Docker is a powerful platform for building, shipping, and running distributed applications. However, when working with Docker, you may come across an error message that says “cannot connect to the Docker daemon”. This error typically occurs when the Docker daemon is not running or the user running the command does not have permission to connect to the Docker daemon. In this article, we will cover the ways to resolve this error with proper instructions and examples.
First, let’s understand why this error occurs. The Docker daemon is a background process that manages Docker containers and images. When you run a command such as a docker run, it sends a request to the Docker daemon to perform the requested action. If the Docker daemon is not running or the user running the command does not have permission to connect to the Docker daemon, the command will fail and display the “cannot connect to the Docker daemon” error.
Solutions to Resolve Error
Solution 1: Ensure that the Docker daemon is running
The first step in resolving the error is to check if the Docker daemon is running. You can do this by running the below command. If the Docker daemon is running, you will see an output similar to the following output screenshot:
systemctl status docker

If the Docker daemon is not running, you can start it by running the above command.
Solution 2: Add the current user to the docker group
On Linux systems, the user running the command must be a member of the docker group to connect to the Docker daemon. You can check if the user is a member of the docker group by running the command id. If the output shows that the user is not a member of the docker group, you can add the user to the group by running the below command:
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER

Solution 3: Check the Ownership of used Files
There are several ways to check the ownership of the files used by the Docker daemon on a Linux system. Here are a few methods:
1. Use the ls -l command to view the file ownership and permissions of the Docker socket:
ls -l /var/run/docker.sock

2. Use the stat command to view the file ownership and permissions of the Docker socket:
stat /var/run/docker.sock

Solution 4: Restart the Docker daemon
There are several ways to restart the Docker daemon on a Linux system, here are a few common methods:
1. Use the systemctl command to restart the Docker service:
sudo systemctl restart docker
2. Use the service command to restart the Docker service:
sudo service docker restart

Solution 5: Check the status of the Docker daemon:
You can check the status of the Docker daemon by running the command «docker info» or «docker version» in the command line. This will display information about the Docker daemon, including its version number, the number of containers and images running, and the amount of memory and storage it is using. If the daemon is not running, the command will return an error message.
sudo docker info

Solution 6: Assign Ownership to the Docker Unix Socket
To assign ownership to the Docker Unix socket, you can use the chown command. The command should be executed as the root user or a user with superuser privileges.
Here is the basic syntax for the command:
sudo chown <user>:<group> /var/run/docker.sock

Replace <user> and <group> with the appropriate user and group to that you want to assign ownership.
Running Docker after resolving the error
Below is an example of how the error message looks like if docker is not running:
$ docker run hello-world Cannot connect to the Docker daemon at unix:///var/run/docker.sock. Is the docker daemon running?
And here is an example of how you can resolve the error by starting the Docker daemon:
$ sudo systemctl start docker $ docker run hello-world Hello from Docker! This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the “cannot connect to the Docker daemon” error can be caused by several factors such as the Docker daemon not running or the user running the command not having permission to connect to the Docker daemon. By following the steps outlined in this article, you should be able to resolve the error and continue working with Docker.
It’s always a good practice to check the Docker daemon logs for any error messages, it might help you troubleshoot the problem. Additionally, you can refer to the official Docker documentation for more information on troubleshooting this error. Furthermore, you can also join the Docker community, where you can find answers to common problems and ask for help from other experienced users.
In short, to resolve the error “cannot connect to the Docker daemon”, check if the Docker daemon is running, ensure the user has permission to connect to the Docker daemon, restart the machine, run the command with sudo, and check the Docker daemon logs if all above steps fail.
- I have tried with the latest version of Docker Desktop
- I have tried disabling enabled experimental features
- I have uploaded Diagnostics
- Diagnostics ID:
BFFA18B7-78B3-41A4-99A6-B5074A933B57/20230202102932
Actual behavior
When starting Docker desktop with WSL 2 based engine and accessing from Ubuntu WSL 2 using the Docker CLI it works correctly as expected. All commands work and are responsive. But after roughly 4 minutes all connectivity to Docker is lost and the following error is displayed when attempting a docker ps -a command:
Cannot connect to the Docker daemon at unix:///var/run/docker.sock. Is the docker daemon running?
Docker connectivity remains broken until Docker Desktop is restarted. Then it will last for 4 minutes again before the same issue reoccurs. The behaviour is reproducible.
I have tried uninstalling and re-installing Docker Desktop and WSL 2 multiple times but the issue remains.
Connectivity from within Windows via Powershell or cmd is fine and Docker connectivity is never interrupted.
Expected behavior
Docker commands from WSL 2 should continue to work after 4 minutes and all Docker commands should work within WSL 2.
Information
The problem is reproducible on my machine. Looking at the logs under C:\Users\%username%\AppData\Local\Docker\log.txt shows the following error:
[2023-02-02T09:32:39.614027700Z][com.docker.backend.exe][I] [2023-02-02T09:32:39.613469800Z][com.docker.wsl-distro-proxy.exe for Ubuntu][F] Proxy error: docker-<HOST>-user-distro proxy has not started after 4 minutes, killing it
[2023-02-02T09:32:39.614609400Z][com.docker.backend.exe][I] [main.main()
[2023-02-02T09:32:39.614609400Z][com.docker.backend.exe][I] [ win/backend/cmd/com.docker.wsl-distro-proxy/main.go:191 +0x14e5
[2023-02-02T09:32:39.710956600Z][com.docker.backend.exe][I] ipc.NewClient: f267c915-WSLIntegrationService -> \\.\pipe\dockerBackendNativeApiServer CSharpAPI
The problem has been with me for quite a while now, across around 4 successive updates of Docker Desktop.
I’m not sure if the problem appeared with a particular update, but Docker Desktop and WSL 2 have worked well for me in the past.
- Windows Version: Microsoft Windows 11 Pro — 10.0.22621 Build 22621
- Docker Desktop Version: v4.16.3
- WSL2 or Hyper-V backend? WSL2 Ubuntu
Linux desktop 5.15.79.1-microsoft-standard-WSL2 #1 SMP Wed Nov 23 01:01:46 UTC 2022 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux - Are you running inside a virtualized Windows e.g. on a cloud server or a VM: No
Output of & "C:\Program Files\Docker\Docker\resources\com.docker.diagnose.exe" check
[2023-02-02T09:39:21.140935600Z][com.docker.diagnose.exe][I] set path configuration to OnHost
Starting diagnostics
[PASS] DD0027: is there available disk space on the host?
[PASS] DD0028: is there available VM disk space?
[PASS] DD0002: does the bootloader have virtualization enabled?
[SKIP] DD0018: does the host support virtualization?
[PASS] DD0001: is the application running?
[PASS] DD0022: is the Virtual Machine Platform Windows Feature enabled?
[PASS] DD0021: is the WSL 2 Windows Feature enabled?
[PASS] DD0024: is WSL installed?
[PASS] DD0025: are WSL distros installed?
[PASS] DD0026: is the WSL LxssManager service running?
[PASS] DD0029: is the WSL 2 Linux filesystem corrupt?
[PASS] DD0035: is the VM time synchronized?
[PASS] DD0017: can a VM be started?
[PASS] DD0016: is the LinuxKit VM running?
[PASS] DD0011: are the LinuxKit services running?
[PASS] DD0004: is the Docker engine running?
[PASS] DD0015: are the binary symlinks installed?
[PASS] DD0031: does the Docker API work?
[PASS] DD0013: is the $PATH ok?
[PASS] DD0003: is the Docker CLI working?
[PASS] DD0005: is the user in the docker-users group?
[PASS] DD0038: is the connection to Docker working?
[FAIL] DD0014: are the backend processes running? 1 error occurred:
* com.docker.wsl-distro-proxy.exe is not running
[PASS] DD0007: is the backend responding?
[PASS] DD0008: is the native API responding?
[PASS] DD0009: is the vpnkit API responding?
[PASS] DD0010: is the Docker API proxy responding?
[PASS] DD0006: is the Docker Desktop Service responding?
[SKIP] DD0030: is the image access management authorized?
[PASS] DD0033: does the host have Internet access?
[PASS] DD0002: does the bootloader have virtualization enabled?
[PASS] DD0018: does the host support virtualization?
[PASS] DD0001: is the application running?
[PASS] DD0022: is the Virtual Machine Platform Windows Feature enabled?
[PASS] DD0021: is the WSL 2 Windows Feature enabled?
[PASS] DD0024: is WSL installed?
[PASS] DD0025: are WSL distros installed?
[PASS] DD0026: is the WSL LxssManager service running?
[PASS] DD0029: is the WSL 2 Linux filesystem corrupt?
[PASS] DD0035: is the VM time synchronized?
[PASS] DD0017: can a VM be started?
[PASS] DD0016: is the LinuxKit VM running?
[PASS] DD0011: are the LinuxKit services running?
[PASS] DD0004: is the Docker engine running?
[PASS] DD0015: are the binary symlinks installed?
[PASS] DD0031: does the Docker API work?
[PASS] DD0032: do Docker networks overlap with host IPs?
segment 2023/02/02 09:39:28 ERROR: sending request - Post "https://api.segment.io/v1/batch": dial tcp: lookup api.segment.io: getaddrinfow: The requested name is valid, but no data of the requested type was found.
segment 2023/02/02 09:39:28 ERROR: 1 messages dropped because they failed to be sent and the client was closed
Please investigate the following 1 issue:
1 : The test: are the backend processes running?
Failed with: 1 error occurred:
* com.docker.wsl-distro-proxy.exe is not running
Not all of the backend processes are running.
Also here is the results of diagnostics being run straight after a Docker Desktop restart, within the 4 minutes, where no errors are detected:
[2023-02-02T10:47:34.075672900Z][com.docker.diagnose.exe][I] set path configuration to OnHost
Starting diagnostics
[PASS] DD0027: is there available disk space on the host?
[PASS] DD0028: is there available VM disk space?
[PASS] DD0002: does the bootloader have virtualization enabled?
[SKIP] DD0018: does the host support virtualization?
[PASS] DD0001: is the application running?
[PASS] DD0022: is the Virtual Machine Platform Windows Feature enabled?
[PASS] DD0021: is the WSL 2 Windows Feature enabled?
[PASS] DD0024: is WSL installed?
[PASS] DD0025: are WSL distros installed?
[PASS] DD0026: is the WSL LxssManager service running?
[PASS] DD0029: is the WSL 2 Linux filesystem corrupt?
[PASS] DD0035: is the VM time synchronized?
[PASS] DD0017: can a VM be started?
[PASS] DD0016: is the LinuxKit VM running?
[PASS] DD0011: are the LinuxKit services running?
[PASS] DD0004: is the Docker engine running?
[PASS] DD0015: are the binary symlinks installed?
[PASS] DD0031: does the Docker API work?
[PASS] DD0013: is the $PATH ok?
[PASS] DD0003: is the Docker CLI working?
[PASS] DD0005: is the user in the docker-users group?
[PASS] DD0038: is the connection to Docker working?
[PASS] DD0014: are the backend processes running?
[PASS] DD0007: is the backend responding?
[PASS] DD0008: is the native API responding?
[PASS] DD0009: is the vpnkit API responding?
[PASS] DD0010: is the Docker API proxy responding?
[PASS] DD0006: is the Docker Desktop Service responding?
[SKIP] DD0030: is the image access management authorized?
[PASS] DD0033: does the host have Internet access?
[PASS] DD0002: does the bootloader have virtualization enabled?
[PASS] DD0018: does the host support virtualization?
[PASS] DD0001: is the application running?
[PASS] DD0022: is the Virtual Machine Platform Windows Feature enabled?
[PASS] DD0021: is the WSL 2 Windows Feature enabled?
[PASS] DD0024: is WSL installed?
[PASS] DD0025: are WSL distros installed?
[PASS] DD0026: is the WSL LxssManager service running?
[PASS] DD0029: is the WSL 2 Linux filesystem corrupt?
[PASS] DD0035: is the VM time synchronized?
[PASS] DD0017: can a VM be started?
[PASS] DD0016: is the LinuxKit VM running?
[PASS] DD0011: are the LinuxKit services running?
[PASS] DD0004: is the Docker engine running?
[PASS] DD0015: are the binary symlinks installed?
[PASS] DD0031: does the Docker API work?
[PASS] DD0032: do Docker networks overlap with host IPs?
No fatal errors detected.
Steps to reproduce the behavior
It’s not related to an individual container but the Docker engine itself, so no reproduction Dockerfiles to provide.
Docker daemon is a background process used by the Docker engine to manage containers, images, and other aspects of Docker via API requests. The «Cannot connect to the Docker daemon» error appears if the engine has a problem communicating with the daemon.
This tutorial covers the possible causes of the «Cannot connect to the Docker daemon» error and how to solve it.

Prerequisites
- Access to the command line or terminal.
- A working Docker installation.
Resolving the «Cannot connect to the Docker daemon» Error
The «Cannot connect to the Docker daemon» error occurs when the user attempts to issue a command using the Docker CLI. Below is an example of the error shown when you list running containers:

The sections below provide methods to troubleshoot and fix the error. If one solution does not work, move on to the next until you resolve the issue.
Method 1: Check User Privileges
Insufficient privileges can sometimes be the reason for the «Cannot connect to the Docker daemon» error. To ensure this is not the cause of the issue, try adding sudo to the docker command:
sudo docker [subcommand] [options]If sudo solves the problem, follow the steps below to access Docker CLI without the sudo command.
1. Create the docker group if it does not already exist:
sudo groupadd -f docker2. Add the current user to the docker group via the usermod command:
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER3. Log out, then log back in.
4. Start the Docker service again with:
sudo service docker startMethod 2: Check Docker Service
If the Docker service is not running, commands issued from the CLI cannot access the daemon. The steps below explain how to troubleshoot this issue.
1. View the status of the Docker service:
sudo service docker statusThe Active section should report the service as active (running). Any other message means that the service is experiencing a problem.
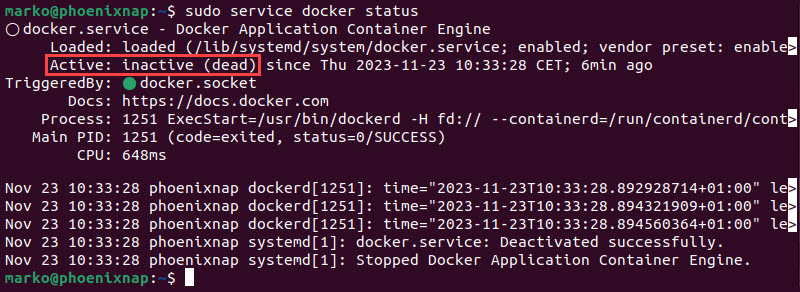
2. If the Docker service is inactive, start it with the following command:
sudo service docker startNow, you can attempt to run the command that reported the error.
Method 3: Start Docker Daemon Manually
Starting the Docker service also starts the Docker Daemon. However, if you receive the «Cannot connect to the Docker daemon» error, the daemon may have failed to initiate.
Use the following command to run the daemon manually:
sudo dockerdAs the daemon initiates, the startup process information is displayed in the output.
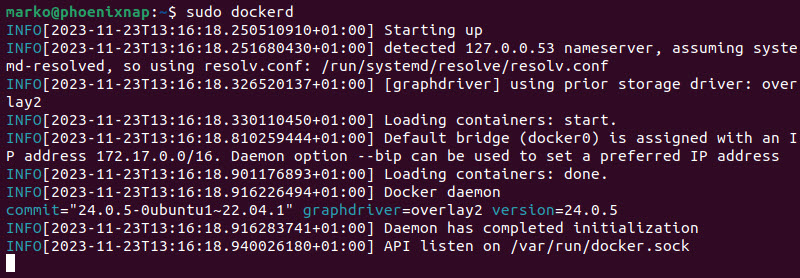
If the daemon starts successfully, you can run Docker commands in another terminal window. If an error occurs, the output provides a specific reason for the error.
Method 4: Assign Ownership to Docker Unix Socket
The «Cannot connect to the Docker daemon» error also occurs if the Unix socket file for Docker does not have the correct ownership assigned.
1. Check ownership for the Docker Unix socket:
sudo ls -l /var/run/docker.sockThe expected owner of the socket is root, as shown in the example below:

2. If the owner is a user not currently logged into the system, change the ownership to root by typing:
sudo chown root:docker /var/run/docker.sockAlternatively, grant the ownership to the current user:
sudo chown $USER:docker /var/run/docker.sockMethod 5: Switch to Default Docker Context
In some cases, installing Docker Desktop may cause the CLI commands to be forwarded to Docker Desktop instead of the Docker engine. Changing back to the default context may resolve the issue.
1. Check the current context of the Docker deployment:
docker context ls
2. If the value in the name column is anything other than default, switch back to the default context by typing:
docker context use defaultRun a Docker command to see if the error has been fixed by setting the default context.
Method 6: Check File Ownership
Ownership issues can also extend to files used by your Docker build. If Docker needs to use a file it cannot access, the «Cannot connect to the Docker daemon» error may appear.
Follow the steps below to troubleshoot this issue:
1. Run the docker build command for each container. It gives you a detailed output that points out any potential errors.
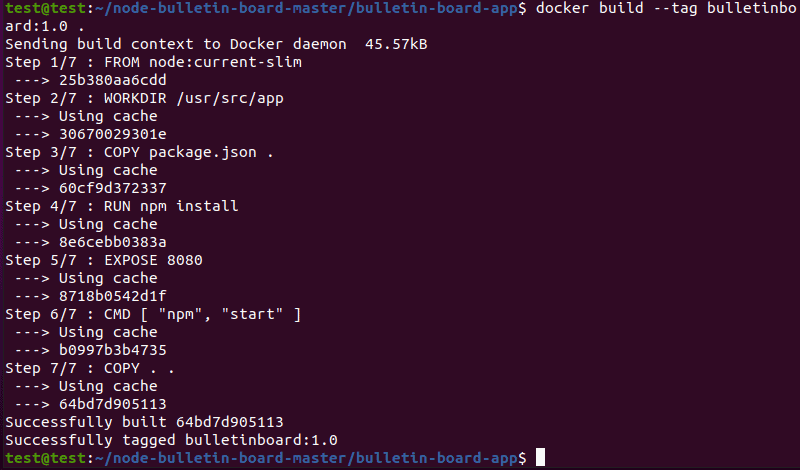
2. Check the output for each container, looking for a «Cannot connect to the Docker daemon» error report. If there is a problem with the file ownership, the error report lists the files the docker build command cannot access.
3. There are several ways to resolve the issue of ownership of used files:
- Remove the files in question by deleting them. However, this deletion affects other builds using the files.
- Another method is to add the
.dockerignorefile to your current build, thus excluding the files your build cannot access. - Finally, you can change the file ownership with:
sudo chown $USER:docker [path-to-file]Conclusion
After following this tutorial, you should know the potential causes of the «Cannot connect to the Docker daemon» error and how to address each by following one of the methods.
Next, learn Docker container management best practices for an efficient and safe Docker environment.
Was this article helpful?
YesNo
Table of Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Understanding the Docker Daemon
- 2.1 What is the Docker Daemon?
- 2.2 Common Causes of Docker Daemon Connection Errors
- 3 Basic Troubleshooting Steps
- 3.1 1. Verify Docker Service Status
- 3.2 2. Check User Permissions
- 3.3 3. Restart Docker Service
- 3.4 4. Verify Docker Installation
- 4 Advanced Troubleshooting Steps
- 4.1 1. Check Docker Logs
- 4.2 2. Examine Docker Configuration
- 4.3 3. Network Troubleshooting
- 4.4 4. Reinstall Docker
- 5 FAQs
- 5.1 What does “Cannot connect to Docker daemon” mean?
- 5.2 How do I check if the Docker daemon is running?
- 5.3 Why do I need to add my user to the docker group?
- 5.4 How can I view Docker logs?
- 6 Conclusion
Introduction
Docker is an essential tool for developers, allowing them to create, deploy, and manage containerized applications. However, encountering the Cannot connect to Docker daemon error can be frustrating and hinder your workflow. This guide will help you understand the causes of this error and provide step-by-step solutions to resolve it, ensuring the smooth operation of your Docker environment.
Understanding the Docker Daemon
What is the Docker Daemon?
The Docker daemon (dockerd) is a background service responsible for managing Docker containers on your system. It listens for Docker API requests and manages Docker objects such as images, containers, networks, and volumes.
Common Causes of Docker Daemon Connection Errors
- Docker service not running: The Docker daemon may not be running on your system.
- Incorrect permissions: Your user may not have the necessary permissions to interact with Docker.
- Configuration issues: Misconfigured Docker settings can lead to connection problems.
- Network issues: Network problems can prevent your system from communicating with the Docker daemon.
Basic Troubleshooting Steps
1. Verify Docker Service Status
First, check if the Docker service is running on your system.
sudo systemctl status dockerIf the service is not running, start it using the following command:
sudo systemctl start docker2. Check User Permissions
Ensure your user is added to the docker group, which allows non-root users to run Docker commands.
sudo usermod -aG docker $USERAfter adding the user to the group, log out and log back in for the changes to take effect.
3. Restart Docker Service
Sometimes, restarting the Docker service can resolve connection issues.
sudo systemctl restart docker4. Verify Docker Installation
Check if Docker is installed correctly and the client can communicate with the daemon.
docker infoAdvanced Troubleshooting Steps
1. Check Docker Logs
Inspect Docker logs for any error messages that might indicate the cause of the connection issue.
sudo journalctl -u docker.service2. Examine Docker Configuration
Verify that your Docker configuration files are correct. Check the daemon.json file for any misconfigurations.
cat /etc/docker/daemon.json3. Network Troubleshooting
Ensure there are no network issues preventing your system from communicating with the Docker daemon. Check firewall settings and network configurations.
sudo ufw status4. Reinstall Docker
If the issue persists, consider reinstalling Docker. First, uninstall Docker:
sudo apt-get remove docker docker-engine docker.io containerd runcThen, install Docker again following the official installation guide for your operating system.
FAQs
What does “Cannot connect to Docker daemon” mean?
This error means that the Docker client cannot communicate with the Docker daemon, which manages Docker containers.
How do I check if the Docker daemon is running?
You can check the status of the Docker daemon using the command sudo systemctl status docker.
Why do I need to add my user to the docker group?
Adding your user to the docker group allows you to run Docker commands without using sudo.
How can I view Docker logs?
You can view Docker logs by running sudo journalctl -u docker.service.
Conclusion
Encountering the Cannot connect to Docker daemon error can disrupt your workflow, but with the troubleshooting steps outlined in this guide, you should be able to identify and resolve the issue. From verifying the Docker service status to checking user permissions and network configurations, these steps will help ensure your Docker environment runs smoothly.
By following these guidelines, you can overcome Docker connection errors and maintain an efficient and productive development environment. If problems persist, consider seeking help from Docker community forums or consulting Docker’s official documentation for further assistance. Thank you for reading the DevopsRoles page!
DevOps, Docker
“Experiencing a ‘Cannot Connect to the Docker Daemon’ error in WSL2 is often due to insufficient permissions or incorrect configurations, making it crucial to cross-check your setup and ensure your user account has the necessary Docker privileges.”
| Error Type | Possible Cause | Common Solution |
|---|---|---|
| “Cannot Connect to the Docker Daemon” | WSL2 not configured correctly for Docker Desktop | Enabled WSL2 in Docker Desktop settings or Reinstall/update Docker Desktop |
| “Cannot Connect to the Docker Daemon” | Docker service not running or failed to start | Start/restart Docker service manually. |
| “Cannot Connect to the Docker Daemon” | Permission issues- Non-root user trying to run Docker commands | Add the user to the Docker group to provide necessary permissions. |
You might be getting a “Cannot Connect to the Docker Daemon” error in WSL2 due to several reasons, and I can help you figure out why. It’s common for users to come across this error while working with Docker on Windows Subsystem for Linux 2 (WSL2). Keep in mind; these issues are not unique to WSL2 – they occur in various operating systems where Docker is used.
In many cases, it’s because WSL2 hasn’t been set up to integrate properly with Docker Desktop. To fix this, you need to ensure that WSL2 integration is enabled in your Docker Desktop settings.
Another common issue is Docker service not running or failing to launch. The Docker daemon must be actively running so that Docker CLI commands can interact with the system. You can start or restart the Docker service manually if this happens.
Finally, permission issues can also cause the error, particularly when non-root users try to execute Docker commands. Docker restricts access to Docker’s socket file as a security measure. You can work around this by adding the non-root user to the Docker group, which should grant the necessary permissions. Here, remember that this can pose some security risk, as members of the Docker group virtually have root accesssource!
A relevant piece of
code for checking the status of Docker service would look something like this:sudo systemctl status dockerAnd if you need to add a user to the Docker group, you may use the following command:
sudo usermod -aG docker [username]Remember to replace '[username]' with your actual username!Understanding the relationship between WSL2, Windows Subsystem for Linux 2, and Docker is essential to resolving issues like the "Cannot connect to the Docker daemon" error. Docker has become a prominent tool for containerization, allowing developers to package an application with all of its dependencies into a standardized unit for software development.WSL2, on the other hand, is Microsoft's new version of the Windows Subsystem for Linux that improves system performance and supports full system call compatibility, which is a game-changer for Docker.
The Docker Desktop’s WSL 2 backend architecture introduces support for Kubernetes, provides an updated Docker Daemon, and comes with improved speed and resource usage.(source) However, the intricacies of these systems can sometimes cause common errors like the aforementioned one.
To put it into perspective:
Error: Cannot connect to the Docker daemon at unix:///var/run/docker.sock. Is the docker daemon running?
The “Cannot connect to Docker daemon” error in WSL2 typically surfaces when the Docker service isn’t running, or if there's a missing connection between the Docker client and the Docker daemon.
Here's how you can better understand and possibly resolve this issue:
$ sudo service docker startThe above command ensures that your Docker service is running. In fact, this should be your first step towards troubleshooting.
Upon receiving this message, there might be connectivity complications between the Docker client and the Docker daemon. Typically, Docker clients communicate with daemons via unix:///var/run/docker.sock (a UNIX socket file), but this can vary. The Docker daemon must always run before any Docker client commands can be executed.(source)
You can verify whether the DOCKER_HOST environmental variable is properly set or not by using this command:
Keep in mind that a crucial part of Docker Desktop's integration with WSL2 includes ensuring that certain environment variables are correctly set within WSL2, including DOCKER_HOST, to enable the Docker CLI in WSL2 to interact with the Docker server in Docker Desktop.
A practical way to ensure this setup is maintained is to add the following command to your WSL2 shell startup file (i.e., .bashrc, .zshrc):
$ echo "export DOCKER_HOST=unix:///var/run/docker.sock" >> ~/.bashrcThis adds the DOCKER_HOST environmental variable setup command to the bash startup file and reloads your shell configuration.
For those users who have installed a standalone Docker in WSL2 instead of using Docker Desktop’s custom WSL2 backend, ensure that your Docker service in WSL2 is automatically started. You can achieve this by adding the Docker service start command to your shell startup script as follows:
$ echo "sudo service docker start" >> ~/.bashrcRemember, understanding how WSL2 and Docker are integrated is key to discerning why such problems arise and how to tackle them effectively. With in-depth knowledge about the workings of the tools we use daily, we empower ourselves to build better, optimally functioning software ecosystems.Getting a 'Cannot Connect to the Docker Daemon' error in WSL2 can be quite frustrating. This error commonly occurs due to a combination of several factors, which I will explore in more detail below:
Improper Docker Client and Server Configuration
One key component that may underlie this problem results from an inaccurate configuration between the Docker client and server. A mismatch in the versions or installation paths can lead to failures when attempting connections. Therefore, you should ensure that both the Docker client and server are installed correctly and match in version requirements.
If you suspect your setup is defective, you can confirm by comparing your socket connection with the expected default, which in general cases should look something like this:
$DOCKER_HOST=unix:///var/run/docker.sock.
In case it does not match, reconfigure it to get things back on track.
Docker Service Not Running
Another common root cause for this Docker daemon error message stems from the Docker service not running as expected. Docker runs as a background daemon but it can cease to function if it crashes, if there's a system update, or if the system was rebooted unexpectedly.
You can check and manage its status using these command line instructions:
- To check if the service is active:sudo systemctl status docker- And if it's not running, you can start it with:
sudo systemctl start dockerIt is of vital importance to concurrently verify if the Docker daemon is being run on startup using this command:
sudo systemctl enable docker.
Inadequate User Permissions
At times, you might be receiving this error because your user doesn't have necessary permissions to access the docker daemon. A user requires "docker group" membership to interact effectively with Docker without requiring superuser permissions.
This command adds a user to the docker group:
sudo usermod -aG docker $USERThen, either log out and log back in again for these changes to take effect, or alternatively use:
.
Please note that any changes you made from everything shared above will only touch upon your local WSL environment and won't affect the Windows host.
Networking Issues in WSL2
WSL2 has been known to occasionally encounter networking problems that impede its communication with Docker. One workaround can involve creating a script with a line like so:
echo "export DOCKER_HOST=tcp://localhost:2375" >> ~/.bashrc && source ~/.bashrc, which exports Docker's host configuration settings (referring to localhost at port 2375).
Additionally, remember these corrective measures in your quest to tackle these challenges:
- Fiddling with your firewall settings. Sometimes, firewall settings can prevent Docker from accessing the internet
- Switching the WSL version. Some users report success after switching from WSL2 to WSL1.
- Trying different network interfaces. In other situations, switching the network interface can unblock Docker's internet access
- Checking VPN interference. Your VPN might restrict access to certain ports, which could undermine Docker's ability to connectThese are some of the primary root causes of the “Cannot Connect to the Docker Daemon” error message and how they relate to WSL2. However, each case could involve unique variables, necessitating a custom troubleshooting process to identify and rectify the issue. It would be great to check on Docker official troubleshooting documentation to have a better understanding where the error could be coming from specifically in your configuration. Aside from the points mentioned here, inadequate system resources or software conflicts could also incite error messages.When it comes to diagnoses of network issues in Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL2), in particular, your conundrum about the "Cannot connect to the Docker daemon" error, there might be a few plausible causes.
shell
$ docker run hello-world
docker: Cannot connect to the Docker daemon at unix:///var/run/docker.sock. Is the docker daemon running?.
See ‘docker run –help’.
## Docker Daemon
Primarily, the error suggests that Docker daemon could not be accessed. For Docker to work correctly, it relies heavily on the Docker daemon, which potentially isn’t started yet or is experiencing issues. Generally speaking, this happens when the Docker service isn’t running properly. This could be due to the fact that it wasn’t initiated at boot, crashed, or currently has incorrect settings.
You should try manually initiating it using the following commands:
shell
sudo service docker start
or
shell
systemctl start docker
If the Docker daemon was previously set up to autoload on boot and didn’t, then you might want to inspect those settings.
## User Permissions
Next, you have to make sure that the user trying to run Docker has proper permissions. In some configurations, only root or users in the Docker group can access Docker. A simple command to add the current user to the Docker group is:
shell
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
**Keep in mind**: If you add the user to a new group, typically, you will need to log out and back in for changes to take effect.
## WSL2-Specific Issues
With WSL2 there can be unique network issues because it uses a dynamic IP address by default, which often leads to connectivity problems with Docker. To fix this issue, we make use of a static IP address.
A known issue causing “Cannot connect to the Docker daemon” error in Docker Desktop with WSL 2 backend derives from changes in networking in Docker
Desktop [2.2.0.0](https://github.com/docker/for-win/issues/5515). So, updating Docker Desktop could help resolve the problem.
Also, consider checking firewall rules as sometimes, they prevent communication with Docker’s Unix socket or local network loopbacks.
Presented solutions should cover most of Docker issues related to “Cannot connect to the Docker daemon” error. Any further troubleshooting might require a more detailed investigation, including system configuration, installed packages and versions, and console output of failed commands.
Hyperlinks:
– [Understanding WSL 2](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/about)
– [Docker post-installation steps for Linux](https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/linux-postinstall/)
– [Troubleshooting Docker authorization in WSL 2](https://github.com/microsoft/WSL/issues/4177)Analyzing user permissions is vital in Docker Configuration to avoid errors like ‘Cannot Connect to the Docker Daemon’ on WSL2.
Docker utilizes a client-server model where the Docker client interacts with the Docker daemon, which is responsible for building, running, and managing containers. If you do not have proper user permissions set up, you might receive this error message.
The issue can be caused by:
– The Docker daemon not running. Since you’re relying on WSL2, it’s possible that the Docker daemon might not be actively running despite Docker Desktop indicating so.
– Incorrect user permissions. Docker operates using the ‘root’ (superuser) as default. So, if your current user does not have appropriate superuser permissions, this could prevent connection to the Docker daemon.
– Misconfiguration within the Docker daemon itself. Despite having Docker installed appropriately within WSL2, any misconfigurations, especially with regards to access controls and permission settings can cause a failure in establishing connections.
Now let’s dive more into how we could resolve this:
Ensure the Docker Daemon is Running
For Docker to function effectively, the Docker daemon should be running. You can check this by entering the command
or
. This should indicate whether Docker is running optimally.
Grant User Permissions
Ensuring that the user has sufficient permissions to operate Docker is crucial. As Docker runs with ‘root’ privileges by default, you need to ensure that the rights of the current user are properly configured. Maybe adding the user to the ‘docker’ group would solve the issue because it grants them the necessary permissions without needing ‘sudo.’ To do as such you use the command
sudo usermod -aG docker ${USER}
(source).
Check Docker Daemon Configuration
Any issues related to the Docker daemon configuration can also play a significant role in triggering the ‘Cannot connect to the Docker daemon’ error. Ensuring all settings correctly point to the right Docker binaries and library locations within the WSL2 distribution is important. You can find these configurations inside the Docker service file.
Resolving these issues can mitigate the chances of getting the ‘Cannot Connect to the Docker Daemon’ error in WSL2. Regularly checking to make sure these aspects are managed accordingly can help in successfully managing your Docker environment.
When working with Docker on a WSL2 (Windows Subsystem for Linux) environment, the “Cannot connect to the Docker daemon” error typically happens due to incorrect or missing environment variables. The Docker daemon must be accessible to the terminal from which you are running Docker commands. This isn’t happening if you’re receiving this error, and it’s likely due to problems with your configuration.
How Environment Variables Impact Docker Daemon Access
Environment variables provide important connectivity parameters for your Docker processes. In other words, they are used to specify how command-line operations interface with the Docker daemon.
The error you’ve encountered is commonly caused by issues with these two key environment variables:
DOCKER_HOST DOCKER_CERT_PATH
- DOCKER_HOST: This variable lets your Docker client know just where to go to communicate with the Docker daemon. If unset or set incorrectly, your client may not be able to do its job, leading to errors like the one you’re currently experiencing.
- DOCKER_CERT_PATH: Your client needs a secure connection to your Docker daemon. DOCKER_CERT_PATH must be set to the path location of the certificate to facilitate this. If there’s an error here, communication between client and daemon could undeniably break down.
Setting up Correct Environment Variables in WSL2
To traverse to the crux of this problem, let’s discuss how to set up these environment variables correctly:
export DOCKER_HOST=tcp://localhost:2375 export DOCKER_CERT_PATH=/mnt/c/Users/your_username/.docker/machine/machines/default
You should replace /mnt/c/Users/your_username/ with the appropriate directory path for your Docker certificates. These commands export and set your environment variables as required, but only temporarily for the current open terminal session.
Adding Them Permanently
The corrections exist until you end the shell session. To avoid resetting each time you initialize WSL2, add them permanently into your bash profile. You can do this by editing your profile file. The process varies depending on the shell type but typically involves adding the exports to .bashrc or .bash_profile:
echo "export DOCKER_HOST=tcp://localhost:2375" >> ~/.bashrc echo "export DOCKER_CERT_PATH=/mnt/c/Users/your_username/.docker/machine/machines/default" >> ~/.bashrc
These changes will take effect the next time you start a new terminal session or reload the profile with source ~/.bashrc.
Ultimately, ensuring that your environment variables are configured correctly allows seamless interaction with the Docker daemon, circumventing the error you initially encountered.
For further reading, refer to the official Docker documentation on environment variableshere.
First off, the error message “Cannot connect to Docker daemon” might hint that your system is experiencing operational issues. There are several factors that may contribute to this dysfunction. Below we’ll delve into some elements impacting your overall system health and potentially causing this Docker-related snag.
Factor One: Docker Service Status
The first section to check is the Docker service status. This error can pop up if the Docker service is not running on your machine.
You may verify the Docker service status using the following command:
sudo systemctl status docker
If Docker is not actively running, use this commmand to start the service:
sudo systemctl start docker
A huge caveat here is, WSL2 (Windows Subsystem for Linux version 2) doesn’t support systemd, meaning the commands above won’t work directly in WSL2. You can follow alternative steps to manage Docker service in WSL2, which often involves having to run Docker Desktop for Windows.
Factor Two: User Access Privileges to Docker
Another possible reason why you are encountering this error may be because the user does not have sufficient permissions to access the Docker daemon.
For a user to gain these privileges without needing root access or prefixed “sudo”, they need to be added to the “docker” group. To add a user to the “docker” group, enter:
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
As before, WSL2 doesn’t support Linux groups as fully as native Linux environments do. Still, it might be worthwhile checking your
file in case a workaround was used at any point to assign such access levels.
Factor Three: Docker Desktop Settings
WSL2 uses Docker Desktop as part of its integration with Windows, and sometimes the settings in Docker Desktop can cause connectivity problems.
Under Docker Desktop’s “Settings > Resources > WSL Integration,” ensure that your desired WSL2 distro is selected for Docker Desktop integration.
Factor Four: Network Connectivity Issues
Lastly, network configuration issues could also result in a “cannot connect to Docker daemon” problem. Docker Desktop proxies requests from WSL2 to the underlying host OS, which means any networking issue between WSL2 and the host can affect Docker connections.
In this regard, it can be useful to perform some basic network debugging commands in WSL2 to test the connection to the host, like pinging the host IP or attempting other forms of network access.
These are the primary things to look into when understanding why you’re seeing the “Cannot connect to Docker daemon” error with WSL2. By taking a thorough peek at these areas, you should hopefully be able to identify the issue and put effective solutions in place. Restoring your system’s health and perfectly interlacing Docker services with WSL2 will require careful inspection of these aspects. Therefore, make sure to utilize insightful debugging tools as well as reliable online guides to navigate you through this technical predicament.Why getting a “Cannot Connect to the Docker Daemon” error in WSL2 can be quite irritating, especially when you’re trying to navigate your way around Docker CLI commands. This error is often a result of several culprits, including incorrect configurations and permission issues.
Understanding DockerCLI Commands
Firstly, it’s important that we briefly examine DockerCLI commands (source). These commands are integral for managing Docker images and containers, networks, and volumes. For example:
docker run hello-world docker ps docker stop my_container
Without correct execution of these commands, one might face the “Cannot Connect to the Docker Daemon” error.
Cause of Docker Daemon Connection Error in WSL2
Problems connecting to the Docker daemon in WSL2 are typically caused by:
- Incorrect Docker Configurations: If Docker is not configured correctly, the Docker daemon might not start automatically leading to difficulties establishing a connection.
- Insufficient User Permissions: The user may lack permissions to interact with the Docker daemon.
- Docker Service Not Running: If the Docker service isn’t running, you can’t connect to it.
To avoid the cannot connect to Docker daemon error, ensuring correct configuration, assigning appropriate permissions, and confirming the Docker service is running are necessary steps.
Solutions & Code Examples
As a coder dealing with this error, consider taking the following steps:
**1. Start Docker Service**
If the Docker service isn’t running, you’ll want to start it using the command:
sudo service docker start
**2. Run Docker as Non-root User**
Running Docker as a root user could pose serious security risks. Therefore, you should add your user to the Docker group to gain sufficient permissions:
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER newgrp docker
You could then verify this using:
**3. Configure Docker to Start on Boot**
Ensuring Docker starts whenever your system boots up can prove efficient in avoiding this error. You can do this by enabling the Docker service:
sudo systemctl enable docker
**4. Correct Environment Configuration in WSL2**
Improper configuration of the environment in WSL2 could lead to a failure in connecting to the Docker daemon. Make sure Docker Desktop is set to use the WSL2 backend. This can be confirmed in Docker Desktop settings. Then, ensure that your .bashrc or .zshrc file contains
export DOCKER_HOST=unix:///var/run/docker.sock
Omitting this line could give rise to the dreaded “Cannot connect to the Docker daemon” error message.(source)
In conclusion, experiencing errors while trying to establish a connection to the Docker daemon in WSL2 is not uncommon. However, understanding DockerCLI commands and the potential roots of these problems can guide you through troubleshooting them successfully. Implement the above solutions and you should be able to overcome the issues efficiently.This is a common concern when working with Windows Subsystem for Linux 2 (WSL2) and Docker. The issue typically arises when there’s security software or firewall interference preventing the connection to the Docker daemon.
It is important to clarify that, often, “Cannot connect to the Docker daemon” error occurs due to:
- Security programs blocking essential network traffic.
- Improper configuration of Environment Variables.
To resolve this issue, I suggest following these steps:
Check Your Security Software
Some anti-virus software, Internet security services, and firewall settings could hinder your Docker daemon connectivity. These services could see activities from WSL2 as potential threats and, therefore, block them. To resolve this:
1. Temporarily disable these services. 2. Try re-establishing a connection to the Docker daemon.
If it works, you’ll know that these services were causing the issues and you’ll need to adjust their settings to allow Docker’s functionality without interruption. Note that procedures differ based on the software used; please refer to respective user manuals or support channels for instructions.(source)
Set Environment Variables Correctly
Another possible solution is checking if the Docker environment variables have been set correctly. For instance, when using Docker with WSL2, the DOCKER_HOST environment variable should be assigned the value tcp://localhost:2375. If it’s not set correctly, it can interfere with WSL2 and Docker communication.
export DOCKER_HOST=tcp://localhost:2375
You can add this line to your shell startup script (like .bashrc or .zshrc) so the variable is properly set every time you start a new terminal session.
Ensure the Docker Desktop WSL 2 backend
WSL integration in Docker Desktop’s settings can sometimes turn off automatically. This setting ensures Docker Desktop supports the running of the Linux operating system using the built-in Hyper-V virtualization technology.
The process of enabling it again:
1. Open Docker Dashboard > Go to Settings.
2. On the left-hand side, select Resources.
3. From the expandable list, choose WSL Integration.
4. Make sure you've selected the relevant distributions.
Afterward, save the changes and restart Docker. This should ideally fix any connectivity problems.
See also
Remember, in some cases, you might encounter the problem because of combinations of these factors. Therefore, I suggest trying out all solutions and check which one(s) work for you.
Working with Docker on WSL2 is quite an extensive topic, and there are many resources available online to help you navigate through it. Here are a few additional resources to consult(source).
The “Cannot connect to the Docker daemon” error in Windows Subsystem for Linux 2 (WSL2) typically originates from the differences between UNIX and TCP sockets. Understanding these two critical socket types helps a lot in troubleshooting connectivity errors in WSL2.
Coding on WSL mainly involves using UNIX domain sockets which are driven by the operating system’s ability to connect, send or receive data. They offer fast, reliable communication close to interprocess communication (IPC) mechanisms. In WSL2’s context, they’re a means of interaction between containers run by Docker daemon.
A UNIX socket is created using the NFS protocol with code that somewhat resembles the following C programming syntax:
#include #include int socket(int domain, int type, int protocol);
However, a UNIX socket alone doesn’t depict the entire image as it only allows two running processes on the same host to share data. With WSL2, we’re mainly dealing with a virtual machine running your Docker daemon and your host machine running WSL2. Here, the keyword is ‘different hosts’, sparking the entry of TCP sockets.
Conversely, TCP sockets act as two points connected over the network providing a way to exchange data between hosts frequently used in client-server architecture. They employ IP addresses and port numbers ensuring that your data gets delivered to the right process on the potentially remote system effectively. When we establish a connection utilizing TCP, we initiate a session that persists until one side terminates it.
A typical syntax to create a TCP socket in C looks something like this:
socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
Now, coming back to the “Cannot connect to the Docker daemon” error message in WSL2. It happens when Docker Desktop’s engine doesn’t start automatically even though the service may be running. The daemon operates in a different environment where the UNIX socket can’t reach. As a result, you need to export the DOCKER_HOST variable with the appropriate TCP address of the Docker Desktop’s engine.
Here’s how:
export DOCKER_HOST=tcp://localhost:2375
Remember, this is usually a temporary solution. For a long-term fix, go through your Docker Desktop settings and ensure that the option “Expose daemon on tcp://localhost:2375 without TLS” is checked. Following that, ensure that at the starting of every session, there’s an automatic execution of the export command exemplified before.
Notably, various post-installation steps on Docker’s official documentation site go a long way in identifying and solving related hitches. By analyzing both UNIX and TCP sockets roles, understanding their interaction with Docker daemon under the WSL2 environment, you’re on track to mitigating connectivity issues as developers in the current ecosystem.It’s not uncommon to encounter the “Cannot connect to the Docker daemon” error when installing Docker in Windows Subsystem for Linux 2 (WSL2) environment. Tackling this issue involves understanding its causes and knowing how to approach its resolution.
The root cause of the error is typically a misconfiguration with Docker or WSL2, leading to an inability to establish a connection between Docker client and Docker daemon.
Here are some common steps for troubleshooting that may help identify and resolve the problem:
1. Ensure the Docker Desktop Service is Running
An underlying reason for this error could be due to Docker’s desktop service not running on your system.
You can verify this using the Windows Services Manager:
– Open run by pressing Win+R
– Type ‘services.msc’ and hit enter
– Check if Docker Desktop Service is running. If it’s not, right click and select ‘Start’.
2. Check Your Environment Variables
Environment variables play a crucial role in defining where the Docker client should connect. If DOCKER_HOST environment variable is unset or set incorrectly, you might face the said error.
To check this, open your WSL2 terminal and type:
If this doesn’t return tcp://localhost:2375, then DOCKER_HOST is set incorrectly. You can correct this with the following command:
export DOCKER_HOST=tcp://localhost:2375
Then, add this line to bashrc file as well, so that it gets automatically set up upon opening WSL2 terminal:
echo "export DOCKER_HOST=tcp://localhost:2375" >> ~/.bashrc
3. Confirm Your Docker Daemon Configuration
Docker daemon configuration could also lead to errors. Particularly ensure ‘Expose daemon on tcp://localhost:2375 without TLS’ is checked in Docker Desktop settings under General settings. This allows connections from the WSL2 Docker client.
4. Check the Release Version of Your WSL2
If you recently updated your Windows OS, chances are your WSL might have been upgraded to version 3. Since Docker currently only supports WSL2, you should downgrade it back to version 2.
Check with:
Downgrade using this command (replace “distro” with your distribution name):
wsl --set-version distro 2
5. Reinstall Docker and Restart WSL2
If all else fails, reinstalling Docker can sometimes fix the issue. Uninstall your current Docker Desktop, download the latest stable version from Docker, and reinstall. Remember to restart your WSL2 instance after reinstallation.
These structured steps address common issues encountered during Docker installation on the WSL2, offering potential solutions for the “Cannot connect to the Docker daemon” error. By properly configuring Docker services, adjusting environment variables, and ensuring compatibility through updates or re-installation, successful Docker deployment within the WSL2 distribution can be achieved. Lastly, though these approaches should cover most cases, remember to consider any uniquely specific requirements for your own system and software configurations.Updating your operating system can definitely be an effective solution when you confront the ‘Cannot Connect to the Docker Daemon’ error in WSL2. This error usually surfaces because your OS might not support certain features required by Docker, and thereby updating your system may rectify this.
Let’s peel off the layers:
Docker is a tool designed to simplify the process of creating and handling isolated workspaces called containers where developers can package their software along with the dependencies it requires. As such, it makes use of specific features provided by the kernel operating system to isolate these workspaces.
On the other side, WSL2 (Windows Subsystem for Linux version 2), is a compatibility layer that allows Windows users to run a GNU/Linux environment — including most command-line tools, utilities, and applications — directly on Windows.source
Now if you are getting a ‘Cannot Connect to The Docker Daemon’ error, it means WSL2 can’t communicate with Docker. While there could be multiple reasons behind this, one potential cause might be the outdated versions of either Docker or the Windows Operating System itself, causing compatibility issues. For instance, WSL2 is only fully supported on Windows 10 versions 1903, 18917 or highersource. Hence, if you’re using a lesser version, updating your Windows OS should ideally resolve this issue.
To check your version of Windows 10: 1. Press Win + R to open Run dialog box. 2. Type winver, press Enter
The second part would be ensuring you have a compatible Docker desktop version installed. Here’s the code snippet to check the Docker version:
If you find you’re not running on the approved Windows or Docker versions, understanding how to update is essential.
For updating the Windows Version, follow these steps:
1. Open your Windows Settings 2. Navigate to Update & Security 3. Click on Windows Update 4. Click on Check for updates button on your right hand
As for Docker Desktop, you should receive automatic update notifications once a new version release. Alternatively, download the latest version directly from the Docker Hub. More details are available on the official Docker documentationsource.
Moreover, Docker needs administrative rights to function properly. Providing it with the requisite privileges can also help resolve this error. To switch Docker client under WSL2 to have sudo rights, include this in your shell profile.
export DOCKER_HOST=tcp://localhost:2375
Once these processes are completed, restart your system for all changes to take effect, and ideally, your error should be resolved.
In the end, one should remember that to keep things running smoothly and avoid technical errors like ‘Cannot connect to the Docker daemon error’, keeping your Docker and Windows OS updated is crucial. Regular updates signify bug fixes, performance improvements, and frequently new features too, thereby enhancing user experience at large.
Be sure to also keep a close eye on the release notes both by Microsoft and Docker, as they routinely drop valuable insights about system requirements, potential known issues, resolutions available, and what merits most – what’s new therein!source source
Running into a ‘Cannot Connect to the Docker Daemon Error’ in WSL2 can be a frustrating experience, especially when you’re keen on making your development environment run smoothly. It’s crucial to understand that this issue may arise due to compatibility conflicts between WSL 2 Kernel and your installed Linux distributions. Let’s delve deep to fully grasp the situation, potential causes, and solutions.
Understanding the Interaction between WSL2 and Linux Distributions
In WSL2, a significant architectural change took place where a real Linux kernel is running inside a lightweight utility virtual machine. This has drastically improved the system performance, full system call capability, and reduced boot time. However, it also means that we require seamless integration of WSL2 and your chosen Linux distribution for ideal functionality.
| WSL2 Characteristic | Significance for Linux Distribution Compatibility |
|---|---|
| Complete Linux Kernel | This implies that Linux distributions must be compatible with the provided kernel for optimal operation. |
| Improved Performance | A higher performing kernel allows Linux distributions to execute commands faster. However, it also means that poorly optimized distributions can struggle to prove effective. |
| Full System Call Capability | Linux distributions must be capable of accommodating these calls to ensure a competent operation process. |
Why the ‘Cannot Connect to the Docker Daemon Error’ May Be Occurring
Despite the impressive upgrades of WSL2, challenges may occur if there’s a snag in communication between the overarching Windows system, WSL2 and the working Linux distribution. In context, if the Docker Desktop that operates via WSL2 backend fails to integrate well with the Linux distribution or vice versa, it may lead to the dreaded “Cannot connect to the Docker daemon error.”
Solving the Compatibility Issue & Ensuring Smooth Operation
Ideally, solving this issue involves understanding how your Docker Desktop, WSL2, and Linux distribution communicate and ensuring smooth collaboration. Here are some vital steps that can help:
- Cross-checking your configurations: Ensure Docker Desktop is set up correctly to use the WSL2 backend. Whilst creating a new Docker context for WSL2, confirm the successful implementation by checking it in the command line (
) to ensure it’s the active one.
- Inspecting firewall and security settings: In some cases, overzealous security settings could cause the problem. You may need to check whether certain ports required by Docker aren’t being blocked.
- Upgrading WSL2 Kernel & Installed Linux distribution: Keeping your systems updated ensures max compatibility. Remember to regularly update both your WSL2 kernel and Linux distributions for best results.
- Dig a bit deeper with Docker: When all else fails, analyze your Docker logs for any notable error messages that could suggest where things are going wrong using this command:
sudo journalctl -fu docker.service
.
You may find valuable information in the official Docker documentation and Microsoft’s comprehensive guide on WSL troubleshooting here. Also, consider referring to online communities such as StackOverflow and GitHub for further insight. With the right approach, you’ll resolve these issues, ensuring excellent coexistence between WSL2 Kernel, Docker, and your preferred Linux distributions.
Persistent connection issues can be frustrating, especially when dealing with Docker as it becomes crucial to your project development. Before diving into the advanced troubleshooting steps for resolving ‘cannot connect to the Docker daemon’ error in WSL2, let’s briefly comprehend why this error might occur.
Primarily, Docker daemon is a background service running on your system which manages building, running and distributing Docker containers. WSL2 (Windows Subsystem for Linux 2) lets developers run a GNU/Linux environment – including most command-line tools, utilities, and applications – directly on Windows, unmodified and without needing an entire virtual machine. If you’re facing Docker daemon connectivity problems in WSL2, it generally means that your WSL2 instance isn’t able to communicate with the Docker daemon.
Troubleshooting Steps:
Here are some analytical steps you can take to resolve these persistent connection issues:
- Verify Docker Desktop Installation: The first step should always be to confirm if Docker Desktop is installed correctly. Open your terminal, type
, and press enter. If Docker is installed correctly, it will return the version of Docker currently installed on your system. If this returns a ‘command not found’ message or doesn’t output the correct Docker version, reinstalling Docker may be required.
- Docker Service Status: Another common reason for this error could be that the Docker service isn’t running. Use
(or similar command depending on your operating system) to view the status of Docker services.
- Check Environment Variables: Your environment variables also have a role to play in this. Make sure the DOCKER_HOST variable is set correctly. You can do this by using
.
- Update WSL2 Kernel: An outdated WSL2 kernel could also result in Docker issues. It’s important to make sure you’re using the latest WSL2 Linux Kernel.
- Switch to Linux Containers: Sometimes, it might just be that you’re trying to use Linux-based images while having the Docker Desktop set to use Windows containers. In Docker Desktop settings, switch the container platform to Linux since WSL 2 is a Linux framework.
- Docker Daemon Configuration: Also check the Docker daemon configuration file located at /etc/docker/daemon.json. Invalid entries in this file could prevent the Docker daemon from starting properly.
- Adjust Resource Allocation: Finally, it could be a resource allocation issue. Docker Desktop allows you to specify how much system resources (memory, CPU, file swapping etc.) you want to allocate to your Docker containers. Reducing these allocations could potentially solve this issue.
If none of these proposed solutions work, an even deeper dive would be required. This might include examining logs, both from the Docker side and the host system side, consulting Docker documentation, forums and support channels.
To demonstrate a more practical analysis, let’s use code example to show how to check the Docker service status:
$ systemctl status docker
● docker.service - Docker Application Container Engine
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/docker.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Tue 2020-11-24 18:02:51 PST; 1min 25s ago
Docs: https://docs.docker.com
Main PID: 24321 (dockerd)
Tasks: 8
Memory: 41.4M
CGroup: /system.slice/docker.service
└─24321 /usr/bin/dockerd -H fd:// --containerd=/run/containerd/containerd.sock
If the Docker service isn’t running, start it using the following command:
Remember, Docker is a widely used platform, and many possible solutions will be given by the community. However, the bottom line is understanding what could potentially cause these issues and troubleshooting them accordingly contributes to effective problem solving and consistent productivity.
Typically, getting a ‘Cannot Connect to the Docker Daemon’ error in WSL2 arises from a series of conditions such as incorrect environment variables, insufficient permissions, or issues with the Docker Desktop installation.
Incorrect Environment Variables: Understand that when Docker is installed on your system, certain environment variables are created which dictate the path Docker will use to execute commands. It’s possible for these variables to be initialized incorrectly, resulting in an inability to communicate with the Docker Daemon. To fix this, ensure these variables are pointing to correct paths.
export DOCKER_HOST=tcp://localhost:2375
This command tells the docker client to connect to the docker daemon running at tcp://localhost:2375.
Insufficient Permissions: Docker’s architecture typically requires administrative or root access to perform tasks. If you’re executing Docker commands in WSL2 without appropriately elevated permissions, this can lead to a ‘Cannot Connect to the Docker Daemon’ error. In order to rectify this, use sudo during command invocation.
sudo docker run hello-world
The above command asks for superuser permission to run the docker command and should overcome any potential permission issues.
Docker Desktop Issues: In some cases, the issue might lie squarely with Docker’s software itself. Improper configuration during installation, software bugs, or compatibility issues with other services may prevent successful communication between your Docker client and daemon in WSL2. An uninstallation followed by a clean reinstallation of Docker Desktop could effectively address these issues. After the reinstallation, ensure Docker Desktop is correctly configured within the WSL2 environment.
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Uninstall Docker Desktop |
| 2 | Reboot your system |
| 3 | Reinstall Docker Desktop |
| 4 | Configure Docker within WSL2 |
By taking into account these factors – correcting environment variables, ensuring appropriate execution permissions, and ensuring Docker Desktop has been properly installed and configured – it should mitigate the ‘Cannot Connect to the Docker Daemon’ error in WSL2.
For more detailed insights and troubleshooting tips, concept exploration from Docker’s official documentation or community support forums like StackOverflow can be invaluable.
