- Automatically Start Docker Container
- How do I make a Docker container start automatically on system boot?
- How do I auto-start docker containers at system boot?
- Start containers automatically
- How to automatically start docker container on windows boot ~ Wait for
- How do I autostart docker container at system reboot?
- Automatically Start Docker Container
- docker update —restart unless-stopped <container> [<container> ] Enable
- Web developer & entrepreneur
- Starting Docker at System Boot for Windows
- How to Start Docker Containers Automatically After a Reboot?
Automatically Start Docker Container
People also askHow to start Docker containers automatically after a reboot?How
to start Docker containers automatically after a reboot?The four policies are:
# docker run -d --restart always <image>
# docker update --restart unless-stopped <container> [<container> ...]
# systemctl enable docker
# systemctl is-enabled docker
# systemctl status dockerHow do I make a Docker container start automatically on system boot?
To start a container and set it to restart automatically on system reboot use.
docker run -d —restart unless-stopped ecstatic_ritchie Where ecstatic_ritchie
is an example name specifying the container in interest. Use docker ps -a to
list all container names. To make particular running containers start
automatically on system reboot
$ docker run ...
$ docker pull alexeiled/docker-oracle-xe-11g
$ docker run -d --name=MYPROJECT_oracle_db --shm-size=2g -p 1521:1521 -p 8080:8080 alexeiled/docker-oracle-xe-11g
$ vim /etc/systemd/system/docker-MYPROJECT-oracle_db.service
[Unit]
Description=Redis container
Requires=docker.service
After=docker.service
[Service]
Restart=always
ExecStart=/usr/bin/docker start -a MYPROJECT_oracle_db
ExecStop=/usr/bin/docker stop -t 2 MYPROJECT_oracle_db
[Install]
WantedBy=default.target
sudo systemctl enable docker-MYPROJECT-oracle_db.service
docker update --restart=always 0576df221c0b
Flag Description
no Do not automatically restart the container. (the default)
on-failure Restart the container if it exits due to an error, which manifests as a non-zero exit code.
always Always restart the container if it stops. If it is manually stopped, it is restarted only when Docker daemon restarts or the container itself is manually restarted. (See the second bullet listed in restart policy details)
unless-stopped Similar to always, except that when the container is stopped (manually or otherwise), it is not restarted even after Docker daemon restarts.
$ sudo systemctl enable docker
$ docker-compose up -d
docker run -d --restart unless-stopped ecstatic_ritchie
docker update --restart unless-stopped ecstatic_ritchie
docker update --restart unless-stopped $(docker ps -q)
docker run -dit --restart unless-stopped <image_name>
$ docker run -dit --restart unless-stopped <image name OR image hash>
$ docker update --restart=<options> <container ID OR name>
docker inspect gateway | grep RestartPolicy -A 3
$ systemctl enable docker
@reboot sleep 10 ; docker start <container name> 2>&1 | /usr/bin/logger -t 'docker start'
● docker.service - Docker Application Container Engine
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/docker.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: inactive (dead) TriggeredBy: ● docker.socket
Docs: https://docs.docker.com
● docker.service - Docker Application Container Engine
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/docker.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Sun 2020-11-22 08:33:23 PST; 1h 25min ago
TriggeredBy: ● docker.socket
Docs: https://docs.docker.com
Main PID: 3135 (dockerd)
Tasks: 13
Memory: 116.9M
CGroup: /system.slice/docker.service
└─3135 /usr/bin/dockerd -H fd:// --containerd=/run/containerd/containerd.sock
... [various messages not shown ]
[Unit]
# This service is provided to force Docker containers
# that should automatically restart to restart when the system
# is booted. While the Docker daemon will start automatically,
# it will not be fully initialized until some Docker command
# is actually run. This unit merely runs "docker ps": any
# Docker command will result in the Docker daemon completing
# its initialization, at which point all containers that can be
# automatically restarted after booting will be restarted.
#
Description=Docker-Container Startup on Boot
Requires=docker.socket
After=docker.socket network-online.target containerd.service
[Service]
Type=oneshot
ExecStart=/usr/bin/docker ps
[Install]How do I auto-start docker containers at system boot?
I’ve used the ‘always’ option so far, and can confirm that it makes Docker
auto-start the container at system boot: sudo docker run —restart=always -d
myimage Documentation Excerpt. Restart Policies Using the —restart flag on
Docker run you can specify a restart policy for how a container should or
should not be restarted on exit. no — Do not restart the container …
sudo docker run --restart=always -d myimage
$ sudo docker run --restart=always redis
$ sudo docker run --restart=on-failure:10 redisStart containers automatically
Docker recommends that you use restart policies, and avoid using process
managers to start containers. Restart policies are different from the —live-
restore flag of the dockerd command. Using —live-restore allows you to keep
your containers running during a Docker upgrade, though networking and user
input are interrupted. Use a restart policy
$ docker run -d --restart unless-stopped redis
$ docker update --restart unless-stopped redis
$ docker update --restart unless-stopped $(docker ps -q)How to automatically start docker container on windows boot ~ Wait for
docker to be running
1 Answer. to the container in your docker-compose.yml, then use docker-compose
up manually once more. This will make Docker to start the container after
Docker itself is started. @TamasHegedus sorry for the confusion, I’ve edited
the last line.
restart: unless-stopped
restart: alwaysHow do I autostart docker container at system reboot?
[Unit] Description=Some service Requires=docker.service After=docker.service
[Service] Restart=always ExecStart=/usr/bin/docker start -a container_name
ExecStop=/usr/bin/docker stop -t 2 container_name [Install] WantedBy=multi-
user.target More available on docker site. P.S. Pretty cute config 
sudo docker run --restart=always -d your_image
[Unit]
Description=Some service
Requires=docker.service
After=docker.service
[Service]
Restart=always
ExecStart=/usr/bin/docker start -a container_name
ExecStop=/usr/bin/docker stop -t 2 container_name
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Description "My container"
start on filesystem and started docker
stop on runlevel [!2345]
respawn
script
/usr/bin/docker start -a mycontainer
end script
pre-stop script
/usr/bin/docker stop mycontainer
end scriptAutomatically Start Docker Container
docker update —restart unless-stopped <container> [<container> ] Enable
Docker Service. Once you have your containers running with a restart policy,
you need to enable the Docker service. If the Docker daemon doesn’t start
automatically, none of your containers will start. Depending on your system,
the process to enable the Docker daemon will vary. Enable …
# docker run -d --restart always <image>
# docker update --restart unless-stopped <container> [<container> ...]
# systemctl enable docker
# systemctl is-enabled docker
# systemctl status dockerWeb developer & entrepreneur
Restart Policies. This is the official technique provided by Docker. You could
control whether your containers start automatically when they exit, or when
Docker restarts. To configure the restart policy for a container use the — …
1
sudo docker run --name my-agario-server -p 3000:3000 --restart unless-stopped kafebob/rpi-agario
1
sudo docker inspect -f "{{ .HostConfig.RestartPolicy }}" my-agario-server
1
sudo docker update --restart=no my-agario-server
123456789101112
[Unit]Description=My Agario ServerRequires=docker.serviceAfter=docker.service[Service]#Restart=alwaysExecStart=/usr/bin/docker start -a my-agario-serverExecStop=/usr/bin/docker stop -t 2 my-agario-server[Install]WantedBy=default.target
1
sudo systemctl enable rpi-agario
1
sudo systemctl status rpi-agario
1
sudo systemctl disable rpi-agario
12345678910111213
[Unit]Description=NextCloud Secure Drive mountRequires=docker.serviceAfter=network-online.target docker.service[Service]Type=oneshotExecStart=/home/pi/laboratory/geheim/secure-mount.shRemainAfterExit=yesExecStop=/home/pi/laboratory/geheim/secure-unmount.sh[Install]WantedBy=multi-user.targetStarting Docker at System Boot for Windows
We can create a scheduled task that runs at the system boot. The scheduled
task will allow the Docker services to start and allow your containers to
restart without any human interaction. Creating a scheduled task via
PowerShell. The first step is to create a scheduled task that executes when
the system boots.
$trigger = New-ScheduledTaskTrigger -AtStartup
$action = New-ScheduledTaskAction -Execute "C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe" -Argument "-File $EXECUTIONSCRIPTPATH"
$settings = New-ScheduledTaskSettingsSet -Compatibility Win8 -AllowStartIfOnBatteries
Register-ScheduledTask -Action $action -Trigger $trigger -TaskName "Start Docker on Start up" -Settings $settings -User "$USERNAME" -Password "$PASSWORD" -RunLevel Highest
# Add the user to the docker-users user-group
# This is needed so that this user has access to docker services
try {
Add-LocalGroupMember -Group docker-users -Member "$USERNAME" -ErrorAction Stop
} catch [Microsoft.PowerShell.Commands.MemberExistsException] {
}
$WSL_CLIENT = bash.exe -c "ip addr show eth0 | grep -oP '(?<=inet\s)\d+(\.\d+){3}'";
$WSL_CLIENT -match '\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}';
$WSL_CLIENT = $matches[0];
iex "netsh interface portproxy add v4tov4 listenport=5000 listenaddress=$WSL_CLIENT connectport=5000 connectaddress=$WSL_CLIENT"
start-service -Name com.docker.service
start "C:\Program Files\Docker\Docker\Docker Desktop.exe"How to Start Docker Containers Automatically After a Reboot?
docker update —restart unless-stopped container_id. Then if you run a docker
inspect for your container and look for RestartPolicy you should be able to
see something like this: «RestartPolicy»: { «Name»: «unless-stopped», There
are a few other flags that you could specify to the —restart argument.
Argument.
docker run -dit --restart unless-stopped httpd
docker run -dit httpd
docker ps -a
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
ab9025e61abb httpd "httpd-foreground" About a minute ago Up 26 seconds 80/tcp container1
4d801fec7c0c httpd "httpd-foreground" About a minute ago Exited (0) About a minute ago container2
docker update --restart unless-stopped container_id
"RestartPolicy": {
"Name": "unless-stopped",
Sep 04 04:00:03 rev5 systemd[1]: Stopped Docker Application Container Engine.
-- Reboot --
Sep 04 08:29:23 rev5 systemd[1]: Starting Docker Application Container Engine...
systemctl enable docker.service
- name: Autostart service docker after reboot
service:
name: docker
enabled: trueStart Docker at Windows startup
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| # | |
| # We are now configuring docker to start when Windows starts using the Windows Task Scheduler. | |
| # | |
| # create a scheduled task… | |
| $trigger = New-ScheduledTaskTrigger —AtStartup | |
| $trigger.Delay = ‘PT1M‘ | |
| $action = New-ScheduledTaskAction —Execute «%SystemRoot%\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe« —Argument «-File $PSScriptRoot\startDocker.ps1« | |
| $settings = New-ScheduledTaskSettingsSet —Compatibility Win8 —AllowStartIfOnBatteries —StartWhenAvailable —RestartCount 999 | |
| $settings.ExecutionTimeLimit = ‘PT0S‘ | |
| $settings.RestartInterval = ‘PT1M‘ | |
| Register-ScheduledTask —Action $action —Trigger $trigger —TaskName «Start Docker on Start up« —Settings $settings —User $env:UserName | |
| # Add the user to the docker-users user-group… | |
| # This is needed so that this user has access to docker services | |
| try { | |
| Add-LocalGroupMember —Group docker—users —Member $env:UserName —ErrorAction Stop | |
| } catch [Microsoft.PowerShell.Commands.MemberExistsException] { | |
| } |
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| # | |
| # We are starting docker and containers (at windows startup) | |
| # | |
| # start service… | |
| echo «Starting service com.docker.service… « | |
| start-service —Name com.docker.service | |
| echo «Starting docker desktop… « | |
| start «%ProgramFiles%\Docker\Docker\Docker Desktop.exe« | |
| # wait a bit before starting containers… | |
| echo «Waiting… « | |
| Start-Sleep 10 | |
| # start containers | |
| echo «Starting containers… « | |
| #docker compose up -d -file <docker-compose.yml> | |
| echo «Done. « |
-
#1
I’m having trouble finding any good documentation on how to get docker containers to autostart with Windows. Can someone point me towards how to do this?
-
#3
i would probably create a batch file to start the dockers, then put it into windows scheduler with task to run whenever the system boots.
There might be a better way to do this but the above first thing that came to me.
The problem is that requires login. I want to get a docker and specific containers to auto start with Windows without user login.
-
#6
You can have tasks run at startup with Task Scheduler
I believe you can with the below option.
View attachment 8305
This works with non-local (domain) accounts?
-
#8
Sweet. I’ll give this a shot. Thanks!
-
#9
Alright, I accomplished this by creating a scheduled task that calls «C:\Program Files\Docker\Docker\Docker for Windows.exe». My container is set to —restart always so it starts with the docker service.
Last edited:
If necessary, download and install Docker. Create the container that you wish to run as a service.
For this tutorial, we’ve:
- Installed Docker Desktop version 4.12.0.
- Deployed a
container
running the NGINX web server. - Confirmed that the container and NGINX work as expected.
As you can see here, we named our container «Webserver»:
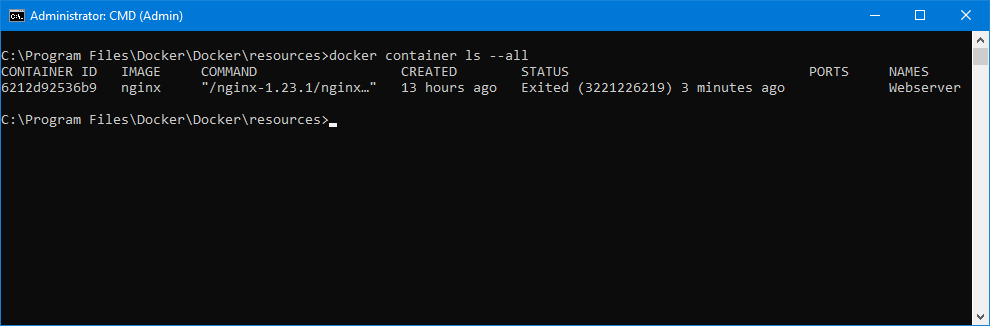
If necessary, install Docker daemon as a Windows Service.
Your container needs the Docker daemon to do its work.
The service (named «Docker Engine») was installed on our computer:
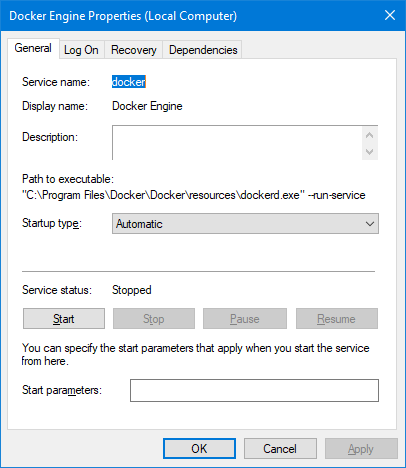
Create a batch file that runs your Docker container.
The file should contain two commands — one to start the container and another to block until the container closes.
Here’s what our batch file looks like:
«C:\Program Files\Docker\Docker\resources\bin\docker.exe» start Webserver
«C:\Program Files\Docker\Docker\resources\bin\docker.exe» wait Webserver
Note that your path to docker.exe (and your container name) may be different. Be sure to update accordingly!
At this point, please confirm that your batch file starts the container.
Create a batch file that gracefully stops your container.
Our batch file contains a single command:
«C:\Program Files\Docker\Docker\resources\bin\docker.exe» stop Webserver
Please confirm that your batch file stops the container.
Next, download and install AlwaysUp, if necessary.
Start AlwaysUp.
Select Application > Add to open the Add Application window:
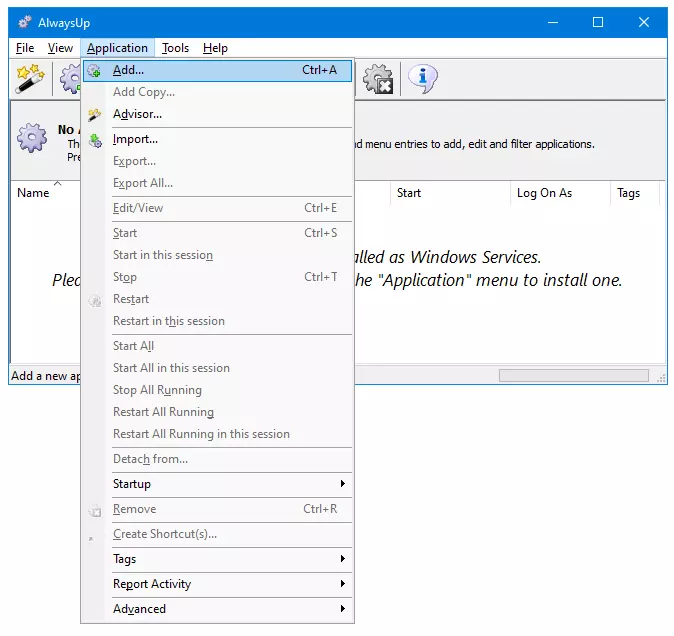
On the General tab:
-
In the Application field, enter the full path to the batch file you created in step 3 (to launch the container).
AlwaysUp will run the batch file to start the Docker container as a Windows Service. -
In the Start the application field, choose Automatically, but shortly after the computer boots.
With that setting, Docker will start a couple of minutes after boot — once all the machine’s critical services are
fully up and running. -
And in the Name field, enter the name that you will call the application in AlwaysUp.
We have used NGINX Docker Container but you can specify almost anything you like.
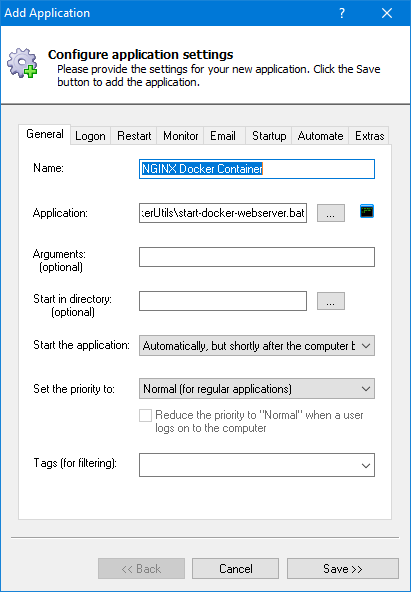
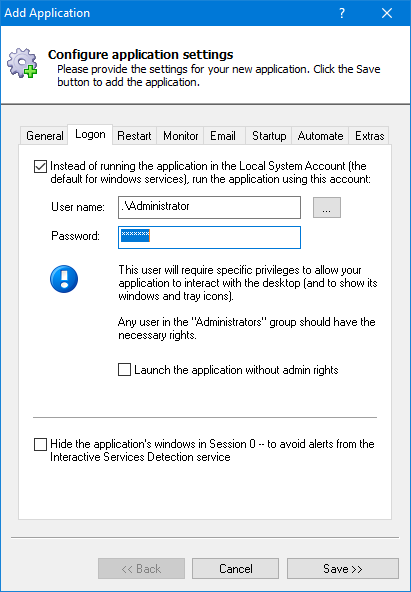
Click over to the Logon tab and enter the user name and password of the Windows account where you installed and run Docker.
It’s best to run Docker in that account, where you know it works.
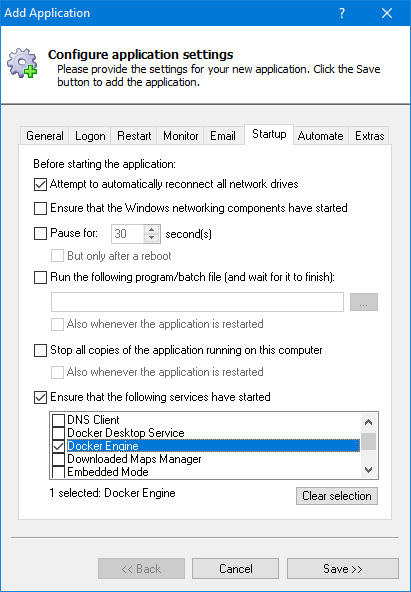
Click over to the Startup tab.
Enable the Ensure that the following services have started option and check the Docker Engine entry.
This informs AlwaysUp that your container needs the Docker daemon to operate.
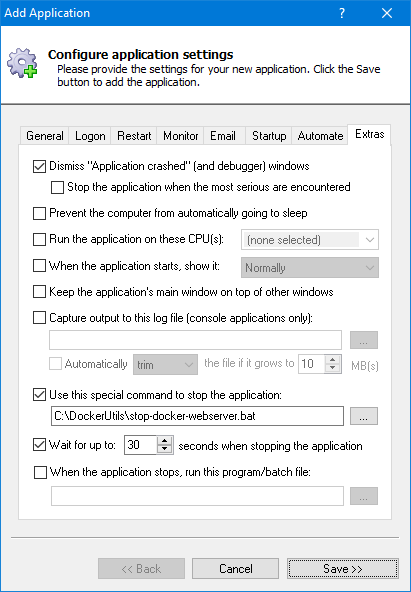
Switch to the Extras tab, where we’ll ensure that the container exits gracefully whenever the service stops.
-
Check the Use this special command to stop the application box.
-
Enter the full path to the batch file you created in step 4 (to stop the container).
-
Check the Wait for up to box and enter 30 seconds. That should be enough time for your container to close.
We’re done configuring the container to run as a service with AlwaysUp. Click the Save button to record your settings.
In a couple of seconds, a new entry will show up in the AlwaysUp window:
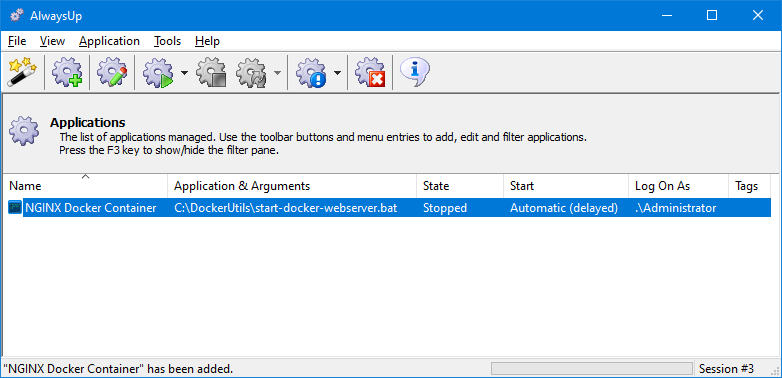
To start your container, choose Application > Start.
The state should transition to «Running» after a few seconds:
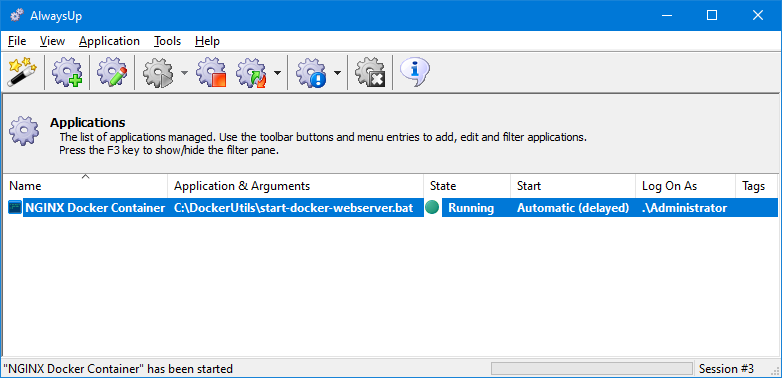
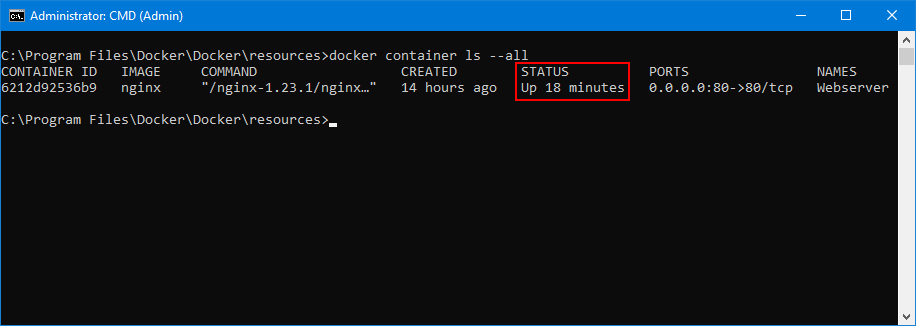
At this point, you should confirm that your container is up and running as expected.
For example, run «docker container ls —all» to check the status. Our container was up:
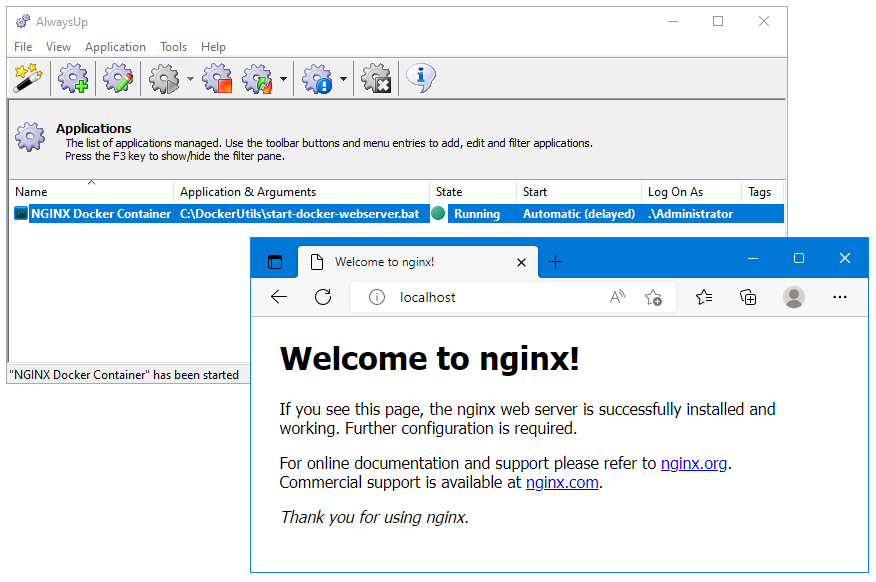
And because our container is running NGINX, we were also able to validate by browsing to the web server’s URL:
That’s it! Next time your computer boots, your Docker container will start immediately, before anyone logs on.
We encourage you to edit the Docker entry in AlwaysUp and check out the many other settings that may be appropriate for your environment.
For example, send an email if Docker stops, run a customized failure detection script, and much more.
After your Docker containers are set up and running, you might need to be able to start some of them automatically on system reboot, or when it crashes. This post covers both cases.
The best article that I found is
and I’ll repost from here. I’d say I should do the reposting more in the future, because as of now, the following article that I quoted in my previous post but not reposted here, is no longer accessible:
It might be just a temporary thing, but, speaking of needing it when it is not available… anyway,
To restart docker container when it crashes itself, use the restart policies provided by Docker. They can be set to control whether your containers start automatically when they exit, or when Docker restarts.
$ docker run -dit --restart always my-docker-image
NB, IMHO, the content of the first-hit by google, named «How to Start Docker Containers Automatically» from codeburst, is … errr… junk — pardon me for not able to find a more polity word to describe it. Its command line is even not in the correct syntax, and it copied the --restart policy of unless-stopped from doc without thinking.
Now, as for starting docker containers automatically on system reboot with systemd, I’ll be copying the start-docker-containers-automatically article as-is:
Create the Service File
To create a service file that will be used by systemd (systemctl command), we will first need to get your container name. This can be done by running the following command in your shell:
$ docker ps -a
The output will look something like this. Select the right container from the list, and note its name in the last column. In this example, we will be using mywiki container.
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
573193cf1d5e hypriot/rpi-busybox-httpd "/bin/busybox http..." 2 days ago Exited (0) 5 hours ago mytest
e85753d57a67 easypi/dokuwiki-arm "/bin/sh -c 'php-f..." 1 days ago Up 23 hours 0.0.0.0:80->80/tcp mywiki
Now, we will need to create a file (choose an appropriate file name for the service):
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
$ sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/docker-dokuwiki.service
Paste the following into the file. Set a proper Description, and make sure to update the container name in ExecStart and ExecStop:
[Unit]
Description=DokuWiki Container
Requires=docker.service
After=docker.service
[Service]
Restart=always
ExecStart=/usr/bin/docker start -a mywiki
ExecStop=/usr/bin/docker stop -t 2 mywiki
[Install]
WantedBy=local.target
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
A couple of notes about the script above:
- This file is called a unit file for
systemd. - Make sure you don’t have any extra line brakes within the sections, like
Unit, orService. - The
-aoption in the Docker command forExecStartmakes sure it is running in attached mode, i.e., attaching STDOUT/STDERR and forwarding signals. - The
-toption in the Docker command forExecStopspecifies seconds to wait for it to stop before killing the container.
Activate the Service
Before we can activate the service we have created, we need to reload the unit file. You will also need to run this command anytime you do any modifications to the unit files:
$ sudo systemctl daemon-reload
To activate the service run the following commands (remember to change the service name):
$ sudo systemctl start docker-dokuwiki.service
$ sudo systemctl enable docker-dokuwiki.service
To disable the service run the following commands (remember to change the service name):
$ sudo systemctl stop docker-dokuwiki.service
$ sudo systemctl disable docker-dokuwiki.service
Changes will come to effect on a reboot:
$ sudo reboot
Now you should have a container that will start on a server reboot, Docker restart, or a crash. Congratulations!
