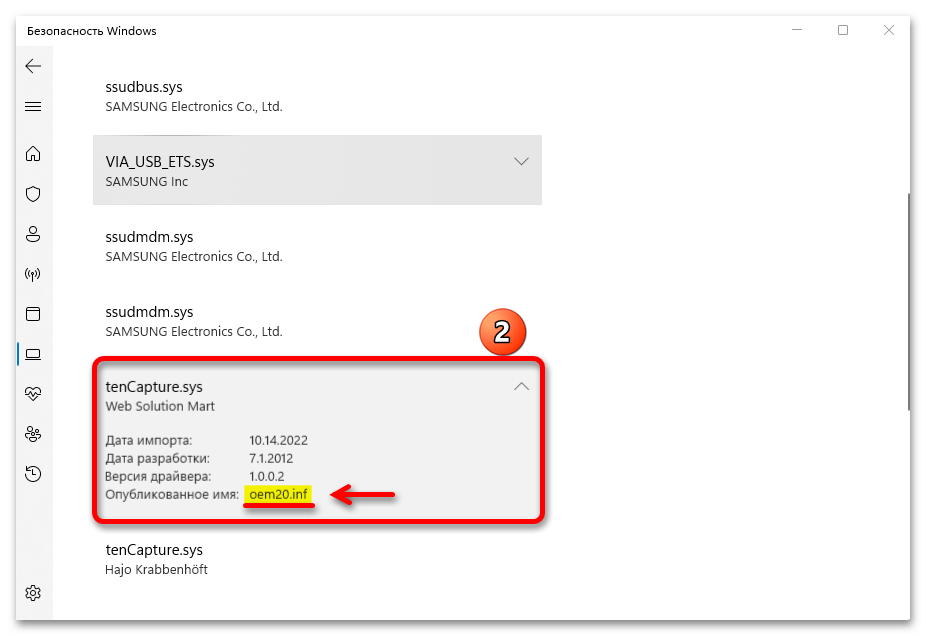
- Один из драйверов, как видно на скриншоте ниже, не имеет конкретного названия, поэтому мы не смогли его найти в «Диспетчере устройств».
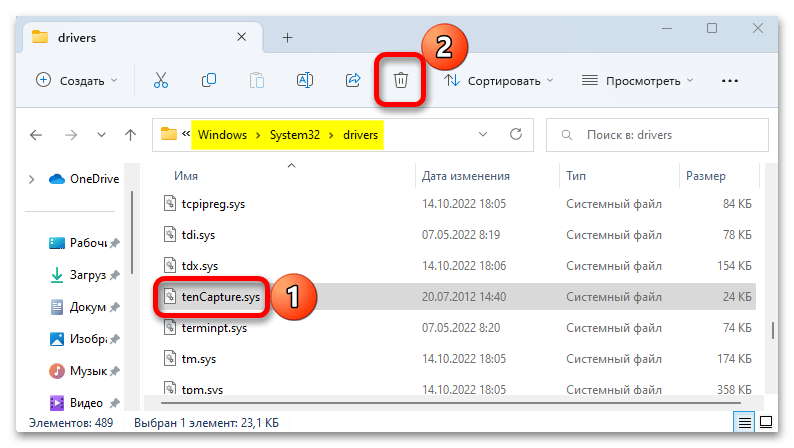
- В этом случае его можно поискать и удалить в системной папке. Переходим в директорию:
C:\Windows\System32\driversищем и удаляем запись.
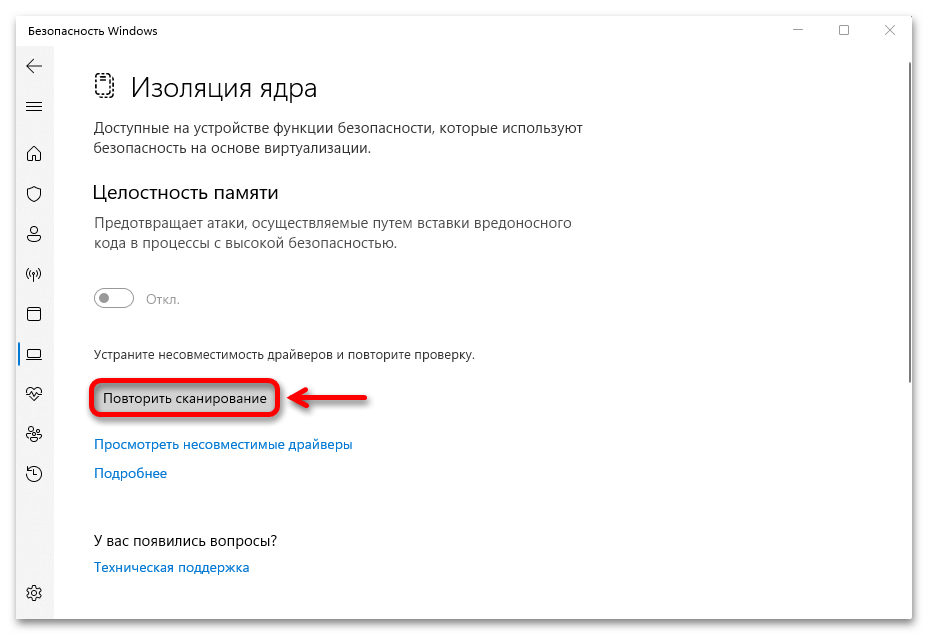
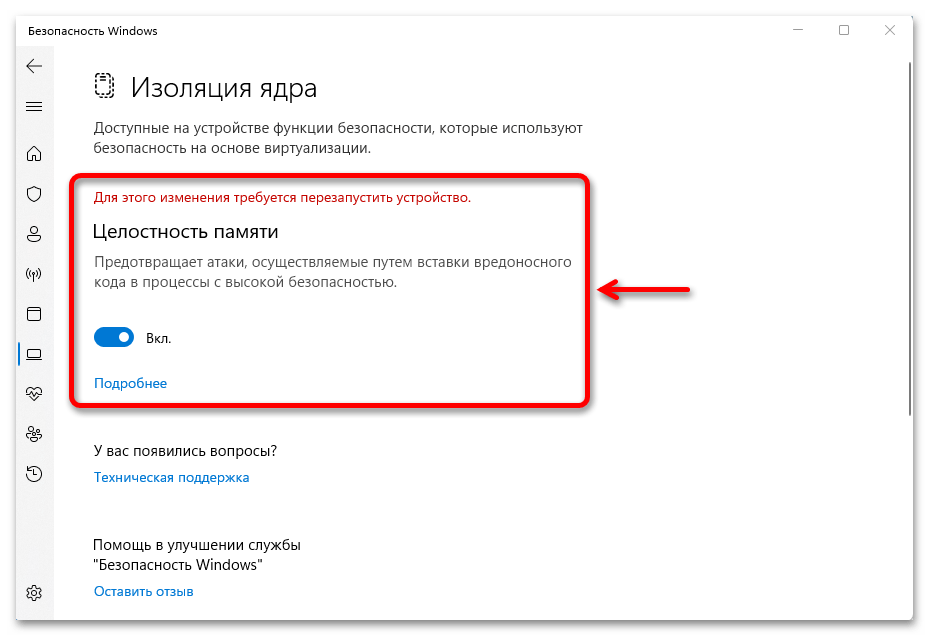
- После этого запускаем повторное сканирование
и, если все нормально, функция включится сразу после перезагрузки системы.
Процесс удаления драйверов не всегда завершается успешно, и если это ваш случай, ознакомьтесь с отдельной статьей на нашем сайте, где помимо системных инструментов, используется для этого стороннее программное обеспечение.
Подробнее: Полное удаление драйвера с компьютера
Наша группа в TelegramПолезные советы и помощь
As technology advances, the need for robust cybersecurity measures becomes ever more crucial. Enter Core Isolation, a groundbreaking feature in Windows 11 that aims to fortify your device against malicious attacks and protect your sensitive data. With Core Isolation, Microsoft takes a proactive approach to secure your system by isolating critical components from potential threats, creating a fortified barrier that enhances overall cybersecurity.
Core Isolation is a security feature in Windows 11 that helps protect your computer against advanced threats. It isolates critical processes in a secure system environment, safeguarding them from malicious attacks. By using hardware-based virtualization and memory protection technologies, Core Isolation adds an extra layer of security to your device. It prevents malware from accessing important system resources and protects sensitive data from unauthorized access. With Core Isolation enabled, you can enjoy a more secure computing experience on Windows 11.

Introduction to Core Isolation in Windows 11
Core isolation is a security feature in Windows 11 that provides additional protection against various types of attacks and vulnerabilities. It works by separating critical system components and processes from potentially malicious or untrusted applications. By isolating these critical components, Windows 11 enhances the overall security and stability of the operating system.
How Core Isolation Works
Core isolation in Windows 11 is based on a technology called Virtual Secure Mode (VSM) that utilizes hardware virtualization features of modern CPUs. It creates a separate, isolated environment within the operating system known as the Virtual Trust Level (VTL). This VTL is a small, secure operating system where critical system processes and components execute. It provides a barrier between the VTL and the rest of the operating system, preventing unauthorized access or tampering.
Under core isolation, sensitive processes like the Windows kernel, drivers, and other critical components run in the VTL, while user-mode applications and processes execute in the regular operating system. This separation ensures that even if an application or process is compromised, it cannot directly access or modify critical system resources. It adds an extra layer of protection against attacks like kernel-level exploits, privilege escalation, and unauthorized access to system memory.
In addition to the VTL, core isolation also includes Memory Integrity Protection. This feature uses virtualization-based security to protect system memory from unauthorized modifications. It prevents certain types of attacks, such as code injection and memory-based exploits, by ensuring the integrity of the system’s memory pages. It achieves this by using hardware memory virtualization features to isolate and protect critical memory regions.
Benefits of Core Isolation in Windows 11
Core isolation provides several key benefits in terms of security, stability, and performance:
- Enhanced Security: By isolating critical system components, core isolation prevents breaches and unauthorized access, protecting against a wide range of exploits and attacks.
- Protection against Kernel-Level Attacks: Core isolation safeguards the Windows kernel and prevents malicious applications from executing privileged operations.
- Memory Integrity Protection: The memory integrity feature ensures that system memory is protected from unauthorized modifications, reducing the risk of memory-based attacks.
- Improved Stability: By isolating critical processes, core isolation helps maintain system stability by preventing conflicts and crashes caused by malicious or poorly coded applications.
- Minimal Performance Impact: Core isolation leverages hardware virtualization capabilities, minimizing the impact on system performance while providing enhanced security.
Enabling Core Isolation in Windows 11
Enabling core isolation in Windows 11 is a straightforward process:
- Open the Windows Security app by searching for it in the Start menu.
- Click on «Device Security» in the left-hand navigation menu.
- Under the «Core isolation» section, click on «Core isolation details.»
- Toggle the switch to enable «Memory integrity» or «Core isolation.»
Note that enabling core isolation may require compatible hardware and virtualization features to be enabled in the system’s BIOS or UEFI settings.
Enhancing Security with Core Isolation in Windows 11
In addition to the Virtual Trust Level (VTL) and memory integrity features, core isolation in Windows 11 includes other security enhancements:
Secure Boot
Windows 11 with core isolation leverages Secure Boot, a feature that ensures the integrity of the system’s boot process. It verifies the digital signatures of bootloader components, preventing any unauthorized modifications at the boot level.
Secure Boot ensures that only trusted and signed code is loaded during system startup, protecting against rootkits and boot-level attacks. It is a crucial component in securing the overall system and is closely integrated with core isolation to provide a layered security approach.
Enabling Secure Boot is typically done through the system’s BIOS or UEFI firmware settings. It is recommended to keep Secure Boot enabled for optimal system security.
Windows Defender Antivirus
Core isolation complements Windows Defender Antivirus, the built-in security solution in Windows 11. Windows Defender Antivirus provides real-time protection against malware, viruses, and other threats.
When core isolation is enabled, Windows Defender Antivirus can further enhance its threat detection capabilities by leveraging the isolated Virtual Trust Level (VTL) environment. It can monitor critical processes and resources within the VTL for any signs of malicious activity.
Combining core isolation with Windows Defender Antivirus creates a robust defense against various types of threats, helping to keep the system secure.
Application Compatibility
While core isolation provides significant security benefits, it is essential to consider application compatibility. Some applications may not function correctly in an isolated environment, as they may require direct access to certain system resources or interact with critical components.
Before enabling core isolation, it is recommended to test critical applications and verify their compatibility. This can be done by enabling core isolation on a test system or using compatible virtualization solutions to ensure that all necessary functionalities work as expected.
Microsoft provides documentation and resources to help users assess application compatibility with core isolation.
Overall, core isolation in Windows 11 is a valuable security feature that enhances the protection and stability of the operating system. By isolating critical system components and employing memory integrity protection, it provides an additional layer of defense against various security threats. Combined with features like Secure Boot and Windows Defender Antivirus, core isolation helps maintain a secure computing environment.

Understanding Core Isolation in Windows 11
Core Isolation is a feature in Windows 11 that enhances the security of your system by isolating critical processes from potential threats. This feature provides a secure environment for running sensitive tasks and protects against attacks like malware and ransomware.
When Core Isolation is enabled, Windows 11 creates a separate and isolated environment, known as a «virtualization-based security container.» This container isolates critical processes, such as the Windows kernel, from the rest of the system. It ensures that these processes operate in a secure and protected space, separate from potentially malicious applications.
By isolating critical processes, Core Isolation helps prevent attacks that try to exploit vulnerabilities in the kernel or inject malicious code into the system. It also provides protection against memory attacks and unauthorized access to sensitive data.
To enable Core Isolation in Windows 11, you can go to the «Windows Security» settings, navigate to «Device Security,» and then choose «Core Isolation.» From there, you can toggle the feature on and configure its settings according to your requirements.
Key Takeaways
- Core Isolation is a security feature in Windows 11 that helps protect your system from malicious attacks.
- Core Isolation uses virtualization technology to create a secure environment for running sensitive processes.
- It isolates critical system components from regular user processes, preventing unauthorized access.
- This feature reduces the risk of malware and other exploits gaining control of your system.
- You can enable Core Isolation in the Windows Security settings on your Windows 11 device.
Frequently Asked Questions
Welcome to the frequently asked questions section about Core Isolation in Windows 11. Here, we will answer some common questions you may have about this feature and how it works.
1. What is Core Isolation in Windows 11?
Core Isolation in Windows 11 is a security feature that helps protect your system against various types of malware and attacks. It isolates the core components of your computer, such as processors and memory, from other processes and applications running on your system. This isolation helps prevent malicious software from accessing sensitive data and compromising the security and stability of your device.
Core Isolation uses technologies like Hypervisor-Protected Code Integrity (HVCI) and Windows Defender System Guard to create a secure environment for your system’s core components. By isolating these components, Core Isolation provides an additional layer of defense against advanced threats.
2. How does Core Isolation work in Windows 11?
Core Isolation uses hardware virtualization technology to create a virtualized container, known as a secure enclave, for your system’s core components. Inside this enclave, the core components run in a highly secure and isolated environment, separate from the rest of your system and other applications.
To achieve this isolation, Core Isolation utilizes the virtualization features of modern processors, such as Intel VT-x and AMD-V. These technologies enable the creation of virtual machines, allowing the core components to run in their own protected environment.
3. What are the benefits of using Core Isolation in Windows 11?
Using Core Isolation in Windows 11 offers several benefits:
Enhanced Security: Core Isolation helps protect your system from various types of malware and attacks by isolating the core components from other processes and applications.
Better Performance: By running the core components in a separate, optimized environment, Core Isolation can potentially improve the performance of your system.
Compatibility: Core Isolation is designed to be compatible with most modern hardware and software. It works seamlessly with Windows Defender System Guard and other security features in Windows 11.
4. How can I enable Core Isolation in Windows 11?
To enable Core Isolation in Windows 11, follow these steps:
1. Open the «Settings» app on your Windows 11 device.
2. Go to the «System» section.
3. Click on «Security & Privacy».
4. Under «Core Isolation», click on the toggle switch to enable it.
Once enabled, Core Isolation will provide an additional layer of security to your Windows 11 device.
5. Can I disable Core Isolation in Windows 11?
Yes, you can disable Core Isolation in Windows 11 if needed. To disable it, follow these steps:
1. Open the «Settings» app on your Windows 11 device.
2. Go to the «System» section.
3. Click on «Security & Privacy».
4. Under «Core Isolation», click on the toggle switch to disable it.
Disabling Core Isolation will remove the additional layer of security it provides, but it may be necessary for troubleshooting or compatibility purposes.
In summary, Core Isolation is a security feature in Windows 11 that helps protect your computer from malicious attacks. It isolates critical parts of the operating system, such as the kernel, from potential threats. By creating a virtualized environment, Core Isolation prevents unauthorized access and reduces the risk of malware compromising your system.
With Core Isolation enabled, you can enjoy a safer computing experience. It provides an additional layer of security by separating critical system components and guarding against advanced threats. By leveraging virtualization technology, Windows 11 ensures that your sensitive data and system processes remain protected, giving you peace of mind while using your computer.
The device security page of the Windows Security app is designed to manage the security features built into your Windows device. The page is divided into the following sections:
-
Secured-core PC: If your device is a Secured-core PC, it shows information about the Secured-core PC features
-
Core isolation: Here you can configure security features that protect the Windows kernel
-
Security processor: Provides information about the security processor, which is call the trusted platform module (TPM)
-
Secure boot: If secure boot is enabled, you can find more information about it
-
Data encryption: Here you can find a link to Windows Settings, where you can configure device encryption and other BitLocker settings
-
Hardware security capability: Assesses your device’s hardware security features
In the Windows Security app on your PC, select Device security, or use the following shortcut:
Device security

Secured-core PC
A Secured-core PC is designed to provide advanced security features right out of the box. These PCs integrate hardware, firmware, and software to offer robust protection against sophisticated threats.
In the Windows Security app on your PC, select Device security > Security details.
For more information, see Windows 11 Secured-core PCs.
Core isolation
Core isolation provides security features designed to protect core processes of Windows from malicious software by isolating them in memory. It does this by running those core processes in a virtualized environment.
In the Windows Security app on your PC, select Device security > Core isolation details or use the following shortcut:
Core isolation
Note: the features exposed on the core isolation page vary depending on what version of Windows you’re running, and the hardware components installed.
Memory integrity, also known as Hypervisor-protected Code Integrity (HVCI) is a Windows security feature that makes it difficult for malicious programs to use low-level drivers to hijack your PC.
A driver is a piece of software that lets the operating system (Windows in this case) and a device (like a keyboard or a webcam) talk to each other. When the device wants Windows to do something, it uses the driver to send that request.
Memory integrity works by creating an isolated environment using hardware virtualization.
Think of it like a security guard inside a locked booth. This isolated environment (the locked booth in our analogy) prevents the memory integrity feature from being tampered with by an attacker. A program that wants to run a piece of code which may be dangerous has to pass the code to memory integrity inside that virtual booth so that it can be verified. When memory integrity is comfortable that the code is safe it hands the code back to Windows to run. Typically, this happens very quickly.
Without memory integrity running, the security guard stands right out in the open where it’s much easier for an attacker to interfere with or sabotage the guard, making it easier for malicious code to sneak past and cause problems.
You can turn memory integrity On or Off using the toggle button.
Note: To use memory integrity, you must have hardware virtualization enabled in your system’s UEFI or BIOS.
What if it says I have an incompatible driver?
If memory integrity fails to turn on, it may tell you that you have an incompatible device driver already installed. Check with the manufacturer of the device to see if they have an updated driver available. If they don’t have compatible driver available, you might be able to remove the device or app that uses that incompatible driver.
Note: If you try to install a device with an incompatible driver after turning on memory integrity, you might receive the same message. If so, the same advice applies — check with the device manufacturer to see if they have an updated driver you can download, or don’t install that particular device until a compatible driver is available.
Hardware enforced stack protection is a hardware-based security feature that makes it difficult for malicious programs to use low-level drivers to hijack your PC.
A driver is a piece of software that lets the operating system (Windows in this case) and a device (like a keyboard or a webcam) talk to each other. When the device wants Windows to do something, it uses the driver to send that request.
Hardware enforced stack protection works by preventing attacks that modify return addresses in kernel-mode memory to launch malicious code. This security feature requires a CPU that contains the ability to verify the return addresses of running code.
When executing code in kernel-mode, return addresses on the kernel-mode stack can be corrupted by malicious programs or drivers in order to redirect normal code execution to malicious code. On supported CPUs, the CPU maintains a second copy of valid return addresses on a read-only shadow stack that drivers cannot modify. If a return address on the regular stack has been modified, the CPU can detect this discrepancy by checking the copy of the return address on the shadow stack. When this discrepancy occurs, the computer prompts a stop error, sometimes known as a blue screen, to prevent the malicious code from executing.
Not all drivers are compatible with this security feature, as a small number of legitimate drivers engage in return address modification for non-malicious purposes. Microsoft has been engaging with numerous driver publishers to ensure that their latest drivers are compatible with hardware enforced stack protection.
You can turn hardware enforced stack protection On or Off using the toggle button.
To use hardware enforced stack protection, you must have memory integrity enabled, and you must be running a CPU that supports Intel Control-Flow Enforcement Technology or AMD Shadow Stack.
What if it says I have an incompatible driver or service?
If hardware enforced stack protection fails to turn on, it might tell you that you have an incompatible device driver or service already installed. Check with the manufacturer of the device or the application publisher to see if they have an updated driver available. If they don’t have a compatible driver available, you might be able to remove the device or app that uses that incompatible driver.
Some applications might install a service instead of a driver during the application’s installation and install the driver only when the application is launched. For more accurate detection of incompatible drivers, services that are known to be associated with incompatible drivers are also enumerated.
Note: If you try to install a device or app with an incompatible driver after turning on hardware enforced stack protection, you may see the same message. If so, the same advice applies — check with the device manufacturer or app publisher to see if they have an updated driver you can download, or don’t install that particular device or app until a compatible driver is available.
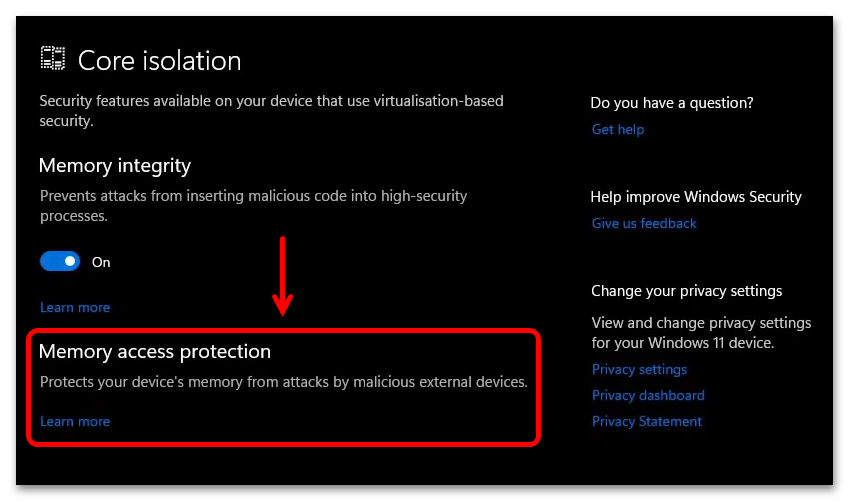
Also known as Kernel DMA protection this security feature protects your device against attacks that can occur when a malicious device is plugged into a Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) port like a Thunderbolt port.
A simple example of one of these attacks would be if someone leaves their PC for a quick coffee break, and while they were away, an attacker steps in, plugs in a USB-like device and walks away with sensitive data from the machine, or injects malware that allows them to control the PC remotely.
Memory access protection prevents these kinds of attacks by denying direct access to the memory to those devices except under special circumstances, particularly when the PC is locked, or the user is signed out.
Every device has some software that’s been written to the read-only memory of the device — basically written to a chip on the system board — that is used for the basic functions of the device, such as loading the operating system that runs all the apps we’re used to using. Since that software is difficult (but not impossible) to modify we refer to it as firmware.
Because the firmware loads first and runs under the operating system, security tools and features that run in the operating system have a difficult time detecting it or defending against it. Like a house that depends on a good foundation to be secure, a computer needs its firmware to be secure in order to ensure that the operating system, applications, and data on that computer are safe.
System Guard is a set of features that helps to ensure that attackers can’t get your device to start with untrusted or malicious firmware.
Platforms that offer firmware protection typically also protect the System Management Mode (SMM), a highly privileged operating mode, to varying degrees. You can expect one of the three values, with a higher number indicating a greater degree of SMM protection:
-
Your device meets firmware protection version one: this offers the foundational security mitigations to help SMM resist exploitation by malware, and prevents exfiltration of secrets from the OS (including VBS)
-
Your device meets firmware protection version two: in addition to firmware protection version one, version two ensures that SMM can’t disable Virtualization-based Security (VBS) and kernel DMA protections
-
Your device meets firmware protection version three: in addition to firmware protection version two, it further hardens the SMM by preventing access to certain registers that have the ability to compromise the OS (including VBS)
Local Security Authority (LSA) protection is a Windows security feature to help prevent the theft of credentials used for signing into Windows.
The Local Security Authority (LSA) is a crucial process in Windows involved in user authentication. It’s responsible for verifying credentials during the login process and managing authentication tokens and tickets used to enable single sign-on for services. LSA protection helps prevent untrusted software from running inside LSA or from accessing LSA memory.
How do I manage Local Security Authority protection?
You can turn LSA protection On or Off using the toggle button.
After you have changed the setting, you must reboot for it to take effect.
Note: To help keep credentials safe, LSA protection is enabled by default on all devices. For new installs, it is enabled immediately. For upgrades, it is enabled after rebooting after an evaluation period of five days.
What if I have incompatible software?
If LSA protection is enabled and it blocks the loading of software into the LSA service, a notification indicates the blocked file. You might be able to remove the software loading the file, or you can disable future warnings for that file when it’s blocked from loading into LSA.
Note: Credential Guard is available on devices running Enterprise or Education versions of Windows.
While you’re using your work or school device it will be quietly signing into and gaining access to a variety of things such as files, printers, apps, and other resources in your organization. Making that process secure, yet easy for the user, means that your PC has a number of authentication tokens on it at any given time.
If an attacker can gain access to one, or more, of those tokens, they might be able to use them to gain access to the organizational resource (sensitive files, etc) that the token is for. Credential Guard helps to protect those tokens by putting them in a protected, virtualized, environment where only certain services can access them when necessary.
A driver is a piece of software that lets the operating system (Windows in this case) and a device (like a keyboard or a webcam) talk to each other. When the device wants Windows to do something, it uses the driver to send that request. Because of this, drivers have a lot of sensitive access in your system.
Windows 11 includes a blocklist of drivers that have known security vulnerabilities, have been signed with certificates used to sign malware, or that circumvent the Windows Security Model.
If you have memory integrity, Smart App Control, or Windows S mode on, the vulnerable driver blocklist will be on too.
Note: If you encounter a banner titled Program Compatibility Assistant with a message indicating that a driver cannot load, or that a security setting is preventing a driver from loading, check for updated drivers via Windows Update or through Device Manager. If no updates are available, contact your hardware manufacturer for an updated driver.
Security processor
The Security processor settings under the Device Security page in the Windows Security app provide details about the Trusted Platform Module (TPM) on your device. The TPM is a hardware component designed to enhance security by performing cryptographic operations.
Note: If you don’t see a Security processor entry on this screen then it’s likely that your device doesn’t have the TPM (Trusted Platform Module) hardware necessary for this feature or that it’s not enabled in UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface). Check with your device manufacturer to see if your device supports TPM and, if so, steps to enable it.
This is where you’ll find info about the security processor manufacturer and version numbers, as well as about the security processor’s status.
In the Windows Security app on your PC, select Device security > Security processor details or use the following shortcut:
Security processor details
If your security processor isn’t working properly, you can select the Security processor troubleshooting link to see any error messages and advanced options, or use the following shortcut:
Security processor troubleshooting
The security processor troubleshooting page provides any relevant error messages about the TPM. Here’s a list of the error messages and details:
|
Message |
Details |
|---|---|
|
A firmware update is needed for your security processor (TPM). |
Your device’s motherboard doesn’t appear to support TPM currently, but a firmware update might resolve this. Check with your device’s manufacturer to see if a firmware update is available and how to install it. Firmware updates are usually free. |
|
TPM is disabled and requires attention. |
The trusted platform module is probably turned off in the system BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) or UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface). Refer to your device manufacturer’s support documentation, or contact their technical support, for instructions on how to turn it on. |
|
TPM storage is not available. Please clear your TPM. |
The clear TPM button is on this page. You’ll want to make sure you have a good backup of your data before proceeding. |
|
Device health attestation isn’t available. Please clear your TPM. |
The clear TPM button is on this page. You’ll want to make sure you have a good backup of your data before proceeding. |
|
Device health attestation isn’t supported on this device. |
This means the device doesn’t give us enough information to determine why TPM may not be working properly on your device. |
|
Your TPM isn’t compatible with your firmware and may not be working properly. |
Check with your device’s manufacturer to see if a firmware update is available and how to get and install it. Firmware updates are usually free. |
|
TPM measured boot log is missing. Try restarting your device. |
|
|
There is a problem with your TPM. Try restarting your device. |
If you still encounter problems after addressing an error message, contact your device manufacturer for assistance.
Select Clear TPM to reset your security processor to its default settings.
Caution: Make sure to back up your data before you clear the TPM.
Secure boot
Secure boot prevents a sophisticated and dangerous type of malware — a rootkit — from loading when your device starts. Rootkits use the same permissions as the operating system and start before it, which means they can completely hide themselves. Rootkits are often part of an entire suite of malware that can bypass local logins, record passwords and keystrokes, transfer private files, and capture cryptographic data.
You might have to disable secure boot to run some graphics cards, hardware, or operating systems such as Linux or earlier versions of Windows.
To learn more, see Secure boot.
Hardware security capability
The last section of the device security page displays information indicating the security capability of your device. Here’s a list of messages and details:
|
Message |
Details |
|---|---|
|
Your device meets the requirements for standard hardware security. |
This means your device supports memory integrity and core isolation and also has:
|
|
Your device meets the requirements for enhanced hardware security. |
This means that in addition to meeting all the requirements of standard hardware security, your device also has memory integrity turned on. |
|
Your device has all Secured-core PC features enabled. |
This means that in addition to meeting all the requirements of enhanced hardware security, your device also has System Management Mode (SMM) protection turned on. |
|
Standard hardware security not supported. |
This means that your device does not meet at least one of the requirements of standard hardware security. |
Improving hardware security
If the security capability of your device isn’t what you’d like it to be, you might need to turn on certain hardware features (such as secure boot, if supported) or change the settings in your system’s BIOS. Contact your hardware manufacturer to see what features are supported by your hardware and how to activate them.
PC Manager
|
The PC Manager app may also be useful in this scenario. For more information, see Microsoft PC Manager. Note: Microsoft PC Manager isn’t available in all locales. |
Table of contents
- What Is Core Isolation?
- What Is Memory Integrity?
- Core Isolation and Memory Integrity: How They Work Together?
- Should You Enable or Disable Memory Integrity?
- How to Turn On/Off Core Isolation Memory Integrity
- Method 1: Use Windows Security
- Method 2: Use the Registry Editor to enable core isolation
- What to Do if Memory Integrity Is Off?
- 1. Check for incompatible drivers
- 2. Remove incompatible drivers
- 3. Check for Windows updates
- 4. Repair system files
- 5. Perform a clean boot
- Core Isolation Memory Integrity: Explained
- FAQ
Is it necessary to enable the memory integrity feature? What happens if memory integrity is off ? Am I vulnerable to attacks? These are valid questions that many users ask. Depending on your situation, you may need to enable or disable memory integrity. In this guide, I’ll explain how core isolation and memory integrity work together and provide other helpful tips. Let’s begin.
What Is Core Isolation?
Windows has a security feature called core isolation, which isolates essential core processes in memory to protect them from malicious programs . Core isolation can protect your PC because it runs the core process in a virtualized environment. Examples of features that fall within core isolation are memory integrity and Kernel-mode Hardware-enforced Stack Protection .
What Is Memory Integrity?
So, what does memory integrity do?
Core isolation memory integrity, or Hypervisor-Protected Code Integrity (HVCI), is a Windows security feature that prevents malicious software from using low-level drivers to take over your computer.
You can access this feature via Windows Defender Security under the Device security section.
Windows memory integrity lets you activate features to improve protection by providing status reporting and managing security integrated into your devices.
However, device security depends on hardware support.
So, your firmware must support virtualization to run programs on your Windows 11 or 10 PC inside a container and restrict their access to other areas of the system.
Hardware and software requirements
Before you can enable core isolation, your device must support second-level address translation (SLAT) and virtualization-based security (VBS).
Keep in mind that some operating systems don’t support memory integrity. But if you’re using Windows 10/11 Enterprise or Pro, you should have this feature.
You should have the core isolation feature if you have a Windows 11 PC. If you can’t find it, it’s possible that it’s not enabled. Skip to the next section to learn how to enable the feature.
PRO TIP
When you turn on memory integrity, it checks for incompatible drivers on your system. If it finds incompatible drivers, it won’t turn on.
If core isolation doesn’t turn on, I recommend using Auslogics Driver Updater to update your drivers automatically.
This software checks for outdated and missing drivers and updates them according to the manufacturer’s version.
Learn more: Auslogics Driver Updater: New Drivers in One Click!
Core Isolation and Memory Integrity: How They Work Together?
Windows 10 or Windows 11 core isolation and memory integrity work together to offer complete security against different types of cyber threats when they are both enabled. Memory integrity ensures the safety of system memory, whereas core isolation establishes a secure environment for system processes. This collaboration reduces the chances of malware attacks and protects important system components, improving your device’s overall security.
Should You Enable or Disable Memory Integrity?
Based on what I’ve outlined so far, if you disable core isolation, the system processes will function with less isolation, which could make your system more susceptible to malware attacks.
In other words, you make it easier for cybercriminals to access sensitive data on your computer and compromise system processes.
However, if you’re a gamer like me, you can optimize Windows 11 for gaming by turning off memory integrity.
That’s because Windows 11 or Windows 10 core isolation uses a lot of CPU resources. If core isolation memory integrity is off , you can use the free resources to run your games.
So, whether you disable or enable Windows memory integrity depends on your preference.
Regardless, we’ll show you how to enable or disable memory integrity on your PC.
How to Turn On/Off Core Isolation Memory Integrity
In this section, we’ll show you how to turn core isolation on or off. Go through the various steps below to enable the feature:
Method 1: Use Windows Security
Here’s how to enable or disable core isolation:
- Type
Windows Securityin the search bar and click to open it. - Click the three horizontal lines in the upper left corner.
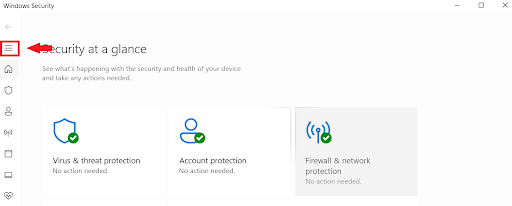
- Go to Device security.
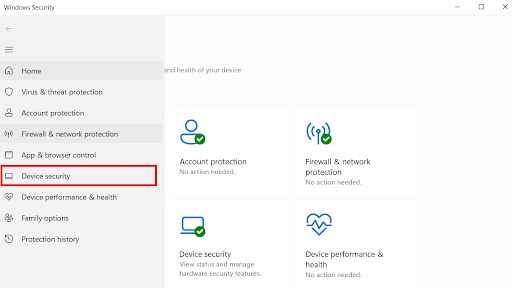
- Select the Core isolation details under Core isolation .
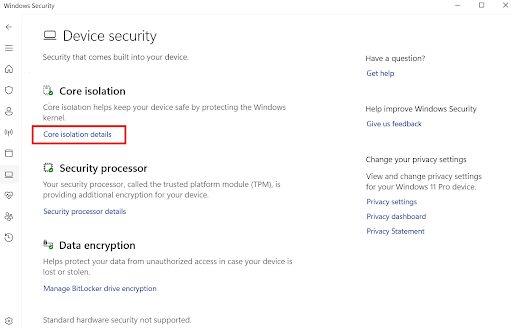
- Toggle the switch to turn it on and off.
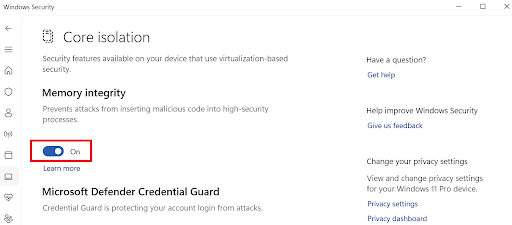
Restart your computer to apply the changes.
Related:Fix Windows Defender Service That Won’t Start
Method 2: Use the Registry Editor to enable core isolation
Follow the steps below to allow core isolation memory integrity:
Warning
I highly recommend backing up your data before making any changes to the Windows Registry, especially if you are not completely knowledgeable about what you’re doing.
Please read our guide on Windows 10 backup and restore to learn how to back up your data.
- Type
regeditin the search bar and pressEnterto open the Registry Editor. - Enter the following in the search field:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\DeviceGuard\Scenarios\HypervisorEnforcedCodeIntegrity
- Double-click on Enabled.
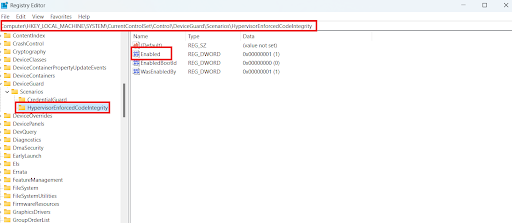
- Set Value date to 1 and click on OK to save the settings.
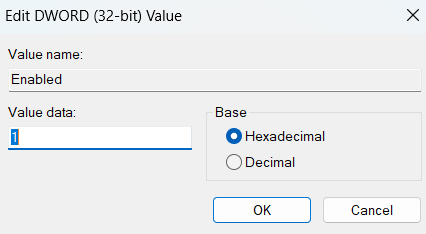
Restart your computer to implement the changes.
Also read:How to Back Up and Restore the Windows 10 Registry
What to Do if Memory Integrity Is Off?
If you can’t turn on your Windows memory integrity, follow the steps to correct the problem:
1. Check for incompatible drivers
If you can’t enable Windows 11 core isolation, it could be because of incompatible or outdated drivers. Follow the steps below to fix the problem:
If you recently installed any third-party drivers and noticed that you can’t enable memory integrity, roll back your drivers . This may solve the problem.
- Type
Windows securityin the search box and click on it to open. - Select Device security from the left-hand side.
- Click on Core isolation details and enable Memory integrity .
- Click Review incompatible drivers if you get this error message: Resolve any driver incompatibilities and scan again.

- Jot down every driver that you suspect may be the reason why your core isolation memory integrity is off .
- Open Device Manager by typing
Device Managerin the search box and hittingEnter. - Then, click View and select Show hidden devices .
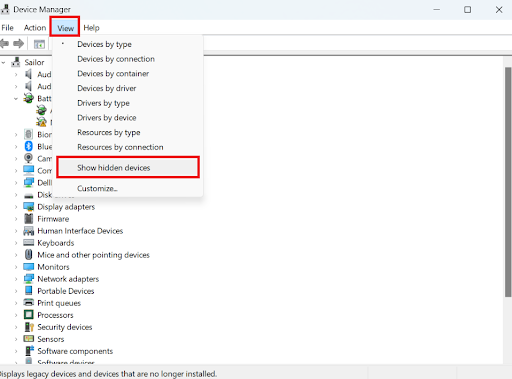
- Right-click the faulty driver, choose Uninstall device , and then follow the on-screen instructions to complete the process.
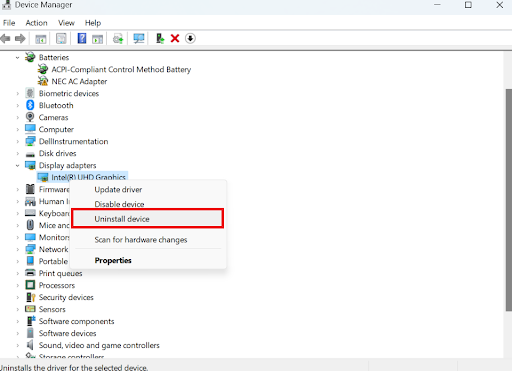
- If it still doesn’t work, you can choose Update driver to update the driver.
Download Auslogics Driver Updater
Prevent hardware errors and ensure problem-free device operation with this advanced tool that detects outdated drivers and safely gets them updated.
2. Remove incompatible drivers
Another way to resolve the problem if your core isolation memory integrity is off is to delete all the incompatible drivers.
Here’s how to do it using the Command Prompt :
- Type
command promptin the search bar, right-click the first option, and select Run as administrator . - Type the following command and press
Enter. Remember to jot down the faulty drivers:
dism /online /get-drivers /format:table
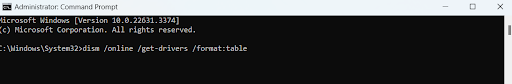
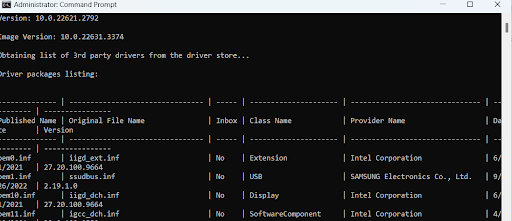
- Next, type the following command to delete the problematic drivers:
pnputil /delete-driver (driver’s published name) /uninstall /force
Enter the faulty driver’s name instead of ( driver’s published name) in the Command Prompt. For example, you can see the driver oem0.inf in the screenshot above.
So, if I want to delete that driver, the command will be:
pnputil /delete-driver oem0.inf /uninstall /force.
Make sure to enter the correct driver’s published name, or you may delete other drivers that are not causing the problem. So, it’s better to copy and paste.
3. Check for Windows updates
Sometimes, you can update your Windows system to get rid of the problem. That’s how I fixed the problem when I couldn’t enable Windows core isolation . All you have to do is press the Windows + I keys, select Windows Update, and click on Check for updates.
Related: How to Fix Windows Update Error 0x80070057
4. Repair system files
Another way to fix the problem if your core isolation memory integrity is off is to use an SFC scan to repair system files. Here’s how to do it:
- Open the Command Prompt with administrative privileges.
- Type
sfc /scannowand pressEnter.
Wait for the process to complete and check if the problem is resolved.
Related:How to Find and Fix Corrupted Files in Windows 10?
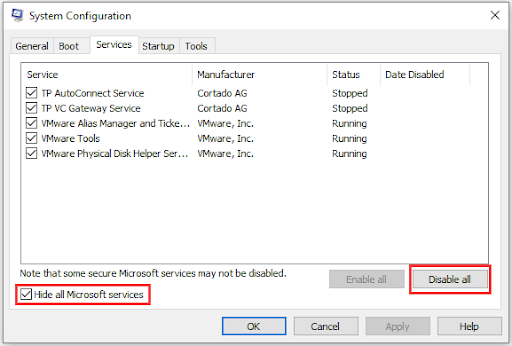
5. Perform a clean boot
Sometimes, performing a clean boot can fix the problem. When you perform a clean boot, your computer will only boot with the essentials, allowing you to troubleshoot the problem. If you find conflicting software, you can uninstall it. Here’s how to do it:
- Type
msconfigin the search box and pressEnter. - Click on the Services tab.
- Check the Hide all Microsoft services option.
- Click Disable all .
- Restart your computer.
Core Isolation Memory Integrity: Explained
Whether you enable or disable Windows core isolation, it is a crucial decision only you can make, since it affects security and performance.
Throughout this tutorial, I’ve examined how these features work together to protect system memory and isolate essential processes to improve system security.
While core isolation and memory integrity offer crucial security advantages, speed optimization is also worth considering, especially if you’re a gamer.
So, your priorities and risk tolerance will ultimately determine whether you activate or disable these features.
Was this article helpful? Share it with your friends who might need it, and let us know your thoughts or additions in the comments below!
FAQ
Why is memory integrity important?
Memory integrity is important because it shields your computer from several types of attacks, including those that use memory vulnerabilities in the operating system. Memory integrity protects against viruses and other harmful applications that could try to change or corrupt your computer’s memory. This feature improves the general security of your device and helps protect sensitive information.
Are there any system requirements for enabling memory integrity?
Yes. There are system requirements to enable memory integrity in Windows 10/11. Your device must fulfill specific hardware and software requirements to use this feature. Your computer’s CPU must support second-level address translation and virtualization-based security. Furthermore, not every operating system version supports memory integrity. Therefore, you must have Windows 10/11 Enterprise or Pro.
How does memory core isolation affect system performance?
The degree to which memory core isolation affects system performance depends on several factors, like your PC’s hardware configuration and the amount of work it processes. Because memory integrity imposes additional security measures, such as runtime integrity checks and memory encryption, it may cause a slight drop in overall system performance. However, for most users, the performance hit is small and is usually offset by the increased security that comes with memory integrity enabled.