Встроенная утилита CHKDSK.exe (check disk) используется в Windows для проверки диска на ошибки. Сhkdsk проверяет файловую систему на физические и логические ошибки, находит поврежденные секторы (bad sectors) и исправляет найденные проблемы.
Содержание:
- Проверка и восстановление диска с помощью команды chkdsk
- Просмотр результатов проверки Chkdsk в Windows
Проверка и восстановление диска с помощью команды chkdsk
Чтобы проверить жесткий диск на ошибки, запустите командную строку с правами администратора и выполните:
chkdsk E: /F /R
Данная команда:
- Выполнит проверку диска E:\
- Исправит автоматически найденные ошиьки (/F)
- Попытаться восстановить данные при обнаружении поврежденных секторов, она попытается восстановить информации (/R).
Полная проверка диска может занять длительное время в зависимости от емкости носителя и количества файлов. После окончания проверки диска вы увидите подробную статистику диска, информацию о поврежденных секторах и файлах, предпринятых действиях по восстановлению.
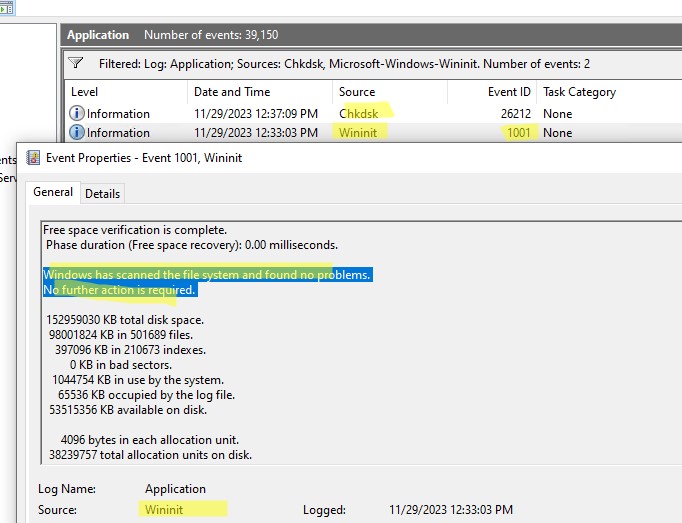
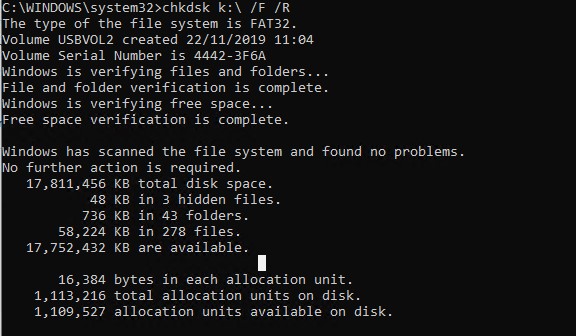
Если утилита chkdsk не обнаружила проблем на диске, появится сообщение:
Windows has scanned the file system and found no problems. No further action is required.
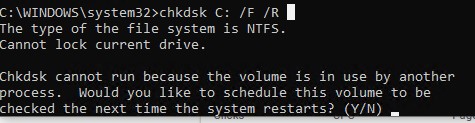
Утилита chkdsk не позволяет выполнить online проверку системного диска (C:\). При запуске команды chkdsk C: /F /R появится уведомление:
Cannot lock current drive. Chkdsk cannot run because the volume is in use by another process. Would you like to schedule this volume to be checked the next time the system restarts? (Y/N).
Невозможно выполнить команду Chkdsk, так как указанный том используется другим процессом. Следует ли выполнить проверку этого тома при следующей перезагрузке системы?
Чтобы запланировать проверку диска при следующей загрузке Windows, нажмите
Y
->
Enter
.
This volume will be checked the next time the system restarts
.
Чтобы отменить запланированную проверку диска, выполните:
chkntfs /x c:
Чтобы отключить топ перед проверкой, добавьте атрибут /X в команде chkdsk. В этом случае Windows принудительно закрое все открытые файловые дескрипторы, отмонтирует диск и выполнит проверку на ошибки.
Если вам нужно выполнить проверку большого NTFS тома, но вы не хотите блокировать диск, можно сначала просканировать диск на ошибки:
chkdsk E: /f /offlinescanandfix
Утилита найдет ошибки и сохранит их в файл $corrupt для дальнейшего исправления
Чтобы исправить найденные ошибки, не тратя время на полное сканирование тома, выполните:
chkdsk D: /spotfix
Это существенно сократит время недоступности тома для пользователя при исправлении ошибок.
В консоли PowerShell для проверки диска можно использовать командлет Repair-Volume как аналог команды chkdsk:
Repair-Volume -driveletter C -scan
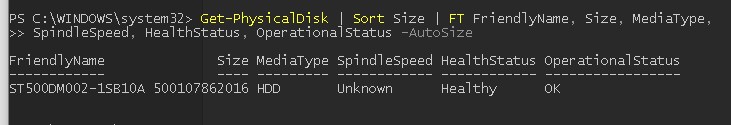
Также рекомендуем перед проверкой проверить SMART состояние жестких дисков с помощью встроенных PowerShell командлетов из модуля управления дисками:
Get-PhysicalDisk | Sort Size | FT FriendlyName, Size, MediaType,SpindleSpeed, HealthStatus, OperationalStatus -AutoSize
Просмотр результатов проверки Chkdsk в Windows
Chkdsk при онлайн сканировании диска выводит результаты прямо в консоль. Если вы запланировали проверку диска при загрузке Windows, то результаты можно получить только из журнала событий Windows (Event Viewer).
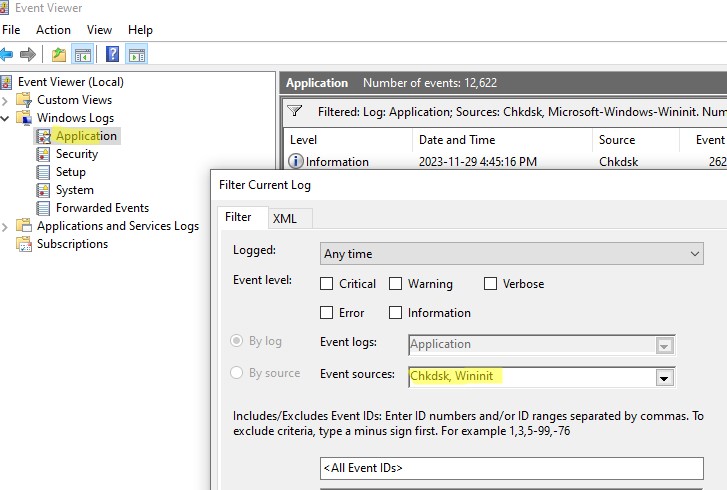
- Откройте консоль Event Viewer (
Eventvwr.msc
) и перейдите в раздел Windows Logs -> Application; - Щелкните правой клавишей по разделы Application и выберите Filter Current Log. В поле Event Source выберите Chkdsk и Wininit и нажмите ОК;
- Подробные результаты проверки диска содержатся в описании события. Обратите внимание, что у онлайн событий проверки диска будет указан источник Chkdsk. Если выполнялась офлайн проверка диска при загрузке Windows, у такого события будет источник Wininit и EventID 1001.
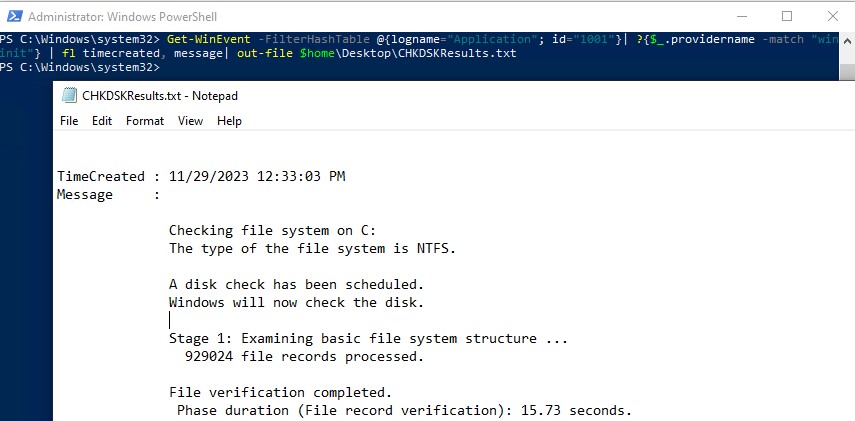
Можно получить лог проверки диска с помощью PowerShell командлета Get-WinEvent. Например, чтобы выгрузить результаты последних 5 проверок диска в текстовый файл CHKDSK_SCAN.txt на рабочем столе, выполните команду:
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashTable @{logname="Application"; id="1001"}| ?{$_.providername –match "wininit"} | fl timecreated, message| out-file $home\Desktop\CHKDSKResults.txt
Открыть полученный файл с логом chkdsk:
notepad.exe $home\Desktop\CHKDSKResults.txt
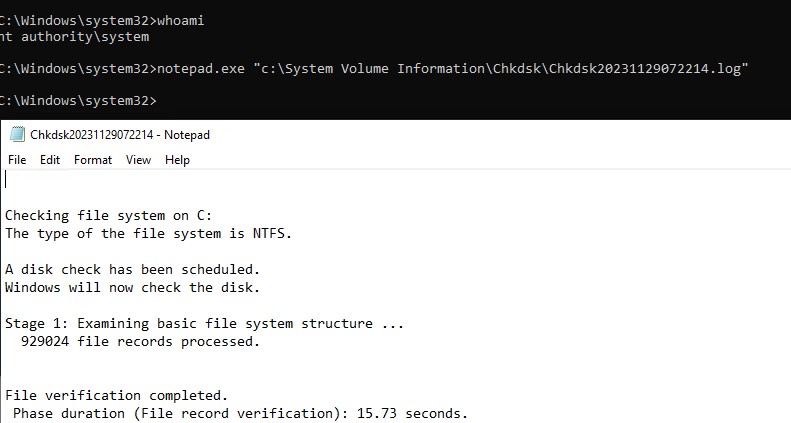
Если размер лога Chkdks очень большой, журнал событий может обрезать его. В этом случае можно открыть полный лог проверки диск в System Volume Information. Чтобы получить доступ к этой папке, нужно запустить командную строку от имени SYSTEM (проще всего с помощью утилиты psexec):
.\PsExec.exe -i -s cmd.exe
После этого можно открыть лог chkdsk:
notepad.exe "c:\System Volume Information\Chkdsk\Chkdsk20231129072214.log"
The Check Disk Utility or chkdsk.exe is a tool in Windows 10 that examines the faulty drives or abnormal drives to pull out the flaws that are obstructing the drives to performing correctly. This tool gives an automatic execution whenever the machine confronts a sudden shut down or it discovers the file system to be distorted. You will read How to Check Faulty Drives with Chkdsk in Windows 10.
In few cases, this tool is scheduled to run but other times Windows itself directs it run, depending upon the nature of errors. Instead of working it once, this tool continues to run all the time the machine is booted. There are multiple ways you can run Chkdsk in Windows 10, Here we see one by one.
How to Check Faulty Drives with Chkdsk in Windows 10
1. Via This PC
- Open up This PC and implement a right click on the Drive for which you need to run Chkdsk. Move off with Properties.
- On the Properties Window of the regarding drive Click the menu Tools and moreover Check button in the Error checking block.
- Click Scan Drive in the middle of the pop up.
- Error checking begins and shows you the status of the process.
- Click Show Details link after the accomplishment of the operation.
2. Via Command Prompt
- Running a tiny size of command in the Elevated Command prompt Checks Faulty Drives with Chkdsk in windows 10. The Command for C drive is
CHKDSK C: /F
If the name of the drive is different from the written then replace with letter C.
- Copy this command from here make the desired change and hit Enter. Chkdsk commences. Read the result in Event Viewer.
3. Through Cortana Search
- Copy the above command and paste in the text field under Cortana and hit Enter
Chkdsk cannot run because the volume is in use by another process
Sometimes you get a twist when you run Chkdsk in Command Prompt. The result in the command prompt conveys like Chkdsk cannot run because the volume is in use by another process. The note intimates to schedule Chkdsk to subsequent reboot and when you schedule it will complete checking before the volume will not be in other use at the startup. The fix is also written ahead. Follow the process written below to fix Chkdsk cannot run because the volume is in use by another process
- Read the next line of the message which says Would you like to schedule this volume to be checked the next time the system restarts (Y/N). Just ahead of the sentence Type Y which indicates yes but if you don’t like to run Chkdsk moreover type N. If you write Y this means Chkdsk is scheduled to be started at the next startup.
How to Access Chkdsk Scan Result in windows 10
Windows Event Viewer stores data in bulk about all the occurrences of your system. In this current OS, Microsoft decided to hide the results of Chkdsk scan if it is operated before Windows has booted. It only displays the percentage of the scan completed. And it does not convey the user if it has traced any defect or amended any changes in the file system. The only place to see the Chkdsk results is Windows Event Viewer. Obey the method to see:
- Together press Windows and Q keys and write event in the text field.
- Event Viewer is seen at the top when the results are fetched out. Click on it.
- Upon the emergence of Event Viewer, travel this path on the left pane: Windows Log => Application.
- On the extreme right pane, conduct a click on Filter Current Log.
- This will bring a separate window of the same where you have to type either the number 26226 or chkdsk in the event ID field.
- As you click Ok you will see the results of all the checks.
In a normal way, the link Show details emerged at the completion of Chkdsk is good enough to find the outcome of Chkdsk in the event viewer.
Check Disk Utility or chkdsk.exe is a tool in Windows 10 that examines damage on disks. This tool turns on automatically when your computer encounters a sudden shutdown or detects a corrupted file system. In a few cases, this tool is recommended to run, but in other cases, Windows itself launches it, depending on the nature of the errors. CHKDSK scans the volume of the disk and verifies that the integrity of the file system has not been compromised – and if it detects any logical errors, it corrects them. Let’s take a look at how to use the CHKDSK tool to check and repair the hard disk in Windows 10/8/7.
Error checking and recovery of bad sectors on the hard disk
What exactly does this tool check? It’s very simple, it checks in 5 steps: checking the basic structure of the file system, checking file name associations, checking security descriptors, searching for damaged clusters in user data files, searching for damaged and free clusters. The format of the commands to be specified on the command line is similar to chkdsk [Drive:] [parameters] and looks like chkdsk c: / f / r / x. Please note that the local C: drive is specified. If you need to check the entire hard drive, then remove the C: and the command will look like this chkdsk / f / r / x. If you need to check and restore the flash drive, then specify the volume letter instead of C :. Let’s dive into the advanced options, which can help fix errors on the hard disk.
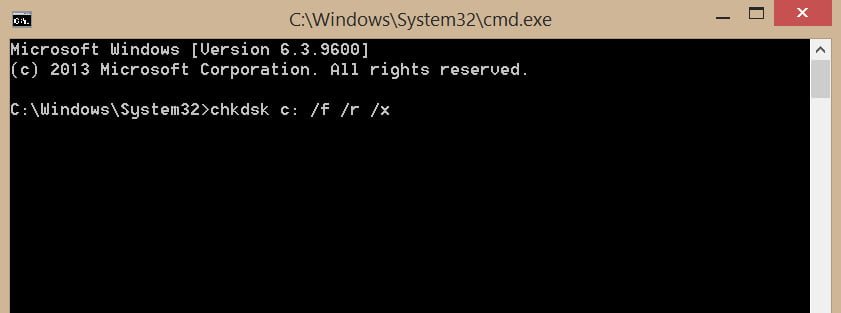
Open a command prompt as an administrator and enter the command chkdsk C: / f / r / x to scan the hard disk for errors and press Enter.
C – Local disk or volume that you want to check. If you want to check the entire hard disk for errors, just use the command chkdsk / f / r / x
/ f – Corrects errors that he finds.
/ r – Searches for bad sectors and restores them.
/ x – Performs a volume shutdown before checking it, if necessary.
I brought more meaningful commands to one at once, but you can see additional commands by typing chkdsk /? On the command line.

Related :
How to free up space and clean the C drive from unnecessary files
Back to top button
Quick Links
-
What Is CHKDSK, and What Does It Do?
-
How to Check Up On or Cancel a Scheduled Disk Check
-
How to Use the ChkDsk Command
-
Important Chkdsk Commands
Summary
- Chkdsk is a utility that scans and fixes problems with your hard drive, including file system errors and bad sectors.
- It is recommended to run chkdsk regularly as part of routine maintenance and after abnormal shutdowns to prevent data loss and bigger problems.
- Running «chkdsk /f /r» can repair logical file system errors and scan for bad sectors, providing a thorough check of your hard drive.
Any time you have hard drive errors — or even strange behavior you might not at first associate with a hard drive — Check Disk can be a lifesaver. Here’s how to use the Chkdsk tool that comes with Windows 10, Windows 11, and other versions of Windows
What Is CHKDSK, and What Does It Do?
The Check Disk utility, also known as chkdsk (since that’s the command you use to run it) scans through your entire hard drive to find and fix problems. It’s not a terribly exciting tool — and running it can take some time — but it can really help prevent bigger problems and loss of data in the long run. Chkdsk performs a couple of functions, depending on how it’s run:
- Chkdsk’s basic function is to scan the integrity of the file system and file system metadata on a disk volume and fix any logical file system errors that it finds. Such errors might include corrupt entries in a volume’s master file table (MFT), bad security descriptors associated with files, or even misaligned time stamp or file size information about individual files.
- Chkdsk can also optionally scan every sector on a disk volume looking for bad sectors. Bad sectors come in two forms: soft bad sectors, which can occur when data is written badly, and hard bad sectors, which can occur because of physical damage to the disk. Chkdsk attempts to fix these problems by repairing soft bad sectors and marking hard bad sectors so they won’t be used again.
That may all sound very technical, but don’t worry: you don’t need to understand the ins and outs of how it works to know when you should run it.
You may want to run chkdsk every few months as part of routine maintenance along with using a S.M.A.R.T. tool for drives that support it. You should also consider running it any time Windows has shut down abnormally — such as after a power loss or system crash. Sometimes Windows will automatically run a scan during startup, but most often you’ll have to do it yourself. Even if you’re just having strange problems with apps not loading or crashing that you haven’t been able to resolve another way, you might consider checking the disk.
For example: I once had a problem where Outlook suddenly started crashing on me shortly after loading. After a lot of troubleshooting, a chkdsk scan revealed I had bad sectors where my Outlook data file was stored. Fortunately, chkdsk was able to recover the sectors in my case, and everything went back to normal afterward.
If chkdsk does encounter problems — especially hard bad sectors — that it can’t repair, data can become unusable. It’s not very likely, but it can happen. For that reason, you should always make sure you have a good backup routine in place and back up your PC before running chkdsk.
The chkdsk tool works pretty much the same in all versions of Windows. We’ll be working with Windows 10 in this article, so the screenshots may look slightly different if you’re using Windows 11, but chkdsk performs the same, and we’ll point out where any procedures differ. We’ll also talk about running it from the Command Prompt, in cases where you can’t even boot into Windows.
How to Run Chkdsk
Running the Check Disk tool from the Windows desktop is easy. In File Explorer, right-click the drive you want to check, and then choose «Properties.»

In the properties window, switch to the «Tools» tab and then click the «Check» button. In Windows 7, the button is named «Check Now.»
In Windows 10 and Windows 11, Windows may inform you that it hasn’t found any errors on the drive. You can still perform a manual scan by clicking «Scan drive.» This will first perform a scan without attempting any repairs, so it will not restart your PC at this point. If the quick disk scan reveals any problems, Windows will present that option to you. If you want to force it, though, you’ll have to use the command prompt to run chkdsk — something we’ll be covering a bit later in the article.
After Windows scans your drive, if no errors were found, you can just click «Close.»
How to Check Up On or Cancel a Scheduled Disk Check
If you’re not sure whether a disk check is scheduled for your next restart, it’s easy enough to check at the Command Prompt. You’ll need to run Command Prompt with administrative privileges. Open the Start Menu and then type «cmd.» Right-click the result and then choose «Run as administrator.»
This works identically in Command Prompt, PowerShell, or Windows Terminal as long as it is launched as administrator.
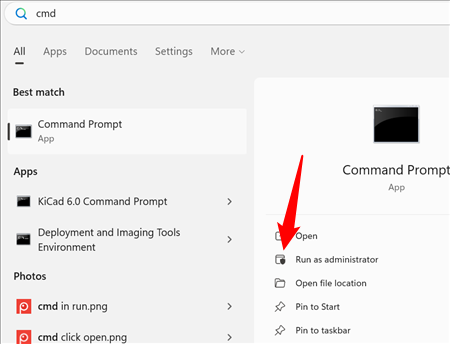
At the prompt, type the following command — substituting the drive letter if necessary.
chkntfs c:
If you have scheduled a manual check of the drive, you’ll see a message to that effect.
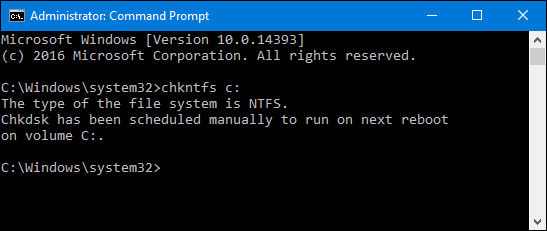
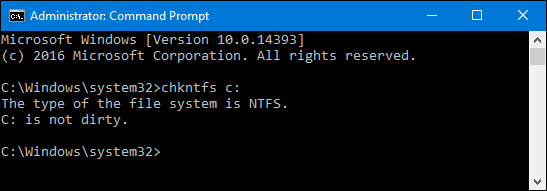
If Windows has scheduled an automatic check of the drive, you’ll see a message letting you know that the volume is dirty, which just means it’s been flagged with potential errors. This serves as indication that Windows will run a check the next time it starts. If no automatic scan is scheduled, you’ll just see a message letting you know that the volume is not dirty.
If a disk check is scheduled for the next time you start Windows, but have decided you don’t want the check to happen, you can cancel the check by typing the following command:
chkntfs /x c:
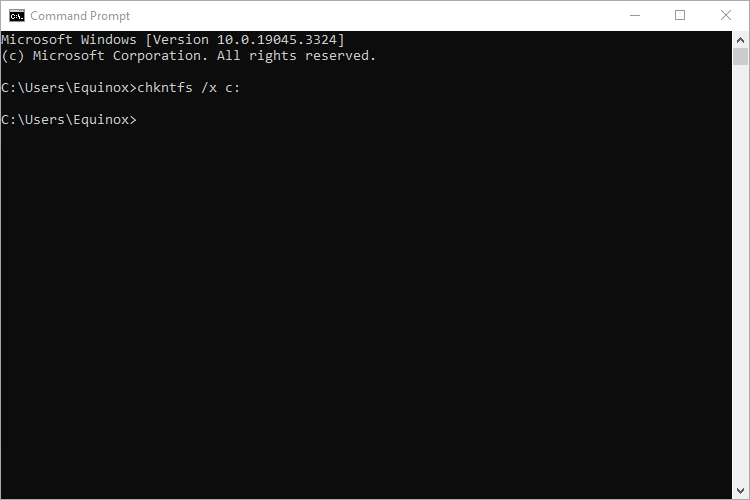
You won’t get any kind of feedback that the scan has been canceled, but it will have been. This command actually excludes the drive from the chkdsk command for the next start. If you do restart to find that a scan has been scheduled, Windows is also kind enough to provide you with about ten seconds to skip the scan if you want to.

How to Use the ChkDsk Command
If you’re willing to use the Command Prompt (or you have to because Windows won’t boot properly), you can exert a little more control over the disk-checking process. Plus, if you’re using Windows 10 or Windows 11 , it’s the only way to force automatic fixing or bad sector scanning into the mix. Open up the Command Prompt with administrative privileges by hitting Windows+X and selecting «Command Prompt (Admin).» You’ll be using the chkdsk command. The command supports a number of optional switches, but we’re mostly concerned with two of them: /f and /r.
You can also use PowerShell or Windows Terminal if you want. The process is identical. Just make sure that you launch them as administrator.
If you just use the chkdsk command by itself, it will scan your drive in read-only mode, reporting errors but not attempting to repair them. For this reason, it can usually run without having to restart your PC.

If you want chkdsk to attempt to repair logical file system errors during the scan, add the /f switch. Note that if the drive has files that are in use (and it probably will), you’ll be asked to schedule a scan for the next restart.
chkdsk /f c:
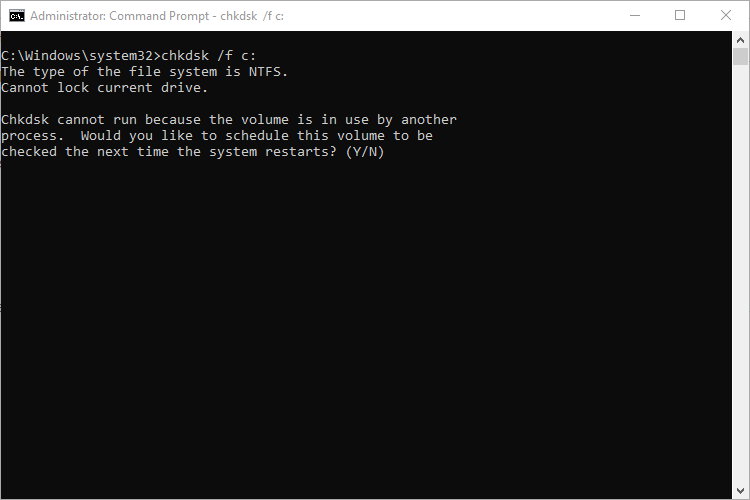
If you want chkdsk to scan for bad sectors as well, you’ll use the /r switch. When you use the /r switch, the /f switch is implied, meaning that chkdsk will scan for both logical errors and bad sectors. But while it’s not really necessary to explicitly write chkdsk /f /r, it also won’t hurt anything if you throw both the /r and /f switches on the command at the same time.
chkdsk /r c:
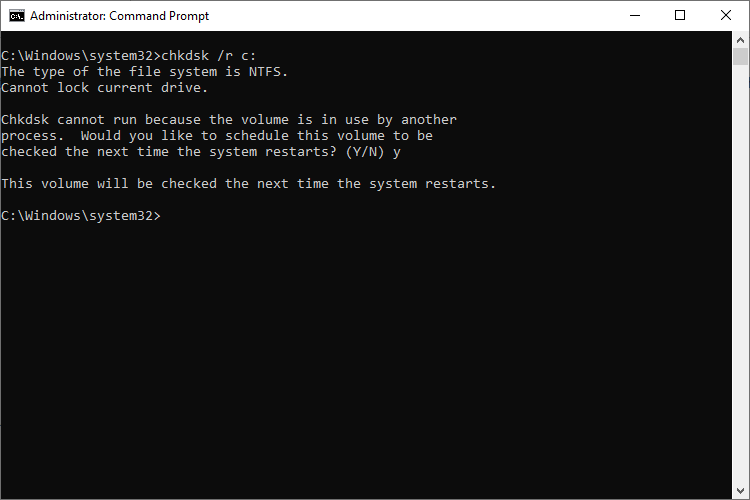
Running chkdsk /r gives you the most thorough scan you can perform on a volume, and if you have some time to spare for the sector check, we highly recommend running it at least periodically.
Important Chkdsk Commands
There are, of course, other parameters you can use with chkdsk . So, for the sake of completeness — and your geeky enjoyment — here they are:
- C:\>chkdsk /? Checks a disk and displays a status report.
-
CHKDSK [volume[[path]filename]]] [/F] [/V] [/R] [/X] [/I] [/C] [/L[:size]] [/B]
- volume Specifies the drive letter (followed by a colon), mount point, or volume name.
- filename FAT/FAT32 only: Specifies the files to check for fragmentation.
- /F Fixes errors on the disk.
- /V On FAT/FAT32: Displays the full path and name of every file on the disk. On NTFS: Displays cleanup messages if any.
- /R Locates bad sectors and recovers readable information (implies /F).
- /L:size NTFS only: Changes the log file size to the specified number of kilobytes. If size is not specified, displays current size.
- /X Forces the volume to dismount first if necessary. All opened handles to the volume would then be invalid (implies /F).
- /I NTFS only: Performs a less vigorous check of index entries. /C NTFS only: Skips checking of cycles within the folder structure.
- /B NTFS only: Re-evaluates bad clusters on the volume (implies /R) /scan NTFS only: Runs an online scan on the volume
- /forceofflinefix NTFS only: (Must be used with «/scan») Bypass all online repair; all defects found are queued for offline repair (i.e. «chkdsk /spotfix»).
- /perf NTFS only: (Must be used with «/scan») Uses more system resources to complete a scan as fast as possible. This may have a negative performance impact on other tasks running on the system.
- /spotfix NTFS only: Runs spot fixing on the volume /sdcleanup NTFS only: Garbage collect unneeded security descriptor data (implies /F).
- /offlinescanandfix Runs an offline scan and fix on the volume.
- /freeorphanedchains FAT/FAT32/exFAT only: Frees any orphaned cluster chains instead of recovering their contents.
- /markclean FAT/FAT32/exFAT only: Marks the volume clean if no corruption was detected, even if /F was not specified.
The /I or /C switch reduces the amount of time required to run Chkdsk byskipping certain checks of the volume
Hopefully, Chkdsk will fix whatever hard drive problems you may have, and you can go back to using your computer normally.
CHKDSK is a Windows utility that can check the integrity of your hard disk and can fix various file system errors.
CHKDSK (or chkdsk.exe) is short for “check disk”.
It’s recommended to use this utility when your computer shows various boot errors. The check disk utility can be run if you need a fix for the following errors:
- 0x00000024
- Various blue screen of death errors
- NTDETECT failed
- Fatal error reading boot.ini
- NTOSKRNL.EXE is missing or corrupt
- 0x0000007B
- 0xc0000001 on a Windows Vista computer
- 0xc000014C on a Windows 8 computer
- and others
The check disk utility can repair problems such as:
- bad sectors
- lost clusters
- cross-linked files
- directory errors
Screenshots
The check disk tool can be run via Command Prompt or, if you can boot into Windows from My Computer > Properties > Tools depending on the Windows version you installed on your PC.
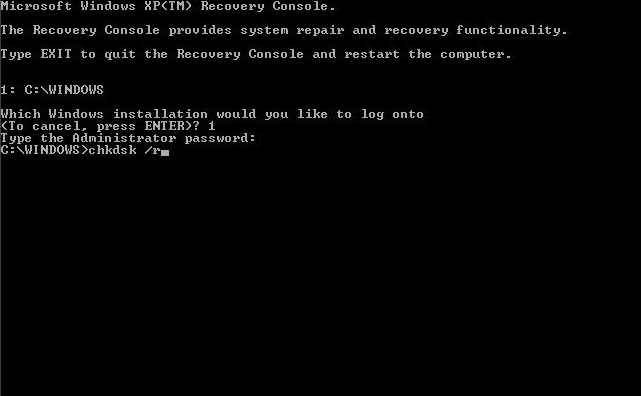
The command line tool can be ran on a Windows XP computer from within the Windows XP Recovery Console:
The utility from within Windows XP, from My Computer and not Command Prompt:
This is how you start a scan with the disk utility if you can boot into Windows Vista:
How to run CHKDSK in Windows
This utility is available for Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7 and Windows 8 or 8.1.
If you can boot into Windows, you can run the check disk utility on each hard drive or partition you have available in My Computer.
If you can’t boot the operating system, you can run the tool from Command Prompt either by booting your computer into the Recovery Mode or by using the original installation disc to run Command Prompt.
CHKDSK in Windows XP
If you can boot into Windows XP, you can run the utility either from the Command Prompt or from My Computer.
From Command Prompt
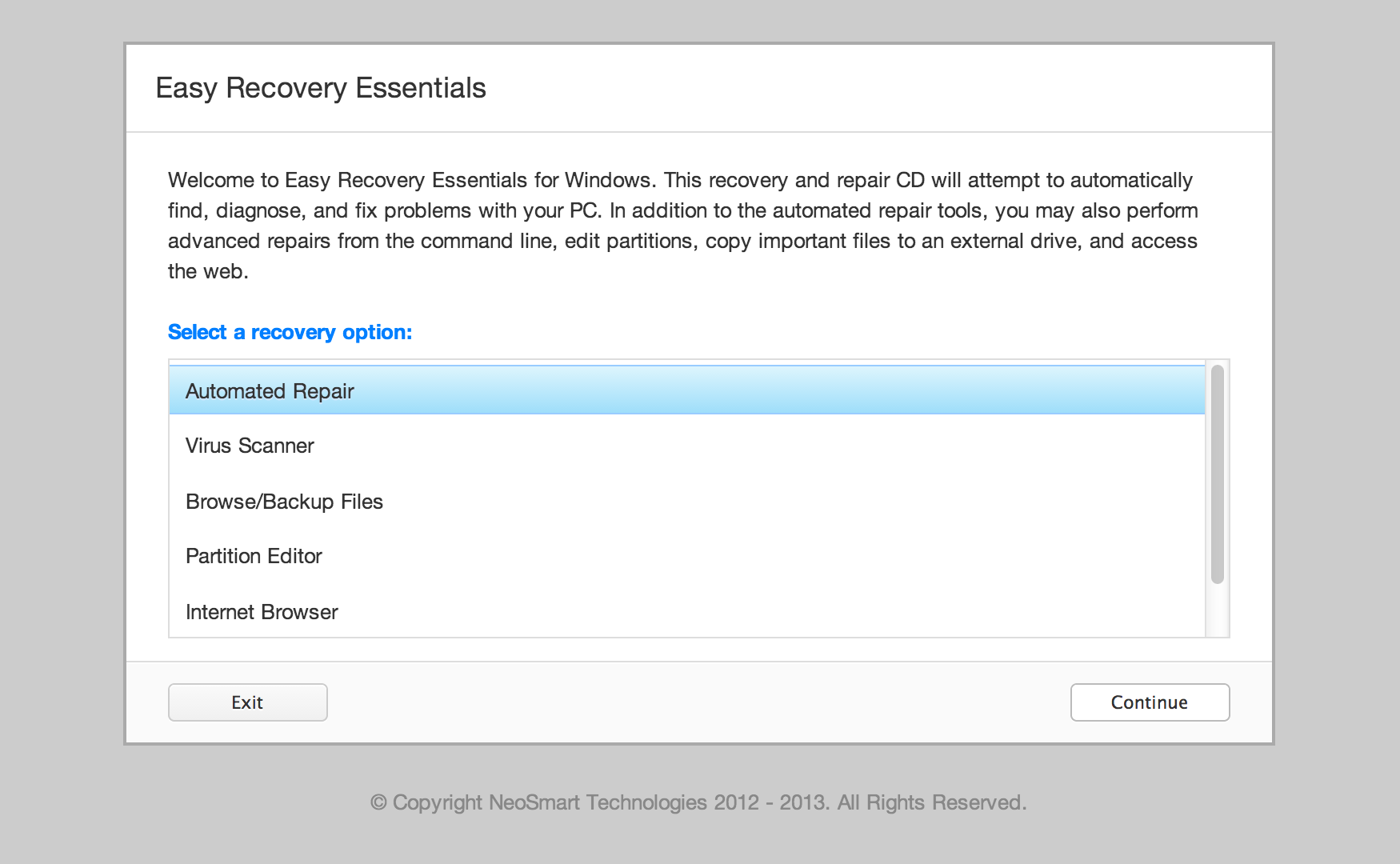
If you can’t boot into Windows XP to run chkdsk, download Easy Recovery Essentials – our recovery disk for Windows XP – and run Automated Repair or Command Prompt directly. You can burn EasyRE on CDs, DVDs or USBs.
To run the utility from the Command Prompt, follow these steps:
- Boot your computer
- Go to Start
- Click Run
- Type
cmdin the box: - Press Enter
- You can now type
chkdskto open the utility in a read-only mode - Press Enter
- To repair errors, follow these instructions:
- To repair errors without scanning for any bad sectors, type
chkdsk volume: /fand press Enter, wherevolumeis the letter of the drive you’d like to run a scan for, e.g.C:orD:
Example of a command you need to type if your volume isC:chkdsk C: /f
- To repair errors and scan for bad sectors, type
chkdsk volume: /rand press Enter, where volume is the letter of the drive you’d like to repair, e.g.C:orD:
Example of command you need to type if the volume you want to scan isD:chkdsk D: /r
- To repair errors without scanning for any bad sectors, type
From My Computer
If you can’t boot into Windows XP to run chkdsk, download Easy Recovery Essentials – our recovery disk for Windows XP – and run Automated Repair or Command Prompt directly. You can burn EasyRE on CDs, DVDs or USBs.
To run CHKDSK from within Windows XP, but without Command Prompt, follow these steps:
- Boot your computer
- Go to on My Computer (double-click on the icon)
- Right-click on the hard disk you’d like to run the utility on
- Click Properties
- Click Tools
- At the Error-checking tab, select Check Now
- To run the utility in the read-only mode, simply click Start
- To repair errors, follow these instructions:
- To repair errors without scanning for bad sectors, select the Automatically fix file system errors box and click Start
- To repair errors and scan for bad sectors, select the Scan for and attempt recovery of bad sectors box and click Start
- Once finished, the utility will notify you if the scan reported errors (Errors were found and fixed.) or not (No errors were found.)
From the installation disc
If you don’t have the installation disc to run chkdsk, download Easy Recovery Essentials – our recovery disk for Windows XP – and run Automated Repair or Command Prompt directly. You can burn EasyRE on CDs, DVDs or USBs.
If you can’t boot into Windows XP to run the utility use your original Microsoft Windows XP installation disc to open Recovery Console.
To do so, follow these steps:
- Insert the installation CD in the disk tray
- Restart your computer to boot from the CD
- At the “Press any key” message, press any key to make sure you boot from the CD
- At the Windows Options menu, press R to open Recovery Console
- Enter the Administrator password
- When Command Prompt appears on your screen, type the command you need:
chkdsk C: /r
where
C:is the letter of the drive where Windows is installed and the/rparameter will try to repair errors and scan for bad sectors.
CHKDSK in Windows Vista
To run this utility on Windows Vista computer, you can choose any of the following methods:
- From Command Prompt, if you can boot into Windows Vista
- From My Computer
- From the Recovery Console of your original installation
disk
From Command Prompt
If you can’t boot into Windows Vista to run chkdsk, download Easy Recovery Essentials – our recovery disk for Windows Vista – and run Automated Repair or Command Prompt directly. You can burn EasyRE on CDs, DVDs or USBs.
If you can boot into your operating system, run Command Prompt:
- Open Windows Vista
- Go to Start > All Programs > Accessories > Command Prompt or in the search box type
Command Promptand double-click the Command Prompt item available in the search results list. - When Command Prompt launches, type the command:
chkdsk C: /r
- If Windows Vista is installed on another drive that’s not labeled as
C:, replaceC:with the letter of your hard disk:chkdsk D: /r
- Press Enter
If Command Prompt shows errors, try to run the command again until it shows no errors.
From My Computer
If you can’t boot into Windows Vista to run chkdsk, download Easy Recovery Essentials – our recovery disk for Windows Vista – and run Automated Repair or Command Prompt directly. You can burn EasyRE on CDs, DVDs or USBs.
You can also run the utility by going to Computer (My Computer):
- Click the Start button
- Go to Computer
- Right-click on the drive you want check
- Click Properties
- At the Tools tab, under the Error-checking section, click Check Now
- If prompted, enter the Administrator password
- You can now run the disk check tool:
- To automatically repair errors, select Automatically fix file system errors
- To perform a thorough check, select Scan for and attempt recovery of bad sectors
- You can also check both Automatically fix file system errors and Scan for and attempt recovery of bad sectors
- To automatically repair errors, select Automatically fix file system errors
- Click Start
Don’t use the computer until the disk check is done. It may take several minutes depending on the hard disk size.
From the installation disc
If you don’t have the installation disc to run chkdsk, download Easy Recovery Essentials – our recovery disk for Windows Vista – and run Automated Repair or Command Prompt directly. You can burn EasyRE on CDs, DVDs or USBs.
If you can’t boot into Windows Vista, use the original installation disc to open Command Prompt (the Recovery Console) and run the commands you need:
- Insert the install disc and restart your computer
- Press any key when the message appear to boot from the disk
- Click Repair your computer
- Select Command Prompt
- Enter the Administrator password, if prompted
- When Command Prompt appears, type the command:
chkdsk c: /r
where
C:is your hard disk drive’s letter (can be different fromC:used here). - Press Enter
CHKDSK in Windows 7
The steps to run this utility in Windows 7 are similar to those of Windows Vista.
From Command Prompt
If you can’t boot into Windows 7 to run chkdsk, download Easy Recovery Essentials – our recovery disk for Windows 7 – and run Automated Repair or Command Prompt directly. You can burn EasyRE on CDs, DVDs or USBs.
If you can boot into Windows 7, run the utility from Command Prompt directly:
- Click Start
- Type
cmdat the Search program and files search box - Right-click on cmd.exe
- Click Run as Administrator
- Type in your Administrator password
- When cmd.exe opens, type the command:
chkdsk
- Press Enter
- You can run the tool with more parameters, like this:
chkdsk c: /r
This will check the drive for errors and will automatically try to fix any found errors.
- If you receive the “Chkdsk cannot run because the volume is in use by another process.” message, type
Yto restart the computer and let the utility to run a scan at the next boot of your PC - After you typed
Y, close the Command Prompt - Restart the computer by going to Start > Shutdown > Restart
- At the next boot, the check disk utility will automatically run a scan
From My Computer
If you can’t boot into Windows 7 to run chkdsk, download Easy Recovery Essentials – our recovery disk for Windows 7 – and run Automated Repair or Command Prompt directly. You can burn EasyRE on CDs, DVDs or USBs.
The check disk utility can also be ran from My Computer to check for errors on your hard disk.
To do so, follow these instructions:
- Right-click on the Start icon
- Click Open Windows Explorer
- On the left side of the window, click Computer
- At the Hard Disk Drives section, right-click on the volume you want to check for errors
- Click Properties
- Go to the Tools Tab
- At the Error-checking section click Check now
- You can now run the check disk utility: select Scan for and attempt recovery of bad sectors to let the utility attempt to repair any hard drive errors found
- Click Start
If the volume you want to check is in use, e.g. C:/ where Windows Vista is installed, you may receive the following error message:
Windows can't check the disk while it's in use Do you want to check for hard disk errors the next time you start your computer? Schedule disk check | Cancel
If so, follow these steps:
- Click Schedule disk check
- Exit any open programs
- Restart your computer
- Your computer will now restart and automatically boot and the utility will perform a scan automatically
If you receive the “Do you want to dismount this volume first?” message, follow the steps below. This message appears if the volume you want to checked is locked, even if it’s not in use (e.g. the C:/ drive):
Windows can't check the disk while it's in use Do you want to dismount this volume first? Note: All opened handles to this volume will become invalid. Force a dismount | Cancel
If so, follow these steps:
- Click Force a dismount
- A scan will automatically start now
From the installation disc
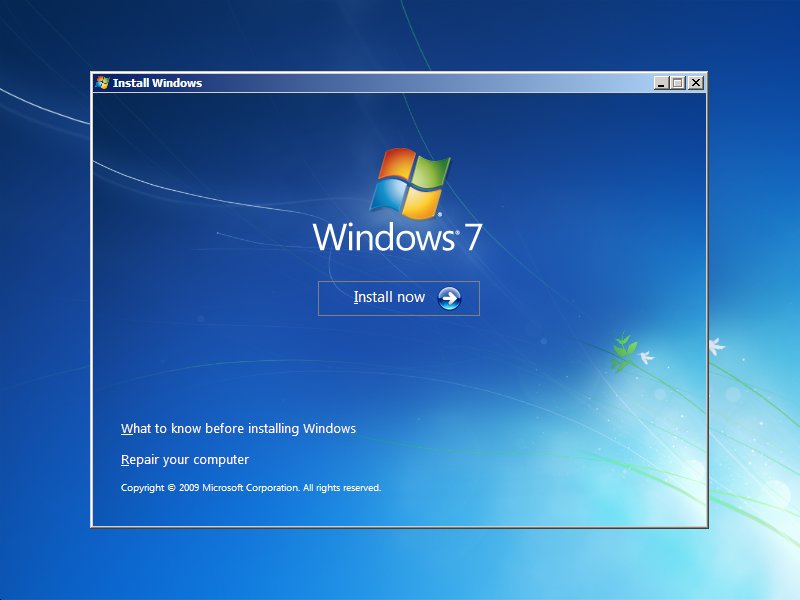
If you don’t have the installation disc to run chkdsk, download Easy Recovery Essentials – our recovery disk for Windows 7 – and run Automated Repair or Command Prompt directly. You can burn EasyRE on CDs, DVDs or USBs.
Follow these steps:
- Insert the original Windows disc
- Restart your PC and boot from the disc
- Click Repair your computer
- Choose the operating system from the list
- Click Next
- Choose Command Prompt
- When it opens, type the command:
chkdsk C: /f /r
- Press Enter
CHKDSK in Windows 8 or 8.1
Windows 8 or 8.1 users can run this utility by choosing any of the following methods:
- From Command Prompt
- From My Computer
- From installation disc
From Command Prompt
If you can’t boot into Windows 8/8.1 to run chkdsk, download Easy Recovery Essentials – our recovery disk for Windows 8/8.1 – and run Automated Repair or Command Prompt directly. You can burn EasyRE on CDs, DVDs or USBs.
To run it from Command Prompt, here are the instructions:
- Log into Windows 8/8.1
- Press the and C key to open the Charm bar
- Select Search
- Type-in
cmd - Right-click on Command Prompt from the search results list
- Click Run as administrator
- Log in as an Administrator
- When Command Prompt launches, type the command:
chkdsk C: /f /r /x
The parameters for this command are:
/foption will attempt to fix any found errors/roption will locate for bad sectors and recovery any readable information/xoption will force the volume you’re about to check to be dismounted before the utility begins a scan If theC:drive is in use, typeYto run a scan at your PC’s next restart. If so, exit Command Prompt and restart the computer.
From My Computer
If you can’t boot into Windows 8/8.1 to run chkdsk, download Easy Recovery Essentials – our recovery disk for Windows 8/8.1 – and run Automated Repair or Command Prompt directly. You can burn EasyRE on CDs, DVDs or USBs.
To run the check disk utility from Computer (My Computer), follow these steps:
- Boot into Windows 8/8.1
- Double-click on Computer (My Computer) to open it
- Select the drive you want to run a check on, e.g.
C:\ - Right-click on the drive
- Click Properties
- Go to the Tools tab
- Select Check, at the Error checking section
- If you receive the following message, click Scan drive to begin the scan:
You don't need to scan this drive We haven't found any errors on this drive. You can still scan the drive for errors if you want. Scan Drive
- You can keep using the drive during the scan. If errors are found, you can decide if you want to fix them. Depending on the results of this scan, the utility will report the results:
If no errors were found, you’ll see this message:
Your drive was successfully scanned Windows successfully scanned the drive. No errors were found.
If errors were found, you’ll see this message instead:
Restart your computer to repair file system. You can restart right away or schedule the error fixing on next restart.
From the installation disc
If you don’t have the installation disc to run chkdsk, download Easy Recovery Essentials – our recovery disk for Windows 8/8.1 – and run Automated Repair or Command Prompt directly. You can burn EasyRE on CDs, DVDs or USBs.
If you can’t boot into Windows 8/8.1 to run Command Prompt, you can use the original Windows 8/8.1 installation disc to run Command Prompt from there.
To do so, follow these instructions:
- Insert the installation disc
- Restart your computer
- Press any key to boot from the disc, at the “Press any key to boot from CD or DVD…” message
- Choose your keyboard layout
- Select your language, time and a keyboard method
- Click Next
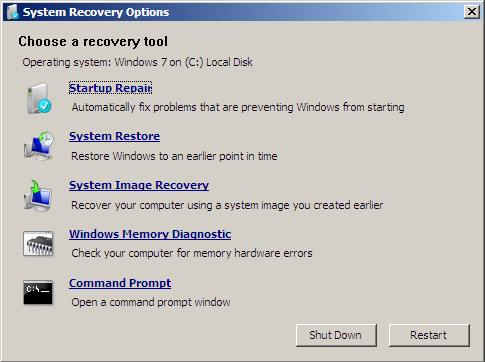
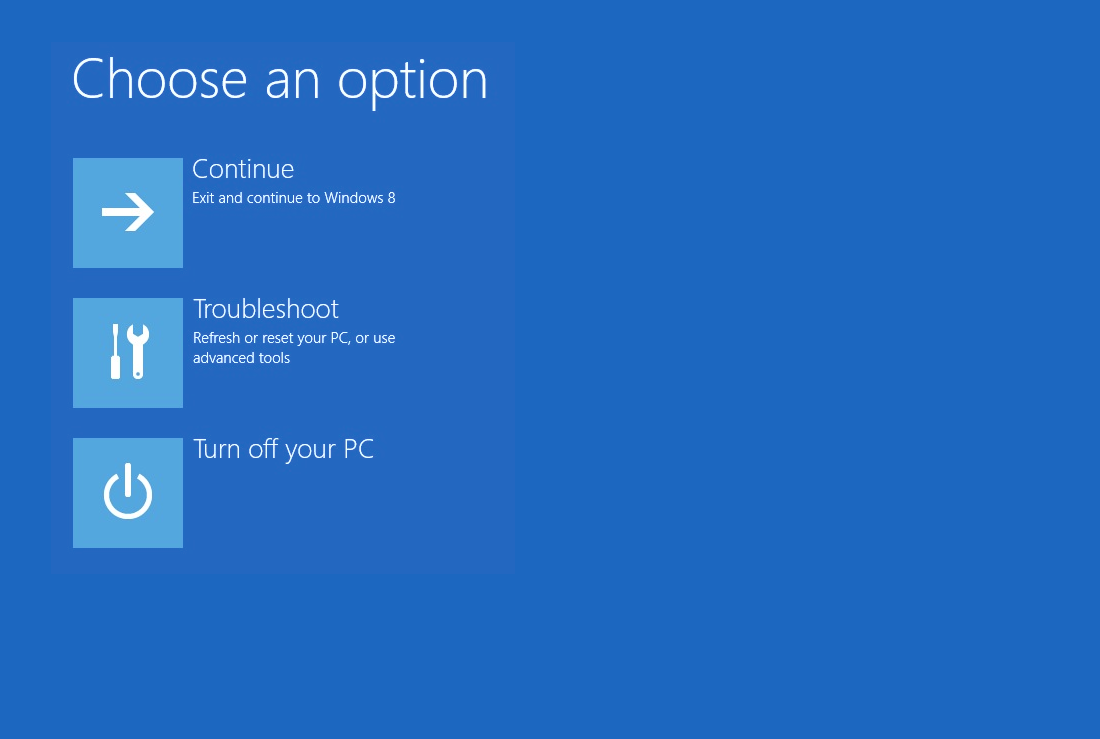
- Click Repair your computer
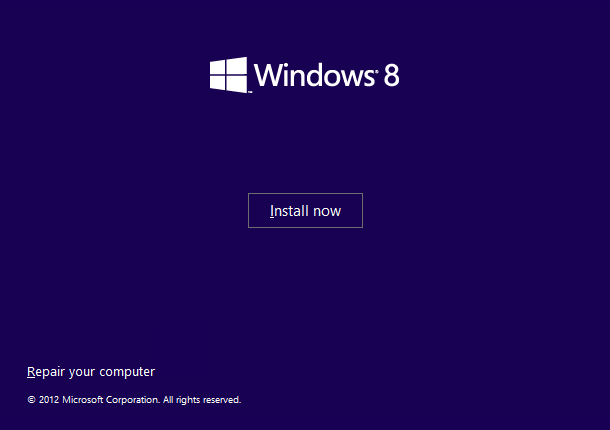
- At the Choose an option screen, click Troubleshoot
- At the Troubleshoot screen, click Advanced options
- At the Advanced options screen, click Command Prompt
- When Command Prompt launches, type the command:
chkdsk C: /f /x /r
- Press Enter
CHKDSK in Windows 10
Windows 10 users can run this utility by choosing any of the following methods:
- From Command Prompt
- From My Computer
- From installation disc
From Command Prompt
If you can’t boot into Windows 10 to run chkdsk, download Easy Recovery Essentials – our recovery disk for Windows 10 – and run Automated Repair or Command Prompt directly. You can burn EasyRE on CDs, DVDs or USBs.
To run it from Command Prompt, here are the instructions:
- Log into Windows 10
- Press the key to open the Start Menu
- Select Search
- Type-in
cmd - Right-click on Command Prompt from the search results list
- Click Run as administrator
- Log in as an Administrator
- When Command Prompt launches, type the command:
chkdsk C: /f /r /x
The parameters for this command are:
/foption will attempt to fix any found errors/roption will locate for bad sectors and recovery any readable information/xoption will force the volume you’re about to check to be dismounted before the utility begins a scan If theC:drive is in use, typeYto run a scan at your PC’s next restart. If so, exit Command Prompt and restart the computer.
From My Computer
If you can’t boot into Windows 10 to run chkdsk, download Easy Recovery Essentials – our recovery disk for Windows 10 – and run Automated Repair or Command Prompt directly. You can burn EasyRE on CDs, DVDs or USBs.
To run the check disk utility from Computer (My Computer), follow these steps:
- Boot into Windows 10
- Double-click on Computer (My Computer) to open it
- Select the drive you want to run a check on, e.g.
C:\ - Right-click on the drive
- Click Properties
- Go to the Tools tab
- Select Check, at the Error checking section
- If you receive the following message, click Scan drive to begin the scan:
You don't need to scan this drive We haven't found any errors on this drive. You can still scan the drive for errors if you want. Scan Drive
- You can keep using the drive during the scan. If errors are found, you can decide if you want to fix them. Depending on the results of this scan, the utility will report the results:
If no errors were found, you’ll see this message:
Your drive was successfully scanned Windows successfully scanned the drive. No errors were found.
If errors were found, you’ll see this message instead:
Restart your computer to repair file system. You can restart right away or schedule the error fixing on next restart.
From the installation disc
If you don’t have the installation disc to run chkdsk, download Easy Recovery Essentials – our recovery disk for Windows 10 – and run Automated Repair or Command Prompt directly. You can burn EasyRE on CDs, DVDs or USBs.
If you can’t boot into Windows 10 to run Command Prompt, you can use the original Windows 10 installation disc to run Command Prompt from there.
To do so, follow these instructions:
- Insert the installation disc
- Restart your computer
- Press any key to boot from the disc, at the “Press any key to boot from CD or DVD…” message
- Choose your keyboard layout
- Select your language, time and a keyboard method
- Click Next
- Click Repair your computer
- At the Choose an option screen, click Troubleshoot
Commands and parameters
The check disk utility has several parameters that you can use:
/c – applicable to a NTFS volume only
/f – this option fixes errors on a volume
/i – applicable to a NTFS volume only. This option performs a check of index entries
/r – this option also implies the /f and /p option. This option locates the bad sectors of your hard drive and recovers any readable information
Depending if you run the utility from Command Prompt or Recovery Console, the following parameters are different:
/p – this fixes any errors on a volume. In your standard Command Prompt /p is only read-only
The mandatory requirement of this utility is the volume you’re about to check must not be locked. If a volume you’re about to scan is locked, you’ll receive this message:
Chkdsk cannot run because the volume is in use by another process. Would you like to schedule this volume to be checked the next time the system restarts? (Y/N)
If so, type Y and press Enter to perform a scan at the next boot of your system.
Download chkdsk
chkdsk can’t be downloaded as it’s a command available with Windows. You can use the original installation disc to run the utility tool.
You can download Easy Recovery Essentials and open Command Prompt to run specific chkdsk commands:
You can burn Easy Recovery Essentials to CDs, DVDs or USBs and run Command Prompt.
- Download Easy Recovery Essentials
- Burn the ISO Image. Follow our instructions on how to burn a bootable ISO image. If you’d like to have a recovery USB instead, follow our instructions on how to make a recovery USB.
- Boot into the recovery media
- Select Launch Command Line
Troubleshooting
Cannot continue in read-only mode
If you receive the “Errors found. CHKDSK cannot continue in read-only mode.” error message after running a check disk command, make sure you run the command with the /r parameter:
chkdsk /f
If the disk check utility must be ran on another volume, update the command with the letter of the drive you want to run a scan for:
chkdsk D: /f
Cannot run because the volume is in the use by another process
If you receive this error message when running the tool:
Chkdsk cannot run because the volume is in the use by another process. Would you like to schedule this volume to be checked the next time the system restarts.
You need to type Y to make sure the utility runs at the next boot. If so, type Y, restart the computer and let the tool to perform the scan.
Cannot lock current drive
If the check disk utility shows the “Cannot lock current drive.” error message, make sure the command you’re performing has the /r option:
chkdsk /r
If this doesn’t work, try disabling System Restore for the entire session you’re trying to run a scan and other protection software, such as: antivirus, firewall, spyware etc.
Another alternative command is:
chkdsk C: /f /r /x
stop chkdsk on every boot
If the utility runs a scan at every boot without stopping, you can try a few solutions.
Before you follow the instructions below, make sure you let the scan to be 100% completed and then restart your computer.
If the check disk runs again, even if the previous scan was 100% complete, continue with the steps below.
Fix #1: Check if there is a scheduled scan. To do so, follow these steps:
- Open Command Prompt
- Type
chkntfs c:, wherec:is the letter of the drive you ran a check - Press Enter
- If the message is the following, then a check scan is scheduled on the c: drive:
The type of file system is NTFS. Chkdsk has been scheduled manually to run on next reboot on volume C:.
- If there isn’t any scheduled scan, the message will be:
The type of the file system is NTFS. C: is not dirty.
- To cancel a scheduled scan, type:
chkntfs /x c:
Fix #2: Another option to fix this issue is to open the Registry Editor:
- Boot into Windows
- Open the Registry Editor
- Go to this key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager
- At the BootExecute key, check the value.If the value is
autocheck autochk * /., you need to change it toautocheck autochk *
chkdsk won’t finish
If the utility won’t finish a scan, make sure you run the command with the /r parameter, like this:
chkdsk /r
chkdsk won’t run at startup
If the check disk won’t run a scan at startup after being scheduled to do so, follow any of the following fixes.
Fix #1: Check the BootExecute key in the Registry Editor:
- Open Registry Editor
- Find this key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager key
- Check the value for the BootExecute key.If the value is
autocheck autochk * /., you need to change it toautocheck autochk *
Fix #2: Run sfc
You can also run the sfc /scannow command and then run chkdsk /r again:
- Open Command Prompt
- Type the command:
sfc /scannow
- Press Enter
- After the sfc process is complete, run the check disk utility.
More Information
Support Links
- Easy Recovery Essentials for Windows – our repair and recovery disk.
It’s an easy-to-use and automated diagnostics disk. It’s available for Windows 8, Windows 7 and Windows Vista. It’s also available for Windows XP and Windows Server.
Read more at Windows Recovery Disks.
- The NeoSmart Support Forums, member-to-member technical support and troubleshooting.
- Get a discounted price on replacement setup and installation discs: Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11, Windows Server 2022.
Applicable Systems
This Windows-related knowledgebase article applies to the following operating systems:
- Windows XP (all editions)
- Windows Vista (all editions)
- Windows 7 (all editions)
- Windows 8 (all editions)
- Windows 8.1 (all editions)
- Windows 10 (all editions)
- Windows 11 (all editions)
- Windows Server 2003 (all editions)
- Windows Server 2008 (all editions)
- Windows Server 2012 (all editions)
- Windows Server 2016 (all editions)
- Windows Server 2019 (all editions)
- Windows Server 2022 (all editions)
Propose an edit