Просматривая диспетчере задач на наличие подозрительных процессов, пользователи могут обратить внимание на один или множество процессов conhost.exe «Хост окна консоли», некоторые из них могут заметно нагружать процессор или памяти.
В этой статье подробно о том, что такое conhost.exe в Windows 11 и Windows 10, почему таких процессов может быть более одного, как проверить, не вирус ли это и определить, к какой программе относится указанный процесс.
Назначение conhost.exe
Процесс conhost.exe или Хост окна консоли — специальный процесс, который может создаваться программами или операционной системой и представляет собой консоль или окно командной строки как с отображением соответствующего окна, так и без него, в случае, когда программа использует Windows Console API в работе.

В большинстве случаев какой-либо угрозы процесс не представляет, а высокая нагрузка может быть объяснена тем, что в настоящий момент программа, создавшая экземпляр conhost.exe выполняет задачи с использованием этого процесса.
Однако, в некоторых случаях запуск хоста окна консоли возможен и со стороны вирусов на компьютере. Если у вас есть основания полагать, что какие-то из экземпляров conhost.exe относятся к вредоносным процессам, это можно проверить.
Как определить, к какой программе относится процесс
Для определения программы, которая запустила и использует хост окна консоли можно использовать бесплатную утилиту Process Explorer, скачать которую можно с сайта Майкрософт.
Для того, чтобы проанализировать, что вызывает запуск conhost.exe используйте следующие шаги:
- Запустите Process Explorer от имени администратора (правый клик по исполняемому файлу — «Запустить от имени администратора»).
- Включите отображение дерева процессов, нажав по соответствующей кнопке в панели инструментов (если кнопка не активна, соответствующий вид уже включен). Переключение режима отображения также возможно путем нажатия по заголовку столбца «Process».
- Проверьте, «внутри» каких из запущенных процессов был выполнен запуск conhost.exe. Например, на следующем скриншоте можно увидеть, что он относится к Photoshop.
- А процесс со следующего изображения — к svchost.exe (процесс для работы служб) и wlanext.exe (один из системных процессов, используемый службой автонастройки WLAN).
- Если родительский процесс вам неизвестен и есть подозрение, что он не является безопасным, можно нажать по нему правой кнопкой мыши и выбрать пункт контекстного меню «Check VirusTotal.com» для проверки соответствующего файла на наличие вирусов.
- В случае, если conhost.exe не имеет родительского процесса, а в свойствах процесса (можно открыть, дважды нажав по имени процесса) параметры командной строки отличаются от
\??\C:\WINDOWS\system32\conhost.exe 0x4
это может говорить, о том, что его запуск был инициирован вредоносным процессом и стоит проверить компьютер на вирусы и другие угрозы.
Учитывайте, что оригинальный файл процесса conhost.exe находится в папке C:\Windows\System32 и при отличающихся расположениях имеет смысл проверить файл на вирусы. Посмотреть расположение файла можно в Process Explorer, дважды нажав по соответствующему процессу или в диспетчере задач: правый клик мышью — открыть расположение файла.
Хост окна консоли грузит процессор или память
Если вы столкнулись с тем, что процесс conhost.exe значительно нагружает процессор, возможные следующие варианты решения и способы разобраться с проблемой:
- В некоторых случаях высокая нагрузка со стороны процесса может быть результатом штатной работы программы: например, некоторые редакторы видео могут использовать conhost.exe при рендеринге, а Windows может запускать и активно использовать соответствующий процесс при обновлениях и в задачах обслуживания системы. Нагрузка в данном случае должна исчезнуть после завершения выполнения соответствующих задач.
- Определите, какой программой был вызван нагружающий систему conhost.exe и закройте соответствующую программу, при условии, что она не является обязательной. Также может иметь смысл убрать её из автозагрузки, если она запускается автоматически.
- В случае, если родительский процесс обязателен для работы системы, попробуйте разобраться, в каких случаях и по каким причинам он может сильно нагружать систему и предпринять соответствующие действия для решения проблемы.
- Если у вас есть подозрения на то, что процесс conhost.exe вызван вредоносным ПО, проверьте компьютер на вирусы, майнеры и другие угрозы, например, с помощью Kaspersky Virus Removal Tool, AdwCleaner и аналогичных инструментов.
Надеюсь, материал пригодился. Если же остаются вопросы, касающиеся рассмотренного процесса, вы можете задать их в комментариях ниже, подробно описав ситуацию.
conhost.exe: The Console Window Host
conhost.exe, also known as the Console Window Host, is a critical system process in Windows. It plays a vital role in managing and displaying console windows (also referred to as command-line windows or terminal windows). Understanding conhost.exe is essential for system administrators, developers, and anyone who interacts with the command-line interface.
Origin and Purpose
Prior to Windows Vista, the csrss.exe (Client Server Runtime Subsystem) process handled console windows directly. This presented security vulnerabilities because csrss.exe runs with high privileges. If a malicious program exploited a vulnerability in a console application, it could potentially gain system-level access through csrss.exe.
To mitigate this risk, Microsoft introduced conhost.exe in Windows Vista. Its primary purpose is to act as an intermediary between console applications (like cmd.exe or PowerShell) and csrss.exe. Instead of csrss.exe directly managing the visual aspects of the console window, conhost.exe handles these tasks. This creates a security boundary:
- Console Application (e.g.,
cmd.exe): This is the application running within the console window. It sends input/output toconhost.exe. conhost.exe(Console Window Host): This process manages the visual representation of the console window, handles user input (keyboard, mouse), and communicates withcsrss.exeon behalf of the console application.csrss.exe(Client Server Runtime Subsystem): This core system process still handles lower-level system functions, but no longer directly manages the console window’s presentation.
This separation significantly reduces the attack surface. If a vulnerability is exploited in a console application or even in conhost.exe itself, it’s much less likely to compromise the entire system because conhost.exe runs with lower privileges than csrss.exe.
Is conhost.exe a Virus?
No, conhost.exe is a legitimate and essential Windows system process. However, like any executable, it’s possible (though rare) for malware to masquerade as conhost.exe. Here’s how to distinguish between the genuine process and a potential imposter:
-
Location: The legitimate
conhost.exeis located in the%SystemRoot%\System32directory (typicallyC:\Windows\System32). If you find aconhost.exefile in any other location, it should be treated with suspicion. There can be multiple instances of the genuineconhost.exerunning, but they should all originate from theSystem32folder. -
Digital Signature: The genuine
conhost.exeis digitally signed by Microsoft. To verify the signature:- Right-click on the
conhost.exefile in Task Manager (or File Explorer). - Select «Properties.»
- Go to the «Digital Signatures» tab.
- You should see «Microsoft Windows Publisher» in the signature list. If you see a different name, or no signature at all, it is almost certainly malware. Click the signature and choose «Details» to view more information.
- Right-click on the
-
Resource Usage: While
conhost.exeuses system resources (CPU, memory), excessive or unusual resource consumption could indicate a problem. However, this is not a definitive sign of malware, as legitimate console applications might be performing resource-intensive tasks. -
Multiple Instances: It’s normal to see multiple instances of
conhost.exerunning in Task Manager, especially if you have multiple command-line windows open. Each console window typically has its own associatedconhost.exeprocess. -
Process Tree: In Task Manager (Details tab), you can often see the «Command line» column (you might need to enable it). This can help you understand which console application is associated with a particular
conhost.exeprocess. This is not foolproof, as malware can manipulate this, but it provides helpful context. Process Explorer (from Sysinternals, now part of Microsoft) provides a more robust «Process Tree» view, making it easier to see parent-child relationships between processes.
Can conhost.exe Become a Virus?
conhost.exe itself cannot become a virus. Viruses are malicious code that infects other files. conhost.exe is an executable file, not a virus. However, as mentioned above, malware can:
- Masquerade as
conhost.exe: A malicious executable file can be named «conhost.exe» and placed in a different directory to trick users. - Exploit vulnerabilities: While less likely now due to the security improvements mentioned earlier, it’s theoretically possible (though highly improbable) that a vulnerability could be found in
conhost.exethat malware could exploit. This is why keeping your Windows system up-to-date with the latest security patches is crucial.
conhost.exe Usage (or Lack Thereof)
Unlike many .exe files, conhost.exe is not a tool you directly interact with or configure. It runs automatically in the background whenever a console application is launched. You don’t launch conhost.exe directly; it’s launched by the system as needed. There are no command-line options or user interfaces for conhost.exe itself.
However, you indirectly interact with conhost.exe all the time. Whenever you use:
- Command Prompt (
cmd.exe) - PowerShell
- Windows Terminal
- Any other application that uses a console window
conhost.exe is working behind the scenes to manage that window. The settings you configure for your console windows (font, colors, size, etc.) are actually applied by conhost.exe. These settings are usually managed through the properties of the console application itself (e.g., right-clicking on the title bar of a Command Prompt window and selecting «Properties»). Windows Terminal provides a more centralized way to manage console profiles and settings.
Troubleshooting
If you suspect issues related to conhost.exe:
-
Run a full system scan with your antivirus software. This is the first and most important step if you suspect malware.
-
Use System File Checker (
sfc) and DISM:- Open an elevated Command Prompt (run as administrator).
- Run
sfc /scannow. This command will scan and attempt to repair corrupted system files, includingconhost.exe. - If
sfcfinds issues it can’t fix, run:DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth. This command uses Windows Update to download and replace corrupted system files.
-
Check Event Viewer: Windows Event Viewer (eventvwr.msc) may contain error messages related to
conhost.exethat can provide clues about the problem. Look in the «Windows Logs» -> «Application» and «System» logs. -
Perform a clean boot: A clean boot starts Windows with a minimal set of drivers and startup programs. This can help determine if a third-party application is interfering with
conhost.exe. See Microsoft’s documentation for instructions on performing a clean boot. -
Update Windows: Ensure your Windows system is fully up-to-date with the latest updates and patches.
Conclusion
conhost.exe is a crucial, albeit often unseen, component of the Windows operating system. It plays a vital role in securing and managing console windows, acting as a crucial intermediary between console applications and the core system. While it’s not a tool you directly interact with, understanding its purpose and how to identify potential issues is essential for maintaining a healthy and secure Windows environment.
Want to know what a console window host is? There are few programs on which our Windows depend entirely. You might not know them, but they keep running in the background, so you don’t have to worry about Windows. You might have also noticed many files and folders in the C drive. All these files have their function to keep your PC running. But what is Console Window Host?
Conhost.exe in Windows 10 allows the command prompt to work with Windows Explorer. The console Window Host Process is related to the Command prompt. Each time the Command Prompt runs in Windows, it will create a window. It will do the same when other applications use the command line.
Console Window Host is one of them and the most important. It is also known as conhost.exe. When something goes wrong with your PC, you might have noticed this file popping up when you open Task Manager.
What is Conhost.exe
Conhost.exe is Microsoft authenticated and digitally signed. You will find conhost.exe in the C:\Windows\System32 directory, which does not appear as a separate window. It runs in your Task Manager.
Conhost.exe in Windows 10 allows the command prompt to work with Windows Explorer. It helps you to drag and drop files into the command prompt. Similarly, it adds new external features that Windows’ previous versions didn’t have.

It is also related to CSRSS, ClientServer Runtime System Service. Its file is denoted as csrss.exe. You will read more about it in the article.
Conhost.exe might use high memory or CPU usage. In this case, you might need to check if the Windows Host process is original. Open the Task Manager, right-click the conhost.exe file, and open the file location. If the place matches the directory mentioned above, everything is going well. If the file location differs, it might be a virus or threat issue.
After knowing what Console Window Host is, you can conclude that this program should not be deleted, stopped, or removed.
Further in this article, you will find more about conhost.exe and its process. Keep reading for a better understanding.
Read more: How Much Does a Minecraft Server Cost – TechWhoop’s Guide
History of Console Window Host
Let’s go back in time and understand why the console window host came into the picture.
In the early day of Windows XP, CSRSS, ClientServer Runtime System Service, was used to handle command prompts. It offered system-level service that later became problematic.

If CSRSS crashes, the whole system will come down. It increased reliability and security issues. Also, developers couldn’t theme the CSRSS as running a theme code in a system process was risky. The command prompt always had the same old look without any new elements or changes.
At that time, Windows Vista introduced the Desktop View Manager, which handled a composite view of the applications on your desktop. It helped Command Prompt with some styling like a glassy frame in other Windows versions but removed the drag and drop functionality.

If you look closely, you will find the same old scroll bars in the Windows Vista console. The Desktop View Manager kept the old frame and title bars intact.
Console Windows Host came into the picture with Windows 7. It handled both CSRSS and Command Prompt to fix interface issues and restore the drag-and-drop functionality. This method is supported in Windows 8 and Windows 10 as well.
The console window host still runs under CSRSS. Console Window Host is like a shell maintaining the power of running a service-level system that is CSRSS. It incorporates the new elements interface reliably and securely.
What is the Process of the Console Window Host
Now that you know what Console Window Host let us understand its process. The process is easy to understand and explained here in simple words.
The console Window Host Process is related to the Command prompt. Each time the Command Prompt runs in Windows, it will create a window. It will do the same when other applications use the command line.

It is why the console window hosts multiple times in the Task Manager. Each conhost process takes up to 10MB of memory, not too much, and CPU usage is almost zero if the process is inactive.
Console Window Host Process uses DLL system resources for any operation, similar to almost every application. It is a Dynamic Link Library file. Dynamic, as the files are loaded with an application that needs them. These files have separate components and modules, which takes less space as everything doesn’t need to load simultaneously.
For example, you use a dialogue box to select files to share. It will be the same for all the applications.

DLL files are not applications. Windows uses the application Rundll32.exe to open DLL files. Other applications open DLL files to use their features. Although, not DLL files use the .exe extension. There use other extensions as per the requirement, such as .ocx, .cpl, and .drv.
Although the information about the process is enough for you to understand the basic functionality of conhost.exe, you can go deep into technicalities to completely understand.
How to Remove Conhost.exe Virus
Conhost.exe is not a virus. It is a program that needs to run all the time to keep Windows functioning intact. It is explained above in detail what is console window host and how it works.
Well, there are scenarios where you need to remove the conhost.exe program. If you see conhost.exe using excess memory and CPU space, it might be a virus or malware faking to be a console window host. You might also realize it reappears when you try to close that session.
First, check the location of conhost.exe to be C:\Windows\System32. If it shows a different file location, it is a virus or malware attack. Viruses or malware could be in any form on your PC. They can corrupt your Windows file and any crucial data on your computer. They can even delete files and erase your hard drive.
You need not panic about that. There are ways through which you can protect your PC. Follow the steps below to remove the fake conhost.exe program from your PC.
- Scan your PC with a reliable antivirus.
- It should remove all the unwanted files and activities going on. It should close and remove all the viruses and malware trying to get into your PC.
- You need to restart your PC and check for the conhost.exe session running in the Task Manager.
- If the location of the conhost.exe is in the correct directory, then your PC is safe now.
- Else you need to End Task from Task Manager or again scan your PC to look for malicious files and remove them.
FAQS
Why is Console Window Host running on my computer?
Console Window Host runs automatically when you launch command-line programs or applications that rely on console-base interfaces. It’s a vital part of the Windows operating system, ensuring proper execution and interaction with these programs.
Can I terminate Console Window Host?
Terminating Console Window Host abruptly can disrupt command-line applications and potentially cause data loss. Closing the associate command prompt or application is recommended instead of terminating the process directly. Closing the command prompt will complete the Console Window Host process.
Does Console Window Host consume system resources?
Console Window Host typically consumes minimal system resources. However, resource usage may increase when running resource-intensive command-line applications or if there are multiple console windows open simultaneously. Generally, it has a negligible impact on system performance.
Can I customize the appearance of the Console Window Host?
Yes, you can customize the appearance of the Console Window Host. Right-clicking on the title bar of a console window allows you to access properties such as font size, colors, and layout options. These settings can be adjusted to suit your preferences and improve readability.
Is the Console Window Host a virus?
No, Console Window Host is not a virus. It is a legitimate system process integral to the Windows operating system. However, like any other process, malware can disguise itself as Console Window Host. Ensure you have reliable antivirus software installed and regularly scan your system for security threats.
Can I disable the Console Window Host?
Console Window Host cannot be disabled as it is a critical Windows operating system component. Disabling it would prevent the execution of command-line programs and impact the system’s overall functionality. It’s recommended to enable it to ensure the proper operation of console-base applications.
Conclusion
It would be best to use a good-rated antivirus to help you detect viruses and malware. It is advised to run a scan occasionally to keep it safe from malicious activities. This way, you not only protect your PC, and applications but also your data.
In this article, you learned about Console Window Host and how to protect your PC from viruses and malware. When you see something is wrong with your PC, at that time, you need to check your system. Following the tips mentioned above will fix your PC.
See Also: WMI Provider Host High CPU Usage (WmiPrvSE.exe) Fixed
When a Windows PC is running, millions of computations are taking place, telling the computer how to do everything from loading a web page to opening a piece of software. This process requires any number of system services to take you from A to B, with processes like ntoskrnl.exe designed to play a part in the overall user experience.
This includes conhost.exe, a system process that will appear any time you open a command prompt window. But what is conhost.exe exactly? And is it safe to leave this process running on your PC? This guide will explain everything you need to know about conhost.exe, including how to spot a fake system process.

The conhost.exe process, also known as the Console Window Host process, originated in Windows XP as a way for the command prompt (cmd.exe) to interface with other elements of Windows, including Windows Explorer as part of the Client Server Runtime System Service (csrss.exe).
If you decided to drag a file onto a command prompt window, for instance, CSRSS would ensure that the location of the file would correctly appear on the command prompt line.
Unfortunately, as a major system process, this presents huge security risks. Allowing the command line (with full control over your PC) this kind of access to the file system could bring down your PC. This security threat forced Microsoft to make changes to how the system operated.
Windows Vista offered greater security but with reduced functionality, making it impossible to drag-and-drop files onto a command line window. For Windows 10, Microsoft introduced the conhost.exe process, which (along with a much-smaller csrss.exe process) allows the command line to safely work with other processes without the same level of security risks that csrss.exe presented in Windows XP.
This allows Microsoft to more closely integrate processes like the command line into Windows 10, with modern themes and drag-and-drop features like those seen in XP’s version of csrss.exe. If you’re using the modern Windows Powershell, you’ll see even greater security, with csrss.exe and conhost.exe disregarded entirely.
Can Conhost.exe Cause High CPU, RAM or Other High System Resource Usage?
While unlikely, it has been reported that conhost.exe causes high CPU or RAM usage (or high system resource usage generally) on Windows 10 PCs. If this happens to you, it could point to a larger problem with your PC.
Under normal circumstances, conhost.exe should not cause high system resource usage. It should only appear if you (or a background app) is using the command line. With the Windows PowerShell now the default terminal tool in Windows, you shouldn’t find it necessary to open cmd.exe at all.
That doesn’t discount the possibility that other background apps might still be using a hidden command line to run, however. While playing old DOS games isn’t likely to cause a spike in system resource usage, some newer system apps may cause problems.
To find the culprit, you can use the Microsoft-developed Process Explorer app. This allows you to see which running apps might be interfacing with conhost.exe and causing high CPU usage.
- To do this, download and run Process Explorer from the Microsoft website. In the Process Explorer window, select Find > Find Handle or DLL to open the search box. Alternatively, press Ctrl + F on your keyboard.
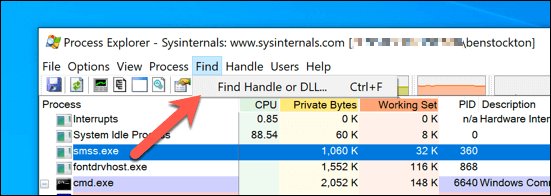
- In the Process Explorer Search box, search for conhost, then select the Search button. In the list, select one of the results. Process Explorer will immediately change view to bring the item into focus.
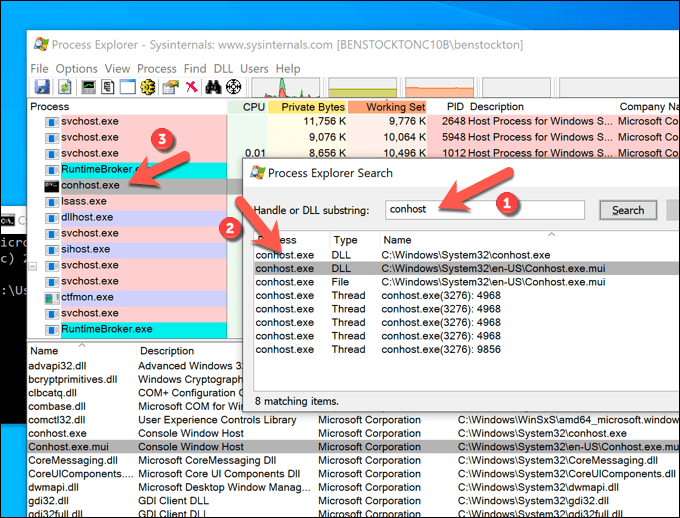
- Do this for each example of conhost.exe running on your PC. If the system resource usage (for example, CPU under the CPU column) is too high, you can end the process by right-clicking and selecting the Kill Process option.
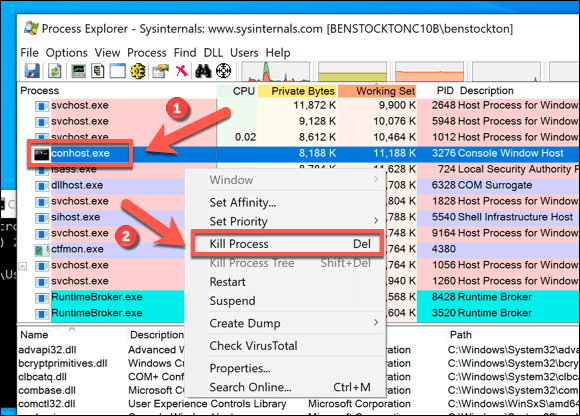
If you find conhost.exe is interfacing with another app or service that you don’t recognize, it may point to a malware infection. If this happens, scan your PC for malware to make sure that your PC is safe to use.
How to Remove Conhost.exe from Windows 10
The interface that conhost.exe provides for background apps continues to prove essential, even as the command line becomes less important in Windows 10. As an important system process in its own right, you can’t remove conhost.exe from running. And attempting to do so could prevent other apps and services from running.
For most users, the conhost.exe process doesn’t cause any issues and is entirely safe to leave running. If it runs, it runs in the background, allowing other apps to interface with lower levels of the Windows operating system.
If you’re running it yourself, it still shouldn’t be a problem, although we’d still recommend switching to the newer PowerShell in the long run. Where conhost.exe can prove to be problematic, however, is when it’s co-opted by rogue software.
Some malware will run fake processes (using the conhost.exe name) to disguise itself, while others will interface with conhost.exe to gain additional control over your PC and its resources. If you’re worried about this (even after scanning for malware), you can check if conhost.exe is a legitimate system process.
How to Check if Conhost.exe is Real and Safe
In almost all cases, system processes like conhost.exe and msmpeng.exe should only run from one place on your PC: the Windows folder (C:Windows) or one of its subfolders (eg. C:WindowsSystem32). While there are exceptions for packaged UWP apps like yourphonexe.exe, this is still true for conhost.exe.
This makes it easy to determine if conhost.exe is safe and legitimate or whether it’s fake by using Windows Task Manager to open the location of any running conhost.exe processes. If you want to be sure that conhost isn’t interfacing with malware, you can use the Process Explorer (as explained above) to check first.
- To check if conhost.exe is safe, right-click the taskbar and select the Task Manager option.
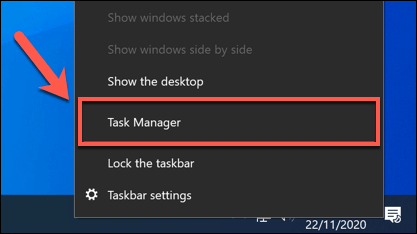
- In the Processes tab of the Task Manager window, look for the Console Window Host process. You may need to press the arrow icon next to each process to find it listed under another process. Alternatively, search for conhost.exe in the Details tab instead.
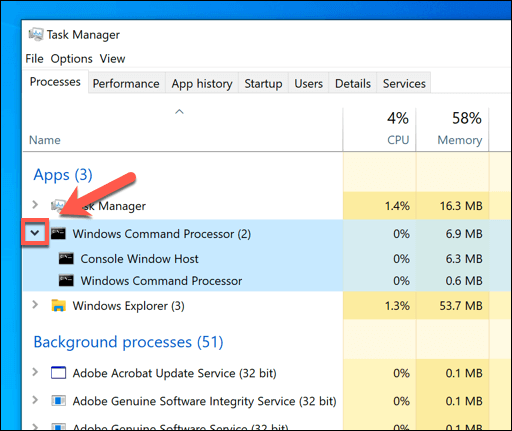
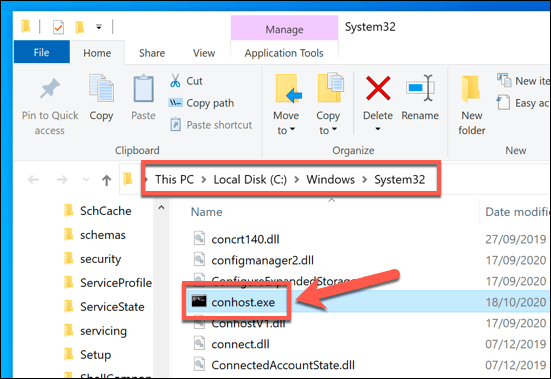
- To check if the conhost.exe process is real, right-click it in the Processes or Details tab, then select the Open file location option.
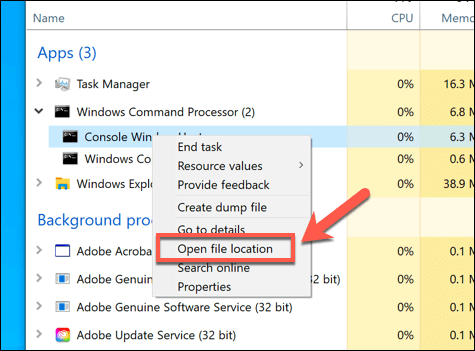
- This will open the C:WindowsSystem32 folder in Windows File Explorer. If it doesn’t, then the currently running conhost.exe process is fake. You’ll need to take steps to scan your PC to get rid of the likely malware infection if this is the case.
Securing a Windows 10 System
Conhost.exe is just one of many different system processes that play a part in making the overall Windows operating system work properly. By following the steps above, you can be confident that the processes your PC relies are on are safe to run and use without needing to stop or remove them.
That doesn’t mean that every process running on your PC is safe. If you’re worried, you can schedule a boot-level Windows Defender scan to check every file on your PC for malware. And, if that doesn’t work, there are plenty of third-party apps out there that can remove stubborn malware instead.
Related Posts
- How to Fix a “This file does not have an app associated with it” Error on Windows
- How to Fix an Update Error 0x800705b4 on Windows
- How to Resolve “A JavaScript error occured in the main process” Error on Windows
- How to Fix the Network Discovery Is Turned Off Error on Windows
- How to Change Folder Icons in Windows
The conhost.exe (Console Windows Host) file is provided by Microsoft and is usually legitimate and completely safe. It can be seen running on Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, and Windows 7.
Conhost.exe needs to run for Command Prompt to interface with File Explorer. One of its duties is to provide the ability to drag and drop files/folders directly into Command Prompt. Even third-party programs can use conhost.exe if they need access to the command line.
In most circumstances, it’s entirely safe and does not need to be deleted or scanned for viruses. It’s even normal for this process to be running several times simultaneously (you’ll often see multiple instances of conhost.exe in Task Manager).
However, there are situations where a virus could be masquerading as the conhost EXE file. One sign that it’s malicious or fake is if it’s using up lots of memory.
Software That Use Conhost.exe
The conhost.exe process is started with each instance of Command Prompt and with any program that utilizes this command-line tool, even if you don’t see the program running (like if it’s running in the background).
Here are some processes known to start conhost.exe:
- Dell’s “DFS.Common.Agent.exe”
- NVIDIA’s “NVIDIA Web Helper.exe”
- Plex’s “PlexScriptHost.exe”
- Adobe Creative Cloud’s “node.exe”
Is Conhost.exe a Virus?
Most of the time, there’s no reason to assume conhost.exe is a virus or that it needs to be deleted. However, there are some things you can check if you’re not sure.
For starters, if you see it running in Windows Vista or XP, then it most certainly is a virus, or at least an unwanted program, because those versions of Windows don’t use this file. If you see conhost.exe in either of those Windows versions, skip down to the very bottom of this page to see what you need to do.
Read the file name closely. A clever attacker might purposely misspell the file (e.g., c0nhost.exe) so you think it’s a necessary system file. Plenty of other examples could be given, like conhot.exe or conbost.exe.
Another indicator that it might be fake or malicious is if it’s stored in the wrong folder. The real conhost.exe file runs from a very specific folder and from that folder only. The easiest way to learn whether the process is dangerous or not is to use Task Manager to do two things: a) verify its description, and b) check the folder that it’s running from.
-
Open Task Manager. The easiest way to do this is by pressing the Ctrl+Shift+Esc keys on your keyboard.
-
Find the conhost.exe process in the Details tab (or Processes tab in Windows 7).
There might be multiple instances of conhost.exe, so it’s important to follow the next steps for each and every one you see. The best way to gather all of the conhost.exe processes together is to sort the list by selecting the Name column (Image Name in Windows 7).
Don’t see any tabs in Task Manager? Use the More details link at the bottom of Task Manager to expand the program to full size.
-
Within that conhost.exe entry, look to the far right under the Description column, to make sure it reads Console Windows Host.
The correct description here doesn’t necessarily mean the process is safe, since a virus might use the same description. However, if you see any other description, there’s a strong chance that the EXE file isn’t the real Console Windows Host process and should be treated as a threat.
-
Right-click or tap-and-hold the process and choose Open file location.
-
The folder that opens will show you exactly where conhost.exe is stored.
If you can’t open the file location this way, use Microsoft’s Process Explorer program instead. In that tool, double-click or tap-and-hold conhost.exe to open its Properties window, and then use the Image tab to find the Explore button next to the file’s path.
This is the real location of the non-harmful process:
C:\Windows\System32\
If this is the folder where conhost.exe is being stored and running from, there’s a really good chance you’re not dealing with a dangerous file. Remember that this is an official file from Microsoft that has a real purpose to be on your computer, but only if it exists in that folder.
However, if the folder that opens at Step 4 is not the System32 folder, or if it’s using a ton of memory, and you suspect that it shouldn’t need that much, keep reading to learn more about what’s happening and how you can remove the conhost.exe virus.
To reiterate: conhost.exe should not be running from any other folder, not even the root of the C:\Windows\ folder. It might seem fine for this EXE file to be stored there, but it really only serves its purpose in the system32 folder, not in C:\Users\[username]\, C:\Program Files\, etc.
Why Is Conhost.exe Using So Much Memory?
A normal computer running conhost.exe without any malware might see the file use around several hundred kilobytes (e.g., 500 KB) of RAM, but likely no more than 10 MB even when you’re using the program that launched conhost.exe.
If conhost.exe is using a lot more memory than that, and Task Manager shows that the process is utilizing a significant portion of the CPU, there’s a good chance the file is fake. This is especially true if the steps above lead you to a folder that isn’t C:\Windows\System32\.
There’s a particular conhost.exe virus called Conhost Miner that stores itself in this folder, and possibly others:
%userprofile%\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\
This virus attempts to run a Bitcoin or other cryptocurrency mining operation without you knowing, which can be very demanding of the memory and processor.
How to Remove a Conhost.exe Virus
If you confirm or even suspect that conhost.exe is a virus, it should be fairly straightforward to get rid of it. A super easy way to see if it shows signs of something malicious is to upload the file to VirusTotal. There are lots of free tools available to you that can delete a conhost.exe virus from your computer, and others to help make sure it doesn’t come back.
However, your first attempt should be to shut down the parent process that’s using the file so it will no longer be running its malicious code, and to make it easier to delete.
If you know which program is using conhost.exe, you can skip these steps below and just try to remove the application in hopes that the associated conhost.exe virus gets removed, too. Your best bet is to use a free uninstaller tool to make sure all of it gets deleted.
-
Download Process Explorer and double-click (or tap-and-hold) the conhost.exe file you want to remove.
-
From the Image tab, select Kill Process.
-
Confirm with an OK.
If you get an error that the process can’t be shut down, skip to the next section below to run a virus scan.
-
Press OK to return to the main screen. You can close Process Explorer at this time if you’d like.
Now that the file is no longer attached to the parent program that started it, it’s time to remove the fake conhost.exe file:
Follow the steps below in order, restarting your computer after each one and then checking to see if conhost.exe is really gone. To do that, run Task Manager or Process Explorer after each reboot to make sure the virus has been deleted.
-
Try deleting conhost.exe. Open the folder from above and just delete it like you would any file.
Use the Everything tool to do a full search across your whole computer to make sure the only conhost.exe file you see is in the System32 folder. You might actually find another in the C:\Windows\WinSxS\ folder, but that conhost.exe file should not be what you find running in Task Manager or Process Explorer (it’s safe to keep). You can safely delete any other conhost.exe imitation.
-
Install Malwarebytes and run a full system scan to find and remove the conhost.exe virus.
-
Install a full antivirus program if Malwarebytes or another spyware removal tool doesn’t do the trick.
This should not only delete the fake conhost.exe file, but will also to set up your computer with an always-on scanner that can help prevent viruses like this one from getting on your computer again.
-
Use a free bootable antivirus tool to scan the whole computer before the OS even starts up. This will surely work to fix the conhost.exe virus since the process won’t be running at the time of the virus scan.
FAQ
-
No. The cmd.exe file is the executable file for the Command Prompt, so opening it will bring up the command window. Watch out for viruses that masquerade as the cmd.exe file.
-
Deleting the real conhost.exe can affect how Windows functions, so you should only delete the file if you’re sure it’s a virus.
-
A running process could be triggering the conhost.exe file. Force quit programs that you can’t identify. If the problem persists, it could be a virus.
Thanks for letting us know!
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
Subscribe




