Command
Description
Append
The append command can be used by programs to open files in another directory as if they were located in the current directory. The append command is available in MS-DOS as well as in all 32-bit versions of Windows. The append command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows.
Arp
The arp command is used to display or change entries in the ARP cache. The arp command is available in all versions of Windows.
Assoc
The assoc command is used to display or change the file type associated with a particular file extension. The assoc command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
At
The at command is used to schedule commands and other programs to run at a specific date and time. The at command is available in Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. Beginning in Windows 8, command-line task scheduling should instead be completed with the schtasks command.
Atmadm
The atmadm command is used to display information related to asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) connections on the system. The atmadm command is available in Windows XP. Support for ATM was removed beginning in Windows Vista, making the atmadm command unnecessary.
Attrib
The attrib command is used to change the attributes of a single file or a directory. The attrib command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Auditpol
The auditpol command is used to display or change audit policies. The auditpol command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Bcdboot
The bcdboot command is used to copy boot files to the system partition and to create a new system BCD store. The bcdboot command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, and Windows 7.
Bcdedit
The bcdedit command is used to view or make changes to Boot Configuration Data. The bcdedit command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. The bcdedit command replaced the bootcfg command beginning in Windows Vista.
Bdehdcfg
The bdehdcfg command is used to prepare a hard drive for BitLocker Drive Encryption. The bdehdcfg command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, and Windows 7.
Bitsadmin
The bitsadmin command is used to create, manage, and monitor download and upload jobs. The bitsadmin command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. While the bitsadmin command is available in those versions of Windows, it is being phased out—the BITS PowerShell cmdlets should be used instead.
Bootcfg
The bootcfg command is used to build, modify, or view the contents of the boot.ini file, a hidden file that is used to identify in what folder, on which partition, and on which hard drive Windows is located. The bootcfg command is available in Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The bootcfg command was replaced by the bcdedit command beginning in Windows Vista. Bootcfg is still available in Windows 10, 8, 7, and Vista, but it serves no real value since boot.ini is not used in these operating systems.
Bootsect
The bootsect command is used to configure the master boot code to one compatible with BOOTMGR (Vista and later) or NTLDR (XP and earlier). The bootsect command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, and Windows 8. The bootsect command is also available in Windows 7 and Windows Vista but only from the Command Prompt available in System Recovery Options.
Break
The break command sets or clears extended CTRL+C checking on DOS systems. The break command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. The break command is available in Windows XP and later versions of Windows to provide compatibility with MS-DOS files but it has no effect in Windows itself.
Cacls
The cacls command is used to display or change access control lists of files. The cacls command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The cacls command is being phased out in favor of the icacls command, which should be used instead in all versions of Windows after Windows XP.
Call
The call command is used to run a script or batch program from within another script or batch program. The call command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. The call command has no effect outside of a script or batch file. In other words, running the call command at the Command Prompt or MS-DOS prompt will do nothing.
Cd
The cd command is the shorthand version of the chdir command. The cd command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Certreq
The certreq command is used to perform various certification authority (CA) certificate functions. The certreq command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Certutil
The certutil command is used to dump and display certification authority (CA) configuration information in addition to other CA functions. The certutil command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Change
The change command changes various terminal server settings like install modes, COM port mappings, and logons. The change command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Chcp
The chcp command displays or configures the active code page number. The chcp command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Chdir
The chdir command is used to display the drive letter and folder that you are currently in. Chdir can also be used to change the drive and/or directory that you want to work in. The chdir command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Checknetisolation
The checknetisolation command is used to test apps that require network capabilities. The checknetisolation command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, and Windows 8.
Chglogon
The chglogon command enables, disables, or drains terminal server session logins. The chglogon command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. Executing the chglogon command is the same as executing change logon.
Chgport
The chgport command can be used to display or change COM port mappings for DOS compatibility. The chgport command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. Executing the chgport command is the same as executing change port.
Chgusr
The chgusr command is used to change the install mode for the terminal server. The chgusr command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. Executing the chgusr command is the same as executing change user.
Chkdsk
The chkdsk command, often referred to as check disk, is used to identify and correct certain hard drive errors. The chkdsk command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Chkntfs
The chkntfs command is used to configure or display the checking of the disk drive during the Windows boot process. The chkntfs command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Choice
The choice command is used within a script or batch program to provide a list of choices and return the value of that choice to the program. The choice command is available in MS-DOS and all versions of Windows except Windows XP. Use the set command with the /p switch in place of the choice command in batch files and scripts that you plan to use in Windows XP.
Cipher
The cipher command shows or changes the encryption status of files and folders on NTFS partitions. The cipher command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Clip
The clip command is used to redirect the output from any command to the clipboard in Windows. The clip command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Cls
The cls command clears the screen of all previously entered commands and other text. The cls command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Cmd
The cmd command starts a new instance of the cmd.exe command interpreter. The cmd command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Cmdkey
The cmdkey command is used to show, create, and remove stored user names and passwords. The cmdkey command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Cmstp
The cmstp command installs or uninstalls a Connection Manager service profile. The cmstp command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Color
The color command is used to change the colors of the text and background within the Command Prompt window. The color command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Command
The command command starts a new instance of the command.com command interpreter. The command command is available in MS-DOS as well as in all 32-bit versions of Windows. The command command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows.
Comp
The comp command is used to compare the contents of two files or sets of files. The comp command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Compact
The compact command is used to show or change the compression state of files and directories on NTFS partitions. The compact command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Convert
The convert command is used to convert FAT or FAT32 formatted volumes to the NTFS format. The convert command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Copy
The copy command does simply that — it copies one or more files from one location to another. The copy command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. The xcopy command is considered to be a more «powerful» version of the copy command.
Cscript
The cscript command is used to execute scripts via Microsoft Script Host. The cscript command is available in all versions of Windows. The cscript command is most popularly used to manage printers from the command line using scripts like prncnfg.vbs, prndrvr.vbs, prnmngr.vbs, and others.
Ctty
The ctty command is used to change the default input and output devices for the system. The ctty command is available in Windows 98 and 95 as well as in MS-DOS. The functions provided by the ctty command were no longer necessary beginning in Windows XP because the command.com interpreter (MS-DOS) is no longer the default command line interpreter.
Date
The date command is used to show or change the current date. The date command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Dblspace
The dblspace command is used to create or configure DoubleSpace compressed drives. The dblspace command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. DriveSpace, executed using the drvspace command, is an updated version of DoubleSpace. Windows began handling compression beginning in Windows XP.
Debug
The debug command starts Debug, a command line application used to test and edit programs. The debug command is available in MS-DOS as well as in all 32-bit versions of Windows. The debug command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows.
Defrag
The defrag command is used to defragment a drive you specify. The defrag command is the command line version of Microsoft’s Disk Defragmenter. The defrag command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Del
The del command is used to delete one or more files. The del command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. The del command is the same as the erase command.
Deltree
The deltree command is used to delete a directory and all the files and subdirectories within it. The deltree command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. Beginning in Windows XP, a folder and its files and subfolders can be removed using the /s function of the rmdir command. Deltree was no longer needed with this new rmdir ability so the command was removed.
Diantz
The diantz command is used to losslessly compress one or more files. The diantz command is sometimes called Cabinet Maker. The diantz command is available in Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The diantz command is the same as the makecab command.
Dir
The dir command is used to display a list of files and folders contained inside the folder that you are currently working in. The dir command also displays other important information like the hard drive’s serial number, the total number of files listed, their combined size, the total amount of free space left on the drive, and more. The dir command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Diskcomp
The diskcomp command is used to compare the contents of two floppy disks. The diskcomp command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS, with the exclusion of Windows 11 and Windows 10.
Diskcopy
The diskcopy command is used to copy the entire contents of one floppy disk to another. The diskcopy command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS, with the exclusion of Windows 11 and Windows 10.
Diskpart
The diskpart command is used to create, manage, and delete hard drive partitions. The diskpart command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The diskpart command replaced the fdisk command beginning in Windows XP.
Diskperf
The diskperf command is used to manage disk performance counters remotely. The diskperf command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Diskraid
The diskraid command starts the DiskRAID tool which is used to manage and configure RAID arrays. The diskraid command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Dism
The dism command starts the Deployment Image Servicing and Management tool (DISM). The DISM tool is used to manage features in Windows images. The dism command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, and Windows 7.
Dispdiag
The dispdiag command is used to output a log of information about the display system. The dispdiag command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Djoin
The djoin command is used to create a new computer account in a domain. The djoin command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Doskey
The doskey command is used to edit command lines, create macros, and recall previously entered commands. The doskey command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Dosshell
The dosshell command starts DOS Shell, a graphical file management tool for MS-DOS. The dosshell command is available in Windows 95 (in MS-DOS mode) and also in MS-DOS version 6.0 and later MS-DOS versions that were upgraded from previous versions that contained the dosshell command. A graphical file manager, Windows Explorer, became an integrated part of the operating system beginning in Windows 95.
Dosx
The dosx command is used to start DOS Protected Mode Interface (DPMI), a special mode designed to give MS-DOS applications access to more than the normally allowed 640 KB. The dosx command is available in Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The dosx command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows. The dosx command and DPMI is only available in Windows to support older MS-DOS programs.
Driverquery
The driverquery command is used to show a list of all installed drivers. The driverquery command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Drvspace
The drvspace command is used to create or configure DriveSpace compressed drives. The drvspace command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. DriveSpace is an updated version of DoubleSpace, executed using the dblspace command. Windows began handling compression beginning in Windows XP.
Echo
The echo command is used to show messages, most commonly from within script or batch files. The echo command can also be used to turn the echoing feature on or off. The echo command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Edit
The edit command starts the MS-DOS Editor tool which is used to create and modify text files. The edit command is available in MS-DOS as well as in all 32-bit versions of Windows. The edit command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows.
Edlin
The edlin command starts the Edlin tool which is used to create and modify text files from the command line. The edlin command is available in all 32-bit versions of Windows but is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows. In MS-DOS, the edlin command is only available up to MS-DOS 5.0, so unless your later version of MS-DOS was upgraded from 5.0 or prior, you won’t see the edlin command.
Emm386
The emm386 command is used to give MS-DOS access to more than 640 KB of memory (RAM). The emm386 command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. Windows itself has access to extended and expanded memory beginning in Windows 95.
Endlocal
The endlocal command is used to end the localization of environment changes inside a batch or script file. The endlocal command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Erase
The erase command is used to delete one or more files. The erase command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. The erase command is the same as the del command.
Esentutl
The esentutl command is used to manage Extensible Storage Engine databases. The esentutl command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Eventcreate
The eventcreate command is used to create a custom event in an event log. The eventcreate command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Eventtriggers
The eventtriggers command is used to configure and display event triggers. The eventtriggers command is available in Windows XP. Beginning in Windows Vista, event triggers are created using the Attach Task To This Event feature in Event Viewer, making the eventtriggers command unnecessary.
Exe2bin
The exe2bin command is used to convert a file of the EXE file type (executable file) to a binary file. The exe2bin command is available in 32-bit versions of Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The exe2bin command is not available in any 64-bit version of Windows.
Exit
The exit command is used to end the cmd.exe (Windows) or command.com (MS-DOS) session that you’re currently working in. The exit command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Expand
The expand command is used to extract the files and folders contained in Microsoft Cabinet (CAB) files. The expand command is available in MS-DOS as well as in all versions of Windows. The expand command is not available in the 64-bit version of Windows XP.
Extrac32
The extrac32 command is used to extract the files and folders contained in Microsoft Cabinet (CAB) files. The extrac32 command is available in all versions of Windows. The extrac32 command is actually a CAB extraction program that can extract any Microsoft Cabinet file. Use the expand command instead of the extrac32 command if possible.
Extract
The extract command is used to extract the files and folders contained in Microsoft Cabinet (CAB) files. The extract command is available in Windows 98 and 95. The extract command was replaced by the expand command beginning in Windows XP.
Fasthelp
The fasthelp command provides more detailed information on any of the other MS-DOS commands. The fasthelp command is only available in MS-DOS. The help command replaced the fasthelp command beginning in Windows 95.
Fastopen
The fastopen command is used to add a program’s hard drive location to a special list stored in memory, potentially improving the program’s launch time by removing the need for MS-DOS to locate the application on the drive. The fastopen command is available in MS-DOS as well as in all 32-bit versions of Windows. The fastopen command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows. Fastopen is only available in Windows 10, Windows 8, 7, Vista, and XP to support older MS-DOS files.
Fc
The fc command is used to compare two individual or sets of files and then show the differences between them. The fc command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Fdisk
The fdisk command is used to create, manage, and delete hard drive partitions. The fdisk command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. The fdisk command was replaced by the diskpart command beginning in Windows XP. Partition management is also available from Disk Management in Windows 11, 10, 8, 7, Vista, and XP.
Find
The find command is used to search for a specified text string in one or more files. The find command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Findstr
The findstr command is used to find text string patterns in one or more files. The findstr command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Finger
The finger command is used to return information about one or more users on a remote computer that’s running the Finger service. The finger command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Fltmc
The fltmc command is used to load, unload, list, and otherwise manage Filter drivers. The fltmc command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Fondue
The fondue command, short for Features on Demand User Experience Tool, is used to install any of the several optional Windows features from the command line. The fondue command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, and Windows 8. Optional Windows features can also be installed from the Programs and Features applet in Control Panel.
For
The for command is used to run a specified command for each file in a set of files. The for command is most often used within a batch or script file. The for command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Forcedos
The forcedos command is used to start the specified program in the MS-DOS subsystem. The forcedos command is only available in 32-bit versions of Windows XP. The forcedos command is only used for MS-DOS programs that are not recognized as such by Windows XP.
Forfiles
The forfiles command selects one or more files to execute a specified command on. The forfiles command is most often used within a batch or script file. The forfiles command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Format
The format command is used to format a drive in the file system that you specify. The format command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. Drive formatting is also available from Disk Management in Windows 11, 10, 8, 7, Vista, and XP.
Fsutil
The fsutil command is used to perform various FAT and NTFS file system tasks like managing reparse points and sparse files, dismounting a volume, and extending a volume. The fsutil command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Ftp
The ftp command can be used to transfer files to and from another computer. The remote computer must be operating as an FTP server. The ftp command is available in all versions of Windows.
Ftype
The ftype command is used to define a default program to open a specified file type. The ftype command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Getmac
The getmac command is used to display the media access control (MAC) address of all the network controllers on a system. The getmac command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Goto
The goto command is used in a batch or script file to direct the command process to a labeled line in the script. The goto command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Gpresult
The gpresult command is used to display Group Policy settings. The gpresult command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Gpupdate
The gpupdate command is used to update Group Policy settings. The gpupdate command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Graftabl
The graftabl command is used to enable the ability of Windows to display an extended character set in graphics mode. The graftabl command is available in all versions of Windows and in MS-DOS up to version 5.0. The graftabl command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows.
Graphics
The graphics command is used to load a program that can print graphics. The graphics command is available in MS-DOS as well as in all 32-bit versions of Windows. The graphics command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows.
Help
The help command provides more detailed information on any of the other Command Prompt or MS-DOS commands. The help command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Hostname
The hostname command displays the name of the current host. The hostname command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Hwrcomp
The hwrcomp command is used to compile custom dictionaries for handwriting recognition. The hwrcomp command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7.
Hwrreg
The hwrreg command is used to install a previously compiled custom dictionary for handwriting recognition. The hwrreg command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7.
Icacls
The icacls command is used to display or change access control lists of files. The icacls command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. The icacls command is an updated version of the cacls command.
If
The if command is used to perform conditional functions in a batch file. The if command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Interlnk
The interlnk command is used to connect two computers via a serial or parallel connection to share files and printers. The interlnk command is only available in MS-DOS. The ability to directly connect two computers is handled by the networking functions in all versions of Windows.
Intersvr
The intersvr command is used to start the Interlnk server and to copy Interlnk files from one computer to another. The intersvr command is only available in MS-DOS. The ability to directly connect two computers is handled by the networking functions in all versions of Windows.
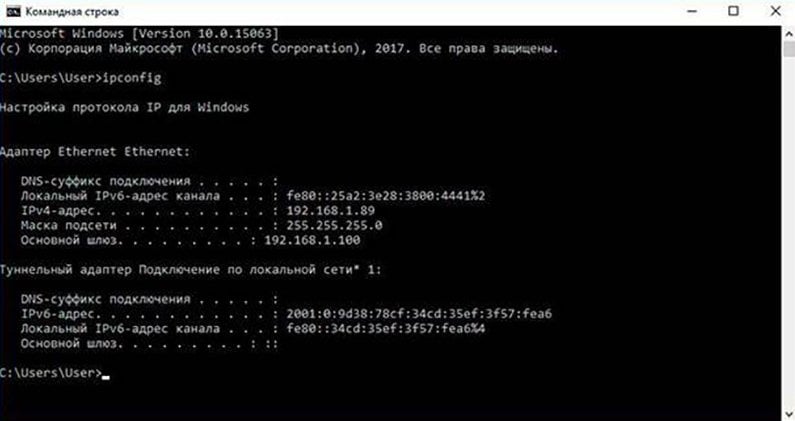
Ipconfig
The ipconfig command is used to display detailed IP information for each network adapter utilizing TCP/IP. The ipconfig command can also be used to release and renew IP addresses on systems configured to receive them via a DHCP server. The ipconfig command is available in all versions of Windows.
Ipxroute
The ipxroute command is used to display and change information about IPX routing tables. The ipxroute command is available in Windows XP. Microsoft removed their built-in NetWare client beginning in Windows Vista, removing the associated ipxroute command as well.
Irftp
The irftp command is used to transmit files over an infrared link. The irftp command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Iscsicli
The iscsicli command starts the Microsoft iSCSI Initiator, used to manage iSCSI. The iscsicli command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Kb16
The kb16 command is used to support MS-DOS files that need to configure a keyboard for a specific language. The kb16 command is available in Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The kb16 command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows. The kb16 command replaced the keyb command beginning in Windows XP but only exists to support older MS-DOS files.
Keyb
The keyb command is used to configure a keyboard for a specific language. The keyb command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. See the kb16 command for an equivalent command in later versions of Windows. Keyboard language settings are handled by the Region and Language or Regional and Language Options (depending on the version of Windows) Control Panel applets in Windows beginning in Windows XP.
Klist
The klist command is used to list Kerberos service tickets. The klist command can also be used to purge Kerberos tickets. The klist command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, and Windows 7.
Ksetup
The ksetup command is used to configure connections to a Kerberos server. The ksetup command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, and Windows 7.
Ktmutil
The ktmutil command starts the Kernel Transaction Manager utility. The ktmutil command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Label
The label command is used to manage the volume label of a disk. The label command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Lh
The lh command is the shorthand version of the loadhigh command. The lh command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS.
Licensingdiag
The licensingdiag command is a tool used to generate a text-based log and other data files that contain product activation and other Windows licensing information. The licensingdiag command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, and Windows 8.
Loadfix
The loadfix command is used to load the specified program in the first 64K of memory and then runs the program. The loadfix command is available in MS-DOS as well as in all 32-bit versions of Windows. The loadfix command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows.
Loadhigh
The loadhigh command is used to load a program into high memory and is usually used from within the autoexec.bat file. The loadhigh command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. Memory usage is handled automatically beginning in Windows XP.
Lock
The lock command is used to lock a drive, enabling direct disk access for a program. The lock command is only available in Windows 98 and 95. Drive locking is no longer available as of Windows XP.
Lodctr
The lodctr command is used to update registry values related to performance counters. The lodctr command is available in all versions of Windows.
Logman
The logman command is used to create and manage Event Trace Session and Performance logs. The logman command also supports many functions of Performance Monitor. The logman command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Logoff
The logoff command is used to terminate a session. The logoff command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Lpq
The lpq command displays the status of a print queue on a computer running Line Printer Daemon (LPD). The lpq command is available in all versions of Windows. The lpq command is not available by default in Windows 11, 10, 8, 7, or Vista, but can be enabled by turning on the LPD Print Service and LPR Port Monitor features from Programs and Features in Control Panel.
Lpr
The lpr command is used to send a file to a computer running Line Printer Daemon (LPD). The lpr command is available in all versions of Windows. The lpr command is not available by default in Windows 11, 10, 8, 7, or Vista, but can be enabled by turning on the LPD Print Service and LPR Port Monitor features from Programs and Features in Control Panel.
Makecab
The makecab command is used to losslessly compress one or more files. The makecab command is sometimes called Cabinet Maker. The makecab command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The makecab command is the same as the diantz command, a command that was removed after Windows 7.
Manage-bde
The manage-bde command is used to configure BitLocker Drive Encryption from the command line. The manage-bde command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, and Windows 7. A script by the name of manage-bde.wsf exists in Windows Vista and can be used with the cscript command to perform BitLocker tasks from the command line in that operating system.
Md
The md command is the shorthand version of the mkdir command. The md command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Mem
The mem command shows information about used and free memory areas and programs that are currently loaded into memory in the MS-DOS subsystem. The mem command is available in MS-DOS as well as in all 32-bit versions of Windows. The mem command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows.
Memmaker
The memmaker command is used to start MemMaker, a memory optimization tool. The memaker command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. Memory usage is automatically optimized beginning in Windows XP.
Mkdir
The mkdir command is used to create a new folder. The mkdir command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Mklink
The mklink command is used to create a symbolic link. The mklink command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Mode
The mode command is used to configure system devices, most often COM and LPT ports. The mode command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Mofcomp
The mofcomp command properly displays the data within a Managed Object Format (MOF) file. The mofcomp command is available in all versions of Windows.
More
The more command is used to display the information contained in a text file. The more command can also be used to paginate the results of any other Command Prompt or MS-DOS command. The more command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Mount
The mount command is used to mount Network File System (NFS) network shares. The mount command is available in Windows 7 and Windows Vista. The mount command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Services for NFS Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. The mount command is not available in Windows 11, 10, or 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued.
Mountvol
The mountvol command is used to display, create, or remove volume mount points. The mountvol command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Move
The move command is used to move one or more files from one folder to another. The move command is also used to rename directories. The move command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Mrinfo
The mrinfo command is used to provide information about a router’s interfaces and neighbors. The mrinfo command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Msav
The msav command starts Microsoft Antivirus. The msav command is only available in MS-DOS. Microsoft Antivirus was designed for MS-DOS and Windows 3.x only. Microsoft provides an optional virus protection suite called Microsoft Security Essentials for Windows XP and later operating systems, and third-party antivirus tools are available for all versions of Windows.
Msbackup
The msbackup command starts Microsoft Backup, a tool used to back up and restore one or more files. The msbackup command is only available in MS-DOS. The msbackup command was replaced with Microsoft Backup beginning in Windows 95 and then Backup and Restore in later versions of Windows.
Mscdex
The mscdex command is used to provide CD-ROM access to MS-DOS. The mscdex command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. Windows provides access to CD-ROM drives for the MS-DOS subsystem beginning in Windows XP, so the mscdex command is unnecessary in this and later operating systems.
Msd
The msd command starts Microsoft Diagnostics, a system information tool. The msd command is only available in MS-DOS. The msd command was replaced with System Information beginning in Windows 95.
Msg
The msg command is used to send a message to a user. The msg command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Msiexec
The msiexec command is used to start Windows Installer, a tool used to install and configure software. The msiexec command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Muiunattend
The muiunattend command starts the Multilanguage User Interface unattended setup process. The muiunattend command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Nbtstat
The nbtstat command is used to show TCP/IP information and other statistical information about a remote computer. The nbtstat command is available in all versions of Windows.
Net
The net command is used to display, configure, and correct a wide variety of network settings. The net command is available in all versions of Windows.
Net1
The net1 command is used to display, configure, and correct a wide variety of network settings. The net1 command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The net command should be used instead of the net1 command. The net1 command was made available in Windows NT and Windows 2000 as a temporary fix for a Y2K issue that the net command had, which was corrected before the release of Windows XP. The net1 command remains in later versions of Windows only for compatibility with older programs and scripts that utilized the command.
Netcfg
The netcfg command is used to install the Windows Preinstallation Environment (WinPE), a lightweight version of Windows used to deploy workstations. The netcfg command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Netsh
The netsh command is used to start Network Shell, a command-line utility used to manage the network configuration of the local, or a remote, computer. The netsh command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Netstat
The netstat command is most commonly used to display all open network connections and listening ports. The netstat command is available in all versions of Windows.
Nfsadmin
The nfsadmin command is used to manage Server for NFS or Client for NFS from the command line. The nfsadmin command is available in Windows 7 and Windows Vista. The nfsadmin command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Services for NFS Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. The nfsadmin command is not available in Windows 11, 10, or 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued.
Nlsfunc
The nlsfunc command is used to load information specific to a particular country or region. The nlsfunc command is available in MS-DOS as well as in all 32-bit versions of Windows. The nlsfunc command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows. Nlsfunc is only available in Windows 10, 8, 7, Vista, and XP to support older MS-DOS files.
Nltest
The nltest command is used to test secure channels between Windows computers in a domain and between domain controllers that are trusting other domains. The nltest command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, and Windows 7.
Nslookup
The nslookup is most commonly used to display the hostname of an entered IP address. The nslookup command queries your configured DNS server to discover the IP address. The nslookup command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Ntbackup
The ntbackup command is used to perform various backup functions from the Command Prompt or from within a batch or script file. The ntbackup command is available in Windows XP. The ntbackup command was replaced with the wbadmin beginning in Windows Vista.
Ntsd
The ntsd command is used to perform certain command line debugging tasks. The ntsd command is available in Windows XP. The ntsd command was removed beginning in Windows Vista due to the addition of dump file support in Task Manager.
Ocsetup
The ocsetup command starts the Windows Optional Component Setup tool, used to install additional Windows features. The ocsetup command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. Beginning in Windows 8, Microsoft is depreciating the ocsetup command in favor of the dism command.
Openfiles
The openfiles command is used to display and disconnect open files and folders on a system. The openfiles command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Path
The path command is used to display or set a specific path available to executable files. The path command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
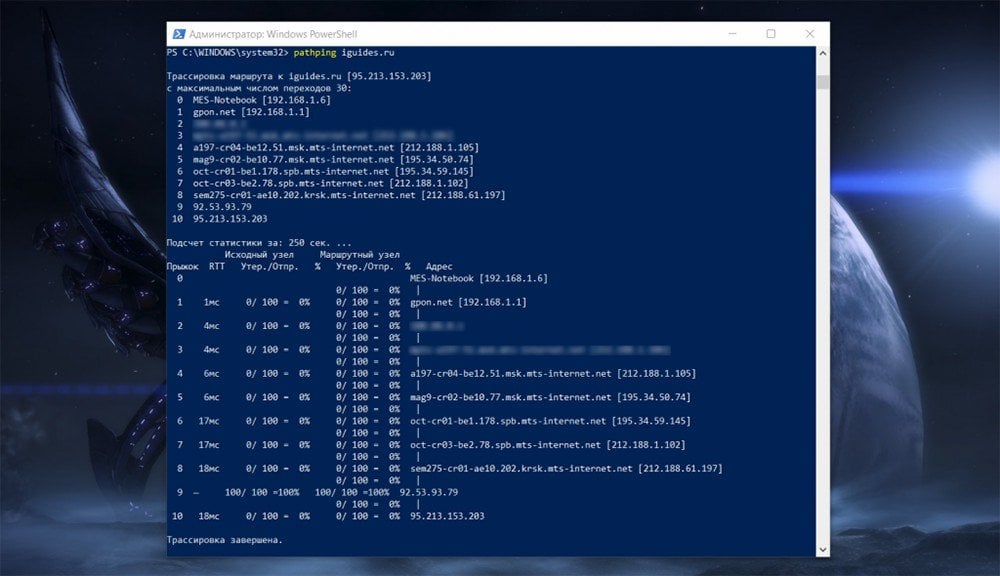
Pathping
The pathping command functions much like the tracert command but will also report information about network latency and loss at each hop. The pathping command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Pause
The pause command is used within a batch or script file to pause the processing of the file. When the pause command is used, a «Press any key to continue…» message displays in the command window. The pause command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Pentnt
The pentnt command is used to detect floating point division errors in the Intel Pentium chip. The pentnt command is also used to enable floating point emulation and disable floating point hardware. The pentnt command is available in Windows XP. The pentnt command was removed beginning in Windows Vista due to the lack of Intel Pentium CPU use at the time of this operating system release.
Ping
The ping command sends an Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Echo Request message to a specified remote computer to verify IP-level connectivity. The ping command is available in all versions of Windows.
Pkgmgr
The pkgmgr command is used to start the Windows Package Manager from the Command Prompt. Package Manager installs, uninstalls, configures, and updates features and packages for Windows. The pkgmgr command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Pnpunattend
The pnpunattend command is used to automate the installation of hardware device drivers. The pnpunattend command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Pnputil
The pnputil command is used to start the Microsoft PnP Utility, a tool used to install a Plug and Play device from the command line. The pnputil command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Popd
The popd command is used to change the current directory to the one most recently stored by the pushd command. The popd command is most often utilized from within a batch or script file. The popd command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Power
The power command is used to reduce the power consumed by a computer by monitoring software and hardware devices. The power command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. The power command was replaced by operating system integrated power management functions beginning in Windows XP.
Powercfg
The powercfg command is used to manage the Windows power management settings from the command line. The powercfg command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Print
The print command is used to print a specified text file to a specified printing device. The print command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Prompt
The prompt command is used to customize the appearance of the prompt text in Command Prompt or MS-DOS. The prompt command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Pushd
The pushd command is used to store a directory for use, most commonly from within a batch or script program. The pushd command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Pwlauncher
The pwlauncher command is used to enable, disable, or show the status of your Windows To Go startup options. The pwlauncher command is available in Windows 11, 10, and 8.
Qappsrv
The qappsrv command is used to display all Remote Desktop Session Host servers available on the network. The qappsrv command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Qbasic
The qbasic command starts QBasic, the MS-DOS based programming environment for the BASIC programming language. The qbasic command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. The qbasic command is not installed by default with Windows 98 or 95 but is available from the installation disc or disks.
Qprocess
The qprocess command is used to display information about running processes. The qprocess command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Query
The query command is used to display the status of a specified service. The query command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Quser
The quser command is used to display information about users currently logged on to the system. The quser command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Qwinsta
The qwinsta command is used to display information about open Remote Desktop Sessions. The qwinsta command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Rasautou
The rasautou command is used to manage Remote Access Dialer AutoDial addresses. The rasautou command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Rasdial
The rasdial command is used to start or end a network connection for a Microsoft client. The rasdial command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Rcp
The rcp command is used to copy files between a Windows computer and a system running the rshd daemon. The rcp command is available in Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The rcp command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Subsystem for UNIX-based Applications Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel and then installing the Utilities and SDK for UNIX-based Applications available here for Windows Vista and here for Windows 7. The rcp command is not available in Windows 11, 10, or 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued.
Rd
The rd command is the shorthand version of the rmdir command. The rd command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Rdpsign
The rdpsign command is used to sign a Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) file. The rdpsign command is available in Windows 7.
Reagentc
The reagentc command is used to configure the Windows Recovery Environment (RE). The reagentc command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, and Windows 7.
Recimg
The recimg command is used to create a custom refresh image. The recimg command is available in Windows 8.
Recover
The recover command is used to recover readable data from a bad or defective disk. The recover command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Reg
The reg command is used to manage the Windows Registry from the command line. The reg command can perform common registry functions like adding registry keys, exporting the registry, etc. The reg command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Regini
The regini command is used to set or change registry permissions and registry values from the command line. The regini command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Register-cimprovider
The register-cimprovider command is used to register a Common Information Model (CIM) Provider in Windows. The register-cimprovider command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, and Windows 8.
Regsvr32
The regsvr32 command is used to register a DLL file as a command component in the Windows Registry. The regsvr32 command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Relog
The relog command is used to create new performance logs from data in existing performance logs. The relog command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Rem
The rem command is used to record comments or remarks in a batch or script file. The rem command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Ren
The ren command is the shorthand version of the rename command. The ren command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Rename
The rename command is used to change the name of the individual file that you specify. The rename command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Repair-bde
The repair-bde command is used to repair or decrypt a damaged drive that’s been encrypted using BitLocker. The repair-bde command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, and Windows 7.
Replace
The replace command is used to replace one or more files with one or more other files. The replace command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Reset
The reset command, executed as reset session, is used to reset the session subsystem software and hardware to known initial values. The reset command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Restore
The restore command is used to restore files that were backed up using the backup command. The restore command is only available in MS-DOS. The backup command was only available up to MS-DOS 5.00 but the restore command was included by default with later versions of MS-DOS to provide a way to restore files that were backed up in previous versions of MS-DOS.
Rexec
The rexec command is used to run commands on remote computers running the rexec daemon. The rexec command is available in Windows Vista and Windows XP. The rsh command is not available by default in Windows Vista but can be enabled by turning on the Subsystem for UNIX-based Applications Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel and then installing the Utilities and SDK for UNIX-based Applications available here. The rexec command is not available in Windows 7 but can be executed in Windows XP via Windows XP Mode if need be.
Rmdir
The rmdir command is used to delete an existing or completely empty folder. The rmdir command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Robocopy
The robocopy command is used to copy files and directories from one location to another. This command is also called Robust File Copy. The robocopy command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. The robocopy command is superior to both the copy command and the xcopy command because robocopy supports many more options.
Route
The route command is used to manipulate network routing tables. The route command is available in all versions of Windows.
Rpcinfo
The rpcinfo command makes a remote procedure call (RPC) to an RPC server and reports what it finds. The rpcinfo command is available in Windows 7 and Windows Vista. The rpcinfo command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Services for NFS Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. The rpcinfo command is not available in Windows 11, 10, or 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued.
Rpcping
The rpcping command is used to ping a server using RPC. The rpcping command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Rsh
The rsh command is used to run commands on remote computers running the rsh daemon. The rsh command is available in Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The rsh command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Subsystem for UNIX-based Applications Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel and then installing the Utilities and SDK for UNIX-based Applications available here for Windows Vista and here for Windows 7. The rsh command is not available in Windows 11, 10, or 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued.
Rsm
The rsm command is used to manage media resources using Removable Storage. The rsm command is available in Windows Vista and Windows XP. The rsm command was optional in Windows Vista and then removed in Windows 7 due to Removable Storage Manager being removed from the operating system. Search for the rsm command in the C:\Windows\winsxs folder in Windows Vista if you’re having trouble executing the command.
Runas
The runas command is used to execute a program using another user’s credentials. The runas command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Rwinsta
The rwinsta command is the shorthand version of the reset session command. The rwinsta command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Sc
The sc command is used to configure information about services. The sc command communicates with the Service Control Manager. The sc command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Scandisk
The scandisk command is used to start Microsoft ScanDisk, a disk repair program. The scandisk command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. The scandisk command was replaced by the chkdsk command beginning in Windows XP.
Scanreg
The scanreg command starts Windows Registry Checker, a basic registry repair program and backup utility. The scanreg command is available in Windows 98 and Windows 95. The functions provided by the scanreg command were no longer necessary beginning in Windows XP due to changes in how the Windows Registry functions.
Schtasks
The schtasks command is used to schedule specified programs or commands to run at certain times. The schtasks command can be used to create, delete, query, change, run, and end scheduled tasks. The schtasks command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Sdbinst
The sdbinst command is used to deploy customized SDB database files. The sdbinst command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Secedit
The secedit command is used to configure and analyze system security by comparing the current security configuration to a template. The secedit command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Set
The set command is used to display, enable, or disable environment variables in MS-DOS or from the Command Prompt. The set command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Setlocal
The setlocal command is used to start the localization of environment changes inside a batch or script file. The setlocal command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Setspn
The setspn command is used to manage the Service Principal Names (SPN) for an Active Directory (AD) service account. The setspn command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, and Windows 7.
Setver
The setver command is used to set the MS-DOS version number that MS-DOS reports to a program. The setver command is available in MS-DOS as well as in all 32-bit versions of Windows. The setver command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows.
Setx
The setx command is used to create or change environment variables in the user environment or the system environment. The setx command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Sfc
The sfc command is used to verify and replace important Windows system files. The sfc command is also referred to as System File Checker or Windows Resource Checker, depending on the operating system. The sfc command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Shadow
The shadow command is used to monitor another Remote Desktop Services session. The shadow command is available in Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Share
The share command is used to install file locking and file sharing functions in MS-DOS. The share command is available in MS-DOS as well as in all 32-bit versions of Windows. The share command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows. Share is only available in Windows 10, 8, 7, Vista, and XP to support older MS-DOS files.
Shift
The shift command is used to change the position of replaceable parameters in a batch or script file. The shift command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Showmount
The showmount command is used to display information about NFS-mounted file systems. The showmount command is available in Windows 7 and Windows Vista. The showmount command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Services for NFS Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. The showmount command is not available in Windows 11, 10, or 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued.
Shutdown
The shutdown command can be used to shut down, restart, or log off the current system or a remote computer. The shutdown command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Smartdrv
The smartdrv command installs and configures SMARTDrive, a disk caching utility for MS-DOS. The smartdrv command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. Caching is automatic beginning in Windows XP, making the smartdrv command unnecessary.
Sort
The sort command is used to read data from a specified input, sort that data, and return the results of that sort to the Command Prompt screen, a file, or another output device. The sort command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Start
The start command is used to open a new command line window to run a specified program or command. The start command can also be used to start an application without creating a new window. The start command is available in all versions of Windows.
Subst
The subst command is used to associate a local path with a drive letter. The subst command is a lot like the net use command except a local path is used instead of a shared network path. The subst command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. The subst command replaced the assign command beginning with MS-DOS 6.0.
Sxstrace
The sxstrace command is used to start the WinSxs Tracing Utility, a programming diagnostic tool. The sxstrace command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Sys
The sys command is used to copy the MS-DOS system files and command interpreter to a disk. The sys command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. The sys command is used most often to create a simple bootable disk or hard drive. The necessary system files for Windows are too large to fit on a disk, so the sys command was removed beginning in Windows XP.
Systeminfo
The systeminfo command is used to display basic Windows configuration information for the local or a remote computer. The systeminfo command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Takeown
The takedown command is used to regain access to a file that that an administrator was denied access to when reassigning ownership of the file. The takeown command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Taskkill
The taskkill command is used to terminate a running task. The taskkill command is the command line equivalent of ending a process in Task Manager in Windows. The taskkill command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Tasklist
Displays a list of applications, services, and the Process ID (PID) currently running on either a local or a remote computer. The tasklist command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Tcmsetup
The tcmsetup command is used to set up or disable the Telephony Application Programming Interface (TAPI) client. The tcmsetup command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Telnet
The telnet command is used to communicate with remote computers that use the Telnet protocol. The telnet command is available in all versions of Windows. The telnet command is not available by default in Windows 11, 10, 8, 7, or Vista, but can be enabled by turning on the Telnet Client Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel.
Tftp
The tftp command is used to transfer files to and from a remote computer that’s running the Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) service or daemon. The tftp command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The tftp command is not available by default in some versions of Windows, but can be enabled by turning on the TFTP Client Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel.
Time
The time command is used to show or change the current time. The time command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Timeout
The timeout command is typically used in a batch or script file to provide a specified timeout value during a procedure. The timeout command can also be used to ignore keypresses. The timeout command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Title
The title command is used to set the Command Prompt window title. The title command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Tlntadmn
The tlntadmn command is used to administer a local or remote computer running Telnet Server. The tlntadmn command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The tlntadmn command is not available by default in some versions of Windows but can be enabled by turning on the Telnet Server Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel.
Tpmvscmgr
The tpmvscmgr command is used to create and destroy TPM virtual smart cards. The tpmvscmgr command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, and Windows 8.
Tracerpt
The tracerpt command is used to process event trace logs or real-time data from instrumented event trace providers. The tracerpt command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Tracert
The tracert command sends Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Echo Request messages to a specified remote computer with increasing Time to Live (TTL) field values and displays the IP address and hostname, if available, of the router interfaces between the source and destination. The tracert command is available in all versions of Windows.
Tree
The tree command is used to graphically display the folder structure of a specified drive or path. The tree command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Tscon
The tscon command is used to attach a user session to a Remote Desktop session. The tscon command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Tsdiscon
The tsdiscon command is used to disconnect a Remote Desktop session. The tsdiscon command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Tskill
The tskill command is used to end the specified process. The tskill command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Tsshutdn
The tsshutdn command is used to remotely shut down or restart a terminal server. The tsshutdn command is available in Windows XP. The ability to shut down a computer remotely is also available in the more powerful shutdown command, so tsshutdn was removed beginning in Windows Vista.
Type
The type command is used to display the information contained in a text file. The type command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Typeperf
The typerperf command displays performance data in the Command Prompt window or writes the data to specified log file. The typeperf command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Tzutil
The tzutil command is used to display or configure the current system’s time zone. The tzutil command can also be used to enable or disable Daylight Saving Time adjustments. The tzutil command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, and Windows 7.
Umount
The umount command is used to remove Network File System (NFS) mounted network shares. The umount command is available in Windows 7 and Windows Vista. The umount command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Services for NFS Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. The umount command is not available in Windows 11, 10, or 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued.
Undelete
The undelete command is used to undo a deletion performed with the MS-DOS delete command. The undelete command is only available in MS-DOS. The undelete command was removed beginning in Windows 95 due to the availability of the Recycle Bin in Windows. Additionally, free file recovery programs are available from third-party software makers.
Unformat
The unformat command is used to undo the formatting on a drive performed by the MS-DOS format command. The unformat command is only available in MS-DOS. The unformat command was removed beginning in Windows 95 due to file system changes.
Unlock
The unlock command is used to unlock a drive, disabling direct disk access for a program. The unlock command is only available in Windows 98 and 95. Drive locking is no longer available as of Windows XP.
Unlodctr
The unlodctr command removes Explain text and Performance counter names for a service or device driver from the Windows Registry. The unlodctr command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Vaultcmd
The vaultcmd command is used to create, remove, and show stored credentials. The vaultcmd command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, and Windows 7.
Ver
The ver command is used to display the current Windows or MS-DOS version number. The ver command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Verify
The verify command is used to enable or disable the ability of Command Prompt, or MS-DOS, to verify that files are written correctly to a disk. The verify command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Vol
The vol command shows the volume label and serial number of a specified disk, assuming this information exists. The vol command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS.
Vsafe
The vsafe command is used to start VSafe, a basic virus protection system for MS-DOS. The vsafe command is only available in MS-DOS. VSafe was designed for MS-DOS and Windows 3.x only. Microsoft provides an optional virus protection suite called Microsoft Security Essentials for Windows XP and later operating systems, and third-party antivirus tools are available for all versions of Windows.
Vssadmin
The vssadmin command starts the Volume Shadow Copy Service administrative command line tool which displays current volume shadow copy backups and all installed shadow copy writers and providers. The vssadmin command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
W32tm
The w32tm command is used to diagnose issues with Windows Time. The w32tm command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Waitfor
The waitfor command is used to send or wait for a signal on a system. The waitfor command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Wbadmin
The wbadmin command is used to start and stop backup jobs, display details about a previous backup, list the items within a backup, and report on the status of a currently running backup. The wbadmin command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. The wbadmin command replaced the ntbackup command beginning in Windows Vista.
Wecutil
The wecutil command is used to manage subscriptions to events that are forwarded from WS-Management supported computers. The wecutil command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Wevtutil
The wevtutil command starts the Windows Events Command Line Utility which is used to manage event logs and publishers. The wevtutil command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Where
The where command is used to search for files that match a specified pattern. The where command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Whoami
The whoami command is used to retrieve user name and group information on a network. The whoami command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Winmgmt
The winmgmt command starts the command line version of WMI, a scripting tool in Windows. The winmgmt command is available in all versions of Windows.
Winrm
The winrm command is used to start the command line version of Windows Remote Management, used to manage secure communications with local and remote computers using web services. The winrm command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Winrs
The winrs command is used to open a secure command window with a remote host. The winrs command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Winsat
The winsat command starts the Windows System Assessment Tool, a program that assesses various features, attributes, and capabilities of a computer running Windows. The winsat command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Wmic
The wmic command starts the Windows Management Instrumentation Command line (WMIC), a scripting interface that simplifies the use of Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) and systems managed via WMI. The wmic command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Wsmanhttpconfig
The wsmanhttpconfig command is used to manage aspects of the Windows Remote Management (WinRM) service. The wsmanhttpconfig command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
Xcopy
The xcopy command can copy one or more files or directory trees from one location to another. The xcopy command is generally considered a more «powerful» version of the copy command through the robocopy command trumps even xcopy. The xcopy command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. A command by the name of xcopy32 existed in Windows 95 and Windows 98. To avoid a long and confusing explanation here, just know that no matter if you executed the xcopy command or the xcopy32 command, you were always executing the most updated version of the command.
Xwizard
The xwizard command, short for Extensible Wizard, is used to register data in Windows, often from a preconfigured XML file. The xwizard command is available in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, and Windows 7.
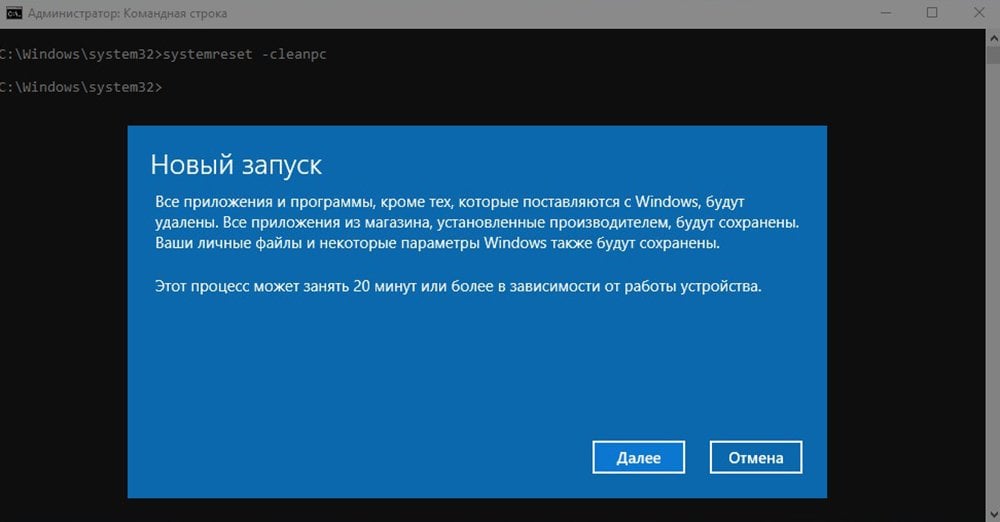
В наших статьях про работу Windows 10 и других версий часто можно встретить упоминание командной строки. Все дело в том, что это удобный системный инструмент, который позволяет настраивать ОС под себя и управлять разными ее частями с помощью простых текстовых команд. Например, мгновенно запускать разные приложения или проводить проверку и сканирование файлов.
Для командной строки существует огромное количество различных кодов, которые мы можете использовать для того, чтобы упростить себе работу с системой и использовать ее функции по максимуму. Ниже разберемся, как открывается командная строка и какие команды можно в нее вводить.
Виды командной строки
Утилита для выполнения команд в Windows разделена на два интерфейса: непосредственно командную строку и оболочку PowerShell. Каждая из них — это консоль, которая напрямую соединяет вас с компонентами ОС или конкретными приложениями на вашем ПК.
Первой появилась командная строка. Ее встроили в систему для того, чтобы оптимизировать стандартные задачи, например, работу с учетными записями на ПК или создание резервных копий по ночам. Вы можете запускать и куда более сложные сценарии. Скрипты командной строки помогают вам облегчить и ускорить работу.
командная строка виндовс 10
PowerShell же создан как расширенная версия прошлой утилиты и использует собственные скрипты — командлеты. Они представляют собой язык сценариев, который можно расширять. По сути, вы можете использовать ту утилиту, которая удобнее вам, но помните, что командная строка не может использовать командлеты для PowerShell.
командная строка виндовс 10
Открываем командную строку
Проще всего запустить командную строку через системную утилиту «Выполнить». Ее можно вызвать с помощью комбинации клавиш Windows + R. В открывшемся окне введите cmd и подтвердите выполнение запроса.
командная строка виндовс 10
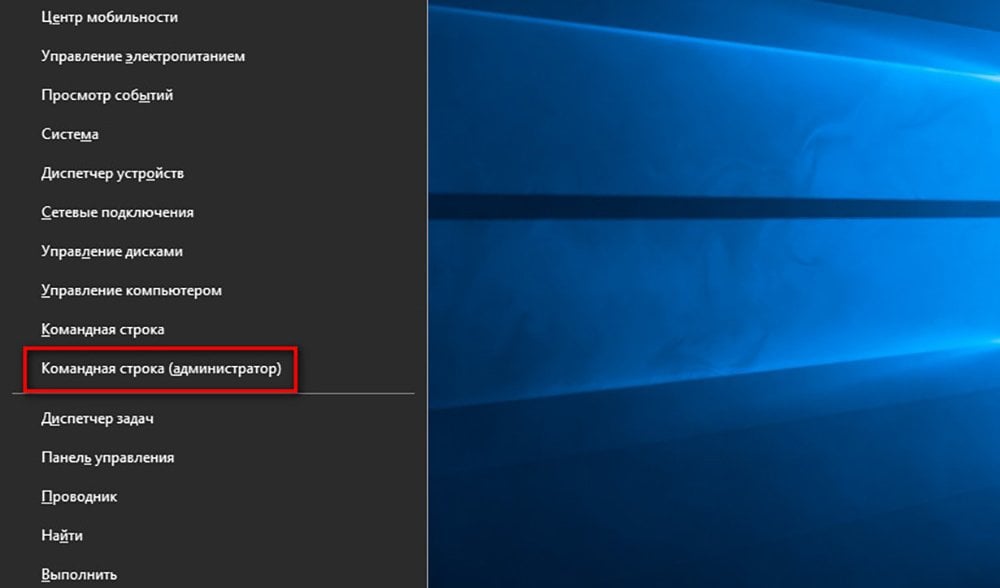
Еще один вариант — запуск через меню «Пуск». Нажмите правой кнопкой мыши по иконке меню и выберите «Командная строка» или «Windows PowerShell». Также вы таким образом можете запустить командную строку от имени администратора и получить максимальный ее функционал. Но помните, что этот способ сработает только если у вас не стоит модификации на меню «Пуск». В ином случае у вас откроется другое всплывающее окно.
командная строка виндовс 10
Какой бы способ вы не выбрали — итог будет одинаковым. В результате откроется окно командной строки, в которое вы сразу же можете вводить нужные вам команды для системы и прочих файлов.
Список команд
Как мы уже отметили ранее, в командной строке есть очень много различных команд, но большинство из них настолько специфичны, что нужны только в редких случаях. В статье мы постарались собрать только основные команды, которые могут помочь вам быстро открывать системные утилиты и работать с папками на вашем ПК.
командная строка виндовс 10
Помните об осторожности при работе с системными файлами и инструментами, и не забывайте делать бэкапы файлов, если вам нужно что-то серьезно изменить.
Программы и утилиты
Эти команды позволят вам моментально запускать программы и открывать разные системные утилиты. С их помощью вы можете быстро перемещаться по разным компонентам системы, без необходимости делать несколько шагов в меню пуск. А еще это позволяет запускать важные утилиты, для доступа к которым нужно лезть вглубь ПК.
- appwiz.cpl — программы и компоненты;
- certmgr.msc — меню управление системными сертификатами
- control — панель управления;
- control printers — меню управления подключенными устройствами и принтерами;
- control userpasswords2 — учетные записи на ПК;
- compmgmt.msc — управление параметрами ПК;
- devmgmt.msc — диспетчер устройств;
- dfrgui — меню оптимизации дискового пространства;
- diskmgmt.msc — управление дисками и пространством;
- dxdiag — средство диагностики DirectX.
командная строка виндовс 10
- hdwwiz.cpl — диспетчер устройств (другая команда);
- firewall.cpl — брандмауэр Защитника Windows;
- gpedit.msc — редактор локальной групповой политики;
- lusrmgr.msc — локальные пользователи и группы на вашем ПК;
- mblctr — центр мобильности;
- mmc — консоль управления системными оснастками;
- msconfig — системная конфигурация;
- odbcad32 — панель администрирования источника данных ODBC;
- perfmon.msc — системный монитор (можно смотреть изменения в производительности ПК и системы);
- presentationsettings — режим презентации;
- powershell — PowerShell (расширенная версия командной строки);
- powershell_ise — интегрированная среда сценариев для PowerShell;
- regedit — редактор реестра.
командная строка виндовс 10
- resmon — монитор ресурсов;
- rsop.msc — результирующая политика Windows;
- shrpubw — мастер создания общих ресурсов;
- secpol.msc — локальная политика безопасности;
- services.msc — средство управления службами операционной системы;
- taskmgr — диспетчер задач;
- taskschd.msc — планировщик заданий.
Приложения
Команд для работы с приложениями довольно мало. Они направлены в основном на уже открытые программы, которые выполняют определенные процессы на ПК.
- schtasks – отложенный запуск приложения через планировщик задач;
- shutdown – выключить или перезагрузить ПК;
- tasklist – список выполняемых задач на ПК;
- taskkill – остановить выполнение задачи и закрыть процесс (нужен PID, его вы можете узнать из прошлой команды);
- reg – редактор реестра;
- runas – запустить задачу от имени другого пользователя.
командная строка виндовс 10
Управление системой
С этим пунктом нужно обращаться осторожнее, ведь команды в нем связаны непосредственно с работой вашей системы. Конечно, если вы просто запустите утилиты с помощью этих запросов, и ничего не будете менять, все будет нормально. Но если вам нужно что-то изменить в системе — будьте крайне осторожны.
- computerdefaults — параметры программ по умолчанию;
- control admintools — папка со средствами администрирования;
- date — управление датой на ПК;
- displayswitch — управление подключенными экранами;
- dpiscaling — параметры дисплея;
- eventvwr.msc — журнал событий;
- fsmgmt.msc — средство работы с общими папками;
- fsquirt — работа с файлами по Bluetooth;
- intl.cpl — региональные настройки;
- joy.cpl — внешние игровые устройства;
- logoff — выход из системы.
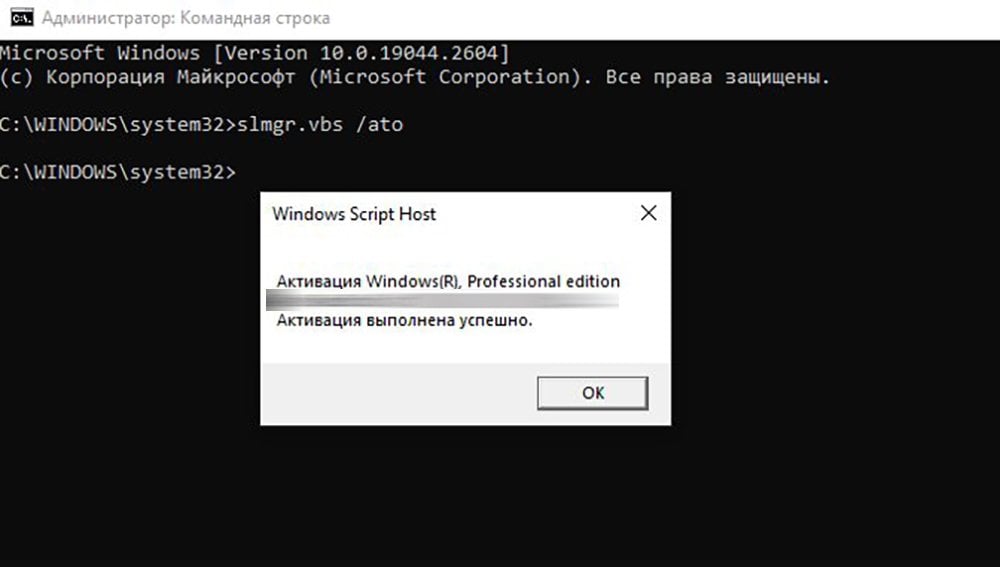
командная строка виндовс 10
- lpksetup — управлениее языками интерфейса;
- mobsync — центр синхронизации Windows;
- msdt — средство диагностики службы поддержки Microsoft;
- msra — удаленный помощник Windows;
- msinfo32 — сведения о системе;
- mstsc — удаленный рабочий стол;
- napclcfg.msc — конфигурация операционной системы;
- netplwiz — управление учетными записями пользователей;
- optionalfeatures — управление стандартными компонентами операционной системы;
- shutdown — завершение работы компьютера;
- sigverif — средство проверки подлинности файлов;
- sndvol — запуск микшера громкости;
- slui — активация лицензии Windows;
- sysdm.cpl — свойства системы;
- systempropertiesperformance — параметры быстродействия;
- systempropertiesdataexecutionprevention — запуск службы DEP параметров быстродействия.
командная строка виндовс 10
- timedate.cpl — дата и время ПК;
- tpm.msc — управление доверенным платформенным модулем TPM на локальном компьютере;
- useraccountcontrolsettings — параметры управления учетными записями пользователей;
- utilman — специальные возможности;
- ver — сведения о текущей версии Windows;
- wf.msc — режим повышенной безопасности брандмауэра;
- winver —общие сведения о Windows;
- WMIwscui.cpl — центр поддержки Windows;
- wscript — параметры сервера сценария;
- wusa — автономный установщик обновлений Windows.
Сеть и интернет
С помощью этих команды вы можете проверить работоспособность вашего интернета и изменить настройки. Также вам будет доступна информация о сетевых устройствах и интерфейсах.
- control netconnections — просмотр и настройка сетевых подключений;
- inetcpl.cpl — свойства интернета;
- NAPncpa.cpl — аналог первой команды;
- telephon.cpl — настройка модемного подключения к интернету;
- ipconfig – информация о сетевых интерфейсах;
- ping – отправляет ICMP-запросы на целевой хост, проверяет его доступность.
командная строка виндовс 10
- tracert – путь пакетов в сети;
- nslookup – поиск IP-адреса по имени ресурса;
- route – таблицы сетевых маршрутов;
- arp – таблицу с IP-адресами, преобразованными в физические адреса;
- netsh – программа управления сетевыми настройками;
- getmac – MAC-адрес сетевого адаптера;
- tftp – запускает TFTP-клиент в консоли.
Периферия
Команды для управления оборудованием, подключенным к вашему ПК тоже есть. Их немного и они вызывают в основном окна настройки разных устройств, от мышки для принтера и графического планшета.
- main.cpl — панель настройки мыши;
- mmsys.cpl — панель настройки звука;
- printui — пользовательский интерфейс принтера;
- printbrmui — средство переноса принтера, с возможностью экспорта и импорта программ и драйверов;
- printmanagement.msc — управление параметрами печати.
командная строка виндовс 10
- sysedit — редактирование системных файлов с расширениями .ini и .sys;
- tabcal — средство калибровки дигитайзера;
- tabletpc.cpl — свойства планшета и пера;
- verifier — диспетчер проверки драйверов;
- wfs — факсы и сканирование;
- wmimgmt.msc — элемента управления WMI стандартной консоли.
Файлы и диски
Здесь мы рассмотрим команды для работы с дисками, папками и хранящимися в них файлами. Некоторые из них будут работать только если вы уже вызвали какую-то утилиту или запустили программу. А если вы запутаетесь, то всегда можно воспользоваться командой help, чтобы получить справку по командной строке.
- assoc — связь между расширениями имени и типа пакетного файла;
- attrib — редактирование атрибутов файла или папки;
- bcdboot — создание/восстановление системного раздела;
- cd — смена диска или просмотр выбранного;
- chdir — просмотр папки или переход к другой;
- chkdisk — проверка дисков и внешних накопителей;
- cleanmgr — очистка диска.
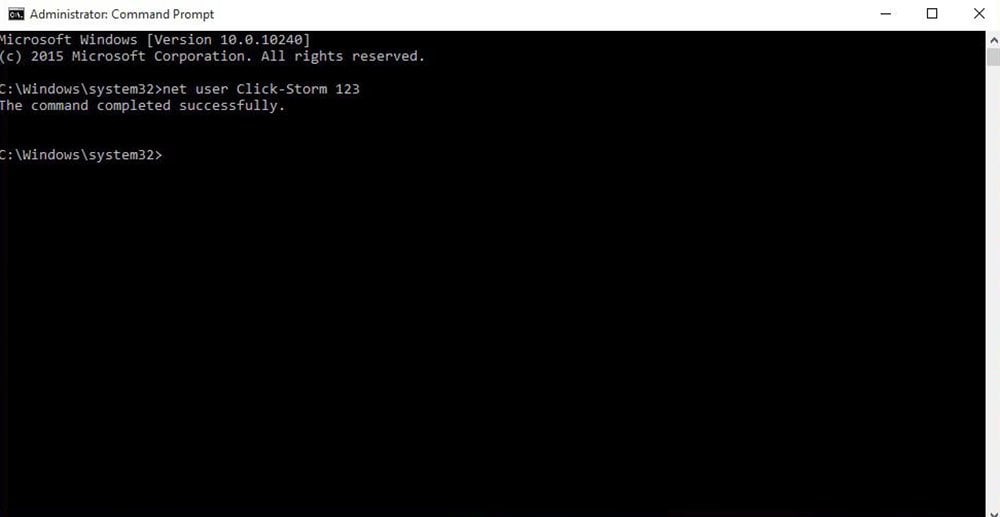
командная строка виндовс 10
- convert — смена файловой системы тома;
- copy — копирование файлов (с выбором конечного каталога);
- del — удаление выделенных файлов;
- dir — просмотр файлов и папок по выбранному пути;
- diskcopm — сравнить содержимое двух дисков;
- dickcopy — скопировать содержимое одного диска на любой другой;
- diskpart — утилита для работы с дисками (открывается в отдельном окне командной строки);
- erase — удаление одного или нескольких файлов;
- fc — сравнение файлов и поиск различий;
- format — форматирование дисков Windows;
- label — изменение меток тома для дисков;
- md — новая папка;
- mdsched — проверка оперативной памяти;
- move — перемещение файлов по указанному пути.
командная строка виндовс 10
- ntmsmgr.msc — средство работы с внешними накопителями;
- recdisc — создание диска восстановления операционной системы (только оптические накопители);
- recover — восстановление данных;
- rekeywiz — шифрующая файловая система (EFS);
- RSoPrstrui — восстановление системы;
- sdclt — резервное копирование и восстановление;
- sfc /scannow — проверка целостности системных файлов;
- tree — графическое отображение структуры каталогов;
- verify — анализ правильности записи файлов на диск;
- vol — метка и серийный номер тома диска.
Настройка командной строки
Командную строку также можно кастомизировать под себя. Изменить ее цвет, установить приветствие, очистить содержимое, если кода стало слишком много. Словом, всячески управлять ей.
- cls — очистить экран командной строки;
- color — изменить цвет фона (нужен идентификатор цвета);
- exit — закрыть утилиту;
- help — полный список команд;
- prompt — изменяет слева название.
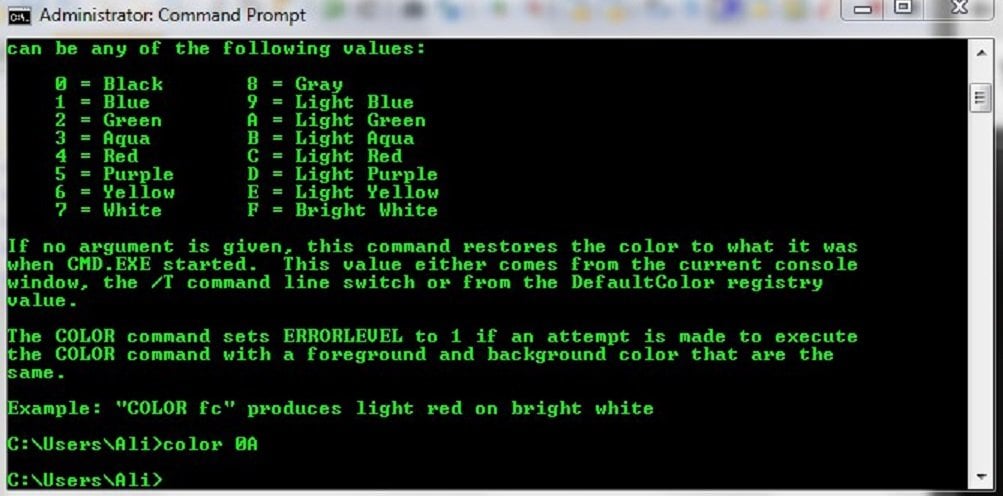
командная строка виндовс 10
В статье мы собрали самые полезные команды для командной строки. Пользуйтесь ими при необходимости, но не забывайте об осторожности. Все действия с системными файлами и утилитами вы выполняете на свой страх и риск.
Заглавное изображение: wall.alphacoders.com
Все способы:
- Команды для «Командной строки» в Виндовс 10
- Запуск приложений и компонентов системы
- Действия, управление и настройка
- Настройка и использование оборудования
- Работа с данными и накопителями
- Сеть и интернет
- Заключение
- Вопросы и ответы: 10
«Командная строка» или консоль — один из важнейших компонентов Windows, предоставляющий возможность быстрого и удобного управления функциями операционной системы, ее тонкой настройки и устранения множества проблем как с программной, так и с аппаратной составляющей. Но без знания команд, с помощью которых все это можно сделать, данный инструмент является бесполезным. Сегодня мы расскажем именно о них – различных командах и операторах, предназначенных для использования в консоли.
Команды для «Командной строки» в Виндовс 10
Так как команд для консоли существует огромное множество, мы рассмотрим лишь основные из них — те, которые рано или поздно могут прийти на помощь рядовому пользователю Windows 10, ведь именно на них и ориентирована эта статья. Но прежде чем приступить к изучению информации, рекомендуем вам ознакомиться с представленным по ссылке ниже материалом, в котором рассказывается обо всех возможных вариантах запуска консоли как с обычными, так и с административными правами.
Читайте также:
Как открыть «Командную строку» в Виндовс 10
Запуск консоли от имени администратора в Windows 10
Запуск приложений и компонентов системы
Первым делом рассмотрим простые команды, с помощью которых можно быстро запускать стандартные программы и оснастки. Напомним, что после ввода любой из них нужно нажимать «ENTER».
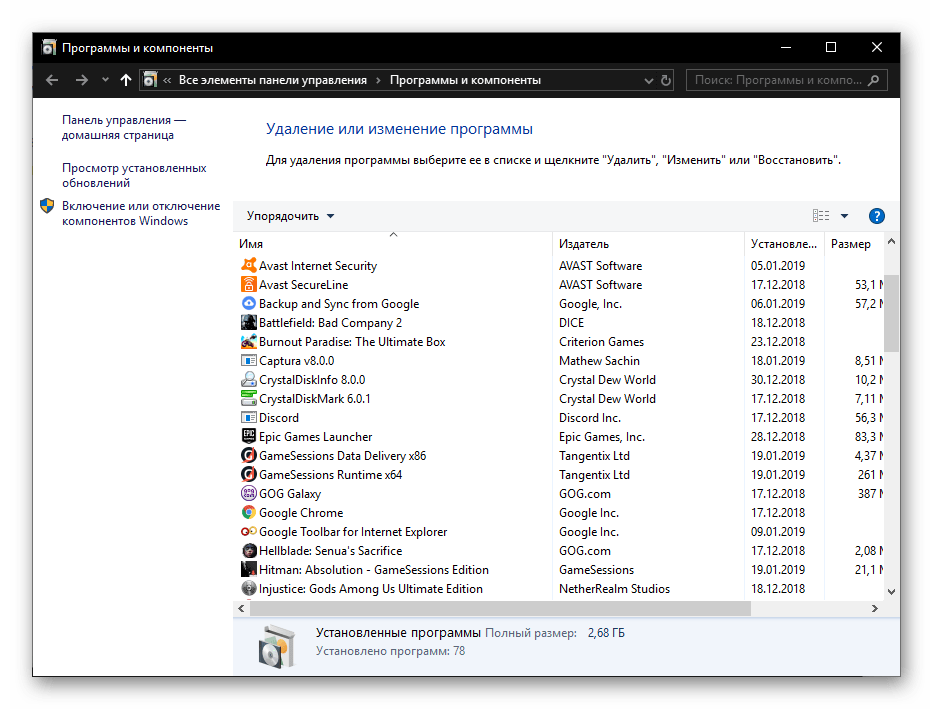
Читайте также: Установка и удаление программ в Виндовс 10
| appwiz.cpl | Запуск средства «Программы и компоненты» |
| certmgr.msc | Консоль управления сертификатами |
| control | «Панель управления» |
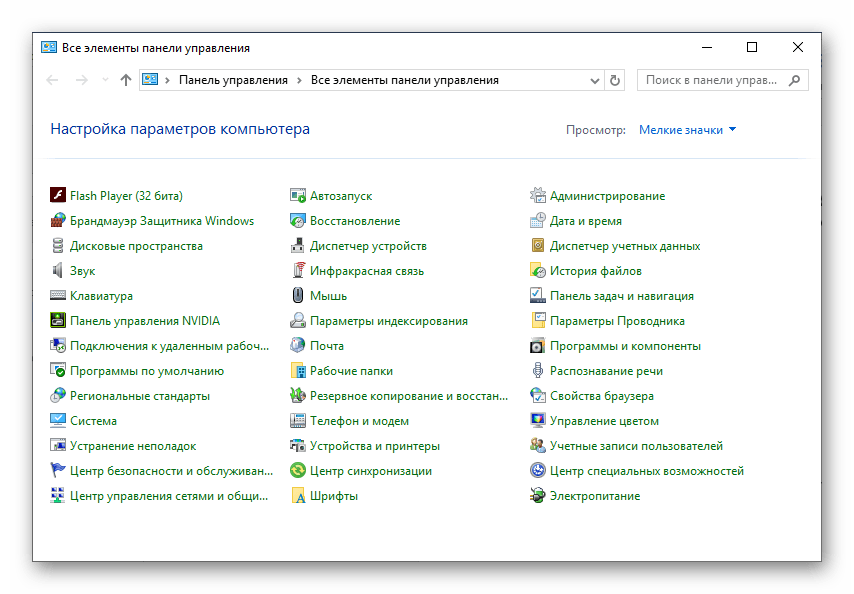
| control printers | «Принтеры и факсы» |
| control userpasswords2 | «Учетные записи пользователя» |
| compmgmt.msc | «Управление компьютером» |
| devmgmt.msc | «Диспетчер устройств» |
| dfrgui | «Оптимизация дисков» |
| diskmgmt.msc | «Управление дисками» |
| dxdiag | Средство диагностики DirectX |
| hdwwiz.cpl | Еще одна команда для вызова «Диспетчера устройств» |
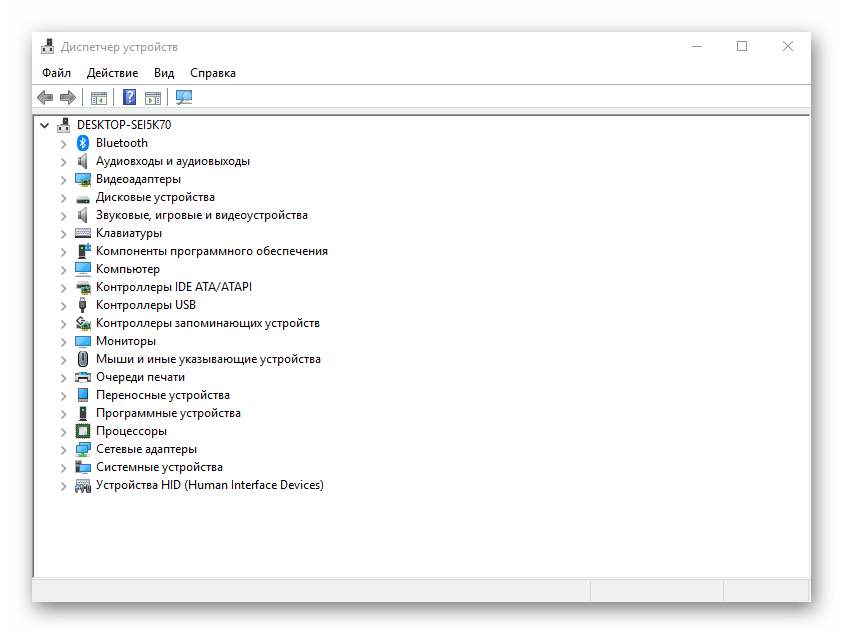
| firewall.cpl | Брандмауэр Защитника Windows |
| gpedit.msc | «Редактор локальной групповой политики» |
| lusrmgr.msc | «Локальные пользователи и группы» |
| mblctr | «Центр мобильности» (по понятным причинам доступен только на ноутбуках) |
| mmc | Консоль управления системными оснастками |
| msconfig | «Конфигурация системы» |
| odbcad32 | Панель администрирования источника данных ODBC |
| perfmon.msc | «Системный монитор», предоставляющий возможность просмотра изменений в производительности компьютера и системы |
| presentationsettings | «Параметры режима презентации» (доступно только на ноутбуках) |
| powershell | PowerShell |
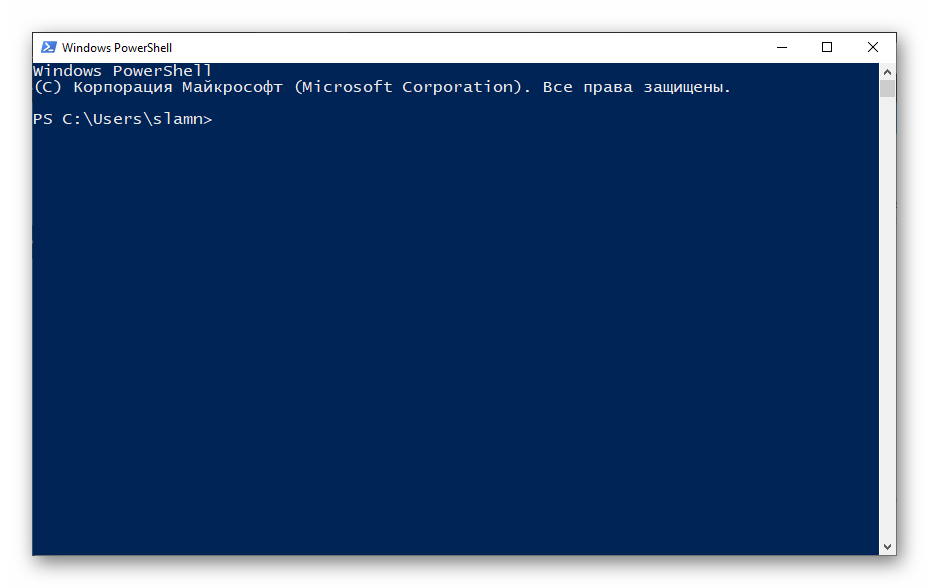
| powershell_ise | «Интегрированная среда сценариев» оболочки PowerShell |
| regedit | «Редактор реестра» |
| resmon | «Монитор ресурсов» |
| rsop.msc | «Результирующая политика» |
| shrpubw | «Мастер создания общих ресурсов» |
| secpol.msc | «Локальная политика безопасности» |
| services.msc | Средство управления службами операционной системы |
| taskmgr | «Диспетчер задач» |
| taskschd.msc | «Планировщик заданий» |
Действия, управление и настройка
Здесь будут представлены команды для выполнения различных действий в среде операционной, а также управления и настройки входящих в ее состав компонентов.
| date | Просмотр текущей даты с возможностью ее изменения |
| displayswitch | Выбор экранов |
| dpiscaling | Параметры дисплея |
| eventvwr.msc | Просмотр журнала событий |
| fsmgmt.msc | Средство работы с общими папками |
| fsquirt | Отправка и прием файлов по Bluetooth |
| intl.cpl | Региональные настройки |
| joy.cpl | Настройка внешних игровых устройств (геймпадов, джойстиков и т.д.) |
| logoff | Выход из системы |
| lpksetup | Установка и удаление языков интерфейса |
| mobsync | «Центр синхронизации» |
| msdt | Официальное средство диагностики службы поддержки Microsoft |
| msra | Вызов «Удаленного помощника Windows» (может использоваться как для получения, так и для оказания помощи удаленно) |
| msinfo32 | Просмотр сведений об операционной системе (отображает характеристики программных и аппаратных компонентов ПК) |
| mstsc | Подключение к удаленному Рабочему столу |
| napclcfg.msc | Настройка конфигурации операционной системы |
| netplwiz | Панель управления «Учетными записями пользователей» |
| optionalfeatures | Включение и отключение стандартных компонентов операционной системы |
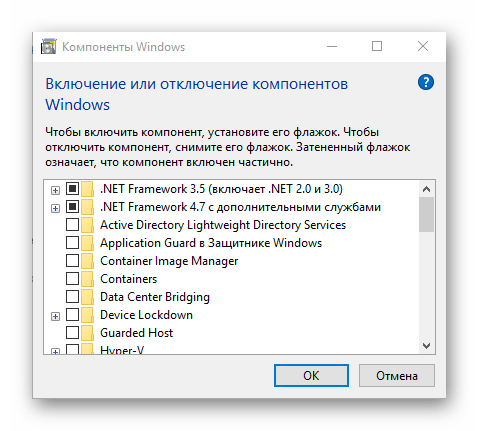
| shutdown | Завершение работы |
| sigverif | Средство проверки подлинности файлов |
| sndvol | «Микшер громкости» |
| slui | Средство активации лицензии ОС Windows |
| sysdm.cpl | «Свойства системы» |
| systempropertiesperformance | «Параметры быстродействия» |
| systempropertiesdataexecutionprevention | Запуск службы DEP, компонента «Параметров быстродействия» ОС |
| timedate.cpl | Изменение даты и времени |
| tpm.msc | «Управление доверенным платформенным модулем TPM на локальном компьютере» |
| useraccountcontrolsettings | «Параметры управления учетными записями пользователей» |
| utilman | Управление «Специальными возможностями» в разделе «Параметров» операционной системы |
| wf.msc | Активация режима повышенной безопасности в стандартном Брандмауэре ОС Windows |
| winver | Просмотр общих (кратких) сведений об операционной системе и ее версии |
| WMIwscui.cpl | Переход к Центру поддержки операционной системы |
| wscript | «Параметры сервера сценария» ОС Windows |
| wusa | «Автономный установщик обновлений Windows» |
Настройка и использование оборудования
Есть ряд команд, предназначенных для вызова стандартных программ и элементов управления и предоставляющих возможность настройки оборудования, подключенного к компьютеру или ноутбуку либо интегрированного.
| Команда | Описание |
|---|---|
| main.cpl | Настройка мыши |
| mmsys.cpl | Панель настройки звука (устройства ввода/вывода аудиосигнала) |
| printui | «Пользовательский интерфейс принтера» |
| printbrmui | Средство переноса принтера, предоставляющее возможность экспорта и импорта программных компонентов и драйверов оборудования |
| printmanagement.msc | «Управление печатью» |
| sysedit | Редактирование системных файлов с расширениями INI и SYS (Boot.ini, Config.sys, Win.ini и др.) |
| tabcal | Средство калибровки дигитайзера |
| tabletpc.cpl | Просмотр и настройка свойств планшета и пера |
| verifier | «Диспетчер проверки драйверов» (их цифровой подписи) |
| wfs | «Факсы и сканирование» |
| wmimgmt.msc | Вызов «Элемента управления WMI» стандартной консоли |
Работа с данными и накопителями
Ниже представим ряд команд, предназначенных для работы с файлами, папками, дисковыми устройствами и накопителями, как внутренними, так и внешними.
Примечание: Некоторые из представленных ниже команд работают только в контексте – внутри предварительно вызванных консольных утилит или с обозначенными файлами, папками. Для получения более подробных сведений по ним вы всегда можете обратиться к справке, воспользовавшись командой «help» без кавычек.
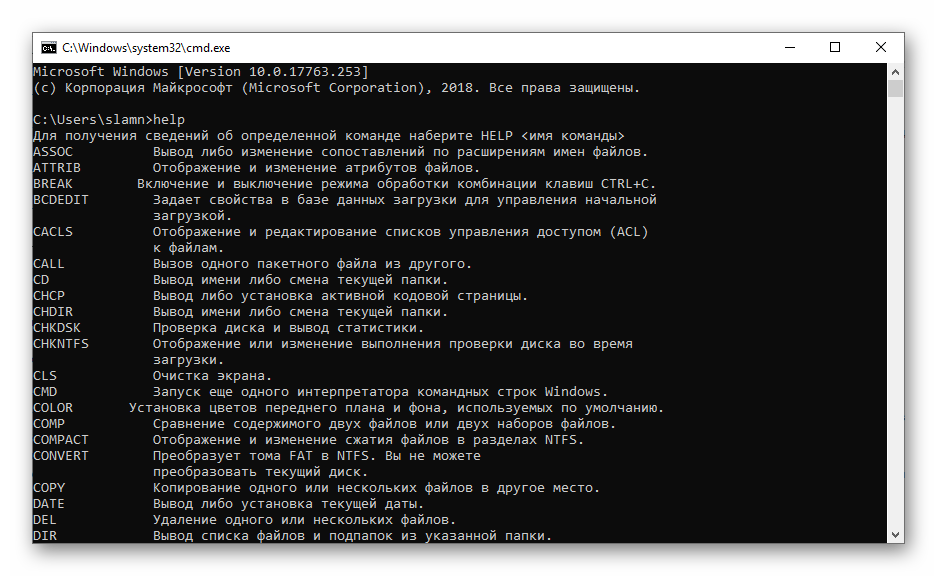
| attrib | Редактирование атрибутов предварительно обозначенного файла или папки |
| bcdboot | Создание и/или восстановление системного раздела |
| cd | Просмотр наименования текущей директории или переход в другую |
| chdir | Просмотр папки или переход к другой |
| chkdsk | Проверка жестких и твердотельных дисков, а также подключенных к ПК внешних накопителей |
| cleanmgr | Инструмент «Очистка диска» |
| convert | Преобразование файловой системы тома |
| copy | Копирование файлов (с указанием конечного каталога) |
| del | Удаление выбранных файлов |
| dir | Просмотр файлов и папок по указанному пути |
| diskpart | Консольная утилита для работы с дисками (открывается в отдельном окне «Командной строки», для просмотра поддерживаемых команд обратитесь к справке – help) |
| erase | Удаление файлов |
| fc | Сравнение файлов и поиск различий |
| format | Форматирование накопителя |
| md | Создание новой папки |
| mdsched | Проверка оперативной памяти |
| migwiz | Средство миграции (переноса данных) |
| move | Перемещение файлов по заданному пути |
| ntmsmgr.msc | Средство работы с внешними накопителями (флешками, картами памяти и т.д.) |
| recdisc | Создание диска восстановления операционной системы (работает только с оптическими накопителями) |
| recover | Восстановление данных |
| rekeywiz | Инструмент для шифрования данных («Шифрующая файловая система (EFS)») |
| RSoPrstrui | Настройка средства «Восстановление системы» |
| sdclt | «Резервное копирование и восстановление» |
| sfc /scannow | Проверка целостности системных файлов с возможностью их восстановления |
Читайте также: Форматирование флешки через «Командную строку»
Сеть и интернет
Напоследок ознакомим вас с несколькими простыми командами, предоставляющими возможность получения быстрого доступа к сетевым параметрам и настройке интернета.
| control netconnections | Просмотр и настройка доступных «Сетевых подключений» |
| inetcpl.cpl | Переход к свойствам интернета |
| NAPncpa.cpl | Аналог первой команды, предоставляющий возможность настройки сетевых подключений |
| telephon.cpl | Настройка модемного подключения к интернету |
Заключение
Мы ознакомили вас с довольно большим количеством команд для «Командной строки» в Windows 10, но по факту это лишь малая их часть. Запомнить все получится вряд ли, но этого и не требуется, тем более что при необходимости вы всегда можете обратиться к данному материалу или встроенной в консоль справочной системе. Кроме того, если у вас остались вопросы по рассмотренной нами теме, смело задавайте их в комментариях.
Наша группа в TelegramПолезные советы и помощь
The Windows Command Prompt (CMD) is a powerful tool that allows users to interact with their operating system through text-based commands. Whether you’re a beginner exploring CMD for the first time, an expert troubleshooting advanced issues, or just looking for utility-focused tasks, this guide has you covered.
In this guide, we will provide you with some of the most useful commands for the following:
- CMD Commands for Beginners
- CMD Commands for Experts
- CMD Commands for Utility
- CMD Commands for Troubleshooting
- CMD Commands for Students
- CMD Commands for Programmers
CMD Commands for Beginners
These commands are essential for users who are new to CMD and provide basic functionalities to help them navigate and perform simple tasks.
1. View Directory ‘dir‘
- Function: Displays the contents of the current directory.
- How to use: Type
dirand press Enter. Usedir /sto include subdirectories. - Use case: Quickly view files and folders in your current location.
Syntax: dir
2. Change Directories ‘cd’
- Function: Lets you navigate between folders.
- How to use: Type
cd [folder_name]to move into a directory. Usecd ..to go up one level. - Use case: Navigate to specific directories to manage files or execute commands
Syntax: cd [folder name]
3. Create a New Directory ‘mkdir’ or ‘md’
- Function: Allows you to create a new directory
- How to use: Type mkdir [file_name]– Here the new directory name is GFG
- Use case: When you need a new directory for any separate work, you may create a new directory
Syntax: mkdir [GFG]
4. Rename a File ‘ren’
- Function: Helps in renaming any file or directory.
- How to use: Type
renorrename [old_name] [new_name]and press Enter. - Use case: Discover new method of renaming file or any directory.
Syntax: ren xyz.txt newxyz.txt
5. Delete a File ‘del’
- Function: Lets you to remove one or more files
- How to use: Type del [file_name]– This will erase the provided file name
- Use case: This function allows you to erase any file if you’re unable to fetch
Syntax: del[file_name]
6. Close ‘exit’
- Function: Closes the Command Prompt window.
- How to use: Type
exitand press Enter. - Use case: Ends your session with CMD.
Syntax: exit
7. Clear Screen ‘cls’
- Function: Clears all text from the CMD window.
- How to use: Type
clsand press Enter. - Use case: Removes clutter after multiple commands
Syntax: cls
8. View Available Command ‘help’
- Function: Lists all available commands and their descriptions.
- How to use: Type
helpand press Enter. - Use case: Discover new commands and learn their functions.
Syntax: help
9. Display or Set the System time ‘time’
- Function: Lets you set the system time or display the current time.
- How to use: Type
time [new_time] and press Enter. - Use case: Allows the user to set their system’s time without additional navigation
Syntax: time [new_time]
10. Copy Files ‘copy’
- Function: Lists all available commands and their descriptions.
- How to use: Type
copy [source1] [destination2] and press Enter. - Use case: Discover new commands and learn their functions.
Syntax: copy file.txt Backup\
| Command | Description | Syntax | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
dir |
View the contents of a directory | dir |
dir C:\Users\Documents |
cd |
Change the current working directory | cd [directory_name] |
cd Downloads |
mkdir |
Create a new directory | mkdir [directory_name] |
mkdir NewProject |
ren |
Rename a file | ren [old_name] [new_name] |
ren draft.txt final.txt |
del |
Delete a file | del [file_name] |
del unwanted.txt |
exit |
Close the Command Prompt | exit |
exit |
cls |
Clear the Command Prompt screen | cls |
cls |
help |
View available CMD commands and their descriptions | help |
help |
time |
Display or set the system time | time |
time 14:30:00 |
copy |
Copy files from one location to another | copy [destination] |
copy report.docx D:\Backup\ |
CMD Commands for Experts
These commands are more advanced and suitable for users comfortable with troubleshooting and system management tasks.
1. System File Checker ‘sfc’
- Function: Scans and repairs corrupted system files.
- How to use: Type
sfc /scannowin CMD (run as administrator). - Use case: Fix system errors related to missing or corrupted files.
Syntax: sfc /scannow
2. Disk Error ‘chkdsk’
- Function: Scans the hard drive for bad sectors and file system errors.
- How to use: Type
chkdsk [drive letter]: /f(e.g.,chkdsk C: /f) in CMD. - Use case: Identify and fix disk issues.
Syntax: chkdsk C: /f
3. View Running Processor ‘tasklist’
- Function: Displays all running processes and their details.
- How to use: Type
tasklistto list processes. Usetasklist /fi "imagename eq [process name]"to filter. - Use case: Identify resource-heavy or unresponsive processes.
Syntax: tasklist /fi "imagename eq [process name]
4. Restart ‘shutdown’
- Function: Allows you to shut down or restart the computer via CMD.
- How to use:
- Shutdown:
shutdown /s /f /t [seconds]. - Restart:
shutdown /r /f /t [seconds].
- Shutdown:
- Use case: Automate shutdown or restart tasks
Syntax:
Shutdown: shutdown /s /f /t [seconds].
Restart: shutdown /r /f /t [seconds].
5. Network Statistics ‘netstat’
- Function: Displays active connections and listening ports.
- How to use: Type
netstatto view all active connections. - Use case: Diagnose network-related issues or monitor network activity.
Syntax: netstat
6. Kill a Running Process ‘taskkill’
- Function: Lets you terminate a process using its process ID (PID)
- How to use: Type
taskkill /[PID] /F to terminate - Use case: Can be helpful for terminating any dedicated PID.
Example (PID: 1124)
Syntax: taskkill /PID 11234 /F
7. View Saved Passwords ‘netsh wlan show profiles’
- Function: Retrieve the password of a saved Wi-Fi network.
- How to use: Type netsh wlan show profile name=”WiFi-Name” key=clear
- Use case: Discover new commands and learn their functions.
Example: netsh wlan show profile name="MyHomeWiFi" key=clear
| Command | Description | Syntax | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
sfc |
System File Checker – Scans and repairs system files | sfc /scannow |
sfc /scannow |
chkdsk |
Check Disk – Scans and fixes disk errors | chkdsk [drive]: /f /r |
chkdsk C: /f /r |
tasklist |
View running processes | tasklist |
tasklist |
shutdown |
Shutdown or restart the system | shutdown /r /t [seconds] |
shutdown /r /t 10 (Restart in 10 seconds) |
netstat |
View network statistics and active connections | netstat -a |
netstat -an (Show all connections numerically) |
taskkill |
Kill a running process using its process ID (PID) | taskkill /PID [PID] /F |
taskkill /PID 4567 /F (Kill process with ID 4567) |
netsh wlan show profiles |
View saved Wi-Fi network names | netsh wlan show profiles |
netsh wlan show profiles |
CMD Commands for Utility
These commands are focused on specific tasks and utilities to enhance productivity and system performance.
1. Network Configuration ‘ipconfig’
- Function: Displays IP address, subnet mask, and gateway information.
- How to use:
- Basic: Type
ipconfig. - Detailed: Type
ipconfig /all.
- Basic: Type
- Use case: Troubleshoot internet connectivity issues.
Syntax: ipconfig
2. Network Connectivity ‘ping’
- Function: Sends packets to test communication with another device or website.
- How to use: Type
ping[destination] - Use case: Check if a device or website is reachable.
Syntax: ping geeksforgeeks.org
3. System Information ‘systeminfo’
- Function: Displays detailed information about your computer.
- How to use: Type
systeminfo. - Use case: Quickly access system specifications for troubleshooting or reporting.
Syntax: systeminfo
4. Trace Route ‘tracert’
- Function: Shows the path packets take to reach a specific destination.
- How to use: Type
tracert[destination] - Use case: Identify network bottlenecks or connectivity issues.
Syntax: tracert geeksforgeeks.org
5. Manage Drives ‘diskpart’
- Function: Opens a command-line utility for managing disk partitions.
- How to use: Type
diskpartto enter the disk management interface. - Use case: Create, delete, or modify partitions on your drives.
Syntax: diskpart
6. Delete a Directory ‘rmdir’
- Function: Removes directory from the origin
- How to use: Type rmdir [directory_name] and press Enter.
- Use case: Discover new commands and learn their functions.
Example: GFG – Directory name
Syntax: rmdir GFG
7. View ‘rmdir’
- Function: Removes directory from the origin
- How to use: Type rmdir [directory_name] and press Enter.
- Use case: Discover new commands and learn their functions.
Example: GFG - Directory name
8. Manage User Account ‘net user’
- Function: To list all the user accounts
- How to use: Type net user and press Enter.
- Use case: Discover new commands and learn their functions.
Syntax: net user username password /add
9. View Startup Programs ‘wmic startup get caption,command’
- Function: To check what programs launch on startup.
- How to use: Type wmic startup get caption,command, and press Enter.
- Use case: Discover new commands and learn their functions.
Syntax: wmic startup get caption,command
| Command | Description | Syntax | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
ipconfig |
View network configuration, including IP address, subnet mask, and gateway | ipconfig |
ipconfig /all (Displays detailed network info) |
ping |
Test network connectivity by sending packets to a host | ping [host or IP] |
ping google.com (Check connection to Google) |
systeminfo |
Display detailed system information, including OS version, installed memory, and processor | systeminfo |
systeminfo |
tracert |
Trace the route packets take to a network destination | tracert [hostname or IP] |
tracert google.com (View network path to Google) |
diskpart |
Manage disk partitions, including creating, formatting, and deleting partitions | diskpart |
diskpart → list disk → select disk 1 → create partition primary |
rmdir |
Delete a directory (folder) | rmdir [directory_name] |
rmdir /s /q OldFolder (Delete a folder and its contents without confirmation) |
dir |
View contents of a directory | dir |
dir C:\Users\Documents (List files in a specific directory) |
net user |
Manage user accounts, including adding, modifying, or deleting users | net user |
net user John password123 /add (Create a new user account) |
wmic startup get caption,command |
View startup programs and their commands | wmic startup get caption,command |
wmic startup get caption,command |
CMD Commands for Troubleshooting
1. File Comparison ‘fc’
- Function: Compares two files and highlights differences.
- How to use: Type
fc [file1] [file2]to compare files. - Use case: Detect changes or errors in files
Syntax: fc 1 2
2. Advanced Network Diagnostics ‘pathping’
- Function: Combines
pingandtracertfunctionalities to provide detailed network path diagnostics. - How to use: Type
pathping[destination] - Use case: Troubleshoot complex network issues.
Syntax: pathping geeksforgeeks.org
3. Registry Editor ‘regedit’
- Function: Launches the Windows Registry Editor.
- How to use: Type
regeditto open the registry. - Use case: Modify registry keys for advanced configuration or troubleshooting.
Syntax: regedit
4. View MAC ‘getmac’
- Function: Displays the MAC address of your network adapter.
- How to use: Type
getmacto view the MAC address. - Use case: Identify your device’s hardware address for network configurations
Syntax: getmac
5. Power Configuration ‘powercfg’
- Function: Displays and manages power settings.
- How to use: Type
powercfg/[option] - Use case: Optimize power usage and troubleshoot battery issues.
Syntax: powercfg /energy for a detailed power usage report
6. Enable Boot Manager ‘bcdedit’
- Function: Used to modify boot configuration settings
- How to use: Type
bcdedit/ set current - Use case: Discover new commands and learn their functions.
Syntax: bcdedit /set {current} bootmenupolicy standard
7. Format a Drive ‘format’
- Function: To erase any specific drive.
- How to use: Type format [drive]: /FS:NTFS and press Enter.
- Use case: Discover new commands and learn their functions.
Syntax: format D: /FS:NTFS
| Command | Description | Syntax | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
fc |
Compare two files and highlight differences | fc [file1] [file2] |
fc file1.txt file2.txt (Compare two text files) |
pathping |
Perform advanced network diagnostics with packet loss details | pathping [destination] |
pathping google.com (Analyze network route to Google) |
regedit |
Open the Windows Registry Editor (GUI) | regedit |
regedit (Opens the registry editor – use with caution!) |
getmac |
Display the MAC (Media Access Control) address of your network adapters | getmac |
getmac /v /fo list (View MAC addresses in detailed format) |
powercfg |
Manage and analyze power configurations | powercfg /[option] |
powercfg /batteryreport (Generate a battery usage report) |
bcdedit |
Enable, disable, or modify Windows Boot Configuration | bcdedit /set {current} [option] |
bcdedit /set {current} bootmenupolicy standard (Enable boot menu in Windows 10/11) |
format |
Format a drive (erase all data) | format [drive]: /FS:[filesystem] |
format D: /FS:NTFS (Format drive D: with NTFS file system) |
CMD Commands for Students
Students can use these commands to manage files, perform simple calculations, and even help with tasks like coding and studying.
1. Calculator ‘calc’
- Function: Opens the Windows Calculator application.
- How to use: Type
calcand press Enter. - Use case: Quickly open the calculator for
Syntax: calc
CMD Commands for Programmers
Programmers often use CMD to automate tasks, compile code, and test network functionality. These commands can be especially useful for developers working in command-line environments.
1. Compile Java Code ‘javac’
- Function: Compiles Java source files into bytecode.
- How to use: Type
javac [file name].javato compile Java code. - Use case: Compile and test Java programs directly from the command line.
Syntax: javac
2. Version Control ‘git’
- Function: Interacts with Git repositories from the command line.
- How to use: Type
git [command] - Use case: Manage version control, clone repositories, or push commits from the command line.
Syntax: git clone [repository URL]
3. Execute Python Script ‘python’
- Function: Runs Python scripts in the command prompt.
- How to use: Type
python [script.py]to execute a Python program. - Use case: Test and run Python code directly in the command line.
Syntax: python [script.py]
4. Run Node.js Scripts ‘node’
- Function: Executes Node.js scripts.
- How to use: Type
node [script.js]to run a JavaScript file using Node.js. - Use case: Run backend scripts and test JavaScript programs in the command line.
Syntax: node [script.js]
5. Node Package Manager ‘npm’
- Function: Installs and manages JavaScript packages.
- How to use: Type
npm install [package]to install a package. - Use case: Manage dependencies and libraries in Node.js applications.
Syntax: npm install [package]
| Command | Description | Syntax | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
javac |
Compile Java source code into bytecode (.class files) | javac [filename].java |
javac HelloWorld.java (Compile a Java file) |
git |
Version control system for tracking changes in files | git [command] |
git clone https://github.com/user/repo.git (Clone a repository) |
python |
Execute a Python script or enter interactive mode | python [script.py] |
python script.py (Run a Python script) |
node |
Execute JavaScript code using Node.js | node [script.js] |
node app.js (Run a Node.js script) |
npm |
Manage Node.js packages and dependencies | npm [command] |
npm install express (Install the Express.js package) |
Bonus: CMD Tricks and Tips
To make CMD usage even more efficient, here are some bonus tips:
1. Save CMD Output to a File
Use the > operator to save the output of a command to a text file.
2. Open CMD in a Specific Directory
Instead of navigating manually, you can directly open CMD in a folder by typing cmd in the File Explorer’s address bar.
3. Use && for Multiple Commands
You can run multiple commands sequentially:
ipconfig && ping google.com
Conclusion
Mastering the most useful CMD commands in Windows can empower you to perform tasks more efficiently, troubleshoot problems, and gain deeper control over your system. By familiarizing yourself with these essential CMD commands, you’ll be better equipped to handle a variety of situations, from simple file management to advanced system configurations. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced user, these commands are invaluable tools to have at your disposal.
With an interface as attractive as Windows 10’s, it is easy to forget that the OS comes with a command line interface as well. You might have forgotten about Command Prompt, but Microsoft hasn’t, and it has brought some handy improvements to Command Prompt with Windows 10 and Windows 11. While it’s not as powerful as its Unix counterpart, there are many Command Prompt tricks that can make it a helpful tool to have. A lot of things that the Command Prompt (also known as CMD) can let you do are not even available in the GUI of the Windows OS, so it’s something you should be using. In this article, we have listed 20+ Command Prompt tricks that you should know in 2024.
If you’re new to Windows, we suggest glancing at our Windows 10 beginner tips article to get a better idea about how the OS works and its features. Now, let’s dive in and check out what you can do with Command Prompt.
1. Encrypt Files Using Command Prompt
One of the most useful things that you can do using the Command Prompt, is encrypting your sensitive data. Encryption is a way to prevent others from taking a peek at your data, and it’s a really important part of ensuring (to some extent, at least), that your files are only yours. With this simple Command Prompt trick, you can easily encrypt files on your Windows PC.
- Launch the Command Prompt, and change your working directory to the folder where your files are. This can be done by using the “cd” command.
- Once you’re done, type “Cipher /E“, and hit Enter. This will encrypt all the files that were inside the folder.
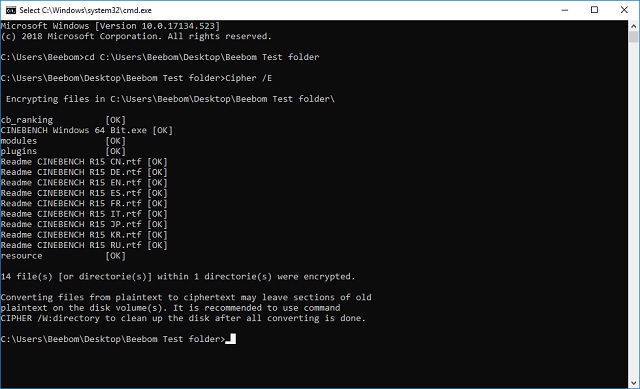
Note: If you try and open these encrypted files, they will open normally for you, however, any other user will not be able to view the files, unless they log in using your account. So make sure that you have a password set.
2. Change the Color of the Command Prompt Window
The Command Prompt window can be unexciting with the default black background and light gray text color. But Windows does allow you to change these colors to suit yourself and make things a bit more intriguing.
- Launch CMD and Right-click on the title bar
- Click on “Properties” and in the separate window that opens, click on “Colors”`
- Here you can choose the colors for the screen text or background as well as for the popup text and background, and also change the transparency of the CMD window
- After you’re done choosing the most fitting colors for your personality, Click OK
Note: There are a lot of other colors available, and you can check out the entire list by typing “help color“.
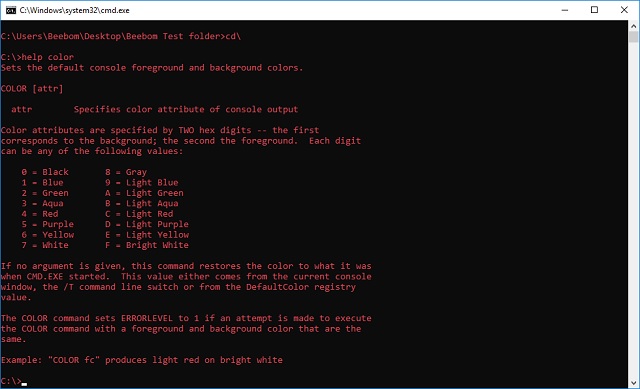
3. Change the Prompt Text in Command Prompt
When you first open Command Prompt, the default text of the prompt is very boring. It does reflect the current working directory that the user is in, but it sure could use some customization. If you would like the prompt in your cmd window to say something other than the default, you can use the following trick.
- Launch Command Prompt, and type “prompt” followed by the text that you want. Make sure you add “$G” to the end, to ensure that there is always the “>” sign at the end of the prompt, and you know where your command begins at.
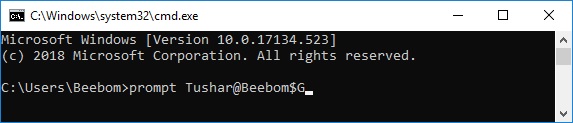
- Hit Enter, and you will see the prompt in the cmd window change to your custom text.
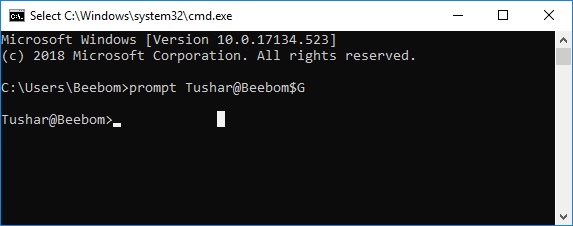
Note: There are some more options like “$G” available, and you check out the entire list by typing “help prompt“. Also, you can reset the prompt back to its original state by typing “prompt” and hitting Enter.
4. Change the Title of the Command Prompt Window
When you launch Command Prompt, you must have seen that the title bar reads “Command Prompt”, or maybe “Administrator Command Prompt”, if you launch it with Administrator privileges. While that is okay, but if you have a lot of cmd windows open, and each of them are working on a different task, then this “Command Prompt” title is not helpful at all. Fortunately, you can change that too.
- Open Command Prompt, and type “title”, followed by the text that you want the Title bar to read.
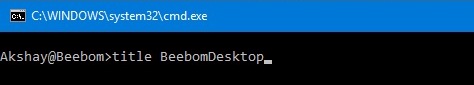
- Hit Enter, and you will see the Title of the cmd window change to the text that you entered.
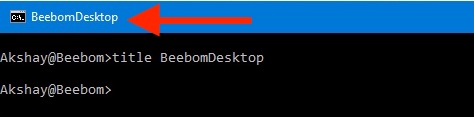
Note: The title changes back to “Command Prompt” once you quit cmd and relaunch it.
5. List Every Driver Installed on Your Windows 10 PC
If you’re trying to troubleshoot an issue or merely looking for a list of all the drivers on Windows 10/11, there’s a command prompt trick you can use. Follow the steps below to see the list of drivers:
- Type in driverquery /FO list /v in CMD, and you will see a list of drivers on your screen.
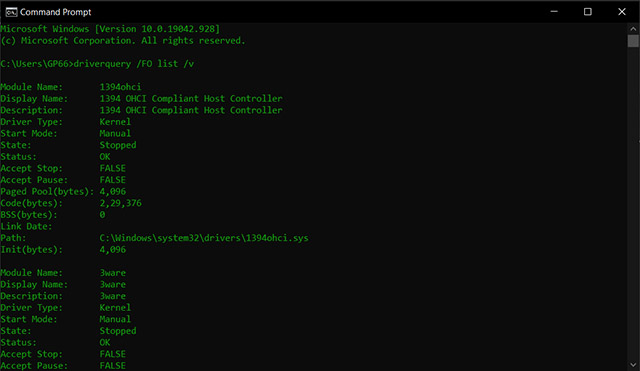
- If you want, you can also copy this output into a text file for easy viewing later. Use this command to save the drivers list to a document:
driverquery > C:\Users\YourUsername\Desktop\driver.txt
6. F1 to F9 Keys are Shortcuts in CMD
All the function keys on your keyboard are also shortcuts for various Command Prompt functions. Here’s what each function key on your keyboard does in CMD:
- F1: Tap or hold this key to retype your last command letter by letter.
- F2: Copies the current command up to a specified character.
- F3: Retypes the entire previous line
- F4: Auto-deletes the current command up to a specified character.
- F5: Similar to F3, but lets you cycle through previous commands.
- F6: Enters the EOF indicator into CMD.
- F7: Opens a list of previously entered commands.
- F8: Similar to F5, but doesn’t stop at the end of your command history in the session. Instead, it goes all the way to the start.
- F9: Enters a previous command by entering a number associated with that line.
7. Hide Folders using Command Prompt
While there is an easy way to hide folders on Windows by using the properties pane of the folder and checking the checkbox that says “Hidden”, the method is not very useful as the folders hidden using this method can easily be viewed if the view options are changed to “Show hidden files and folders”, making it a pretty useless feature. However, just like you can hide folders using Terminal on Mac, using this cmd trick, you can hide your folders in such a way that they will be completely hidden, and Explorer won’t be able to display them at all. Simply follow the steps outlined below:
- Launch Command Prompt, and navigate to the directory where your target folder resides.
- Type “Attrib +h +s +r folder_name“, replacing the “folder_name” with the name of the folder that you want to hide, and press Enter.
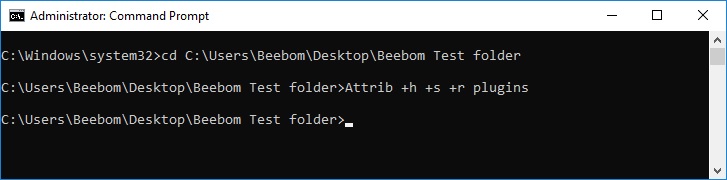
- You can now check that the folder is indeed hidden inside Windows Explorer and can not be seen by anyone.
- To unhide the folder, you can use the command “Attrib -h -s -r folder_name“.
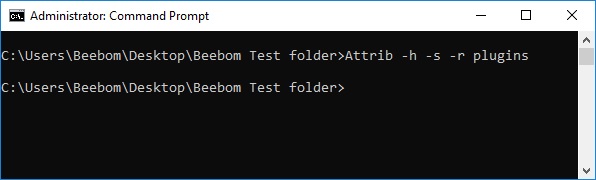
Note: Hidden folders can be viewed using the cmd command “dir /AH”.
8. Copy Command Output to Clipboard
If you have ever tried to copy stuff off the Command Prompt, you must have realized that it is exceedingly difficult, not to mention un-intuitive. However, with this simple trick you can copy the output of any command that you want, directly to your computer’s clipboard, and you can then paste it into any text editor that you want.
- Launch Command Prompt and type the command that you want to copy the output for, followed by “| clip“. For example, I’m using the command “ipconfig | clip“. Hit Enter, and you will see that the cmd window shows no output.
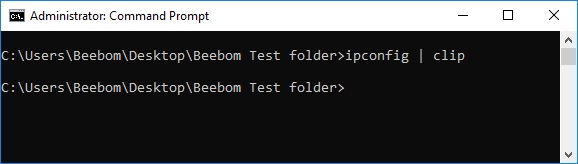
- Open a text editor, such as Notepad, and press Control + V, and you can simply paste the output of the command directly inside Notepad.
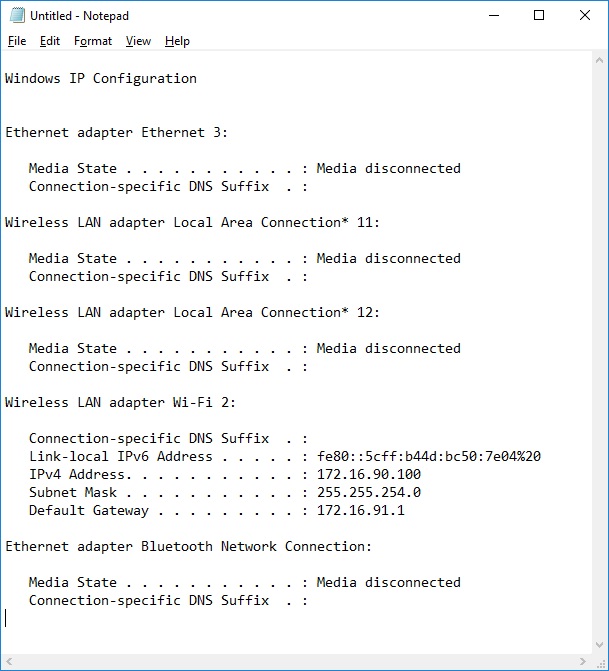
9. List all Installed Programs
Another cool trick on the Command Prompt involves listing out all of the Windows 10 apps and programs that are installed on your PC. This is particularly helpful if you need to uninstall a program using the Command Prompt. To list out all the installed programs, simply follow the steps outlined below:
- Launch Command Prompt, and type “wmic product get name“.
- Hit Enter, and you will see a list of all the programs that are installed on your PC.
You can also use wmic to uninstall programs, directly from the cmd window. Simply type “wmic product where “name like ‘%NAMEOFAPP%’” call uninstall /nointeractive” and hit Enter. Obviously, replace “NAMEOFAPP” with the name of the app that you want to uninstall from your PC.
10. Open CMD Window Inside a Directory
Let’s face it, the way Windows handles changing directories using the “cd” command is rather weird. Fortunately, there is a simple way to open Command Prompt windows inside a directory so you don’t have to change directories. This is a really handy trick, especially if the folders you want to access are buried deep inside the filesystem. To open a cmd window inside a directory, just follow the steps below:
- Open the directory in Windows Explorer. In the address bar, type “cmd”, and hit Enter.
- A command window will open inside the directory you had opened in Windows Explorer.
11. Generate Battery Health Report
Windows 10 lets you track vital stats related to the battery’s health by maintaining data related to the battery. This includes stats like factory specifications, full battery capacity, and the current capacity and these are updated with each session. You can generate a report about these stats by using a CMD command, which can be executed as follows:
- Launch Command Prompt as an Administrator or change directory using cd C:\Windows\System32
- Enter command powercfg/energy
- The system will take 60 seconds to analyze and then generate a report in form of an HTML documents
- To access the report, you can head to this location on your Windows 10 computer:
C:\Windows\system32\energy-report.html
As you can see in our laptop’s case, the battery’s capacity has dropped to 82% to what it was shipped with. If you want a step-by-step direction for generating battery health on Windows, click on the link to read the article.
12. Hide Sensitive RAR Files in Images
CMD facilitates a command which lets you concatenate or fuse two files into a single file. While this command comes in handy in merging the contents of basic file types such as TXT or CSV, you can also use the command to hide a RAR, ZIP, or another archived file inside an image or text file. To achieve this, follow these steps:
- Open CMD in the directory which contains both files using the 10th item in this list or use the cd command to change the directory
- Use command copy /b <RAR_filename>.rar + <image_filename>.<extension> <result_filename>.<extension>.
- In our case, we used copy /b modules.rar+wave.png test2.png
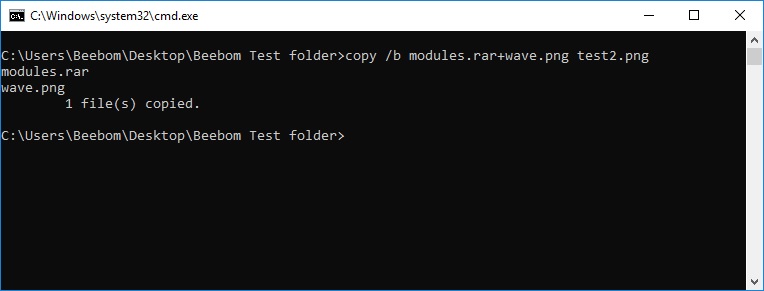
Note: make sure you enter the RAR file first followed by the other file, else you won’t be able to recover the RAR package. The method also works on most common file types including documents and PDFs as long as you add the archive file first.
- This will generate the result file, which in our case is test2.png
This PNG file displays as a normal image file but when you open it with WinRAR or any other extraction tool, it will extract the RAR file which is buried under the image file. This is a good way of saving your sensitive files from curious friends or co-workers or even prevent them from being misused even in case of a data breach.
13. Abort Command Execution
This is one of the best Command Prompt tricks and everyone should know about it. Say, you want to run a specific command but accidentally execute a different command. In that case, to quickly stop the command execution, simply press “Ctrl +C” together and the operation will be aborted instantly.
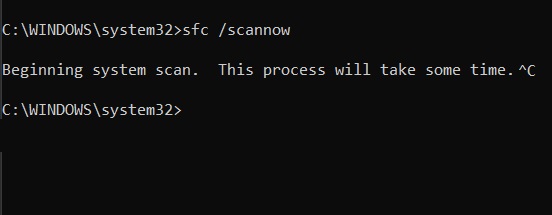
14. Always Run Command Prompt as Administrator
For users who deal with system files and applications know that they always need elevated privileges to tweak and move around things. But on the other hand, Command Prompt always defaults to the normal account which makes it harder for users to gain Administrator access in the middle of an operation. So to save yourself from such situations, you can change the behavior permanently and run Command Prompt with Administrator privilege always.
- Just search for “cmd” in the Start menu and right-click on it. After that, open its file location.
- Now copy the Command Prompt shortcut to your desktop.
- Move to desktop and right-click on the shortcut and open “Properties”.
- Here, click on Advanced and enable “Run as administrator”.
- Now onwards, open CMD from the desktop shortcut and it will always start with the Administrator privilege.
15. SFC /Scannow
SFC (System File Checker) is a relatively new addition to Command Prompt to keep your computer clean and bug-free. It’s a handy command-line tool that will help you fix many system issues. Just run sfc /scannow on Command Prompt and it will start verifying the integrity of all protected system files. Further, it will also repair the damaged files wherever possible. So in the future, if you face any issue, make sure to run this command on your Windows computer.
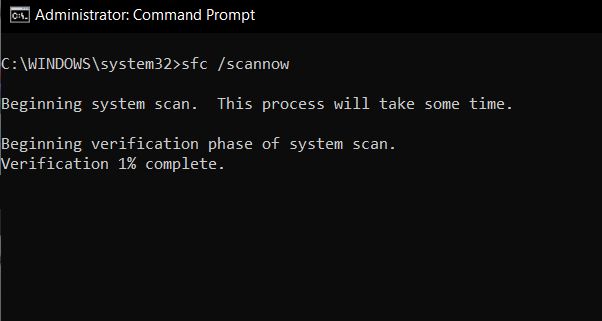
16. Find Information About Commands
Sometimes we run a command to achieve a certain task, but don’t know much about it. So to learn about specific commands, add /? at the end of any command, and hit enter. Command Prompt will give you a good overview of its usage and syntax. Take an example of SFC from the above point, type sfc /? and hit enter. It will tell you the sub-commands with examples, and what are the other commands related to SFC in a lucid language. This command is similar to the “man” command in Linux.
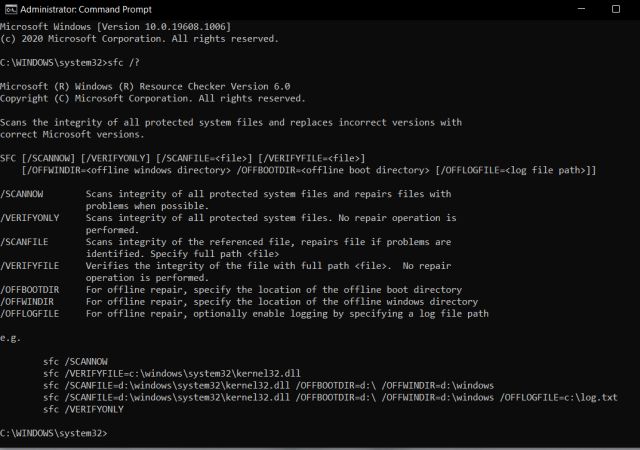
17. Command Line History
Many users are aware of the ‘UP’ navigation key to move forth and back between commands, but circling back to previous commands that were executed way back is difficult. However, there is the doskey /history command to check all your executed commands in a chronological list. The con is you can’t select the commands and execute them instantly and will have to type it out manually, which is not the best solution.
As a result, if you want to quickly navigate through all your past commands with the ability to execute them immediately, just press the F7 key. You will get a separate window where you can choose a command and execute it then and there. It’s one of the best Command Prompt tricks. Keep in mind, some users need to press the “Fn” key along with F7 to trigger this action.
18. Delete Temp Files to Clear Space
If you’re running low on space and urgently need to clear some trash out, getting rid of temporary files on your PC might be the swiftest action plan. Here’s what you can do to clean out temp files from your PC and regain a considerable amount of space.
- Use the command del /q /f /s %temp%\*
- Use the command del /s /q C:\Windows\temp\* (requires admin privileges)
- You can also use both the commands in one go by typing del /q /f /s %temp%\* && del /s /q C:\Windows\temp\*
19. Play an RPG Game in Command Prompt
Do you like playing role-playing games? If so, you should definitely check out Ateraan, which is a text-only role-playing game that works inside the command prompt on your Windows PC.
- Type the command telnet ateraan.com 4002 into CMD and press enter. That will launch the game, and you can create your character and start your journey. GLHF!
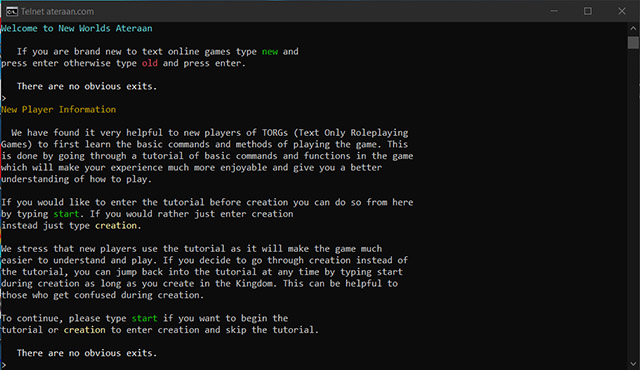
20. Move to Windows Terminal
Command Prompt is one of the oldest Windows programs, but recently Microsoft announced a universal command-line tool for Windows that integrrated Powershell, WSL, and Command Prompt at once place; The program’s called the Windows Terminal. One of the advantages of running Command Prompt in Windows Terminla is you get the ability to run multiple tabs to execute multiple commands in the same Window. If you’re wondering how to try out the new Windows Terminal, refer to our guide on the same.
21. View a Directory’s Structure
Using the dir command to get an idea about the structure of a directory could be a hard affair since the command isn’t very presentable. Hence, if you want to look at a directory’s structure in a more neat and precise way, use the tree command. Here’s how the command looks.
tree
The command will show you the structure of your default directory “C:” If you want to check the structure of other drives, use the drive letter followd by a colon after typing the command.
tree A: