Глобальный каталог Active Directory (Global catalog) очень часто называют шестой ролью FSMO и это имеет под собой некоторый смысл. Дело в том, что фактически глобальный каталог ролью FSMO являться не может хотя бы по причине того, что эту роль может в конкретный момент времени держать как один контроллер домена, так и все контроллеры домена леса враз. В то время как роли Flexible single-master operations может размещать на себе только один DC и если вдруг в лесу каким-то образом окажутся например два хозяина схемы, это непременно приведет к катастрофе.
Но почему же все-таки “шестая роль fsmo”? Подобное определение, на мой взгляд, могли дать только по одной причине – чтобы подчеркнуть важность этой роли для работы всего леса AD. Задача размещения на сервере глобального каталога действительно является очень важной для нормального функционирования не только служб AD DS, но и ряда других доменнозависимых сервисов, например Exchange Server.
В этой статье я постараюсь пролить свет на задачи и принцип работы серверов глобального каталога, ведь о них периодически совершенно не заслуженно забывают.
Основная статья по Active Directory – Active Directory Domain Services. Читайте также другие статьи по ролям хозяев операций – FSMO — Fexible Single Master Operations.
Если вам интересна тематика Windows Server, рекомендую обратиться к рубрике Windows Server на моем блоге.
Содержание
- 1 Global catalog – Теория
- 1.1 Назначение
- 1.2 UPN
- 1.3 Универсальные группы
- 1.4 Краткие выводы
- 2 Лучшие практики
- 3 Администрирование
- 3.1 Добавить роль GC для КД
- 3.2 Добавление UPN-суффикса
- 3.3 Создание дополнительного атрибута
- 3.4 SRV-запись GC в DNS
- 3.5 Проверка готовности GC
Начнем с теории.
Назначение
Как и было сказано выше, глобальным каталогом могут быть одновременно несколько (или даже все враз) контроллеров домена в лесу. В средах со сложной иерархией доменов и множеством DC необходимо обеспечить приемлемое быстродействие повседневного функционала, например поиска объектов леса. Обычный рядовой контроллер домена хранит у себя полную реплику объектов своего домена, но не других доменов леса. То есть, чтобы найти, например, пользователя из домена А, контроллер домена В должен обратиться к одному из DC домена А для выполнения операции поиска, но такая операция однозначно займет сравнительно продолжительное время, тем более если все контроллеры домена А территориально располагаются совсем в другом месте и к тому же с не самым хорошим каналом связи.
Чтобы иметь возможность быстро выполнить поиск объектов из других доменов, к вам на помощь приходит глобальный каталог, который хранит у себя частичные реплики данных всего леса, помимо БД с объектами собственного домена.
Сказанное выше лучше всего иллюстрирует изображение из официальной документации 1:
Как видно из рисунка, контроллер домена А, он же и глобальный каталог (сервер справа), содержит частичные реплики доменов B, C, D. Таким образом, для выполнения операции поиска пользователей домена D (или любого другого) сотрудником из домена A, даже не придется обращаться к контроллерам домена D, ведь вся информация уже доступна на сервере глобального каталога его родного домена A. Это также справедливо по отношению к поиску 2 любых объектов, которые опубликованы в AD 3 (пользователи, компьютеры, файлы, принтеры, службы).
Поиск объектов, пожалуй, одна из самых важных и частых задач, но есть и другие, в которых главную роль выполняет именно глобальный каталог. Например он участвует в процессе проверки подлинности с помощью основного имени пользователя (User principal name – UPN – имя, которое выглядит как e-mail пользователя).
UPN
Насколько известно, в доменах могут быть заданы альтернативные – дополнительные – “имена доменов”. Это может потребоваться для упрощения входа пользователей или для повышения безопасности. Если у вас уже несколько UPN-суффиксов, для каждой конкретной учетной записи вы можете определить суффикс при создании учетки или в свойствах уже созданной:
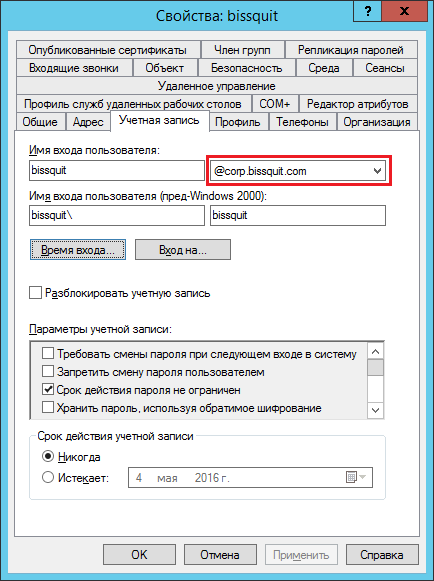
Чтобы пользователь bissquit@corp.bissquit.com мог залогиниться на рабочей станции домена dev.corp.bissquit.com, контроллеры домена dev.corp.bissquit.com должны иметь доступ к глобальному каталогу, чтобы проверить подлинность пользователя и предоставленные ему разрешения (разумеется этот пользователь должен иметь права для локального входа на данную рабочую станцию).
Универсальные группы
Global catalog предоставляет сведения о членстве пользователя в универсальных группах в мультидоменной среде. При попытке пользователя залогиниться, контроллер домена, через который проходит процесс авторизации, формирует токен, содержащий идентификаторы (SID’ы) всех групп, в которые включена учетная запись пользователя. В свою очередь, получить сведения о членстве учетной записи в универсальных группах, контроллер домена может только у глобального каталога 4. Иначе процесс аутентификации в домене с универсальными группами не пройдет (при этом о членстве в других типах групп известно и обычным контроллерам домена).
Если глобальный каталог недоступен при входе в домен с уровнем функциональности основного режима Windows 2000 или более высокого, то для пользователя, уже выполнявшего вход в домен, будут использоваться кэшированные учетные данные. Если пользователь еще не входил в домен, он может выполнить вход только на локальный компьютер. Однако вход в домен в качестве администратора (учетная запись «Встроенный администратор») всегда разрешен, даже если глобальный каталог недоступен.
Дополнительные сведения об универсальных группах см. в разделе Область действия группы. Дополнительные сведения об универсальных группах и о репликации см. в разделах Репликация глобального каталога и Глобальные каталоги и сайты.
Как было сказано выше, некоторые приложения очень сильно зависят от доступности глобального каталога. Например Exchange Server извлекает информацию о получателях именно через GC.
Краткие выводы
Сделаем вывод из сказанного выше, а также дополним информацию некоторыми другими фактами:
- При установке AD DS на первом контроллере домена в лесу, этот же контроллер становится и глобальным каталогом;
- Данные глобального каталога (частичные реплики других доменов леса) распространяются через механизм репликации;
- Доступность глобального каталога сильно зависит от сервисов DNS, поскольку при запуске контроллера или при окончании начальной репликации, netlogon публикует SRV-записи, указывающие, что этот сервер является сервером глобального каталога. Впоследствии клиенты узнают о существовании этого сервера GC именно из сведений DNS;
- Глобальный каталог осуществляет “связь” одного домена леса с другими – выполняет поиск объектов в других доменах, участвует в процессе аутентификации пользователей других доменов на своих рабочих станциях, определяет членство в универсальных группах, разрешает UPN-имена.
Из всего этого следует вывод, что глобальный каталог особенно важен, если речь идет о многодоменной инфраструктуре.
Примечание: для лесов с одним доменом, тем не менее, глобальный каталог все также нужен. Помимо приложений, жестко завязанных на GC, он необходим и для нормальной работы пользователей. Подробнее см. в блоге Ask the Directory Services Team, вопрос “If I have only one domain in my forest, do I need a Global Catalog? Plenty of documents imply this is the case.”.
Далее перейдем к лучшим практикам администрирования.
Лучшие практики
Для целей отказоустойчивости крайне важно держать глобальным каталогом как минимум несколько контроллеров домена. Будет лучше, если в каждом домене будет минимум по одному GC. Тем не менее, если у вас есть возможность, лучше сделать серверами Global catalog все DC в лесу. Это положительно скажется ещё и на балансировке нагрузки, не говоря уже о том, что с этого момента можно будет практически не заботиться о FSMO-роли хозяин инфраструктуры (подробнее см. в статье ).
Если все же не получается сделать все DC серверами глобального каталога, то позаботьтесь о том, чтобы сервер-владелец роли хозяин инфраструктуры не располагался на сервере глобального каталога, иначе это приведет к остановке его функционирования (фантомные записи не будут создаваться/изменяться) и как следствие – появлению неактуальных данных.
Администрирование
Некоторые базовые задачи администрирования, связанные с GC, рассмотрены ниже.
Добавить роль GC для КД
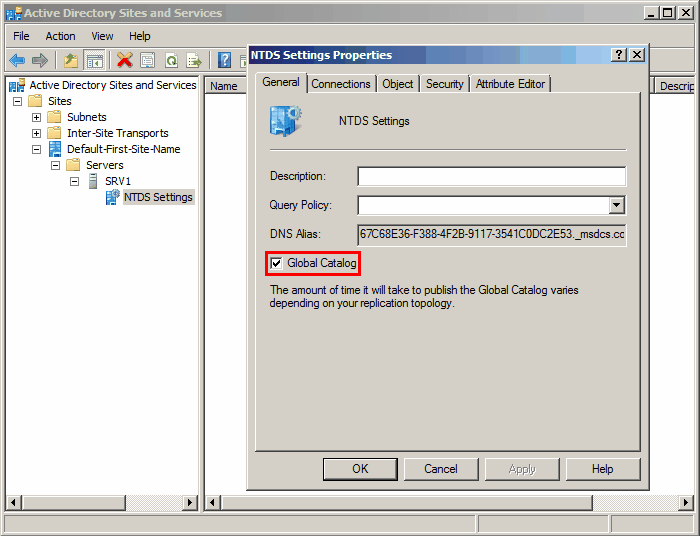
Сделать 5 сервер глобальным каталогом вы можете из оснастки Active Directory — сайты и службы 6. Для этого откройте оснастку, найдите контроллер домена (1), который хотите сделать сервером GC и нажмите правой кнопкой на NTDS Settings (2) нужного вам сервера, открыв свойства:
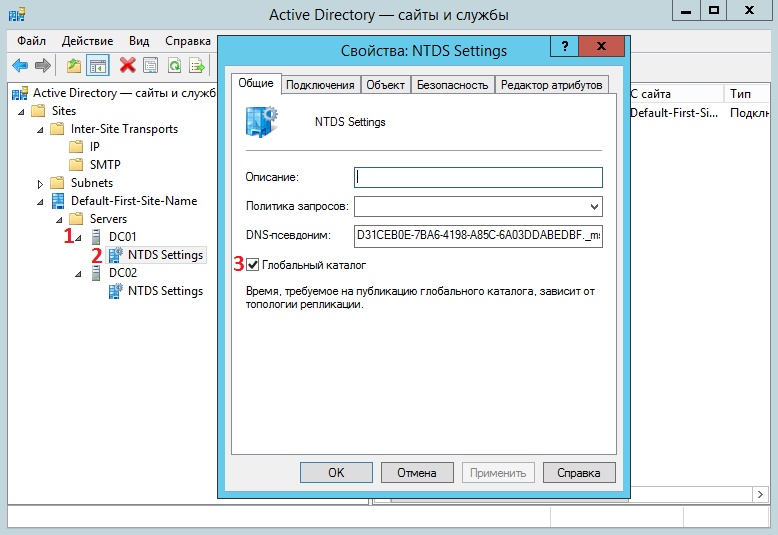
Откроется окно свойств и на вкладке Общие вам необходимо поставить галочку рядом с Глобальный каталог. Как только репликация данных глобального каталога завершится, через SRV-запись он объявит себя сервером GC.
Добавление UPN-суффикса
Выше я упоминал об UPN-суффиксах. Чтобы добавить дополнительные суффиксы 7, нужно зайти в оснастку Active Directory – домены и доверие. Далее – нажать правой кнопкой на имя оснастки и зайти в свойства:
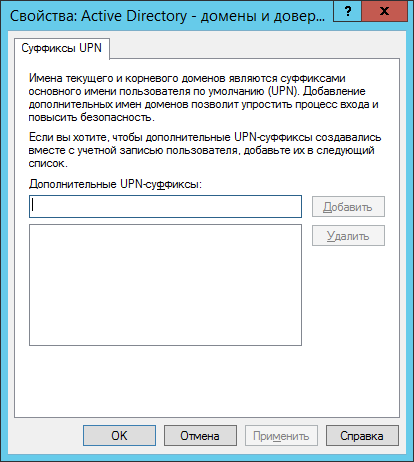
Тут вы сможете добавить дополнительные UPN-суффиксы и уже при создании/изменении учетных записей пользователей выбирать нужные.
Создание дополнительного атрибута
Также есть возможность создания собственных 8 9 атрибутов AD. Сделать это можно через оснастку Схема Active Directory (подробнее см. в статье Schema master — Хозяин схемы Active Directory):
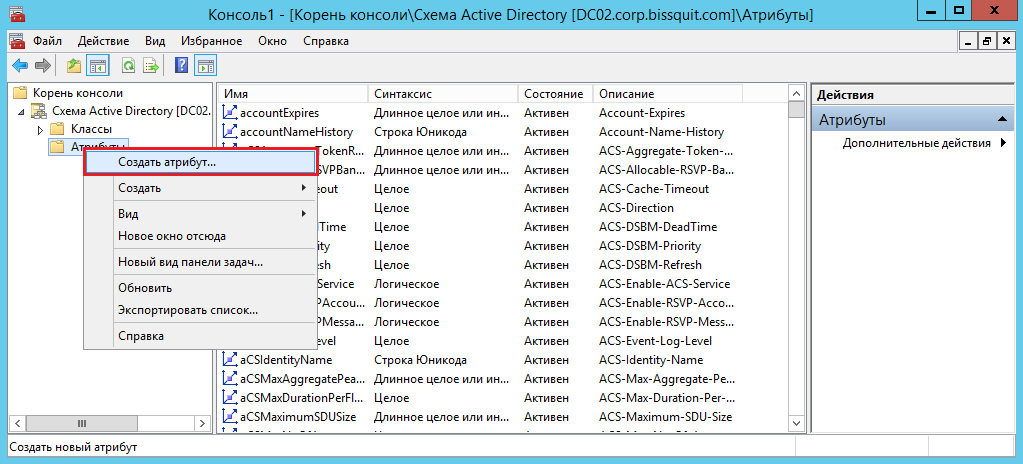
Разумеется при любых изменениях схемы необходимо проявлять осторожность и четко понимать к чему могут привести те или иные действия, в противном случае лучше не лезьте
SRV-запись GC в DNS
Проверить регистрацию 10 серверов глобального каталога в DNS вы можете в соответствующей оснастке в контейнере _tcp зоны прямого просмотра вашего домена:
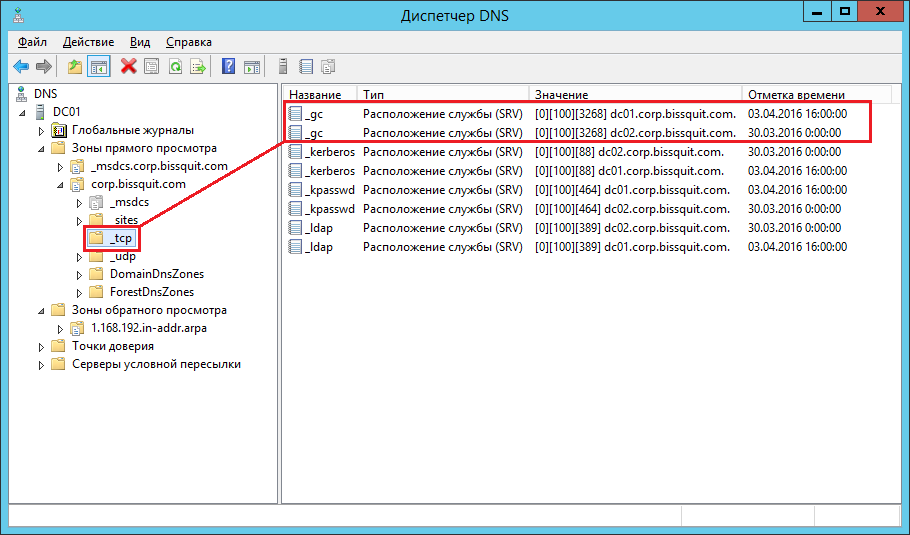
Ну и последнее.
Проверка готовности GC
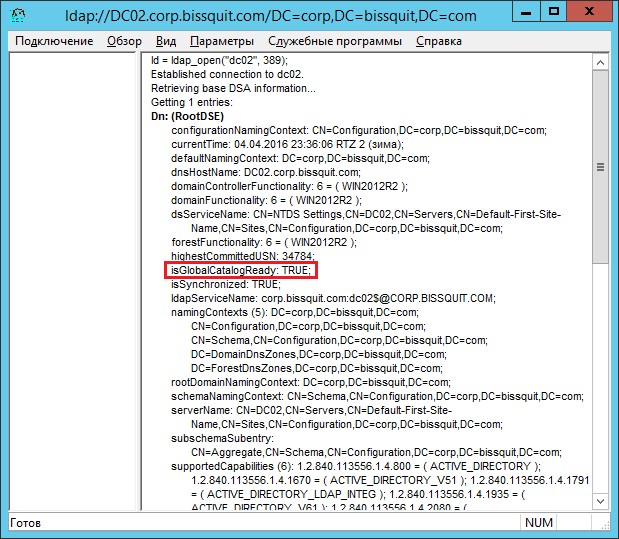
Ну а проверить готовность сервера GC можно по инструкции 11:
1) Откройте оснастку Ldp. Чтобы открыть Ldp, нажмите кнопку Пуск, выберите команду Выполнить, введите ldp, а затем нажмите кнопку ОК.
Чтобы открыть Ldp в , ldp.
2) В меню Подключение выберите команду Подключить.
3) В поле Подключиться введите имя сервера, на котором имеется глобальный каталог, чью готовность необходимо проверить.
4) В поле Порт введите 389, если значение 389 не появилось.
5) Снимите флажок Без подключения и нажмите кнопку ОК.
6) В области сведений проверьте, что значение атрибута isGlobalCatalogReady равно TRUE.
7) В меню Подключение выберите команду Отключиться, затем закройте оснастку Ldp.
На этом обзор одной из важнейших ролей контроллеров домена – глобального каталога – завершен. Оставляйте в комментариях свои мнения и замечания.
Кроме пяти ролей FSMO в Active Directory cуществует еще шестая роль контроллера домена – глобальный каталог (Global catalog, GC). В отличие от FSMO роль глобального каталога может иметь любой контроллер в домене, т.е. она не требует уникальности сервера в пределах домена или леса. Тем не менее, глобальный каталог — самая важная с практической точки зрения роль контроллера домена. И вот почему.
Глобальный каталог является контроллером домена, хранящим копии всех объектов Active Directory в лесу. В нем хранится полная копия всех объектов каталога своего домена и частичная копия всех объектов всех других доменов леса. Таким образом, глобальный каталог позволяет пользователям и приложениям находить объекты в любом домене текущего леса посредством поиска атрибутов, включенных в глобальный каталог.
Глобальный каталог содержит основной, но неполный набор атрибутов (Partial Attribute Set, PAT) для каждого объекта леса в каждом домене. Данные GC получает из всех разделов каталога доменов в лесу, они копируются с использованием стандартного процесса репликации службы AD. Будет ли атрибут скопирован в глобальный каталог определяется схемой. При необходимости можно сконфигурировать дополнительные атрибуты, которые будут реплицироваться в GC, используя оснастку Схема Active Directory (Active Directory Schema). Чтобы добавить атрибут в глобальный каталог, надо выбрать опцию Копировать этот атрибут в глобальный каталог (Replicate This Attribute To The Global catalog) на самом атрибуте. В результате значение параметра атрибута isMemberOfPartialAttributeSet будет установлено на true (истина).
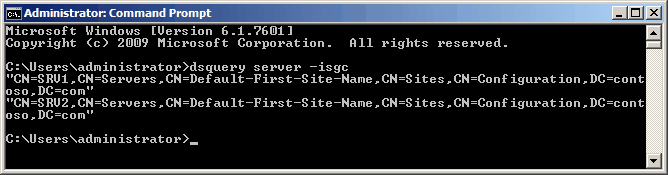
Как узнать, где находится глобальный каталог? Для текущего домена достаточно просто набрать в командной строке:
dsquery server –isgc
В результате мы получим список DN серверов глобального каталога, например: «CN=SRV1,CN=Servers, CN=Default-First-Site- Name, CN=Sites, CN=Configuration, DC=contoso, DC=com»
Команду dsquery server также можно использовать для поиска серверов GC в конкретном домене, лесе или сайте. Например:
dsquery server –domain contoso.com –isgc — ищем серверы глобального каталога в домене contoso.com;
dsquery server –forest –isgc — поиск серверов GC во всем лесу;
dsquery server –site Default-First-Site-Name — поиск по сайту Default-First-Site-Name.
Имейте в виду, что для поиска глобального каталога по сайту нужно знать полное имя сайта и нельзя использовать символы подстановки.
Как происходит размещение глобального каталога? Первый сервер GC создается автоматически на первом контроллере домена в лесу при установке доменных служб Active Directory. В случае одного сайта, пусть даже и содержащего несколько доменов, одного сервера глобального каталога обычно достаточно для обработки запросов и входов в Active Directory. В среде с несколькими сайтами, для оптимизации производительность сети стоит рассмотреть возможность добавления серверов GC в для обеспечения быстрого ответа на поисковые запросы и быстрого входа в систему. Также на каждом сайте AD, где предполагается установить Exchange, должен иметься в наличии хотя бы один сервер глобального каталога.
Дополнительные контроллеры домена можно назначить как GC, выбирая опцию Глобальный каталог (Global catalog) в оснастке администрирования Сайты и службы Active Directory (Active Directory Sites And Services).
Сервер глобального каталога используется в следующих ситуациях:
- Поиск объектов
Для доступа к объектам Active Directory использует протокол облегченного доступа к каталогам (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol, LDAP). Запросы поиска LDAP могут быть отправлены и получены службой каталогов AD по порту 389 (порт LDAP по умолчанию) и по порту 3268 (порт GC).
Когда запрос поиска отправляется на порт 389, поиск осуществляется в разделе каталога одного домена. Если объект не находится в текущем домене, контроллер домена пересылает запрос на контроллер домена в домене, указанный в различающемся имени объекта (distinguished name, DN).
Примечание. DN объекта — это атрибут каждого объекта, представляющий его имя и местоположение в лесу AD, например ″CN=Mike, OU=users, DC=contoso, DC=com″.
Если же запрос поиска отправляется на порт 3268, то опрашиваются все разделы каталога в лесу, то есть поиск обрабатывается сервером глобального каталога. Поскольку глобальный каталог содержит полный список всех объектов леса, сервер GC может ответить на любой запрос без необходимости передавать его другому контроллеру домена. Кстати, только серверы глобального каталога могут получать запросы LDAP через порт 3268.
Таким образом, если пользователь выполняет поиск какого-либо объекта, указав в запросе параметр «Весь каталог», данный запрос перенаправляется на порт 3268 и отправляется для разрешения на сервер GC. Если же по каким-либо причинам в домене нет сервера GC, пользователи и приложения не смогут выполнять поиск в лесу. Также стоит отметить, что глобальный каталог содержит все права доступа для каждого объекта и атрибута, и если вы ищете объект, доступ к которому у вас нет доступа, вы его не увидите в списке результатов поиска. Соответственно, пользователи могут найти только те объекты, для которых им предоставлен доступ.
- Проверка подлинности
Кроме функции поиска в мультидоменном лесу, сервер GC играет роль источника аутентификации во время входа пользователя в домен. Сервер глобального каталога разрешает имя пользователя в том случае, если контроллер домена, проверяющий подлинность, не имеет сведений об учетной записи этого пользователя. Другими словами, если учетная запись пользователя находится в одном домене, но сам пользователь входит в систему с компьютера, расположенного в другом домене, контроллер домена не cможет найти учетную запись пользователя и для того, чтобы завершить процесс входа в систему, он должен связаться с сервером глобального каталога.
- Проверка членства в универсальных группах в мультидоменной среде
В процессе проверки контроллер домена проверяет подлинность пользователя, после чего пользователь получает данные авторизации для доступа к ресурсам. Для предоставления этих данных контроллер домена извлекает идентификаторы безопасности (SID) для всех групп безопасности, членом которых является пользователь и добавляет эти идентификаторы в маркер доступа пользователя. Поскольку универсальные группы могут содержать учетные записи пользователей и групп из любого домена в лесу, групповое членство в них может быть разрешено только тем контроллером домена, который имеет информацию каталога на уровне леса, т.е. сервером GC. Например, пользователь в лесу с несколькими доменами подключается к домену, в котором разрешены универсальные группы. В этом случае контроллер домена, для получения членства в универсальных группах, должен связаться с сервером глобального каталога. Если пользователь уже подключался к данному домену и сервер глобального каталога недоступен, то клиентский компьютер пользователя может использовать для входа кэшированные учетные данные. Но если сервер глобального каталога недоступен при входе пользователя в домен, в котором используются универсальные группы и пользователь ни разу не подключался к данному домену, войти в домен он не сможет (только локально в систему). Исключение составляет учетная запись доменного администратора, он всегда может входить в домен, даже если сервер GC недоступен.
Примечание. Если в составе леса находится только один домен, то при входе в систему нет необходимости получать в глобальном каталоге членство в универсальных группах. Это обусловлено тем, что AD обнаруживает отсутствие в лесу других доменов и предотвращает отправление глобальному каталогу запроса на эти сведения.
- Проверка ссылок на объекты внутри леса
Контроллеры домена используют глобальный каталог для подтверждения ссылок на объекты других доменов в лесу. То есть, если контроллер домена содержит объект с атрибутом, который содержит ссылку на объект в другом домене, то контроллер домена проверяет ссылку, устанавливая связь с сервером глобального каталога.
- Поиск в адресной книге Exchange
Когда пользователи в своем почтовом клиенте хотят найти человека в пределах своей организации, как правило они выполняют поиск через глобальную адресную книгу (global address list, GAL). GAL — это список, который Exchange создает в результате выполнения запроса LDAP на поиск всех объектов, получающих почту — пользователей, контакты и группы. Когда пользователь пробует открыть в Microsoft Outlook адресную книгу, или пишет сообщение и вводит имя или адрес в поле «Кому», Outlook использует сервер глобального каталога, указанный сервером Exchange. Для поиска серверов глобального каталога, почтовые сервера Exchange используют Active Directory и DNS.
Подведем итог: При отсутствии доступа к серверу глобального каталога пользователи не смогут войти в систему, а почтовый сервер Exchange не сможет отправлять и принимать почту. Вот именно поэтому глобальный каталог и является самой важной ролью контролера домена, без которой функционирование Active Directory практически невозможно.
The global catalog is a feature of Active Directory (AD) that allows a domain controller (DC) to provide information on any object in the forest, regardless of whether the object is a member of its domain. Domain controllers with the global catalog feature enabled are referred to as global catalog servers.
Core Functionality
Global catalog servers perform several functions, which are especially important in a multi-domain forest environment:
- Authentication. During an interactive domain logon, a DC will process the authentication request and provide authorization information regarding all of the groups the user account is a member of, which will be included in the generated user access token. The DC must access a global catalog server to obtain the following:
- User principal name resolution. Logon requests made using a user principal name (e.g., “username@domain.com”) require a search of the global catalog to identify the distinguished name of the associated user object.
- Universal group membership. Logon requests made in multi-domain environments require the use of a global catalog that can check for the existence of any universal groups and determine if the user logging on is a member of any of those groups. Because the global catalog is the only source of universal group membership information, access to a global catalog server is a requirement for authentication in a multi-domain forest.
- Object Search. The global catalog makes the directory structure within a forest transparent to users who perform a search. For example, any global catalog server in a forest is capable of identifying a user object given only the object’s samAccountName. Without a global catalog server, identifying a user object given only its samAccountName could require separate searches of every domain in the forest.
How a Global Catalog Works
Active Directory Partitions
To understand how the global catalog works, it is important to first understand a little bit about how the Active Directory database is structured. Domain controllers store the Active Directory database in a single file, NTDS.dit. To simplify administration and facilitate efficient replication, the database is logically separated into partitions.
Every domain controller maintains at least three partitions:
- The domain partition contains information about a domain’s objects and their attributes. Every DC contains a complete writable replica of its local domain partition.
- The configuration partition contains information about the forest’s topology, including domain controllers and site links. Every DC in a forest maintains a complete writable replica of the configuration partition.
- The schema partition is a logical extension of the configuration partition; it contains definitions of every object class in the forest and the rules that control the creation and manipulation of those objects. Every DC in a forest maintains a complete replica of the schema partition. The schema partition is read-only on every DC except the DC that owns the Schema Master operations role for the forest.
Domain controllers may also maintain application partitions. These partitions contain information relating to AD-integrated applications and can contain any type of object except for security principals. Application partitions have no specific replication requirements; they are not required to replicate to other domain controllers but can be configured to replicate to any DC in a forest.
You can identify the partitions present on a DC using the following PowerShell cmdlet:
Get-ADDomainController -Server <SERVER> | Select-Object -ExpandProperty Partitions Global Catalog Partitions
Consider a forest that consists of three domains, each with one global catalog server, as depicted below:
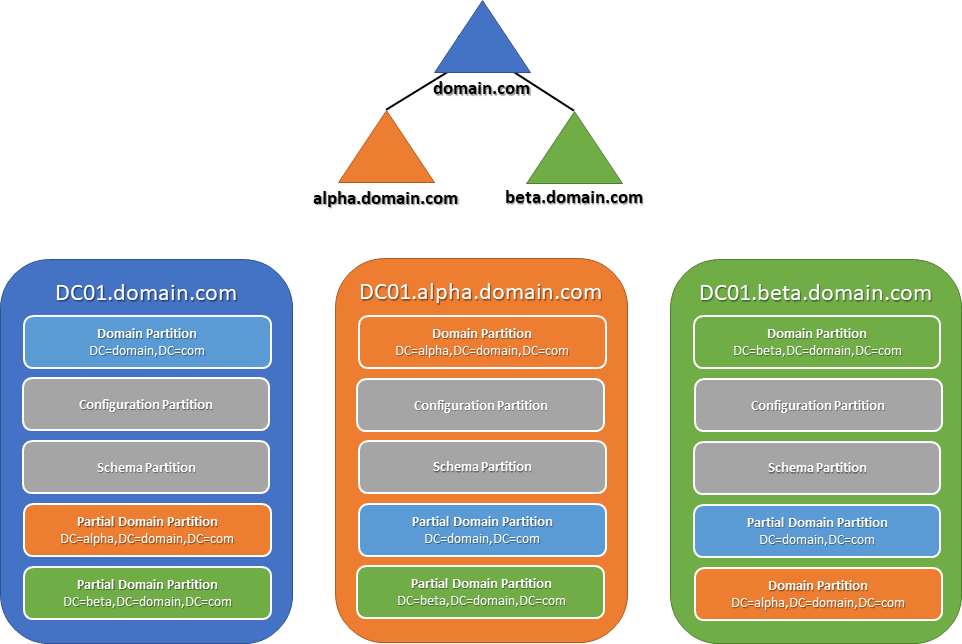
As explained earlier, every DC maintains a replica of its local domain partition, the configuration partition and the schema partition. In a multi-domain forest like this one, global catalog servers also host an additional set of read-only partitions, each of which contains a partial, read-only replica of the domain partition from one of the other domains in the forest. It is the information in these partial, read-only partitions that allow global catalog servers to process authentication and forest-wide search requests in a multi-domain forest.
The subset of object attributes that are replicated to global catalog servers is called the Partial Attribute Set (PAS). The members of the Partial Attribute Set in a domain can be listed using this PowerShell cmdlet:
Get-ADObject -SearchBase (Get-ADRootDSE).SchemaNamingContext -LDAPFilter "(isMemberOfPartialAttributeSet=TRUE)" -Properties lDAPDisplayName | Select lDAPDisplayName In a single-domain forest, all DCs host the only domain partition in the forest; therefore, each one contains a record of all of the objects in the forest and can process authentication and domain service requests.
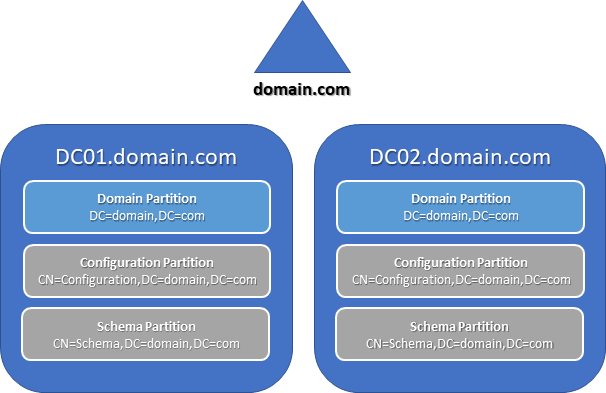
Active Directory takes advantage of this by allowing any domain controller in a single-domain forest to function as a virtual global catalog server, regardless of whether it has been configured as a global catalog server. The only limitation is that only DCs configured as global catalog servers can respond to queries directed specifically to a global catalog.
Deploying Global Catalog Servers
When a new domain is created, the first DC will be made a global catalog server. To configure additional DCs as global catalog servers, either enable the Global Catalog checkbox in the server’s NTDS Settings properties in the Active Directory Sites and Services management console, or use the following PowerShell cmdlet:
Set-ADObject -Identity (Get-ADDomainController -Server <SERVER>).NTDSSettingsObjectDN -Replace @{options='1'} Each site in the forest should contain at least one global catalog server to eliminate the need for an authenticating DC to communicate across the network to retrieve global catalog information. In situations where it is not feasible to deploy a global catalog server in a site (such as a small remote branch office), Universal Group Membership Caching can reduce authentication-related network traffic and allow the remote site’s DC to process local site login requests using cached universal group membership information. This feature requires the remote DC to communicate with a global catalog server to process initial logons and perform search requests.
It is recommended that all DCs be configured as global catalog servers unless there is a specific reason to avoid doing so.
Director of Product Management at Netwrix. Kevin has a passion for cyber security, specifically understanding the tactics and techniques attackers use to exploit organizations environments. With eight years of experience in product management, focusing on Active Directory and Windows security, he’s taken that passion to help build solutions for organizations to help protect their identities, infrastructure and data.

In addition to the 5 FSMO roles in Active Directory, there is the sixth (unofficial) domain controller role — Global Catalog (GC). Unlike FSMO roles, any controller in a domain can host a Global Catalog role. This role doesn’t need to be unique within an Active Directory domain or forest. However, the Global Catalog is the most important DC role from a practical point of view.
What is the Global Catalog?
A Global Catalog server is a domain controller that stores copies of all Active Directory objects in the forest. It stores a complete copy of all objects in the directory of your domain and a partial copy of all objects of all other forest domains. Global catalogs allow users and applications to find objects in any domain of the current forest by searching for attributes included in GC. For instance, user principal name resolution requires global catalog servers for UPN logons to be successful.
A typical domain controller stores a complete replica of objects in its own domain, but not for other domains in the forest.
The Global Catalog contains a basic (but incomplete) set of attributes for each forest object in each domain (Partial Attribute Set, PAT). The GC receives data from all the domain directory partitions in the forest, they are copied using a standard AD replication service. The set of attributes that are copied to the Global Catalog is defined in the AD schema. If necessary, you can configure additional attributes that will be replicated to the GC using the Active Directory Schema mmc snap-in.
Imagine a workstation requesting information about an object from another domain in the current AD forest. The computer contacts the nearest GC with a request to provide it with information about this object. The GC server can perform one of the following things:
- Immediately return the necessary information to the workstation (if this information is stored on the GC server);
- Redirect the query to the correct Domain Controller, where this information will definitely be located. Use GC search to understand which domain controller to redirect the request to.
Select Replicate This Attribute to the Global catalog to add an attribute to the GC. As a result, the value of the isMemberOfPartialAttributeSet attribute parameter is set to True.

You can use PowerShell to find domain controllers with GC roles in the domain. First, import the PowerShell Active Directory module into your current sessions:
Import-Module ActiveDirectory
To find the list of DCs that contains the Global Catalog role in the current forest, run the command:
Get-ADForest |select -ExpandProperty GlobalCatalogs |Format-Table

You can check if the current DC you are logged on has the global catalog role enabled:
Get-ADDomainController | ft Name,IsGlobalCatalog
Or to check GC role in all DC across AD site links:
Get-ADDomainController-Filter {Site -eq 'New-York'}} | FT Name,IsGlobalCatalog
Or use the dsquery command-line tool. To list all GC servers in the current Active Directory forest:
dsquery server -forest –isgc
Finding GC servers in a specific forest domain:
dsquery server –domain theitbros.com –isgc
The first GC server was automatically created on the first domain controller in the forest when you promote DC during installing the Active Directory Domain Services role. In the case of a single Active Directory site, even if it contains multiple domains, a single Global Catalog server is usually sufficient to process Active Directory requests. In a multi-site environment (in order to optimize network traffic and reduce service delays) consider adding GC servers to ensure a quick response to search queries and fast logon. Also, at least one GC server must be present on each AD site where Exchange is supposed to be installed.
You can assign additional domain controllers as GC by selecting the Global Catalog option in the “Active Directory Sites and Services” snap-in (dssite.msc).
The global catalog server is used for the following purposes:
- Object search — if a user searches for an object by specifying All directory parameter in the query, this LDAP query is redirected to the port TCP/3268 (or TCP/3269 for LDAP over SSL) and sent to the nearest GC server. If for any reason there is no GC server in the domain, users and applications won’t be able to perform searches across the AD forest;
- Authentication — the GC server is the source of authentication at the time the user logs on to the domain. The global catalog server resolves the user name if the authenticating domain controller does not have information about the user’s account (the UserPrincipalName attribute is used in this case);
- Verifying universal group membership in a multi-domain environment — in the verification process, the domain controller verifies the authenticity of the user, after which the user receives authorization data to access the resources. To provide this information, the domain controller retrieves the security identifiers (SIDs) for all Active Directory groups that the user is a member of and adds these identifiers to the user’s access token. Because universal groups can contain user accounts and groups from any domain in the forest, the group membership in them can only be resolved by the GC Server that has catalog information at the forest level;
- Checking references to objects within the forest — Domain controllers use a Global Catalog to validate references to objects in other domains in the forest. That’s why if the domain controller contains an object with an attribute, that contains a reference to an object in another domain — the domain controller checks the link by establishing a connection to the Global Catalog server;
- Exchange Address Book Search — when users want to find a person within the organization in Outlook, they usually search through the Global Address List (GAL). The GAL is a list that is created by Exchange as a result of an LDAP query to search for all mail-enabled objects — users, contacts, and distribution groups. When a user tries to open an address book in Microsoft Outlook, or writes an email and enters a name or recipient address in the To field, Outlook uses the GC Server specified by the Exchange server. Exchange mail servers use Active Directory and DNS to locate Global Catalog servers.
How to Optimize Global Catalog Server Placement?
For resiliency purposes, it is important to keep at least a few domain controllers with the Global Catalog role. It will be better if each domain has a minimum of one GC. However, it is better to make all DCs in the forest as Global catalog servers. This will also have a positive effect on load balancing. Also, it is important to notice that from now you won’t have to worry about the Infrastructure master role.
If you can’t make all DCs the Global Catalog, then make sure the infrastructure master FSMO role do not host on the GC Server. Otherwise, it will stop its functioning (phantom records will not be created/changed) and as a consequence — you will get irrelevant data in AD.
If there are no Global Catalog servers available, users can not log in, and the Exchange Server can’t send and receive emails. That’s why the Global Catalog is the most important role of the domain controller. Without GC role the functioning of Active Directory is almost impossible.
How to Enable/Disable the Global Catalog Role on a Domain Controller?
You can enable the Global Catalog role on a domain controller in several ways:
- Using the graphical Active Directory Sites and Services mmc console;
- Using PowerShell;
- Using the dsmod.exe tool.
Run the mmc snap-in “Active Directory Sites and Services” (Start > Windows Administrative Tools, or run the dssite.msc command).

Expand the Sites section and find the AD site that contains your domain controller. Expand it, right-click on NTDS Settings and then select Properties.
Set the Global Catalog checkbox on the General tab to enable the GC role, or uncheck it to disable it. Click OK to save your changes.

Once promoted to a GC server, an event with Event ID 1110 should appear in the Directory Service section of Event Viewer:
Event Source: NTDS General
Event Category: Replication
After successful installation of the role, Event ID 1119 will appear:
This domain controller is now a global catalog
In this case, the value of the Global Catalog Promotion Complete registry setting under the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\NTDS\Parameters key registry should be 1.

You can make a read-only domain controller a Global Catalog server. A Global Catalog (GC) server is a read-only copy of a partial set of attributes of all domains in an AD forest, so you can use this role on a Read-Only Domain Controller (RODC). But some applications will not work correctly with a GC server running on an RODC. That’s why it’s important to make sure your apps support a GC server running on an RODC.
You can enable the Global Catalog role on a DC using the PowerShell command:
Set-ADObject -Identity (Get-ADDomainController DC03).ntdssettingsobjectdn -Replace @{options='1'}
To disable the GC role, use the command:
Set-ADObject -Identity (Get-ADDomainController DC02).ntdssettingsobjectdn -Replace @{options='0'}
Hint. Each Active Directory domain must have at least one DC with the Global Catalog role. Therefore, you won’t be able to disable the GC option if it’s the only domain controller with this role.
These commands can be used to move the global catalog server functionality from one domain controller to another.
You can also use the dsmod.exe command to enable the GC role. For example:
dsmod server "CN=dc03,OU=USA,DC=theitbros,DC=com" -isgc yes
The amount of time it takes to publish the Global Catalog in a forest depends on the replication topology. The domain controller doesn’t publish the DNS record that has become a global catalog server until it receives all partial domain directory partitions through AD replication.
You can check the registration of a Global Catalog server in DNS by using the dnsmgmt.msc snap-in. Make sure you have an SRV record named gc for your DC in the tcp forward lookup zone.

Note that the Active Directory DNS zone has a msdcs container that contains infrastructure AD DNS records. There is a separate gc.msdcs… entry in the AD root domain namespace for Global Catalog servers. This entry contains a list of all GCs in the forest. You can view the records of servers with the Global Catalog role in a domain using the built-in nslookup tool:
nslookup gc._msdcs.theitbros.com
Clients use these DNS records to look up Global Catalog servers in the Active Directory domain.
After activating the Global Catalog role on DC, you can check its readiness. For this, the ldp.exe utility is used. Run the tool, select Connection > Connect > specify the DC name and a 389 as a connection port. Click Ok.

Verify the isGlobalCatalogReady: TRUE value in the LDP window. This means that your GC is ready.
Also, you can check GC readiness from the command prompt:
nltest /server:dc01 /dsgetdc:test.com

Check for a GC value in the Flags field.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can the Global Catalog role be enabled on any domain controller?
Absolutely! The Global Catalog role can be enabled on any domain controller. The process can be executed using the Active Directory Sites and Services MMC console, PowerShell commands, or the dsmod.exe tool. However, remember to consider the Infrastructure Master FSMO role when configuring your Global Catalog servers.
How do you ascertain that a domain controller is ready after activating the Global Catalog role?
The readiness of a Global Catalog server post-activation can be checked with tools like LDP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) or the command prompt using specific commands. Checking for values like isGlobalCatalogReady: TRUE or GC in the flags field confirms the server’s readiness.
Why should I be concerned about the placement of Global Catalog servers?
Optimal placement of Global Catalog servers improves load balancing and ensures resilience in your network. Placing GC servers intelligently, especially in a multi-site environment, can optimize network traffic, reduce service delays, and provide quicker responses to search queries and logons.
Wrapping up
Understanding the role of the Global Catalog (GC) in an Active Directory environment is vital for the effective management of your network. It not only aids in Active Directory object searches across the forest but also plays a crucial role in user authentication, group membership verification, and even supporting Exchange Server functionalities.
While the ability to assign the GC role to any domain controller adds flexibility, it’s important to optimize the placement of these servers for better load balancing, improved network traffic management, and faster response times. Remember, a well-configured Global Catalog is pivotal for your network’s resilience and overall performance.
Cyril Kardashevsky
I enjoy technology and developing websites. Since 2012 I’m running a few of my own websites, and share useful content on gadgets, PC administration and website promotion.
Overview#
Global Catalog in Microsoft Active Directory is is a Distributed system Data Store Service where only the Partial Attribute Set Replicated to specific Global Catalog Domain Controllers.
Global Catalog is primarily used for as a Discovery Mechanism and to enhance searching. Global Catalog provides a searchable catalog of all objects in every AD DOMAIN in an AD Forest.
Global Catalog Servers#
A Global Catalog server is a Domain Controller that stores Global Catalog information; its database stores rows for every object in the AD Forest instead of rows for only the objects in one AD DOMAIN.
The rows that store objects that occur in AD DOMAIN directory partitions other than the local domain partition hold only a subset of attributes for each object. In this way, the Global Catalog enables forest-wide searches without requiring replication of the entire contents of Active Directory to every Domain Controller.
The Knowledge Consistency Checker (KCC) process creates a replication topology that ensures delivery of the contents of every Microsoft Active Directory partition to every Global Catalog server in the AD Forest.
A Global Catalog server stores full (writable) copies of the schema and configuration directory partitions — the same as any domain controller.
Characteristics of Global Catalog#
- Global Catalogs are also Domain Controllers
- Global Catalog servers stores information about all objects of all domains of the entire forest.
- Global Catalog servers do Not the complete set of attributes for these objects are stored.
- Global Catalog servers replicate the data with all other Global Catalogs in the forest.
- Global Catalog function increases replication load on the regarding server.
- Global Catalog access over LDAP is done as a normal LDAP connection over TCP port 3268 (or 3269 for LDAP over SSL).
- Global Catalog requests are Read Only.
- Global Catalog Domain Controller have a DNS SRV Record is created in DNS.
By default, the server on which you install Active Directory to create the first domain in a new forest is a Global Catalog server. Thereafter, you must designate additional Global Catalog servers, if they are needed.
Searches That Use the Global Catalog by Default#
Any time that you specify port 3268, you are searching in the Global Catalog.
In addition, the Global Catalog is searched by default under the following conditions:
- During the logon process when a user principal name is presented. The Global Catalog is searched to find the domain and account name on the basis of the user principal name.
- During the logon process to expand Universal Groups as Universal Group membership can span domains.
- When you choose Entire Directory in a search-scope list.????
- When you write the value for a distinguished name-valued property, where the distinguished name represents a nonlocal object. For example, if the member that you are adding is from a different domain, the Global Catalog is used to verify that the user object represented by the distinguished name actually exists.
Locating Global Catalog Domain Controllers#
In an Microsoft Active Directory environment, all Global Catalog are anchored in DNS. The DNS SRV Records ‘GC._msdcs.example.com’ So if your root domain in the forest is e.g. example.com, then you get a list of all GCs with this command:
nslookup -type=any gc._msdcs.example.com
Will return all the Domain Controllers that are Global Catalog
You can also use dsquery
Will return the distinguished Names of all the Domain Controllers that are Global Catalog for the current domain.
And using an Search Request LDAP SearchFilters
(&(objectClass=nTDSDSA)(options:1.2.840.113556.1.4.803:=1))
Active Directory Groups#
Not all Active Directory Groups and their members are available within the Global Catalog.
More Information#
There might be more information for this subject on one of the following:
- AD DOMAIN
- AD Forest
- Active Directory Groups
- Active Directory Schema Related LDAP Searches
- DS_FLAG
- Directory Partition Hierarchy
- Domain Directory Partition
- Global Catalog
- Infrastructure Master FSMO Role
- IsMemberOfPartialAttributeSet
- LDAP Query Examples for AD
- LDAP and Global Catalog
- Microsoft Active Directory
- Microsoft Active Directory Attributes
- Partial Attribute Set
- TokenGroups
- WhenChanged
