На сервере стоит ESET File Security. Ловит сетевую активность — т.е. сервак спамит какие-то айпи.
Как вылечиться от заразы?
KVRT также засекает exe левые, удаляет, но они появляются вновь.
Логи такие:
16.04.2020 9:36:32;Фильтр HTTP;файл;178.20.208.37/server.exe;Win32/Farfli.CEN троянская программа;соединение прервано;NT SERVICE\MSSQLSERVER;Событие произошло при попытке доступа к Интернету следующим приложением: C:\Windows\System32\cscript.exe (4147B73B1224BF0D778D57B0D1391C6EE043FCFE).;72912F8B315C033A643DEAEEA62A519F3D2D328C;07.04.2020 9:23:33
16.04.2020 9:36:32;Фильтр HTTP;файл;178.20.208.37/server.exe;Win32/Farfli.CEN троянская программа;соединение прервано;NT SERVICE\MSSQLSERVER;Событие произошло при попытке доступа к Интернету следующим приложением: C:\Windows\System32\cscript.exe (4147B73B1224BF0D778D57B0D1391C6EE043FCFE).;72912F8B315C033A643DEAEEA62A519F3D2D328C;07.04.2020 9:23:33
17.04.2020 4:43:54;Фильтр HTTP;файл;178.20.208.37/server.exe;Win32/Farfli.CEN троянская программа;соединение прервано;NT SERVICE\MSSQLSERVER;Событие произошло при попытке доступа к Интернету следующим приложением: C:\Windows\System32\cscript.exe (4147B73B1224BF0D778D57B0D1391C6EE043FCFE).;72912F8B315C033A643DEAEEA62A519F3D2D328C;07.04.2020 9:23:33
17.04.2020 4:43:54;Фильтр HTTP;файл;178.20.208.37/server.exe;Win32/Farfli.CEN троянская программа;соединение прервано;NT SERVICE\MSSQLSERVER;Событие произошло при попытке доступа к Интернету следующим приложением: C:\Windows\System32\cscript.exe (4147B73B1224BF0D778D57B0D1391C6EE043FCFE).;72912F8B315C033A643DEAEEA62A519F3D2D328C;07.04.2020 9:23:33
17.04.2020 18:45:31;Фильтр HTTP;файл;178.20.208.37/server.exe;Win32/Farfli.CEN троянская программа;соединение прервано;NT SERVICE\MSSQLSERVER;Событие произошло при попытке доступа к Интернету следующим приложением: C:\Windows\System32\cscript.exe (4147B73B1224BF0D778D57B0D1391C6EE043FCFE).;72912F8B315C033A643DEAEEA62A519F3D2D328C;07.04.2020 9:23:33
17.04.2020 18:45:31;Фильтр HTTP;файл;178.20.208.37/server.exe;Win32/Farfli.CEN троянская программа;соединение прервано;NT SERVICE\MSSQLSERVER;Событие произошло при попытке доступа к Интернету следующим приложением: C:\Windows\System32\cscript.exe (4147B73B1224BF0D778D57B0D1391C6EE043FCFE).;72912F8B315C033A643DEAEEA62A519F3D2D328C;07.04.2020 9:23:33
20.04.2020 21:28:04;Фильтр HTTP;файл;178.20.208.37/server.exe;Win32/Farfli.CEN троянская программа;соединение прервано;NT SERVICE\MSSQLSERVER;Событие произошло при попытке доступа к Интернету следующим приложением: C:\Windows\System32\cscript.exe (4147B73B1224BF0D778D57B0D1391C6EE043FCFE).;72912F8B315C033A643DEAEEA62A519F3D2D328C;07.04.2020 9:23:33
20.04.2020 21:28:04;Фильтр HTTP;файл;178.20.208.37/server.exe;Win32/Farfli.CEN троянская программа;соединение прервано;NT SERVICE\MSSQLSERVER;Событие произошло при попытке доступа к Интернету следующим приложением: C:\Windows\System32\cscript.exe (4147B73B1224BF0D778D57B0D1391C6EE043FCFE).;72912F8B315C033A643DEAEEA62A519F3D2D328C;07.04.2020 9:23:33
-
Вопрос задан
-
442 просмотра
Пригласить эксперта
Подмените cscript.exe на свою простую прогу, выдающую инфу в текстовик о стартовавшем её процессе, с какими аргументами он это сделал, под каким юзером.
И дальше — по логу находите.
SFC /scannow
попробуйте
и в автозагрузке приберитесь
Автозагрузка проверить
Drweb cureit прогнать, посмотреть что нашел, вручную удали эти файлы вирусни
Вычестить папку appdata (далее скорее всего temp) от вирусни
Войдите, чтобы написать ответ
-
Показать ещё
Загружается…
Минуточку внимания
Administrators can diagnose and treat a buggy server operating system by using the Windows SFC and DISM utilities for image analysis and repairs.
Over time, system files in a Windows Server installation might require a fix. You can often repair the operating system without taking the server down by using Windows SFC or the more robust and powerful Deployment Image Servicing and Management commands.
Windows System File Checker (SFC) and Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) are administrative utilities that can alter system files, so they must be run in an administrator command prompt window.
Start with Windows SFC
The Windows SFC utility scans and verifies version information, file signatures and checksums for all protected system files on Windows desktop and server systems. If the command discovers missing protected files or alterations to existing ones, Windows SFC will attempt to replace the altered files with a pristine version from the %systemroot%\system32\dllcache folder.
The system logs all activities of the Windows SFC command to the %Windir%\CBS\CBS.log file. If the tool reports any nonrepairable errors, then you’ll want to investigate further. Search for the word corrupt to find most problems.
Windows SFC command syntax
Open a command prompt with administrator rights and run the following command to start the file checking process:
C:\Windows\System32>sfc /scannow
The /scannow parameter instructs the command to run immediately. It can take some time to complete — up to 15 minutes on servers with large data drives is not unusual — and usually consumes 60%-80% of a single CPU for the duration of its execution. On servers with more than four cores, it will have a slight impact on performance.
There are times Windows SFC cannot replace altered files. This does not always indicate trouble. For example, recent Windows builds have included graphics driver data that was reported as corrupt, but the problem is with Windows file data, not the files themselves, so no repairs are needed.
If Windows SFC can’t fix it, try DISM
The DISM command is more powerful and capable than Windows SFC. It also checks a different file repository — the %windir%\WinSXS folder, aka the «component store» — and is able to obtain replacement files from a variety of potential sources. Better yet, the command offers a quick way to check an image before attempting to diagnose or repair problems with that image.
Run DISM with the following parameters:
C:\Windows\System32>dism /Online /Cleanup-Image /CheckHealth
Even on a server with a huge system volume, this command usually completes in less than 30 seconds and does not tax system resources. Unless it finds some kind of issue, the command reports back «No component store corruption detected.» If the command finds a problem, this version of DISM reports only that corruption was detected, but no supporting details.
Corruption detected? Try ScanHealth next
If DISM finds a problem, then run the following command:
C:\Windows\System32>dism /Online /Cleanup-Image /ScanHealth
This more elaborate version of the DISM image check will report on component store corruption and indicate if repairs can be made.
If corruption is found and it can be repaired, it’s time to fire up the /RestoreHealth directive, which can also work from the /online image, or from a different targeted /source.
Run the following commands using the /RestoreHealth parameter to replace corrupt component store entries:
C:\Windows\System32>dism /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth
C:\Windows\System32>dism /source:<spec> /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth
You can drive file replacement from the running online image easily with the same syntax as the preceding commands. But it often happens that local copies aren’t available or are no more correct than the contents of the local component store itself. In that case, use the /source directive to point to a Windows image file — a .wim file or an .esd file — or a known, good, working WinSXS folder from an identically configured machine — or a known good backup of the same machine to try alternative replacements.
By default, the DISM command will also try downloading components from the Microsoft download pages; this can be turned off with the /LimitAccess parameter. For details on the /source directive syntax, the TechNet article «Repair a Windows Image» is invaluable.
DISM is a very capable tool well beyond this basic image repair maneuver. I’ve compared it to a Swiss army knife for maintaining Windows images. Windows system admins will find DISM to be complex and sometimes challenging but well worth exploring.
Next Steps
Rebuild missing SYSVOL in Active Directory
Networking enhancements coming in Windows Server 2016
Manage a library of images for Windows deployment
Dig Deeper on Microsoft messaging and collaboration
-
10 troubleshooting steps for when Windows Update is frozen
By: Robert Sheldon
-
7 steps to fix a black screen in Windows 11
By: Robert Sheldon
-
How to create a custom Windows 11 ISO file
By: Ed Tittel
-
Windows Imaging Format (WIM)
By: Rahul Awati
Troubleshooting issues on a Windows Server environment can be a complex and challenging task, especially considering the critical nature of server systems in delivering services and applications. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an in-depth overview of the principles, methodologies, and tools involved in Windows Server troubleshooting. Whether you’re a seasoned IT professional or a newcomer to server administration, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and techniques needed to effectively diagnose and resolve issues.
Introduction to Windows Server Troubleshooting
Understanding the Importance of Server Reliability
Server reliability is paramount because servers serve as the backbone of an organization’s IT infrastructure. They host critical applications, services, and data required for daily operations. If a server experiences downtime or performance issues, it can lead to productivity losses, revenue reduction, and customer dissatisfaction. Ensuring server reliability through effective Windows server troubleshooting is essential to maintain business continuity.
Common Types of Server Issues
Server issues can encompass a wide range of problems. Here are some common types of issues you might encounter:
- Performance Degradation: Slow response times, high resource usage, and unresponsiveness can indicate performance problems.
- Application and Service Failures: Applications crashing, services not starting, or unexpected behavior can disrupt services.
- Networking Problems: Network connectivity issues, DNS resolution failures, and routing problems can hinder communication.
- Security and Authentication Challenges: User login problems, unauthorized access attempts, and security breaches can compromise server integrity.
- Hardware and Driver-Related Troubles: Hardware failures, driver conflicts, and blue screen errors can impact server stability.
- Storage and Disk Issues: Disk corruption, low storage space, and data loss risks can arise.
- Backup and Recovery Challenges: Backup failures, data corruption, and recovery process difficulties can lead to data loss.
- Virtualization and Hypervisor Problems: Virtual machine failures, resource allocation issues, and migration problems can affect virtualized environments.
Preparation and Initial Assessment
Gathering Relevant Information
Before diving into Windows server troubleshooting, gather crucial information such as:
- Server Specifications: Note down server hardware details, including CPU, RAM, storage, and network adapters.
- Recent Changes: Identify any recent software installations, updates, or configuration changes.
- User-Reported Problems: Understand the user’s perspective by gathering detailed information about reported issues.
Analyzing Event Logs and System Messages
Event logs provide insights into the server’s activities, errors, and warnings. Pay attention to:
- Application Logs: Record application-related events and errors.
- System Logs: Capture system-level events and warnings.
- Security Logs: Monitor security-related events for potential breaches.
Identifying Recent Changes
Changes in software, configurations, or hardware can trigger problems. Investigate:
- Software Changes: Look for recently installed or updated applications.
- Configuration Changes: Check for modifications in system settings or configurations.
- Hardware Changes: Verify if any new hardware components were added or removed recently.
Windows Server Troubleshooting Methodology
Establishing a Logical Approach
To tackle complex server issues, it’s crucial to follow a logical approach. This approach ensures that no critical steps are missed and that Windows server troubleshooting efforts are directed toward the root cause:
- Define the Problem: Clearly identify the issue at hand. This initial step helps focus your efforts.
- Hypothesize the Cause: Formulate hypotheses about the potential causes of the problem. This helps guide your investigation.
- Test the Hypotheses: Conduct tests and gather data to validate or rule out each hypothesis.
- Develop a Plan: Create a plan of action based on the results of your tests. This plan outlines the steps you’ll take to resolve the problem.
- Implement the Plan: Execute the plan you’ve developed. This might involve applying configurations, updates, or fixes.
- Verify the Solution: Ensure that the problem has been resolved and that the server is functioning as expected.
- Document the Process: Keep a detailed record of the troubleshooting process, including the steps you’ve taken and their outcomes. This documentation is invaluable for future reference.
Networking Issues
Diagnosing Network Connectivity Problems
Network connectivity problems can manifest in various ways, from slow response times to complete unavailability. Key Windows server troubleshooting steps include:
- Ping and Tracert: Use the ping command to test basic connectivity. tracert can help identify where the communication is breaking down.
- IPConfig and Network Settings: Verify that the server’s IP configuration is correct, including IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS servers.
Investigating DNS and DHCP Issues
DNS and DHCP are fundamental services. Troubleshoot as follows:
- DNS Resolution: Ensure that DNS records are accurate and resolve to the correct IP addresses.
- DHCP Lease Issues: Check DHCP leases to prevent IP address conflicts and ensure proper lease duration.
Addressing Firewall and Routing Problems
Firewalls and routing play a critical role in network communication. Steps to address issues include:
- Firewall Rules: Review firewall rules to ensure they’re not blocking necessary traffic. Adjust rules if needed.
- Routing Table: Check the routing table to ensure traffic is being directed correctly. Incorrect routes can lead to connectivity problems.
Performance Degradation
Monitoring Server Performance
Proactively monitoring server performance helps you identify issues before they become critical. Use tools such as:
- Task Manager: This utility provides an overview of running processes, CPU usage, memory consumption, and disk activity.
- Resource Monitor: Resource Monitor offers deeper insights into resource usage by processes and provides real-time data on CPU, memory, disk, and network activity.
Utilizing Performance Counters and Resource Monitor
Performance counters offer a wealth of data related to server health. Key counters include:
- CPU Usage: Monitor CPU usage to identify if a particular process or application is consuming excessive resources.
- Memory Usage: Keep an eye on memory usage to prevent memory bottlenecks that can lead to slowdowns.
- Disk Activity: Monitor read/write activities to determine if disk performance is a contributing factor to performance issues.
- Network Traffic: Track network traffic to identify if network congestion is causing problems.
Resource Monitor supplements these counters by providing more in-depth information about individual processes and their resource consumption.
Identifying Resource Bottlenecks: CPU, Memory, Disk, and Network
Resource bottlenecks can significantly impact server performance. Address them as follows:
- CPU Bottlenecks: If CPU usage is consistently high, identify the processes responsible and consider optimizing them or upgrading hardware.
- Memory Bottlenecks: When memory usage is maxed out, applications might slow down or crash. Consider adding more RAM or optimizing memory usage.
- Disk Bottlenecks: Slow disk performance can lead to sluggish application response. Address disk bottlenecks by optimizing storage or upgrading to faster disks.
- Network Bottlenecks: Network congestion can result in slow data transfers. If network traffic is an issue, consider upgrading network hardware or optimizing network configuration.
Application and Service Failures
Analyzing Application Crash Dumps
When applications crash, analyzing crash dump files can provide valuable insights:
- Crash Dumps: These files contain information about the application’s state at the time of the crash. Analyze them using tools like WinDbg to pinpoint the cause.
Checking Service Dependencies and Startup Types
Application and system services often depend on one another. To troubleshoot:
- Service Dependencies: Ensure that services on which others depend are running. One failing service can affect others.
- Startup Types: Verify that services are set to start automatically or manually as required by their dependencies.
Utilizing Windows Reliability Monitor
Windows Reliability Monitor provides a timeline of system events, including application crashes, installations, and updates:
- Timeline of Events: Reliability Monitor gives you an overview of events in a graphical format, helping you correlate issues with changes.
By staying informed about these aspects, you’re better equipped to handle application and service failures effectively.
Security and Authentication Problems
Investigating User Login Issues
Login problems can stem from various sources. Troubleshoot as follows:
- Incorrect Credentials: Verify that users are entering the correct username and password.
- Account Lockouts: Check for account lockouts due to too many failed login attempts. Unlock or reset the account as needed.
- Expired Accounts: Ensure that users’ accounts are not expired, which can prevent logins.
Auditing Security Events and Logs
Security logs contain information about authentication and authorization events. Key steps include:
- Audit Policies: Configure security audit policies to log relevant events, such as logon attempts and privilege usage.
- Reviewing Logs: Regularly review security logs to identify unauthorized access attempts or anomalies.
Reviewing Group Policies and Permissions
Group policies and permissions control system behavior. To address issues:
- Group Policy Settings: Verify that group policies are correctly configured and applied.
- Permissions: Ensure that users have appropriate permissions to access resources. Misconfigured permissions can lead to authentication problems.
Hardware and Driver-Related Problems
Diagnosing Hardware Failures
Server hardware can fail due to various reasons. Troubleshoot using these steps:
- Hardware Diagnostics: Use built-in hardware diagnostic tools to test components like memory, CPU, and storage.
- System Event Log: Check the system event log for hardware-related error messages.
Updating and Verifying Drivers
Drivers play a crucial role in system stability. Follow these steps:
- Driver Updates: Ensure that all drivers, including network and storage drivers, are up to date.
- Device Manager: Use Device Manager to check for devices with driver issues.
Handling Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) Errors
BSOD errors indicate critical system issues. Address them as follows:
- Error Code: Note the error code displayed on the BSOD screen, which can provide clues about the problem.
- Minidump Analysis: Analyze minidump files using tools like WinDbg to determine the cause of the BSOD.
Remote Desktop and Terminal Services Issues
Windows Server Troubleshooting Remote Desktop Connectivity
Remote Desktop allows remote access to servers. For connectivity problems:
- Network Connectivity: Ensure the server is reachable over the network.
- Firewall Settings: Verify that firewall rules allow Remote Desktop traffic.
- User Permissions: Confirm that users have the right to access the server remotely.
Handling Licensing and Authentication Problems
Remote Desktop licensing and authentication can cause issues. Address them as follows:
- Licensing: Ensure Remote Desktop Licensing is configured correctly.
- Authentication: Verify that users are using valid credentials for Remote Desktop access.
Optimizing Remote Desktop Performance
For better Remote Desktop performance:
- Network Quality: Ensure sufficient network bandwidth for smooth Remote Desktop sessions.
- Remote Desktop Settings: Adjust Remote Desktop settings for optimal performance, including display and connection speed options.
Storage and Disk Problems
Checking Disk Integrity and Health
Healthy disks are crucial for server stability. Perform these checks:
- Disk Checks: Run built-in disk checking utilities like chkdsk to identify and fix disk errors.
- SMART Data: Use SMART (Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology) data to monitor disk health.
Resolving Disk Space and File Corruption Issues
Running out of disk space or encountering file corruption can disrupt services:
- Disk Space: Monitor disk space regularly and free up space if necessary.
- File Integrity: Use tools like sfc (System File Checker) to scan and repair corrupted system files.
Managing RAID and Storage Spaces
If using RAID or Storage Spaces:
- RAID Status: Check the status of RAID arrays to ensure redundancy is intact.
- Storage Spaces: Monitor Storage Spaces for disk failures and rebalance storage as needed.
Experts assistance for Windows server troubleshooting
While troubleshooting after reading our comprehensive guide is easy, it still requires constant effort. Hiring a team for these tasks is an expensive affair. To help businesses with all types of server management tasks, supportfly offers server management services. Our managed server administration services make sure your server is always free of issues. Our certified server admins make sure that your windows server is monitored 24×7.
Conclusion
Windows Server troubleshooting is a skill that combines technical expertise, systematic thinking, and a deep understanding of the server environment. By following a structured approach and utilizing the various tools and techniques outlined in this guide, administrators can effectively identify and resolve issues, ensuring the reliability and stability of their server systems. Remember, Windows server troubleshooting is not only about fixing problems but also about learning and growing as an IT professional. With continuous learning and hands-on experience, you’ll become a proficient troubleshooter capable of handling even the most challenging server issues.
FAQs
What is Windows Server troubleshooting?
Windows Server troubleshooting is the process of identifying and resolving issues that affect the functionality, performance, or security of a Windows Server environment. It involves diagnosing problems, identifying their root causes, and implementing solutions to restore normal operation.
Why is Windows Server troubleshooting important?
Windows Server troubleshooting is vital to maintain the reliability, performance, and security of server systems. It helps prevent downtime, data loss, and disruptions to critical services, ensuring smooth operations for organizations.
What are some common issues that require Windows Server troubleshooting?
Common issues that require Windows Server troubleshooting include network connectivity problems, application crashes, slow performance, login issues, security breaches, hardware failures, and storage-related concerns.
What steps should I take before starting Windows Server troubleshooting?
Before Windows Server troubleshooting, gather information about the issue, review event logs, identify recent changes, and assess the scope and impact of the problem.
How can I recover from data loss during Windows server troubleshooting?
Regular backups are crucial. If data loss occurs, restore from a backup to recover lost data. Implement backup and disaster recovery plans to minimize the impact of such situations. This makes Windows server troubleshooting easy.
Исправление поврежденного образа Windows Server 2012
Posted on 15/10/2015 by sie
Долгое время никак не мог отловить проблему с Windows Server 2012 (не R2), на которых в частности работает Exchange Server. Внешне выглядело так, что к серверу невозможно подключиться по RDP. На консоли время тикает, но Ctrl-Alt-Del не работает. Постепенно остальные сервисы на сервере перестают работать, но пинг остаётся. Подлезть на сервер никак не получается – только принудительная перезагрузка.
Проверка sfc /scannow написала о неисправимой проблеме. В логе cbs.log было упоминание ошибок с Amd64\CNBJ2530.DPB и Package_86_for_KB2769165. Появилась гипотеза, что именно это может вызывать проблему.
Нашлась масса обсуждений по этому поводу. В том числе на Technet, где рекомендовали лечить проблему так:
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth
Но даже это не помогло.
Тут удачно под руку попался сервер, который только начал «помирать». Удалённо удалось увидеть, что сервисы Windows Update и Trusted Installer находятся в состоянии Stopping. После их «убийства» сервер всё же успешно перезагрузился. Это ещё раз укрепило в мысли, что образ системы нужно вылечить.
Наконец нашлась волшебная утилита SFCFix.exe, которая действительно устранила проблемы с образом системы. Как работает не знаю. Даже не могу рекомендовать её использование.
Тем не менее контрольная проверка после запуска этой утилиты:
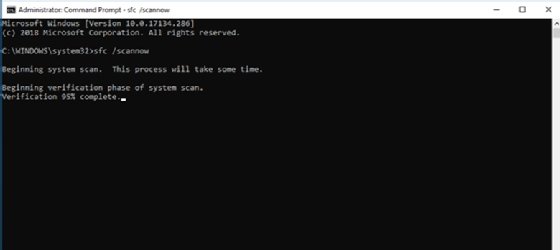
C:\install>sfc /scannow Beginning system scan. This process will take some time. Beginning verification phase of system scan. Verification 100% complete. Windows Resource Protection found corrupt files and successfully repaired them. Details are included in the CBS.Log windir\Logs\CBS\CBS.log. For example C:\Windows\Logs\CBS\CBS.log. Note that logging is currently not supported in offline servicing scenarios.
– завершилась успешно. Осталось подождать год J и убедиться, что сервер работает и не блокируется.
Filed under: Exchange, Windows | Tagged: Exchange, Windows, Windows Server 2012 |
Имеем вот такую картину например:
При подключении всех дисков одновременно (физически) WinServer-2008-64 стартует нормально , она на Диске №2.
Если отключить все диски физически и пробовать по отдельности по одному подключать , то стартовать никак не получается — не хватает какого-то другого диска. Почему? Пытаемся разобраться…
Тома без названий — это по-видимому Ubuntu , о которых Windows тактично умалчивает, и при этом с удовольствием предлагает их задействовать для других целей : удалить,ну хотя бы оформатировать.
Интерес представляет «Зарезервировано системой H: 100Мb» — это по-видимому область Windows Loader и она на другом диске см. Диск №1. Эта такая хрень , которая и мешает жить нормальным людям.
Как я понял сначала с диска запускается MBR (Master Boot Record). Вопрос — с какого диска? Ответ похоже такой — с любого первого (по порядку по Биосу), на котором есть MBR.
Удобно еще пользоваться например ОС Ubuntu. Установили рядом с Windows на то же или другом диске и с помощью Grubber Customizer копируем MBR на любой диск (клонируем так сказать), но есть нюанс.
- Загружаемся без диска №0 (500Gb физически отключаем) и все равно видим такое:
- error: no such device xxxxxxxxxxx…. тут какой-то уникальный GUID
- grub rescue>
Похоже grub (а он понятно не от Windows пришел) где-то на оставшихся 2 дисках есть, но не может он запустить что-то и предлагаем восстановить что-то. Покопашись в интернете похоже проясняется смысл grub : Ubuntu прописывает в MBR первую часть grub (ибо туда совсем мало что может поместиться), а именно только ссылку на вторую часть grub и консоль (командную строку) для нашего как раз случая, когда вторая часть grub отсутствует (или осталась на другом изъятом диске) , то через консоль Grub rescue> подключения к ОС можно все восстановить вручную.
1. Лечим опять все тем же способом через Ubuntu , т.е. устанавливаем Ubuntu рядом с Windows , опять устанавливаем grub Customizer.
2. Или запускаемся с диска Ubuntu и устанавливаем grub.
4. из консоли grub rescue> набираем несколько команд..
3. Но есть еще более быстрый способ программа Boot-Repair-disk — 5 минут и сама найдет все ОС(Win,Ubuntu,..), все Windows Loader-ы !!! Перезагружаемся и все ОК !!!
Ну и вот , что мы видим в результате:
Примечание sda,sdb,sdc … диски в Ubuntu , а также Диск 0,1,2… в Windows — условные и не фиксируются, поэтому различать конкретный диск лучше например по его размеру. Разделы на дисках различаем по Имени (Меткам) , которые можно редактировать.
Ну и еще надо добавить , что отключил я после Boot-Repair-disk диск на 1000Gb и к удивлению Win-Server-2008-2000Gb-sdc3 стартанул нормально, хотя 100Мб «Зарезервировано системой» остался на отключенном 1000Gb диске. Т.е. этот 100Мб раздел не повлиял на загрузку ОС , зачем он нужен? (точнее кому)? Как я понял у меня было 2 диска , 2 Windows Bootlodear-а и каждый появлялся при установке нового Windows на соответствующий диск.
Новый момент истины. Удалили системный (как его называет Windows ) Диск №1 раздел D:
Надо было освободить букву D: для другого раздела Диска №0. Просто для D: изменить букву или удалить полностью раздел Windows категорически отказывался , поэтому его тупо удалил через Ubuntu. А он был-то системный. Таким образом потом WinServer-2008-64 2000Gb или другая ОС на Диске №0 : теперь даже намека на старт не было. Это нормально, т.к. на удаленном разделе находился Windows bootloader, наверное поэтому он и назывался системный.
Так вот восстановить сам Windows bootloader программой Boot-Repair-disk не удалось. По-видимому Boot-Repair-disk может только найти рабочий Windows bootloader , но нарисовать его самостоятельно не может.
Шеф все пропало!? Целый день почти ушел на выяснения чем (и кого) лечить? Смысл такой, что в интернете на этом почти все программы хотят заработать деньги. А как вы понимаете попытка скорее всего одна будет и очень хочется ,чтобы была удачная. Хочется чего-то бесплатного, но платные программы только и ждут как ты выберешь какую-нибудь бесплатную утилитку и у тебя все накроется и тогда только они тебе помогут. Поэтому тут лучше остановиться и один раз на будущее во всем попробовать разобраться.
Кстати пробовал до удаления раздела файл bcd.. запустить, но на Windows Server 2008-64 его не нашел. Что и было причиной прямого удаления раздела.
В интернете нашел бесплатный Hiren’s Boot CD 15.2 , но не смог найти там где , что восстанавливать (бывает и такое, какой безумный набор всяких утилит). Paragon disk Manager — платное г…, которое только и только мечтает , чтобы у вас раздел накрылся. Извините, эмоции…
Далее все пишут про команды из командной строки , которые надо запускать с консоли дистрибутивного диска ваше ОС в режиме восстановления.
Но нашлась все-таки программа с простым интерфейсов и бесплатная EasyBCD по Windows. Рискнул попробовал , помогло (частично). Запускаем EasyBCD под Win7-64 Диск №1 (там Windows bootloader сохранился). Далее программа EasyBCD увидела тупо разделы с Диска №0 и я их добавил в загрузку, конечно это все зафиксировалось только в bootloader Диска №1, но и то уже хорошо.
Но вот что интересно — лицензия 1С 8.3 слетела, хотя сам-то раздел WinServer-2008-64 2000Gb целиком сохранился, не менялся. Какая тут связь? И это нормально (привыкаем). 1С 8.3 вгрызается в ваш ПК намертво, даже область загрузки для нее имеет значение.
Теперь как решается проблема с восстановлением загрузочной области Windows Server 2008-64 R2 (именно Windows Server 2008, ибо с другим этого скорее всего не будет). По русскому интернету нифига не нашел, зато на https://social.technet.microsoft.com/Forums/ люди всего мира благодарили человека, даже в любви признавались, за то , что он догадался вставить для восстановления Windows Server 2008 DVD Windows7-64:
Сначала как-бы загружаем Windows Server 2008 DVD и у нас там вообще сначала не видно никаких ОC которые надо восстановить.
Потом на каком-то этапе Windows Server 2008 DVD увидел наши 2 ОС. Но восстановить загрузочную область для них не смог. Остановились на BOOTMGR is missing.
Вот тут-то и делаем так (извините подробно не записывал):
1. Windows Server 2008 DVD:
rename c:\boot\BCD bcd.old сохраняем копию чего-то похожего на загрузочную область, а оригинал BCD удаляется
проверяем результат это как-то так см. dir
2. перезагружаемся с Windows7-64 DVD:
он видим наши ОС на разделах и выбираем восстановление нашего (какое-то типа автоматическое) и делаем его может несколько раз (у меня 2 раза хватило) и НАКОНЕЦ стартует НОРМАЛЬНО Windows (остальные Win7-64,.. тоже нормально стартуют).
Смысл этого , что в MS похоже просто забыли проверить восстановление загрузки ОС Windows Server 2008. Да и как-то интереснее стало жить на свете наверное…




