Тестовые задания для МДК
02.01 «Информационные технологии и платформы»
1)
Какой тег встраивает изображение в HTML страницу?
- TABLE
- ALIGN
- IMG
- ALT
2)
Какой тег не является тегом форматирования ТАБЛИЦЫ?
- TABLE
- TD
- HD
- COLSPAN
3)
Какие теги не содержат закрывающийся эквивалент?
- <TABLE>
- <IMG>
- <HEAD>
- <ТITLE>
4)
Что делает тег <U>
- Выделение полужирным
- Увеличение
кегля символов - Выделение
курсивом - Выделение
подчеркиванием
5)
Что делает тег <i>
- Выделение полужирным
- Увеличение
кегля символов - Выделение
курсивом - Выделение
подчеркиванием
6)
Что делает тег <b>
- Выделение полужирным
- Увеличение
кегля символов - Выделение
курсивом - Выделение
подчеркиванием
7)
Какой атрибут тега определяет ширину объекта?
- ROWS
- HEIGHT
- WIDTH
- RIGHT

Какой атрибут тега определяет высоту объекта?
- ROWS
- HEIGHT
- WIDTH
- RIGHT
9)
Какой параметр тега определяет цвет фона?
- BGCOLOR
- BODY LINK
- BODY TEXT
- BACKGROUND
10)
Где находится тег HEAD
- перед
<HTML> - внутри
<BODY> - внутри
<HTML> до <BODY> - внутри
<HTML> после <BODY>
11)
Какие теги могут находиться только внутри HEAD
- P, BR, HR
- OL, UL, LI
- META, TITLE
- SCRIPT,
OBJECT
12) Тег TITLE находится
- внутри HEAD
- между HEAD и BODY
- перед HEAD
- внутри BODY
13)
Внутри TITLE обычно находится
- набор
служебных символов - заголовок
страницы - заголовок
первого уровня - информация
об авторском праве (copyright)
14)
Тег <br> выполняет …
1. перевод
текста на новую станицу
2. окончание
работы с таблицей
3. перенос
строки в начало новой строки
4. окончание HTML страницы
15)
Тег <tr> используется …
1. в
таблицах
2. в
рисунках
3. в
гиперссылках
4. в
заголовках
16)
Какой тег из перечисленных не является обязательным для
создания Web страницы?
- HTML
- CAPTION
- HEAD
- BODY
17)
Код каждого HTML документа должен содержать тег
1. <HTML>
… </HTML>
2. <BODY>
… </BODY>
3. <FONT>
… </FONT>
4. <P>
… </P>
18) Какие из перечисленных графических форматов вы можете
использовать в HTML страничке?
1. MAX,FLA
2. GIF,JPEG
3. DOC,
TXT
4. EXL
19)
Какой тег является тегом перевода строки?
1. BR
2. TT
3. A
4. P
20)
Какой тег не является тегом форматирования текста?
1. B
2. TABLE
3. I
4. BIG
21)
Какой тег не является тегом организации СПИСКА?
1. UL
2. TYPE
3. OL
4. LI
22) Гиперссылки
на Web странице могут обеспечить переход…
- только
в пределах данной web страницы - только
на web страницы данного сервера - на
любую web страницу данного региона - на
любую web страницу любого сервера Интернет
23)
Между тегами <title> </ title > расположен текст, который
- отображает
информацию о самом документе - Отображается
в строке заголовка Web браузера - Идентификатор
перевода строки - Отображен на
самой Web странице
24)
Какие из нижеперечисленных программ используются для
создания Web страниц
- Блокнот и WordPad
- Turbo
Pascal и QBasic - Visual
Basic и ACDSee - ScanDisk и Defrag
25)
В атрибутах тега BODY нельзя задать
- цвет
фона - URL фонового
изображения - цвет
текста и гипертекстовых ссылок - размер
окна браузера
26)
Тег H2
- задает
заголовок второго уровня - должен
находиться внутри тега H1 - Отображаются
так же, как и обычный текст - Используется
для изменения цвета текста
27)
В таблице всегда используются теги
- TBODY и CAPTION
- TABLE и TR
- COL и
P - TITLE и А
28)
Тег A нужен для…
- создания
ссылок на другие страницы и сайты - выделения
текста синим - подчеркивания
фрагмента текста - выделения
ключевых слов на странице
29)
В теге A адрес (URL) перехода по гиперссылке задается с помощью атрибута
- type
- href
- name
- id
30)
Местонахождение изображения в теге IMG задается в значении
- атрибута src
- атрибута usemap
- атрибута alt
- текста
между <img> и </img >
31) Pазмер изображения
в теге IMG задается в значении
- атрибута src
- атрибута alt
- атрибутов height и width
- текста
между <img> и </img >
32) Web —
страница (документ HTML) представляет собой:
- Текстовый
файл с расширением txt или doc - Текстовый
файл с расширением htm или html - Двоичный
файл с расширением com или exe - Графический
файл с расширением gif или jpg
33)
Для просмотра Web — страниц в Windows по умолчанию
используются программы:
- MicroSoft Word или Word
Pad - MicroSoft Access
- Internet
Explorer - Блокнот или Front
Page
34)
Тег — это:
- Команды,
которые управляют отображением текста, но сами не отображаются - Текст,
в котором используются спецсимволы - Указатель
на другой файл или объект - Фрагмент
программы, включённой в состав Web страницы
35)
Тег <BODY> это:
- Идентификатор
заголовка окна просмотра - Идентификатор
заголовка документа HTML - Идентификатор
перевода строки - Идентификатор HTML команд документа для просмотра
36)
Между тегами <body> </body> расположен текст, который
- Отображает
информацию о самом документе - Отображается
в строке заголовка Web браузера - Идентификатор
перевода строки - Отображен на
самой Web странице
37)
Для вставки изображения в документ HTML используется тег вида:
- <img src=»ris.jpg»>
- <body
background=»ris.jpg»> - <a rel=»nofollow ugc» target=»_blank» href=»ris.jpg»>
- <input=»ris.jpg»>
38)
Гиперссылка задается тегом вида:
- <font color=»fil htm»>
- <img src=»http://www.chat.ru«>
- <a rel=»nofollow ugc» target=»_blank» href=»fil htm»>текст</a>
- <embed=»http://www.d ru»>
39)
Для создания заголовка Web страницы используется тэг:
1. <H1>…</H1>
2. <P>…</P>
3. <CAPTION>…</CAPTION>
4. <FONT>…</FONT>
40)
Какие теги способны изменить цвет фона документа?
- <HTML>
… </HTML> - <BODY>
… </BODY> - <FONT>
… </FONT> - <P>
… </P>
41)
Какие теги способны изменить цвет шрифта документа?
1. <HTML>
… </HTML>
2. <BODY>
… </BODY>
3. <FONT>
… </FONT>
4. <P>
… </P>
42)
Файл, содержащий внедренный в него вирус, называется …
1. зараженным
2. испорченным
3. вирусным
4. неправильным
43)
По разрушительным возможностям выделяют вирусы …
1. неопасные
2. информационные
3. архивные
4. программные
44)
По особенностям алгоритма выделяют вирусы …
1. троянские
2. сетевые
3. опасные
4. загрузочные
45)
Антивирусной программой является …
1. Kaspersky AntiVirus
2. Internet Explorer
3. Corel
Draw
4. Microsoft
Publisher
46)
В зависимости от принципа работы выделяют антивирусные программы …
1. редакторы
2. сканеры
3. макросы
4. базы
данных
47) Определяющим параметром эффективности работы антивирусной программы
является …
1. стабильность
и надежность работы
2. принцип
работы программы
3. фирма
— производитель
4. емкость,
занимаемая на диске антивирусной программы
48)
Редко используются антивирусные программы, называемые …
1. вакцинаторы (иммунизаторы)
2. фильтры
(сторожа)
3. ревизоры
(инспекторы)
4. доктора
(фаги)
49)
Наиболее распространены антивирусные программы: …
1. доктора
и фильтры
2. фильтры
и вакцинаторы
3. детекторы
и фаги
4. ревизоры
и детекторы
50)
Основным признаком появления вируса является …
1. некорректная
работа компьютера
2. невоспроизводимость мультимедиа
3. отсутствие
звука
4. невозможность
открытия файла
51)
Основным условием защиты от компьютерных вирусов является …
1. установка
на компьютере антивирусной программы
2. установка
на компьютере ОС Windows
3. отсутствие
Интернета
4. отсутствие
сканера
52) Что такое компьютерный вирус?
1) Прикладная
программа
2) Системная
программа
3) Программы,
которые могут «размножаться» и скрытно внедрять свои копии в файлы, загрузочные
секторы дисков и документы
4) База
данных
53) Завершите предложение, выбрав из предложенных
вариантов верный.
Основные типы компьютерных вирусов:
1) Аппаратные,
программные, загрузочные
2) Файловые,
загрузочные, макровирус, сетевые
3) Файловые,
программные, макровирусы
54) Какие существуют основные средства защиты от
компьютерных вирусов?
1) Резервное
копирование наиболее ценных данных
2) Аппаратные
средства
3) Программные
средства
55) На чем основано действие антивирусной программы?
1) На
ожидании начала вирусной атаки
2) На
сравнение программных кодов с известными вирусами
3) На
копировании зараженных файлов
56) Какие программы относятся к антивирусным?
1) AVP, DrWeb, Norton AntiVirus
2) MS-DOS,
MS Word, AVP
3) MS
Word, MS Excel, Norton Commander
57) Определите тип антивирусной программы. DrWeb относится:
1) Полифаги
2) Ревизоры
3) Блокировщики
4) Вакцины
58) Антивирусная программа, созданная в «Лаборатории Касперского»
относится к…….
1) Полифагам
2) Ревизорам
3) Блокировщикам
4) Вакцинам
59) По предложенному описанию определите тип вируса.
Заражают файлы документов Word и Excel.
Являются фактически макрокомандами, которые встраиваются в документ.
1) Файловые
вирусы
2) Загрузочные
вирусы
3) Сетевые
вирусы
4) Макровирусы
60) С
помощью электронной почты можно…
1. отправлять
сообщения
2. разговаривать
с собеседником
3. смотреть
видео
4. отправлять
файлы от 100 Гб
61)Гостевая
книга размещается …
1. На
некоторых сайтах по желанию владельца сайта
2. В Skype
3. На видеохостинге
4. В
информационно-поисковых системах
62) Блоггерами являются
пользователи…
1. постоянно
ведущие записи на каких-либо сайтах
2. использующие электронную
почту
3. выходящие
в социальные сети для общения
4. владельцы
Интернет – магазина
63)Социальные
сети используются для…
1. общения
людей
2. перевода
денег знакомым людям
3. создания
персональных сайтов
4. дистанционного
обучения
64)Комментарии
можно оставлять везде, кроме…
1. социальных
сетей
2. справочно-правовых
систем
3. сайтов
государственных служб
4. мобильных
банков
65)Выберите
сайт, не являющийся социальной сетью:
1. Одноклассники
2. Вконтакте
3. Яндекс
4. Faсebook
66)Чат
можно использовать в …
1. Вебинарах
2. Поисковых системах
3. Справочно-правовых системах
4. Новостных сайтах
67)Сайты каких
организаций не имеют отношение к медицине?
1. Министерство
здравоохранения Волгоградской области
2. Ассоциация
медицинских сестер Волгоградской области
3. Интернет- магазин Biglion
4. Сайт
медицинского университета
68)Дружественный
интерфейс определяет …
1. удобство
работы с меню и экранными формами
2. оснащенность
системой помощи и подсказками
3. возможность
добавления новых данных
4. использование
специальных средств настройки
69)Популярными
браузерами являются …
1. Microsoft Internet Explorer
2. Mozilla Firefox
3. Adobe Reader
4. Skype
70) Поисковыми системами в сети Интернет являются …
1. специальные web-узлы,
предназначенные для поиска информации
2. сайты
Министерства внутренних дел
3. информационные
ресурсы сети, связанные с базами данных организаций
4. Интернет-магазины
71)Владельцы
поисковых систем получают доходы …
1. от
рекламы, размещаемой на страницах портала
2. от
количества запрашиваемой информации
3. от
всех провайдеров данного региона
4. в
зависимости от релевантности информации
72)В
строку поиска информационно-поисковой системы вводится…
1. ключевое
слово или несколько слов
2. адрес
пользователя
3. IP-адрес
используемого компьютера
4. паспортные
данные пользователя
73)
Что предполагает семантическая паутина?
1. Отсутствие
рекламы
2. Строгую
цензуру сайтов
3. Улучшение связности и релевантности информации
4. Русификация
всего Интернета
74) Релевантность является …
1. мерой
соответствия результатам поиска
2. мерой
качества отображения информации на экране
3. средством
поиска информации
4. средством
беспроводной передачи данных
75) Поисковая система Яндекс позволяет находить
1. картинки
2. сообщения
в социальных сетях
3. паспортные
данные
4. счета
банковских карт
76) Поисковая система Яндекс содержит…
1. Список
пользователей
2. Карты
3. Skype
4. Облако
77) Что общего в интерфейсе всех поисковых систем?
1. поисковая
строка
2. название
сайта
3. строка
состояния
4. обзор
телепередач
78) На российском сегменте Интернета лучшей поисковой системой
считается…
1. Яндекс
2. Рамблер
3. Mail
4. Гарант
79)
На что указывает доменное имя?
1. На
страну или характер организации
2. На
владельца сайта
3. На
количество страниц сайта
4. На
технологию создания
80)
При построении беспроводных сетей используются следующие схемы
подключения: …
1. точка
— пользователь
2. точка
– точка доступа
3. топология
«звезда»
4. сервер
— терминал
81)
Преимуществами Wi – Fi технологии
являются …
1. построение
сети без прокладки кабеля
2. поддержка
роуминга
3. высокая
скорость передачи данных
4. низкое
потребление энергии
82)
Недостатками технологии Wi – Fi являются …
1. долговременное
обучение для использования
2. ограниченный
радиус действия (до 300 м)
3. высокая
цена
4. низкая
скорость передачи данных
83)
К беспроводным сетях относится…
1. технология Wi—Fi
2. банковская
сеть
3. сеть,
с выходом в Интернет через модем
4. сеть
крупного провайдера
84)
Технология Bluetooth применяется
в основном в…
1. сотовых телефонах
2. iPad
3. нетбуках
4. laptop
85)
Носителем информации в беспроводных сетях являются …
1. радиоволны
2. кабельные
соединения
3. перфокарты
4. бумага
86) Wi—Fi роутер
позволяет подключить…
1. Интернет
2. кабельное
телевидение
3. спутниковую
антенну
4. модем
87)
Какой радиуc действия охватывает Wi—Fi?
1. до
10 метров
2. до
100 метров
3. до
300 метров
4. до
1 километра
88)
Выберите язык программирования для создания Web-страниц.
1. JavaScript
2. TCP
3. E—mail
4. WORD
89)
Возможет ли беспарольный доступ в область Wi—Fi?
1. да,
если установлен режим беспарольного пользования
2. нет,
всегда нужен пароль
3. заранее
определить невозможно
4. да,
если три раза введен неверный пароль
90)Электронная
почта позволяет …
1. выполнять
обмен сообщениями в сети
2. просматривать web-страницы
3. искать
конфиденциальную информацию
4. создавать
сайты
91)Провайдер
предоставляет …
1. подключение
к сети Интернет
2. возможность
работы с прикладными программами
3. услугу
установки операционной системы
4. возможность
изменения тарифа сотовой связи
92)Браузером,
интегрированным в Windows,
является …
1. Internet
Explorer
2. Opera
3. Skype
4. Mozilla
Firefox
93)Выберите
протокол Интернета
1. HTTP
2. ISQ
3. OPERA
4. WINDOWS
94)Специально
созданный и свободно доступный web-узел,
основная функция которого состоит в поиске информации среди различных
информационных ресурсов сети Интернет, называется …
1. поисковым
сервером
2. порталом
3. доменом
4. URL адресом
95)Преимуществом
электронной почты является …
1. оптимально
используется рабочее время отправителя и получателя информации
2. возможность
подключения к Интернету
3. возможность
поиска информации
4. экономия
денежных средств
96)Услуга
Интернет – пейджинга ICQ является
…
1. средством
мгновенной передачи электронных сообщений по каналам сети
2. средством
передачи графических файлов
3. средством
поиска информации в сети Интернет
4. средством
электронной коммерции
97)Перспективой
развития Интернета является …
1. Семантическая
сеть
2. Паспортный
контроль
3. Только
англоязычные сайты
4. Возрастные
ограничения
98)
Что характеризует сервис WEB
2.0?
1. Использование
большого количества цветов
2. Объектно-ориентированный
интерфейс
3. Высокая
релевантность сайтов
4. Использование
гиперссылок
99)
Что является недостатком электронной почты?
1. Дополнительные
вложения
2. Передача
сообщения вне реального времени
3. Возможность
вирусной атаки
4. Быстрая
передача данных
100)
Что предполагает семантическая паутина?
5. Отсутствие
рекламы
6. Строгую
цензуру сайтов
7. Улучшение связности и релевантности информации
8. Русификация
всего Интернета
101) Для объединения двух локальных сетей используются
устройства …
1. мост
2. маршрутизатор
3. витая
пара
4. сетевой
фильтр
102) Более мощный компьютер в сети, обладающий дополнительными
ресурсами, называется…
1. сервером
2. терминалом
3. базой
данных
4. смартфоном
103) Для построения локальной сети используются топологии …
1. шина
2. Рунет
3. Интранет
4. колесо
104) Более мощный компьютер в сети, обладающий дополнительными
ресурсами, называется…
1. сервером
2. терминалом
3. базой
данных
4. смартфоном
105)
К ресурсам компьютерной локальной сети относятся…
5. программное
обеспечение
6. информация
для общего доступа
7. поисковая
система Яндекс
8. аудиосистема
106)
К характеристикам сети относится…
1. пропускная
способность
2. наличие web –
камеры
3. цвет
монитора рабочей станции
4. присутствие
администратора
107)
Для подключения стационарного компьютера к локальной сети необходим …
5. коммуникатор
6. сетевой
адаптер
7. принтер
8. модем
108)
Локальная сеть позволяет…
1. выходить
в Интернет
2. подключать
кабельное телевидение
3. снимать
деньги с банковских счетов
4. печатать
на плоттере, подключенном к этой сети
109)
Преимуществом локальной сети является…
1. возможность
совместного использования периферийного оборудования
2. безграничное
количество ПК, входящих в сеть
3. ограничение
территориального пространства до 100 м
4. зависимость
от сервера
110) В чем основное преимущество WEB 2.0
по сравнению с предыдущей технологией WEB 1.0?
1. В
предоставлении возможности пользователям активно размещать информацию в сети
2. В
предоставлении возможности пользователям бесплатно работать в Интернете
3. В
появлении звуковых и видео файлов
4. В
повышении релевантности искомой информации
Все способы:
- Закрепления сайтов на рабочем столе
- Инструменты для веб-разработчиков
- Do Not Track
- Просмотр в режиме совместимости
- Фильтр SmartScreen
- Преимущества Internet Explorer:
- Недостатки Internet Explorer:
- Скачать Internet Explorer
- Вопросы и ответы: 3
Internet Explorer — это стандартный браузер от компании Microsoft, интегрированные во все версии Windows. Он удобен в использовании, обладает простым и понятным интерфейсом, не грузит систему.
Система: Windows 7, 8, 8.1, 10, XP, Vista
Разработчик: Microsoft Corporation
Размер: 14 MB
Язык: Русский
Версия: 11.0.26
Internet Explorer (IE) 11 — это финальная версия встроенного браузера для ОС Windows. Этот патч веб-обозревателя IE во многом превосходит более ранние версии этого программного продукта, поэтому стоит более внимательно присмотреться к этому браузеру и оценить все его преимущества и недостатки.
IE 11 — современный, относительно быстрый веб-обозреватель, который поддерживает много новых стандартов и технологий. Он умеет работать с интернет-вкладками, блокировать нежелательные всплывающие окна и много другое. Далее речь пойдет о новых ключевых особенностях этого браузера
Закрепления сайтов на рабочем столе
В данной версии IE появилась возможности интегрировать любой сайт с рабочим столом ОС Windows. Это нововведение достаточно удобно, так как позволяет открывать часто используемые Интернет-ресурсы в новом окне браузера всего лишь за один клик на панели задач.
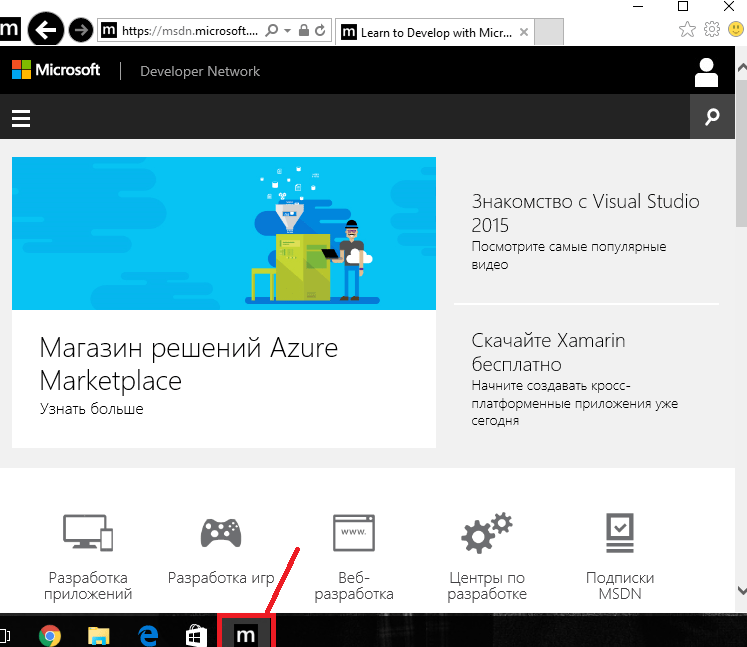
Инструменты для веб-разработчиков
Этот пункт будет интересен, тем кто занимается разработкой веб-страниц. Internet Explorer 11 предоставляет улучшенные инструменты разработчика F12, включая в новом патче функции для исправления багов пользовательского интерфейса, консоли, а также неплохой отладчик, эмулятор, средства профилирования памяти и инструменты для определения скорости отклика интерфейса пользователя.
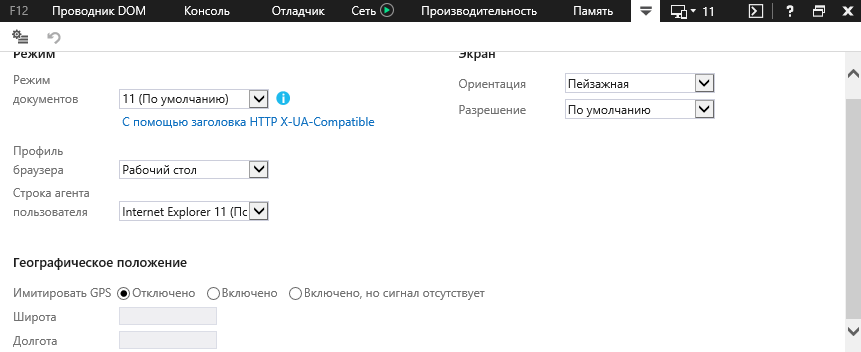
Do Not Track
IE 11 позволяет повысить конфиденциальность пользователя за счет функции «Do Not Track», которая предотвращает отправку сторонним поставщикам контента на посещаемых сайтах информации об отправленных на данную веб-страницу данных. То есть она, попросту говоря, блокирует содержимое сторонних поставщиков.
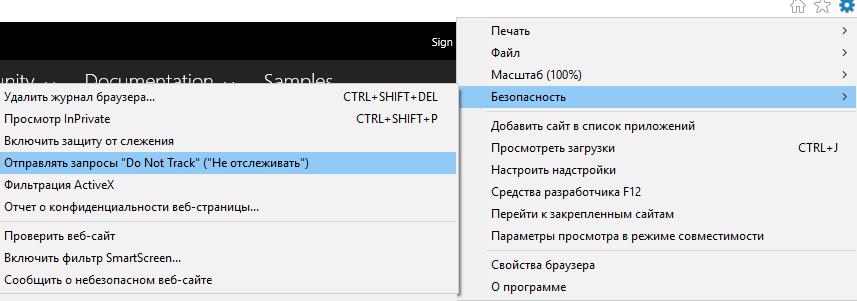
Просмотр в режиме совместимости
Перенастройка Internet Explorer 11 в режиме совместимости позволяет устранить проблему некорректного отображения веб-сайтов, например, растянутости изображений, хаотично разбросанного текста и тому подобное.
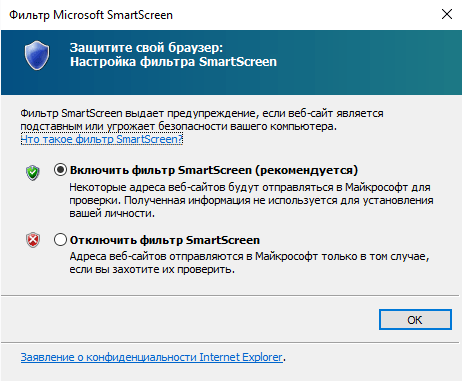
Фильтр SmartScreen
Фильтр SmartScreen предупреждает пользователя о скачивании потенциально опасных файлов с интернета. Он анализирует файлы на предмет количества скачиваний, и если количество скачиваний данного файла не велико, то он предупредит Вас о возможности угрозы. Также фильтр проверяет сайты, а потом сопоставляет их со списком фишинговых сайтов и, если такие сопоставления найдены, веб-ресурс будет заблокирован.
Преимущества Internet Explorer:
- Простота использования
- Русскоязычный интерфейс
- Поддержка горячих клавиш
- Удобный HTML редактор
- Работа с JavaScrip
- Поддержка горячих клавиш
- Поддержка Web Cryptography API
- Поддержка SPDY (протокола для передачи веб-контента)
Недостатки Internet Explorer:
- Ограничений набор расширений для браузера
В целом Internet Explorer 11 — это браузер с приятным интерфейсом, удобный в работе, поэтому стоит скачать бесплатно Интернет Эксплорер новой версии и самостоятельно оценить новые возможности этого веб-обозревателя.
Скачать Internet Explorer
Загрузить последнюю версию программы
Наша группа в TelegramПолезные советы и помощь
Почти каждый человек ежедневно открывает браузер на компьютере или смартфоне. Даже сейчас вы читаете эту статью с помощью одной из таких программ. При этом не всегда бывает понятно, какое ПО выбрать для личного использования и тем более — для веб-разработки. Чтобы вам было проще определиться, мы собрали топ браузеров, которые стоит использовать в 2025 году, а также кратко рассказали об особенностях программ в целом.
Что такое браузер и какие функции он выполняет
Для начинающих пользователей начнем с азов. Браузер — это специальная программа, которая позволяет просматривать страницы сайтов в интернете. Она обрабатывает код из сети и переводит его в элементы, удобные для восприятия. Кроме открывания вес-ресурсов, браузеры нужны, чтобы:
- Скачивать файлы на компьютер или мобильное устройство — от PDF-документа до видео 5K.
- Сохранять важную информацию, например, пароли, ссылки, историю посещенных страниц. Благодаря браузеру не придется вводить эти данные при каждом входе на сайт или оплате покупок на любимом маркетплейсе.
- Общаться с другими людьми в соцсетях, по электронной почте, на форумах и с помощью других инструментов.
- Защищать компьютер от вирусов в интернете.
Можно также выделить тысячи других задач — от обучения онлайн до просмотра фильмов. Но глобально функция браузера одна — предоставлять пользователю доступ к миллионам сайтов в интернете.
Из чего состоит браузер
У большинства современных браузеров есть несколько одинаковых базовых элементов:
- Пользовательский интерфейс. Простыми словами это окно, которое видит пользователь при запуске браузера.
- Движок браузера. Механизм, который преобразует содержимое веб-страниц в вид, удобный для восприятия пользователем.
- Движок рендеринга. Механизм, который отвечает за показ веб-страниц пользователю. Он визуализирует данные, полученные и преобразованные браузерным движком.
- Подсистема постоянного хранения данных. Предоставляет браузеру возможность сохранять данные, например, файлы cookie и закладки.
- Сетевая подсистема. Отвечает за безопасность пользователя в интернете и обработку запросов.
Это лишь основные составляющие современных браузеров. Однако ПО устроены сложнее и имеют намного больше элементов для корректной работы.
Какие элементы интерфейса важны для работы в браузере
Пользовательский интерфейс браузера включает несколько основных элементов, которые делают использование ПО проще и удобнее. Рассмотрим их на примере Google Chrome:
- Адресная строка. Поле в верхней центральной части, в которое можно ввести адрес сайта или поисковый запрос. Браузер отправит его на веб-сервер, и пользователь увидит ответ — страницу конкретного сайта или результаты выдачи.
- Кнопка «Остановить/перезагрузить» страницу. Позволяет обновить текущие данные или перезапустить страницу, если она некорректно отображается. При нажатии на кнопку браузер стирает кэш страницы и загружает его заново.
- Кнопки «Возврат к предыдущей странице» и «Переход к следующей странице». Первая нужна, чтобы загружать еще раз страницы, которые пользователь уже открывал в браузере. Вторая возвращает вперед вплоть до последней просмотренной страницы.
- Кнопка «Добавить в закладки». Позволяет сохранять страницы, которые пользователь открывает часто, для более быстрого доступа к ним. После добавления в закладки ссылка сохраняется в верхней центральной или правой боковой панели.
- Дополнения и расширения. Почти у каждого браузера есть магазин с дополнительными программами для более удобной работы. Например, чтобы блокировать навязчивую рекламу или скачивать видео из популярных видеохостингов.
- Настройки и дополнительные инструменты. Это элементы для управления браузером. Например, с их помощью получится изменить масштаб страницы, увидеть историю посещений, найти информацию на странице по ключевым словам или посмотреть загруженные файлы.
Как скачать и установить браузер
В установке браузера нет ничего сложного — с такой задачей справится даже ребенок. Рассмотрим поэтапно, как это сделать, на примере Google Chrome.
Любая операционная система по умолчанию имеет стандартный браузер. Например, в Windows это Microsoft Edge — обновленная версия знакомого многим Internet Explorer. Если хотите скачать Google Chrome, откройте Microsoft Edge и выполните несколько простых шагов:
- Откройте страницу загрузки Google Chrome и кликните на «Скачать Chrome». Также на странице есть QR-код для мобильной версии: отсканируйте его, если хотите установить браузер на смартфон.
- Когда файл скачается, кликните на него. Появится окно «Разрешить этому приложению вносить изменения на устройствах?». Нажмите «Да».
- Начнется установка. Когда она завершится, браузер Google Chrome откроется автоматически.
- Зайдите в настройки ПО и сделайте Google Chrome браузером по умолчанию. В таком случае все ссылки всегда будут открываться в этом обозревателе.
Какой браузер выбрать для работы и личного использования: рейтинг ПО
В интернете сотни браузеров, но далеко не все они удобные и безопасные. Мы собрали топ самых популярных обозревателей, которые подойдут и для серфинга в соцсетях, и для разработки сайтов.
Google Chrome
Браузер от корпорации Google является самым популярным для устройств на Android и Windows. Это первое ПО с поисковиком, интегрированным в адресную строку. То есть прямо в нее можно ввести любой запрос, и Google быстро подберет ответы.
Другие преимущества Google Chrome:
- возможность голосового ввода и качественное распознавание человеческой речи;
- мощная система защиты от фишинговых атак при посещении небезопасных сайтов;
- использование нескольких Google-аккаунтов параллельно;
- интегрированный диспетчер задач для анализа на ОЗУ, процессор и сеть;
- функция экономии памяти в режиме оптимизации производительности;
- технология изоляции процессов: если одна вкладка зависла, остальные продолжают работать нормально;
- большой магазин дополнений для любых задач.
Из минусов отмечают большое потребление оперативной памяти и отсутствие автоматической блокировки рекламы: для этого нужно установить дополнение из магазина.
Для программистов у Google Chrome есть Chrome DevTools — инструменты для разработки и настройки сайтов. Они позволяют просматривать исходный код страниц, отлаживать HTML, CSS и JavaScript, проверять скорость загрузки и сетевой трафик.
Яндекс Браузер
Не самый популярный в мире, но востребованный в России браузер от корпорации Яндекс. Показывает один из самых высоких показателей скорости загрузки страниц на ОС Windows 10 и 11.
Другие преимущества Яндекс Браузера:
- встроенный голосовой помощник Алиса, который ищет информацию в интернете, играет с пользователями, генерирует тексты;
- интеграция с YandexGPT и YandexART для работы с текстами и изображениями;
- быстрый перевод на русский и озвучка текстов на других языках;
- удобная боковая панель с приложениями: здесь можно разместить мессенджеры, сервисы Яндекса и сторонние ссылки для быстрого доступа;
- режим энергосбережения, благодаря которому ноутбук без питания работает примерно на один час дольше.
Из недостатков выделяют большое потребление системных ресурсов, привязку к сервисам Яндекса, которыми многие не пользуются, а также сбор информации о пользователях для показа рекламы.
Safari
В 2024 году Safari стал вторым по популярности браузером в мире сразу после Google Chrome. Это объясняется большим числом пользователей устройств Apple, ведь Safari создан специально для них. Раньше была версия и для Windows, но сейчас ее разработка и поддержка завершены.
Преимущества Safari:
- простой и интуитивно понятный интерфейс;
- быстрая скорость передачи серверных данных и практически моментальная загрузка страниц;
- закрытый исходный код, благодаря чему браузер обладает повышенным уровнем безопасности;
- технология Nitro Engine, с помощью которой можно ускорить скорость загрузки страниц;
- экономный расход заряда устройства;
- непрерывная работа при переключениях между устройствами;
- подгрузка шрифтов;
- предупреждение о возможной утечке данных.
Из недостатков Safari пользователи отмечают практически полное отсутствие дополнений.
Opera
Один из самых старых и известных браузеров в мире со встроенными инструментами для решения разных задач. Хотя Opera вышла еще в 1995 году, ПО постоянно обновляется согласно последним тенденциям. Например, современная версия поддерживает популярные криптокошельки.
Другие преимущества Opera:
- встроенный мессенджер Opera Flow, в котором удобно сохранять тексты, видео и иллюстрации, чтобы обмениваться файлами между своими устройствами;
- доступность не только для популярных, но и для редких операционных систем;
- удобное меню с гибкими настройками и возможностью отладить браузер под себя;
- режим Turbo для ускоренной загрузки страниц при низкой скорости интернета;
- функции экономии заряда в версиях для мобильных устройств и ноутбуков;
- встроенное антивирусное ПО, которое изучает ссылки на фишинг и шифрует персональные данные;
- магазин с большим количеством дополнений.
Главный недостаток Opera — медленная работа, если открыто много вкладок.
Mozilla Firefox
Еще один «ветеран» среди браузеров, который успешно конкурирует с современными программами. Отличается высокой скоростью загрузки, поэтому «Огненную лису» часто выбирают разработчики для создания ПО.
Другие преимущества Mozilla Firefox:
- совместимость с расширениями других браузеров, например, Google Chrome и Яндекс Браузера;
- высокий уровень приватности: Mozilla Firefox не собирает данные пользователей и не следит за ними;
- блокировка рекламы и потенциально опасного контента;
- быстрый перевод иностранного контента на русский язык.
Минусы — сложный интерфейс с большим количеством опций, нет поддержки Adobe Flash Player, небыстрый ответ на запросы
Есть специальная версия браузера для разработчиков — Firefox Developer Edition. Она включает инструменты и функции для создания и отладки сайтов.
Microsoft Edge
Microsoft Edge — встроенный браузер для устройств на Windows. Он не пользуется большой популярностью, но по сравнению со своим предшественником, Internet Explorer, быстрее загружает страницы и имеет приятный минималистичный дизайн.
Другие преимущества Microsoft Edge:
- инструменты для офисной работы, например, комментарии и заметки;
- возможность импортировать данные браузера в сервис Microsoft OneNote;
- функция вертикального расположения вкладок для экономии места и более простой работы;
- встроенный голосовой помощник с элементами искусственного интеллекта Cortana;
- удобный режим невидимости.
При этом есть и существенные минусы. Среди них — небольшое количество дополнений и сложности с синхронизацией. Многие пользователи отказываются от Microsoft Edge из-за навязывания со стороны Windows.
DuckDuckGo
ПО позиционирует себя как браузер для защиты личной жизни и приватности в интернете. Поэтому в DuckDuckGo не сохраняется история посещений, нет сбора данных и персонализированной рекламы.
Другие преимущества DuckDuckGo:
- возможность моментальной очистки всех данных и вкладок;
- перехват и удаление рекламы;
- улучшенное шифрование данных;
- простой и удобный интерфейс.
Из недостатков — отсутствие расширений и синхронизации.
Thorium
Этот браузер пользователи ценят за высокую скорость и минималистичное оформление. Его даже называют Google Chrome в облегченной версии.
Другие преимущества Thorium:
- высокая производительность;
- все функции Google Chrome;
- экспериментальные функции Google Chrome, которых еще нет в «основном» браузере;
- высокий уровень безопасности данных пользователей.
У некоторых пользователей возникают сложности с установкой и обновлением браузера.
Brave
Браузер для ежедневного использования понравится тем, у кого на первом месте — безопасность данных. Так, Brave по умолчанию блокирует рекламу на сайтах и трекеры.
Другие преимущества Brave:
- возможность открывать несколько окон в обычном режиме и режиме инкогнито;
- встроенный криптокошелек для покупки и безопасного хранения крипты;
- заработок за просмотр рекламы партнеров Brave;
- поддержка дополнений Google Chrome.
Основные недостатки — отсутствие синхронизации между разными устройствами, небольшое количество надстроек и скудный выбор тем.
В Brave можно посещать заблокированные сайты, что может быть полезно разработчику при выполнении некоторых задач.
Sizzy
Браузер для ускорения разработки ПО и повышения продуктивности этого процесса. У Sizzy много профессиональных инструментов, которых нет у других обозревателей.
Другие преимущества Sizzy:
- одновременное создание скриншотов на нескольких устройствах;
- встроенная функция Universal Inspect Element для анализа элемента на нескольких устройствах;
- проверка скорости загрузки в разных условиях;
- менеджер сессий, чтобы проще переключаться между пользователями.
Sizzy — платный браузер, но новые пользователи могут оформить пробный доступ ко всем функциям на две недели.
Polypane
Браузер, созданный специально для веб-разработчиков. При этом здесь есть все функции для повседневного использования, поэтому можно сказать, что Polypane — универсальный обозреватель.
Другие преимущества Polypane:
- создание и настройка сайта в нескольких окнах для разных типов устройств — от смартфонов до экранов с разрешением 5K;
- 80+ тестов доступности сайта;
- поддержка расширений популярных фреймворков;
- создание скриншотов в один клик.
Браузер Polypane можно пользоваться бесплатно. Однако для постоянного доступа к инструментам разработчика придется доплатить.
Atom
Завершает рейтинг браузер от разработчиков VK. В него уже встроены сервисы этой компании, например, плеер для прослушивания музыки.
Другие преимущества Atom:
- быстрая загрузка вкладок даже на низкой скорости;
- удобная система заметок: можно создавать их прямо на странице новой вкладки;
- большой выбор вариантов оформления главного экрана;
- Kaspersky Online File Reputation для безопасности данных;
- поддержка расширений Google Chrome.
Основной недостаток Atom — активный сбор персональных данных пользователей.
Современные браузеры: коротко о главном
- Браузер — специальная программа для просмотра сайтов в интернете. Обычно имеет понятный интерфейс, в котором быстро разберется любой человек.
- Один из самых популярных браузеров в мире — Google Chrome. В нем удобно выполнять практически любые задачи.
- Для профессиональной веб-разработки стоит выбрать обозреватель со специальными функциями для создания ПО или версию стандартного браузера с дополнениями.
Другие статьи по теме
- Кто такой веб-разработчик и чем он занимается?
- Совершенный код: 10 книг по веб-разработке для начинающих
- Как стать веб-разработчиком с нуля
Internet Explorer
|
Logo used since 2011 |
|
|
Screenshot of Internet Explorer 11 running on Windows 10, showing the Main Page of the English Wikipedia |
|
| Other names | Microsoft Internet Explorer (versions 1–6) Windows Internet Explorer (versions 7–9) IE |
|---|---|
| Original author(s) | Thomas Reardon |
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
| Initial release | August 24, 1995; 29 years ago[1] (included with Plus! for Windows 95) |
| Engines | MSHTML (Trident), Chakra |
| Operating system | Windows (previously supported: Mac OS X, Solaris, HP-UX) |
| Platform | IA-32, x86-64, ARMv7 (previously supported: MIPS, Alpha, PowerPC, 68k, SPARC, PA-RISC, Itanium) |
| Included with |
|
| Successor | Microsoft Edge |
| Standard(s) | HTML5, CSS3, WOFF, SVG, RSS, Atom, JPEG XR |
| Available in | 95 languages[2] |
| Type |
|
| License | Proprietary, requires a Windows license[3] |
| Website | microsoft |
Internet Explorer[a] (formerly Microsoft Internet Explorer[b] and Windows Internet Explorer,[c] commonly abbreviated as IE or MSIE) is a retired series of graphical web browsers developed by Microsoft that were used in the Windows line of operating systems. While IE has been discontinued on most Windows editions, it remains supported on certain editions of Windows, such as Windows 10 LTSB/LTSC.[4] Starting in 1995, it was first released as part of the add-on package Plus! for Windows 95 that year. Later versions were available as free downloads or in-service packs and included in the original equipment manufacturer (OEM) service releases of Windows 95 and later versions of Windows. Microsoft spent over US$100 million per year on Internet Explorer in the late 1990s,[5] with over 1,000 people involved in the project by 1999.[6][7] New feature development for the browser was discontinued in 2016[8] and ended support on June 15, 2022 for Windows 10 Semi-Annual Channel (SAC), in favor of its successor, Microsoft Edge.
Internet Explorer was once the most widely used web browser, attaining a peak of 95% usage share by 2003.[9] It has since fallen out of general use after retirement. This came after Microsoft used bundling to win the first browser war against Netscape, which was the dominant browser in the 1990s. Its usage share has since declined with the launches of Firefox (2004) and Google Chrome (2008) and with the growing popularity of mobile operating systems such as Android and iOS that do not support Internet Explorer. Microsoft Edge, IE’s successor, first overtook Internet Explorer in terms of market share in November 2019. Versions of Internet Explorer for other operating systems have also been produced, including an Xbox 360 version called Internet Explorer for Xbox and for platforms Microsoft no longer supports: Internet Explorer for Mac and Internet Explorer for UNIX (Solaris and HP-UX), and an embedded OEM version called Pocket Internet Explorer, later rebranded Internet Explorer Mobile, made for Windows CE, Windows Phone, and, previously, based on Internet Explorer 7, for Windows Phone 7.
The browser has been scrutinized throughout its development for its use of third-party technology (such as the source code of Spyglass Mosaic, used without royalty in early versions) and security and privacy vulnerabilities, and the United States and the European Union have determined that the integration of Internet Explorer with Windows has been to the detriment of fair browser competition.
The core of Internet Explorer 11 will continue being shipped and supported until at least 2029 as IE Mode, a feature of Microsoft Edge, enabling Edge to display web pages using Internet Explorer 11’s Trident layout engine and other components.[10] Through IE Mode, the underlying technology of Internet Explorer 11 partially exists on versions of Windows that do not support IE11 as a proper application, including newer versions of Windows 10, as well as Windows 11, Windows Server Insider Build 22463 and Windows Server Insider Build 25110.[11]
Internet Explorer 1
[edit]
The Internet Explorer project was started in the summer of 1994 by Thomas Reardon,[12] who, according to former project lead Ben Slivka,[13] used source code from Spyglass, Inc. Mosaic, which was an early commercial web browser with formal ties to the pioneering National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) Mosaic browser.[14][15] In late 1994, Microsoft licensed Spyglass Mosaic for a quarterly fee plus a percentage of Microsoft’s non-Windows revenues for the software.[15] Although bearing a name similar to NCSA Mosaic, Spyglass Mosaic had used the NCSA Mosaic source code sparingly.[16]
The first version, dubbed Microsoft Internet Explorer, was installed as part of the Internet Jumpstart Kit in the Microsoft Plus! pack for Windows 95.[17] The Internet Explorer team began with about six people in early development.[16][18] Internet Explorer 1.5 was released several months later for Windows NT and added support for basic table rendering. By including it free of charge with their operating system, they did not have to pay royalties to Spyglass Inc, resulting in a lawsuit and a US$8 million settlement on January 22, 1997.[14][15]
Microsoft was sued by SyNet Inc. in 1996, for trademark infringement, claiming it owned the rights to the name «Internet Explorer».[19] It ended with Microsoft paying $5 million to settle the lawsuit.[20]
Internet Explorer 2
[edit]
Internet Explorer 2 is the second major version of Internet Explorer, released on November 28, 1995, for Windows 95 and Windows NT, and on April 23, 1996, for Apple Macintosh[21] and Windows 3.1.[22]
Internet Explorer 3
[edit]
Internet Explorer 3 is the third major version of Internet Explorer, released on August 13, 1996, for Microsoft Windows and on January 8, 1997, for Apple Mac OS.
Internet Explorer 4
[edit]
Internet Explorer 4 is the fourth major version of Internet Explorer, released in September 1997 for Microsoft Windows, Mac OS, Solaris, and HP-UX. It was the first version of Internet Explorer to use the Trident web engine.
Internet Explorer 5
[edit]
Internet Explorer 5 is the fifth major version of Internet Explorer, released on March 18, 1999, for Windows 3.1, Windows NT 3, Windows 95, Windows NT 4.0 SP3, Windows 98, Mac OS X (up to v5.2.3), Classic Mac OS (up to v5.1.7), Solaris and HP-UX (up to 5.01 SP1).
Internet Explorer 6
[edit]
Internet Explorer 6 is the sixth major version of Internet Explorer, released on August 24, 2001, for Windows NT 4.0 SP6a, Windows 98, Windows 2000, Windows ME and as the default web browser for Windows XP and Windows Server 2003.
Internet Explorer 7
[edit]
Internet Explorer 7 is the seventh major version of Internet Explorer, released on October 18, 2006, for Windows XP SP2, Windows Server 2003 SP1 and as the default web browser for Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 and Windows Embedded POSReady 2009. IE7 introduces tabbed browsing.
Internet Explorer 8
[edit]
Internet Explorer 8 is the eighth major version of Internet Explorer, released on March 19, 2009, for Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 and as the default web browser for Windows 7 (later default was Internet Explorer 11) and Windows Server 2008 R2.
Internet Explorer 9
[edit]
Internet Explorer 9 is the ninth major version of Internet Explorer, released on March 14, 2011, for Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Vista Service Pack 2 and Windows Server 2008 SP2 with the Platform Update.
Internet Explorer 10
[edit]
Internet Explorer 10 is the tenth major version of Internet Explorer, released on October 26, 2012, and is the default web browser for Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012. It became available for Windows 7 SP1 and Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 in February 2013.
Internet Explorer 11
[edit]
Internet Explorer 11 is featured in Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows RT 8.1, which was released on October 17, 2013. It includes an incomplete mechanism for syncing tabs. It is a major update to its developer tools,[23][24] enhanced scaling for high DPI screens,[25] HTML5 prerender and prefetch,[26] hardware-accelerated JPEG decoding,[27] closed captioning, HTML5 full screen,[28] and is the first Internet Explorer to support WebGL[29][30][31] and Google’s protocol SPDY (starting at v3).[32] This version of IE has features dedicated to Windows 8.1, including cryptography (WebCrypto),[23] adaptive bitrate streaming (Media Source Extensions)[33] and Encrypted Media Extensions.[28]
Internet Explorer 11 was made available for Windows 7 users to download on November 7, 2013, with Automatic Updates in the following weeks.[34]
Internet Explorer 11’s user agent string now identifies the agent as «Trident» (the underlying browser engine) instead of «MSIE». It also announces compatibility with Gecko (the browser engine of Firefox).
Microsoft claimed that Internet Explorer 11, running the WebKit SunSpider JavaScript Benchmark, was the fastest browser as of October 15, 2013.[35]
Internet Explorer 11 was made available for Windows Server 2012 and Windows Embedded 8 Standard in April 2019.[36]
Microsoft Edge [Legacy] was officially unveiled on January 21, 2015, as «Project Spartan».[37][38] On April 29, 2015, Microsoft announced that Microsoft Edge would replace Internet Explorer as the default browser in Windows 10.[39] However, Internet Explorer remained the default web browser on the Windows 10 Long Term Servicing Channel (LTSC) and on Windows Server until 2021, primarily for enterprise purposes.[40][41][42][43]
Internet Explorer is still installed in Windows 10 to maintain compatibility with older websites and intranet sites that require ActiveX and other legacy web technologies.[37][38] The browser’s MSHTML rendering engine also remains for compatibility reasons.
Additionally, Microsoft Edge (Chromium) shipped with the «Internet Explorer mode» feature, which enables support for legacy internet applications. This is possible through use of the Trident MSHTML engine, the rendering code of Internet Explorer.[44][45] Microsoft has committed to supporting Internet Explorer mode at least through 2029, with a one-year notice before it is discontinued.[46]
With the release of Microsoft Edge [Legacy], the development of new features for Internet Explorer ceased. Internet Explorer 11 was the final release, and Microsoft began the process of deprecating Internet Explorer. During this process, it will still be maintained as part of Microsoft’s support policies.[8]
Since January 12, 2016, only the latest version of Internet Explorer available for each version of Windows has been supported.[47][48] At the time, nearly half of Internet Explorer users were using an unsupported version.[49]
In February 2019, Microsoft Chief of Security Chris Jackson recommended that users stop using Internet Explorer as their default browser.[50]
Various websites have dropped support for Internet Explorer. On June 1, 2020, the Internet Archive removed Internet Explorer from its list of supported browsers, due to the browser’s dated nature.[51] Since November 30, 2020, the web version of Microsoft Teams can no longer be accessed using Internet Explorer 11, followed by the remaining Microsoft 365 applications since August 17, 2021.[52][53] WordPress also dropped support for the browser in July 2021.[54]
Microsoft disabled the normal means of launching Internet Explorer in Windows 11 and later versions of Windows 10,[55] but it is still possible for users to launch the browser from the Control Panel’s browser toolbar settings or via PowerShell.[56]
On June 15, 2022, Internet Explorer 11 support ended for the Windows 10 Semi-Annual Channel (SAC). Users on these versions of Windows 10 were redirected to Microsoft Edge starting on February 14, 2023, and visual references to the browser (such as icons on the taskbar) would have been removed on June 13, 2023. However, on May 19, 2023, various organizations disapproved, leading Microsoft to withdraw the change.[57][58]
Other versions of Windows that were still supported at the time were unaffected. Specifically, Windows 7 ESU, Windows 8.x, Windows RT; Windows Server 2008/R2 ESU, Windows Server 2012/R2 and later; and Windows 10 LTSB/LTSC continued to receive updates until their respective end of life dates.[59][60][61][62]
On other versions of Windows, Internet Explorer will still be supported until their own end of support dates. IE7 was supported until October 10, 2023, alongside the end of support for Windows Embedded Compact 2013, while IE9 is supported until January 13, 2026, alongside the end of [paid and grandfathered] Premium Assurance support for customers on Windows Server 2008.[48] Barring additional changes to the support policy, Internet Explorer 11 will be supported until January 13, 2032, concurrent with the end of support for Windows 10 IoT Enterprise LTSC 2021.[63][48]
Internet Explorer has been designed to view a broad range of web pages and provide certain features within the operating system, including Microsoft Update. During the height of the browser wars, Internet Explorer superseded Netscape only when it caught up technologically to support the progressive features of the time.[65][better source needed]
Internet Explorer, using the MSHTML (Trident) browser engine:
- Supports HTML 4.01, parts of HTML5, CSS Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3, XML 1.0, and DOM Level 1, with minor implementation gaps.
- Fully supports XSLT 1.0 as well as an obsolete Microsoft dialect of XSLT often referred to as WD-xsl, which was loosely based on the December 1998 W3C Working Draft of XSL. Support for XSLT 2.0 lies in the future: semi-official Microsoft bloggers have indicated that development is underway, but no dates have been announced.
- Almost full conformance to CSS 2.1 has been added in the Internet Explorer 8 release.[66][67] The MSHTML browser engine in Internet Explorer 9 in 2011, scored highest in the official W3C conformance test suite for CSS 2.1 of all major browsers.
- Supports XHTML in Internet Explorer 9 (MSHTML Trident version 5.0). Prior versions can render XHTML documents authored with HTML compatibility principles and served with a
text/htmlMIME-type. - Supports a subset[68] of SVG in Internet Explorer 9 (MSHTML Trident version 5.0), excluding SMIL, SVG fonts and filters.
Internet Explorer uses DOCTYPE sniffing to choose between standards mode and a «quirks mode» in which it deliberately mimics nonstandard behaviors of old versions of MSIE for HTML and CSS rendering on screen (Internet Explorer always uses standards mode for printing). It also provides its own dialect of ECMAScript called JScript.
Internet Explorer was criticized by Tim Berners-Lee for its limited support for SVG, which is promoted by W3C.[69]
Non-standard extensions
[edit]
Internet Explorer has introduced an array of proprietary extensions to many of the standards, including HTML, CSS, and the DOM. This has resulted in several web pages that appear broken in standards-compliant web browsers and has introduced the need for a «quirks mode» to allow for rendering improper elements meant for Internet Explorer in these other browsers.
Internet Explorer has introduced several extensions to the DOM that have been adopted by other browsers.
These include the inner HTML property, which provides access to the HTML string within an element, which was part of IE 5 and was standardized as part of HTML 5 roughly 15 years later after all other browsers implemented it for compatibility,[70] the XMLHttpRequest object, which allows the sending of HTTP request and receiving of HTTP response, and may be used to perform AJAX, and the designMode attribute of the content Document object, which enables rich text editing of HTML documents.[citation needed] Some of these functionalities were not possible until the introduction of the W3C DOM methods. Its Ruby character extension to HTML is also accepted as a module in W3C XHTML 1.1, though it is not found in all versions of W3C HTML.
Microsoft submitted several other features of IE for consideration by the W3C for standardization. These include the ‘behavior’ CSS property, which connects the HTML elements with JScript behaviors (known as HTML Components, HTC), HTML+TIME profile, which adds timing and media synchronization support to HTML documents (similar to the W3C XHTML+SMIL), and the VML vector graphics file format. However, all were rejected, at least in their original forms; VML was subsequently combined with PGML (proposed by Adobe and Sun), resulting in the W3C-approved SVG format, one of the few vector image formats being used on the web, which IE did not support until version 9.[71]
Other non-standard behaviors include: support for vertical text, but in a syntax different from W3C CSS3 candidate recommendation, support for a variety of image effects[72] and page transitions, which are not found in W3C CSS, support for obfuscated script code, in particular JScript.Encode,[73] as well as support for embedding EOT fonts in web pages.[74]
Support for favicons was first added in Internet Explorer 5.[75] Internet Explorer supports favicons in PNG, static GIF and native Windows icon formats. In Windows Vista and later, Internet Explorer can display native Windows icons that have embedded PNG files.[76][77]
Usability and accessibility
[edit]
Internet Explorer makes use of the accessibility framework provided in Windows. Internet Explorer is also a user interface for FTP, with operations similar to Windows Explorer. Internet Explorer 5 and 6 had a side bar for web searches, enabling jumps through pages from results listed in the side bar.[78] Pop-up blocking and tabbed browsing were added respectively in Internet Explorer 6 and Internet Explorer 7. Tabbed browsing can also be added to older versions by installing MSN Search Toolbar or Yahoo Toolbar.
Internet Explorer caches visited content in the Temporary Internet Files folder to allow quicker access (or offline access) to previously visited pages. The content is indexed in a database file, known as Index.dat. Multiple Index.dat files exist which index different content—visited content, web feeds, visited URLs, cookies, etc.[79]
Prior to IE7, clearing the cache used to clear the index but the files themselves were not reliably removed, posing a potential security and privacy risk. In IE7 and later, when the cache is cleared, the cache files are more reliably removed, and the index.dat file is overwritten with null bytes.
Caching has been improved in IE9.[80]
Internet Explorer is fully configurable using Group Policy. Administrators of Windows Server domains (for domain-joined computers) or the local computer can apply and enforce a variety of settings on computers that affect the user interface (such as disabling menu items and individual configuration options), as well as underlying security features such as downloading of files, zone configuration, per-site settings, ActiveX control behavior and others. Policy settings can be configured for each user and for each machine. Internet Explorer also supports Integrated Windows Authentication.
Internet Explorer uses a componentized architecture built on the Component Object Model (COM) technology. It consists of several major components, each of which is contained in a separate dynamic-link library (DLL) and exposes a set of COM programming interfaces hosted by the Internet Explorer main executable, iexplore.exe:[81]
- WinInet.dll is the protocol handler for HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP. It handles all network communication over these protocols.
- URLMon.dll is responsible for MIME-type handling and download of web content, and provides a thread-safe wrapper around WinInet.dll and other protocol implementations.
- MSHTML.dll houses the MSHTML (Trident) browser engine introduced in Internet Explorer 4, which is responsible for displaying the pages on-screen and handling the Document Object Model (DOM) of the web pages. MSHTML.dll parses the HTML/CSS file and creates the internal DOM tree representation of it. It also exposes a set of APIs for runtime inspection and modification of the DOM tree. The DOM tree is further processed by a browser engine which then renders the internal representation on screen.
- IEFrame.dll contains the user interface and window of IE in Internet Explorer 7 and above.
- ShDocVw.dll provides the navigation, local caching and history functionalities for the browser.
- BrowseUI.dll is responsible for rendering the browser user interface such as menus and toolbars.[82]
Internet Explorer does not include any native scripting functionality. Rather, MSHTML.dll exposes an API that permits a programmer to develop a scripting environment to be plugged-in and to access the DOM tree. Internet Explorer 8 includes the bindings for the Active Scripting engine, which is a part of Microsoft Windows and allows any language implemented as an Active Scripting module to be used for client-side scripting. By default, only the JScript and VBScript modules are provided; third party implementations like ScreamingMonkey (for ECMAScript 4 support) can also be used. Microsoft also makes available the Microsoft Silverlight runtime that allows CLI languages, including DLR-based dynamic languages like IronPython and IronRuby, to be used for client-side scripting.
Internet Explorer 8 introduced some major architectural changes, called loosely coupled IE (LCIE). LCIE separates the main window process (frame process) from the processes hosting the different web applications in different tabs (tab processes). A frame process can create multiple tab processes, each of which can be of a different integrity level, each tab process can host multiple web sites. The processes use asynchronous inter-process communication to synchronize themselves. Generally, there will be a single frame process for all web sites. In Windows Vista with protected mode turned on, however, opening privileged content (such as local HTML pages) will create a new tab process as it will not be constrained by protected mode.[83]
Internet Explorer exposes a set of Component Object Model (COM) interfaces that allows add-ons to extend the functionality of the browser.[81] Extensibility is divided into two types: Browser extensibility and content extensibility. Browser extensibility involves adding context menu entries, toolbars, menu items or Browser Helper Objects (BHO). BHOs are used to extend the feature set of the browser, whereas the other extensibility options are used to expose that feature in the user interface. Content extensibility adds support for non-native content formats.[81] It allows Internet Explorer to handle new file formats and new protocols, e.g. WebM or SPDY.[81] In addition, web pages can integrate widgets known as ActiveX controls which run on Windows only but have vast potentials to extend the content capabilities; Adobe Flash Player and Microsoft Silverlight are examples.[81] Add-ons can be installed either locally, or directly by a web site.
Since malicious add-ons can compromise the security of a system, Internet Explorer implements several safeguards. Internet Explorer 6 with Service Pack 2 and later feature an Add-on Manager for enabling or disabling individual add-ons, complemented by a «No Add-Ons» mode. Starting with Windows Vista, Internet Explorer and its BHOs run with restricted privileges and are isolated from the rest of the system. Internet Explorer 9 introduced a new component – Add-on Performance Advisor. Add-on Performance Advisor shows a notification when one or more of installed add-ons exceed a pre-set performance threshold. The notification appears in the Notification Bar when the user launches the browser. Windows 8 and Windows RT introduce a Metro-style version of Internet Explorer that is entirely sandboxed and does not run add-ons at all.[84] In addition, Windows RT cannot download or install ActiveX controls at all; although existing ones bundled with Windows RT still run in the traditional version of Internet Explorer.[84]
Internet Explorer itself can be hosted by other applications via a set of COM interfaces. This can be used to embed the browser functionality inside a computer program or create Internet Explorer shells.[81]
Internet Explorer uses a zone-based security framework that groups sites based on certain conditions, including whether it is an Internet- or intranet-based site as well as a user-editable whitelist. Security restrictions are applied per zone; all the sites in a zone are subject to the restrictions.
Internet Explorer 6 SP2 onwards uses the Attachment Execution Service of Microsoft Windows to mark executable files downloaded from the Internet as being potentially unsafe. Accessing files marked as such will prompt the user to make an explicit trust decision to execute the file, as executables originating from the Internet can be potentially unsafe. This helps in preventing the accidental installation of malware.
Internet Explorer 7 introduced the phishing filter, which restricts access to phishing sites unless the user overrides the decision. With version 8, it also blocks access to sites known to host malware. Downloads are also checked to see if they are known to be malware-infected.
In Windows Vista, Internet Explorer by default runs in what is called Protected Mode, where the privileges of the browser itself are severely restricted—it cannot make any system-wide changes. One can optionally turn this mode off, but this is not recommended. This also effectively restricts the privileges of any add-ons. As a result, even if the browser or any add-on is compromised, the damage the security breach can cause is limited.
Patches and updates to the browser are released periodically and made available through the Windows Update service, as well as through Automatic Updates. Although security patches continue to be released for a range of platforms, most feature additions and security infrastructure improvements are only made available on operating systems that are in Microsoft’s mainstream support phase.
On December 16, 2008, Trend Micro recommended users switch to rival browsers until an emergency patch was released to fix a potential security risk which «could allow outside users to take control of a person’s computer and steal their passwords.» Microsoft representatives countered this recommendation, claiming that «0.02% of internet sites» were affected by the flaw. A fix for the issue was released the following day with the Security Update for Internet Explorer KB960714, on Microsoft Windows Update.[85][86]
In 2010, Germany’s Federal Office for Information Security, known by its German initials, BSI, advised «temporary use of alternative browsers» because of a «critical security hole» in Microsoft’s software that could allow hackers to remotely plant and run malicious code on Windows PCs.[87]
In 2011, a report by Accuvant, funded by Google, rated the security (based on sandboxing) of Internet Explorer worse than Google Chrome but better than Mozilla Firefox.[88][89]
A 2017 browser security white paper comparing Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge [Legacy], and Internet Explorer 11 by X41 D-Sec in 2017 came to similar conclusions, also based on sandboxing and support of legacy web technologies.[90]
Security vulnerabilities
[edit]
Internet Explorer has been subjected to many security vulnerabilities and concerns such that the volume of criticism for IE is unusually high. Much of the spyware, adware, and computer viruses across the Internet are made possible by exploitable bugs and flaws in the security architecture of Internet Explorer, sometimes requiring nothing more than viewing of a malicious web page to install themselves. This is known as a «drive-by install». There are also attempts to trick the user into installing malicious software by misrepresenting the software’s true purpose in the description section of an ActiveX security alert.
A number of security flaws affecting IE originated not in the browser itself, but in ActiveX-based add-ons used by it. Because the add-ons have the same privilege as IE, the flaws can be as critical as browser flaws. This has led to the ActiveX-based architecture being criticized for being fault-prone. By 2005, some experts maintained that the dangers of ActiveX had been overstated and there were safeguards in place.[91] In 2006, new techniques using automated testing found more than a hundred vulnerabilities in standard Microsoft ActiveX components.[92] Security features introduced in Internet Explorer 7 mitigated some of these vulnerabilities.
In 2008, Internet Explorer had a number of published security vulnerabilities. According to research done by security research firm Secunia, Microsoft did not respond as quickly as its competitors in fixing security holes and making patches available.[93] The firm also reported 366 vulnerabilities in ActiveX controls, an increase from the previous year.
According to an October 2010 report in The Register, researcher Chris Evans had detected a known security vulnerability which, then dating back to 2008, had not been fixed for at least six hundred days.[94] Microsoft says that it had known about this vulnerability, but it was of exceptionally low severity as the victim web site must be configured in a peculiar way for this attack to be feasible at all.[95]
In December 2010, researchers were able to bypass the «Protected Mode» feature in Internet Explorer.[96]
Vulnerability exploited in attacks on U.S. firms
[edit]
In an advisory on January 14, 2010, Microsoft said that attackers targeting Google and other U.S. companies used software that exploits a security hole, which had already been patched, in Internet Explorer. The vulnerability affected Internet Explorer 6 from on Windows XP and Server 2003, IE6 SP1 on Windows 2000 SP4, IE7 on Windows Vista, XP, Server 2008, and Server 2003, IE8 on Windows 7, Vista, XP, Server 2003, and Server 2008 (R2).[97]
The German government warned users against using Internet Explorer and recommended switching to an alternative web browser, due to the major security hole described above that was exploited in Internet Explorer.[98] The Australian and French governments also issued a similar warning a few days later.[99][100][101][102]
Major vulnerability across versions
[edit]
On April 26, 2014, Microsoft issued a security advisory relating to CVE-2014-1776 (use-after-free vulnerability in Microsoft Internet Explorer 6 through 11[103]), a vulnerability that could allow «remote code execution» in Internet Explorer versions 6 to 11.[104] On April 28, 2014, the United States Department of Homeland Security’s United States Computer Emergency Readiness Team (US-CERT) released an advisory stating that the vulnerability could result in «the complete compromise» of an affected system.[105] US-CERT recommended reviewing Microsoft’s suggestions to mitigate an attack or using an alternate browser until the bug is fixed.[106][107] The UK National Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-UK) published an advisory announcing similar concerns and for users to take the additional step of ensuring their antivirus software is up to date.[108] Symantec, a cyber security firm, confirmed that «the vulnerability crashes Internet Explorer on Windows XP.»[109] The vulnerability was resolved on May 1, 2014, with a security update.[110]
The adoption rate of Internet Explorer seems to be closely related to that of Microsoft Windows, as it is the default web browser that comes with Windows. Since the integration of Internet Explorer 2.0 with Windows 95 OSR 1 in 1996, and especially after version 4.0’s release in 1997, the adoption was greatly accelerated: from below 20% in 1996, to about 40% in 1998, and over 80% in 2000. This made Microsoft the winner in the infamous ‘first browser war’ against Netscape. Netscape Navigator was the dominant browser during 1995 and until 1997, but rapidly lost share to IE starting in 1998, and eventually slipped behind in 1999. The integration of IE with Windows led to a lawsuit by AOL, Netscape’s owner, accusing Microsoft of unfair competition. The infamous case was eventually won by AOL but by then it was too late, as Internet Explorer had already become the dominant browser.
Internet Explorer peaked during 2002 and 2003, with about 95% share. Its first notable competitor after beating Netscape was Firefox from Mozilla, which itself was an offshoot from Netscape.
Approximate usage over time based on various usage share counters averaged for the year overall, or for the fourth quarter, or for the last month in the year depending on availability of reference.[111][112][113][114][115][116]
Internet Explorer’s market share fell below 50% in September 2010.[117] In May 2012, Google Chrome overtook Internet Explorer as the most used browser worldwide, according to StatCounter.[118]
Browser Helper Objects are also used by many search engines companies and third parties for creating add-ons that access their services, such as search engine toolbars. Because of the use of COM, it is possible to embed web-browsing functionality in third-party applications. Hence, there are several Internet Explorer shells, and several content-centric applications like RealPlayer also use Internet Explorer’s web browsing module for viewing web pages within the applications.
While a major upgrade of Internet Explorer can be uninstalled in a traditional way if the user has saved the original application files for installation, the matter of uninstalling the version of the browser that has shipped with an operating system remains a controversial one.
The idea of removing a stock install of Internet Explorer from a Windows system was proposed during the United States v. Microsoft Corp. case. One of Microsoft’s arguments during the trial was that removing Internet Explorer from Windows may result in system instability. Indeed, programs that depend on libraries installed by IE, including Windows help and support system, fail to function without IE. Before Windows Vista, it was not possible to run Windows Update without IE because the service used ActiveX technology, which no other web browser supports.[119][120]
Impersonation by malware
[edit]
The popularity of Internet Explorer led to the appearance of malware abusing its name. On January 28, 2011, a fake Internet Explorer browser calling itself «Internet Explorer – Emergency Mode» appeared. It closely resembled the real Internet Explorer but had fewer buttons and no search bar. If a user attempted to launch any other browser such as Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Opera, Safari, or the real Internet Explorer, this browser would be loaded instead. It also displayed a fake error message, claiming that the computer was infected with malware and Internet Explorer had entered «Emergency Mode». It blocked access to legitimate sites such as Google if the user tried to access them.[121][122]
- Bing Bar
- History of the web browser
- List of web browsers
- Month of bugs
- Web 2.0
- Windows Filtering Platform
- Winsock
- ^ Since versions 10–11
- ^ In versions 1–6
- ^ In versions 7–9
- ^ «The History of Internet Explorer». News Center. Microsoft. August 25, 2005. Archived from the original on October 1, 2005.
- ^ «Internet Explorer 10 for Windows 7 released in 95 languages – Microsoft Language Portal Blog». blogs.technet.microsoft.com. August 28, 2023.
- ^ «Microsoft Pre-Release Software License Terms: Internet Explorer 11 Developer Preview». microsoft.com. Microsoft. Retrieved July 27, 2013.
- ^ «Internet Explorer 11 desktop app retirement FAQ». TECHCOMMUNITY.MICROSOFT.COM. May 19, 2021. Retrieved February 20, 2023.
- ^ «Victor: Software empire pays high price». CNET News. Archived from the original on February 21, 2021. Retrieved October 17, 2008.
- ^ «The rise, fall, and rehabilitation of Internet Explorer». citeworld.com. Archived from the original on June 26, 2015. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ Paul Maritz. «U.S. Antitrust Case 98-1232». justice.gov. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
There is talk about how we get more $’s from the 1000+ people we have working on browser related stuff…
- ^ a b «Frequently Asked Questions». Microsoft Edge Development. Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 16, 2016.
The latest features and platform updates will only be available in Microsoft Edge. We will continue to deliver security updates to Internet Explorer 11 through its supported lifespan. To ensure consistent behavior across Windows versions, we will evaluate Internet Explorer 11 bugs for servicing on a case by case basis.
- ^ «Microsoft’s Internet Explorer losing browser share». BBC News.
- ^ «What is Internet Explorer (IE) mode?». March 2, 2022. Archived from the original on June 13, 2022. Retrieved June 13, 2022.
- ^ Tom Warren (June 25, 2021). «Windows 11 is deleting Internet Explorer». The Verge. Retrieved August 12, 2021.
- ^ «Thomas Reardon, 34». MIT Technology Review. Archived from the original on February 25, 2021. Retrieved January 18, 2015.
- ^ «Internet Explorer: A Brief History [6/2022 update]». Ben Slivka. May 28, 2021. Archived from the original on June 22, 2022. Retrieved August 7, 2023.
- ^ a b Elstrom, Peter (January 22, 1997). «Microsoft’s $8 Million Goodbye to Spyglass». Businessweek. Bloomberg L.P. Archived from the original on June 29, 1997. Retrieved February 9, 2011.
- ^ a b c Thurrott, Paul (January 22, 1997). «Microsoft and Spyglass kiss and make up». IT Pro. Penton. Archived from the original on September 19, 2012. Retrieved February 9, 2011.
- ^ a b «Memoirs From the Browser Wars». Ericsink.com. Retrieved October 17, 2008.
- ^ «The History of Internet Explorer». Microsoft. Archived from the original on October 1, 2005. Retrieved February 16, 2008.
- ^ Borland, John (April 15, 2003). «Software empire pays high price». CNET News. CBS Interactive. Retrieved February 9, 2011.
- ^ Goodwins, Rupert (August 15, 1996). «Microsoft sued by minnow over Internet Explorer name». ZDNet. Archived from the original on January 1, 2016. Retrieved May 30, 2022.
- ^ «Microsoft Settles ‘IE’ Suit For $5M». www.cbsnews.com. July 2, 1998. Retrieved February 5, 2022.
- ^ «Chronology of Personal Computers (1996)». www.islandnet.com. Retrieved November 27, 2024.
- ^ «Microsoft Internet Explorer Web Browser Available on All Major Platforms, Offers Broadest International Support». Stories. April 30, 1996. Retrieved February 5, 2022.
- ^ a b Thurrott, Paul (July 25, 2013). «Internet Explorer 11 Developer Preview for Windows 7». Paul Thurrott’s SuperSite for Windows. Penton. Archived from the original on July 26, 2013. Retrieved July 26, 2013.
- ^ «What’s new in F12 Tools (Preliminary)». MSDN. Microsoft. June 26, 2013. Retrieved July 13, 2013.
- ^ «High DPI support (Preliminary)». MSDN. Microsoft. July 25, 2013. Retrieved July 26, 2013.
- ^ «Prerender and prefetch support (Preliminary)». MSDN. Microsoft. July 25, 2013. Retrieved July 26, 2013.
- ^ Bradley, Tony (July 26, 2013). «Why Internet Explorer 11 is the right browser for business». PC World. IDG. Retrieved July 27, 2013.
- ^ a b Brinkmann, Martin (July 25, 2013). «The Internet Explorer 11 Preview for Windows 7 is now available». Ghacks.net. ghacks Technology News. Archived from the original on July 27, 2013. Retrieved July 27, 2013.
- ^ «Latest Windows 8.1 build beefs up IE developer tools». CNET. CBS Interactive. Retrieved May 29, 2013.
- ^ «Microsoft teases Internet Explorer 11 WebGL support on Vine». The Verge. May 22, 2013. Retrieved May 29, 2013.
- ^ «WebGL (Preliminary)». MSDN. Microsoft. July 25, 2013. Retrieved July 26, 2013.
- ^ Lardinois, Frederic (June 26, 2013). «Microsoft Confirms IE11 Will Support Google’s SPDY Protocol». TechCrunch. Aol. Retrieved September 10, 2013.
- ^ Williams, Mike (July 26, 2013). «Internet Explorer 11 Developer Preview now available for Windows 7». BetaNews. BetaNews, Inc. Retrieved July 27, 2013.
- ^ «IE11 for Windows 7 Globally Available for Consumers and Businesses». Retrieved November 8, 2013.
- ^ «WebKit SunSpider JavaScript Benchmark Results». ie.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on October 23, 2013. Retrieved October 23, 2013.
- ^ «Bringing Internet Explorer 11 to Windows Server 2012 and Windows Embedded 8 Standard». January 28, 2019. Retrieved March 26, 2019.
- ^ a b Weber, Jason (January 21, 2015). «Spartan and the Windows 10 January Preview Build». IEBlog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 22, 2015.
- ^ a b Warren, Tom (January 27, 2015). «Microsoft reveals its Internet Explorer successor will support extensions». The Verge. Vox Media.
- ^ Goldman, David (April 29, 2015). «‘Microsoft Edge’ will replace Internet Explorer». CNN. Retrieved January 3, 2023.
- ^ «Microsoft is killing off the Internet Explorer brand». The Verge. Vox Media. March 17, 2015. Retrieved March 18, 2015.
- ^ «What’s new in the Windows Server 2019 Insider Preview Builds». docs.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on December 10, 2019. Retrieved February 12, 2019.
- ^ «What’s new in Windows 10 Enterprise LTSC 2021». Microsoft. December 9, 2022. Retrieved January 3, 2023.
- ^ «What’s new in Windows Server 2022». Microsoft. December 14, 2022. Retrieved January 3, 2023.
- ^ «What is Internet Explorer mode?». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved October 12, 2021.
- ^ Blog, Windows Experience (May 19, 2021). «The future of Internet Explorer on Windows 10 is in Microsoft Edge». Windows Experience Blog. Retrieved May 20, 2021.
- ^ «Lifecycle FAQ — Internet Explorer and Microsoft Edge». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved October 12, 2021.
- ^ «Stay up-to-date with Internet Explorer». Microsofts’s MSDN blog. August 7, 2014. Archived from the original on August 8, 2014. Retrieved January 3, 2023.
- ^ a b c «Internet Explorer Support Lifecycle Policy FAQ». Retrieved March 18, 2015.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg (December 1, 2015). «Nearly 370M IE users have just 6 weeks to upgrade». Computerworld. Retrieved January 3, 2023.
- ^ Jackson, Chris (February 6, 2019). «The perils of using Internet Explorer as your default browser». Windows IT Pro Blog. Microsoft. Retrieved May 14, 2020.
- ^ «Farewell to IE11». Internet Archive Blogs. Internet Archive. May 1, 2020. Retrieved May 14, 2020.
- ^ «Microsoft Internet Explorer is finally dead». The Independent. August 20, 2020. Retrieved March 26, 2021.
- ^ «Microsoft 365 apps say farewell to Internet Explorer 11 and Windows 10 sunsets Microsoft Edge Legacy». Retrieved September 18, 2020.
- ^ Desrosiers, Jonathan (May 19, 2021). «Dropping support for Internet Explorer 11». WordPress. Retrieved January 3, 2023.
- ^ «Internet Explorer 11 desktop app retirement FAQ». Retrieved November 13, 2023.
- ^ Warren, Tom (August 3, 2022). «You can bring Internet Explorer back to life in Windows 11 if you’re a glutton for punishment». theverge.com. Vox Media, LLC. Retrieved October 22, 2022.
It’s just a matter of searching for Internet Options in the Start menu, launching the control panel applet, selecting the programs tab, hitting «manage add-ons,» and then clicking the «Learn more about toolbars and extensions.» For some reason, this launches Internet Explorer, bypassing the commands that force you into Edge.
- ^ «Lifecycle FAQ — Internet Explorer and Microsoft Edge». November 3, 2021. Archived from the original on June 13, 2022. Retrieved June 13, 2022.
- ^ «Internet Explorer 11 desktop app retirement FAQ». Microsoft. June 13, 2022. Archived from the original on June 13, 2022. Retrieved June 13, 2022.
- ^ «Internet Explorer 11 desktop app retirement FAQ». TECHCOMMUNITY.MICROSOFT.COM. May 19, 2021. Retrieved June 15, 2022.
- ^ Taylor, Josh (June 15, 2022). «Microsoft to retire Internet Explorer browser and redirect users to Edge». The Guardian.
- ^ «Lifecycle FAQ — Internet Explorer and Microsoft Edge». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved July 10, 2021.
- ^ «Microsoft is finally getting rid of its most-hated product». CNN. May 20, 2021. Retrieved May 20, 2021.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT Enterprise LTSC 2021». Microsoft. Retrieved January 3, 2023.
- ^ «How to set the zoom level in Internet Explorer 9 — Browsers». docs.microsoft.com. January 25, 2022.
You can zoom from 10% to 1,000%.
- ^ Brian wilson. «Netscape Navigator — Browser History: Netscape explains that by the fourth generations of both browsers, Internet Explorer had caught up technologically with Netscape’s browser … Netscape 6.0 was considered slow and buggy, and adoption was slow to occur». blooberry.com. Retrieved September 26, 2010.
- ^ «Internet Explorer 8 Beta 1 Whitepapers». MSDN. Archived from the original on March 9, 2008. Retrieved March 11, 2008.
- ^ Hopkins, James. «IE8 Bugs». Archived from the original on August 1, 2009.
- ^ «Summary results of W3C test suite on multiple browsers, different versions and browser plugins». Retrieved April 15, 2011.
- ^ Svensson, Peter (September 10, 2008). «Creator of Web spots a flaw in Internet Explorer». NBC News. Retrieved November 16, 2008.
- ^ «innerHTML and compatibility». www.xul.fr.
- ^ Schiller, Jeff. «SVG Support Tables». codedread.com. Retrieved April 20, 2019.
- ^ «Filter Tool (WebFX)». webfx.eae.net. May 12, 2005. Archived from the original on October 16, 2010. Retrieved October 4, 2008.
- ^ «Using Script Encoder». Microsoft Docs. Microsoft. October 24, 2011. Retrieved April 20, 2019.
- ^ «Font Embedding for the Web». Microsoft Typography. Microsoft. February 26, 2001. Archived from the original on April 28, 2005. Retrieved April 20, 2019.
- ^ «How to Add a Shortcut Icon to a Web Page». MSDN. Microsoft. Archived from the original on December 17, 2008. Retrieved April 20, 2019.
- ^ Davis, Jeff (December 27, 2007). «why doesn’t the favicon for my site appear in IE7?». jeffdav on code. Retrieved March 11, 2013.
- ^ «Fun with Favicons». Microsoft Developer Network. Microsoft. September 7, 2013. Retrieved April 20, 2019.
- ^ Shultz, Greg (October 9, 2002). «Internet Explorer’s Search Assistant gives you plenty of search options». Tech Republic. Retrieved October 11, 2021.
- ^ Windows Core Networking Team (August 4, 2006). «A bit about WinInet’s Index.dat». Microsoft Developer Network. Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 12, 2008. Retrieved April 20, 2019.
- ^ «Internet Explorer 9 Network Performance Improvements». Microsoft Developer Network. Microsoft. March 17, 2011. Retrieved April 20, 2019.
- ^ a b c d e f «Internet Explorer Architecture». MSDN. Retrieved January 10, 2007.
- ^ Wilson, Chris. «Inside IE8 Beta 1 for Developers». MSDN Channel9. Retrieved March 7, 2008.
- ^ Zeigler, Andy (March 11, 2008). «IE8 and Loosely Coupled IE». Microsoft Developer Network. Microsoft. Retrieved April 20, 2019.
- ^ a b McSherry, Tony (January 20, 2013). «A look at Internet Explorer 10 on Windows RT». TechRepublic. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on February 4, 2023.
- ^ «Security risk detected in Internet Explorer software». Belfast Telegraph. December 16, 2008. Archived from the original on January 27, 2009.
- ^ «Serious security flaw found in IE». BBC News. December 16, 2008. Retrieved May 5, 2010.
- ^ Wingfield, Nick; McGroarty, Patrick (January 19, 2010). «Business Technology: Microsoft’s Internet Explorer Is Under Fire in Europe». The Wall Street Journal.
- ^ Goodin, Dan (December 9, 2011). «Chrome is the most secured browser – new study». The Register. Retrieved October 15, 2012.
- ^ «Accuvant Study Finds Chrome is Most Secure Browser». eSecurity Planet. December 13, 2011. Retrieved May 22, 2012.
- ^ «Browser Security White Paper» (PDF). X41-Dsec GmbH. September 18, 2017. Retrieved September 21, 2017.
- ^ Seltzer, Larry (April 14, 2005). «The Lame Blame of ActiveX». Security—Opinions. eWeek. Retrieved April 7, 2006.
- ^ Lemos, Robert (July 31, 2006). «ActiveX security faces storm before calm». Security Focus. Archived from the original on July 25, 2008. Retrieved July 11, 2009.
- ^ «Secunia 2008 Report» (PDF). Secunia.
- ^ Goodin, Dan (November 1, 2010). «Internet Explorer info leak festers for 2 years». The Register. San Francisco. Retrieved November 2, 2010.
- ^ Naraine, Ryan (November 1, 2010). «Two-year-old data leakage flaw still haunts Internet Explorer». ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on November 4, 2010. Retrieved November 2, 2010.
- ^ «Researchers bypass Internet Explorer Protected Mode». The Register. December 3, 2010. Retrieved December 4, 2010.
- ^ Mills, Elinor (January 14, 2010). «New IE hole exploited in attacks on U.S. firms». CNET News. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on December 24, 2013. Retrieved September 26, 2010.
- ^ Emery, Daniel (January 16, 2010). «Germany issues Explorer warning». BBC News. Retrieved March 26, 2010.
- ^ Fildes, Jonathan (January 18, 2010). «France in fresh Explorer warning». BBC News. Retrieved March 26, 2010.
- ^ Emily Bourke for AM (January 19, 2010). «Govt issues IE security warning». abc.net.au. Archived from the original on January 23, 2010. Retrieved September 26, 2010.
- ^ Martinez-Cabrera, Alejandro (January 18, 2010). «The Technology Chronicles : France and Germany warn users not to use Internet Explorer». The San Francisco Chronicle.
- ^ Govan, Fiona (January 18, 2010). «Germany warns against using Microsoft Internet Explorer». The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on January 11, 2022. Retrieved March 26, 2010.
- ^ «CVE-2014-1776». Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE). January 29, 2014. Archived from the original on April 30, 2017. Retrieved May 16, 2017.
- ^ «Microsoft Security Advisory 2963983». Microsoft. April 26, 2014. Retrieved April 28, 2014.
- ^ Finkle, Jim (April 28, 2014). «U.S., UK advise avoiding Internet Explorer until bug fixed». Reuters. Retrieved April 28, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft Internet Explorer Use-After-Free Vulnerability Guidance». United States Computer Emergency Readiness Team. April 28, 2014. Retrieved April 28, 2014.
- ^ «Vulnerability Note VU#222929 – Microsoft Internet Explorer use-after-free vulnerability». Carnegie Mellon University. April 27, 2014. Retrieved April 28, 2014.
- ^ «U.S.: Stop using Internet Explorer until security holes are fixed». Chicago Tribune. April 28, 2014. Retrieved April 28, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft warns of Internet Explorer flaw». BBC. April 28, 2014. Retrieved April 28, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft Security Bulletin MS14-021 – Critical Security Update for Internet Explorer (2965111)». Microsoft Technet. May 1, 2014. Retrieved July 6, 2014.
- ^ «Market share for browsers, operating systems and search engines». marketshare.hitslink.com. Retrieved February 9, 2011.
- ^ Borland, John. Browser wars: High price, huge rewards, ZDNet, April 15, 2003. Accessed June 2, 2012.
- ^ «TheCounter.com: The Full-Featured Web Counter with Graphic Reports and Detailed Information». Thecounter.com. Archived from the original on October 3, 2008. Retrieved October 17, 2008.
- ^ «TheCounter.com: The Full-Featured Web Counter with Graphic Reports and Detailed Information». Thecounter.com. Archived from the original on October 2, 2008. Retrieved October 17, 2008.
- ^ «CNN — Behind the numbers: Browser market share — October 8, 1998». Cnn.com. Archived from the original on August 16, 2000. Retrieved October 17, 2008.
- ^ «Web Analytics | Online Business Optimization by Omniture». Omniture.com. Archived from the original on April 20, 2008. Retrieved October 17, 2008.
- ^ Goldman, David (October 6, 2010). «Internet Explorer usage falls below 50%». CNN. Retrieved October 6, 2010.
- ^ «Google Chrome Overtakes Internet Explorer». PCWorld. May 21, 2012. Retrieved January 19, 2019.
- ^ «Business Week Online/Microsoft Watch». November 3, 1999. Archived from the original on November 3, 1999. Retrieved November 16, 2023.
- ^ McCullagh, Declan (January 15, 2011). «Feds Accuse MS of Falsification». Wired. Archived from the original on January 15, 2011. Retrieved November 16, 2023.
- ^ «IE Emergency Mode». im-infected.com. January 28, 2011. Archived from the original on June 30, 2011. Retrieved June 23, 2013.
- ^ «Bleeping Computer – Fake IE Emergency Mode (by fake AVG)». January 28, 2011. Retrieved June 23, 2013.
- «Index DOT Html and Index DOT Css». Browser History: Windows Internet Explorer. Retrieved December 22, 2013.
- Hachamovitch, Dean (July 27, 2005). «Windows Vista & IE7 Beta 1 Available». IEBlog. Microsoft. Retrieved December 22, 2013.
- Wilson, Chris (July 30, 2005). «Standards and CSS in IE». IEBlog. Microsoft. Retrieved December 22, 2013.
- Graff, Scott (October 7, 2006). «IE7 Is Coming This Month». IEBlog. Microsoft. Retrieved December 22, 2013.
- «IE7 Platforms And Outlook Express». IEBlog. Microsoft. March 1, 2005. Retrieved December 22, 2013.
- «Gates Highlights Progress on Security, Outlines Next Steps for Continued Innovation». News Center. Microsoft. February 15, 2005. Retrieved December 22, 2013.
- Williams, Mary-Lynne; MacNeil, Leslie; Hall, Marty (September 17, 2010). Hachamovitch, Dean (ed.). «User Experiences: Evolving the blue «e»«. IEBlog. Microsoft. Retrieved December 22, 2013.
- Official website
- Internet Explorer Architecture
Обзор популярных браузеров
Несмотря на существование большого количества браузеров, все они, в целом, выполняют одну функцию — отображают веб-страницы. По этой причине управление в разных браузерах почти ничем не отличается.
Microsoft Edge
Браузер, уже встроенный в ОС Windows, в последние годы набирает всё большую популярность. Обладает всеми возможностями современного браузера, однако некоторые узкоспециализированные сервисы могут не поддерживать работу с ним. Основным достоинством браузера является хорошая интеграция с другими функциями системы Windows. Для незрячих пользователей главным недостатком является излишняя многословность при работе — браузер заставляет произносить NVDA очень много лишней информации во время загрузки страниц и других действий, и это мешает комфортному интернет-сёрфингу. Однако при желании использовать этот браузер его поведение можно подкорректировать с помощью специального NVDA-дополнения.
Google Chrome
На сегодняшний день это самый популярный браузер. Разработчики сайтов и веб-сервисов в первую очередь будут ориентироваться на него, значит, с большой вероятностью сайты любой сложности будут доступны в Chrome. Основным достоинством браузера является быстрота его работы, а также внушительный магазин расширений, позволяющий настроить браузер под себя и добавить дополнительную функциональность. К недостаткам можно отнести большое потребление оперативной памяти, поэтому, если у тебя не очень мощный компьютер, Google Chrome может серьёзно замедлять систему.
Скачать: https://www.google.com/chrome/
Mozilla Firefox
Ещё один популярный браузер — на этот раз свободный, разрабатываемый некоммерческим фондом Mozilla. Этот браузер подойдёт тем, кто заботится о своей конфиденциальности — в браузере есть множество настроек, позволяющие тонко настроить блокирование отслеживаний на сайтах и другие параметры конфиденциальности. Firefox потребляет немного ресурсов, но и сам работает чуть медленнее, чем Google Chrome. Кроме того, некоторые сайты в этом браузере могут отображаться иначе, чем в Chrome, и иногда это может приводить к неудобствам — сайт хорошо работает в Chrome, но плохо — в Firefox. Однако это редкость.
Скачать: https://www.mozilla.org/ru/firefox/new/
Яндекс Браузер
Браузер, разработанный отечественной компанией «Яндекс». Отличительной особенностью браузера является интеграция с другими сервисами «Яндекса»: в нём доступен голосовой ассистент Алиса, Яндекс.Почта, автоматический перевод видео с YouTube и много других уникальных возможностей, которых нет в других браузерах. Однако необходимо заметить, что периодически при обновлениях браузера у незрячих пользователей могут возникать проблемы, поскольку невизуальной доступности продукта уделяется недостаточное внимание.
Скачать: https://browser.yandex.ru/
Атом
Ещё один отечественный браузер – на этот раз от VK. Как и в «Яндекс Браузере», здесь присутствуют уникальные возможности, такие как голосовой ассистент «Маруся», встроенный аудиоплеер для музыки из социальной сети «ВКонтакте» и другие сервисы от VK. К сожалению, как и в случае с «Яндекс Браузером», нельзя быть застрахованным от проблем с невизуальным использованием.
Скачать: https://browser.ru/
Основные приёмы навигации по веб-страницам и список горячих клавиш
Независимо от того, какой браузер ты выбрал, ты можешь ввести адрес сайта или произвольный поисковый запрос в адресную строку. Чтобы перейти в неё, в открытом браузере всегда можно нажать CTRL+L. После ввода запроса или адреса конкретного сайта нажми Enter.
Просмотр страниц сайтов во многом похож на просмотр текста: ты можешь перемещаться по символам, словам, строкам и абзацам, можешь выделять и копировать текст, но не можешь редактировать, перемещать и удалять. Важное отличие от обычного текстового файла состоит в том, что перед тобой так называемый гипертекст, то есть текст, размеченный определённым образом. Вот основные элементы, с которыми ты будешь встречаться.
- Ссылки. Ссылки нужны, чтобы связывать разные веб-страницы между собой. Установив курсор на такую ссылку и нажав Enter, ты попадёшь на другую страницу.
- Заголовки. Они нужны, чтобы обозначать начало нового логического раздела на странице. Заголовки бывают шести уровней: от первого до шестого. Если сайт разработан грамотно, на каждой его странице будет соблюдена некоторая иерархия заголовков: вложенные подразделы будут на более нижних уровнях, чем разделы-родители. Например, в выдаче поисковых результатов в Google есть разделы «Специальные ссылки», «Режимы поиска» и «Результаты поиска», обозначенные заголовками первого уровня, а каждый поисковый результат обозначен заголовком второго уровня, потому что этот контент относится к разделу «Результаты поиска».
- Формы. Серия текстовых полей, списков, флажков и кнопок для сбора какой-либо информации. Например, форму нужно заполнять при регистрации на каком-либо ресурсе, при оставлении заявки на консультацию и т. д. Формы во многом напоминают диалоговые окна, набор возможных элементов у них одинаковый. Например, на сайте Google есть простая форма – текстовое поле для ввода поискового запроса, кнопка для очистки поля и для выбора разных вариантов поиска: «поиск по картинке», «голосовой поиск» и обычный «поиск Google».
- Списки. Используются для перечисления чего-либо — например, может быть список ингредиентов в кулинарном рецепте. Обычно встречаются два вида списков: нумерованный или маркированный. У первых каждый элемент пронумерован, тогда как у вторых цифры отсутствуют, каждый новый элемент начинается со специального значка — маркера.
- Таблицы. Некоторую информацию удобнее представлять в табличном виде, в виде строк и столбцов. Например, это может быть сводка по курсам валют, где в левом столбце будет записаны названия валют, а в правом — курс относительно рубля.
- Ориентиры. Многие сайты поделены на большие логические разделы: обычно это «шапка», «основная часть» и «подвал». Обычно «шапка» и «подвал» одинаковые на всех страницах одного сайта, а «основная часть» меняется в зависимости от страницы. При навигации скринридер будет называть эти ориентиры: «баннер» для шапки, «основное содержимое» для основной части, «информация о содержимом» — для подвала. Есть ещё и некоторые другие ориентиры: «навигация» для меню, «поиск» — для поиска по сайту и др.
Это самые основные элементы, которые могут встретится на веб-страницах. Существуют ещё цитаты, фреймы и многие другие элементы разметки.
Быстрая навигация по странице
Скринридер NVDA предоставляет клавиши, с помощью которых можно быстро переходить к элементам определённого типа, что серьёзно ускоряет твою работу в Интернете. Например, перемещаясь по заголовкам, ты можешь быстро просмотреть разделы страницы и перейти к интересующему тебя. Ниже мы предоставим список основных горячих клавиш для навигации по странице. Ко всем клавишам из списка можно добавить клавишу Shift — тогда будет происходить перемещение в обратном порядке.
- Tab — перемещение по ссылкам, кнопкам, полям форм и некоторым другим элементам, которые можно активировать;
- H — перемещение по заголовкам;
- D — перемещение по ориентирам;
- K — перемещение по ссылкам;
- F — перемещение по полям форм;
- E — перемещение только по текстовым полям;
- X — перемещение только по флажкам;
- R — перемещение только по радиокнопкам;
- Q — перемещение по цитатам.
- T — перемещение по таблицам;
- CTRL+Alt+стрелки влево и вправо — перемещение по столбцам текущей таблицы;
- CTRL+Alt+стрелки вверх и вниз — перемещение по строкам текущей таблицы.
Таким образом, комбинируя обычные команды для перемещения по тексту и специальные горячие клавиши, можно быстро находить необходимую информацию на любом сайте.
