The Command Prompt: Understanding C:WindowsSystem32Cmd.Exe
The Command Prompt, located at C:WindowsSystem32Cmd.Exe, is more than just a simple program; it serves as a powerful command-line interpreter on Windows operating systems. While many users may prefer graphical user interfaces (GUIs) for interacting with their systems, the Command Prompt offers a depth of functionality that can enhance productivity, facilitate advanced troubleshooting, and even allow for automation of tasks. This article explores the significance, functionality, historical context, and common uses of cmd.exe in detail.
Historical Context of Command-Line Interfaces
Before delving into Command Prompt specifically, it is vital to understand the historical significance of command-line interfaces (CLIs). Command-line interfaces originated in the early days of computing, where users interacted with computer systems through text-based commands. The first operating systems, such as CP/M and DOS, relied heavily on CLIs, allowing users to execute commands by typing text into a terminal.
As graphical user interfaces (GUIs) gained popularity in the late 1980s and early 1990s, command-line interfaces began to see a decline in everyday usage. However, for many technical operations and advanced users, CLIs remained crucial due to their speed, flexibility, and scripting capabilities. This led to the birth of various command-line tools across different operating systems, including Windows.
The Rise of Cmd.Exe
With the introduction of Windows NT in 1993, Microsoft included the Command Prompt to provide users with a powerful tool to manage system tasks. The full executable path, C:WindowsSystem32Cmd.Exe, indicates its presence in the System32 directory, which houses essential system files for the Windows operating system.
Cmd.exe has evolved over the years, adapting to various versions of Windows, including Windows 95, Windows 98, XP, Vista, 7, 8, 10, and the most recent iterations, such as Windows 11. Despite the evolution of Windows and the prevalence of GUIs, Cmd.exe holds a vital position—enabling efficient system management, scripting, and more.
Understanding Command Prompt Basics
At its core, cmd.exe functions as a command-line interpreter, allowing users to interact with the operating system by typing commands. Upon launching the Command Prompt, users are greeted with a command line, typically showing the current working directory, which by default may be C:UsersYourUsername>.
Key Features of Command Prompt
-
Command Execution: Users can execute a variety of commands to perform system tasks, such as file management, process handling, network troubleshooting, and system administration.
-
Batch Scripts: Cmd.exe supports batch scripting, which allows users to automate repetitive tasks by writing a series of commands into a
.bator.cmdfile. This functionality can enhance productivity markedly. -
Redirecting Input/Output: Cmd.exe provides tools to redirect input and output, allowing users to save command results to files or read input from files.
-
Piping Commands: The ability to pipe command output to another command is a powerful feature. This allows users to compose more complex command structures.
-
Environment Variables: Users can utilize and manipulate the system’s environment variables, which are dynamic values that the operating system uses to configure how processes and applications run.
-
Help Functionality: The Command Prompt comes with built-in help options. Typing a command followed by
/helpor simply/?will provide users with details regarding command usage.
Common Command Prompt Commands
Exploring Cmd.exe would be incomplete without mentioning some of the most common commands used:
1. DIR
The DIR command displays a list of files and directories in the current directory. Options allow users to format the output, including showing hidden files and detailed information.
2. CD
The CD (Change Directory) command allows users to navigate between directories. Specifying a path enables users to change the working directory to a desired location.
3. COPY
The COPY command is used to duplicate files from one location to another. Options allow for copying multiple files or directories.
4. MOVE
Similar to COPY, the MOVE command transfers files from one location to another, but removes them from the original location.
5. DEL
The DEL command permanently deletes files from the specified directory. Care should be taken while using this command, as recovery is often not possible once files are deleted.
6. PING
The PING command is a widely used network utility. It determines the reachability of a host on an IP network and measures round-trip time for messages sent from the originating host to a destination computer.
7. IPCONFIG
IPCONFIG displays the current configuration of the network interfaces on a machine. It is invaluable for troubleshooting network issues.
8. TASKLIST and TASKKILL
TASKLIST shows all the currently running processes along with their process IDs (PIDs), while TASKKILL allows users to terminate processes based on their PIDs.
Using Command Prompt for System Administration
Disk Management
Cmd.exe can be utilized for various disk management tasks. The DISKPART command opens the Disk Partition tool where users can create, delete, and manage disk partitions. This is particularly useful for advanced users who need to manage large storage systems.
User Account Management
System administrators can manage user accounts through the Command Prompt. Commands such as NET USER allow the creation, deletion, and modification of user accounts directly via command line, streamlining administrative tasks.
Network Configuration
Cmd.exe is integral for network management. Commands like NETSTAT, TRACERT, and ROUTE provide insights into network connections, tracking routes, and configuring routing tables. This is essential for diagnosing network issues and managing server settings.
Advanced Scripting with Batch Files
Batch files are scripts written for the Command Prompt that allow users to automate tasks. A .bat file can contain a series of commands that Cmd.exe will execute sequentially.
Creating a Batch File
- Open Notepad: Write your commands in a new Notepad document.
- Save as .bat: Save the file with a .bat extension, for example,
myScript.bat. - Run the Batch File: Double-clicking the file in Windows Explorer or executing it in the Command Prompt runs the included commands automatically.
Example Batch Script
@echo off
echo Starting Maintenance Tasks...
mkdir C:Backup
xcopy C:Files*.* C:Backup /s /e
echo Backup Complete!
pauseThis script creates a backup folder and copies files, providing a simple example of automation.
Troubleshooting and Recovery
Command Prompt can be invaluable during troubleshooting and recovery processes. If a system fails to boot properly, users might use the Windows Recovery Environment, which includes Command Prompt functionalities to fix various issues.
Running System File Checker
The System File Checker (SFC) tool can scan for corrupted files and restore them. By executing the command sfc /scannow, users can find and repair system files, which is vital for maintaining system integrity.
Booting into Safe Mode
If you encounter issues starting Windows, booting into Safe Mode can help. Accessing the Command Prompt in Safe Mode allows for recovery commands to be executed, including restoring system images and performing repairs.
Security Implications and Permissions
Using Cmd.exe effectively often requires administrative privileges. Running the Command Prompt as an administrator grants enhanced capabilities, allowing users to perform system-level changes.
User Permissions and UAC
User Account Control (UAC) impacts how commands are executed, especially when elevated permissions are necessary. Users need to be familiar with managing permissions effectively to use Cmd.exe without hindrance.
Malware and Security Risks
With great power comes great responsibility. Command Prompt can be misused for malicious purposes, such as executing harmful scripts or commands. Users should remain vigilant against unauthorized commands and scripts, ensuring that only trusted commands are executed.
The Future of Command Prompt
As technology continues to evolve, so do command-line tools. Microsoft has recognized the need for a more powerful command-line interface and has introduced alternatives, such as PowerShell. PowerShell is a task automation framework that includes a command-line shell and scripting language, allowing for more advanced task automation and control over the Windows operating system.
Despite these advancements, the classic Command Prompt remains widely used, especially for quick command execution and legacy applications. Its simplicity and direct interface make it a favorite among system administrators and advanced users.
Conclusion
The Command Prompt, accessible via C:WindowsSystem32Cmd.Exe, stands as a testament to the enduring utility of command-line interfaces. By understanding and mastering the capabilities of the Command Prompt, users can take full advantage of their Windows operating system, performing tasks quickly and efficiently.
Whether it’s troubleshooting system issues, automating repetitive tasks, or managing system files, the Command Prompt remains a vital tool in the arsenal of both casual and advanced users. As we look toward the future, the Command Prompt’s legacy will undoubtedly continue, supplemented by new tools and technologies while retaining its essential role in system management.
The genuine cmd.exe file is a software component of Microsoft Windows Operating System by .
The genuine Microsoft command line prompt utility, «Cmd.exe», formerly called ‘MS-DOS Prompt’, resides in «C:\Windows\System32.» When simply executed without parameters, it opens the Win32 console to accept and interpret commands entered by the user, (cd, runas, shutdown, ipconfig, ping, nslookup, and others), and display results. Once the console window opens, «cmd.exe» can be used within it but must have parameters. Its parameters give it power and versatility, allowing use of it in scripts to execute batch («.bat») or application («.exe») files. Information about its parameters and uses can be viewed in the console via «cmd /?», or via the Internet.
Cmd stands for Windows Command Processor
The .exe extension on a filename indicates an executable file. Executable files may, in some cases, harm your computer. Therefore, please read below to decide for yourself whether the cmd.exe on your computer is a Trojan that you should remove, or whether it is a file belonging to the Windows operating system or to a trusted application.
Click to Run a Free Scan for cmd.exe related errors
Cmd.exe file information

The process known as Windows Command Processor or Stub or TWqCKeM.exe belongs to software Microsoft Windows Operating System or KaV5esH06pkjKEmuj or wyflEMBhddchRY by Microsoft (www.microsoft.com) or OyVw5w.
Description: The original cmd.exe from Microsoft is an important part of Windows, but often causes problems. Cmd.exe is located in the C:\Windows\System32 folder or sometimes in a subfolder of C:\Windows.
Known file sizes on Windows 10/11/7 are 302,592 bytes (21% of all occurrences), 236,544 bytes and 20 more variants.
The file is a Microsoft signed file. The program has no visible window. The file is a Windows system file.
Therefore the technical security rating is 4% dangerous; but you should also compare this rating with the user reviews.
Uninstalling this variant:
In case of any problems with cmd.exe, you can uninstall the software GIGABYTE FORCE(M6900) or Windows Repair Toolbox using the Uninstall a Program function of Windows Control Panel (Windows: Start, Settings, Control Panel, Uninstall a Program) or use the software publisher’s support site [1][2].
Recommended: Identify cmd.exe related errors
Viruses with the same file name
Is cmd.exe a virus? No, it is not. The true cmd.exe file is a safe Microsoft Windows system process, called «Windows Command Processor».
However, writers of malware programs, such as viruses, worms, and Trojans deliberately give their processes the same file name to escape detection. Viruses with the same file name are for instance TROJ_GEN.R3ECDBP or TROJ_GEN.R001C0PIP17 (detected by TrendMicro), and Backdoor:Win32/Bifrose or Trojan:Win32/CoinMiner (detected by Microsoft).
To ensure that no rogue cmd.exe is running on your PC, click here to run a Free Malware Scan.
How to recognize suspicious variants?
- If cmd.exe is located in a subfolder of the user’s profile folder, the security rating is 71% dangerous. The file size is 17,408 bytes (33% of all occurrences), 709,120 bytes, 39,424 bytes, 289,792 bytes or 345,088 bytes.
The file is not a Windows system file. The application starts upon Windows startup (see Registry key: RunOnce, MACHINE\RunOnce, User Shell Folders, TaskScheduler, DEFAULT\Run, Run, MACHINE\Run, cmdfile).
The program is not visible.
Cmd.exe is able to monitor applications. - If cmd.exe is located in a subfolder of «C:\Program Files», the security rating is 71% dangerous. The file size is 434,688 bytes (50% of all occurrences), 407,726 bytes, 2,086,400 bytes or 20,480 bytes.
Cmd.exe is not a Windows core file. The program has no visible window. - If cmd.exe is located in a subfolder of C:\, the security rating is 52% dangerous. The file size is 2,960,384 bytes.
- If cmd.exe is located in the C:\Windows folder, the security rating is 72% dangerous. The file size is 16,384 bytes.
- If cmd.exe is located in a subfolder of C:\Windows\System32, the security rating is 100% dangerous. The file size is 696,000 bytes.
- If cmd.exe is located in the Windows folder for temporary files, the security rating is 84% dangerous. The file size is 61,440 bytes.
Important: Some malware disguises itself as cmd.exe, particularly when not located in the C:\Windows\System32 folder. Therefore, you should check the cmd.exe process on your PC to see if it is a threat. We recommend Security Task Manager for verifying your computer’s security. This was one of the Top Download Picks of The Washington Post and PC World.
Best practices for resolving cmd issues
A clean and tidy computer is the key requirement for avoiding problems with cmd. This means running a scan for malware, cleaning your hard drive using 1cleanmgr and 2sfc /scannow, 3uninstalling programs that you no longer need, checking for Autostart programs (using 4msconfig) and enabling Windows’ 5Automatic Update. Always remember to perform periodic backups, or at least to set restore points.
Should you experience an actual problem, try to recall the last thing you did, or the last thing you installed before the problem appeared for the first time. Use the 6resmon command to identify the processes that are causing your problem. Even for serious problems, rather than reinstalling Windows, you are better off repairing of your installation or, for Windows 8 and later versions, executing the 7DISM.exe /Online /Cleanup-image /Restorehealth command. This allows you to repair the operating system without losing data.
To help you analyze the cmd.exe process on your computer, the following programs have proven to be helpful: ASecurity Task Manager displays all running Windows tasks, including embedded hidden processes, such as keyboard and browser monitoring or Autostart entries. A unique security risk rating indicates the likelihood of the process being potential spyware, malware or a Trojan. BMalwarebytes Anti-Malware detects and removes sleeping spyware, adware, Trojans, keyloggers, malware and trackers from your hard drive.
Other processes
a2hooks32.dll wzcsldr2.exe ishelper.exe cmd.exe cloud.exe hpprintscandoctorservice.exe pubmonitor.exe adaptivesleepservice.exe precomp.exe clmlsvc_p2g8.exe aspnet_state.exe [all]
First Seen: 04 October 2008 at 12:32 am
| No. | Company | File Type | SHA1 | MD5 | Digitally Signed |
File Version |
Product Version |
Submitted From |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Microsoft Corporation | Executable | e9be2f86e3a3bff0 2d1953aeccf0ed22 284596d4 |
cb6cd09f6a25744a 8fa6e4b3e4d260c5 |
No | 10.0.19041 .3636 (WinBuild. 160101.080 0) |
10.0.19041 .3636 |
United States |
| 2 | Microsoft Corporation | Executable | 984b29de3244f878 c8f40c5d936536f9 48c89a7a |
adf77cd50dc93394 a09e82250feb23c9 |
No | 10.0.19041 .1 (WinBuild. 160101.080 0) |
10.0.19041 .1 |
United States |
| 3 | Microsoft Corporation | Executable | ab6164d704b8eb12 953e1ab2543758d8 a69fc329 |
7644ae3bcadae89e 7160e3aff2e7d2bc |
No | 4.00 | 4.00 | United States |
| 4 | Microsoft Corporation | Executable | 9d41d484b79570b3 040909689259d52b 24bf6d21 |
41e25e514d90e9c8 bc570484dbaff62b |
No | 10.0.10586 .0 (th2_relea se.151029- 1700) |
10.0.10586 .0 |
United States |
| 5 | N/A | Non-executable | 33b0555b94fe5061 875685520529aa1e f06807e2 |
b4a50638f9a61ce0 ac639b4f2d5b7018 |
No | N/A | N/A | United States |
| 6 | N/A | Non-executable | 3afc24f318b074a7 3a6f619998260874 1a0b5c81 |
9c483a22ced36e19 72df169c5f661010 |
No | N/A | N/A | United States |
| 7 | Microsoft Corporation | Executable | f81694d223c86e0f 68bf31ebd8242f42 938e94a7 |
ac6179c930990342 cf02124f6a64c9c0 |
No | 10.0.19041 .3636 (WinBuild. 160101.080 0) |
10.0.19041 .3636 |
Turkey |
| 8 | N/A | Non-executable | d4112c3e8957ed71 41f9dccd96d31555 eaca446f |
995b6fe7d3c20048 fad1c0f66a97d417 |
No | N/A | N/A | United States |
| 9 | N/A | Non-executable | 7d55d1282d3b5d48 04883a9a550a3fd0 dc10d626 |
24ea675ed4738e72 4635153aedc352b1 |
No | N/A | N/A | United States |
| 10 | Microsoft Corporation | Executable | 984b29de3244f878 c8f40c5d936536f9 48c89a7a |
adf77cd50dc93394 a09e82250feb23c9 |
No | 10.0.19041 .1 (WinBuild. 160101.080 0) |
10.0.19041 .1 |
104.238.128.144/32 |
| 11 | Microsoft Corporation | Executable | f1efb0fddc156e4c 61c5f78a54700e4e 7984d55d |
8a2122e8162dbef0 4694b9c3e0b6cdee |
No | 10.0.19041 .746 (WinBuild. 160101.080 0) |
10.0.19041 .746 |
United States |
| 12 | Microsoft Corporation | Executable | ee8cbf12d87c4d38 8f09b4f69bed2e91 682920b5 |
ad7b9c14083b52bc 532fba5948342b98 |
No | 6.1.7601.1 7514 (win7sp1_r tm.101119- 1850) |
6.1.7601.1 7514 |
United States |
| 13 | Microsoft Corporation | Executable | 9305f79e08477d21 7bc990c23ed6f18d b1678d82 |
425d8dca76f63582 6acb8bfcb08a3c6c |
No | 10.0.19041 .1 (WinBuild. 160101.080 0) |
10.0.19041 .1 |
104.238.128.144/32 |
| 14 | N/A | Non-executable | 7668560233917f6c 19b688022b3da61d 31aafb96 |
dca129aebfd98b9c cae97ea9bfa36750 |
No | N/A | N/A | United States |
| 15 | Microsoft Corporation | Executable | 32aafce01aca567e 748820eccb8da7da 1a6b9900 |
49a39b84aff09fee 66bb853130bd860d |
No | 10.0.17763 .1 (WinBuild. 160101.080 0) |
10.0.17763 .1 |
United States |
| 16 | N/A | Non-executable | ef9d048c41fe45ab fa286d894d5576af fe725ee8 |
fa924a7ef061d530 37a39a5a13625e37 |
No | N/A | N/A | United States |
| 17 | Microsoft Corporation | Executable | ac4d87e771010698 cdc82116f289abfc f7d67027 |
5996c79fb52bde3f a10f77396654ae42 |
No | 6.2.9200.1 6384 (win8_rtm. 120725-124 7) |
6.2.9200.1 6384 |
United States |
| 18 | N/A | Non-executable | 8aa5e785a70f5ed8 b965199f63c14734 dc1c12bd |
576c909d59bebd50 c67e2b7f56df4832 |
No | N/A | N/A | United States |
| 19 | N/A | Non-executable | 0012b851539e0878 2ed8f75f786fac4f b94bcc64 |
9f5fcf40df077512 ff9fafb63a937c74 |
No | N/A | N/A | United States |
| 20 | N/A | Executable | 5284ad71acb6fbe8 b51271a14bda6f10 d83b949d |
b50c7453e0833663 e53105e9e92301b7 |
No | N/A | N/A | United States |
| 21 | Microsoft Corporation | Executable | 9305f79e08477d21 7bc990c23ed6f18d b1678d82 |
425d8dca76f63582 6acb8bfcb08a3c6c |
No | 10.0.19041 .1 (WinBuild. 160101.080 0) |
10.0.19041 .1 |
United States |
Prev123…6Next
Display 4 items per page
- 4 items per page
- 8 items per page
- 16 items per page
- 32 items per page
Начинающие пользователи компьютерных систем на основе Windows в большинстве своем об исполняемом файле cmd.exe и соответственно запускаемом приложении знают лишь понаслышке, считая, что данный процесс относится к чему-то из области фантастики. А на самом деле это такой мощный инструмент, знание команд которого позволяет исправлять практически неустранимые ошибки самих операционных систем, для которых стандартные инструменты и действия в самих ОС Windows оказываются совершенно недейственными.
cmd.exe: что это за служба?
Но давайте начнем с того, что же это за служба. Файл, расположенный по пути c:/Windows/System32/cmd.exe, отвечает за запуск так называемой командной строки (консоли), которая досталась Windows-системам еще от неиспользуемых сейчас систем DOS.
Но зачем разработчикам понадобилось включать в состав инструментария Windows еще и такую консоль? Дело в том, что даже основные методы объектно-ориентированного программирования на языках С+/С++ в полной мере, как оказывается, не позволяют использовать абсолютно все возможности системы, в частности, функции проверки системных компонентов, винчестеров, служб и т.д.
Как используется командная консоль?
Команд, которые могут вводиться в самой консоли, достаточно много, но знание полного перечня совершенно обязательным не является. По крайней мере, достаточно знать только основные. Скажем, в большинстве случаев можно использовать команды проверки диска вроде chkdsk и сканирования системных файлов с последующим восстановлением (sfc /scannow).
Отдельно стоит сказать о средствах восстановления системы онлайн – командах DISM. Попутно можно упомянуть средства выключения или принудительной перезагрузки любой компьютерной системы shutdown, средства создания логических разделов или съемных носителей с загрузочными записями diskpart.
А вообще, любая команда, вводимая в консоли cmd.exe, может использовать дополнительно множество атрибутов, которые прописываются через пробел и наклонную черту (или правый слэш). Увидеть всю информацию по каждому отлдельно взятому инструменту можно путем ввода в консоли названия основной команды со знаком вопроса (опять же, через слэш). Например, на интересует строка восстановления загрузки с применение инструмента Bootrec.exe. Вводите оригинальную команду таким образом: Bootrec.exe /?, после чего получаете список всех атрибутов. То же самое можно использовать и для всех остальных инструментов.
Ошибка cmd.exe: с чем связан сбой?
Что касается проблем с запуском командной консоли, по существу, можно выделить две основные: либо пользователь не имеет достаточных прав на исполнение запускаемого файла, либо система (и сам файл старт командной строки) была подвержена вирусному воздействию. В некоторых случаях возможна даже подмена оригинального системного компонента тем, который создает вирусный код в процессе своей деятельности или даже трансформации (некоторые вирусы способны создать собственные копии, маскируясь под системные процессы).
Простейший метод устранения проблемы
Выявить такие угрозы достаточно просто. Для этого нужно обратиться к «Диспетчеру задач» и посмотреть, есть ли в дереве процессов cmd.exe. Без вызова пользователем консоли такого процесса там быть не должно.
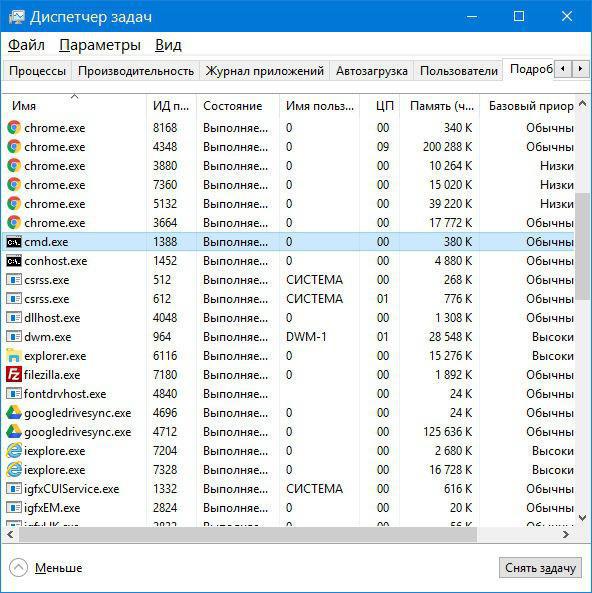
Если же командная строка запущена, а процессов насчитывается два и более (даже с одинаковыми атрибутами), используйте переход к расположению файла через меню ПКМ (оригинальный файл всегда располагается в директории System32).
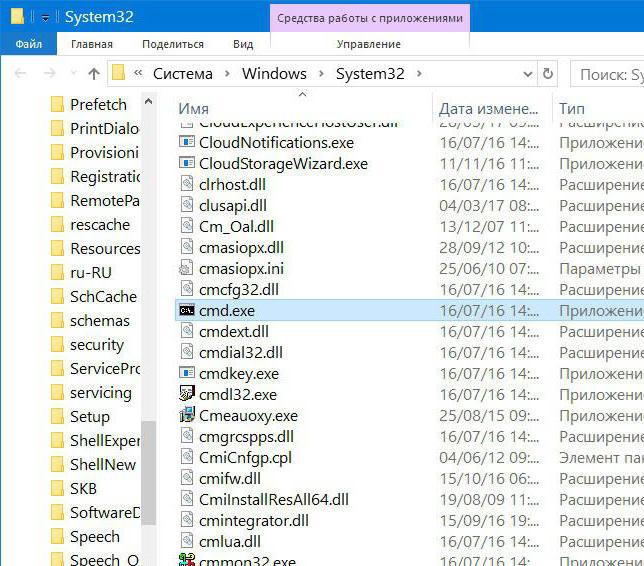
Но и сама служба может вызывать сбои, когда происходят нарушения в работе Windows на системном уровне. Первым решением проблемы станет вызов консоли от имени администратора.
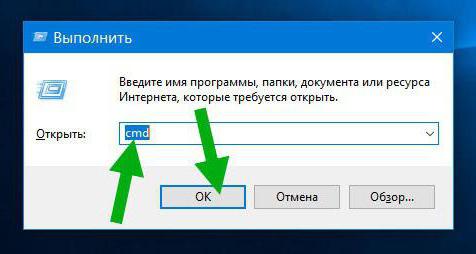
Если такой пункт в меню «Выполнить» отсутствует, найдите файл через «Проводник» и запустите его с соответствующими правами через ПКМ. Также можно использовать и загрузочные носители, в которых командная строка вызывается через сочетание Shift + F10. Но тут проблема в том, что произвести проверку можно, но не факт, что консоль при обычном старте или при загрузке в безопасном режиме будет работать.
Копирование компонента с установочного носителя или файла, загруженного из интернета, ничего не даст, поскольку изначально его нужно регистрировать, опять же, через консоль. Тут придется применять только старт со съемного носителя. Можно, конечно, использовать и удаленный редактор реестра, но лучше для начала проверить системные компоненты командой sfc /scannow, которая устраняет большинство проблем с системными файлами.
Что делать, если это вирус?
Теперь несколько слов о том, как удалить cmd.exe, если данный компонент является исполняемым вредоносным кодом. Как уже было сказано выше, после выявления файла в отличной от оригинальной локации, от него следует избавиться немедленно. Если будет выдан запрет на произведение каких бы то ни было действий, воспользуйтесь программами вроде Unlocker.
Если и это не поможет, запустите любой портативный сканер, а в результат поиска задайте нейтрализацию или удаление угрозы, которая соответствует названию cmd.exe. Иногда целесообразно задать лечение объекта, если программа сигнализирует о том, что это оригинальный файл, и находится он именно в той локации, которая была указана выше.
И еще один момент: о физическом удалении оригинального файла не может быть и речи. Во-первых, сама операционная система сделать этого не позволит, какие бы методы и ухищрения вы не применяли. Во-вторых, удаление этого компонента может привести только к тому, что сама операционная система перестанет работать.
