При возникновении синих экранов BSoD Windows 11, 10 и другие версии системы создают дамп (снимок состояния) оперативной памяти, содержащий отладочную информацию, которую можно использовать для диагностики и определения причин сбоя. Функция обычно включена по умолчанию, но если дампы памяти не создаются, их можно включить: Как включить создание дампов памяти в Windows.
Подробным анализом дампов памяти занимаются разработчики, но и для рядового пользователя, столкнувшегося с синими экранами в Windows это может оказаться полезным: адреса в памяти ему ничего не дадут, но часто можно обнаружить имя файла приложения или драйвера, вызывающее сбой. Здесь помогут специальные программы для анализа дампов памяти, о которых и пойдёт речь далее.
WinDbg

У Майкрософт имеется собственный инструмент отладки и анализа дампов памяти — WinDbg (пока Preview). Скачать его для Windows 11 и Windows 10 можно из Microsoft Store, используя поиск в магазине приложений или прямую ссылку.
Пример простого анализа дампа памяти для обычного пользователя с целью выявления процесса, вызвавшего BSoD с помощью WinDbg:
- Запустите WinDbg от имени Администратора (правый клик по ярлыку в меню «Пуск» — «Запуск от имени администратора»).
- В главном меню программы выберите «Файл» — «Open dump File» и укажите путь к нужному мини-дампу, обычно находящемуся в папке C:\Windows\Minidump, нажмите кнопку «Open».
- Введите команду
!analyze -v
в поле ввода команд (либо нажмите по ссылке с командой в верхней панели WinDbg) и дождитесь завершения анализа.
- В панели «Command» в верхней части окна программы будет отображен результат анализа, где, при удаче, вы сможете найти информацию о том, каким процессом был инициирован сбой (PROCESS_NAME).
- Может быть информация о файле драйвера (.sys) в поле IMAGE_NAME и другая информация, позволяющая найти источник проблемы.
Далее полученную информацию можно использовать для того, чтобы найти, каким устройствам соответствуют драйверы в Интернете, выяснить назначение процессов вызвавших сбой, предпринять те или иные действия с целью их устранения.
BlueScreenView
BlueScreenView — очень простая утилита, которая позволяет выбрать файла дампа памяти в списке и посмотреть, какие файлы драйвера и процессы привели к сбою: в окне программы они будут выделены красным цветом.

Скачать BlueScreenView можно с официального сайта разработчика https://www.nirsoft.net/utils/blue_screen_view.html
WhoCrashed
Ещё одна программа для анализа дампов памяти — WhoCrashed. В бесплатной версии предоставляет не так много информации.
После нажатия кнопки «Analyze» имеющиеся дампы памяти анализируются, и на вкладке «Report» выводятся коды ошибок, а также текстовое описание на английском языке о том, что означает этот код и о возможных причинах сбоя.

Официальный сайт WhoCrashed https://www.resplendence.com/whocrashed, судя по всему, не открывается из РФ, но утилиту легко найти и скачать из сторонних источников.
В момент критического сбоя операционная система Windows прерывает работу и показывает синий экран смерти (BSOD). Содержимое оперативной памяти и вся информация о возникшей ошибке записывается в файл подкачки. При следующей загрузке Windows создается аварийный дамп c отладочной информацией на основе сохраненных данных. В системном журнале событий создается запись о критической ошибке.
Внимание! Аварийный дамп не создается, если отказала дисковая подсистема или критическая ошибка возникла на начальной стадии загрузки Windows.
Содержание:
- Типы аварийных дампов памяти Windows
- Как включить создание дампа памяти в Windows?
- Установка WinDBG в Windows
- Настройка ассоциации .dmp файлов с WinDBG
- Настройка сервера отладочных символов в WinDBG
- Анализ аварийного дампа памяти в WinDBG
Типы аварийных дампов памяти Windows
На примере актуальной операционной системы Windows 10 (Windows Server 2016) рассмотрим основные типы дампов памяти, которые может создавать система:
- Мини дамп памяти (Small memory dump) (256 КБ). Этот тип файла включает минимальный объем информации. Он содержит только сообщение об ошибке BSOD, информацию о драйверах, процессах, которые были активны в момент сбоя, а также какой процесс или поток ядра вызвал сбой.
- Дамп памяти ядра (Kernel memory dump). Как правило, небольшой по размеру — одна треть объема физической памяти. Дамп памяти ядра является более подробным, чем мини дамп. Он содержит информацию о драйверах и программах в режиме ядра, включает память, выделенную ядру Windows и аппаратному уровню абстракции (HAL), а также память, выделенную драйверам и другим программам в режиме ядра.
- Полный дамп памяти (Complete memory dump). Самый большой по объему и требует памяти, равной оперативной памяти вашей системы плюс 1MB, необходимый Windows для создания этого файла.
- Автоматический дамп памяти (Automatic memory dump). Соответствует дампу памяти ядра с точки зрения информации. Отличается только тем, сколько места он использует для создания файла дампа. Этот тип файлов не существовал в Windows 7. Он был добавлен в Windows 8.
- Активный дамп памяти (Active memory dump). Этот тип отсеивает элементы, которые не могут определить причину сбоя системы. Это было добавлено в Windows 10 и особенно полезно, если вы используете виртуальную машину, или если ваша система является хостом Hyper-V.
Как включить создание дампа памяти в Windows?
С помощью Win+Pause откройте окно с параметрами системы, выберите «Дополнительные параметры системы» (Advanced system settings). Во вкладке «Дополнительно» (Advanced), раздел «Загрузка и восстановление» (Startup and Recovery) нажмите кнопку «Параметры» (Settings). В открывшемся окне настройте действия при отказе системы. Поставьте галку в чек-боксе «Записать события в системный журнал» (Write an event to the system log), выберите тип дампа, который должен создаваться при сбое системы. Если в чек-боксе «Заменять существующий файл дампа» (Overwrite any existing file) поставить галку, то файл будет перезаписываться при каждом сбое. Лучше эту галку снять, тогда у вас будет больше информации для анализа. Отключите также автоматическую перезагрузку системы (Automatically restart).
В большинстве случаев для анализа причины BSOD вам будет достаточно малого дампа памяти.
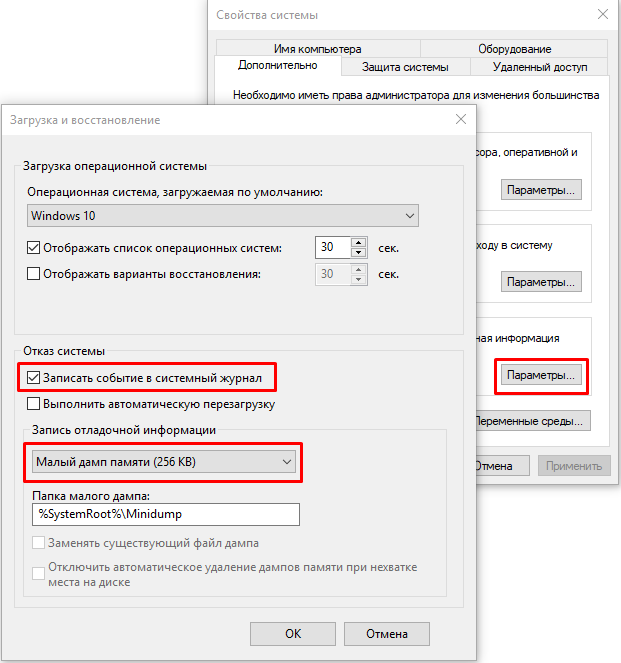
Теперь при возникновении BSOD вы сможете проанализировать файл дампа и найти причину сбоев. Мини дамп по умолчанию сохраняется в папке %systemroot%\minidump. Для анализа файла дампа рекомендую воспользоваться программой WinDBG (Microsoft Kernel Debugger).
Установка WinDBG в Windows
Утилита WinDBG входит в «Пакет SDK для Windows 10» (Windows 10 SDK). Скачать можно здесь.
Файл называется winsdksetup.exe, размер 1,3 МБ.
WinDBG для Windows7 и более ранних систем включен в состав пакета «Microsoft Windows SDK for Windows 7 and .NET Framework 4». Скачать можно здесь.
Запустите установку и выберите, что именно нужно сделать – установить пакет на этот компьютер или загрузить для установки на другие компьютеры. Установим пакет на локальный компьютер.
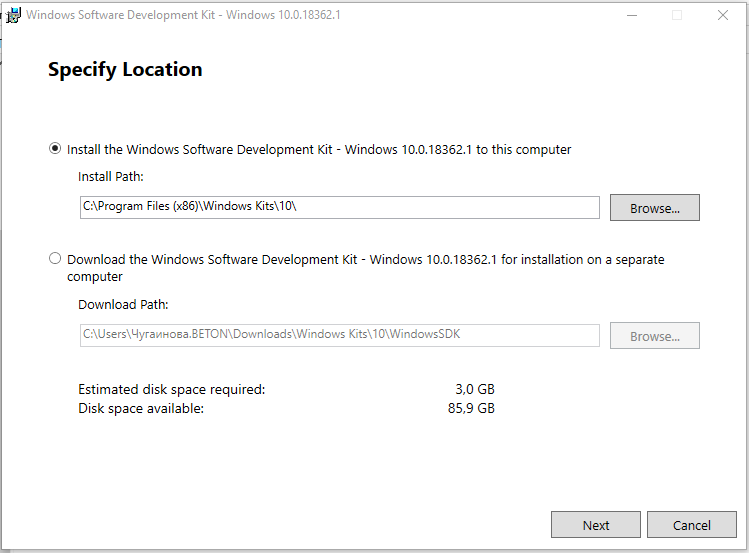
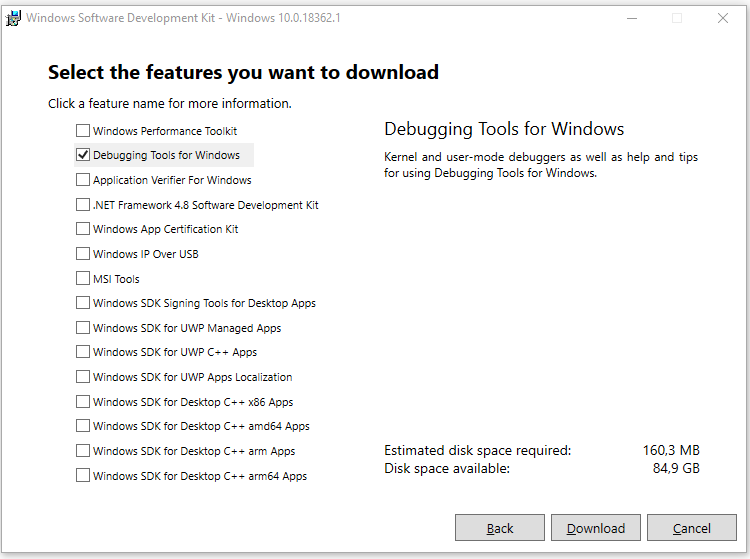
Можете установить весь пакет, но для установки только инструмента отладки выберите Debugging Tools for Windows.
После установки ярлыки WinDBG можно найти в стартовом меню.
Настройка ассоциации .dmp файлов с WinDBG
Для того, чтобы открывать файлы дампов простым кликом, сопоставьте расширение .dmp с утилитой WinDBG.
- Откройте командную строку от имени администратора и выполните команды для 64-разрядной системы:
cd C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\Debuggers\x64
windbg.exe –IA
для 32-разрядной системы:
C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\Debuggers\x86
windbg.exe –IA - В результате типы файлов: .DMP, .HDMP, .MDMP, .KDMP, .WEW – будут сопоставлены с WinDBG.
Настройка сервера отладочных символов в WinDBG
Отладочные символы (debug-символы или symbol files) – это блоки данных, генерируемые в процессе компиляции программы совместно с исполняемым файлом. В таких блоках данных содержится информация о именах переменных, вызываемых функциях, библиотеках и т.д. Эти данные не нужны при выполнении программы, но полезные при ее отладке. Компоненты Microsoft компилируются с символами, распространяемыми через Microsoft Symbol Server.
Настройте WinDBG на использование Microsoft Symbol Server:
- Откройте WinDBG;
- Перейдите в меню File –> Symbol File Path;
- Пропишите строку, содержащую URL для загрузки символов отладки с сайта Microsoft и папку для сохранения кэша:
SRV*E:\Sym_WinDBG*http://msdl.microsoft.com/download/symbols
В примере кэш загружается в папку E:\Sym_WinDBG, можете указать любую. - Не забывайте сохранить изменения в меню File –> Save WorkSpace;
WinDBG произведет поиск символов в локальной папке и, если не обнаружит в ней необходимых символов, то самостоятельно загрузит символы с указанного сайта. Если вы хотите добавить собственную папку с символами, то можно сделать это так:
SRV*E:\Sym_WinDBG*http://msdl.microsoft.com/download/symbols;c:\Symbols
Если подключение к интернету отсутствует, то загрузите предварительно пакет символов с ресурса Windows Symbol Packages.
Анализ аварийного дампа памяти в WinDBG
Отладчик WinDBG открывает файл дампа и загружает необходимые символы для отладки из локальной папки или из интернета. Во время этого процесса вы не можете использовать WinDBG. Внизу окна (в командной строке отладчика) появляется надпись Debugee not connected.
Команды вводятся в командную строку, расположенную внизу окна.
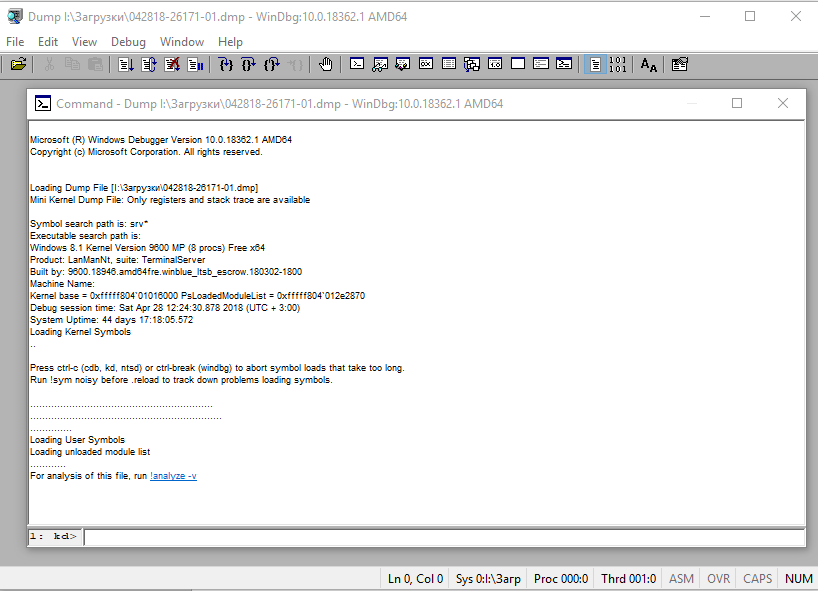
Самое главное, на что нужно обратить внимание – это код ошибки, который всегда указывается в шестнадцатеричном значении и имеет вид 0xXXXXXXXX (указываются в одном из вариантов — STOP: 0x0000007B, 02.07.2019 0008F, 0x8F). В нашем примере код ошибки 0х139.
Полный справочник ошибок можно посмотреть здесь.
Отладчик предлагает выполнить команду !analyze -v, достаточно навести указатель мыши на ссылку и кликнуть. Для чего нужна эта команда?
- Она выполняет предварительный анализ дампа памяти и предоставляет подробную информацию для начала анализа.
- Эта команда отобразит STOP-код и символическое имя ошибки.
- Она показывает стек вызовов команд, которые привели к аварийному завершению.
- Кроме того, здесь отображаются неисправности IP-адреса, процессов и регистров.
- Команда может предоставить готовые рекомендации по решению проблемы.
Основные моменты, на которые вы должны обратить внимание при анализе после выполнения команды !analyze –v (листинг неполный).
1: kd>
!analyze -v
*****************************************************************************
* *
* Bugcheck Analysis *
* *
*****************************************************************************
Символическое имя STOP-ошибки (BugCheck)
KERNEL_SECURITY_CHECK_FAILURE (139)
Описание ошибки (Компонент ядра повредил критическую структуру данных. Это повреждение потенциально может позволить злоумышленнику получить контроль над этой машиной):
A kernel component has corrupted a critical data structure. The corruption could potentially allow a malicious user to gain control of this machine.
Аргументы ошибки:
Arguments:
Arg1: 0000000000000003, A LIST_ENTRY has been corrupted (i.e. double remove).
Arg2: ffffd0003a20d5d0, Address of the trap frame for the exception that caused the bugcheck
Arg3: ffffd0003a20d528, Address of the exception record for the exception that caused the bugcheck
Arg4: 0000000000000000, Reserved
Debugging Details:
------------------
Счетчик показывает сколько раз система упала с аналогичной ошибкой:
CUSTOMER_CRASH_COUNT: 1
Основная категория текущего сбоя:
DEFAULT_BUCKET_ID: FAIL_FAST_CORRUPT_LIST_ENTRY
Код STOP-ошибки в сокращенном формате:
BUGCHECK_STR: 0x139
Процесс, во время исполнения которого произошел сбой (не обязательно причина ошибки, просто в момент сбоя в памяти выполнялся этот процесс):
PROCESS_NAME: sqlservr.exe
CURRENT_IRQL: 2
Расшифровка кода ошибки: В этом приложении система обнаружила переполнение буфера стека, что может позволить злоумышленнику получить контроль над этим приложением.
ERROR_CODE: (NTSTATUS) 0xc0000409 - The system detected an overrun of a stack-based buffer in this application. This overrun could potentially allow a malicious user to gain control of this application.
EXCEPTION_CODE: (NTSTATUS) 0xc0000409 - The system detected an overrun of a stack-based buffer in this application. This overrun could potentially allow a malicious user to gain control of this application.
Последний вызов в стеке:
LAST_CONTROL_TRANSFER: from fffff8040117d6a9 to fffff8040116b0a0
Стек вызовов в момент сбоя:
STACK_TEXT:
ffffd000`3a20d2a8 fffff804`0117d6a9 : 00000000`00000139 00000000`00000003 ffffd000`3a20d5d0 ffffd000`3a20d528 : nt!KeBugCheckEx
ffffd000`3a20d2b0 fffff804`0117da50 : ffffe000`f3ab9080 ffffe000`fc37e001 ffffd000`3a20d5d0 fffff804`0116e2a2 : nt!KiBugCheckDispatch+0x69
ffffd000`3a20d3f0 fffff804`0117c150 : 00000000`00000000 00000000`00000000 00000000`00000000 00000000`00000000 : nt!KiFastFailDispatch+0xd0
ffffd000`3a20d5d0 fffff804`01199482 : ffffc000`701ba270 ffffc000`00000001 000000ea`73f68040 fffff804`000006f9 : nt!KiRaiseSecurityCheckFailure+0x3d0
ffffd000`3a20d760 fffff804`014a455d : 00000000`00000001 ffffd000`3a20d941 ffffe000`fcacb000 ffffd000`3a20d951 : nt! ?? ::FNODOBFM::`string'+0x17252
ffffd000`3a20d8c0 fffff804`013a34ac : 00000000`00000004 00000000`00000000 ffffd000`3a20d9d8 ffffe001`0a34c600 : nt!IopSynchronousServiceTail+0x379
ffffd000`3a20d990 fffff804`0117d313 : ffffffff`fffffffe 00000000`00000000 00000000`00000000 000000eb`a0cf1380 : nt!NtWriteFile+0x694
ffffd000`3a20da90 00007ffb`475307da : 00000000`00000000 00000000`00000000 00000000`00000000 00000000`00000000 : nt!KiSystemServiceCopyEnd+0x13
000000ee`f25ed2b8 00000000`00000000 : 00000000`00000000 00000000`00000000 00000000`00000000 00000000`00000000 : 0x00007ffb`475307da
Участок кода, где возникла ошибка:
FOLLOWUP_IP:
nt!KiFastFailDispatch+d0
fffff804`0117da50 c644242000 mov byte ptr [rsp+20h],0
FAULT_INSTR_CODE: 202444c6
SYMBOL_STACK_INDEX: 2
SYMBOL_NAME: nt!KiFastFailDispatch+d0
FOLLOWUP_NAME: MachineOwner
Имя модуля в таблице объектов ядра. Если анализатору удалось обнаружить проблемный драйвер, имя отображается в полях MODULE_NAME и IMAGE_NAME:
MODULE_NAME: nt
IMAGE_NAME: ntkrnlmp.exe
Если кликнете по ссылке модуля (nt), то увидите подробную информацию о пути и других свойствах модуля. Находите указанный файл, и изучаете его свойства.
1: kd>
lmvm nt
Browse full module list
Loaded symbol image file: ntkrnlmp.exe
Mapped memory image file: C:\ProgramData\dbg\sym\ntoskrnl.exe\5A9A2147787000\ntoskrnl.exe
Image path: ntkrnlmp.exe
Image name: ntkrnlmp.exe
InternalName: ntkrnlmp.exe
OriginalFilename: ntkrnlmp.exe
ProductVersion: 6.3.9600.18946
FileVersion: 6.3.9600.18946 (winblue_ltsb_escrow.180302-1800)
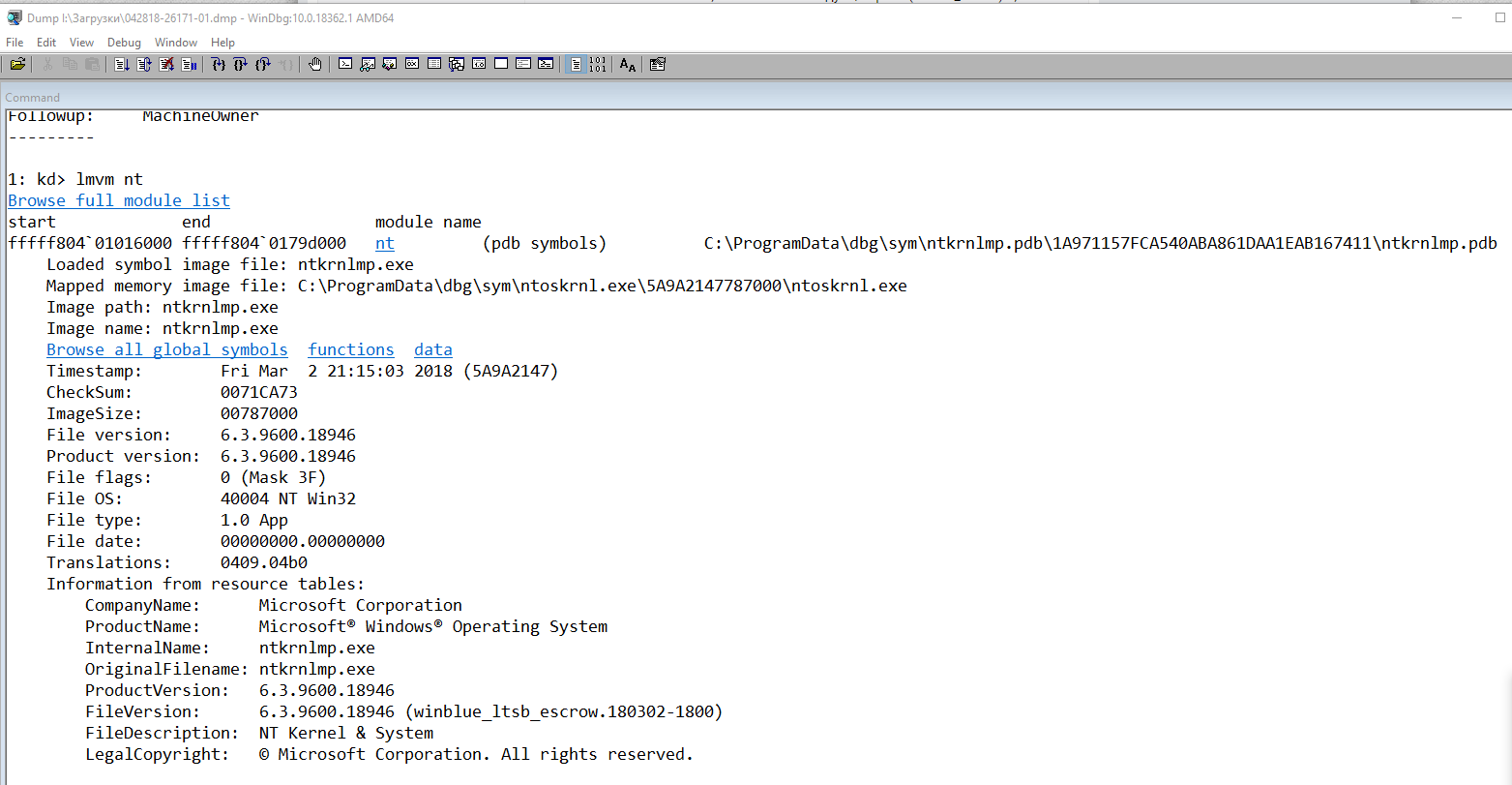
В приведенном примере анализ указал на файл ядра ntkrnlmp.exe. Когда анализ дампа памяти указывает на системный драйвер (например, win32k.sys) или файл ядра (как в нашем примере ntkrnlmp.exe), вероятнее всего данный файл не является причиной проблемы. Очень часто оказывается, что проблема кроется в драйвере устройства, настройках BIOS или в неисправности оборудования.
Если вы увидели, что BSOD возник из-за стороннего драйвера, его имя будет указано в значениях MODULE_NAME и IMAGE_NAME.
Например:
Image path: \SystemRoot\system32\drivers\cmudaxp.sys
Image name: cmudaxp.sys
Откройте свойсва файла драйвера и проверьте его версию. В большинстве случаев проблема с драйверами решается их обнвовлением.
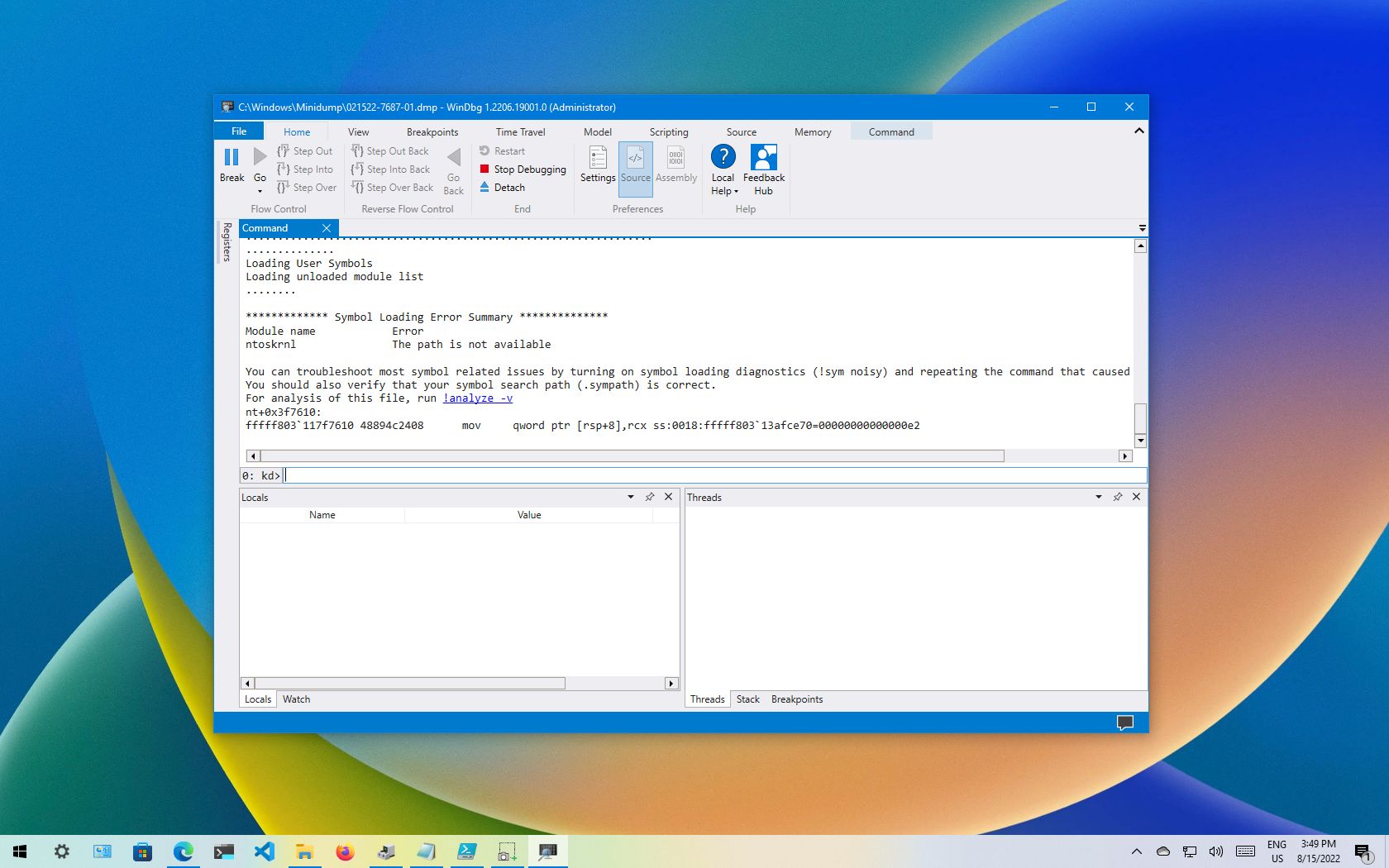
On Windows 10, when there is a crash, the system creates a «dump» file containing the memory information at the time of the error, which can help determine the reason for the problem.
The «.dmp» file includes the stop error message, a list of the drivers loaded at the time of the problem, kernel, processor, and process details, as well as other information depending on the type of dump file you have.
Although Windows 10 automatically creates dump files, the only problem is that you won’t find any built-in tools to open this type of file, and this is when the Microsoft Windows Debugging (WinDbg) tool can help. WinDbg is an advanced tool designed for debugging kernel-mode and user-mode code, reviewing processor registries, and analyzing crash dumps.
This guide will walk you through the steps to open a dump file to determine what caused the crash to resolve the problem on your computer.
How to open dump file with WinDbg on Windows 10
On Windows 10, you may find multiple ways to open and review a dump error file, but the easiest way is to use the WinDbg tool available through the Microsoft Store.
Install WinDbg
To install the WinDbg tool on Windows 10, use these steps:
All the latest news, reviews, and guides for Windows and Xbox diehards.
- Open the WinDbg download page.
- Click the Install button.
- Click the Open button.
- Click the Install button.
Once you complete the steps, the application will install, and it will be available through the Start menu.
Analyze dump file
To open and analyze a dump file created by a crash on Windows 10, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for WinDbg, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Click the File menu.
- Click on Start debugging.
- Select the Open sump file option.
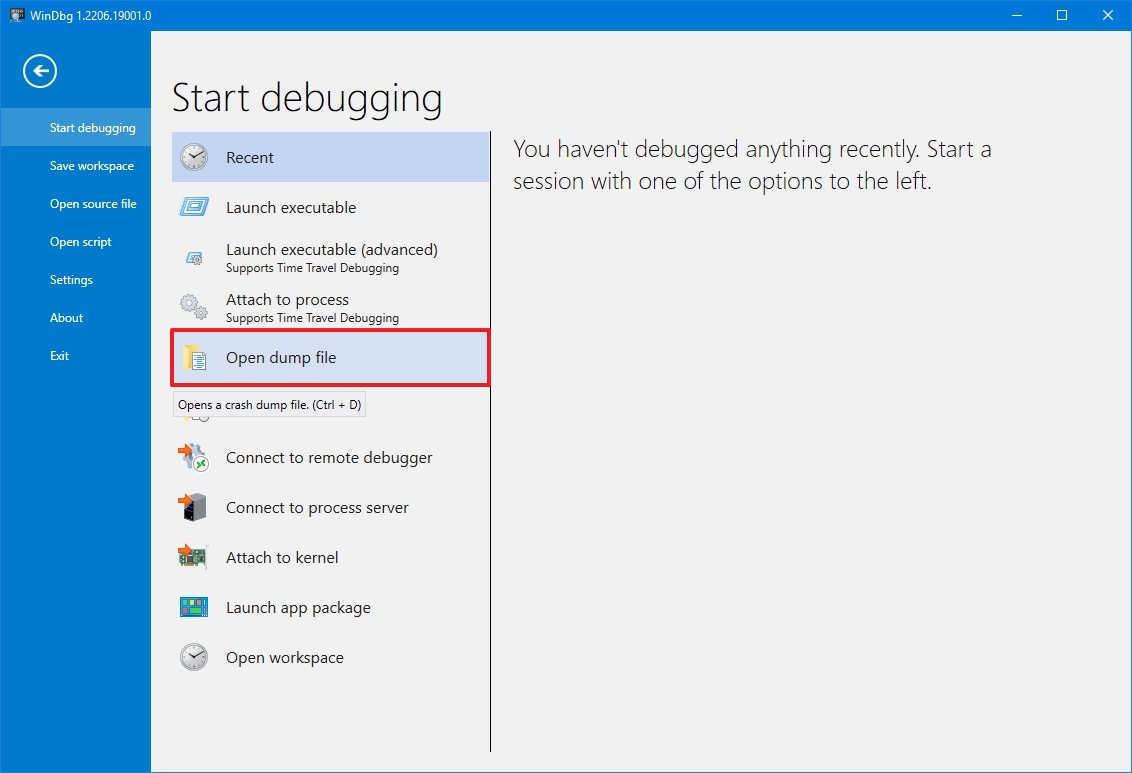
- Select the dump file from the folder location — for example, %SystemRoot%\Minidump.
- Click the Open button.
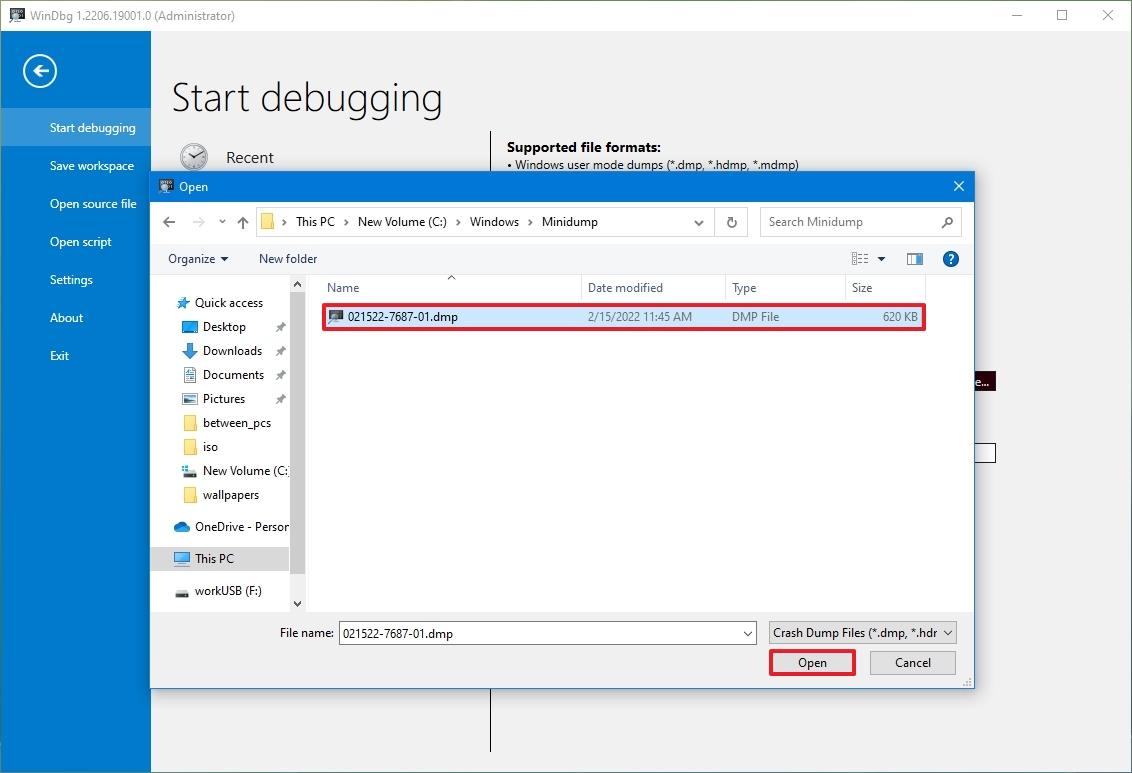
- Click the Open button again.
- Check the progress bar until it loads the dump file (this may take a while).
- Type the following command in the run command and press Enter: !analyze -v
- Quick tip: You can also click the !analyze -v link if available from the main area if available after loading the dump file.
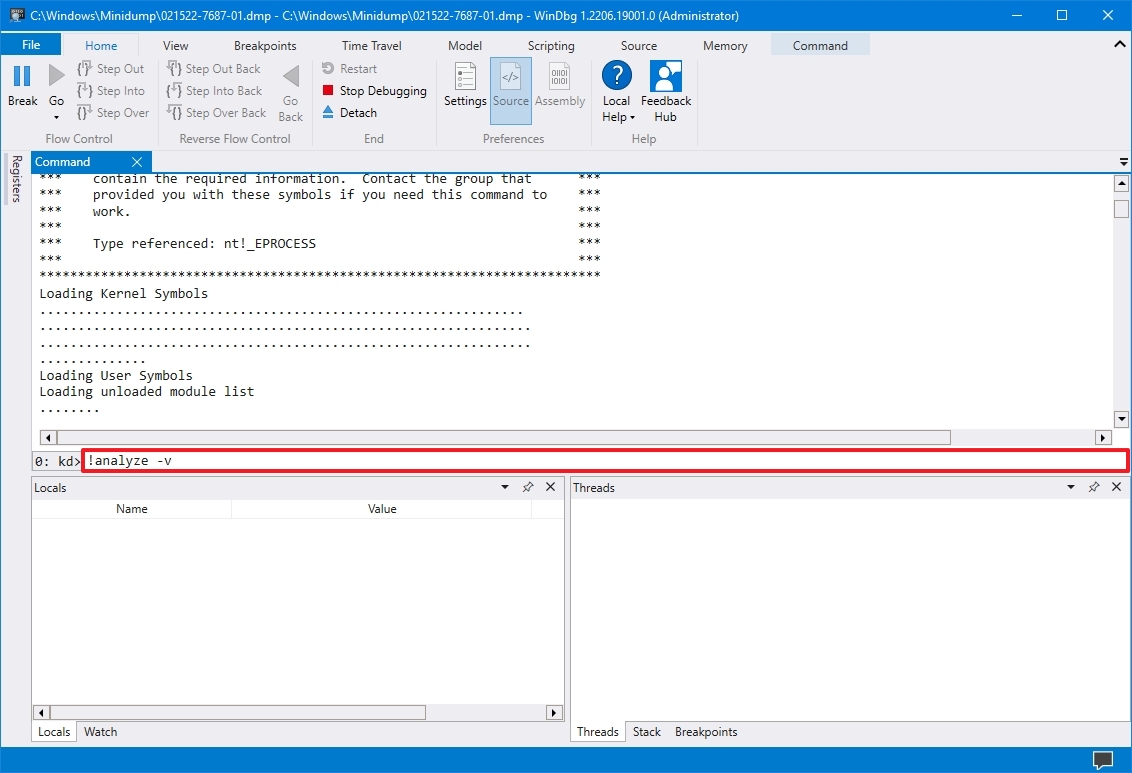
- Check the progress bar until the analysis is complete (this may take a long time depending on the data size).
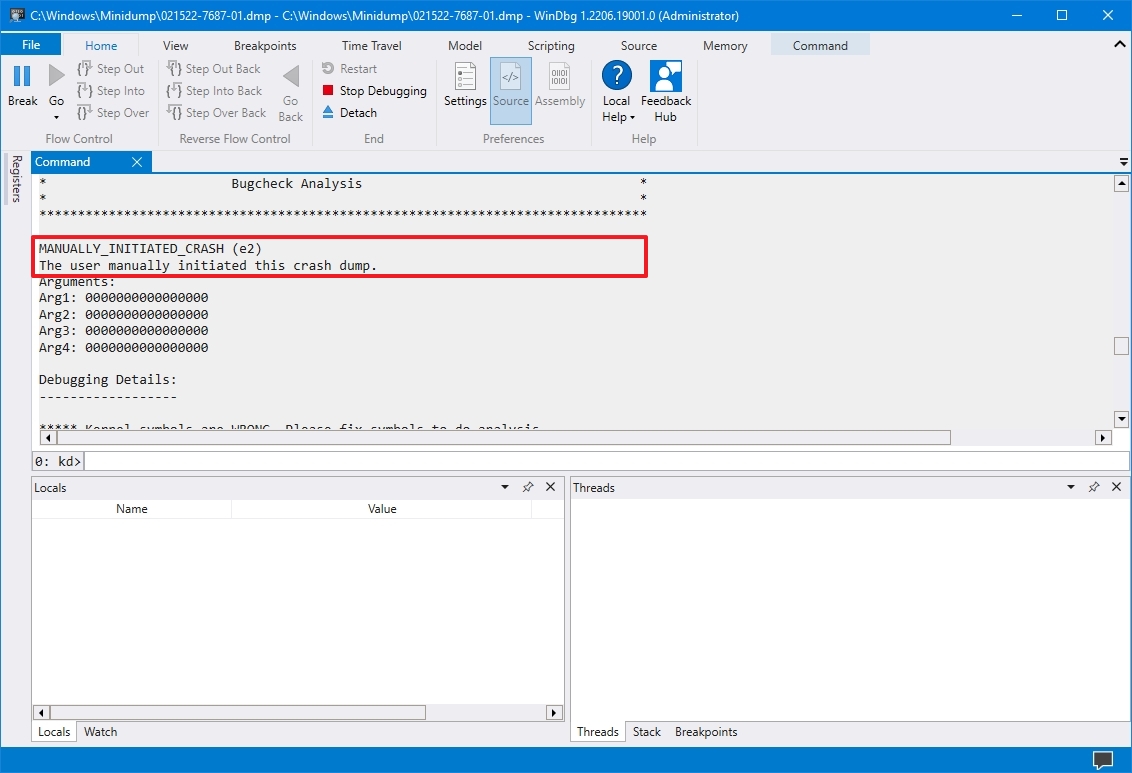
After you complete the steps, the application will return the dump file analyses, which you can then review to determine the reason for the problem to help you resolve the issue.
The information will be different depending on the problem. For example, this result points out that this was a manually initiated crash with an «e2» error code, which is correct since, for this guide, we use these instructions to force a dump file. The WinDbg even makes an excellent job describing the crash in a language anyone can understand («The user manually initiated this crash dump»).
As you continue reviewing the dump file, you will also find more information, such as «FAILURE_BUCKET_ID» and «MODULE_NAME,» which could indicate what is causing the problem.
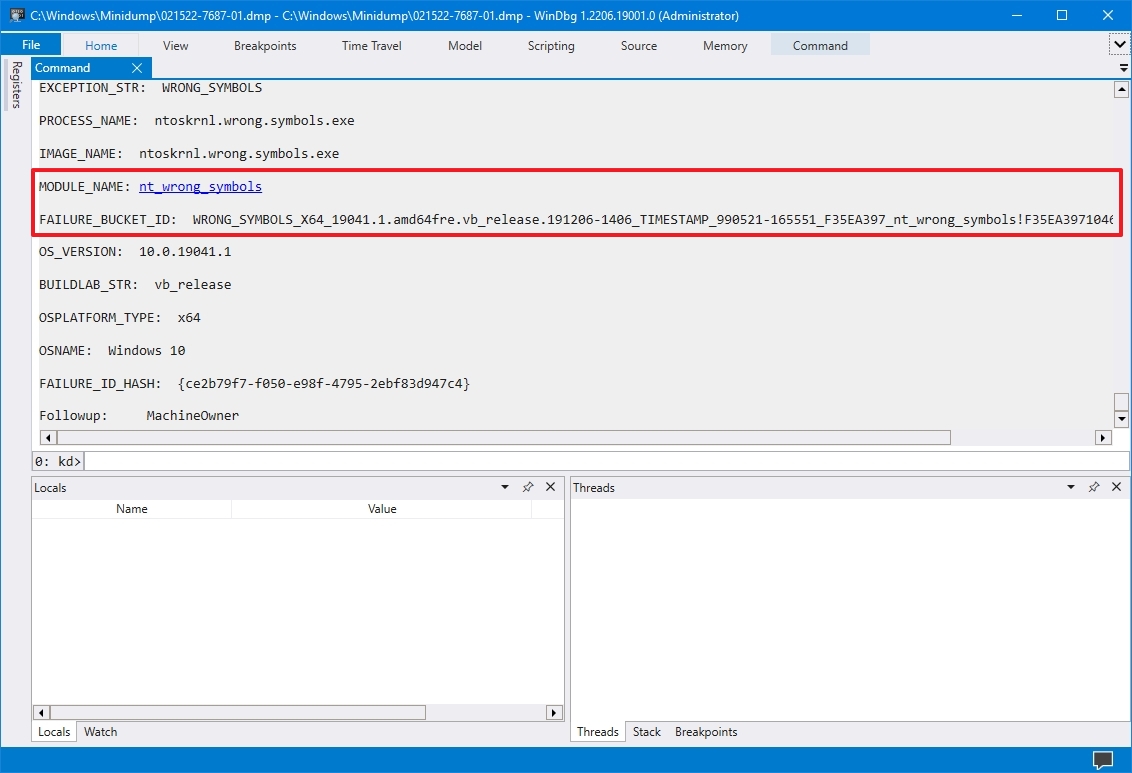
The information can be overwhelming since it is not meant for regular users. If your computer keeps crashing, you can use this tool to get an idea of the problem. If you cannot figure it out, you can use the hints in the report to search online for more information.
More resources
For more helpful articles, coverage, and answers to common questions about Windows 10 and Windows 11, visit the following resources:
- Windows 11 on Windows Central — All you need to know
- Windows 10 on Windows Central — All you need to know
Mauro Huculak has been a Windows How-To Expert contributor for WindowsCentral.com for nearly a decade and has over 15 years of experience writing comprehensive guides. He also has an IT background and has achieved different professional certifications from Microsoft, Cisco, VMware, and CompTIA. He has been recognized as a Microsoft MVP for many years.
If your Windows PC suffers a Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) error, several things will happen. The most obvious is that your PC is forced to restart, as a BSOD is a result of Windows completely crashing. One less obvious result of a BSOD error, however, is the error log that is created that allows you to troubleshoot the issue afterward.
This is called a memory dump file, saved in the DMP file format. These files contain various information on the problem, including your current Windows version, any running apps and drivers at the time of the BSOD, and the error code itself. To help you analyze memory dump files, here’s what you’ll need to do.
What are Memory Dump Files on Windows 10?
A Blue Screen of Death is a critical and unrecoverable error on a Windows PC, but the cause of these errors can vary. For example, an unexpected kernel mode trap BSOD is usually caused by incompatible or overclocked hardware, while a critical process died BSOD can have various causes, including corrupt system files.
To help you troubleshoot the problem, Windows automatically generates a memory dump file. This usually contains the stop code name and value (e.g. a system service exception stop code), a list of any running drivers at the time of the crash, and some additional technical information that you can use to identify the cause.

These dump files (using the DMP file format) are saved automatically in either the root C:\, C:\minidump, or C:\Windows\minidump folders. To help you analyze them, you can install Microsoft’s debugging app WinDbg from the Microsoft Store. This helps you analyze the memory dump files and locate the stop code information.
You can also use older tools like NirSoft BlueScreenView to quickly analyze the dump files created on your PC. This will also help you identify the stop code value and the possible cause (such as a specific driver file).
Once you know the stop code value, you can then search for additional information online about the issue. For instance, if you discovered from your dump file that you suffered a memory management BSOD, you can check out our BSOD error guide for additional advice on how to resolve the issue.
Because a BSOD error can stop your PC from working, you may need to try and restart Windows in Safe Mode. Running Windows in Safe Mode reduces the number of active system processes and drivers to the bare minimum, allowing you to investigate things further.
If you can’t boot into Windows at all, however, your options are limited. Currently, there are no standalone tools that you can run if Windows itself isn’t working properly to analyze BSOD dump files. If this happens, you’ll need to recover the dump files using a Linux live CD using a DVD or a portable USB flash memory stick.
You can then analyze the file using WinDbg or NirSoft BlueScreenView on a working Windows PC or laptop by following the steps below.
Changing Memory Dump File Settings in Windows Settings
Memory dump files are created automatically, but you can set the level of detail included in a memory dump file in Windows Settings. This will only work for BSODs that occur after changing this setting, but if your PC is having problems, you can follow these steps to add additional information to the dump files.
- To start, right-click the Start menu and select Settings.
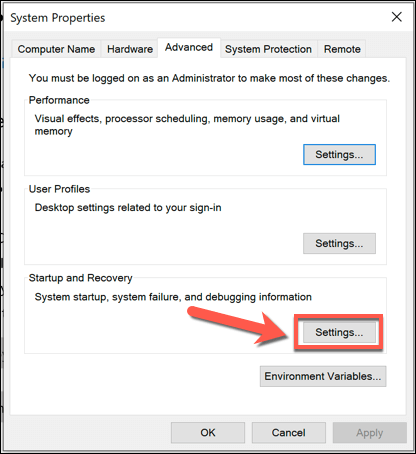
- In the Settings menu, select System > About. In the Related settings panel, in the System > About menu, select the Advanced system settings option.
- In the System Properties menu, select the Settings option listed in the Startup and Recovery section at the bottom.
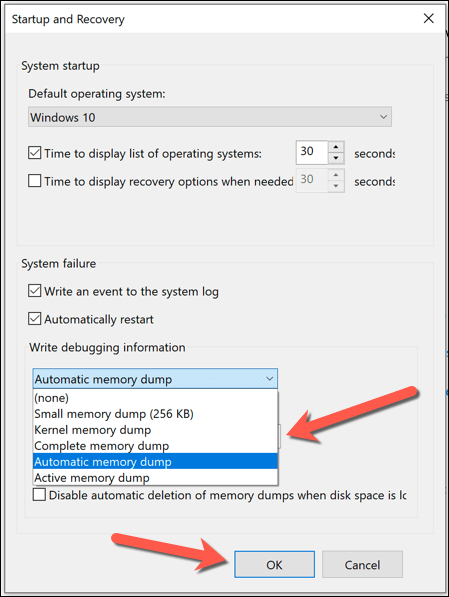
- To change the level of detail recorded by memory dump files when a BSOD occurs, select one of the available options using the Write debugging information drop-down menu in the Startup and Recovery window. Full information on what is included in each memory dump is available at the Microsoft documentation website. Select OK > OK to save your choice.
You may need to restart your PC after making this change to ensure the setting is applied. Any future BSOD errors that occur will generate a memory dump file containing the level of information you selected above.
If you suffer a BSOD error, you can use WinDbg to analyze the memory dump file. This Microsoft-created development tool is the best way to analyze your memory files, but you can also use the older NirSoft BlueScreenView as an alternative, following the steps below.
These steps assume your PC is working well enough to install and use WinDbg. If it isn’t, you’ll need to retrieve the dump files from your hard drive using a Linux live CD or USB to analyze them elsewhere. Live CD environments can be booted using the installation media of most Linux distributions, including Ubuntu and Debian.
- To begin, you’ll need to install WinDbg Preview from the Microsoft Store. On the WinDbg store page, select Get to begin the installation.
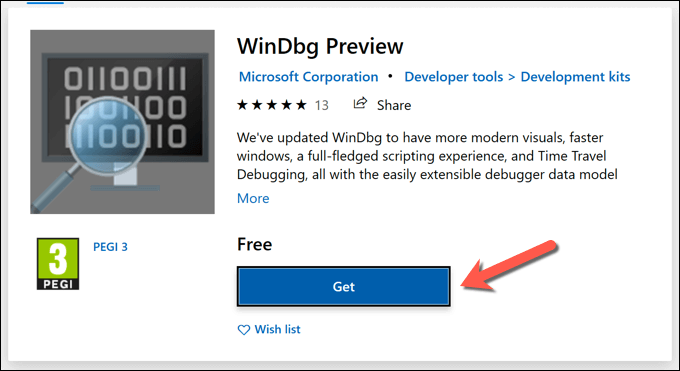
- Once WinDbg is installed, launch it by selecting Launch on the store page or by launching it from the Start menu. If you can’t access your dump files, you’ll need to locate WinDbg in the Start menu, then right-click and select More > Run as administrator to grant it the necessary access.
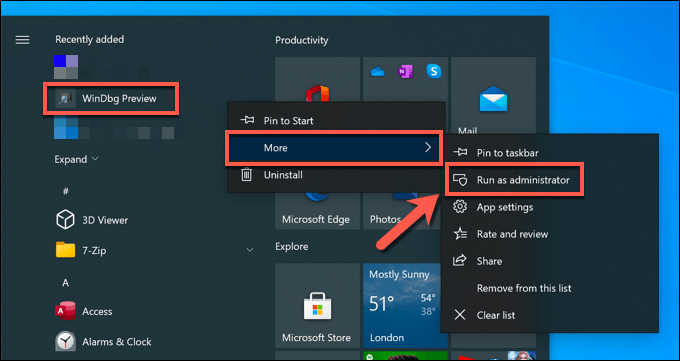
- In the WinDbg window, select File > Start debugging > Open dump file. Use the built-in File Explorer menu to open your latest dump file, which is typically saved in the root C:\ folder, C:\minidump, or C:\Windows\minidump folder.
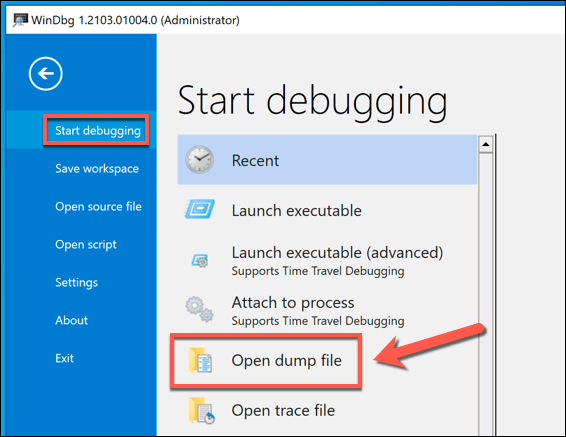
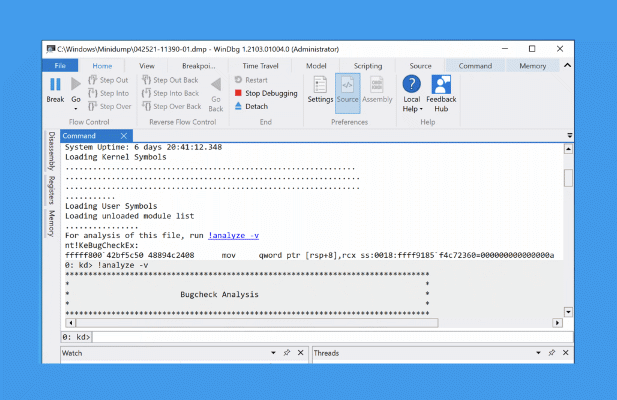
- Opening the DMP file will cause the WinDbg debugger to run and load the file. This could take some time, depending on the size of the file and the level of detail saved. Once this is done, type !analyze -v into the command box at the bottom of the Command tab, then press Enter to run the command.
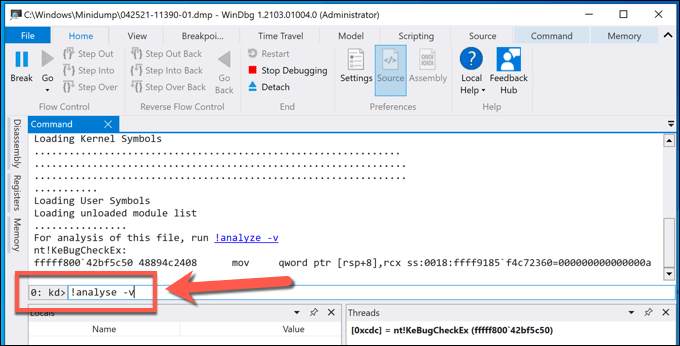
- The !analyze -v command will take some time to load and analyze the log file created by the BSOD error—wait for this process to complete. Once it’s done, you can analyze the full output in the Command tab. In particular, search for the stop code name and value (e.g. DRIVER_IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL and d1) listed under the Bugcheck Analysis section. Along with the stop code, a brief description offering a cause (such as driver issues) will be listed, allowing you to troubleshoot further.
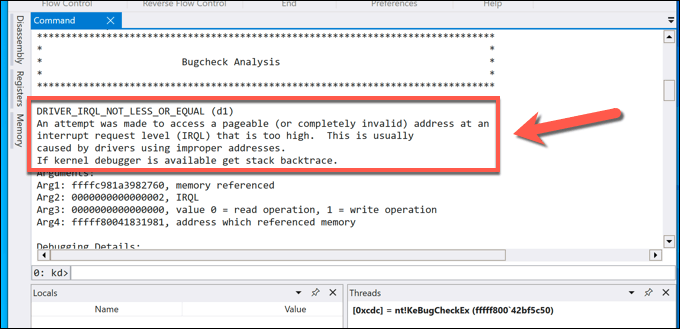
- You can also look at other relevant information listed in the WinDbg analysis (such as the MODULE_NAME value) to identify the cause. In this example instance, the BSOD code was caused by running the NotMyFault system testing tool.
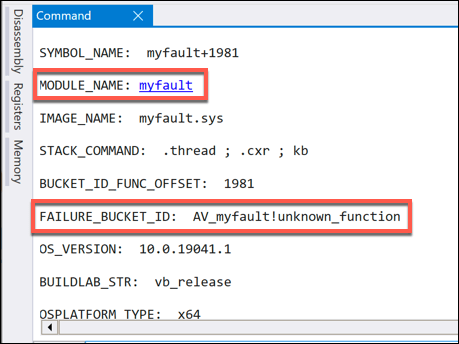
Once you’ve identified the stop code and possible cause of the BSOD error, you can research the issue further to determine a possible fix.
How to Analyze Windows Memory Dump Files Using NirSoft BlueScreenView
While WinDbg isn’t included with Windows, it’s produced by Microsoft to troubleshoot BSOD errors. If you’d prefer, however, you can analyze memory dump files from your PC (or from another PC if you have a copy of the relevant dump files) using the older NirSoft BlueScreenView tool.
BlueScreenView may look dated, but it continues to offer all of the relevant information about your BSOD dump files. This includes the stop code name and value (such as DRIVER_IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL) that you can then use to identify the cause.
- To start, download and install the NirSoft BlueScreenView tool on your Windows PC. Once the tool is installed, launch it from the Start menu.
- BlueScreenView will automatically locate any memory dump files from known sources such as C:/ and C:/Windows/minidump. If you want to load a file manually, however, select Options > Advanced Options.
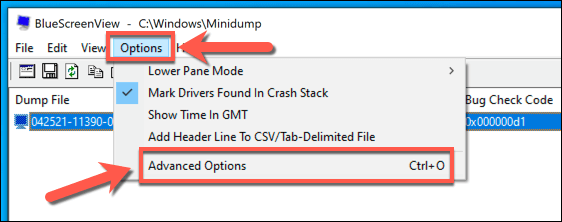
- In the Advanced Options menu, switch to the folder containing your dump files by selecting the Browse button positioned next to the Load from the following MiniDump folder box. To return this to the default location, select Default. Select OK to save your choice and load your files.
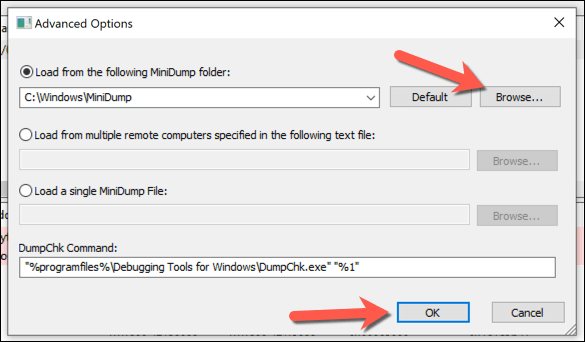
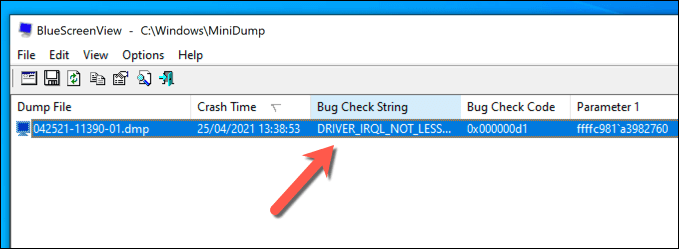
- In the main BlueScreenView window, a list of your saved memory dump files will appear. Select one of the files listed to view more information about it. The stop code name will appear in the Bug Check String column, allowing you to research the issue further.
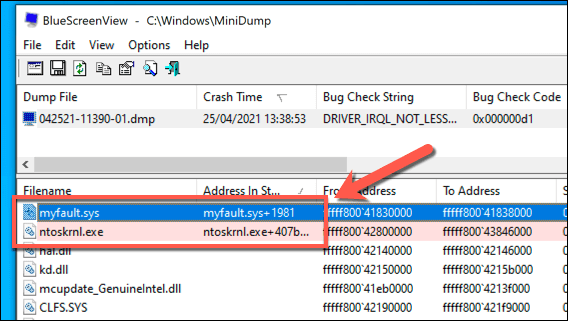
- With the memory dump file selected, a full list of active files and drivers will be listed underneath. Files that are highlighted red will have a direct link to the cause of the BSOD error. For instance, myfault.sys is related to the NotMyFault system testing tool, while ntoskrnl.exe is the Windows system kernel process.
While BlueScreenView is a useful tool for quickly identifying the BSOD error name, it isn’t a full debugging tool like WinDbg. If you can’t troubleshoot the problem using this tool, you’ll need to try WinDbg for a more detailed analysis.
Troubleshooting BSOD Errors Using Memory Dump Files
Using the memory dump file information you recover, you can troubleshoot the BSOD errors by searching for the stop codes or related BSOD error files. The error stop codes, in particular, can help you find the cause behind a BSOD, from a bad system config info BSOD to an unexpected store exception error BSOD.
BSOD errors are caused by everything from faulty hardware to corrupt system files. To help stop them, you should check your PC for malware regularly and use tools like SFC to repair your Windows installation if it becomes corrupted. If all else fails, you can always reset or reinstall Windows 10 to restore your PC to full working order.
Related Posts
- How to Fix a “This file does not have an app associated with it” Error on Windows
- How to Fix an Update Error 0x800705b4 on Windows
- How to Resolve “A JavaScript error occured in the main process” Error on Windows
- How to Fix the Network Discovery Is Turned Off Error on Windows
- How to Change Folder Icons in Windows
If your system has crashed and experienced a Blue Screen of Death (BSoD), or a program or Windows feature suddenly crashes, Windows automatically generates a record of the conditions and circumstances under which the error occurred. This information is stored in dump files with the extension “.dmp.”
These dump files can help troubleshoot the root cause of the error so that it does not occur again.
This article contains everything you need to know about these dump files and how they can be opened in Windows, since there is no native method, so they can be analyzed to determine the cause of the error.
Table of Contents
Windows Crash Dump Files
Crash dump files, also known as “mini-dump files,” are system-generated binary files that contain various information about a crash that may have occurred on your computer. Like Event Viewer, these files can be used to determine the cause of the error, and then use that data to fix it. Dump files can contain the following data in them, which can be helpful for the matter:
The list below highlights the content which can be found inside a mini-dump file.
- The Stop message (error code), its parameters, and other data.
- List of loaded drivers.
- The processor context (PRCB) for the processor that stopped.
- Process information and kernel context (EPROCESS) for the process stopped.
- Process information and kernel context (ETHREAD) for the thread stopped.
- Kernel-mode call stack for the thread that stopped.
Dump files are created by copying the data off the system memory and onto the computer’s storage. It uses the Windows Page File and requires at least 2MB of free space. With this information, you can understand how different dump files are created.
Windows can write debugging information in three types of dump files.
Types of Dump Files
Complete Memory Dump
Complete Memory Dump files are the largest of the dump files. In this case, the complete contents of the memory are written onto the dump file.
When generated by the system, all old Complete Memory Dump files are replaced and overwritten.
Complete Memory Dump files are saved to C:\Windows\MEMORY.DMP file.
Kernel Memory Dump
Kernel Memory Dump files only contain data from kernel memory, which is why they are relatively smaller in size. Such files do not contain data from any unused, unallocated memory or the memory used by user-mode programs.
When generated by the system, all old Kernel Memory Dump files are replaced and overwritten.
Kernel Memory Dump files are also saved to C:\Windows\MEMORY.DMP file, the same as Complete Memory Dump files. However, only one of these is saved at a time and is overwritten when another crash occurs.
Small Memory Dump/Mini Memory Dump
The minidump file, which we will discuss in this post, is the smallest kind of dump file. This file contains the information described above that can assist in determining the cause of the crash.
Minidump files generated by the system are not overwritten. Instead, a new one is generated.
Minidump files can be found at C:\Windows\Minidump. If you do not find a directory named “Minidump,” it is likely because a dump file has not been created yet.
When a minidump file is created, Windows automatically includes the date it was created on. For example, in Windows 11, if a file is named “020322-18890-01.dmp,” “02” indicates the month, “03” indicates the date, and “22” indicates the year the file was created. “-01” at the end indicates it was the first dump file created that day.
The same is true for a minidump file created in Windows 10, which is automatically named something like “mini020322-01.dmp.”
Now let’s move on to opening and analyzing a dump file.
How to Read and Analyze DMP Files
As we mentioned, Windows does not allow you to open dump files directly. However, you can use other tools available online to open and analyze them. One of the most common tools to do so is through the Windows Debugging (WinDbg) tool, which can be downloaded through Microsoft Store. Continue reading the given guide below to use this tool to open and analyze memory dump files in Windows.
Using WinDbg
We have divided this section into 2 parts: Downloading and installing the WinDbg tool and then using it to analyze a dump file.
Download and Install WinDbg
- Open the WinDbg Preview page in the Microsoft Store and click Get.
- The browser will prompted you to open the Microsoft Store app, click Open Microsoft Store.
- From the Store app, click Get again.
The WinDbg tool will now begin to download and then install. We are now done with the installation phase. Let us now use the tool to open and analyze dump files.
Open and Analyze dmp files using WinDbg
- Open the WinDbg tool with administrative rights by searching for it through the search box, right-clicking it, and then clicking Run as administrator from the context menu.
- From the WinDbg tool, click File from the top menu.
- In the Start Debugging tab, click Open dump file.
- Now click Browse from the right pane within the tool and select the dump file that you want to analyze by navigating to
C:\Windows\Minidump. When selected, click Open. - The tool will now open the dump file, which can take a few minutes. When the dump file successfully opens, type in the following command in the text field in front of “0: kd>“:
!analyze -v - WinDbg will now begin analyzing the dump file. This can take a few minutes to complete. Once completed, you should see the results in the top window.
In the example above, since we initiated a BSoD intentionally, it states “The user manually initiated this crash dump.” Otherwise, if it were an actual error, you would see different statements and information after performing the analysis of the dump file.
You can then use this information to troubleshoot the error that caused the crash.
Using WhoCrashed
Download WhoCrashed

WhoCrashed is available in both free and paid editions. However, the free edition is sufficient to open and analyze dump files. With this tool, you can obtain reports on the dump files with a single click. The tool will automatically scan your system files for any .dmp files and fetch the data within.
To do so, download WhoCrashed from the link given above, and run the .exe file to install in a few easy steps. Once installed, click Analyze from the ribbon menu at the top. The tool will then take a few seconds to scan any dump files and present the analysis. You can also view the .dmp files discovered from the Dump files tab.
Using BlueScreenView
Download BlueScreenView

BlueScreenView is a portable and small tool that can provide you with relevant information on minidump files. When you run this tool, it automatically picks up any .dmp files in the Minidump directory and displays the relevant information gathered from them. If there are multiple .dmp files, you can click on the one you want to analyze from the top field within the tool, and the information is presented in the bottom one.
Simply download the app from the link given above, extract the content and run the BlueScreenView application.
Final Thoughts
Dump files, regardless of their type, can be pretty useful when it comes to troubleshooting your operating system. However, the methods we have used above to analyze them may not be everyone’s cup of tea, as some of you may find them complex.
That said, there are more methods to analyze dump files using tools, but they involve using the Command prompt, not a Graphical User Interface (GUI). If you’d still like to learn more about it, you can read this detailed post by Microsoft on memory dump files.












