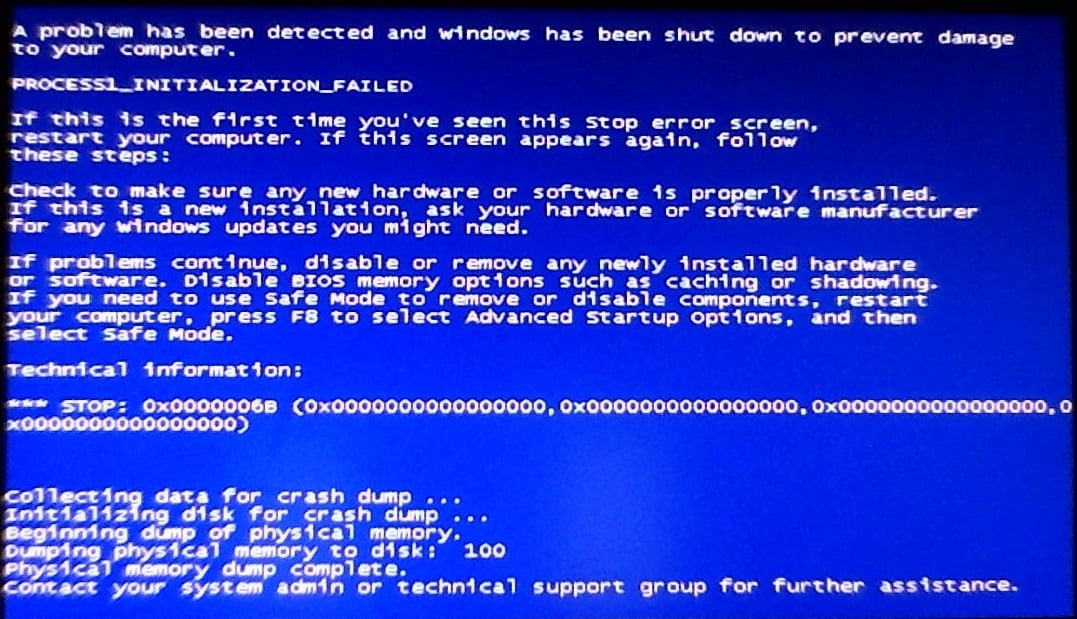
В данной статье мы с вами будем рассматривать синий экран смерти, который именуется PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED и имеет номер 0x0000006B. Что сами Майкрософт говорят по поводу этой проблемы? Они говорят вот что: «Данная проблема появляется вследствие повреждения файла Bootcat.cache или же из-за изменения размера этого файла». Из этого мы точно можем утверждать, что проблема заключается в файле Bootcat.cache. Также нельзя исключать таких вещей, как повреждения системных файлов, аппаратных компонентов, кабелей или прочее. Синий экран смерти PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED может проявлять себя на большинстве версий операционной системы Windows.
В сообщении этого критического сбоя присутствует следующая информация:
STOP: 0x0000006B (Параметр1, Параметр2, Параметр3, Параметр4)
PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED
Заметка: эти четыре параметра могут меняться в зависимости от конфигурации компьютера пользователя.
Помимо прочего, этот синий экран смерти можно увидеть даже на клиентах, серверных машинах и смартфонах. В данной статье мы опишем целых 8 методов, которые помогут разрешить вам эту непростую ситуацию.
Решаем сбой PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED
Метод №1 Удаление файла Bootcat.cache
Следуя из сообщения Майкрософт, первым вашим шагом станет удаление файла Bootcat.cache из папки CodeIntegrity. Данный файл располагается в директории C:\Windows\System32\Codeintegrity. Вам понадобится загрузить компьютер через диск восстановления системы Windows. Если вы не знаете, как создать этот диск, то пройдите по этой ссылке на сайт Майкрософт, где написаны точные инструкции по его созданию. Создав этот диск, сделайте следующее:
- Вставьте диск или же флеш-носитель в свой компьютер.
- Перезапустите компьютер.
- Загрузите систему через диск восстановления Windows.
- Выберите предпочитаемый язык и другие параметры, а затем нажмите «Далее» для продолжения.
- Кликните на кнопку «Восстановление системы».
- Далее пройдите путем «Диагностика→Дополнительные параметры→Командная строка»
- Выберите пункт «Командная строка».
- Впишите в нее команду diskpart.
- Впишите list volume и нажмите Enter.
- Запомните в каком разделе находится ваша ОС, затем впишите Exit и нажмите Enter.
- Впишите C:(укажите тот раздел, в котором находится ваша ОС) и нажмите Enter.
- Впишите cd windows\system32\codeintegrity и нажмите Enter.
- Впишите del bootcat.cache и нажмите Enter.
- Закройте Командную строку.
- Перезагрузите свой компьютер, а затем попытайтесь зайти в систему обычным путем.
Метод №2 Копирование Bootcat.cache с другого компьютера
Если первый метод вам не помог в решении проблемы с синим экраном смерти PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED, то вы должны попробовать этот метод, который включает в себя копирование файла Bootcat.cache с другого компьютера, подразумевая, что тот работает там корректно. Также как и в предыдущем методе, вам снова придется загрузить свою систему через диск восстановления.
- Найдите другой компьютер и зайдите в его операционную систему.
- Вставьте в флеш-устройство в компьютер.
- Нажмите Windows+E чтобы открыть Проводник Windows.
- Пройдите в директорию C:\Windows\System32\Codeintegrity.
- Копируйте файл Bootcat.cache к себе на флеш-устройство.
- Вставьте флеш-хранилище в компьютер, у которого проблемы с синим экраном смерти PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED.
- Запустите проблемный компьютер через диск восстановления Windows и доберитесь до Командной строки, как это было показано в предыдущем методе.
- Открыв Командную строку, впишите в нее команду diskpart.
- Впишите list volume и нажмите Enter.
- Запомните в каком разделе находится ваша ОС, затем впишите Exit и нажмите Enter.
- Впишите C:(укажите тот раздел, в котором находится ваша ОС) и нажмите Enter.
- Впишите cd windows\system32\codeintegrity и нажмите Enter.
- Впишите copy E:\bootcat.cache(впишите ту букву, под которой выступает ваше флеш-хранилище) и нажмите Enter.
- Закройте Командную строку.
- Перезагрузите свой компьютер.
Метод №3 Удаление файла COMPONENTS
Итак, если ничего из вышеперечисленного не помогло, а такое вполне возможно, то давайте двигаться дальше. На этот раз мы с вами попробуем сделать кое-что другое — удаление файла COMPONENTS из директории windows\system32\config. Данное действие также зарекомендовало себя отличным способом по борьбе с синим экраном смерти PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED.
- Снова запустите свою ОС через диск восстановления.
- Пройдите весь путь до Командной строки, как это было уже показано в предыдущих методах.
- Впишите команду diskpart и нажмите Enter.
- Впишите list volume и нажмите Enter.
- Впишите Exit и нажмите Enter.
- Впишите cd windows\system32\config и нажмите Enter.
- Впишите del components и нажмите Enter.
- Закройте Командную строку.
- Перезагрузите свой компьютер.
Ну что, ваша система все еще загружается с синим экраном смерти PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED? Ок, тогда давайте двигаться далее.
Метод No4 Установка Windows 7 SP1
Если вы используете Windows 7 без SP1, то вам нужно попробовать установить этот сервисный пакет для вашей операционной системы. Все что вам нужно сделать, так это пройти в Центр загрузок Майкрософт и скачать от туда необходимый сервисный пакет. Однако, будьте внимательно, что именно вы скачивайте. Обязательно отталкивайтесь от того, какой разрядностью обладает ваша система, т.е. 32-битная или 64-битная. Загрузите Windows 7 SP1, установите его и перезагрузите систему. Затем проверьте, появляется ли синий экран смерти PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED.
Метод No5 Удаление Roxio GoBack
Если вы используете программное обеспечение Roxio GoBack, то вам нужно попробовать удалить его, чтобы проверить, не вызывает ли ли оно уже оговоренный синий экран смерти. Удаляется Roxio GoBack довольно просто через Программы и компоненты.
- Нажмите на клавиатуре Windows+R.
- Впишите appwiz.cpl и нажмите Enter.
- Выберите Roxio GoBack и удалите ее.
- Перезагрузите компьютер.
- Протестируйте систему на стабильность.
Возможно, что именно эта утилита и стояла за таким серьезным сбоем в системе, как PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED. Однако, если ничего не изменилось, то давайте двигаться дальше по нашему списку методов.
Метод №6 Восстановление Windows с помощью утилиты DISM
Для выполнения этого метода, нам потребуется использовать утилиту под названием DISM. DISM — это команда, которая позволяет вам монтировать образ Windows(install.wim) и выполнять такие действия, как установку, удаление, настройку и обновление операционной системы. DISM является компонентом комплекта средств для развертывания и оценки Windows(Windows ADK), который можно загрузить по этой ссылке. Итак, чтобы восстановить Windows с помощью утилиты DISM, вам потребуется сделать следующее:
- Для начала загрузите Windows ADK, а затем установите DISM.
- Нажмите на Пуск и впишите в поисковик запрос «Система обслуживания образов развертывания и управления ими».
- Нажмите на найденный результат ПКМ и выберите Запустить от Администратора.
- Впишите в нее DISM /image:D:\ /cleanup-image /revertpendingactions и нажмите Enter.
- После выполнения команды, перезагрузите свой компьютер, а затем протестируйте систему на наличие синего экрана смерти PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED.
Метод №7 Исключить папку от сканирований
Антивирусное программное обеспечение также может стоять у истоков проблемы с появлением оговоренного синего экрана смерти. Чтобы исправить это, вам нужно исключить папки CodeIntegrity и catroot от сканирования антивирусом. Сейчас мы покажем вам как это делать на примере Защитника Windows. Если вы используете иной антивирус, то это не беда, так как там, скорее всего, будут применимы эти шаги.
- Кликните на Пуск и впишите в поисковик запрос «Защитник Windows».
- Нажмите на найденный результат ПКМ и выберите «Запустить от имени Администратора».
- Перейдите во вкладку «Параметры».
- Кликните на «Добавить исключение».
- Кликните на «Исключить папку».
- Пройдите в директорию C:\Windows\System32\CodeIntegrity.
- Кликните «Исключить эту папку».
- Кликните на «Исключить папку» еще один раз.
- Пройдите в директорию C:\Windows\System32\catroot.
- Кликните «Исключить эту папку».
- Еще раз хорошенько проверьте, исключили ли вы нужные вам папки.
Возможно, синий экран смерти PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED появлялся в случае сканирования этих папок. По крайней мере, так утверждают некоторые пользователи в Интернете. Ну что, проблема все еще преследует вас?
Метод №8 Использование утилиты CHKDSK
Когда ваш жесткий диск не работает как надо, то на нем могут появиться поврежденные данные или же плохие сектора. В этом случае вам поможет довольно неплохая системная утилита CHKDSK, которая поможет найти вам бэдблоки и исправить их, но только если это будет возможно.
- Нажмите ПКМ на Пуск и выберите «Командная строка(администратор)».
- Впишите chkdsk /r и нажмите Enter.
- Далее напишите Y и нажмите Enter, чтобы принять перезагрузку компьютера.
- Подождите, пока утилита завершит починку файловой системы на компьютере. Должны завершиться все пять стадий операции.
Мы надеемся, что данная статья помогла вам преодолеть проблему в виде синего экрана смерти PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED. Если же он так и продолжает постоянно проявляться, то вы также можете еще попробовать выполнить восстановление системы с помощью ранее созданной точки или через бэкап. Если и это не помогло, то это может означать, что у вас присутствуют проблемы аппаратного характера, например, виновниками могли стать ваш HDD/SSD или же оперативная память.
A blue screen error called “Process1 Initialization Failed” appears when the boot files are damaged. This issue most frequently occurs following a hardware or software installation.
This BSOD problem might also result in losing crucial files, much like other BSOD failures. We have provided a solution for this issue, which you may read below.
Your computer often restarts when these blue screen faults occur. Due to the PC’s frequent reboots, users won’t be able to do anything. You could still have a few minutes to try the fixes before it stops you in your tracks, depending on how serious the problem is.
Now, let’s read the article together to find an answer to your issue.
How critical is the process1 initialization failed error?
Process1 Initialization Failed issue might come from corrupted files and software like other BSOD failures. A clean Windows install can frequently fix the problem if it is software-related. However, if this difficulty is hardware-related, a costly replacement of the problematic component may be the only option.
But don’t worry; this error number typically means that Windows is the problem, not any of the hardware on your computer.
How do I fix the PROCESS1 INITIALIZATION FAILED error in Windows 10/11?
1. Update Windows
All features for Windows 10/11 are sent to your device through the Windows Update page in Settings regularly. Windows needs updates to improve constantly. They provide updated features in addition to several solutions for PC-related issues.
Your system will most likely display the error message “Process1 initialization failed” if one of those updates is missing. Therefore, it is necessary to download all of the updates.
If you need to restart your device to finish an update, Windows will let you know, and you may schedule the restart for when it’s most convenient for you.
- Choose Settings from the Start menu to check for updates.
- Select Check for updates after finding Windows Update. You can decide whether to install updates if they are available.
2. Update Drivers
A BSOD issue may result from outdated or incompatible drivers that cannot communicate with your hardware. We advise that you download and install the most recent drivers for your hardware to prevent problems of this nature.
You only need to visit your hardware manufacturer’s website and download the most recent drivers to update a specific driver. There is also another easier way to go about updating your drivers:
- To get the Quick Access Menu, right-click on the Start Menu.
- From the list, select Device Manager.
- Investigate closely and see if there is an error sign near any of the devices’ icons.
- Then, right-click on the device on which you see the error sign.
- Choose Update driver, then select Search automatically for drivers.
- It will download and install the most recent version of the driver.
- After that, restart your computer to apply the changes.
3. Perform CHKDSK
Your hard disk could occasionally stop functioning correctly if it has bad sectors. Bad sectors are most frequently blamed for the Process1 initialization failed problem, like corrupt system files. The CHKDSK command examines and fixes corrupted hard disk sectors.
In essence, scanning involves more than one division. The hard drive’s partitions must all be separately scanned.
- Open Command Prompt (Admin) or Terminal (Admin) by right-clicking the Start Menu button.
- After entering the Command Prompt, type the following and hit Enter: CHKDSK x: / f / r (x stands for the respective drive)
- If an error is found, it will be fixed immediately.
- Restart your computer.
4. Run SFC scan
The operating system depends on system files to operate. They can get corrupted for a variety of causes. Once it is contaminated, it can no longer be read.
You will, therefore, see errors such as Process1 startup failed and others. However, a program called System File Checker may be used to fix corrupted system files (SFC).
This command-line utility checks your computer for damaged files and fixes them.
So, if a faulty system file is to blame for your PROCESS1 INITIALIZATION FAILED error, running an SFC scan should fix it.
- Open Command Prompt (Admin) or Terminal (Admin) by right-clicking the Start Menu button.
- Press Enter after entering the line sfc/scannow.
- If the solution is discovered, it will be used immediately.
- Restart your computer.
5. Utilize DISM
DISM is the third troubleshooter we’ll employ in this case. Redeploying the system image with this tool typically fixes several issues.
DISM could also be beneficial for fixing the PROCESS1 INITIALIZATION FAILED problem.
- Right-click Start from the menu and select Command Prompt (Admin).
- Press Enter after pasting the following command: DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /restorehealth
- Hold off until the Scan is complete.
- Restart your computer, then attempt the update once more.
6. Delete the Bootcat.cache
Windows 10/11 will recreate the Bootcat.cache file after you delete it, which should resolve the PROCESS1 INITIALIZATION FAILED problem.
You may occasionally see Bootcat.cache file corruption will result in the BSOD error PROCESS1 INITIALIZATION FAILED.
You will need to use Command Prompt to erase the problematic file since this mistake might make Windows 10 unable to start.
You may always use Linux from a USB flash drive to identify and remove the file manually if you don’t feel comfortable using Command Prompt.
It’s important to note that some users were able to resolve this issue by transferring Bootcat.cache files from another computer running an identical operating system, so you might want to give it a shot as well.
- Start the command prompt by following the instructions above.
- After entering each command, press Enter.
- C:
- cd windows/system32/codeintegrity
- del bootcat.cache
7. Check your hardware
Hardware is rarely blamed for PROCESS1 INITIALIZATION FAILED and many other BSOD issues. However, it can still be a possible cause.
Because it might not be compatible with your PC, make sure to remove and replace any recently installed hardware. Check other hardware parts if the issue isn’t caused by new hardware.
Note that RAM is a frequent culprit for BSOD issues. Thus, you can simply remove all but one RAM module and test each one individually to test your RAM.
What should I do if I can’t access my important files because of the PROCESS1 INITIALIZATION FAILED error?
Before downloading and installing Stellar Data Recovery Professional software, accessing your data when your PC won’t start up seems unattainable. From the selected hard disk, Stellar Data Recovery Professional for Windows will recover your lost files.
You can make bootable media that will allow you to recover your files from a PC that won’t boot. The how-to is shown below, step-by-step:
- Connect the USB that has at least 1GB of storage to a functional computer.
- Open Stellar Data Recovery Professional after downloading and installing it on the operational computer.
- On the Select What to Recover screen, select Waffle Menu.
- Select Create Recovery Drive.
- Select the USB drive from the drop-down menu of the Create Recovery Drive dialog box.
- Select Create Recovery Drive and OK.
- After purchasing the Stellar Data Recovery Professional activation key, enter the Activation Key you received via email into the box and click Activate.
- Connect the above-mentioned USB media to your unbootable Windows computer.
- Now turn on the PC, then start pressing the F12 boot option key to view any connected bootable USB media.
- Using the arrow down button, move the selection to a bootable data recovery media, then press Enter to boot the computer.
- You will see the interface for Stellar Data Recovery software once the computer has booted from USB media.
- Choose the file type(s) you want to recover from the Select What to Recover screen and press Next.
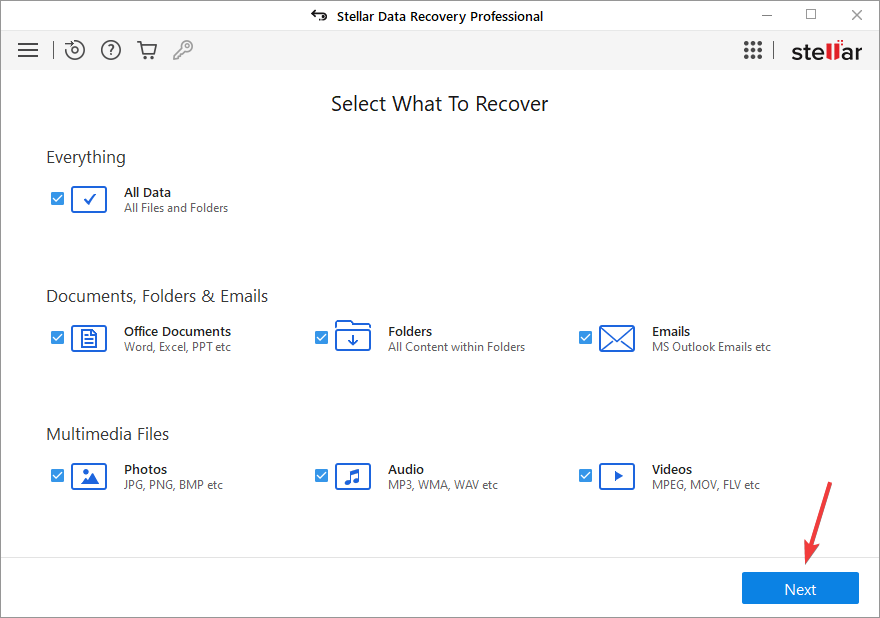
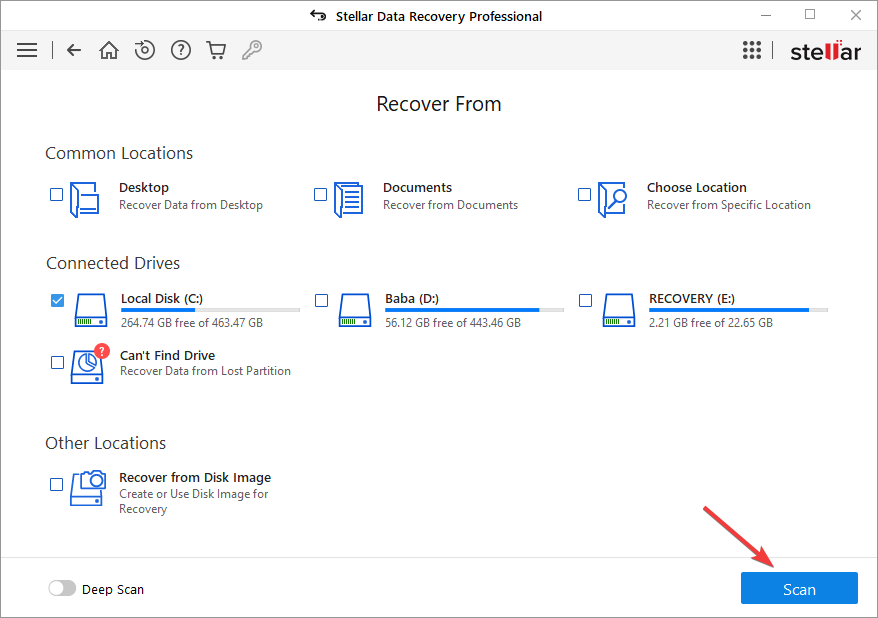
- Click Scan after selecting the Windows drive from which you want to recover data.
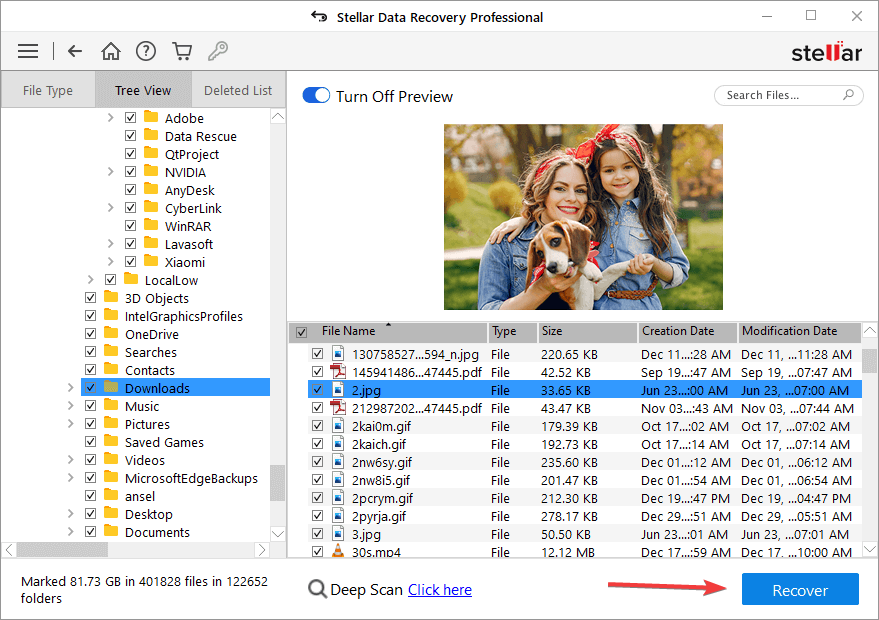
- Click Recover to save the recovered files.
Get rid of the annoying PROCESS1 INITIALIZATION FAILED error!
The strategies discussed above are the ones that have had positive results for numerous people. We advise you to run a clean installation of Windows if you are still experiencing problems with the Process1 startup failed issue.
Once the installation process is finished, a brand-new operating system free of problems will be yours to use. However, Windows will delete your data throughout this procedure, but you may recover them with Stellar Data Recovery Professional software.
FAQ
Where can I check the cause of BSoD error on my computer?
The Event Viewer is a helpful tool for determining the BSOD error’s root cause. This software won’t find the source of the problem; rather, it will offer more details about the crash’s cause. For instance, it will inform you that a particular system file crashed, but it won’t explain why.
When a BSOD causes a computer to crash, would I still be able to access my files?
No, the BSOD issues occur immediately or shortly after the system starts. As a result, you won’t have enough time to transfer or make a backup of your information.
Do I have to pay to activate Stellar Data Recovery Professional Software?
Yes. The software has a free version with significantly fewer features. You must get the paid Professional version of the tool if you want to make a bootable media to recover data from your unbootable PC.
Was this article helpful?
YES0
NO
bootcat.cache — Repair Issues and Download
Sometimes Windows system displays error messages regarding corrupted or missing bootcat.cache files. Situations like that can occur, for example, during a software installation process. Each software program requires certain resources, libraries, and source data to work properly. Corrupted or nonexistent bootcat.cache file can therefore effect in failed execution of the started process.
bootcat.cache file Cache. The file was developed by Microsoft for use with Office software. Here you will find detailed information about the file and instructions how to proceed in the event of bootcat.cache related errors on your device. You can also download bootcat.cache file compatible with Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, Windows 8 devices which will (most probably) allow you to solve the problem.
Compatible with: Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, Windows 8
User popularity
- 1 Information about bootcat.cache file
- 2 Errors related to bootcat.cache file
- 3 How to fix bootcat.cache related errors?
- 3.1 Scanning for malicious software
- 3.2 System and driver update
- 3.3 System File Checker tool
- 3.4 System recovery
- 4 Download bootcat.cache
- 4.1 List of bootcat.cache file versions
File info
| General information | |
|---|---|
| Filename | bootcat.cache |
| File extension | CACHE |
| Type | Temporary |
| Description | Cache |
| Software | |
|---|---|
| Program | Office 2010 |
| Software | Office |
| Author | Microsoft |
| Software version | 2010 |
| Details | |
|---|---|
| File size | 5400089 |
| Oldest file | 2008-01-21 |
| Latest file | 2017-05-10 |

There are various types of errors related to bootcat.cache file. bootcat.cache file may be located in wrong file directory on your device, may not be present in the system, or may be infected with malicious software and therefore not work correctly. Below is a list of most common error messages related to bootcat.cache file. If you encounter one listed below (or similar), please consider the following suggestions.
- bootcat.cache is corrupted
- bootcat.cache cannot be located
- Runtime Error — bootcat.cache
- bootcat.cache file error
- bootcat.cache file cannot be loaded. Module was not found
- cannot register bootcat.cache file:
- bootcat.cache file could not be loaded
- bootcat.cache file doesn’t exist
bootcat.cache
Application could not be started because bootcat.cache file is missing. Reinstall the application to solve the problem.
OK
Problems related to bootcat.cache can be addressed in various ways. Some methods are meant only for advanced users. If you don’t have confidence in your skills, we suggest consulting a specialist. Fixing bootcat.cache file errors should be approached with utmost caution for any mistakes can result in unstable or unproperly working system. If you have the necassary skills, please proceed.
bootcat.cache file errors can be caused by various factors, so its is beneficial to try to fix them using various methods.
Step 1: Scan your computer for any malicious software
Windows files are commonly attacked by malicious software that prevents them from working properly. First step in addressing problems with bootcat.cache file or any other Windows system files should be scanning the system for malicious software using an antivirus tool.
If by any chance you don’t have any antivirus software installed on your system yet, you should do it immediately. Unprotected system is not only a source of file errors, but, more importantly, makes your system vulnerable to many dangers. If you don’t know which antivirus tool to choose, consult this Wikipedia article – comparison of antivirus software.
Step 2: Update your system and drivers.
Installing relevant Microsoft Windows patches and updates may solve your problems related to bootcat.cache file. Use dedicated Windows tool to perform the update.
- Go to the Windows «Start» menu
- Type «Windows Update» in the search field
- Choose the appropriate software program (name may vary depending on your system version)
- Check if your system is up to date. If any unapplied updates are listed, install them immediately.
- After the update has been done,restart your computer in order to complete the process.
Beside updating the system, it is recommended that you install latest device drivers, as drivers can influence proper working of bootcat.cache or other system files. In order to do so, go to your computer or device producer’s website where you will find information regarding latest driver updates.
Step 4: Restoring Windows system
Another approach is to restore system to previous state, before the bootcat.cache file error occured. In order to restore your system, follow the instructions below
- Go to the Windows «Start» menu
- Type «System Restore» in the search field
- Start the system restore tool – it’s name may differ depending on version of the system
- The application will guide you through the process – read the messages carefully
- After the process has finished, restart your computer.
If all the above-mentioned methods failed and the bootcat.cache file problem has not been resolved, proceed to the next step. Remember that the following steps are intended only for advanced users.
Download and replace bootcat.cache file
The last solution is to manually download and replace bootcat.cache file in appropriate folder on the disk. Select file version compatible with your operating system and click the «Download» button. Next, go to your web browser’s «Downloaded» folder and copy the downloaded bootcat.cache file.
Go to the folder where the file should be located and paste the downloaded file. Below is the list of bootcat.cache file example directory paths.
- Windows 10: C:\Windows\System32\CodeIntegrity\
- Windows 8.1: C:\Windows\System32\CodeIntegrity\
- Windows 8: 1: C:\Windows\System32\CodeIntegrity\
- Windows 7: C:\Windows\System32\CodeIntegrity\
- Windows Vista: —
- Windows 8: —
If the steps did not solve your bootcat.cache file problem, you should consult a professional. A probability exists that the error(s) might be device-related and therefore should be resolved at the hardware level. A fresh operating system installation might be necessary – a faulty system installation process can result in data loss.
File versions list
Filename
bootcat.cache
System
Windows 10
File size
2195833 bytes
Date
2017-05-10
| File details | ||
|---|---|---|
| MD5 | d3b0ee62232baa7b7d733b27cc9f2681 | |
| SHA1 | 70802b3a1c9c649175ae5808a0f8ce39a2bc0c99 | |
| SHA256 | d78727d9aa878f50c35d7d4f6f118dcd79a2a8f2665b398ccada377ba4e9372f | |
| CRC32 | 88981e21 | |
| Example file location | C:\Windows\System32\CodeIntegrity\ |
Filename
bootcat.cache
System
Windows 8.1
File size
2445418 bytes
Date
2017-04-24
| File details | ||
|---|---|---|
| MD5 | b865c38b5072f6e85fd11a285ff159ff | |
| SHA1 | 9f46889419f189a7d0af780f697481078a024024 | |
| SHA256 | 527f15a8c88ad915f37aa520b2b1e2d4323dc7a68abc7a6775c166f96f3edfde | |
| CRC32 | 6874cda2 | |
| Example file location | C:\Windows\System32\CodeIntegrity\ |
Filename
bootcat.cache
System
Windows 8
File size
2504032 bytes
Date
2017-04-24
| File details | ||
|---|---|---|
| MD5 | 1fcc0442c27333d844117e9dabfa8058 | |
| SHA1 | 16120f1dff30c1e6c1aff7e98aab677c92f1cd5f | |
| SHA256 | 82be67c4673a5efe103588a430bd639514738708ec368c1396d42ca6c09c3ab8 | |
| CRC32 | b4970df6 | |
| Example file location | 1: C:\Windows\System32\CodeIntegrity\ |
Filename
bootcat.cache
System
Windows 7
File size
5400089 bytes
Date
2017-05-10
| File details | ||
|---|---|---|
| MD5 | 5d953826b02b9daeb2ee2cef36cabea9 | |
| SHA1 | d2883157a824c36e4df6a2d578632be9a9bcc2dc | |
| SHA256 | 09964e586ce92dcd7441d29a9abb40a0f2ed0798ae6833061bfb7bfce470ef30 | |
| CRC32 | b652f14f | |
| Example file location | C:\Windows\System32\CodeIntegrity\ |
Filename
bootcat.cache
System
Windows Vista
File size
4605994 bytes
Date
2008-01-21
| File details | ||
|---|---|---|
| MD5 | 31fe3fa55e9496cfc2aa745d58b4e928 | |
| SHA1 | ea1d22713533575f665dbe1c54c2c589c44f417f | |
| SHA256 | 5ee974cf7131e0c94a2af7edd6383d6b88e83e671b8ec17aa56ec737d43057a3 | |
| CRC32 | 4112e26f | |
| Example file location | — |
Filename
bootcat.cache
System
Windows 8
File size
2195833 bytes
Date
2017-05-10
| File details | ||
|---|---|---|
| MD5 | d3b0ee62232baa7b7d733b27cc9f2681 | |
| SHA1 | 70802b3a1c9c649175ae5808a0f8ce39a2bc0c99 | |
| SHA256 | d78727d9aa878f50c35d7d4f6f118dcd79a2a8f2665b398ccada377ba4e9372f | |
| CRC32 | 88981e21 | |
| Example file location | — |
When Windows detects hardware or software problem, Windows generate error code which identifies what is happening on your computer, notebook, tablet or smartphone. One of these errors is named Blue Screen Of Death (BSOD). End users do not like BSOD because BSOD is stopping our daily work. Every BSOD includes error name and an error code which help us to identify the possible issue. One of the BSOD which will be the topic of this article is PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED, error code 0x0000006B. What Microsoft said about error code 0x0000006B? Microsoft said: “This issue occurs because of the Bootcat.cache file is corrupted or because of the size of the Bootcat.cache file is changed since the last successful start.” We can confirm this problem with Bootcat.cache, and add another reasons including corrupted files, bad hardware, bad or incorrect cables and others. BSOD 0x0000006B occurs on operating system from Windows 2000 to Windows 10, and Windows Server 2008, too.
This is error code:
STOP: 0x0000006B (Parameter1, Parameter2, Parameter3, Parameter4)
PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED
NOTE: The four parameters in the Stop error message may vary, depending on the configuration of the computer.
This error occurs on client and server machines, and on smartphones, too. In 16 methods we will show you how to solve issues on client and server machines, and the last one method will show you how to solve issues on your Windows Phone smartphone.

So what is the best solution for this problem? We will show you all solutions through 17 methods.
Method 1: Delete Bootcat.cache file
As Microsoft said, the first solution is to delete Bootcat.cache file from a CodeIntegrity folder, so, we will start with deleting this file from CodeIntegrity . Bootcat.cache file is a file located at following location C:\Windows\Ssystem32\Codeintegrity. By default, Windows is installed on C: partition and default name is a Local Disk (C:). We will show you how to delete Bootcat.cache file on Windows 7 Enterprise x64. If you are using another operating system, from Windows 2000 to Windows 10, you can follow the same procedure to solve issues with BSOD 0x0000006B. You will need to boot your computer to proper Windows operating system. You can boot your computer using DVD or USB flash drive. You should burn Windows ISO file to DVD or USB Flash drive. If you do not know how to burn ISO file to your USB flash drive, please read instructions on this LINK.
- Insert the Windows 7 installation DVD disk or USB flash drive
- Restart your Windows
- Boot your computer from the DVD drive or USB flash drive
- Enter your language and other preferences and click Next to continue
- Click Repair your computer
- Under System Recovery Options click Windows 7 and then click Next
- Click Command Prompt
- Type diskpart. Diskpart is a command line disk partitioning utility integrated into Windows. Diskpart will provide more information about available volumes on our computer.
- Type list volume and press Enter.
- Type Exit to leave Diskpart
- Type D: to open our system partition, because Windows is installed on D: partition
- Type cd windows\system32\codeintegrity and press Enter
- Type del bootcat.cache and press Enter
- Close Command prompt
- Restart your computer
- Test your computer
Method 2: Copy Bootcat.cache file from another computer
If the first method did not solve your problem, you should try this method, which includes copying Bootcat.cache file from another operating system which is working without any problems. If you have a problem with Windows 7 x64, you need to copy Bootcat.cache file from the same Windows, but a different computer. For this method, you will need USB flash disk with minimal capacity because Bootcat.cache is approximately 5 MB. Also, you will need Windows 7 x64 installation disk, which can be burned to DVD or USB flash disk. We will show you how to copy Bootcat.cache on Windows 7 x64. The first step is copying Bootcat.cache file to USB flash drive, and second step is to paste copied Bootcat.cache file to CodeIntegrity folder.
- Log on another machine
- Insert USB flash drive to working computer
- Hold Windows logo and press E to open Windows Explorer or File Explorer
- Navigate to following location C:\Windows\System32\Codeintegrity
- Right click on Bootcat.cache file and choose Copy
- Open your USB flash disk
- Right click and select Paste
- Eject USB flash drive from machine
- Insert USB flash drive into machine with BSOD issue
- Insert the Windows 7 installation DVD disk or USB flash disk
- Restart your Windows
- Boot your computer from the DVD drive or USB flash disk
- Enter your language and other preferences and click Next to continue
- Click Repair your computer
- Under System Recovery Options click Windows 7 and then click Next
- Click Command Prompt
- Type diskpart. Diskpart is a command line disk partitioning utility integrated into Windows. Diskpart will provide more information about available volumes on our computer.
- Type list volume and press Enter.
- Type Exit to leave Diskpart
- Type D: to open our system partition, because Windows is installed on D: partition
- Type cd windows\system32\codeintegrity and press Enter
- Type copy E:\bootcat.cache and press Enter, because E: is USB flash disk
- Close Command prompt
- Restart your computer
- Test your computer
Method 3: Copy ntdll.dll file from another computer
If the first two methods did not solve your problem, you will need to copy another file, named ntdll.dll, from one to another machine. If you have a problem with Windows 10 x64, you should copy ntdll.dll from the computer which uses the same operating system edition. Again, we will show you how to do it on Windows 7 x64. The procedure is simple as copying Bootcat.cache file. Regardless, we will show you the whole procedure. For this method, you will need USB flash disk with minimal capacity because ntdll.dll is approximately 1.6 MB. Also, you will need Windows 7 x64 installation disk, which can be burned to DVD or USB flash disk. We will show you how to copy ntdll.dll on Windows 7 x64. The first step is copying ntdll.dll file to USB flash drive, and second step is to paste copied ntdll.dll file to a System32 folder.
- Log on another machine
- Insert USB flash drive to working computer
- Hold Windows logo and press E to open Windows Explorer or File Explorer
- Navigate to following location C:\Windows\System32
- Right click on ntdll.dll file and choose Copy
- Open your USB flash disk
- Right click and select Paste
- Eject USB flash drive from machine
- Insert USB flash drive into machine with BSOD issues
- Insert the Windows 7 installation DVD disk or USB flash disk
- Restart your Windows
- Boot your computer from the DVD drive or USB flash disk
- Enter your language and other preferences and click Next to continue
- Click Repair your computer
- Under System Recovery Options click Windows 7 and then click Next
- Click Command Prompt
-
Type diskpart. Diskpart is a command line disk partitioning utility integrated into Windows. Diskpart will provide more information about available volumes on our computer.
- Type list volume and press Enter.
- Type Exit to leave Diskpart
- Type D: to open our system partition, because Windows is installed on D: partition
- Type cd windows\system32 and press Enter
- Type copy E:\ntdll.dll and press Enter, because E: is USB flash disk
- Close Command prompt
- Restart your computer
- Test your computer
Method 4: Delete file COMPONENTS
If deleting and copying Bootcat.cache and ntdll.dll did not solve your problem, next method will include working with file named COMPONENTS. You need to delete file COMPONENTS through Command Prompt. We will show you how to do it on Windows 7 x64. You will need Windows 7 x64 installation disk, which can be burned to DVD or USB flash disk.
- Insert the Windows 7 installation DVD disk or USB flash disk
- Restart your Windows
- Boot your computer from the DVD drive or USB flash disk
- Enter your language and other preferences and click Next to continue
- Click Repair your computer
- Under System Recovery Options click Windows 7 and then click Next
- Click Command Prompt
- Type diskpart. Diskpart is a command line disk partitioning utility integrated in Diskpart will provide more information about available volumes on our computer.
- Type list volume and press Enter.
- Type Exit to leave Diskpart
- Type D: to open our system partition, because Windows is installed on D: partition
- Type cd windows\system32\config and press Enter
- Type del components and press Enter
- Close Command prompt
- Restart your computer
- Test your computer
Method 5: Install Windows 7 SP1
If you are using Windows 7 without SP1, you will need to download SP1 for your Windows 7. If you are using Windows 7 x86, you will need to download and install Windows 7 SP1 x86, if you are using Windows 7 x64, you will need to download and install Windows 7 SP1 x64. Windows 7 SP1 is available on Microsoft Download Center.
- Open Internet browser (Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Edge or other)
- Open web site on this LINK
- Download proper architecture version of Windows 7 SP1
- Install Windows 7 SP1
- Restart your Windows
- Test your computer
Method 6: Uninstall Roxio GoBack
If you are using Roxio GoBack software, you will need to uninstall software and enjoy working on your computer, without boring BSOD error. So, what is Roxio? Roxio GoBack is disk utility developed by Norton which provides recording up to 8 GB of disk changes. If you are not using Roxio GoBack software, then you need to read another method. We will show you how to remove Roxio GoBack software from your computer. We are using Windows 7 x64 and Roxio GoBack Deluxe Edition.
- Hold Windows logo and press R
- Type appwiz.cpl and press Enter
- Select Roxio GoBack Deluxe Edition software
- Right click on Roxio GoBack Deluxe Edition software and choose Uninstall
- Follow the procedure to uninstall Roxio GoBack Deluxe Edition software
- Restart your Windows
- Test your computer
Method 7: Repair a Windows Image using DISM
For this method, we will need to use a tool named DISM (Deployment Image Servicing and Management). The DISM is command line tool which allows you to mount Windows image file (install.wim) and do image servicing including installing, uninstalling, configuring and Windows update. DISM is a part of Windows ADK (Windows Assessment and Deployment Kit) which you can download on this LINK. The procedure of repairing Windows image is the same for operating systems Windows 7 to Windows 10.
- Open Internet browser (Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Edge or other)
- Open website on this LINK to download Windows ADK
- Run Windows ADK
- Choose DISM (Deployment Image Servicing and Management) and click Install
- Click Start menu and type Deployment Image Servicing and Management
- Right click on Deployment Image Servicing and Management and choose Run as Administrator
- Click Yes to accept running DISM as Administrator
- Type DISM /image:D:\ /cleanup-image /revertpendingactions and press Enter
- Restart your Windows
- Test your computer
Method 8: Exclude a folder from scans
The cause of the BSOD problem can be Antivirus, too. To alleviate the problems, you should exclude CodeIntegrity and catroot folders from antivirus scanning. We will show you how to exclude both folders on Windows Defender which is by default integrated into Windows 10. If you are using another antivirus, you should exclude CodeIntegrity and catroot from the scan. If you do not have experience with configuration of antiviruses, please read user manual of antivirus you are using. Terminology is the same, only user experience could be different.
- Click on Start menu and type Windows Defender
- Right click on Windows Defender and choose Run as Administrator
- Click Yes to confirm running Windows Defender as Administrator
- Click Settings at the top right corner
- Click Add and exclusion under Exclusions
- Click Exclude a folder
- Navigate to folder CodeIntegrity on following location C:\Windows\System32\CodeIntegrity
- Click Exclude this folder
- Click Exclude a folder, again
- Navigate to folder catroot on following location C:\Windows\System32\catroot
- Click Exclude this folder
- Check are folders added well
- Test your computer
Method 9: Remove malware
You should be careful when you are browsing the Internet. There are a lot of malware which will try to attack your computer, destroy your operating system, application or your data. BSOD occurs because malware infects your computer and make some damage. The first step you should do is scan your hard disk with Antivirus. If you are home users, you can download freeware antivirus including Avira, Avast, AVG, and others. In case you are using Windows 8 and Window 10, you can use Windows Defender, which is integrated into your operating system. After you remove all malware, you need to restart your Windows. If malware infected some files and your antivirus can not remove malware from file, files will be moved to quarantine or delete from your hard disk. If malware infects Bootcat.cache or ntdll.dll, you should remove that files and copy the same files from another computer. How you will do it? Please read first four methods. To be more secure, we are recommending you to update your operating system, applications and drivers.
Method 10: Restore your operating system from backup
A lot of users are ignoring doing a backup and restore. One of the most important steps in business, and in your home environment is to implement backup and restore strategies. There are few backup tasks you can do including creating a system image, turning on system restore and backup of your data. In the case of failure, you can revert your operating system to the previous state when everything worked without any problems. Few users solved problem with BSOD by doing system image restore.
Method 11: System restore
Sometimes after Windows update or some system changes, computer stops to work. The solution for this to revert your Windows to the previous state, before that update or system changes. One of the steps end users are ignoring is creating a system restore checkpoints. If you are not one of the users who ignored this, we are recommending you to restore your Windows to the previous state using System Restore. If you know when computer worked without problems, revert your Windows to that date. If System Restore is not enabled on your computer, then you need to read Method 9. We are recommending you to enable System Restore, by reading this LINK.
- Hold Windows logo and press Enter
- Type rstrui.exe and press Enter
- Click Choose a different restore point and click Next
- Choose proper checkpoint and click Next
- Click Finish
- Restart your Windows and wait until Windows finished system restore
- Test your computer
Method 12: Disconnect UPS devices
Microsoft said: “If you have an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) connected to your destination computer, disconnect the serial cable before installing the Service Pack. Setup automatically attempts to detect devices that are connected to serial ports, and UPS equipment can cause issues with the detection process. You can leave your computer connected to a UPS for power as long as the UPS itself is plugged in. However, you should make sure that you have enough power for the entire installation, which can take a long time.”
Based on that we are recommending you to disconnect UPS device from your server machine or client machines, install SP1 (method 5) and eliminate BSOD issue. Few users solved issue on their server by using this method.
Method 13: Change CD or DVD
Sometimes, you can not install an operating system from CD or DVD, because you are using scratched CD or DVD. We are recommending you to burn another CD or DVD, or to burn operating system to USB flash drive. If this did not solve the problem, next step is to change cables and CD or DVD disk. If you are using ATA drive (old computers) you should buy ATA CD or DVD drive, and if you are using SATA drive, you should buy SATA CD or DVD drive. Please note that you can not install ATA CD or DVD drive to SATA port, and vice versa.
Method 14: CHKDSK /R
When your HDD is not working good because of file corruption or bad sectors, you should do a check disk. Check disk is a utility which will help you to find bad sectors, and fix them in case there are fixable. You will do it through Command prompt.
- Click on Start menu and type Command prompt
- Right click on Command prompt and choose Run as Administration
- Click Yes to confirm running Command prompt as Administrator
- Type chdksk /r and press Enter. Because you want to check system partition you will need to restart your computer.
- Type Y and press Enter to accept resetting your computer
- Restart your Windows
- Please wait until Windows finished repairing file system on computer. There are 5 stages which should be finished.
- Test your computer
Method 15. Change HDD or SSD
When there is no problem with software, next step will be changing hardware components. HDDs are SSDs are storing our operating systems, drivers, application, and data. When software troubleshooting is not giving a good result, next step should be changing hardware components. You will need to change your HDD or SSD. Be careful when purchasing HDD. There are two different types of HDDs, ATA and SATA. You can not install SATA HDD to ATA port, and vice versa. Also, there are different SATA standards, including SATA I, SATA II, SATA III and SATA 3.1. Different standards provide different transfer rates. If you are using motherboard which supports only SATA I, you do not need to buy HDD SATA III, because HDD SATA III will work as SATA I HDD, because of port limitation. All SSDs are using SATA connectors. Some of HDD’s and SSD’s manufacturer are WD, Seagate, Samsung, Kingston, Adata, and others.
Method 16: Change RAM module
Sometimes because of faulty RAM, Windows’s or application’s instructions can not be stored in RAM address pool, and because of that, you will see BSOD on your monitor. Few users solved their problem by changing RAM module. How will you do it? If you are using more RAM modules, you should try to unplug one by one and test is there a problem with RAM module. Also, if you are planning to purchase another RAM module, you should check which generation of RAM memory is using your motherboard. As always, we are recommending you to check the technical documentation of your motherboard and based on that you can purchase proper RAM module for your computer or notebook. We will show you how to check which RAM module is using notebook HP 2000-2b09WM.
- Open Internet browser (Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Edge or other)
- Open HP’s website on this LINK. We will open HP Support site because we are using HP notebook
- Navigate to Memory section. In our example. HP 2000 is using DDR3 RAM, and there are 2 memory slots available, for maximum 8 GB RAM.
- Purchase RAM module
- Install RAM module
- Test your computer
SOLUTION FOR SMARTPHONES
Method 1: Reset Windows Phone
If you are using Windows Phone, you can see PROCESS1 INITIALIZATION FAILED. It is not weird, because Windows Phone is using Windows 8, Windows 8.1 or Windows 10 operating system. You tried to update your Windows Phone, and update process stopped because of BSOD. What should you do?
- Shutdown your phone
- Hold Volume down and Power button
- Finish updating your smartphone
,
The blue screen error «Process1 Initialization Failed STOP 0x0000006B» may appear on Windows 10 or 8-based computers because of a damage in Windows system files.
The Windows 10 error «Process1 Initialization Failed» can usually occur after a power failure or after updating Windows and in rare cases, the error may be due to a virus attack or to a memory (RAM) problem.
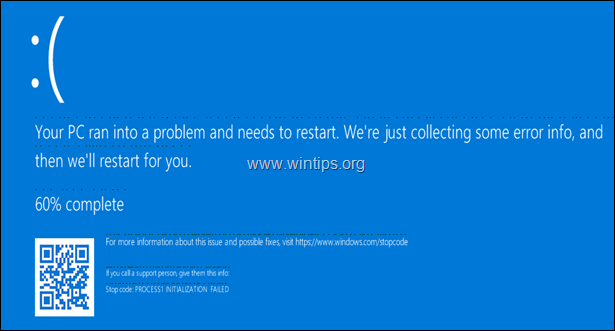
This tutorial contains instructions to resolve the BSOD Error 0x0000006B: «Process1 Initialization Failed» in Windows 10 OS.
How to fix Error 0x0000006B: Process1 Initialization Failed in Windows 10.
Suggestions: Before you continue to the methods below, try the following…
1. Continually press the Power button for 5-6 seconds, to fully power off your PC. Power on it again and try to boot to Windows.
2. Disconnect all the peripheral devices that you don’t need (e.g. USB Drives, SD Cards, USB Wireless Mouse or Keyboard Receiver, USB Wireless Network Card, Printer etc.), and try to boot to Windows.
3. Check the Memory (RAM) for problems.
Requirements: A Windows Installation USB or DVD media.
In order to fix the «Process1 Initialization Failed» problem on Windows 10 you need a Windows 10 USB or DVD Installation Media. If you don’t own a Windows 10 Installation Media, then (from another computer) you can create one, by following the instructions mentioned on these articles:
- How to create a Windows 10 USB boot media.
- How to create a Windows 10 DVD boot media.
Method 1: Perform a Windows Startup Repair.
Method 2. Check Disk and File System for Errors.
Method 3. Delete the «bootcat.cache» file.
Method 4. Rename the NTDLL.DLL File.
Method 5. Replace the NTDLL.DLL from Another Working Computer.
Method 6. Reinstall Windows 10.
Method 1: Perform a Windows Startup Repair
The first method to resolve the «Process1 Initialization Failed (0x0000006B)» error, is to perform a «startup repair» from a Windows Installation Media. TO do that:
1. Boot your computer from the Windows installation media (USB or DVD).
2. At the first setup screen click Next.
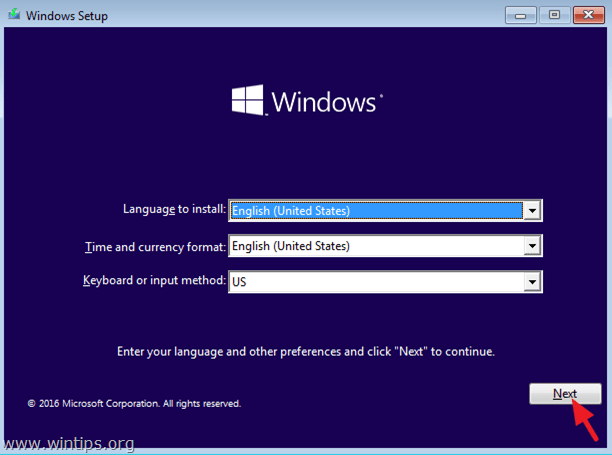
3. At the next screen select Repair your computer.
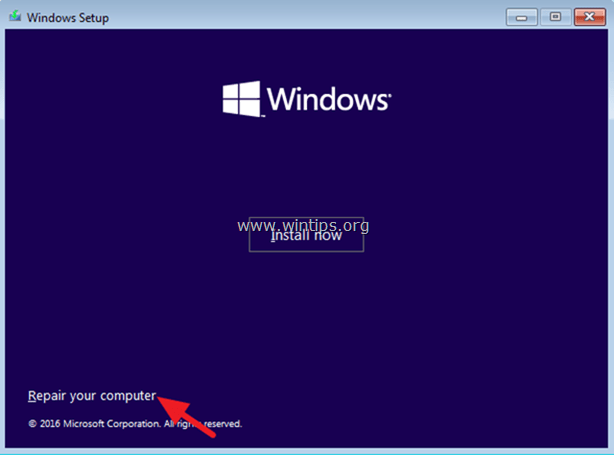
4. Then click Troubleshoot –> Advanced options –> Startup Repair.

5. Wait while Windows diagnosing and fix problems.
6. When the Startup Repair is completed try to boot in Windows normally. If your still receive the «Process1 Initialization Failed » error or if the Startup Repair couldn’t repair your PC, continue to the next method.
Method 2. Check Disk and File System for Errors.
The next method to fix the «Stop 0x0000006B: Process1 Initialization Failed» error, is to repair the hard disk and the file system. To do that:
1. Boot from the Windows installation media.
2. At the Windows Setup screen press SHIFT + F10 to access the Command Prompt. *
* Or choose: NEXT –> REPAIR YOUR COMPUTER -> TROUBLESHOOT -> ADVANCED OPTIONS -> COMMAND PROMPT)
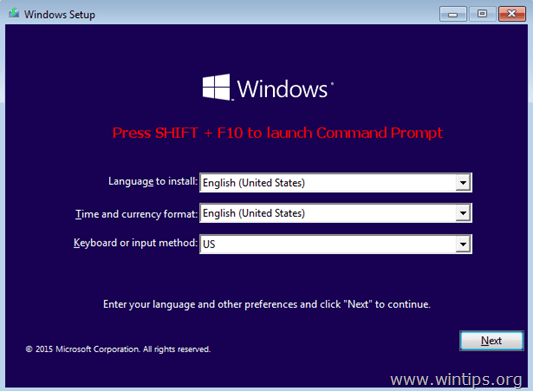
3. In command prompt, give the following command and press Enter, to find out the Windows drive:
- bcdedit
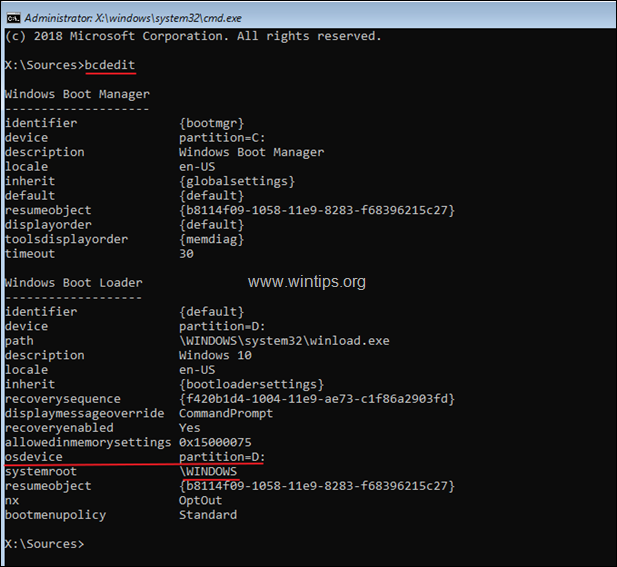
4. Notice the drive letter at «osdevice . . . . . partition=X:» line.
* Info: The «OSDEVICE» is the drive which contains the Windows Operating System (aka: «Windows drive»).
e.g. As you can see at the screenshot below the Windows drive is the drive D:
5. Now proceed and check the Windows drive for problems, by typing this command:
- chkdsk X: /r /x
* Note: Replace the letter «X» according to your case. e.g.:
chkdsk D: /r /x
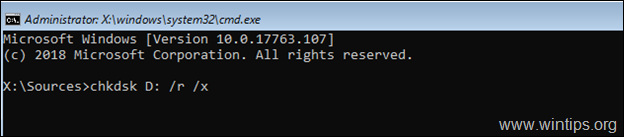
6. When the CHKDSK process is completed, check the Windows System files, by typing this command: *
- sfc /SCANNOW /OFFBOOTDIR=X:\ /OFFWINDIR=X:\windows
* Notes:
1. Replace the letter ‘X‘ according to your case.
sfc /SCANNOW /OFFBOOTDIR=D:\ /OFFWINDIR=D:\windows
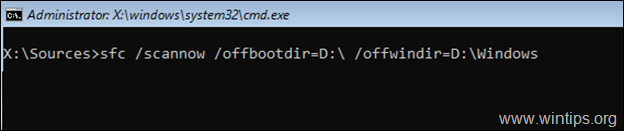
2. If after typing the above command, you receive the error «Windows Resource Protection could not start the repair service», the following may be responsible:
a. You ‘re using a Windows Installation Media, that is incompatible with the installed Windows version & architecture (64 or 32 bit).
b. The Windows Installation Media is damaged. At this case, proceed to recreate the Windows Installation Media.
7. When the SFC repair is completed, type exit to close the command prompt window.
8. Remove the Windows Installation media and close all open windows.
8. Reboot your computer and see if Windows can start normally,
Method 3. Delete the «BOOTCAT.CACHE» file.
The «Process1 Initialization Failed» problem, can be caused because the «BOOTCAT.CACHE» file is corrupted. At that case, proceed and delete the «BOOTCAT.CACHE» file, by following the instructions below:
1. Boot from the Windows 10 installation media and launch command prompt.
2. By using the BCDEDIT command (see the Steps 2 & 3 in the above method), find the Windows Drive Letter.
3. Navigate to the Windows drive, by typing: «Drive_Letter:» (without quotes & press Enter). *
* Note: Replace the Drive_Letter according to your case. In this example the Windows are located at drive «D», so we type:
- D:
4. Now type the following command and press Enter:
- cd windows\system32\CodeIntegrity
5. Then give the following command and press Enter: *
- del bootcat.cache
* Note: If you receive «The file cannot be found» error, after executing the last command, then the «NTDLL.DLL» file is corrupted. (To fix the problem see the next methods…)
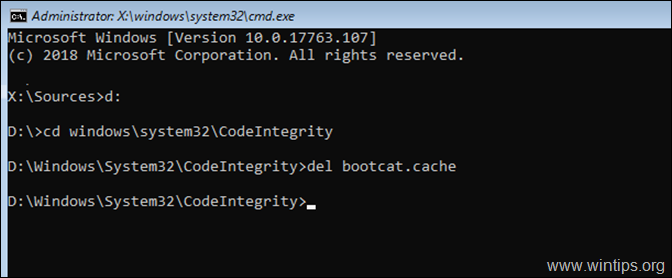
6. Remove the installation media and try to boot to Windows normally.
Method 4. RENAME the NTDLL.DLL File.
The BSOD «Process1 Initialization Failed» commonly appears because the NTDLL.DLL (C:\Windows\System3ntdll.dll) file is damaged. The NTDLL.DLL file is used to create the BOOTCAT.CACHE file which is needed from Windows to boot normally.
To fix the damaged NTDLL.DLL file, proceed as follows:
1. Boot from the Windows 10 installation media and launch command prompt.
2. By using the BCDEDIT command (see the Steps 2 & 3 in the above method), find the Windows Drive Letter.
3. Navigate to the Windows drive, by typing: «Drive_Letter:» (without quotes & press Enter). *
* Note: Replace the Drive_Letter according to your case. In this example the Windows are located at drive «D», so we type:
- D:
4. Now type the following commands in order, to rename the «NTDLL.DLL» file:
- cd windows\system32
- ren ntdll.dll ntdll.BAK
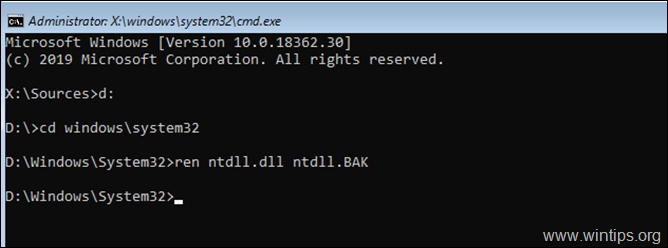
5. Remove the installation media and close all open windows to restart your PC.
6. After restart, Windows will display again the «Process1 Initialization Failed» error screen, but after 2 or 3 automatically restarts, it should start the «Automatic Repair» process.

7. Let Windows fix the issues, and when it’s done, Windows will start normally. *
* Note: If Windows still not start, see the next solution.
Method 5. Replace the NTDLL.DLL from Another Working Computer
Another method, to resolve the blue screen error «0x0000006B: Process1 Initialization Failed» in all Windows versions, is to copy the «NTDLL.DLL» file from another working PC. To do that: *
* Important: In order to apply the steps in this method, you must have access to another working computer, with the same Windows Version and Architecture as the installed Windows version and architecture (e.g. Windows 10 Home 64bit).
1. From another working computer, (with the same Windows version/architecture), copy the «NTDLL.DLL» file from the «C:\Windows\System32\» directory to the root folder of the USB Windows installation media.
2. Boot the PC with the «Process1 Initialization Failed» error, from the Windows Installation media and launch command prompt.
3. At command prompt, list all drive letters (drives), with this command:
- wmic logicaldisk get name
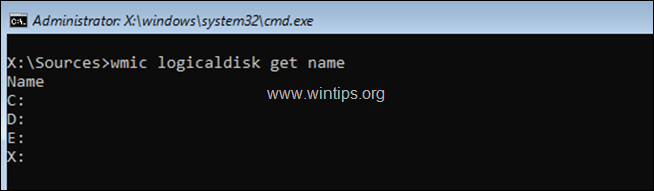
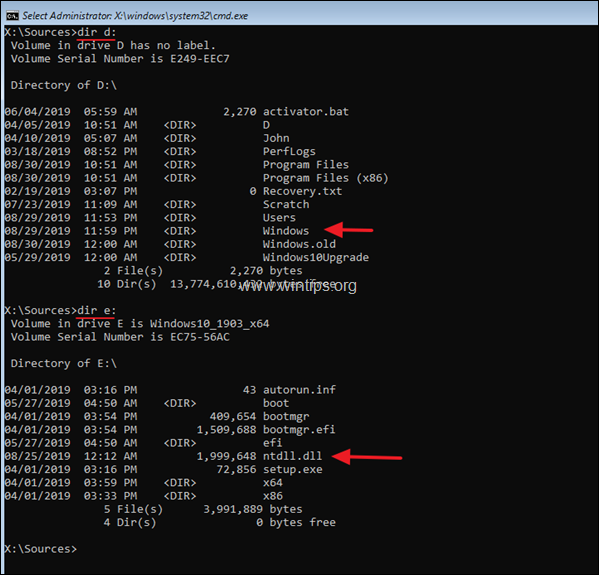
4. Now, by using the «DIR <Drive_Letter>:« command (e.g. «DIR C:», «DIR D:», «DIR E:», etc.), examine the contents of all the listed drives (except the drive X:), and find out which drive contains the ntdll.dll file and which drive contains the Windows folder.
e.g. As you can see in the screenshot below the ‘NTDLL.DLL’ file is located at drive E:\ and the ‘Windows’ folder at drive D:\
5. Once you locate which drive contains the ‘NTDLL.DLL’ file, type its drive letter and : and press Enter. *
* e.g. At this example the ‘NTDLL.DLL’ file is on drive «E:», so we have to type:
- E:
6. Now give the following command to copy the «NTDLL.DLL» file from the USB to the «\windows\system32» folder of the Windows drive («D:» in this example). *
- copy ntdll.dll D:\windows\system32
* Note: Replace the Windows drive letter according your case.
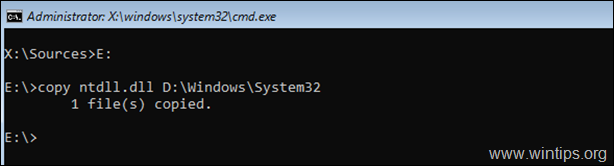
7. When the file is copied, remove the installation media and close all the open windows to restart your PC.
Method 6. Reinstall Windows 10.
If none of the above methods solved your problem, I suggest to backup your files and to RESET your PC to its default state, or to perform a clean Windows 10 installation.
That’s it! Which method worked for you?
Let me know if this guide has helped you by leaving your comment about your experience. Please like and share this guide to help others.
If this article was useful for you, please consider supporting us by making a donation. Even $1 can a make a huge difference for us in our effort to continue to help others while keeping this site free:
- Author
- Recent Posts
Konstantinos is the founder and administrator of Wintips.org. Since 1995 he works and provides IT support as a computer and network expert to individuals and large companies. He is specialized in solving problems related to Windows or other Microsoft products (Windows Server, Office, Microsoft 365, etc.).

























