Рассмотрим ситуацию, когда вам необходимо синхронизировать время вашей Windows машине или Windows сервере с вашим NTP сервером, или внешне доступным сервером времени. Задача простая, но у новичков в системном администрировании это может вызвать некоторые трудности. Так давайте разберемся!
Небольшое отступление: синхронизировать время на всех узлах сети (сервера, рабочие станции, сетевое оборудование, sip телефоны и т.д.) с единым сервером времени является обязательным, для корректной работы всех служб и сервисов в корпоративной сети. Так, например, это необходимо для корректной работы служб Active Directory, контроллеров доменов, почтовых серверов, рабочих станций, обеспечения корректных прав доступа и безопасности.
Операционные системы семейства Windows содержат службу времени W32Time. Эта служба предназначена для синхронизации времени в пределах организации. W32Time отвечает за работу как клиентской, так и серверной части службы времени, причем один и тот же компьютер может быть одновременно и клиентом и сервером NTP (NTP — Network Time Protocol).
Для того чтобы синхронизировать ваш сервер или рабочую станцию вам необходимо выполнить следующие команды, в командной строке (CMD), запущенной от имени администратора:
1. w32tm /query /source – проверяем источник, на который настроена служба времени в данный момент. Вывод команды либо покажет нам имя или адрес существующего ntp сервера, или в случае его отсутствия выдаст “Free-running System Clock”.

2. w32tm /config /syncfromflags:manual /manualpeerlist:”source” – данной командой указываем источник эталонного времени (NTP Сервер) . Заменяем source на ip адрес или на FQDN. В доменной сети стоит указывать адрес контроллера домена. В случае правильности выполнения получим вывод “Команда выполнена успешно”.

3. w32tm /config /update – обновляем службу времени, чтобы новые настройки применились.

4. w32tm /resync – запускаем принудительное обновление с новым сервером времени.

Все. Вы синхронизировали службу времени на вашей машине с внешним источником. Данный подход позволит вам добиться того, что все машины в вашей сети будет иметь единое правильное время, что позволит избежать ряда сбоев из за расхождения во времени.
Дополнительные команды управления службой времени:
w32tm /query /source — выводит источник времени, на который настроена служба Windows Time
w32tm /monitor — при запуске на контроллере домена (КД) показывает, насколько отличается время на других КД и на внешнем источнике времени, на который настроен PDC
w32tm /config /syncfromflags:manual /manualpeerlist:ru.pool.ntp.org — настройка в качестве источника времени пула ntp-серверов ru.pool.ntp.org
w32tm /config /update — эту команду необходимо выполнить, чтобы служба времени применила новые настройки
w32tm /resync — выполнение синхронизации времени
w32tm /unregister — отменяет регистрацию службы и удаляет настройки из реестра
w32tm /register — регистрирует службу и восстанавливает настройки по умолчанию
Всем привет! Сегодня я расскажу, как синхронизация времени с контроллером домена, чтобы компьютеры нормально работали с AD. Если время у разных компьютеров будет отличаться хотя бы на 5 минут, то могут возникнуть проблемы с работой некоторых программных модулей.
Содержание
- Через параметры
- Синхронизация с помощью командной строки
- Видео
- Задать вопрос автору статьи
Через параметры

Вообще вам необязательно делать синхронизацию через команду строку или любым другим способом, так как операционная система Windows сама это делает, если у вас правильно настроен домен синхронизации. Давайте проверим это:
Читаем – чем Виндовс 11 лучше 10-ой версии.
- Перейдите в «Параметры» через меню «Пуск».
- Найдите раздел «Время и язык».
- В первом разделе слева, в правом блоке можно просто нажать «Синхронизировать». Выше также будет отображаться сервер времени, который используется в данный момент.
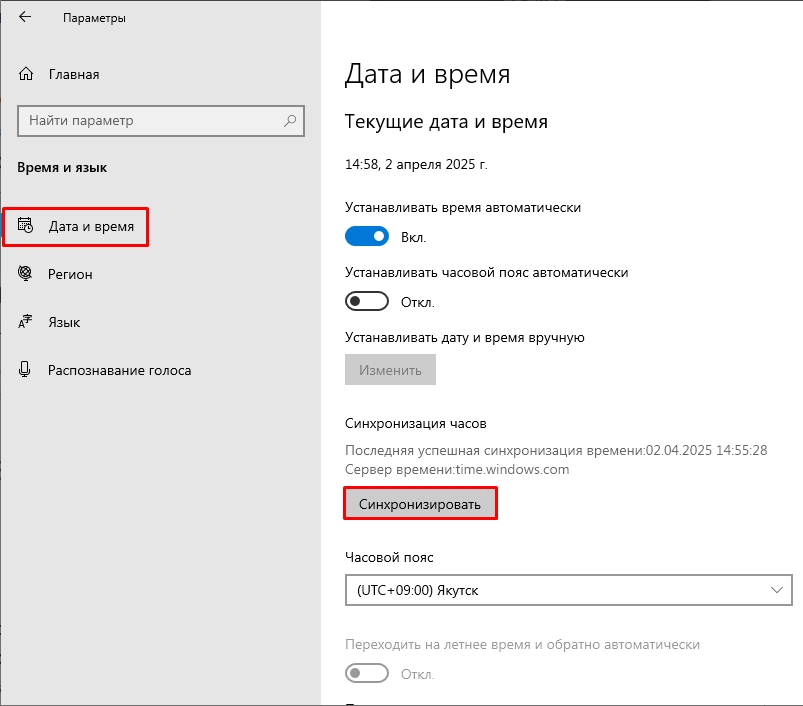
Обратите внимание также, чтобы был правильно установлен «Часовой пояс». Галочку установки автоматического времени лучше включить, но вот пояс лучше ставить вручную. Дата аналогично ставится исходя из сервера.
Синхронизация с помощью командной строки
Также есть дополнительные команды для работы с w32tm. На официальном сайте Microsoft сказано, что устаревшие команды «Net time» – использовать не рекомендуется. Вместо этого используем w32tm и дополнительными атрибуты. Напишу пару примеров.
w32tm /query /source – выводит текущий сервер, с которого идет синхронизация.
w32tm /config /syncfromflags:manual /manualpeerlist: “АДРЕС_СЕРВЕРА” – принудительно указать адрес сервера, с которым будет идти синхронизация времени.
w32tm /config /update – обновляет конфигурационный файл времени.
w32tm /resync /rediscover – выполнить синхронизацию прямо сейчас.
Чтобы синхронизировать время с сервером делаем следующее:
w32tm /query /configuration
Проверяем чтобы в строке «Type» было значение «NT5DS» – это значит, что синхронизация идет с помощью домена AD. Если у вас не так и стоит NTP (локальная синхронизация), то сбрасываем настройки до NT5DS:
w32tm /config /syncfromflags:domhier /update net stop w32time && net start w32time
После этого система сама найдет домен с сервером в иерархии AD и подключиться к нему. Если подключиться не получается. То прописываем команду отмены регистрации и удаления конфига:
w32tm /unregister
Восстанавливаем конфигурацию обратно, как было в настройках:
w32tm /register
Синхронизируем время обратно с Active Directory:
w32tm /config /syncfromflags:domhier /update
Службу теперь надо перезагрузить:
net stop w32time && net start w32time
Апгрейдим настройки:
w32tm /config /update
И теперь можно синхронизировать само время:
w32tm /resync
Проверьте, чтобы служба была запущена и сервер правильно определился:
w32tm /query /status
Основная проблема – это ошибка, что служба не запущена. В таком случае зайдите в «Службы» операционной системы, найдите «Службу времени Windows» и запустите её вручную. После этого уже можно вводить команды дальше. До новых встреч на портале WiFiGiD.RU.
Видео
Материал из support.qbpro.ru
Скрипт для синхронизации времени в Windows:
net time /setsntp:10.10.5.1 net stop w32time && net start w32time net w32tm /resync
или
net w32tm /config /manualpeerlist:pool.ntp.org /syncfromflags:manual /update
Запуск от имени Администратора:
runas /user:Администратор "cmd /C net time /setsntp:10.10.5.1 && net stop w32time && net start w32time && w32tm /resync"
Изменение времени в CMD
- Пример скрипта:
runas /user:127.0.0.1\Администратор "cmd /C w32tm /config /syncfromflags:manual /manualpeerlist:pool.ntp.org && w32tm /config /update"
или
echo password|runas /netonly /user:127.0.0.1\Администратор "cmd /A /C chcp 866>nul time net time /setsntp:pool.ntp.org w32tm /config /syncfromflags:manual /manualpeerlist:pool.ntp.org net stop w32time && net start w32time w32tm /config /update pause "
- Пример команды если компьютер в домене:
runas /user:127.0.0.1\Администратор "cmd /A /C w32tm /config /syncfromflags:manual /manualpeerlist:pool.ntp.org && w32tm /config /update"
- Отключение автоматического перехода на летнее/зимнее время» из пользователя с ограниченными правами:
runas /user:127.0.0.1\Администратор "cmd /A /C regedit"
Ищем в реестре:
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\TimeZoneInformation]
создаем ключ DWORD спараметром «1»:
DisableAutoDaylightTimeSet = 1
Время в командной строке
Пример:
runas /user:127.0.0.1\Администратор "cmd /A /C time 21.45"
Time — задает системное время
Выводит и задает системное время.При использовании без параметров, команад time отображает системное время и предлагает
ввести новое время.
Синтаксис time [/t] [/time] [часы:[минуты[:секунды[.сотые]]][{A|P}]]
Параметры
/t
Выводит на экран текущее системное время без предложения ввода нового.
/time
Такой же как параметр /t.
часы
Задает значение часов. Допустимы величины от 0 до 23.
минуты
Задает значение минут. Допустимы величины от 0 до 59.
секунды
Задает значение секунд. Допустимы величины от 0 до 59.
сотые
Задает значение сотых долей секунды. Допустимы величины от 0 до 99.
{A|P}
Задает время до полудня (A.M.) или после полудня (P.M.) для 12-часового формата времени.
Если указано допустимое 12-ти часовое значение, но не задано значение A или P, команда time использует A (до полудня).
/?
Отображает справку в командной строке.
- Пример скрипта синхронизации для Windows Server 2008
@echo off w32tm /config /manualpeerlist:0.pool.ntp.org,0x1 /syncfromflags:MANUAL net stop w32time net start w32time net w32tm /resync
ИСТОЧНИКИ
взято тут
Windows computers must have their time synchronized with the domain in order to function properly in Active Directory. If the time on a client computer is out of sync with the domain, this can cause a number of problems. The most critical are related to the failure of Kerberos authentication and access to the resource if the time on a client computer is more than 5 minutes off from the domain controller.
In this post we’ll cover how to sync time on a client device with the AD domain and how to troubleshoot when things go wrong.
Understanding the Time Hierarchy in the Active Directory Domain
By default, all domain-joined computers automatically sync their time with the domain controller according to the strict Active Directory domain hierarchy.
- Workstations and member-servers use their authenticating Domain Controller (LogonServer) as the time source (in accordance with AD sites and subnets configuration);
- All domain controllers sync their time DC holding the PDC Emulator FSMO role;
- The PDC synchronizes the time with an external reliable time source (NTP server). The domain controller with the PDC role is the main source of time in the domain.
- In a multi-domain AD forest, the PDC emulator in each domain sync its time with the PDC in the forest root domain.
Hint. Learn more about time syncing in an Active Directory domain using the GPO.
Sync Time with DC on the Domain-Joined Machine
By default, Windows computer should automatically synchronize its time with the nearest domain controller when it joins a domain. In most cases, no additional manual action is required to sync the time with domain.
On a Windows 10/11 computer, check the current time source and sync status. Go to Settings > Time and Language > Date & time > Additional settings and make sure your DC is used as the last time sync source.

There is no graphical interface for managing the Windows Time service (W32Time), so it can be configured from the command line (w32tm command), from the registry (HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\W32Time\Parameters), or via Group Policy.
To check and configure the time sync settings from the command prompt, use the w32tm command. Get the current time source on a computer:
w32tm /query /source
This command should return the name of one of the AD domain controllers on a domain-joined machine:
View the detailed time setting and last sync time:
w32tm /query /status

Force a time sync with DC:
w32tm /resync /rediscover
If the time synchronization is successful, Event ID 37 should appear in the Event Viewer with the Time-Service source:
The time provider NtpClient is currently receiving valid time data from dc01.theitpro.loc (ntp.d|0.0.0.0:123->192.168.8.10:123).

Make sure that the computer is configured to automatically synchronize its time according to the domain hierarchy:
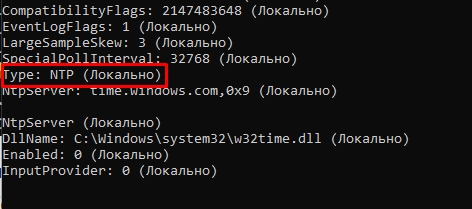
w32tm /query /configuration
Scroll down to the [TimeProviders] sections and ensure that the Type is set to NTDS5. If not, this may be the cause of time sync problems on a computer.
This value can also be found in the Type parameter under the registry key HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\W32Time\Parameters. The NtpServer value is ignored when NTDS5 is used.

To re-enable time synchronization with a DC for computers in an Active Directory domain
w32tm /config /syncfromflags:domhier /update net stop w32time && net start w32time
This will reset the time sync settings back to NT5DS. This means that the machine should find a time server in the Active Directory hierarchy.
If the Windows client fails to synchronize time with the AD domain controller, you must to reset the Windows Time service configuration.
Unregister w32time service and remove settings:
w32tm /unregister
Register the w32tm service and restore the default settings:
w32tm /register
Enable time sync with AD:
w32tm /config /syncfromflags:domhier /update
Restart the service:
net stop w32time && net start w32time
Update settings:
w32tm /config /update
Synchronize the time:
w32tm /resync
Check the new time sync settings:
w32tm /query /status

Time Sync Issues on Windows Domain Joined Computers
The Windows Time Service (W32Time) is responsible for time synchronization. Check that this service is running on a client with Get-Service:
Get-Service W32Time | Select-Object name,status

UDP port 123 is used for time synchronization on Windows. If the port is closed, the w32tm /resync command will return an error:
Sending resync command to local computer
The computer did not resync because no time data was available.

In this case, the following entry appears in the Event Viewer log:
EventID: 129
Source: Time-Service
NtpClient was unable to set a domain peer to use as a time source because of discovery error. NtpClient will try again in 15 minutes and double the reattempt interval thereafter. The error was: The entry is not found. (0x800706E1)

Check that the w32time service is running on the DC and listening on UDP port 123:
netstat -an | find "UDP" | find ":123"

Then check that the UDP inbound rule named Active Directory Domain Controller – W32Time (NTP-UDP-In) is enabled in Windows Defender Firewall (Control Panel > Windows Firewall > Advanced settings > Inbound rules).

Or check Windows Defender Firewall rule status with PowerShell:
Get-NetFirewallrule -DisplayName 'Active Directory Domain Controller - W32Time (NTP-UDP-In)'|select Enabled

If the rule is disabled, you must enable it:
Get-NetFirewallrule -DisplayName 'Active Directory Domain Controller - W32Time (NTP-UDP-In)'|Enable-NetFirewallrule
It is also possible to force a client to manually synchronize its time with another domain controller.
net time \\ny-dc01 /set /y

Configuring the NTP Client Time Sync on Windows Using GPO
In most cases, time sync with a domain on Windows client doesn’t require administrator intervention. However, if you find that time synchronization is not working properly on client workstations in domain, it is possible to centrally configure client time sync settings using Group Policy.
- Use the gpedit.msc console to change Group Policy settings on a single computer (this is the best solution if you need to solve synchronization problems on a single computer or test new time sync settings). To set up a GPO for multiple domain computers, use the Group Policy Management Console (gpmc.msc);
- Expand the following node in GPO editor: Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > System > Windows Time Service;
- Enable the Enable Windows NTP Client policy;
- Then enable the Configure NTP Client policy and set the following settings in the Options panel:
NTPServer: your domain name (preferred) or FQDN name of the domain controller with the PDC Emulator role (you can find it with the command: netdom.exe query fsmo)
Type: NT5DS
CrossSiteSyncFlags: 2
ResolvePeerBackoffMinutes: 15
ResolvePeerBackoffMaxTimes: 7
SpecialPollInterval: 64
EventLogFlags: 0 - Restart your computer to apply the new GPO client time settings.
Cyril Kardashevsky
I enjoy technology and developing websites. Since 2012 I’m running a few of my own websites, and share useful content on gadgets, PC administration and website promotion.
Making sure the clock on your computer is correct might sound like a minor thing, but it’s actually very important for keeping your computer running well. This is also extremely important for businesses that need the right time stamps for log files, syncing data, and keeping things secure. In this guide, I’ll show you how to sync your Windows 11 clock with an internet time server, change your Network Time Protocol (NTP) server, and update your NTP time using the command prompt (CMD).
Also see: How to Change Date and Time Format in Windows 11
Why keeping time right on your PC is important
Having your computer’s clock synced isn’t just about the right time showing on your taskbar. It’s also very important for a bunch of other computer tasks like managing files, scheduling stuff, network authentication, and logging what’s happening. It makes sure everything works together correctly and in order, which is a big deal when your computer’s part of a network.
Windows 11, just like the ones before it, uses the Network Time Protocol (NTP) to keep its clock in line with external time servers. By default, it syncs with time.windows.com, but there are loads of other public NTP servers out there you can use instead of the default one.
Linked issue: Date and Time is Always Wrong in Windows
How to sync your Windows 11 time with the internet using CMD
If you want to make sure your system’s time is correct, Windows 11 lets you sync it up with an internet time server. The following steps will show you how to do that using CMD:
- Start by opening the Command Prompt as an admin. Just search for “cmd” or “command prompt” in the Start menu, right-click on “Command Prompt” in the search results, and pick “Run as administrator” from the menu that pops up.
- With the Command Prompt window open, enter the following command:
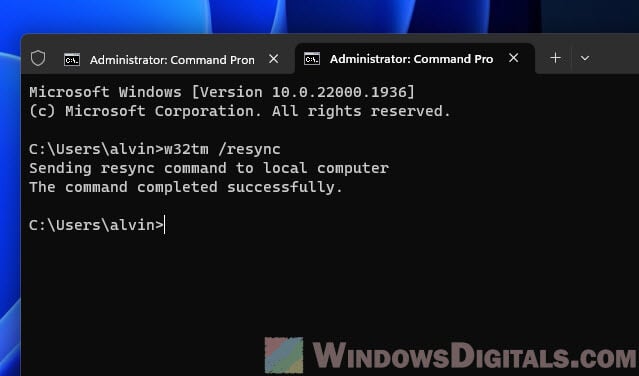
w32tm /resync
- Hit the Enter key after you type in the command. If all goes well, you’ll see a message saying the command worked. This step gets your system’s clock in sync with the default internet time server.
This feature can also help sort out issues if your computer’s clock is running slow or fast, making sure your computer’s time is as accurate as possible.
Related resource: How to Change Date and Time Format in Windows 11
How to switch your NTP time server in Windows 11
Normally, your Windows system will keep its clock synced with Microsoft’s time server (usually time.windows.com). But sometimes, you might need to sync with a different NTP server, such as when the default one isn’t reachable at the moment or you prefer using a local time server in your country. Follow the steps below to switch to your preferred NTP time server in Windows 11 using CMD:
- Start Command Prompt as admin, just like before.
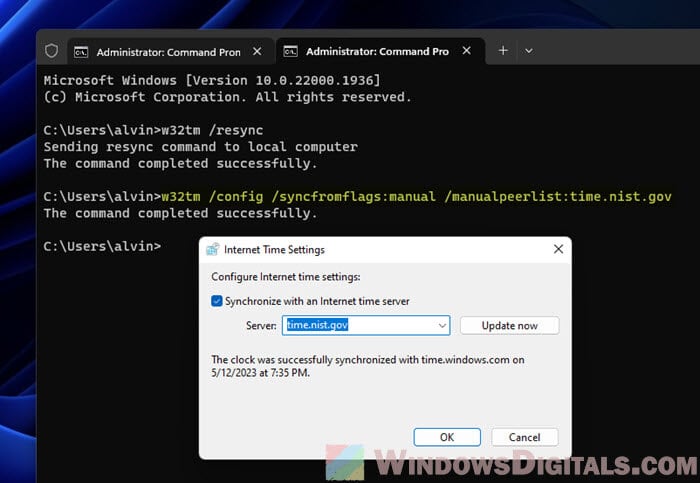
- In the Command Prompt window, type in the following command to change the NTP server. Swap “time.nist.gov” with your chosen NTP server’s address:
w32tm /config /syncfromflags:manual /manualpeerlist:time.nist.gov
- Hit the Enter key after you enter the command. This changes your NTP server to the one you prefer.
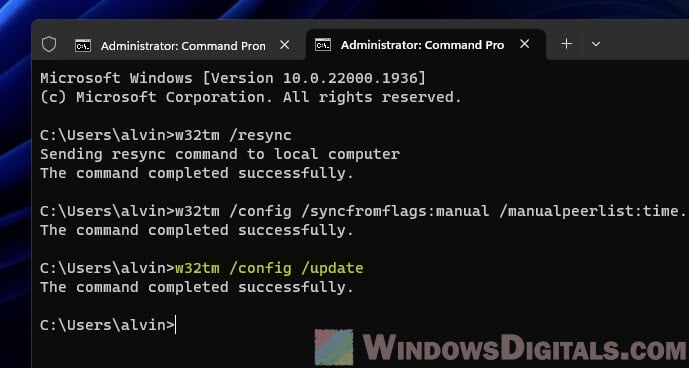
- To make sure the changes take effect, type this command and press Enter:
w32tm /config /update
- Then, get your system’s clock synced up with the new NTP server by using the w32tm /resync command.
How to refresh your NTP time
Refreshing your NTP time in Windows is just a matter of making it resync. Just follow the steps in “How to sync your Windows 11 Clock using CMD” and run the “w32tm /resync” command to get your system clock updated or fixed whenever you need.
What to do if you run into time sync issues
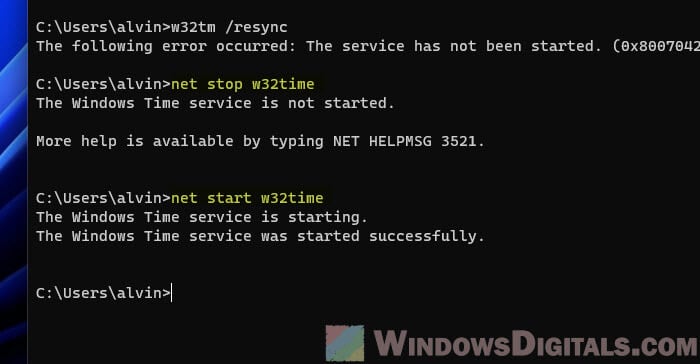
Even if you follow the steps exactly, you might run into problems with the time sync process. Like, you might see an error when trying to use the w32tm /resync command. Common errors include messages like “The service has not been started (0x80070426)” or “The computer did not resync because the time service was shutting down.”
If that happens, try this command to restart the w32time service, which can often kick any time syncing issues to the curb in Windows 11 or 10:
net stop w32time
net start w32time
After the service is back up and running, give the time sync another go with the w32tm /resync command.
If restarting doesn’t smooth things over, consider unregistering and then re-registering the time service in Windows with these steps:
- First, start by unregistering the Windows Time Service with this command:
w32tm /unregister. - Then, stop the Windows Time Service using this command:
net stop w32time. - Next up, re-register the Windows Time Service with this command:
w32tm /register. - Finally, get the Windows Time Service going again with:
net start w32time.
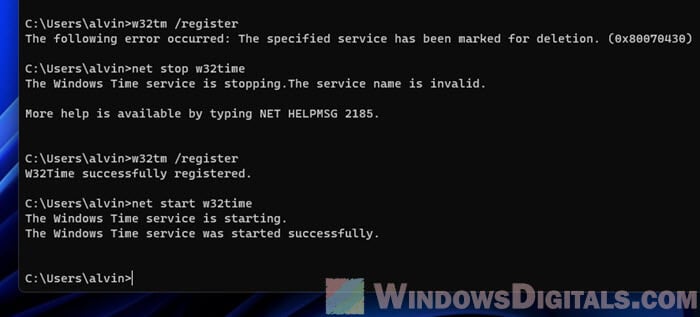
Running through the above steps will unregister, stop, re-register, and then restart the Windows Time Service. It should be able to fix any related issues in the process.
So, what have we learned?
Using the command line lets you set up automatic tasks, which is very helpful if you’re managing several computers—think network administrators, for example. You can write scripts that run these commands automatically at set times. Besides, since you can run CMD commands remotely, it’s also a handy option for network environments.