Для того чтобы иметь относительный порядок на своем компьютере, необходимо свои файлы хранить в соответствующих папках. Это значительно упрощает как поиск отдельных файлов, так и работу с группой файлов: перемещение, копирование, удаление и т.п. Такой принцип организации используется в библиотеках, архивах и канцеляриях.
Документы, систематизированные по общему признаку, хранятся в одной папке (или каталоге). Папки подписываются. Получается, что документы не свалены в одну кучу, а разложены по папкам и в итоге можно легко найти необходимый документ.
По аналогии с этим компьютерные файлы объединяют в группы, для которых на компьютере создают папки. Таким образом, назначение папки состоит в объединении файлов и других папок в группы по любому параметру.
На сегодняшний день три понятия:
- каталог,
- директория,
- папка,
с точки зрения компьютерной грамотности, означают одно и то же, давайте уточним, что именно.
Папка или директория – это специальное место на компьютерном носителе информации, в котором хранятся имена файлов и сведения об этих файлах (размер файлов, время их последнего обновления, свойства файлов и т.п.)
Понятия «каталог», «директория» появились в компьютерном мире одновременно с понятиями «файл», «файловая система» для упрощения организации файлов. Понятие «папка» в мире компьютеров появилось значительно позднее, точнее, вместе с появлением Windows 95.
Можно придумать собственную систему для хранения файлов и папок на своем компьютере. Например, создать папки, где файлы сгруппированы:
по теме – папки «Обучающие программы», «Счета», «Рыбалка» и т.п., по имени автора материалов – папки «Мамонтов», «Воробьёва» и т.п.. по времени создания – папка «01.01-30.06.2010» с файлами, созданными с 1 января по 30 июня 2010г., папка «3 квартал 2010» и т.п.
Если имя файла хранится в папке с именем, например, 01, то говорят, что файл находится в папке 01. Ту же самую мысль можно выразить, если сказать, что файл зарегистрирован в каталоге 01. Обычно один и тот же файл (т.е. с одним и тем же именем) находится в одной папке, но при необходимости его можно хранить в нескольких папках, что можно легко сделать с помощью операции копирования.
Как назвать папку?
Все папки имеют имена. Требования к именам папок те же, что и к именам файлов. Единственное отличие состоит в том, что в имени папки расширение, как правило, не применяется, хотя при необходимости его можно использовать. В каждой папке могут храниться как файлы, так и другие папки, те, в свою очередь, тоже могут содержать файлы и папки и т.д.
Папки чем-то напоминают матрёшки. Про такие папки, находящиеся внутри других папок, говорят, что это вложенные папки. Папка, включающая в себя другие папки, называется родительской или охватывающей.
Если возле названия папки стоит «+», то это значит, что в этой папке есть еще папки и их можно открыть. Для этого надо щёлкнуть по «+» и он поменяется на «-», при этом под названием папки откроется список из папок, содержащихся в открываемой папке.
Если же щелкнуть по «-», то он превратится в «+», а список содержимого папки закроется.
Структура папок
Когда Вы открываете Проводник (Пуск—>Программы—>Стандартные—>Проводник), то видите там некое дерево, конечно, без зеленых листочков, потому что это компьютерное дерево. Дело в том, что если попробовать нарисовать общую структуру всех папок, находящихся на своем компьютере, то получится как раз дерево.
Такую структуру папок (каталогов) называют иерархической древообразной (или древовидной).
Обычно пользователи называют это просто дерево папок.
На каждом диске имеется главная, или корневая, папка (каталог), которая не имеет собственного имени и ее обозначают обратным слешем: \. Например, C:\ — корневая папка диска C, где «C:» — имя самого диска, а «\» — обозначение корневой папки.
Папки и файлы, которые зарегистрированы в корневой папке диска, имеют вложенность 1-ого уровня. Во вложенных папках 1-ого уровня регистрируются папки и файлы 2-ого уровня и т.д. В итоге как раз и получается дерево папок и файлов.
Помимо корневой папки диска, папок 1-го, 2-го и т.д. уровней вложенности, есть еще понятие текущей папки. Текущая папка – это папка, с которой в настоящий момент работает пользователь.
Если Вам понадобился файл не из текущей папки, необходимо указать в какой папке (папках) находится этот файл, то есть указать путь к файлу. По аналогии с матрешками файл является самой маленькой матрешкой, вложенной в матрешки бОльшего размера (папки). Чтобы указать полное имя файла (т.е. имя самой маленькой матрёшки), следует поименно назвать все матрешки бОльшего размера (папки).
Что такое полное имя файла
Полное имя файла начинается с указания имени дисковода, затем идет последовательность из имен папок и, наконец, имя файла.
Имя дисковода, имена папок и имя файла в полном имени разделяются символами « \ ».
Например, запись полного имени файла может выглядеть так: D:\Финансы\Счета\Счет-1.doc. Это означает, что файл с именем Счет-1.doc находится в папке Счета, которая в свою очередь находится в папке Финансы на диске D:.
Полный путь к файлу (или путь к файлу) – это часть полного имени, не включающая само имя файла. Путь к файлу Счет-1.doc выглядит так: D:\Финансы\Счета\.
Упражнение по компьютерной грамотности:
Напишите, как выглядит полное имя какого-нибудь файла, находящегося на вашем компьютере в папке «Мои документы»?
P.S. Статья закончилась, но можно еще прочитать:
Настройка вида папки
Как создать новую папку?
Управление папками
Окно папки Windows 7
Новая папка 7
Overview
In this article, we will delve into the Directory Structure in Operating Systems (OS) and its significance in organizing and retrieving files. We’ll explore what a directory is and how it stores related files. Additionally, we’ll discuss the operations that can be performed on directories and understand the different directory structures in OS that can help the user utilize the structure that best suits their requirements.
What is the Directory Structure in OS?
A directory is a container that stores files and folders, organizing them hierarchically. The Directory Structure in OS manages entries of files, including file names, locations, protection info, and more. This structure enables efficient file retrieval.
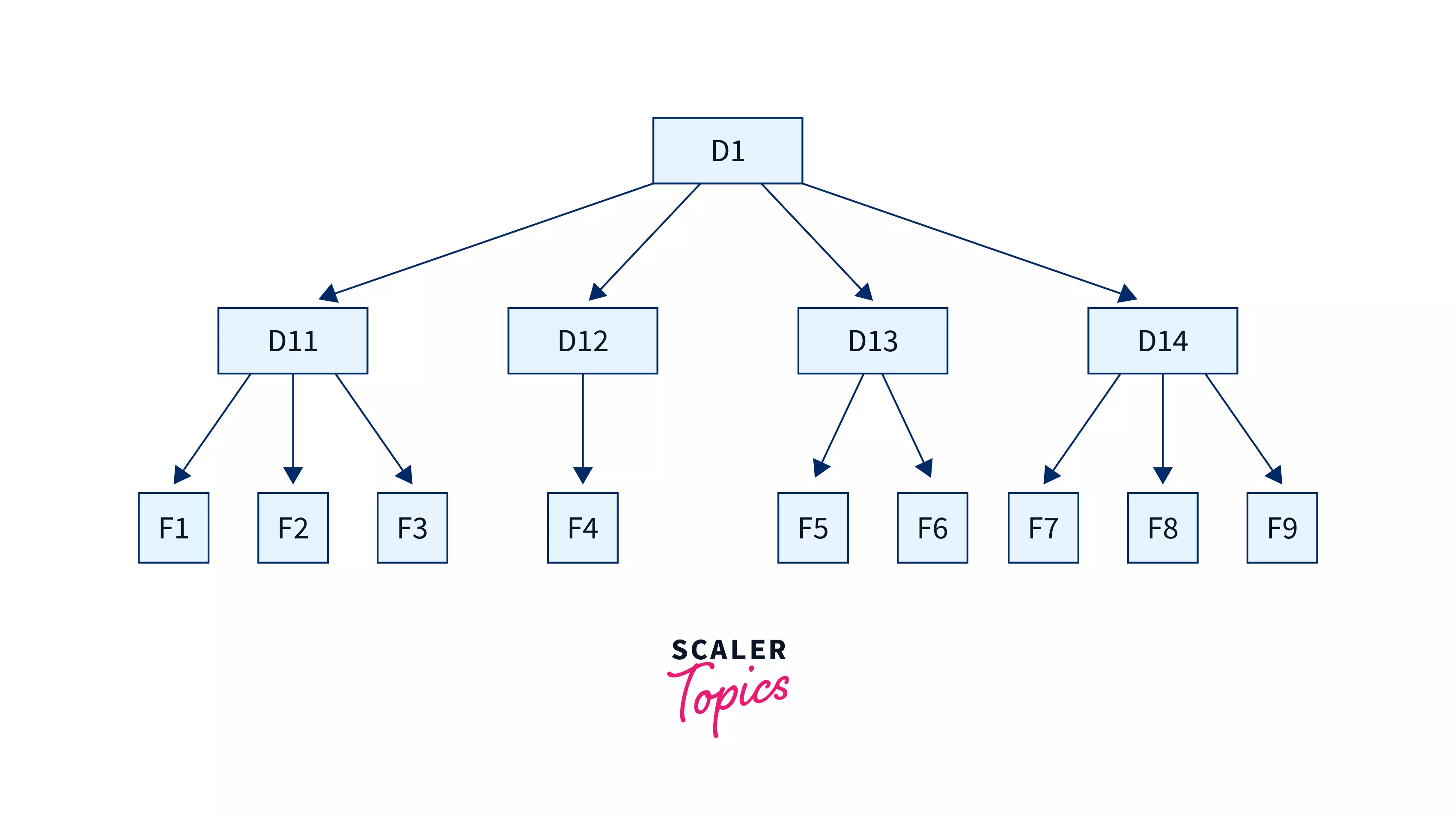
Points to Consider while Maintaining a Directory Structure in an Operating System:
- Users should be able to choose file names without restrictions, promoting flexibility.
- Collaboration is enhanced by allowing users to share and access files created by others.
Operations in Directory Structure in OS
- Creating: Users can create new files and directories, providing unique names for directories.
- Searching: Users can search for specific files or directories within a directory.
- Deleting: Unwanted files or empty directories can be deleted.
- Listing: Users can retrieve a list of files in a directory.
Renaming: Files and directories can be renamed to reflect content changes. - Linking: Files can be linked to appear in multiple directories.
- Unlinking: Removing links from files in multiple directories.
Directory Structure in OS is a fundamental aspect of managing files and ensuring efficient access in an operating system.
The Logical Directory Structures in OS
We have mainly five different types of directory structures in OS. Given below are all the five different directory structures and their sets of advantages and disadvantages along with pictorial representation to dive deeper:
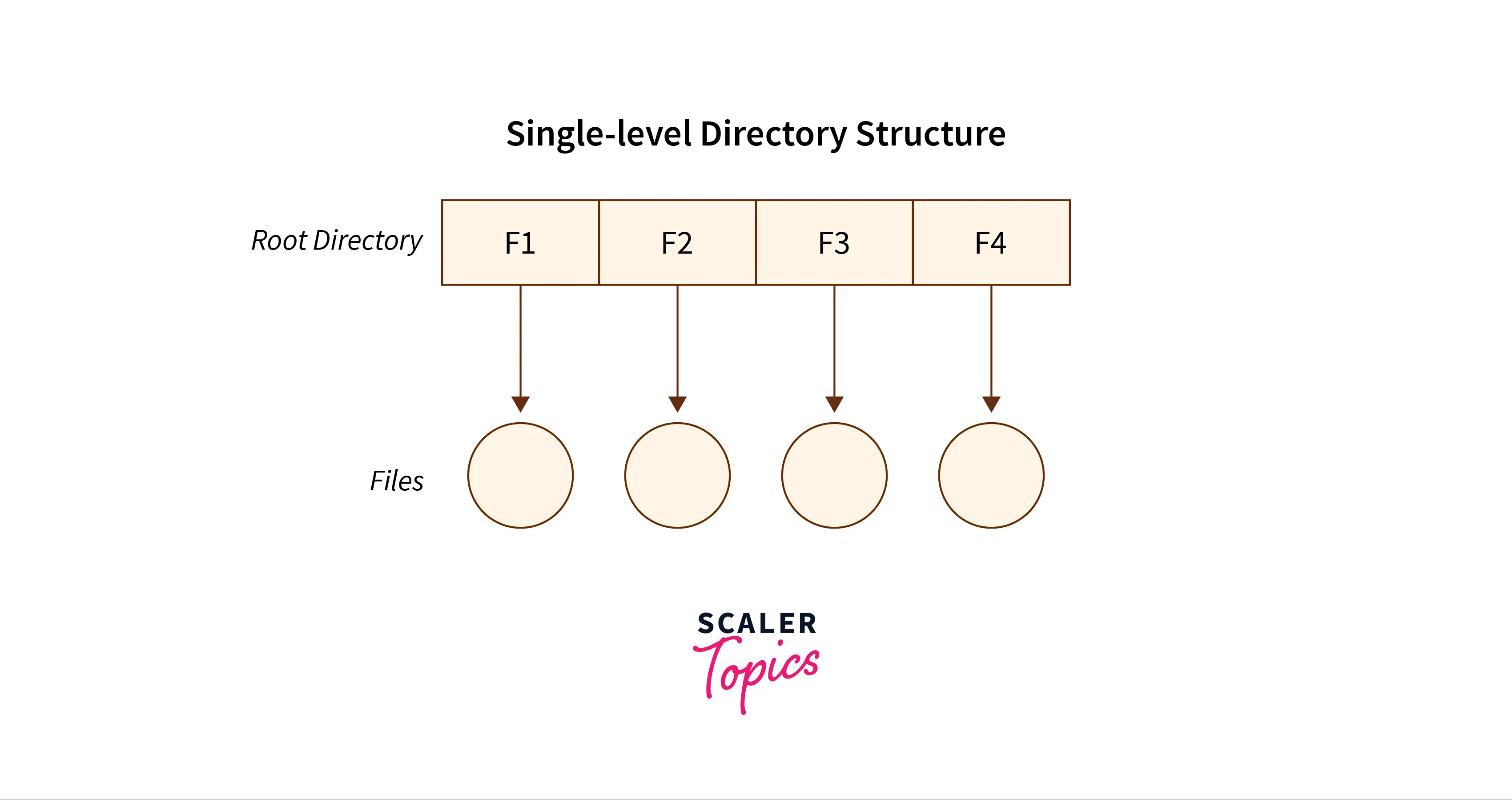
The Single-Level Directory Structure
The single-level directory structure is the simplest and easiest directory structure out of all the other directories. In this directory structure, all the folders/files are contained under the same directory which is called the root directory. The single-level directory structure gathers all the files under one directory or the root directory, this makes it easy to support and understand.
Now as the different files are under the same-root directory the users are not allowed to create the different sub-directories serving their requirements. This also creates a barrier with the single-level directory as when the number of files increases or more than one user logs into the system both of these need to maintain the standards of giving a unique name to it. This also means that if two users call their files ‘apple’, then this, in turn, will violate the unique name standardization.
Below is the pictorial representation of The Single-level directory structure in OS :
The Advantages
- The implementation of a single-level directory structure is simple and easier as compared to other directory structures in OS.
- If the file size is smaller, then the searching of such files with the single-level directory structure becomes simpler.
- The single-level directory structure allows the operations such as searching, creation, deletion and updating as well.
The Disadvantages
- As several users can log in at the same system to log their files maintaining a unique name becomes difficult leading to a collision. This also means that if the file with the same name is created then the old file will get destroyed first, then the new file (having the same name ) created will replace it.
- If the size of the files is bigger then searching the files in one root directory of the single-level directory structure will become time-consuming and hence difficult.
- The single-level directory structure restricts the grouping of the same type of files together.
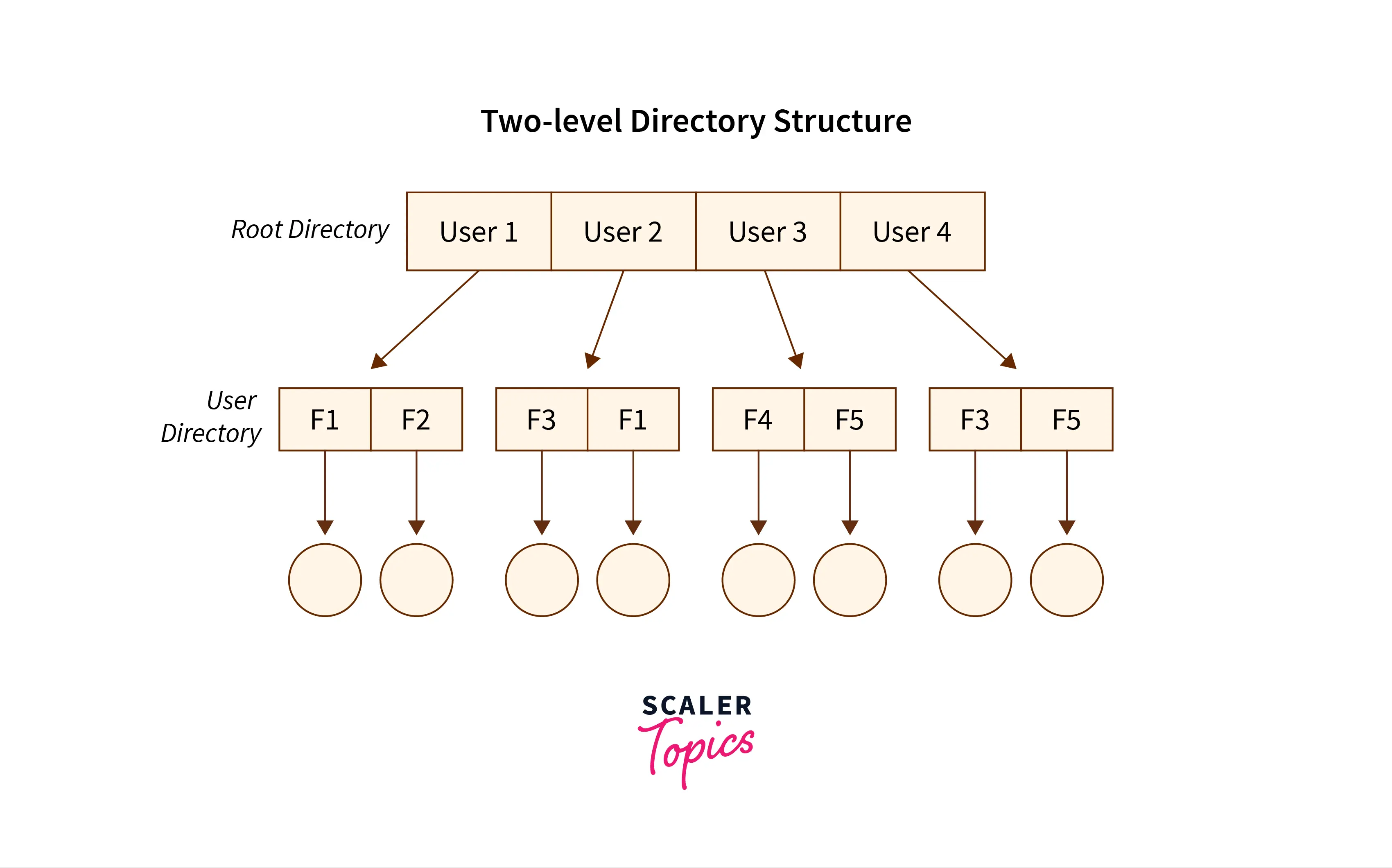
The Two-Level Directory Structure
Overcoming the drawbacks posed by the single-level directory structure, i.e., the confusion created by the same file names given by several users — The Two-level directory structure in OS came into the picture.
The two-level directory structure in OS offers a unique solution to the problem caused by single-level that is, this directory structure gives each user the right to have their own user files directory commonly called User File Directory(UFD). The User File Directory or UFD has a similar structure as that of the single level, but each UFD lists only the files of a single user who owns that UFD. To root all the UFDs, the system’s Master File Directory or (MFD) searches whenever a new user id’s logged into the directory structure.
This can also be defined as the two-level directory structure in OS which gives each of its users the right to create a directory directly inside the root directory. Here the directories created by the user are called the UFDs and to check who logged in as a user the Master File Directory or MFDs are responsible for the same.
Here the MFDs are indexed by username or account number which are pointed to the UFDs with each entry point of the user. In a two-level directory structure searching files becomes, even more, easier as there is only one user’s list, which is required to be traversed along with having a pathname for each file such as /User-name/directory-name/ which is also defined here.
Below is the pictorial representation of The Two-level directory structure in OS :
The Advantages:
- In the two-level directory structure in OS different users have the right to have the same directory as well as a file name as the user has its own USD which can give a filename that can match other users but won’t cause an issue.
- We can also see that searching for files become much simpler.
- As we have a user-defined directory this also provides privacy related to files stored as no user can enter the other user’s directory without permission.
- In a two-level directory structure we cannot group the files which are having the same name into a single directory for a specific user.
The Disadvantages:
- In a two-level directory structure a user is not allowed to share files with other users.
- We also find that scalability is not present in a two-level directory structure as two files of the same type cannot be grouped together in the same user.
- Here users cannot create subdirectories only one user file directory can be defined under one master file directory.
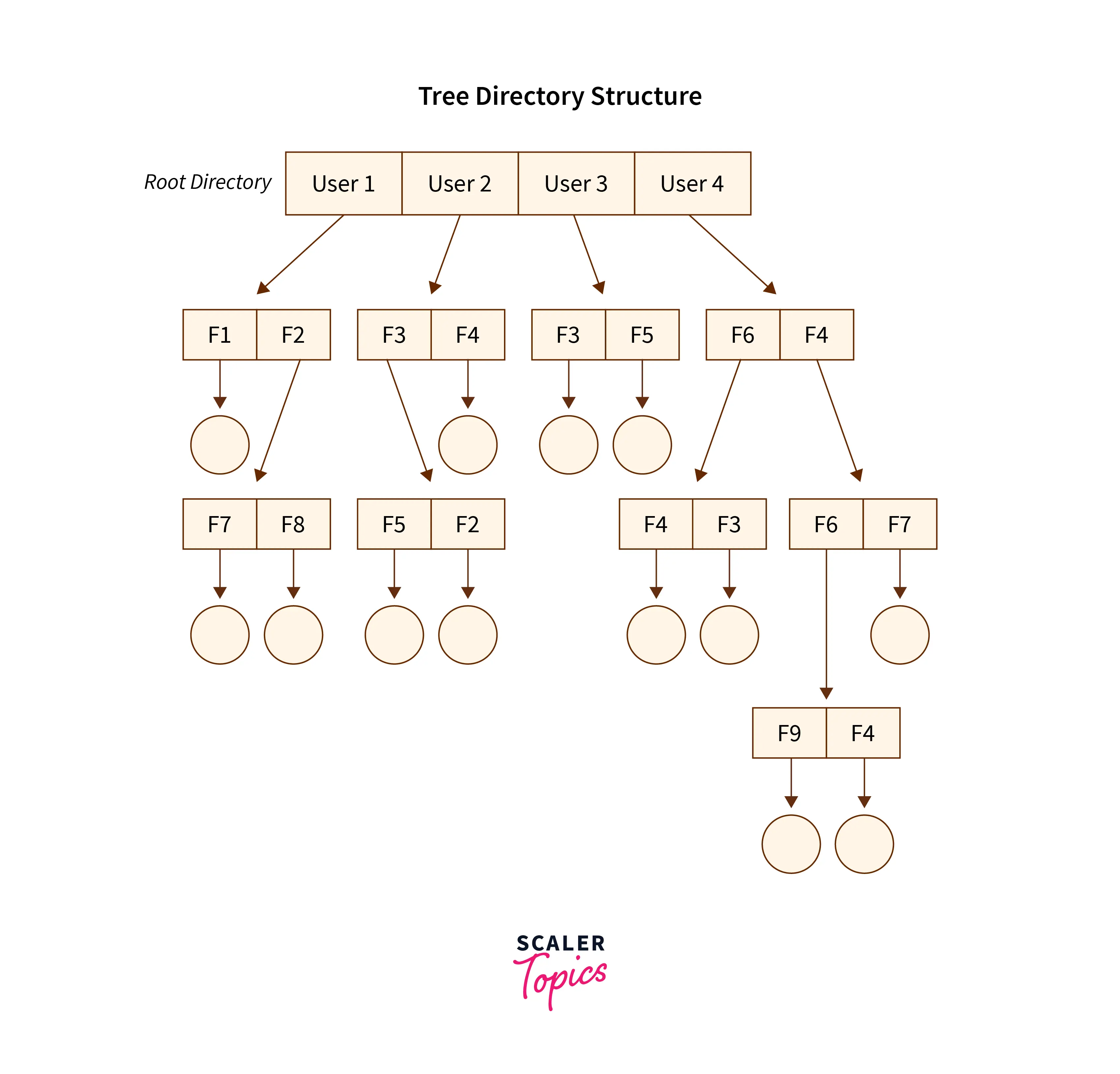
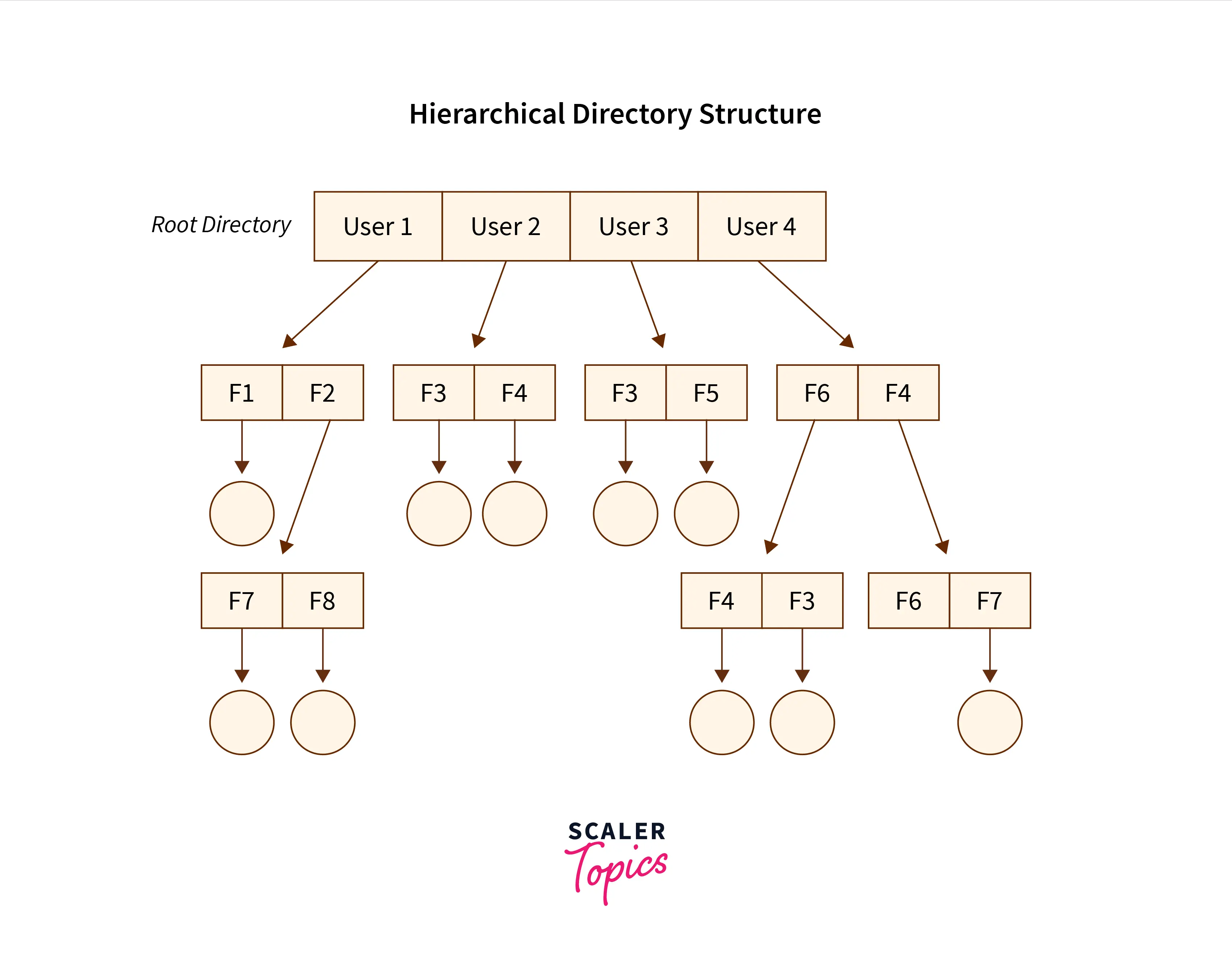
The Tree-Structured Directory Structure
As observed in the two-level directory structure in OS the drawback of users not having the ability to create sub-directories is resolved with The Tree-structured directory structure in OS coming into the picture.
The Tree-Structured directory structure in OS is said to be the most common directory structure among users as it gives the users the capability to create sub-directories under their defined directory. Here we have the natural generalization which extends the directory structure to a tree of arbitrary height whereas, in the case of two-level, it was the tree of two heights. This generalization in tree structure allows the user the ability to create their own subdirectories and organize their files accordingly.
The tree-structured directory structure has separate parent directories for the sub-directories owned by each of their specific users and the parent directories of the users are all under the master-root directory which makes it a tree structure. This helps in total separation between the users which provides complete naming freedom and privacy to users’ information.
The system administrator/ UFD admin only has full access to the root directory. In the Tree-structured directory structure searching is quite effective where we use the current working concept that is we can access the file by using two kinds of paths that are either absolute or relative.
Below is the pictorial representation of The Tree-structured directory structure in OS :
The Advantages:
- In the Tree-structured directory structure searching is quite effective where we use the current working concept that is we can access the file by using two kinds of paths that are either absolute or relative.
- Here we can group the same type of files into one directory.
- In this directory structure the chances of collision of names/types etc are less and hence we can say that the directory structure in OS is scalable.
The Disadvantages:
- In the tree-structure directory structure in OS the files cannot be shared between users. Also, the users cannot modify/update the root directory of other users.
- This directory structure in OS as we have to go under multiple directories to access a file we can say that it is said to be inefficient.
- Here each file does not fit into the hierarchal model and so we have to save the files into multiple directories.
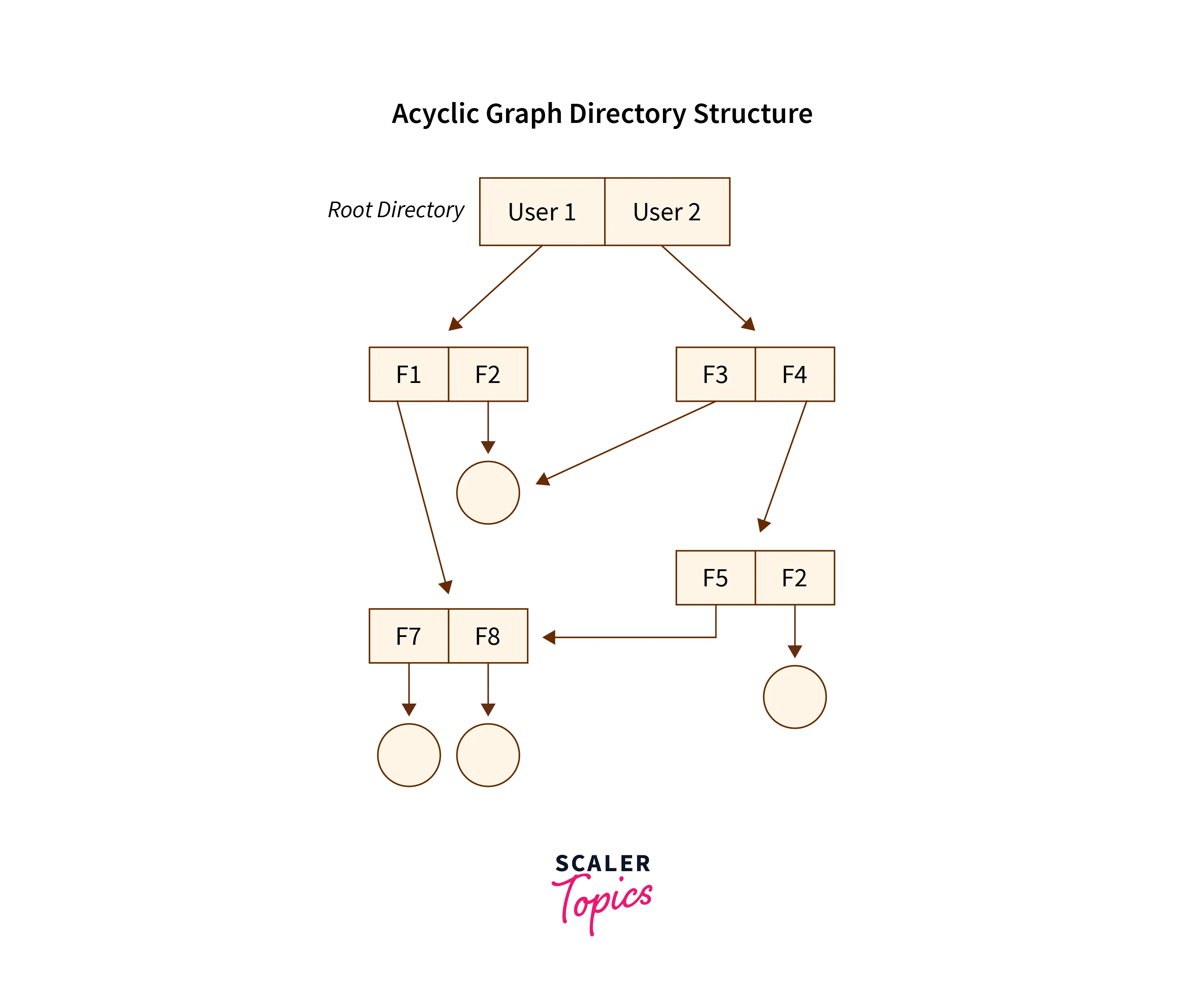
The Acyclic Graph Directory Structure
Overcoming the drawbacks posed by the tree-structured directory structure,i.e, the restriction that it cannot have multiple parent directories and also cannot share files between users — The Acyclic Graph directory structure in OS came into the picture.
In the Acyclic Graph directory structure in OS can be defined as the directory structure that allows a directory or a file to have multiple parent directories so that it can be a shared file in a directory that gets pointed by the other user directories which if has the access to that shared file via the links provided to it. It is often said to be a natural generalization of the tree-structured directory.
Mostly, this is used in situations such as, when two users or two programmers are collaborating on a project and they need to access the files. So we have the associated files which are stored in a subdirectory mostly separated from other projects and files of other programmers/users. Now as they are working on a joint project they want the sub-directories to be present in their own directories. Therefore these common sub-directories where two or more users can collaborate would be shared so that the files can be stored in their individual locations and this is where we use Acyclic directories.
There must be a point noted here that the shared file is not the exact copy file, that is if any programmer/user makes some changes in the sub-directory that change will be reflected in both subdirectories. Here we can (with the help of aliases or links) create the acyclic type of directory graph where we can also provide different paths to the same file. We define the Links into two kinds, popularly known as The Hard Link and The Symbolic Link.
a. The Hard Link: This is also called as the physical link. If we want to delete the files in the acyclic graph directory structures then we need to remove the actual files only if all the references to the files are deleted that is, no link that even references the main file should be established. Here we don’t leave a suspended link.
b. The Symbolic/Soft-Link: This is also called as the logical link. If we want to delete the files in the acyclic graph directory structures then we need to simply delete the files and need to keep in mind that only a dangling/ hanging point is left. Here we leave a suspended link.
Below is the pictorial representation of The Acyclic graph directory structure in OS :
The Advantages:
- In the Acyclic Graph directory structure in OS we can share files between users.
- Here we can search the files easily as compared to the tree-structured directory structure as here we have different-different paths to one file.
The Disadvantages:
- In the Acyclic Graph directory structure in OS as we can share the files via linking, so there are chances that in the case when we want to delete a file in a directory it may create a problem.
a. Also, even if the link is a soft link then after deleting the file we are left with a dangling/suspended point of the link.
b. But in the case of hardlink, when we delete a file we have to vanish all the references associated with it, which can lead to issues associated with referring back to files in case a requirement arises.
The General Graph Directory Structure
As observed in the acyclic-graph directory structure in OS the drawback of links that are established and need to be either terminated or suspended to reach the files/directory is resolved with The General Graph directory structure in OS taking a vital place in the different types of a directory structure in OS.
In the General Graph directory structure in OS users have the capability to create a cycle of the directory within a directory where we have the power to derive the various directories with the help of more than one parent directory in operating systems. In this type of structure, the users are free to create directories under the root directory along with creating sub-directories under the same structure which can also hold true if the users want to create multiple sub-directories that is, the users are free to create different sub-directories for different file types.
Adding to the above, With the help of the file paths if the users feel the need to access the location of the files then that is made possible by the General Graph Directory Structure. In this structure, the file paths or paths can be categorized into two broad categories to locate the files in the directory structure as below :
-
The Absolute Path: Here, the path of the desired files can be determined by considering the root directory as the base directory.
-
The Relative Path: Here, the path of the desired files can be determined by two choices that are, either the file that needs to be retrieved from its directory is considered the base directory, or the user’s directory is considered as the base directory.
Below is the pictorial representation of The General Graph directory structure in OS :
The Advantages:
- The General Graph directory structure allows the cycle or creation of a directory within a directory.
- This directory structure is known to be a flexible version compared to other directory structures.
The Disadvantages:
- The main issue that can overpower this structure is to calculate the total size or space that the directories will take up.
- As this directory structure allows the creation of multiple sub-directories a lot of garbage collection can be required.
- If compared to the other directory structure in OS the General Graph directory structure is a costly structure to be chosen.
Conclusion
-
The Single-level directory structure in OS is the simplest and easiest directory as all the files are under one directory specifically the root directory.
-
The Two-level directory structure in OS gives each of its users the right to create a directory directly inside the root directory.
-
In the Tree-Structured directory structure in OS among users it gives the users the capability to create sub-directories under their defined directory which helps them in compartmentalizing their files/folders well.
-
In the Acyclic Graph directory structure in OS can be defined as the directory structure that allows a directory or a file to have multiple parent directories
-
In the General Graph directory structure in OS users have the capability to create a cycle of the directory within a directory
Файловая структура операционной системы (ОС) — это организация файлов и папок на компьютере или другом устройстве. Понимание основных принципов файловой структуры позволяет пользователям эффективно управлять своими данными и файлами. В этой статье мы рассмотрим основы файловой структуры ОС и как она влияет на вашу работу с компьютером.
Файлы и Папки
Файлы и папки являются основными элементами файловой структуры. Все данные на компьютере хранятся в файлах. Файлы могут быть текстовыми, изображениями, видео, аудио или другими типами данных. Папки служат для организации файлов. Вы можете представить папки как контейнеры, в которых вы можете размещать файлы для удобства их хранения и поиска.
Иерархическая Структура
Файловая структура организована по иерархическому принципу. Это значит, что папки могут содержать в себе другие папки и файлы. Эта иерархия позволяет создавать структуру каталогов, которая удовлетворяет вашим потребностям в организации данных.
Пример иерархии файловой структуры:
«`
Корневая Папка
├── Документы
│ ├── Рабочие
│ │ ├── Проект1.docx
│ │ ├── Проект2.docx
│ │ └── …
│ ├── Личные
│ ├── …
├── Изображения
├── Музыка
├── Видео
└── …
«`
В этом примере «Корневая Папка» — это верхний уровень иерархии. Она содержит в себе папки «Документы», «Изображения», «Музыка», «Видео» и другие. Папка «Документы» далее разделена на подпапки «Рабочие» и «Личные», которые, в свою очередь, содержат различные файлы.
Путь к Файлам
Для доступа к файлам и папкам в файловой структуре используется путь. Путь — это уникальный адрес, который позволяет ОС найти нужный файл или папку. Путь включает в себя имена всех папок, которые нужно пройти, начиная с корневой папки, чтобы достичь нужного элемента.
Примеры путей к файлам:
— `C:\Документы\Рабочие\Проект1.docx` (путь к файлу «Проект1.docx» на диске C)
— `/Пользователи/ИмяПользователя/Изображения/Фотография.jpg` (путь к файлу «Фотография.jpg» на компьютере Mac)
Работа с Файлами и Папками
Для работы с файлами и папками в файловой структуре ОС вы можете выполнять следующие действия:
1. Создание: Вы можете создавать новые папки и файлы для организации и хранения данных.
2. Копирование и Вставка: Вы можете копировать файлы и папки и вставлять их в другие места в файловой структуре.
3. Перемещение: Вы можете перемещать файлы и папки из одной папки в другую.
4. Переименование: Вы можете изменять имена файлов и папок,
чтобы их легче было идентифицировать.
5. Удаление: Вы можете удалять файлы и папки, которые больше не нужны. Будьте осторожны, потому что удаленные файлы могут быть восстановлены только из резервной копии, если они не в корзине.
6. Поиск: Вы можете использовать функцию поиска, чтобы быстро найти нужные файлы и папки.
Работа с Файловой Структурой ОС
В зависимости от операционной системы, которую вы используете (например, Windows, macOS, Linux), существуют различные способы управления файловой структурой. Обычно вы можете воспользоваться проводниками (в Windows), Finder (в macOS), или командной строкой (в Linux) для выполнения операций с файлами и папками.
Заключение
Понимание основ файловой структуры операционной системы помогает пользователям эффективно организовывать и управлять своими данными. Независимо от вашего уровня опыта, умение правильно работать с файлами и папками полезно в повседневной работе с компьютером. Надеемся, что эта статья помогла вам лучше понять основы файловой структуры и сделала вашу работу с компьютером более комфортной.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In computing, a directory is a file system cataloging structure that contains references to other computer files, and possibly other directories. On many computers, directories are known as folders or drawers,[1] analogous to a workbench or the traditional office filing cabinet. The name derives from books like a telephone directory that lists the phone numbers of all the people living in a certain area.
Files are organized by storing related files in the same directory. In a hierarchical file system (that is, one in which files and directories are organized in a manner that resembles a tree), a directory contained inside another directory is called a subdirectory. The terms parent and child are often used to describe the relationship between a subdirectory and the directory in which it is cataloged, the latter being the parent. The top-most directory in such a filesystem, which does not have a parent of its own, is called the root directory.
The freedesktop.org media type for directories within many Unix-like systems – including but not limited to systems using GNOME, KDE Plasma 5, or ROX Desktop as the desktop environment – is «inode/directory».[2] This is not an IANA registered media type.
Historically, and even on some modern embedded systems, the file systems either had no support for directories at all or had only a «flat» directory structure, meaning subdirectories were not supported; there was only a group of top-level directories, each containing files. In modern systems, a directory can contain a mix of files and subdirectories.
A reference to a location in a directory system is called a path.
In many operating systems, programs have an associated working directory in which they execute. Typically, file names accessed by the program are assumed to reside within this directory if the file names are not specified with an explicit directory name.
Some operating systems restrict a user’s access only to their home directory or project directory, thus isolating their activities from all other users. In early versions of Unix, the root directory was the home directory of the root user, but modern Unix usually uses another directory such as /root for this purpose.
In keeping with Unix philosophy, Unix systems treat directories as a type of file.[3] Caveats include not being able to write to a directory file except indirectly by creating, renaming, and removing file system objects in the directory and only being able to read from a directory file using directory-specific library routines and system calls that return records, not a byte-stream.[4]
The name folder, presenting an analogy to the file folder used in offices, and used in a hierarchical file system design for the Electronic Recording Machine, Accounting (ERMA) Mark 1 published in 1958[5] as well as by Xerox Star,[6] is used in almost all modern operating systems’ desktop environments. Folders are often depicted with icons that visually resemble physical file folders.
There is a difference between a directory, which is a file system concept, and the graphical user interface metaphor that is used to represent it (a folder).[original research?] For example, Microsoft Windows uses the concept of special folders to help present the contents of the computer to the user in a fairly consistent way that frees the user from having to deal with absolute directory paths, which can vary between versions of Windows, and between individual installations. Many operating systems also have the concept of «smart folders» or virtual folders that reflect the results of a file system search or other operation. These folders do not represent a directory in the file hierarchy. Many email clients allow the creation of folders to organize email. These folders have no corresponding representation in the filesystem structure.
If one is referring to a container of documents, the term folder is more appropriate. [citation needed] The term directory refers to the way a structured list of document files and folders are stored on the computer. The distinction can be due to the way a directory is accessed; on Unix systems, /usr/bin/ is usually referred to as a directory when viewed in a command line console, but if accessed through a graphical file manager, users may sometimes call it a folder.
|
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (December 2013) |
Operating systems that support hierarchical filesystems (practically all modern ones) implement a form of caching to RAM of recent path lookups. In the Unix world, this is usually called Directory Name Lookup Cache (DNLC), although it is called dcache on Linux.[7]
For local filesystems, cache entries normally expire only under pressure from other more recent entries. For network file systems a coherence mechanism is necessary to ensure that entries have not been invalidated by other clients.[7]
- File folder
|
|
- ^ «Chapter 1: Tutorial». Using The AMIGA Workbench. Commodore-Amiga. July 1991. p. 46.
The path specifies the disk name, or location, and all of the drawers that lead to the specified file.
- ^ Leonard, Thomas (2018-10-02). «Shared MIME-info Database». X Desktop Group. Non-regular files. Retrieved 2023-03-13.
- ^ «Everything is a File». Behavior Genetics Association. c. 2002. Archived from the original on March 10, 2012. Retrieved April 30, 2021.
- ^ «readdir(3) — Linux manual page». The Linux man-pages project. 2021-03-22. Retrieved November 27, 2022.
- ^ Barnard III, G. A.; Fein, L. (1958). «Organization and Retrieval of Records Generated in a Large-Scale Engineering Project». Proceedings of the Eastern Joint Computer Conference: 59–63. doi:10.1109/AFIPS.1958.75.
- ^ ««Xerox Star User Interface (1982)»«. YouTube. 28 August 2009. Archived from the original on 2021-12-21. Retrieved 19 November 2014.
- ^ a b «Close-To-Open Cache Consistency in the Linux NFS Client». Citi.umich.edu. Retrieved 19 November 2014.
- Definition of directory by The Linux Information Project (LINFO)
Файловая система. Папки и файлы. Имя, тип, путь доступа к файлу.
Файл.
Все
программы и данные хранятся в долговременной
(внешней) памяти компьютера в виде
файлов.
Файл
— это определенное количество информации
(программа или данные), имеющее имя и
хранящееся в долговременной (внешней)
памяти.
Имя
файла состоит из двух частей, разделенных
точкой: собственно имя файла и расширение,
определяющее его тип (программа, данные
и т. д.). Собственно имя файлу дает
пользователь, а тип файла обычно задается
программой автоматически при его
создании.
|
Тип |
Расширение |
|
Исполняемые |
exe, |
|
Текстовые |
txt, |
|
Графические |
bmp, |
|
Web-страницы |
htm, |
|
Звуковые |
wav, |
|
Видеофайлы |
avi, |
|
Код |
bas, |
В
различных операционных системах
существуют различные форматы имен
файлов. В операционной системе MS-DOS
собственно имя файла должно содержать
не более восьми букв латинского алфавита
и цифр, а расширение состоит из трех
латинских букв, например: proba.txt
В
операционной системе Windows имя файла
может иметь до 255 символов, причем
допускается использование русского
алфавита, например:
Единицы
измерения информации.doc
Файловая
система.
На
каждом носителе информации (гибком,
жестком или лазерном диске) может
храниться большое количество файлов.
Порядок хранения файлов на диске
определяется установленной файловой
системой.
Файловая
система — это система хранения файлов
и организации каталогов.
Для
дисков с небольшим количеством файлов
(до нескольких десятков) удобно применять
одноуровневую файловую систему, когда
каталог (оглавление диска) представляет
собой линейную последовательность имен
файлов.
Если
на диске хранятся сотни и тысячи файлов,
то для удобства поиска файлы организуются
в много уровневую иерархическую файловую
систему, которая имеет «древовидную»
структуру.
Начальный,
корневой, каталог содержит вложенные
каталоги 1-го уровня, в свою очередь, в
каждом из них бывают вложенные каталоги
2-го уровня и т. д. Необходимо отметить,
что в каталогах всех уровней могут
храниться и файлы.
Путь
к файлу.
Для
того чтобы найти файл в иерархической
файловой структуре необходимо указать
путь к файлу. В путь к файлу входят
записываемые через разделитель «\»
логическое имя диска и последовательность
имен вложенных друг в друга каталогов,
в последнем из которых находится данный
нужный файл.
Например,
путь к файлам на рисунке можно записать
так:
C:\basic\
C:\Музыка\Пикник\
Полное
имя файла.
Путь
к файлу вместе с именем файла называют
полным именем файла.
Пример
полного имени файлов:
C:\basic\prog123.bas
C:\Музыка\Пикник\Иероглиф.mp3
Операции
над файлами.
В
процессе работы на компьютере над
файлами чаще всего производятся следующие
операции: копирование (копия файла
помещается в другой каталог); перемещение
(сам файл перемещается в другой каталог);
удаление (запись о файле удаляется из
каталога); переименование (изменяется
имя файла).
Графическое
представление файловой системы.
Иерархическая
файловая система MS-DOS, содержащая каталоги
и файлы, представлена в операционной
системе Windows с помощью графического
интерфейса в форме иерархической системы
папок и документов. Папка в Windows является
аналогом каталога MS-DOS. Однако иерархические
структуры этих систем несколько
различаются. В иерархической файловой
системе MS-DOS вершиной иерархии объектов
является корневой каталог диска, который
можно сравнить со стволом дерева — на
нем растут ветки (подкаталоги), а на
ветках располагаются листья (файлы).
В
Windows на вершине иерархии папок находится
папка Рабочий стол. (Следующий уровень
представлен папками Мой компьютер,
Корзина и Сетевое окружение (если
компьютер подключен к локальной сети).
9.
Представление данных в памяти персонального
компьютера (числа, символы (symbol), графика,
звук).
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
