Уровень сложностиСредний
Время на прочтение6 мин
Количество просмотров6.3K
Доброго дня, коллеги. Рубрика — администрирование серверов 1С: Предприятие.
Свою статью я хотел бы начать с видов тестирования, применяемых в продукте «1С:Предприятие» для проверки информационной системы (ИС) на технологическое качество и масштабируемость. В мире 1С для этого принято использовать два вида тестирования:
-
тестирование производительности
(есть отдельная статья про интегральную оценку производительности по методике APDEX)
-
и стресс-тестирование
(это когда в тестируемой ИС моделируют программно выполнение конкретных операций и планомерно увеличивают количество потоков их выполнения до отказа ИС, либо снижения ее производительности до неприемлемых значений).
Методика испытаний с такими видами тестирования есть, но некому реализовать, нет требований и т.п.
Почему так происходит? Эксперт по технологическим вопросам на проекте внедрения стоит дорого, да и если он есть, то не всегда получается добиться от заказчика понятных требований по составу ключевых операций, чтобы провести анализ внедряемого продукта досконально.
Следствием отсутствия реальных проверок разработанной информационной системы на технологическое качество и масштабируемость являются регулярные фризы (зависание работы программы на некоторое время или до перезапуска службы 1С на сервере) при одновременной работе пользователей в продуктивной среде.
Чаще всего причина фризов кроется не в ошибочно-подобранных параметрах инфраструктуры (количества процессоров, объема оперативной памяти, быстрых или медленных дисков и т.д.), а именно в плохом коде на языке 1С, который требует рефакторинга экспертом по технологическим вопросам на основании исследования, например, как описано в статье про APDEX.
Если такого эксперта искать, то на это уйдет не один месяц, а на выполнение рефакторинга отводится от месяца и более (зависит от опыта сотрудника и масштаба бедствия).
Все это время надо как-то жить.
Часто проблему удается стабилизировать настройкой кластера 1С на перезапуск рабочих процессов средствами самого кластера 1С, процесс описан в инструкциях на портале its.1c.ru.
Решение с настройкой кластера не всегда подходит, ведь настройка позволяет перезапускать рабочие процессы:
— по таймеру;
— по превышению заданного объема оперативной памяти.
Перезапуск по таймеру неудобен с точки зрения пользователя: при каждом перезапуске пользовательский интерфейс приложения как будто замирает без опознавательных знаков, вызывая недоумение у пользователей.
Перезапуск по превышению заданного объема оперативной памяти не решает проблему завершения именно проблемных рабочих процессов, поскольку не всегда проблема кроется действительно в них. Возможно, такой объем вполне допустим исходя из бизнес-логики приложения, например, при массовом проведении работ по регламенту.
Когда настройками кластера обходиться не получается по каким-то причинам, есть довольно действенный способ — регулярный перезапуск службы 1С с очисткой кеша сеансовых данных. Каталог хранения можно узнать из параметров запуска службы 1С, после ключа -d следует указать каталог службы, например:
C:\Program Files\1cv8\8.3.22.2283\bin\ragent.exe" -srvc -agent -regport 1541 -port 1540 -range 1560:1591 -d "C:\Program Files\1cv8\srvinfo" -debug
Для сервера, запущенного с параметром -regport 1541, каталог сеансовых данных будет размещен в каталоге «reg_1541» и начинаться с «snccntx»:
"C:\Program Files\1cv8\srvinfo\reg_1541\snccntx<ИдентификаторГлавногоМенеджераКластера>",
<ИдентификаторГлавногоМенеджераКластера>
Перезапуск нужно выполнять в нерабочее время (само собой!).
Можно, конечно, просить администратора этим заниматься вручную каждый день, но не каждый на такое согласится.
В Windows нет средств перезапуска служб по таймеру «из коробки», а тем более с чисткой кеша-сеансов.
Решением может быть cmd или powershell-скрипт и встроенный в ОС-планировщик задач `taskschd.msc`, настроенный на выполнение данного скрипта.
Почему же вообще я решил написать данный скрипт? По запросу «Автоматический перезапуск службы(сервиса) 1С на Windows Server» интернет выдавал лишь решения с паузой на фиксированное время между остановкой службы и ее стартом. Такой способ может быть рабочим до тех пор, пока известно за сколько рабочие процессы после подачи команды на остановку службы успевают корректно завершиться. Т.е. если рассматривать вариант именно с ожиданием корректного завершения процессов, стоит ждать столько, сколько нужно, а не фиксированное время, указываемое в скрипте. Поэтому я включил в скрипт проверку наличия в памяти ОС активных процессов с наименованиями, которые соответствуют процессам службы 1С, а именно: «rmngr.exe», «rphost.exe», «ragent.exe».
Прикладываю сам скрипт:
#Указываем наименование службы сервера 1С и останавливаем её
$serviceName = ‘1C:Enterprise 8.3 Server Agent (x86-64)’
stop-service -name $serviceName -force#Ожидаем завершения процессов
Do { $Processes= Get-Process| Where {($_.Name -eq «rphost») -or ($_.Name -eq «rmngr») -or ($_.Name -eq «ragent»)}| select name, starttime}
Until($Processes.Count -eq 0)#Вычисляем каталог хранения сеансовых данных
$o = Get-WmiObject win32_service | ?{$_.Name -like $serviceName} | select-object
$ss = $o.PathName.SubString($o.PathName.LastIndexOf(«-d «))
$sss = $ss.SubString($ss.IndexOf(«»»»)+1)
$ssss=$sss.SubString(0,$sss.IndexOf(«»»»))
$regport= $o.PathName.SubString($o.PathName.LastINdexOf(«regport»)+8,4)
$ServiceDataDir = $ssss+’\reg_’+$regport+’\’
$SessionDataDir = Get-ChildItem -Path $ServiceDataDir -Filter snccntx*#Удаляем сеансовые данные
Remove-Item -recurse $ServiceDataDir$SessionDataDir#Запускаем службу сервера 1С
start-service -name $serviceName
,
‘1C:Enterprise 8.3 Server Agent (x86-64)’ — это имя службы, как оно задано в ветке редактора реестра.
-
Как узнать название службы 1С
Есть два способа:
1. При помощи редактора реестра. Открыть его можно следующим образом: нажимаем сочетание клавиш Win+R, в поле «Открыть» набираем команду regidit, откроется редактор реестра, где имя службы — это имя папки в ветке (выделено жирным):
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\1C:Enterprise 8.3 Server Agent (x86-64)
2. При помощи консоли служб
Нажимаем сочетание клавиш Win+R, далее набираем команду: services.msc
В открывшемся списке служб находим службу 1С, открываем ее карточку, имя, это значение напротив «Service Name» («Имя службы» в русском интерфейсе).
-
Как сохранить скрипт
Для запуска скрипта необходимо сохранить его в текстовый файл и присвоить файлу расширение .ps1. Далее этот файл помещаем в каталог, из-под которого он будет запускаться, например, %appdata%.

-
Как настроить планировщик
Планировщик задач можно открыть так:
1. Нажимаем сочетание клавиш Win+R, далее набираем команду: taskschd.msc.
2. Находим папку Microsoft, нажимаем по ней правой кнопкой мыши и выбираем «создать простую задачу».

3. Заполняем понятное для себя наименование, отражающее сущность выполняемой операции, например, restart1cserviceClearCache. Описание заполнять необязательно, но, поскольку сервер могут обсуживать другие люди в дальнейшем, можете написать что-то вроде «перезапуск службы 1с по расписанию». Поверьте, коллеги вспомнят потом вас добрым словом за понятное представление задачи:).
4. Указываем время и периодичность выполнения на ваше усмотрение.
5. Ставим действие (Action) — «Запустить программу» (Start a program)
6. В поле «Программа или сценарий» (Program/script) указываем программу powershell (у меня путь такой: C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe),
в качестве параметра (поле «Добавить аргументы(необязательно)») указываем через ключ `-File путь к файлу со скриптом`: -File "%appdata%\restart1cserviceClearCache.ps1".

Нажимаем «ОК».
Ваше регламентное задание по перезапуску службы с очисткой кеша готово, осталось проверить его работу.
-
Как проверить работоспособность задания планировщика
Если есть тестовый сервер, где нет работающих пользователей, настройте задание сначала на нем.
Для проверки работоспособности откройте каталог сеансовых данных проводником, чтобы были видны даты создания файлов в нем "C:\Program Files\1cv8\srvinfo\reg_1541\snccntx* и редактор powershell.
В редакторе powershell введите команду:
Get-Process| Where {($_.Name -eq "rphost") -or ($_.Name -eq "rmngr")}| select name, starttime (*)
Результатом этой команды является табличка с датой старта процессов службы 1С, например:
Name StartTime
—- ———
rmngr 06.08.2024 18:33:47
rphost 06.08.2024 18:34:51
rphost 06.08.2024 18:33:50
Редактор не закрывайте.
В планировщике задач следует навести курсор на созданном вами задании и нажать правой кнопкой мыши, после чего выбрать пункт «Выполнить (Run)».

После выполнения перейдите в редактор powershell и повторите команду (*) еще раз. Если вы видите новые значения StartTime для процессов, значит перезапуск выполнен успешно, осталось проверить очистился ли кеш.
Смотрим на даты создания файлов в каталоге "C:\Program Files\1cv8\srvinfo\reg_1541\snccntx*. Если они соответствуют новым значениям StartTime, то скрипт отработал успешно.
На этом все, спасибо за внимание 
In today’s digital world, keeping your Windows Server safe and running well is key. One big part of this is making sure to restart it regularly. But how do you do this the right way on a Windows Server? Is there a simple method that lets you automate and tweak this process?
Enter the Windows Server 2022 Task Scheduler. This tool is a game-changer, bringing lots of new abilities to the table. It lets you set up tasks to run when you want, react to certain events, and trigger tasks based on set times or events. You’ll find it’s really flexible and can do a lot for you!
I’m here to show you how to make the most of the Task Scheduler for scheduling restarts on your Windows Server 2022. I’ll walk you through everything – from starting out to handling any problems you might run into. Let’s dive in and make your server work even better!
Key Takeaways:
- The Windows Server 2022 Task Scheduler offers advanced features to automate and schedule tasks on your server.
- Scheduling regular restarts is crucial for maintaining server performance and security.
- The Task Scheduler allows for customization, offering triggers based on specific times, dates, recurring schedules, or system events.
- In the upcoming sections, we’ll explore the step-by-step process of scheduling restarts on Windows Server 2022 and delve into troubleshooting and optimization tips.
- Stay ahead in server management with the power of the Task Scheduler!
Using Task Scheduler to Schedule Restart on Windows Server 2022
It’s key to regularly restart your Windows Server for best performance. The Task Scheduler in Windows Server 2022 makes it simple to do. Just a few steps and you’re set with automated restarts.
Here’s a step-by-step guide for setting restarts on Windows Server 2022:
- Start by opening Task Scheduler. You can find it by searching in the Windows search bar.
- Create a new folder in the Task Scheduler Library by right-clicking. This step helps keep your tasks organized.
- Now, inside the new folder, right-click and choose “Create Task.”
- Give your task a name and a description.
- Adjust the settings to “Run whether the user is logged on or not” and “Run with highest privileges” for a smooth operation.
- Pick when you want the restart to happen.
- Choose the “shutdown” action and set the arguments to “-r -t 60”. This setting restarts the server in 60 seconds.
- Set other conditions or settings that you might need.
- Finally, save this task. It’s now ready to restart your server at the chosen time.
Scheduling restarts keeps your server fast and avoids problems. It means you don’t have to manually restart, and your server restarts when it’s best.
Always avoid restarting during crucial tasks. It could make them fail. So, choose your restart times carefully to not disturb anything else.
Using Task Scheduler in Windows Server 2022 makes managing your server easier. It helps keep everything running smoothly.
Next, we’ll look at how to schedule regular backups in Windows Server 2022. Backups are crucial for protecting your data and quick recovery after a disaster.
Keep reading: [H2] Scheduling a Weekly Backup on Windows Server 2022.
Scheduling a Weekly Backup on Windows Server 2022
Setting up regular backups is crucial on Windows Server 2022. Not only should you schedule restarts, but also back up your important data weekly. AOMEI Backupper Server is a great tool for this. It lets you back up your system, disks, partitions, and files efficiently.
AOMEI Backupper Server helps you make a backup plan that fits your needs. Weekly backups strike a good balance, protecting your data without using up too much space. This way, you reduce the chances of losing data for long. Setting backups to run every week also makes the whole process smoother and less prone to mistakes.
AOMEI Cyber Backup also shines for managing backups centrally on Windows servers. It lets you set up backups to happen daily, weekly, or monthly. This gives you a dependable routine for your backups.
When you set up backups, think about how much storage space you need. Using external drives that have more than enough space is wise. This guarantees room for many backups and any data you add later.
Choosing the right backup target drives is critical. Make sure they don’t have certain server folders or a special system partition. Including these could mess up your backup.
If a backup fails because the target drive doesn’t have enough space, you might need to fix the drive letter issue. Use a tool in Windows Server Essentials to do this. Then, your backups can run smoothly again.
With AOMEI tools, you get to decide what to back up. You can back up everything or just specific parts. This is great for focusing on what’s most important.
By using good backup software regularly, like AOMEI Backupper Server or AOMEI Cyber Backup, your data stays safe on Windows Server 2022.
About Windows Server 2022 Task Scheduler
Windows Server 2022 Task Scheduler lets users set up and automate tasks on their servers. It’s much better than past versions, making scheduling tasks easier and more reliable.
It has lots of ways to start tasks. You can choose specific start times, set tasks to repeat daily or weekly, or start them when certain events happen on the server.
The Task Scheduler also does actions automatically. Users can make it run scripts, send emails, or do other tasks without someone pressing a button.
This tool gives you lots of control over your tasks. You can say they should only run in certain computer states, like when the power’s on or the internet’s working. This helps make sure your server runs at its best.
Windows Server 2022 Task Scheduler got better with new updates. Now, tasks can start based on specific events. This makes your schedule more flexible and reactive.
It also works great with PowerShell, which is a powerful scripting tool. You can use PowerShell to make your tasks do almost anything, adding a lot of flexibility.
There’s also better logging to help you see what your tasks are doing. This makes it easier to fix problems and keep everything running smoothly.
And it doesn’t stop there. Windows Server 2022 Task Scheduler works with Windows Admin Center. This makes it simpler to manage tasks on several servers and keeps them safe.
So, the Windows Server 2022 Task Scheduler gives you lots of ways to schedule and run tasks. It’s reliable, fast, secure, and easy to use. It’s a great way to handle tasks on Windows Server 2022.
Troubleshooting Tasks in Windows Server 2022 Task Scheduler
Having trouble with tasks in Windows Server 2022 Task Scheduler not running correctly? It’s important to find and fix the problem. By checking the Task Scheduler, you can pinpoint what’s wrong and get things working right again. Here’s how you can troubleshoot:
- Check Task History and Logs: Look at the task history and logs in Task Scheduler. You might find error messages or odd behavior. These clues can show why tasks don’t work as they should.
- Verify Task Settings, Triggers, Actions, and Conditions: Make sure all the task settings are correct. This includes triggers, actions, and conditions. They need to match what you expect the tasks to do.
- Ensure Proper User Account Permissions: Check if the user running the tasks has enough permissions. Not having the right permissions can stop tasks from working.
- Test Tasks Manually: Run the tasks by yourself. This is outside of the Task Scheduler. It can show if the tasks have a problem or if it’s the Task Scheduler setup.
- Utilize Tools like Event Viewer or PowerShell: Use tools like Event Viewer and PowerShell to get more info. They show more details about why tasks might fail. This can help you fix the problem.
- Enable Additional Logging and Debugging Options: Turn on detailed logging in the Task Scheduler. This shows more about how tasks run. It may reveal hidden errors.
Always remember to keep track of the changes you make while troubleshooting. And test each change one at a time. This way, you can clearly see what fixes the issue.
If problems continue, asking for help from the Windows Server community might be smart. They offer many tips and personal experiences on Windows Server community forum.
By using these steps and listening to others’ advice, you can solve issues in Windows Server 2022 Task Scheduler. Good luck!
Automating Task Management in Windows Server 2022 Task Scheduler
Windows Server 2022 Task Scheduler is a tool for automating tasks, scripts, and programs. It saves time and makes tasks more reliable. You can schedule tasks to run at set times, intervals, or when certain events happen.
The Task Scheduler has many trigger options for different needs. You can set tasks to run on certain dates, regularly, or when an event occurs. This lets you decide when tasks happen.
It also allows for advanced actions to make tasks better. For instance, tasks can include running scripts, sending email updates, or making system restore points. These features offer more control over how tasks are completed.
You can add conditions for tasks to follow. For example, make a task run only on certain networks or power statuses. This lets you customize task timing based on your needs.
Task automation is very helpful, like for scheduling a server restart. With the Task Scheduler, users can set specific restart options. You can use commands like “shutdown -r -t 60” to restart after a 60-second delay.
Add backup software to the Task Scheduler for regular backups. AOMEI Backupper Server and AOMEI Cyber Backup work well. They have many backup features and work with the Task Scheduler to automate backups.
PowerShell is great for managing tasks in Task Scheduler. It lets you set up and control tasks easily. PowerShell is a powerful tool for automation.
Group Policy settings can also manage Task Scheduler. This makes it easier to set up and keep tasks the same across multiple systems. It helps maintain order and efficiency.
The Task Scheduler has APIs for creating custom tools for tasks. Developers can use these APIs to build manage tasks uniquely. It opens opportunities for custom task management solutions.
Windows Server 2022 Task Scheduler is great for task automation. It covers scheduling, triggers, advanced actions, and more. It helps users improve how they handle tasks and boost system performance.
To get more info on Windows Server 2022 Task Scheduler, visit the official documentation.
Windows Server Task Scheduler Files Storage Location
The Windows Server Task Scheduler files are saved in three places. They include a file system location and two registry spots.
The file system spot is “C:\Windows\System32\Tasks”. It holds XML files with task settings. Remember this for troubleshooting or making backups.
Also, two places in the registry keep Task Scheduler files. These are: HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Schedule\Taskcache\Tasks and HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Schedule\Taskcache\Tree.
It’s key to know where Task Scheduler files are kept. This helps with managing or fixing tasks on Windows Server. Whether for troubleshooting or backing up, this knowledge is useful.
Conclusion
Using the Task Scheduler to restart your Windows Server is crucial for maintenance and to keep it running smoothly. By setting up restarts following the steps here, you can manage your tasks efficiently. However, rebooting daily could hide deeper issues, as pointed out in discussions among IT experts.
Instead of daily reboots, aim for a monthly restart. This is a balanced approach, ensuring maintenance without causing too many interruptions. For VDI setups, more frequent reboots may be necessary. But, modern systems can handle this well, as mentioned by some experts.
It’s key to reboot servers only for important reasons like updates or fixing hardware. Focus on monitoring the health of your servers regularly, advises experts. Sometimes, shutting down servers at night might be needed for business reasons, affecting operations.
In sum, scheduling regular restarts using the Task Scheduler is the best way to manage your Windows Server. Find the right balance based on your server’s needs and advice from the IT community. This will keep your server running smoothly, reducing issues and managing maintenance effectively.
FAQ
How do I schedule a restart on Windows Server?
To schedule a restart on Windows Server, use the Task Scheduler. The article will guide you through setting a specific restart time.
Can I automate restarts on Windows Server 2022?
Yes, you can automate restarts on Windows Server 2022 with the Task Scheduler. There’s a step-by-step guide in the article for automating restarts.
How do I schedule a weekly backup on Windows Server 2022?
For a weekly backup on Windows Server 2022, try AOMEI tools like Backupper Server or Cyber Backup. These programs help you set up scheduled backups to keep your data safe.
What are the features of Windows Server 2022 Task Scheduler?
Windows Server 2022 Task Scheduler has features such as event triggers and better PowerShell support. It also offers improved logs, Windows Admin Center integration, and stronger security.
How can I troubleshoot tasks in Windows Server 2022 Task Scheduler?
If tasks aren’t working right, you can troubleshoot in several ways. These include checking logs, task settings, and testing tasks. You can also use Event Viewer or PowerShell for more details.
Can I automate task management with Windows Server 2022 Task Scheduler?
Yes, automating task management is possible with the Windows Server 2022 Task Scheduler. The article lists methods like PowerShell, Group Policy, Task Scheduler APIs, and automation tools.
Where are the Windows Server Task Scheduler files stored?
The files for Windows Server Task Scheduler are mostly kept in “C:\Windows\System32\Tasks”. This is where the task settings and configurations are stored.
How can I effectively schedule restarts on Windows Server?
The article explains how to effectively time restarts on Windows Server. Using the Task Scheduler, you can easily set up your restart schedule.
Source Links
- https://www.ubackup.com/windows-server/server-2019-schedule-reboot-0025-rc.html
- https://community.spiceworks.com/t/rebooting-a-server-after-installing-updates-how-soon/674783
- https://www.ubackup.com/windows-server/windows-server-2022-task-scheduler-8523-gc.html
- https://community.spiceworks.com/t/schedule-windows-server-to-reboot/1004131
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server-essentials/manage/set-up-or-customize-server-backup
- https://www.partitionwizard.com/news/windows-server-backup-schedule-not-running.html
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/troubleshoot/windows-server/system-management-components/schedule-server-process
- https://community.spiceworks.com/t/windows-2022-scheduler-issues/948554
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/2913816/how-to-find-the-location-of-the-scheduled-tasks-folder
- https://community.spiceworks.com/t/daily-rebooting-servers-yes-or-no/945357
- About the Author
- Latest Posts
Mark is a senior content editor at Text-Center.com and has more than 20 years of experience with linux and windows operating systems. He also writes for Biteno.com
I want to restart some specific service for a specific time every week. Can I use the NET command?
— Shanmuga
Hi Shanmuga.
Yes. With the help of the Windows Task Scheduler, you can use the NET command to restart a specific service at a specific time.
To do so:
1. Find the name of your service
Each Windows Service has two names — a short service name and a friendly display name. We need the service name for the NET command.
If you don’t already know the service name, or want to validate it:
-
Launch the Windows Services application. You can find it by searching for “services” in the Control Panel, or by running services.msc at a command prompt.
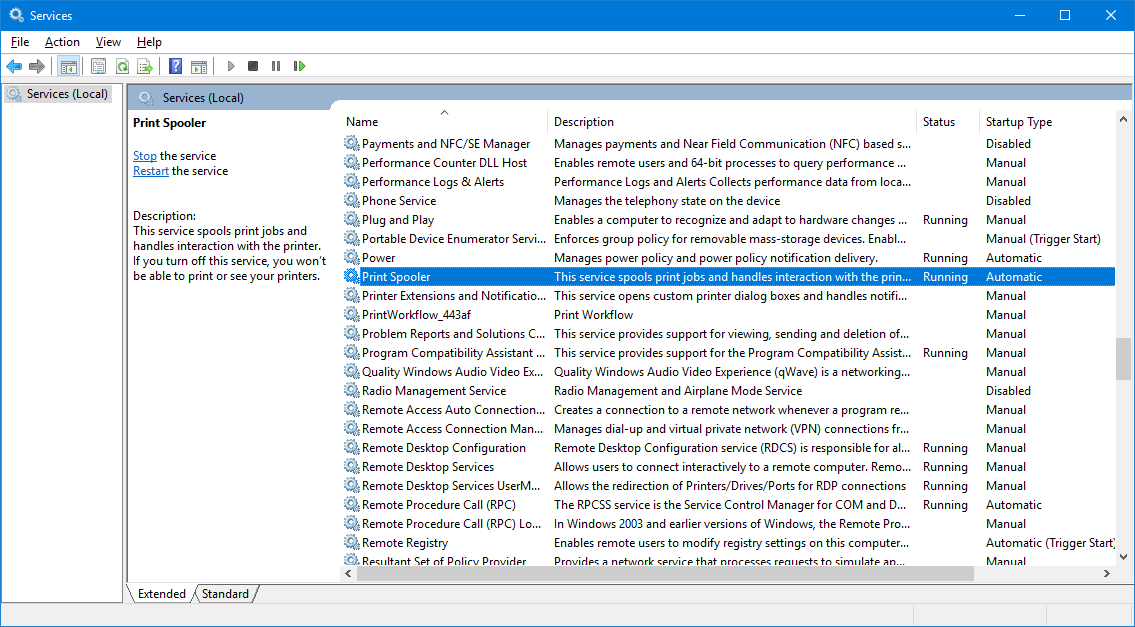
- Scroll to locate your service in the list:
-
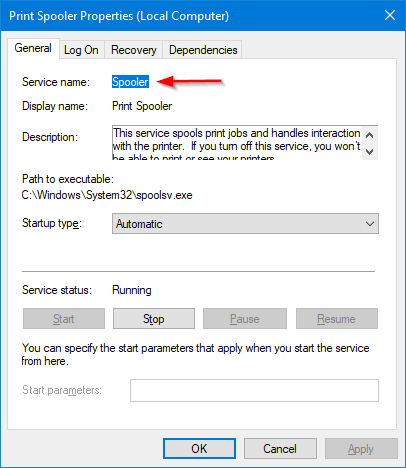
Double-click the entry to open the service’s properties. The service name is displayed at the top.
Here we see that the name of the Print Spooler service is actually “Spooler”:
2. Create a batch file to restart your service
With the service name in hand, we can now use the NET command to restart the service.
Create a new batch file and enter the following two commands:
NET STOP «Your Service Name«
NET START «Your Service Name«
Please replace Your Service Name with the service name identified in step 1. The quotes are required if the service name contains a space.
For example, if your service name is “Spooler”, the batch file should look like this:
NET STOP «Spooler»
NET START «Spooler»
Save the batch file to a well-known location. We’ll use it in the next step.
Test the batch file
At this point, we recommend performing a quick test to ensure that the batch file works as expected. Run it from an administrative command prompt and confirm that it restarts your service.
3. Create a scheduled task to run the batch file at the time you wish to restart the service
Now that you are able to restart the service with the batch file, let’s schedule it to run whenever you like.
For example, here is how we would restart the Print Spooler service every Sunday at 1 AM:
-
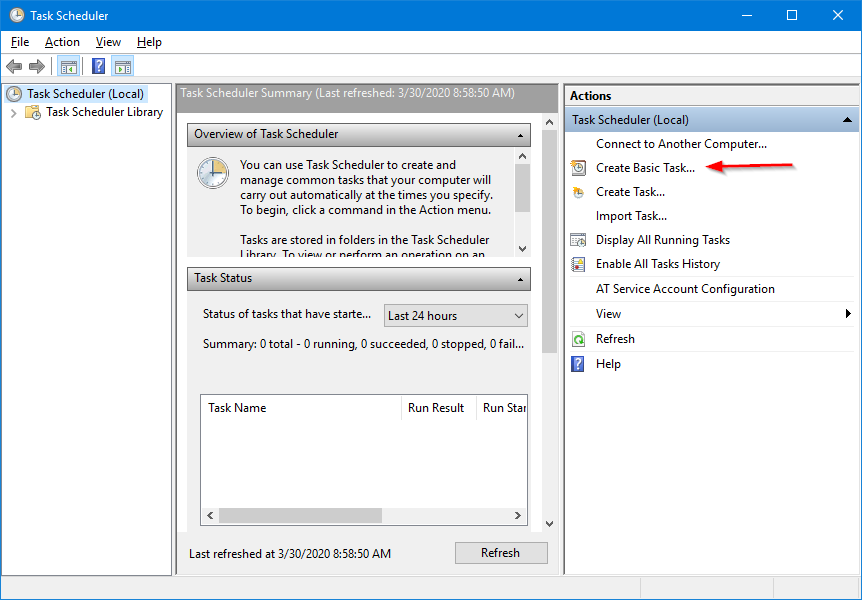
Open the Windows Task Scheduler. You start it from the Control Panel or by running taskschd.msc from a command prompt.
-
Click Create Basic Task on the right:
The Create Basic Task Wizard window will come up.
-
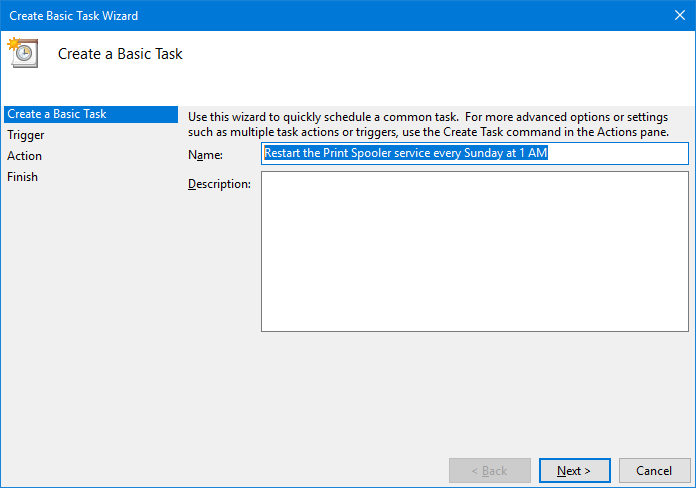
Give the task a descriptive name:
Click Next to continue.
-
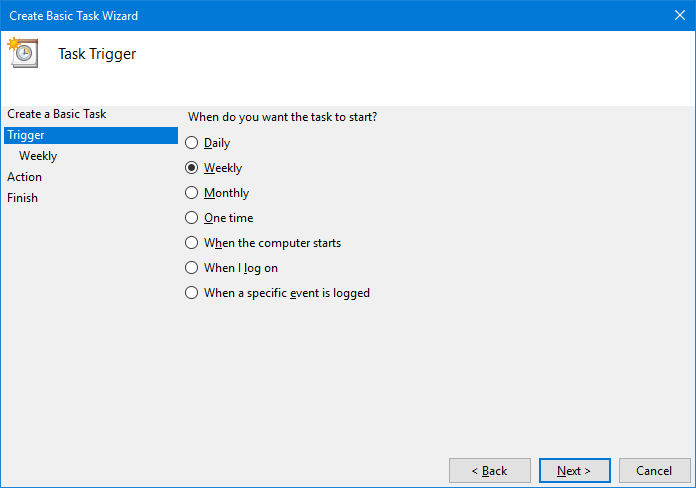
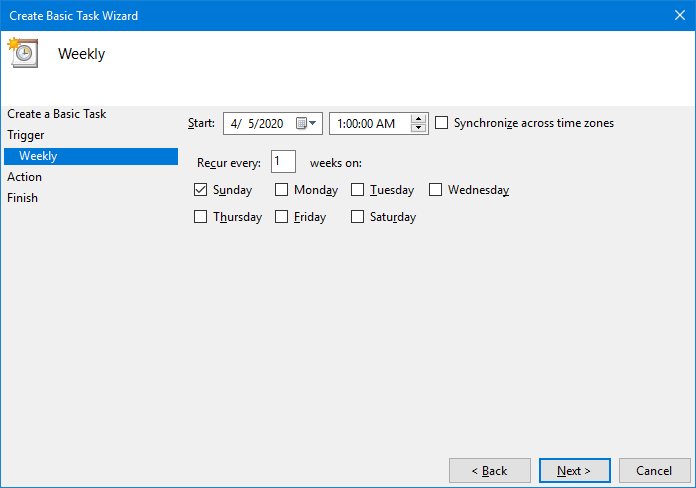
Select Weekly and click Next:
-
Set the day and time to restart the service:
Click Next to continue.
-
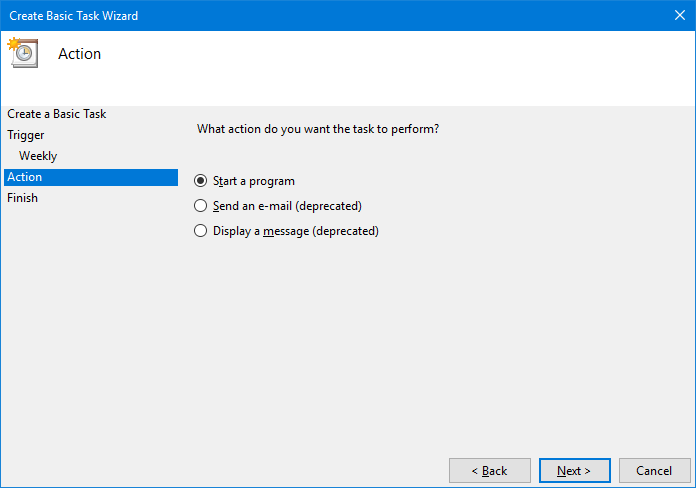
Ensure that the action is Start a program and move to the next step:
-
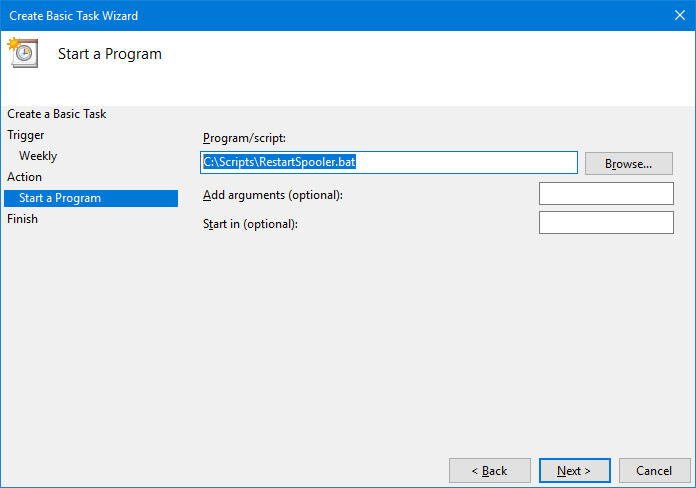
Enter the full path to the batch file you created to restart the service:
Click Next to continue.
-
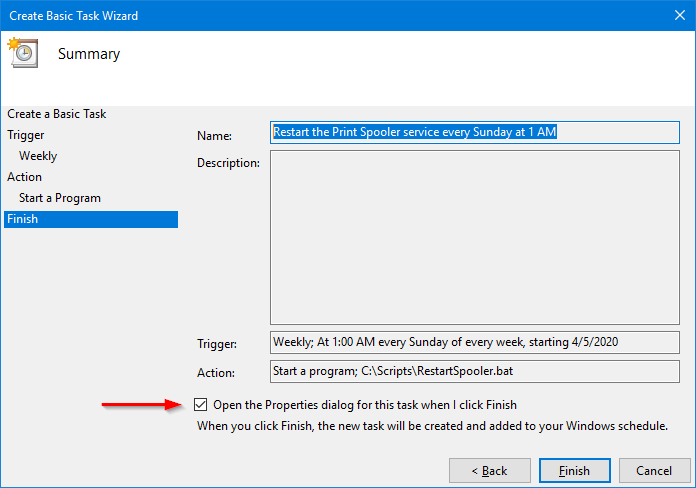
Review the summary and make sure that everything looks good.
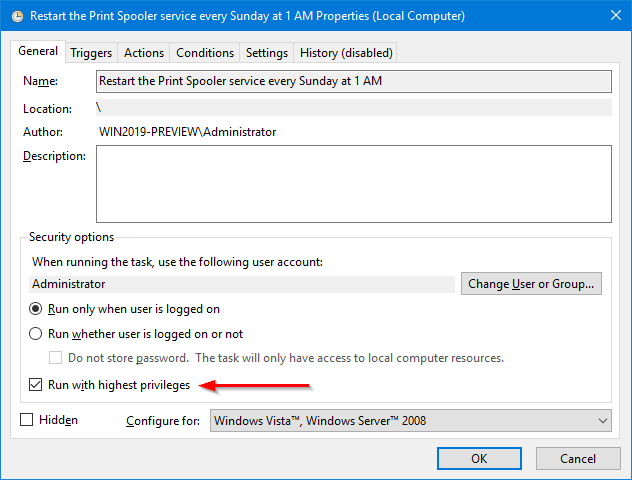
Check the Open the Properties dialog… box at the bottom because we’ll need to adjust one of the tasks properties:
Click Finish.
-
And finally, in the Properties window, check the Run with highest privileges box. The batch file must run with administrative rights so that it can restart the service.
Click OK to save your settings.
Going forward, the new task will come alive at the scheduled time to promptly restart the service. You should be good to go.
Improvement: Use ServicePilot instead of NET for better reliability
While NET.EXE will work for most situations, there are a few scenarios where it may fall short.
Does your service:
- take longer than 30 seconds to shut down?
- occasionally hang and refuse to stop?
If so, the NET STOP command may fail. And when that happens, the subsequent call to NET START will fail too (because the service will not be idle). The end result is that your service will be left in an unusable/unresponsive state!
Our free ServicePilot utility was built to work around NET’s shortcomings. It will wait for longer than 30 seconds if necessary and will do its best to forcibly terminate an unresponsive service.
To use ServicePilot instead of NET:
-
Download ServicePilot from our website. Save the executable in a well-known location (e.g. C:\Apps\ServicePilot\ServicePilot.exe).
-
Edit the batch file you created to restart the service.
-
Delete the two NET lines.
-
Add the following line (adjusting the full path to ServicePilot and your service name as necessary):
C:\Apps\ServicePilot\ServicePilot.exe -restart -wait 300 «Your Service Name«
Note: The -wait 300 parameter instructs ServicePilot to wait up to 300 seconds (5 minutes) for the service to stop and restart. Feel free to increase (or decrease) the timeout based your specific use case.
-
Save the batch file.
As you did with the NET version, please perform a quick test to ensure that the updated batch file works as expected. Launch it from an administrative command prompt and confirm that it restarts your service.
Best of luck with your service!
UPDATE: Use our free Service Scheduler utility instead of the Task Scheduler
We got tired of manually creating batch files and scheduled tasks to control our services so we created a free application to do it all. 🙂
With Service Scheduler, you can easily start, stop or restart any Windows Service — daily, weekly or monthly at a time of your choosing:
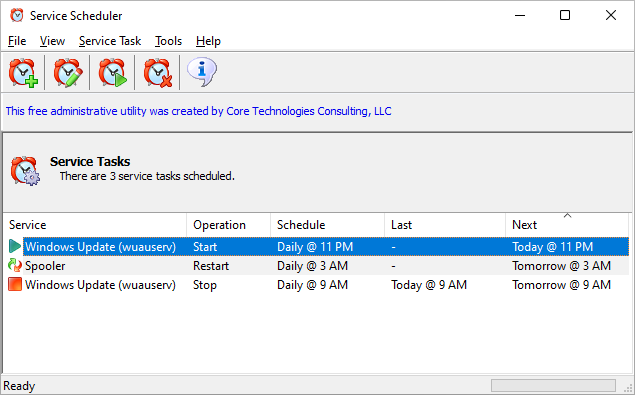
Service Scheduler is completely free and super easy to use. You can schedule your service in seconds:
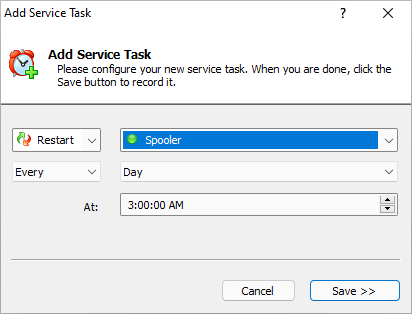
Download Service Scheduler and check it out today!
You may also like…
Task Scheduler
The Task Scheduler is a Windows component that can automatically run tasks at a specific time or in response to a specific event. For example, tasks can be run when the computer starts or when a user logs in. You can start tasks when a specific event occurs and using task scheduler you can run commands and execute scripts on a specific day and time.
Getting Started
Search task scheduler in Windows search.
Right-click on Task Scheduler and click New Folder and give a name to the folder like Server Reboot and click OK.
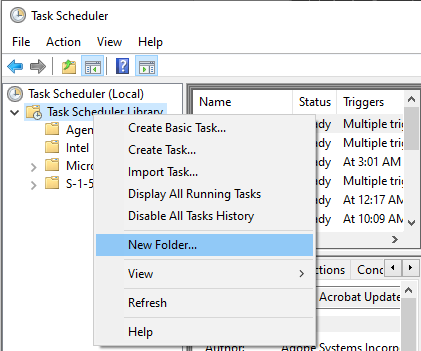
Making a folder makes your tasks separate, so you can manage easily.
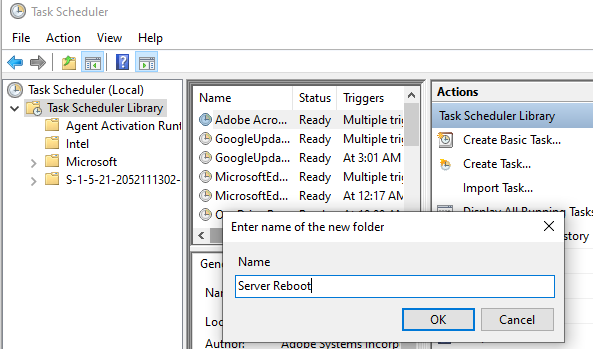
Now right-click on new created folder and select Create Task.
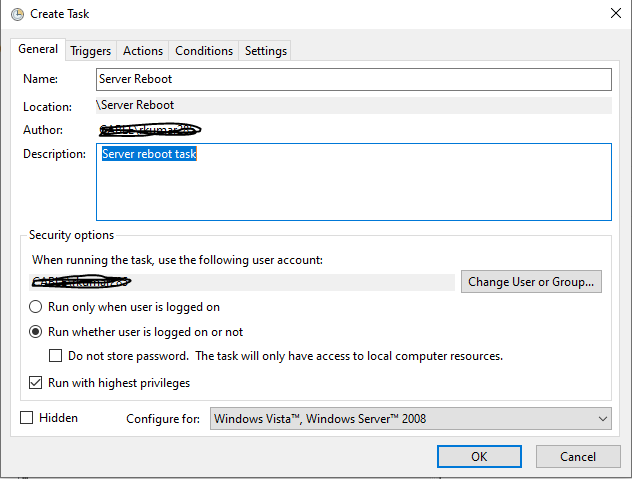
Give a task name and description and select Run whether user is logged on or not and select Run with highest privileges in General tab.
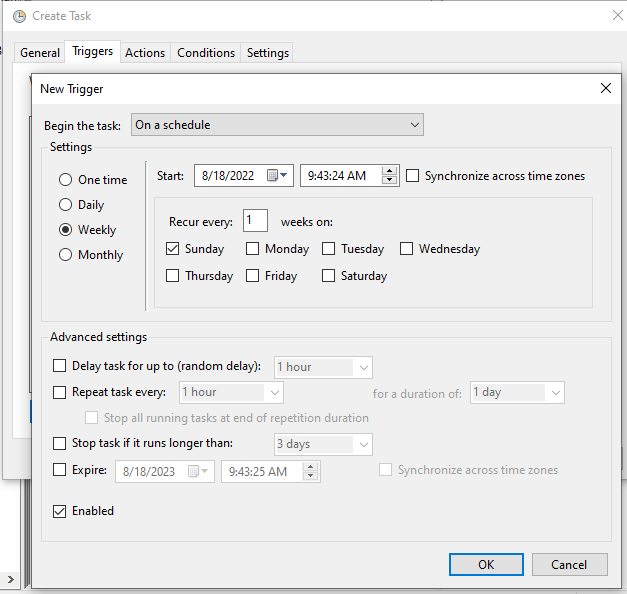
Now click on Triggers tab, which is for restart scheduling date and time. In my trigger I am choosing to run this task every week on Sunday only, you can choose based on your requirement.
Click New.. button to create a new trigger and select required details and click OK.
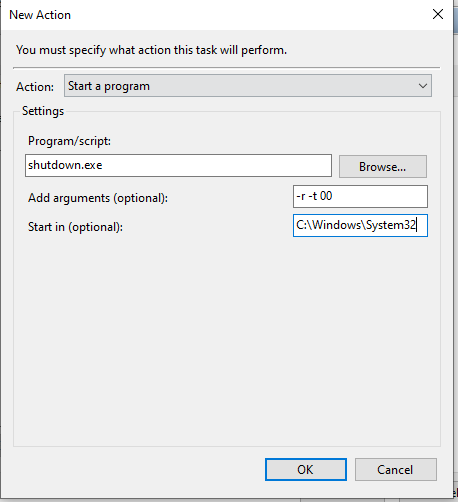
Now let’s go to Actions tab, click new button to create an action. Enter Program/script path and arguments and start in values and click OK.
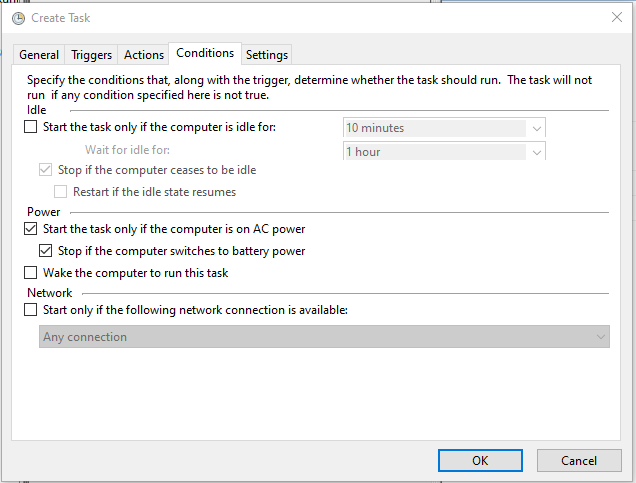
Now select Conditions tab and keep power settings as it if nothing needed.
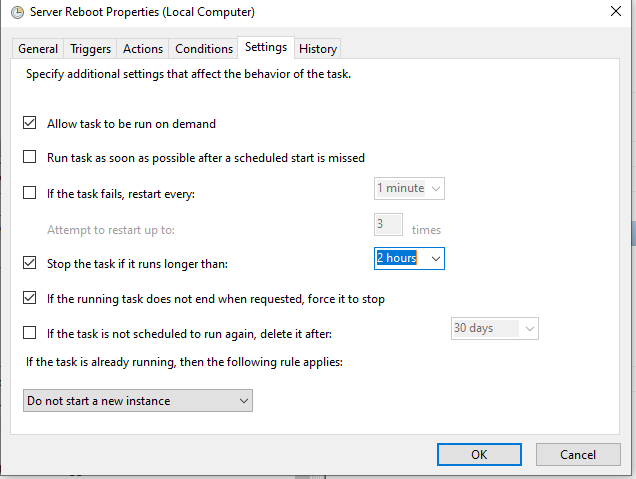
Now click on Settings tab. I am stopping my task if runs longer than 2 hours and click OK.
Now you can see your task is ready to run on given schedule if you want to run anytime just hit the Run button.
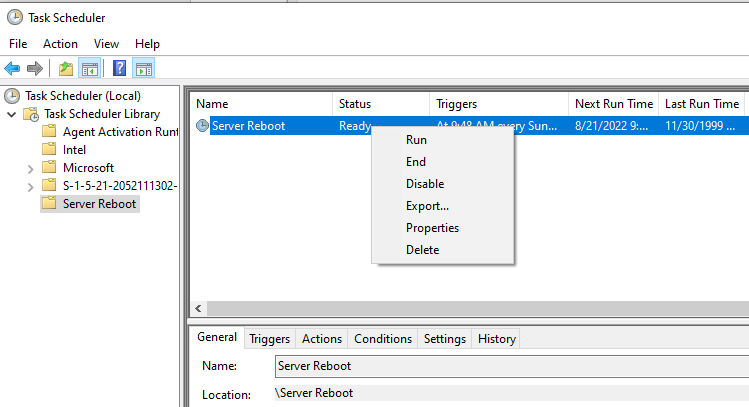
Conclusion
In this article, we have learned how to create a new task and set up a server restart using Windows 10 Task Scheduler.

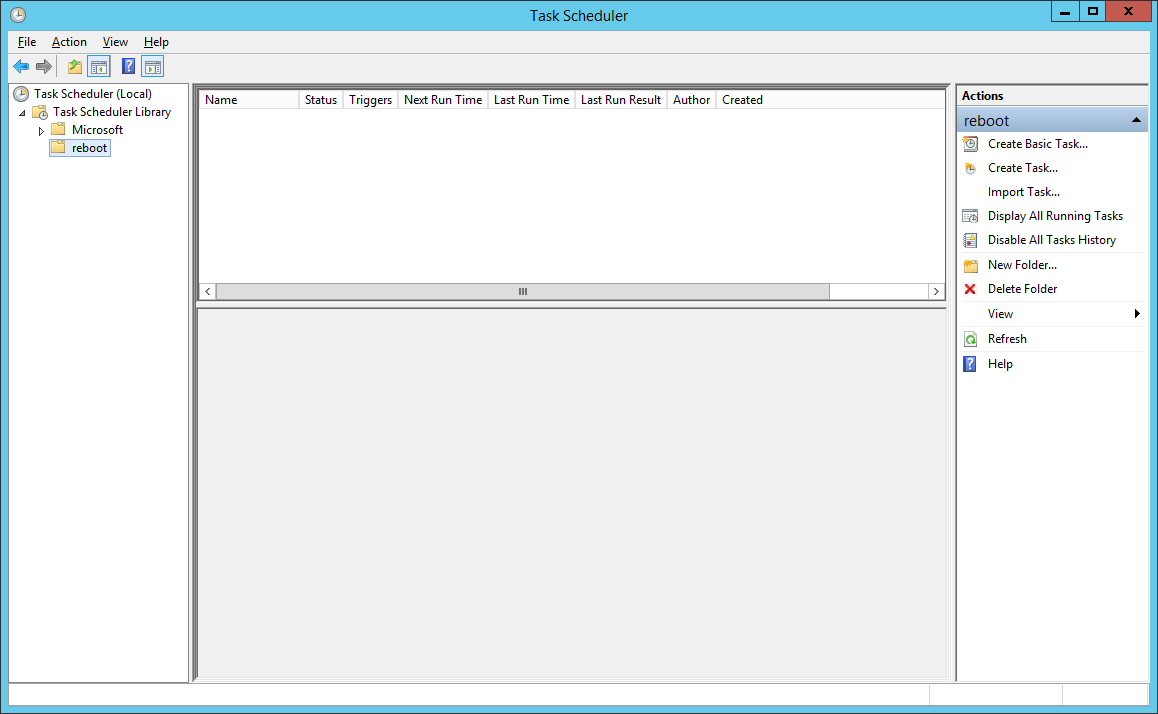
Имеем Windows Server 2012 R2. Задача — автоматически перезагружать сервер каждый понедельник в 5 утра. Приступаем.
Запускаем Планировщик заданий, создаём в нём папку «reboot»:
Делаем Create Basic Task… Запускается мастер:
Указываем Name, Description:
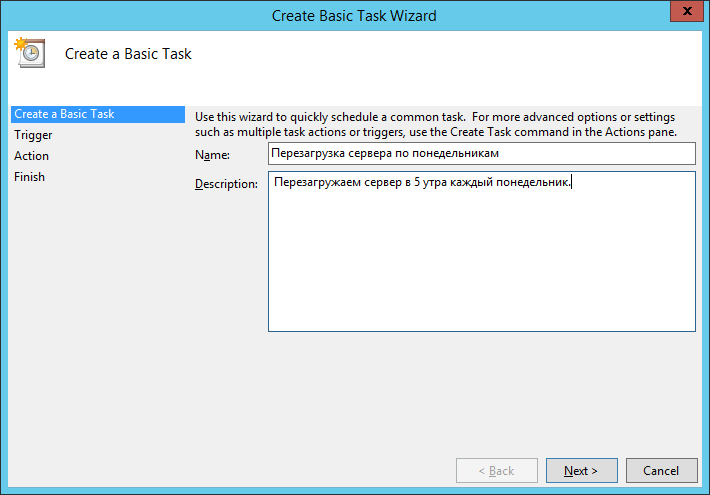
Кликаем Next:
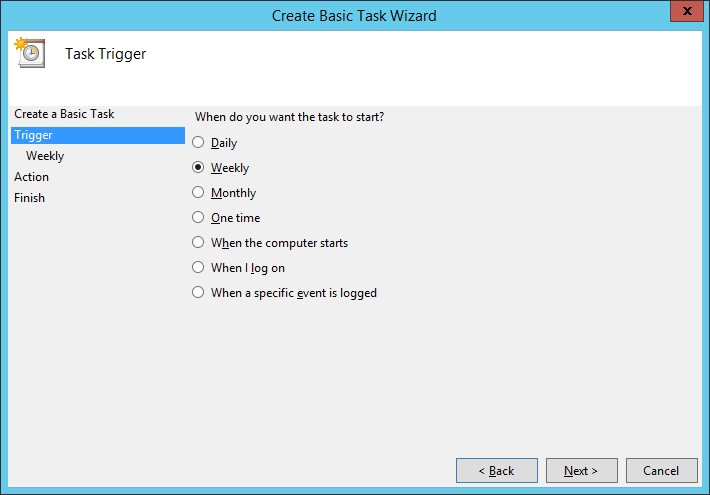
Выбираем период Weekly. Next:
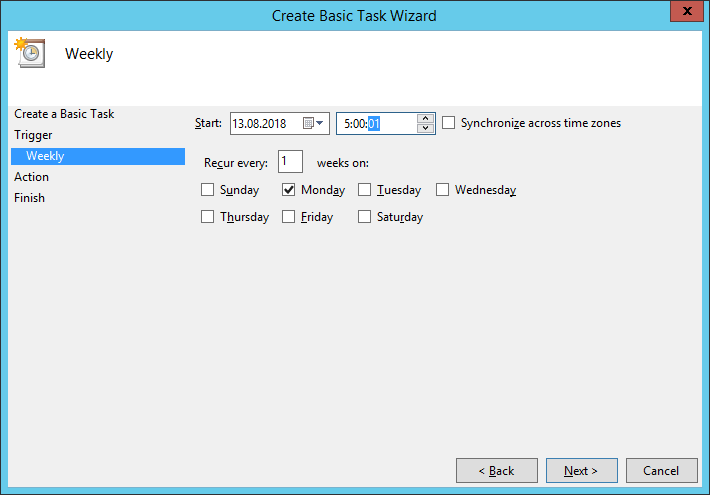
Указываем начало — ближайший понедельник 5 утра. Ставим галку Monday. Next:
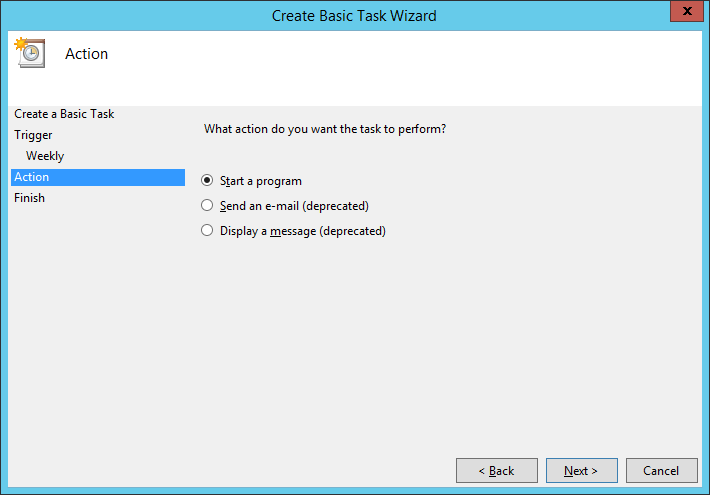
Выбираем Start a program. Next:
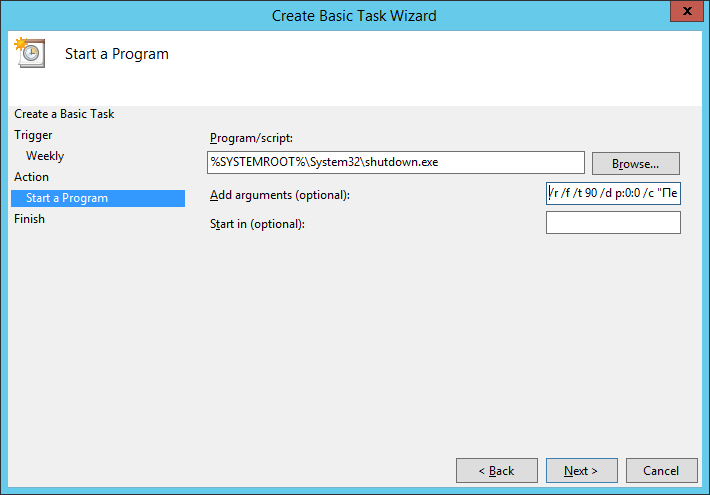
В Program/script: пишем:
%SYSTEMROOT%\System32\shutdown.exeВ Add arguments (optional):
/r /f /t 90 /d p:0:0 /c "Перезапуск по понедельникам. Отмена: shutdown.exe /a"Где:
- /r — перезагрузка,
- /f — принудительное закрытие всех приложений,
- /t 90 — время ожидания до начала перезагрузки 90 сек,
- /d p:0:0 — причины перезагрузки для журнала. В данном случае, мы указали: p — запланированная перезагрузка, 0:0 — «Other (planned)»,
- /c комментарий в свободной форме длинной не более 512 символов. Комментарий будет показываться юзерам 90 секунд. За это время можно отменить перезагрузку командой shutdown.exe /a.
Список параметров и причин перезагрузки можно посмотреть shutdown.exe /?
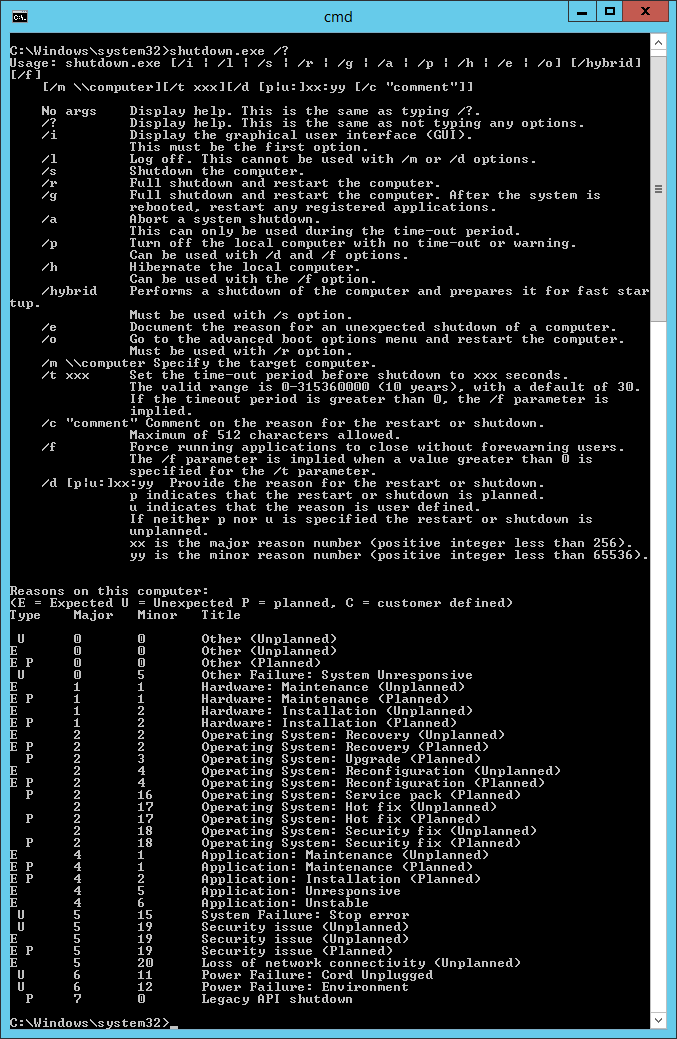
Мастер не доделали, кликаем Finish. Создаётся задача — редактируем её.
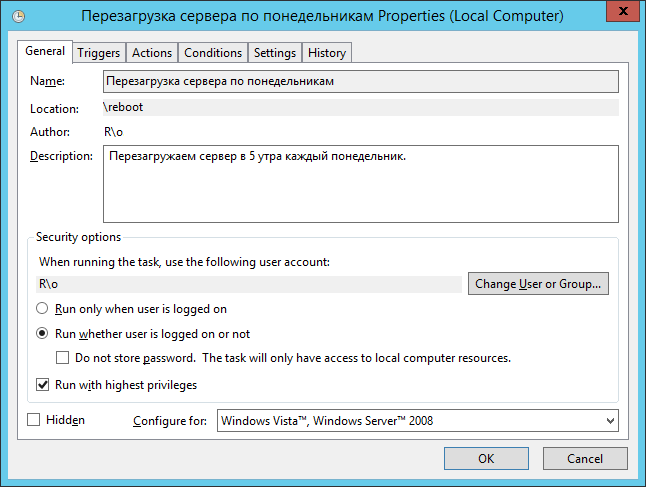
Ставим Run whether user is logged on or not. Добавим галку Run with highest privileges. Ok:
Нас попросят ввести имя пользователя, от имени которого будет выполняться задание. И пароль. Готово:
Сам пока не проверял результатов. В ближайший понедельник посмотрим…
P.S.
Две недели прошло — шедулер нормально перезагружает сервер по понедельникам.